Temporal Changes in the Composition of Beached Holopelagic Sargassum spp. along the Northwestern Coast of Cuba
Abstract
:1. Introduction
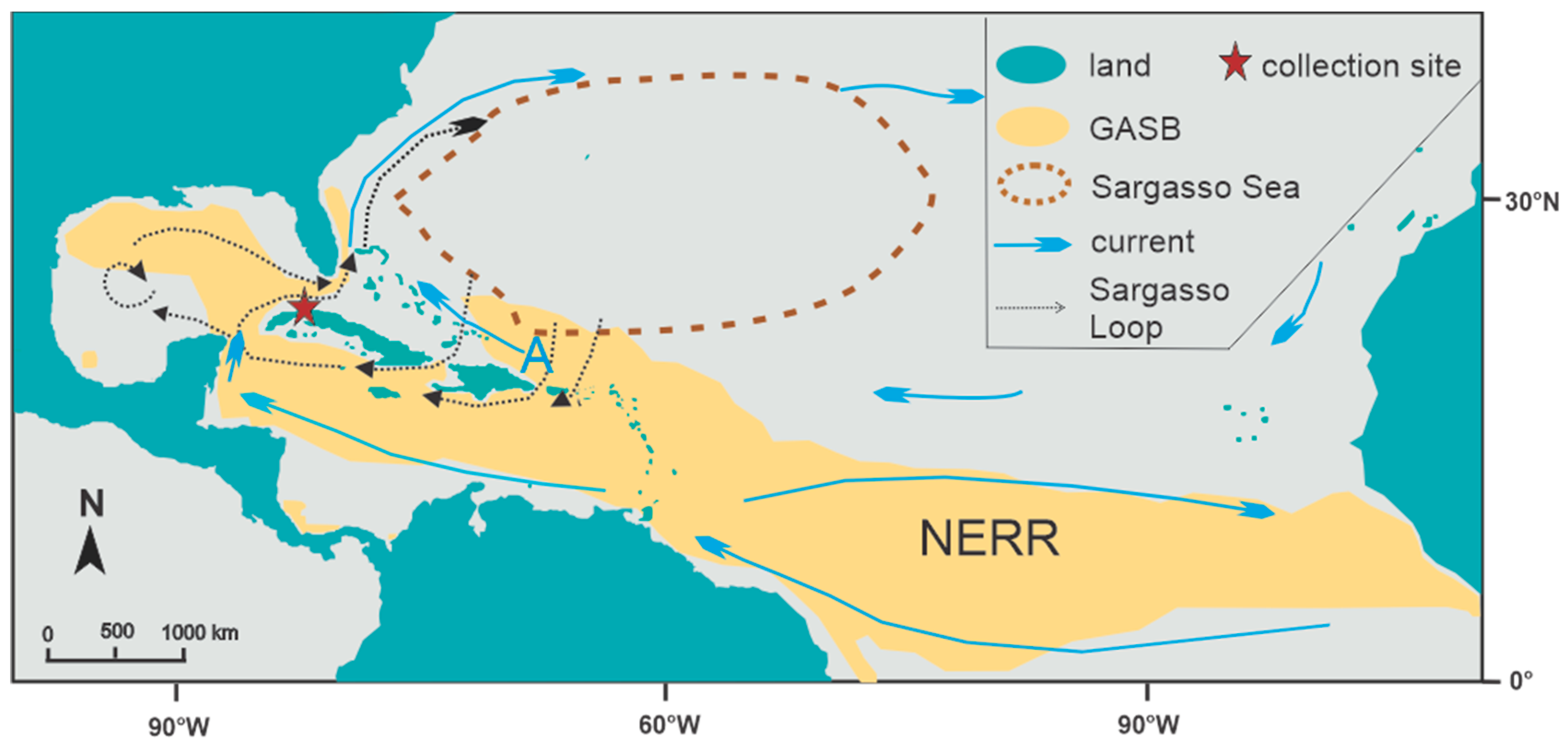
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Beach Surveys
2.2. Data Analysis
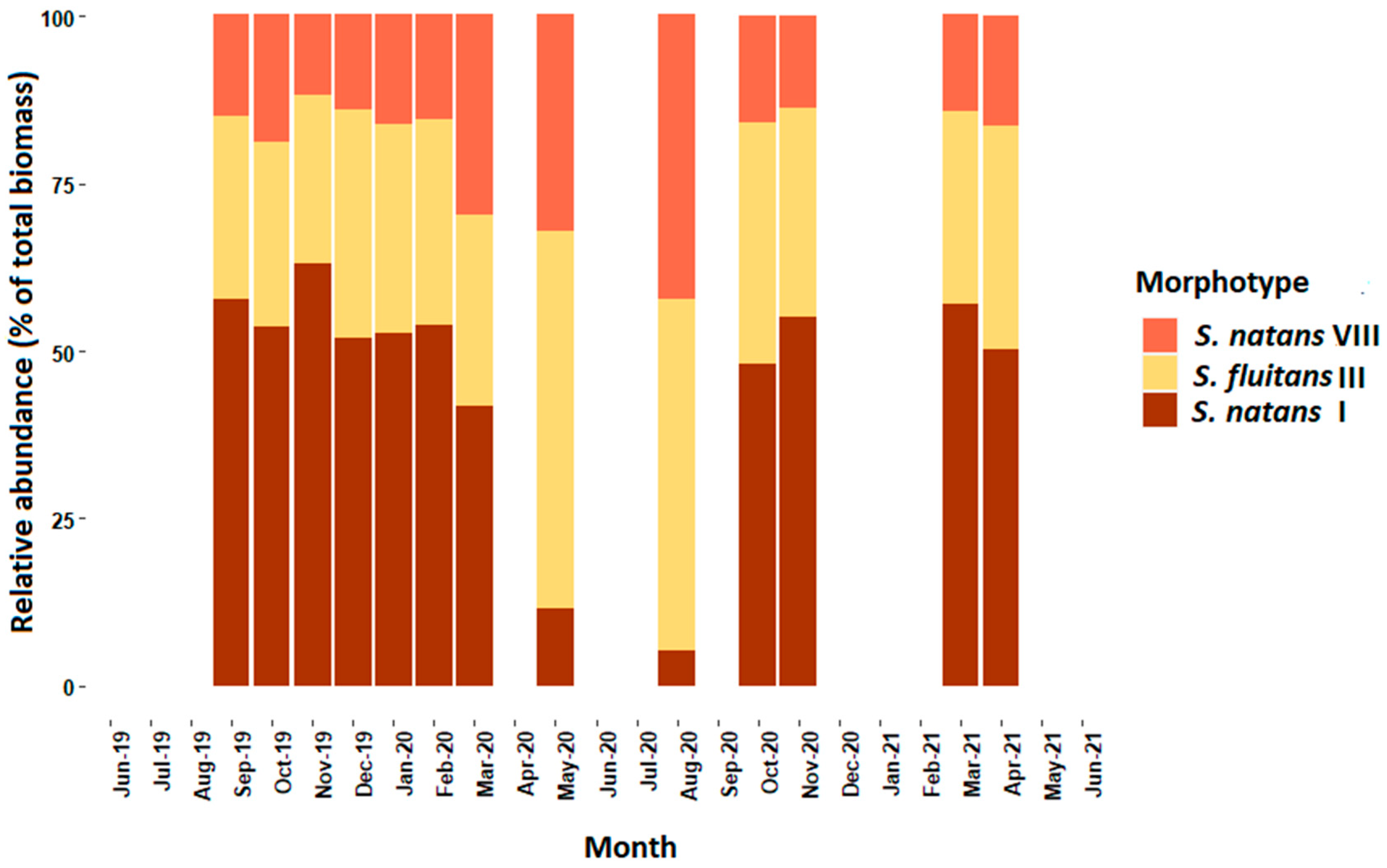
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, M.T.; Coles, V.J.; Hood, R.R.; Gower, J.F.R. Factors controlling the seasonal distribution of pelagic Sargassum. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 599, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Tejeda, R.; Rosado-Jiménez, G.A. Influence of climatic factors on Sargassum arrivals to the coast of the Dominican Republic. J. Oceanogr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 10, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, A. Quantitative observations on the pelagic Sargassum vegetation of the Western North Atlantic. Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Collect. 1939, 6, 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Godínez-Ortega, J.L.; Cuatlán-Cortés, J.V.; López-Bautista, J.M.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. A natural history of floating Sargassum species (Sargasso) from Mexico. In Natural History and Ecology of Mexico and Central America; Hufnagel, L., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, J. Advanced Prediction of the Intra-Americas Sargassum Season through Analysis of the Sargassum Loop System Using Remote Sensing Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2014. Available online: https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/handle/1969.1/153840 (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Laffoley, D.D.; Roe, H.S.; Angel, M.V.; Ardron, J.; Bates, N.R.; Boyd, I.L.; Brooke, S.; Buck, K.N.; Carlson, C.A.; Causey, B.; et al. The Protection and Management of the Sargasso Sea: The Golden Floating Rainforest of the Atlantic Ocean. Summary Science and Supporting Evidence Case; Sargasso Sea Alliance: Bermuda, 2011; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and golden seaweed tides on the rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Mitchum, G.; Lapointe, B.; Montoya, J.P. The great Atlantic Sargassum belt. Science 2019, 365, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, A.S.; De Neef, E.; Stapleton, S. Sargassum accumulation may spell trouble for nesting sea turtles. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Hernández-Arana, H.A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Espinoza-Avalos, J.; Canizales-Flores, H.M.; González-Godoy, C.E.; Barbara-Santos, M.G.; Vega-Zepeda, A.; Collado-Vides, L. Severe impacts of brown tides caused by Sargassum spp. on near-shore Caribbean seagrass communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 272, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Torres-Conde, E.G.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Pelagic Sargassum cleanup cost in Mexico. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 237, 106542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, J.M.; Goodwin, D.S.; Siuda, A.N. Recent Sargassum inundation events in the Caribbean: Shipboard observations reveal dominance of a previously rare form. Oceanography 2015, 28, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.M.; Taylor, M.; Huston, G.; Goodwin, D.S.; Schell, J.M.; Siuda, A.N. Pelagic Sargassum morphotypes support different rafting motile epifauna communities. Mar. Biol. 2021, 168, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibner, S.; Martin, L.; Thibaut, T.; Aurelle, D.; Blanfune, A.; Whittaker, K.; Cooney, L.; Schell, J.; Goodwin, D.; Siuda, A. Consistent genetic divergence observed among pelagic Sargassum morphotypes in the Western North Atlantic. Mar. Ecol. 2022, 43, e12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Dragone, N.B.; Schell, J.; Slikas, B.; Murphy, L.G.; Morrall, C.E.; Zettler, E.R. Comparative mitochondrial and chloroplast genomics of a genetically distinct form of Sargassum contributing to recent “Golden Tides” in the Western Atlantic. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, M.L. Faunal variation on pelagic Sargassum. Mar. Biol. 1970, 7, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Roy, P.D.; Torrescano-Valle, N.; Cabanillas-Terán, N.; Carrillo-Domínguez, S.; Collado-Vides, L.; García-Sánchez, M.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. Element concentrations in pelagic Sargassum along the Mexican Caribbean coast in 2018–2019. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.; Simister, R.; Campbell, S.; Marston, M.; Bose, S.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; Gomez, L.D.; Gallimore, W.A.; Tonon, T. Biomass composition of the golden tide pelagic seaweeds Sargassum fluitans and S. natans (morphotypes I and VIII) to inform valorization pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, T.; Gautier, A.; Connan, S.; Rouget, M.L.; Thibaut, T.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Waeles, M. Trace metal content from holopelagic Sargassum spp. sampled in the tropical North Atlantic Ocean: Emphasis on spatial variation of arsenic and phosphorus. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changeux, T.; Berline, L.; Podlejski, W.; Guillot, T.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Connan, S.; Thibaut, T. Variability in growth and tissue composition (CNP, natural isotopes) of the three morphotypes of holopelagic Sargassum. Hal Open Sci. 2023, 187, 103644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.B.; Maddix, G.M.; Francis, P.; Thomas, S.-L.; Burton, J.-A.; Langer, S.; Larson, T.R.; Marsh, R.; Webber, M.; Tonon, T. Pelagic Sargassum events in Jamaica: Provenance, morphotype abundance, and influence of sample processing on biochemical composition of the biomass. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Flores, P.A.; Gobert, T.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Connan, S.; Robledo, D.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; de Anda Montañez, J.A.; Waeles, M. Inorganic Arsenic in holopelagic Sargassum spp. Stranded in the Mexican Caribbean: Seasonal Variations and Comparison With International Regulations and Guidelines. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 14, 103674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonon, T.; Machado, C.B.; Webber, M.; Webber, D.; Smith, J.; Pilsbury, A.; Cicéron, F.; Herrera-Rodriguez, L.; Jimenez, E.M.; Suarez, J.V.; et al. Biochemical and elemental composition of pelagic Sargassum biomass harvested across the Caribbean. Phycology 2022, 2, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisak, M.D.; Samuel, M.A. Growth rates in culture of several species of Sargassum from Florida, USA. Hydrobiology 1987, 151, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Gallegos, E.; García-Sánchez, M.; Graham, C.; Olivos-Ortiz, A.; Siuda, A.N.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. Growth rates of pelagic Sargassum species in the Mexican Caribbean. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 185, 103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, M.; Oxenford, H.A. Assessing growth of pelagic Sargassum in the Tropical Atlantic. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 187, 103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, M.; Graham, C.; Vera, E.; Escalante-Mancera, E.; Álvarez-Filip, L.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. Temporal changes in the composition and biomass of beached pelagic Sargassum species in the Mexican Caribbean. Aquat. Bot. 2020, 167, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iporac, L.A.; Hatt, D.C.; Bally, N.K.; Castro, A.; Cardet, E.; Mesidor, R.; Olszak, S.; Duran, A.; Burkholder, D.A.; Collado-Vides, L. Community-based monitoring reveals spatiotemporal variation of Sargasso inundation levels and morphotype dominance across the Caribbean and South Florida. Aquat. Bot. 2022, 182, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, R.; Díaz-Larrea, J.; Areces, A.J.; Nuñez-García, L.; Cruz-Aviña, J.R.; Radulovich, R. Registro de arribazón inusual de Sargassum (Phaeophyceae) para la costa Atlántica de Costa Rica. Hidrobiologica 2021, 31, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleyne, K.S.; Johnson, D.; Neat, F.; Oxenford, H.A.; Vallès, H. Seasonal variation in morphotype composition of pelagic Sargassum influx events is linked to oceanic origin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3753. Available online: https://bvearmb.do/handle/123456789/2966 (accessed on 14 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Putman, N.; Hu, C. Sinking Sargassum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluis-Riera, M. Régimen hidrológico de la plataforma insular de Cuba. Cienc. Tierra Espac. 1983, 7, 81–110. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Sissini, M.N.; de Barros Barreto, M.B.B.; Széchy, M.T.M.; de Lucena, M.B.; Oliveira, M.C.; Gower, J.; Liu, G.; de Oliveira Bastos, E.; Milstein, D.; Gusmão, F.; et al. The floating Sargassum (Phaeophyceae) of the South Atlantic Ocean-Likely scenarios. Phycologia 2017, 56, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Conde, E.G.; Martínez-Daranas, B. Oceanographic and spatio-temporal analysis of pelagic Sargassum drifts in Playas del Este, La Habana, Cuba. Rev. Investig. Mar. 2020, 40, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Conde, E.G. Is simultaneous arrival of pelagic Sargassum and Physalis physalis a new threat to the Atlantic coasts? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 275, 107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areces, A.J.; Suárez, A.M.; Valdés, O.; Cano, M. Recomendaciones metodológicas para evaluar el sargazo de arribazón. Arch. Científico Inst. Oceanol. 1993, 1, 758–793. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, L.; Cabrera, R.; Suárez, A.M. Evaluación de macroalgas marinas del género Sargassum C. Agardh (Phaeophyta, Fucales). Rev. Investig. Mar. 2006, 27, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zúñiga, R.D. El género Sargassum (Phaeophyta, Fucales) y sus arribazones a Playa Larga, Cayo Coco, Cuba. Master’s Thesis, Centro de Investigaciones Marinas, Universidad de La Habana, Habana, Cuba, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, E.M.; Lumpkin, R.; Putman, N.F.; Smith, R.H.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Rueda-Roa, D.T.; Hu, C.; Wang, M.; Brooks, M.T.; Gramer, L.J.; et al. The establishment of a pelagic Sargassum population in the tropical Atlantic: Biological consequences of a basin-scale long distance dispersal event. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 182, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ody, A.; Thibaut, T.; Berline, L.; Changeux, T.; André, J.-M.; Chevalier, C.; Blanfuné, A.; Blanchot, J.; Ruitton, S.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; et al. From In Situ to satellite observations of pelagic Sargassum distribution and aggregation in the Tropical North Atlantic Ocean. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martíenz, R.E.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E.; Hu, C. Spatio-temporal variability of pelagic Sargassum landings on the northern Mexican Cariebban. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 27, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satellite-Based Sargassum Watch System (SaWS). Optical Oceanography Laboratory. University of South Florida. 2023. Available online: https://optics.marine.usf.edu/projects/SaWS/pdf/Sargassum_outlook_2021_bulletin11_USF.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Marx, W.; Haunschild, R.; Bornmann, L. Heat waves: A hot topic in climate change research. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 781–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Beach | Coordinates | Length of the Beach (m) | Supralittoral Composition | N | Mean (±SD) Biomass (wet kg m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cojímar | 23°09′47″ N, 82°17′38″ W | ~370 | Sandy | 25 | 1.12 ± 0.4 |
| Bacuranao | 23°10′36″ N, 82°14′30″ W | ~319 | Sandy | 25 | 1.35 ± 0.8 |
| Tarará | 23°10′50″ N, 82°12′11″ W | ~500 | Sandy | 35 | 2.44 ± 1.1 |
| Mégano | 23°10′45″ N 82°11′53″ W | ~500 | Sandy | 35 | 2.25 ± 1.2 |
| Santa María | 23°10′41″ N 82°11′42″ W | ~3000 | Sandy | 35 | 2.45 ± 1.4 |
| Paseo Marítimo | 23°6′49″ N 82°26′24″ W | ~350 | Rocky | 25 | 1.18 ± 0.75 |
| Sampling Date | Wet Biomass (kg m2) | Wind Speed (km/h) | Prevailing Wind Direction | Wave Height (m) | Prevailing Wave Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 June 2019 | 0 | 9 ± 1.1 | E | 0.4 ± 0.2 | E |
| 22 July 2019 | 0 | 12.2 ± 1.2 | SE | 0.7 ± 0.1 | E |
| 25 August 2019 | 0 | 9.26 ± 1.5 | E | 0.5 ± 0.1 | E |
| 21 September 2019 | 0.50 ± 0.16 | 18.5 ± 0.5 | ENE | 1.7 ± 0.3 | ENE |
| 25 October 2019 | 0.81 ± 0.21 | 18.13 ± 0.4 | E | 1.1 ± 0.3 | E |
| 22 November 2019 | 0.90 ± 0.35 | 14.5 ± 2.1 | ENE | 0.9 ± 0.2 | ENE |
| 22 December 2019 | 0.99 ± 0.34 | 21.5 ± 1.2 | ENE | 0.9 ± 0.3 | ENE |
| 22 January 2020 | 1.70 ± 0.46 | 18.75 ± 1.1 | N | 1.7 ± 0.3 | N |
| 23 February 2020 | 1.69 ± 0.25 | 19.5 ± 0.3 | NNE | 1.3 ± 0.2 | NNE |
| 21 March 2020 | 2.39 ± 0.24 | 18 ± 1.12 | E | 1.5 ± 0.3 | E |
| 22April 2020 | 0 | 8.7 ± 1.1 | nd | 0.4 ± 0.1 | W |
| 15 May 2020 | 0.90 ± 0.30 | 21.75 ± 2.3 | ENE | 2 ± 0 | ENE |
| 22 June 2020 | 0 | 9.5 ± 1.2 | E | 0.4 ± 0.1 | E |
| 20 July 2020 | 0 | 11 ± 2.1 | E | 0.85 ± 0.1 | E |
| 25 August 2020 | 2.17 ± 0.8 | 25.5 ± 2.3 | E | 2.5 ± 1.1 | E |
| 22 September 2020 | 0 | 5.25 ± 0.3 | nd | 0.45 ± 0.1 | N |
| 20 October 2020 | 1.63 ± 0.34 | 18.25 ± 2.1 | E | 0.8 ± 0.1 | ENE |
| 20 November 2020 | 1.83 ± 0.68 | 24.25 ± 1.7 | ENE | 2.5 ± 0.2 | ENE |
| 18 December 2020 | 0 | 6.25 ± 1.4 | NNW | 0.43 ± 0.1 | NNW |
| 24 January 2021 | 0 | 6 ± 0.8 | nd | 0.1 ± 0.01 | nd |
| 17 February 2021 | 0 | 7.25 ± 0.7 | S | 0.6 ± 0.5 | S |
| 13 March 2021 | 1.88 ± 0.62 | 19 ± 1.1 | ENE | 1.4 ± 1.3 | ENE |
| 24 April 2021 | 2.06 ± 0.51 | 14.74 ± 1.6 | ENE | 0.4 ± 0.2 | ENE |
| 16 May 2021 | 0 | 12 ± 1.1 | ENE | 0.8 ± 0.2 | ENE |
| 17 June 2021 | 0 | 6.25 ± 0.6 | nd | 0.23 ± 0.01 | nd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Conde, E.G.; van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Martínez-Daranas, B. Temporal Changes in the Composition of Beached Holopelagic Sargassum spp. along the Northwestern Coast of Cuba. Phycology 2023, 3, 405-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040027
Torres-Conde EG, van Tussenbroek BI, Rodríguez-Martínez RE, Martínez-Daranas B. Temporal Changes in the Composition of Beached Holopelagic Sargassum spp. along the Northwestern Coast of Cuba. Phycology. 2023; 3(4):405-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040027
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Conde, Eduardo Gabriel, Brigitta I. van Tussenbroek, Rosa E. Rodríguez-Martínez, and Beatriz Martínez-Daranas. 2023. "Temporal Changes in the Composition of Beached Holopelagic Sargassum spp. along the Northwestern Coast of Cuba" Phycology 3, no. 4: 405-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040027
APA StyleTorres-Conde, E. G., van Tussenbroek, B. I., Rodríguez-Martínez, R. E., & Martínez-Daranas, B. (2023). Temporal Changes in the Composition of Beached Holopelagic Sargassum spp. along the Northwestern Coast of Cuba. Phycology, 3(4), 405-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040027







