Assessing the Biodegradation Characteristics of Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Poly(Lactic Acid) Formulations Under Controlled Composting Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
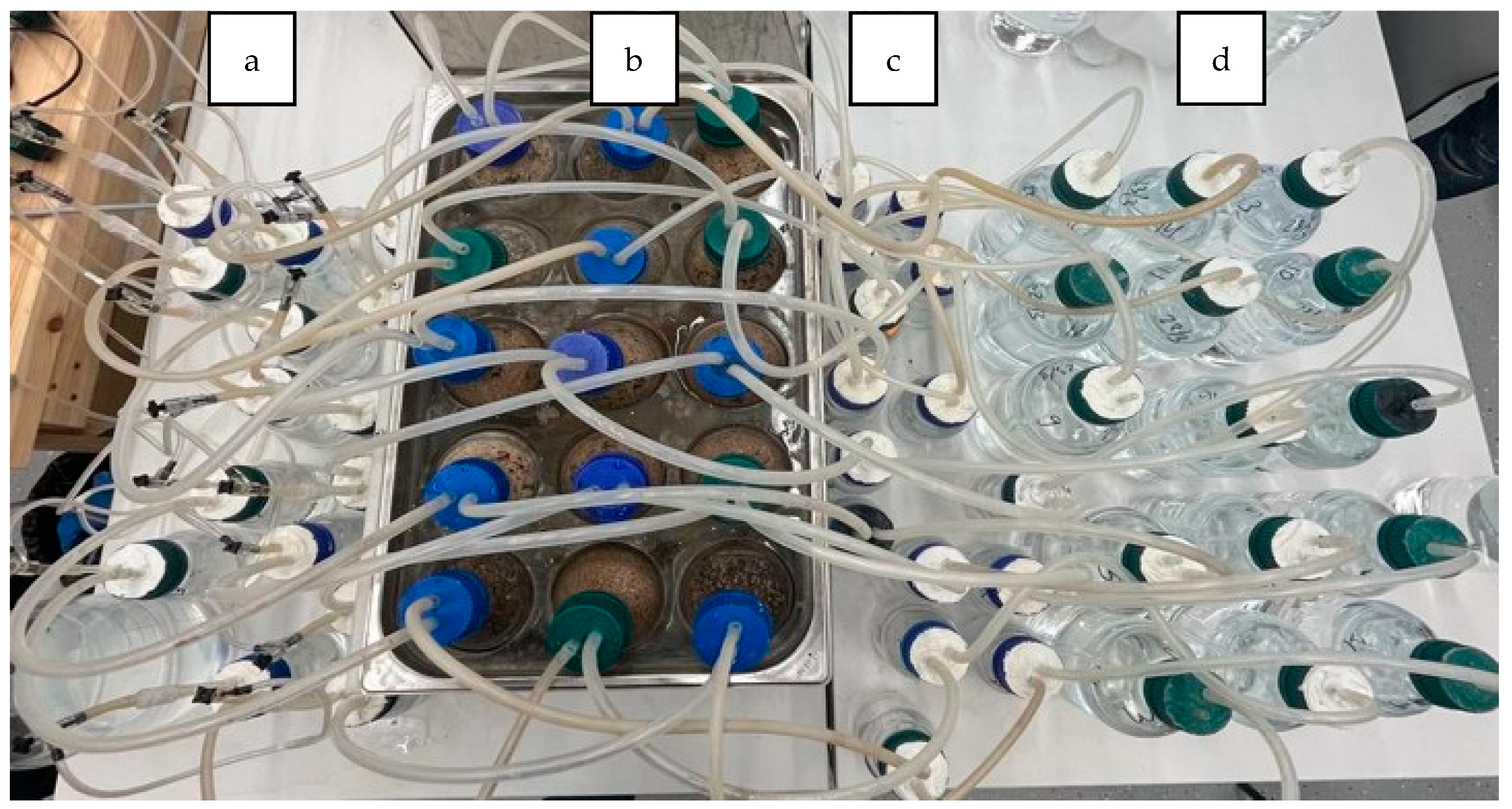
2.2.1. Composting at a Laboratory Scale
2.2.2. CO2 Measurement Using Titration Method
2.2.3. Biodegradation Evaluation
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2.5. Total Organic Carbon
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Degree of Biodegradation
3.1.1. Biodegradation of PBS-Based Compounds
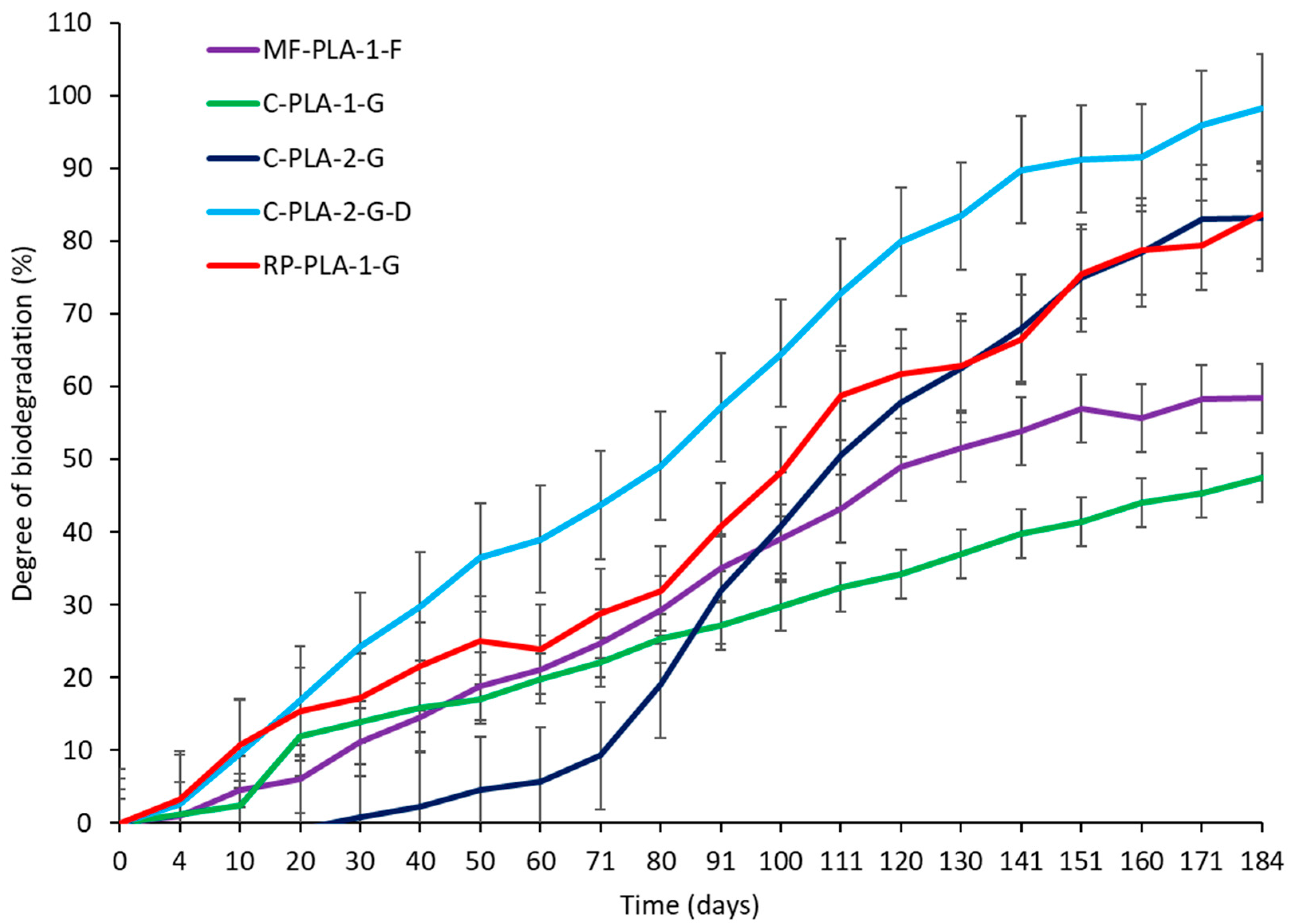
3.1.2. Biodegradation of PLA-Based Compounds
3.2. Surface Morphological Features
3.2.1. Surface Morphology of PBS-Based Compounds
3.2.2. Surface Morphology of PLA-Based Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABM | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| NPL | Directory of open access journals |
| PBAT | Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) |
| PBS | Polybutylene succinate |
| PLA | Polylactide/Polylactic acid |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
References
- Thew, C.X.E.; Lee, Z.S.; Srinophakun, P.; Ooi, C.W. Recent advances and challenges in sustainable management of plastic waste using biodegradation approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Cho, D.-W.; Park, J.; Bhatnagar, A.; Song, H. A review of plastic pollution and their treatment technology: A circular economy platform by thermochemical pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.R.; Fequet, L. Current trends of unsustainable plastic production and micro(nano)plastic pollution. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, T.; Hinzmann, M.; Mederake, L.; Dittmann, S.; Brennecke, D.; Böhm-Beck, M.; Knickmeier, K.; Thiel, M. What potential does the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive have for reducing plastic pollution at coastlines and riversides? An evaluation based on citizen science data. Waste Manag. 2023, 164, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh Kumar, A.; Anjana, K.; Hinduja, M.; Sujitha, K.; Dharani, G. Review on plastic wastes in marine environment—Biodegradation and biotechnological solutions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Perspectives on the Biodegradation of LDPE in Agricultural Systems—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39839104/ (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Lv, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shao, Z. Biodegradation of Typical Plastics: From Microbial Diversity to Metabolic Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Calabia, B.P.; Ugwu, C.U.; Aiba, S. Biodegradability of Plastics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3722–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, S.; Kim, Y.; Won, Y.; Myung, J. Bridging Three Gaps in Biodegradable Plastics: Misconceptions and Truths About Biodegradation. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 671750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, R.; Krzystek, L.; Puchalski, M.; Krucińska, I.; Sitarski, A. Degradation of bio-based film plastics in soil under natural conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.R.A.; Marques, C.S.; Arruda, T.R.; Teixeira, S.C.; de Oliveira, T.V. Biodegradation of Polymers: Stages, Measurement, Standards and Prospects. Macromol 2023, 3, 371–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshood, T.D.; Nawanir, G.; Mahmud, F.; Mohamad, F.; Ahmad, M.H.; AbdulGhani, A. Sustainability of biodegradable plastics: New problem or solution to solve the global plastic pollution? Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, C.; Giacobazzi, G.; Vannini, M.; Totaro, G.; Sisti, L.; Colonna, M.; Marchese, P.; Celli, A. End of Life of Biodegradable Plastics: Composting versus Re/Upcycling. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havstad, M.R. Chapter 5—Biodegradable plastics. In Plastic Waste and Recycling; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 97–129. ISBN 978-0-12-817880-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Sadeghi, K.; Jang, J.; Seo, J. Mechanical, chemical, and bio-recycling of biodegradable plastics: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Lee, H.; Won, W. Unveiling the environmental gains of biodegradable plastics in the waste treatment phase: A cradle-to-crave life cycle assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
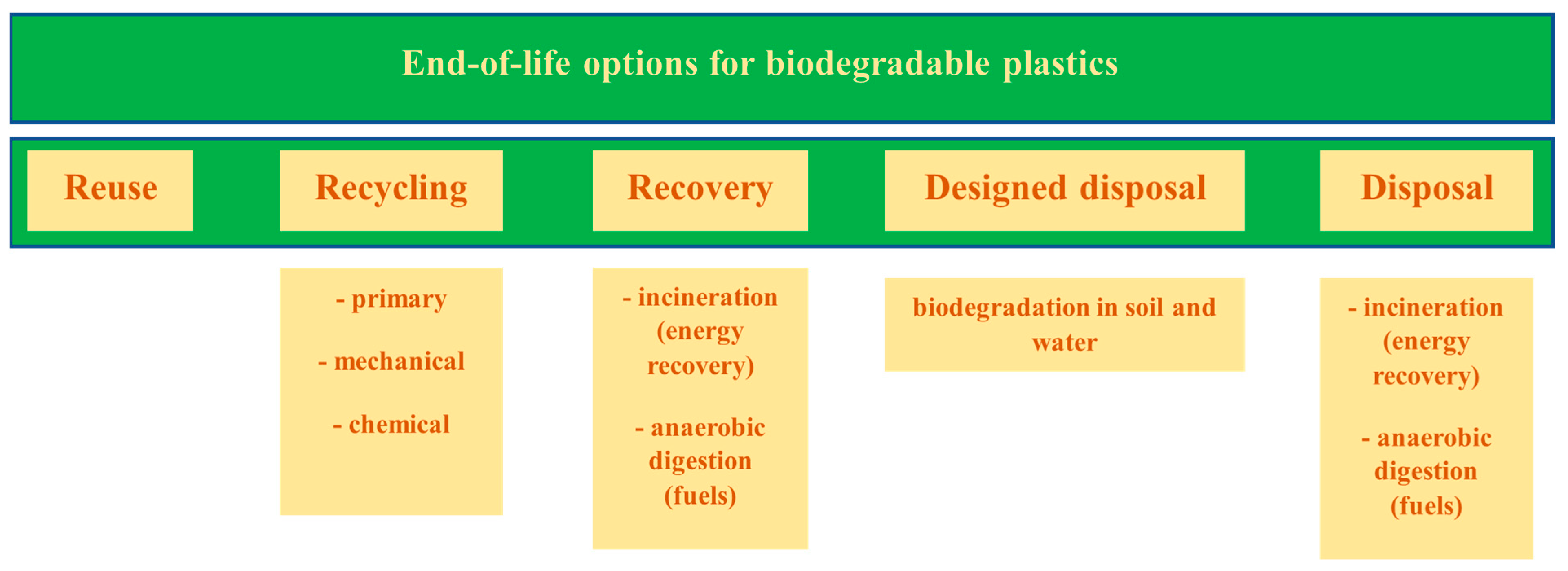
- Sikorska, W.; Musioł, M.; Zawidlak-Węgrzyńska, B.; Rydz, J. End-of-Life Options for (bio)degradable Polymers in the Circular Economy. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2021, 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijzen, F.; de Bie, F. End-of-Life Options for Bioplastics—Clarifying the End-of-Life Options for Bioplastics and the Role of PLA in the Circular Economy; Total Corbion: Gorinchem, The Netherlands, 2020; Available online: https://totalenergies-corbion.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Whitepaper-on-the-end-of-life-options-of-Luminy-PLA.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Weinstein, J.E.; Dekle, J.L.; Leads, R.R.; Hunter, R.A. Degradation of bio-based and biodegradable plastics in a salt marsh habitat: Another potential source of microplastics in coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyshtva, P.; Voronova, V.; Barbir, J.; Filho, W.L.; Kröger, S.D.; Witt, G.; Miksch, L.; Sabowski, R.; Gutow, L.; Frank, C.; et al. Degradation of a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) compound in different environments. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meereboer, K.W.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Review of recent advances in the biodegradability of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) bioplastics and their composites. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5519–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Oluwafemi, O.S.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S.; Songca, S.P.; Mohan, S.; Oluwafemi, O.S.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S.; Songca, S.P. Biopolymers—Application in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. In Recent Advances in Biopolymers; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2255-5. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, V.; Sarsaiya, S.; Anerao, P.; Ghosh, P.; Singh, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K. A comprehensive review on recent advancements in biodegradation and sustainable management of biopolymers. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhoubi, R.; Lasschuijt, M.; Ramon Carrasco, S.; Gojzewski, H.; Wurm, F.R. End-of-life biodegradation? how to assess the composting of polyesters in the lab and the field. Waste Manag. 2022, 154, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Cao, A. Thermal degradation and their kinetics of biodegradable poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene terephthate)s under nitrogen and air atmospheres. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biodegradability of Bio-Flour Filled Biodegradable Poly(Butylene Succinate) Bio-Composites in Natural and Compost Soil—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141391005003150?via%3Dihub (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Khoramnejadian, S.; Zavareh, J.J.; Khoramnejadian, S. Bio-based plastic a way for reduce municipal solid waste. Procedia Eng. 2011, 21, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.K.; Damare, N.A.; Hazarika, D.; Bhagabati, P.; Kalamdhad, A.; Katiyar, V. Biodegradation and characterization study of compostable PLA bioplastic containing algae biomass as potential degradation accelerator. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, M.; Szparaga, G.; Biela, T.; Gutowska, A.; Sztajnowski, S.; Krucińska, I. Molecular and Supramolecular Changes in Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) and Polybutylene Succinate Adipate (PBSA) Copolymer during Degradation in Various Environmental Conditions. Polymers 2018, 10, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-C.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Synthesis and performances of poly(butylene-succinate) with enhanced viscosity and crystallization rate via introducing a small amount of diacetylene groups. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gao, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, Z.; Li, N.; Pan, X.; Dai, J.; Hu, D. Preparation of biodegradable PBST/PLA microcellular foams under supercritical CO2: Heterogeneous nucleation and anti-shrinkage effect of PLA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 197, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S. Polylactide (PLA) and Its Blends with Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS): A Brief Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Moon, H.S.; Kim, M.; Nam, K.; Kim, J.Y. Biodegradability and biodegradation rate of poly(caprolactone)-starch blend and poly(butylene succinate) biodegradable polymer under aerobic and anaerobic environment. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomadolo, N.; Dada, O.E.; Swanepoel, A.; Mokhena, T.; Muniyasamy, S. A Comparative Study on the Aerobic Biodegradation of the Biopolymer Blends of Poly(butylene succinate), Poly(butylene adipate terephthalate) and Poly(lactic acid). Polymers 2022, 14, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Liu, T.-Y.; Nie, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhen, Z.-C.; Xu, P.-Y.; Wang, G.-X.; Zou, G.; Ji, J.-H. Trickily designed copolyesters degraded in both land and sea—confirmed by the successful capture of degradation end product CO2. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 196, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunioka, M.; Ninomiya, F.; Funabashi, M. Biodegradation of Poly(butylene succinate) Powder in a Controlled Compost at 58 °C Evaluated by Naturally-Occurring Carbon 14 Amounts in Evolved CO2 Based on the ISO 14855-2 Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4267–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guan, T.; Wu, G.; Fu, Y.; Weng, Y. Biodegradation Behavior of Degradable Mulch with Poly (Butylene Adipate-co-Terephthalate) (PBAT) and Poly (Butylene Succinate) (PBS) in Simulation Marine Environment. Polymers 2022, 14, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Su, T.; Li, P.; Wang, Z. Blending modification of PBS/PLA and its enzymatic degradation. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-H.; Wang, X.-Q.; Zeng, J.; Yang, G.; Shi, F.-H.; Yan, Q. Biodegradation of poly(butylene succinate) in compost. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 2273–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14855-1; Determination of the Ultimate Aerobic Biodegradability of Plastic Materials Under Controlled Composting Conditions—Method by Analysis of Evolved Carbon Dioxide—Part 1: General Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 19679; Plastics—Determination of Aerobic Biodegradation of Non-Floating Plastic Materials in a Seawater/Sediment Interface—Method by Analysis of Evolved Carbon Dioxide. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Briassoulis, D.; Pikasi, A.; Papardaki, N.G.; Mistriotis, A. Aerobic biodegradation of bio-based plastics in the seawater/sediment interface (sublittoral) marine environment of the coastal zone—Test method under controlled laboratory conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossno, S.K.; Kalbus, L.H.; Kalbus, G.E. Determinations of Carbon Dioxide by Titration: New Experiments for General, Physical, and Quantitative Analysis Courses. J. Chem. Educ. 1996, 73, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firman, N.F.A.; Noor, A.; Zakir, M.; Maming, M.; Fathurrahman, A.F. Absorption of Carbon Dioxide into Potassium Hydroxide: Preliminary Study for its Application into Liquid Scintillation Counting Procedure. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 4907–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Nan, Z.; Sun, X.; Liu, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Zan, J.; Dai, C.; Liu, Y. Characterization of degradation behaviors of PLA biodegradable plastics by infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 279, 121376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 13432; Packaging—Requirements for Packaging Recoverable Through Composting and Biodegradation—Test Scheme and Evaluation Criteria for the Final Acceptance of Packaging. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- ISO 10694; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic and Total Carbon After Dry Combustion (Elementary Analysis). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- Crystal Thew, X.E.; Lo, S.C.; Ramanan, R.N.; Tey, B.T.; Huy, N.D.; Chien Wei, O. Enhancing plastic biodegradation process: Strategies and opportunities. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 44, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.; Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Selke, S.E.; Singh, S.P. Compostability of Bioplastic Packaging Materials: An Overview. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samneingjam, K.; Mahajaroensiri, J.; Kanathananun, M.; Aranda, C.V.; Muñoz, M.; Limwongsaree, S. Enhancing Polypropylene Biodegradability Through Additive Integration for Sustainable and Reusable Laboratory Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggero, F.; Carretti, E.; Gori, R.; Lotti, T.; Lubello, C. Monitoring of degradation of starch-based biopolymer film under different composting conditions, using TGA, FTIR and SEM analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdlík, P.; Borůvka, M.; Běhálek, L.; Lenfeld, P. The Influence of Additives and Environment on Biodegradation of PHBV Biocomposites. Polymers 2022, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.; Ma, P. The effect of surface area on the degradation rate of nano-fibrous poly(L-lactic acid) foams. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3708–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, Z.K.; Hofmann, A.; Haye, M.; Wilson, S.; Sohoo, I.; Kuchta, K. Lab-scale and on-field industrial composting of biodegradable plastic blends for packaging. Open Res. Eur. 2022, 2, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Calabia, B.P. Biodegradability and biodegradation of poly(lactide). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, S.T.R.; Hu, Q.; Kramm, J.; Santin, V.C.; Völker, C.; Wurm, F.R. Plastics of the Future? An Interdisciplinary Review on Biobased and Biodegradable Polymers: Progress in Chemistry, Societal Views, and Environmental Implications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202423406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-S.; Yoon, J.-S.; Kim, M.-N. Dependence of biodegradability of plastics in compost on the shape of specimens. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 87, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.K.; Sarmah, A.; Bhasney, S.M.; Kalamdhad, A.; Katiyar, V. Demonstrating an ideal compostable plastic using biodegradability kinetics of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) based green biocomposite films under aerobic composting conditions. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Tan, W.; Xi, B. Additives for reducing nitrogen loss during composting: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S.; Duhme, M. Progress of Disintegration of Polylactide (PLA)/Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS) Blends Containing Talc and Chalk Inorganic Fillers under Industrial Composting Conditions. Polymers 2020, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.K.; Bhasney, S.M.; Mudenur, C.; Kalamdhad, A.; Katiyar, V. End-of-life evaluation and biodegradation of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/Polycaprolactone (PCL)/Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) polyblends under composting conditions. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergård, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Preziosi, R.; Robson, G.D. Abiotic and biotic environmental degradation of the bioplastic polymer poly(lactic acid): A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 137, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, M.; Corrigan, O.I.; Ramtoola, Z. Influence of particle size and dissolution conditions on the degradation properties of polylactide-co-glycolide particles. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degradation Rates of Plastics in the Environment|ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06635 (accessed on 18 April 2024).







| Polymer Type | Product | Composition | Sample Name | Size (mm) | TDS (%) | TVS (%) | TOC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS-based | Soft packaging | >85% PBS + <15% additives (mostly mineral fillers) | SP-PBS-1-G | 3.5 × 2 | 99.76 | 89.97 | 53 |
| Soft packaging | 85–90% PBS + 8–15% mineral + <3% processing additives + <2% anti-hydrolysis additives | SP-PBS-2-G | 3.2 × 2.7 × 1.9 | 99.83 | 90.35 | 54 | |
| SP-PBS-2-F | 0.1 | 99.78 | 89.76 | 54 | |||
| SP-PBS-2-TF | 0.01 | 99.68 | 89.88 | 54 | |||
| PLA-based | Mulch film | 50–70% PLA + 10–15% PBAT + 5–15% plasticizer + <5% mineral + <5% processing additives + <15% compatibilized plasticized starch | MF-PLA-1-F | 0.15 | 99.19 | 98.03 | 56 |
| Cutlery | 80% PLA-based compound + 20% ArcBiox X5 degradable glass fiber | C-PLA-1-G | 3 × 2.5 | 99.77 | 80.20 | 44 | |
| Cutlery | 80% PLA-based compound + 20% ArcBiox X5 degradable glass fiber + small amount of processing additives | C-PLA-2-G | 1–2 | 99.86 | 82.32 | 45 | |
| C-PLA-2-G-D | 1–2 | 99.86 | 79.80 | 44 | |||
| Rigid packaging | 60% PLA-based compound + 10% ArcBiox X5 degradable glass fiber + 30% filler + small amount of processing additives | RP-PLA-1-G | 1–2 | 99.94 | 61.02 | 38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyshtva, P.; Voronova, V.; Kuusik, A.; Kobets, Y. Assessing the Biodegradation Characteristics of Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Poly(Lactic Acid) Formulations Under Controlled Composting Conditions. AppliedChem 2025, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5030017
Lyshtva P, Voronova V, Kuusik A, Kobets Y. Assessing the Biodegradation Characteristics of Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Poly(Lactic Acid) Formulations Under Controlled Composting Conditions. AppliedChem. 2025; 5(3):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5030017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyshtva, Pavlo, Viktoria Voronova, Argo Kuusik, and Yaroslav Kobets. 2025. "Assessing the Biodegradation Characteristics of Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Poly(Lactic Acid) Formulations Under Controlled Composting Conditions" AppliedChem 5, no. 3: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5030017
APA StyleLyshtva, P., Voronova, V., Kuusik, A., & Kobets, Y. (2025). Assessing the Biodegradation Characteristics of Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Poly(Lactic Acid) Formulations Under Controlled Composting Conditions. AppliedChem, 5(3), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5030017





