Integrative Literature Analysis of Holopelagic Sargassum (Sargasso) in the Western Atlantic (2011–2022): Status, Trends, and Gaps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
- Publication year: The year the scientific paper was published;
- Reporting year: The year in which the species of pelagic sargasso was found. If the study does not present the year of collection/observation, the year of publication was considered;
- Study location: The specific location where the study was conducted. If the article does not present this information, the author’s institution was considered;
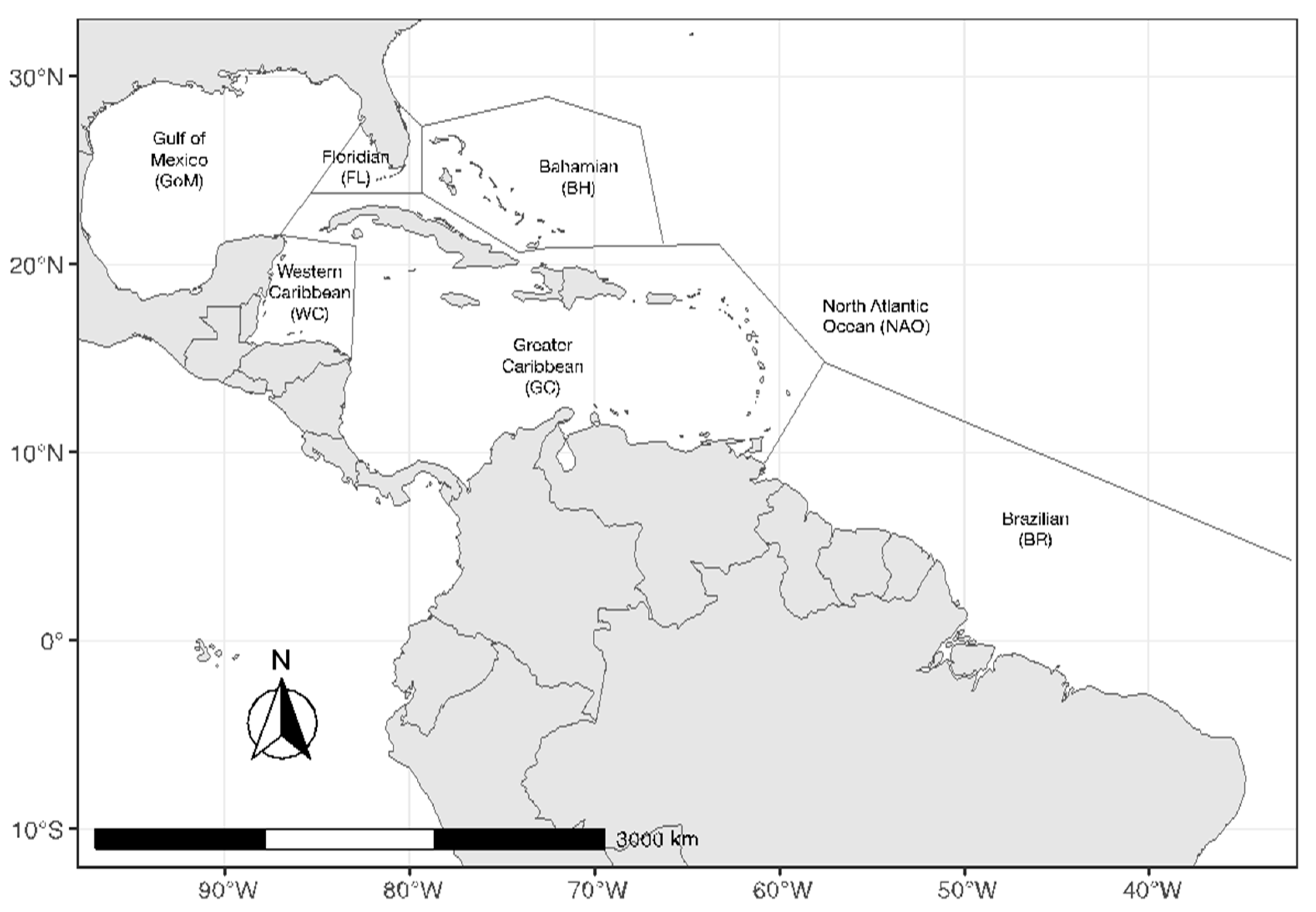
- Subregion: The affected region was divided into subregions to categorize articles based on the location of the study, as shown in Figure 2. For this, seven regions were defined, adapted from Iporac et al. (2022) based on surface current patterns in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea [22,23]. The subregions include the Greater Caribbean (GC), Western Caribbean (WC), Gulf of Mexico (GoM), Floridian (FL), and the Bahamian (BH). Two additional regions were added for this study: Brazilian (BR) and North Atlantic Ocean (NAO). The NAO subregion was used to include studies carried out in the high seas or in multiple locations and subregions;
- Oceanic Zone: Where the pelagic sargasso was found. Only two zones were defined: coastal or oceanic;
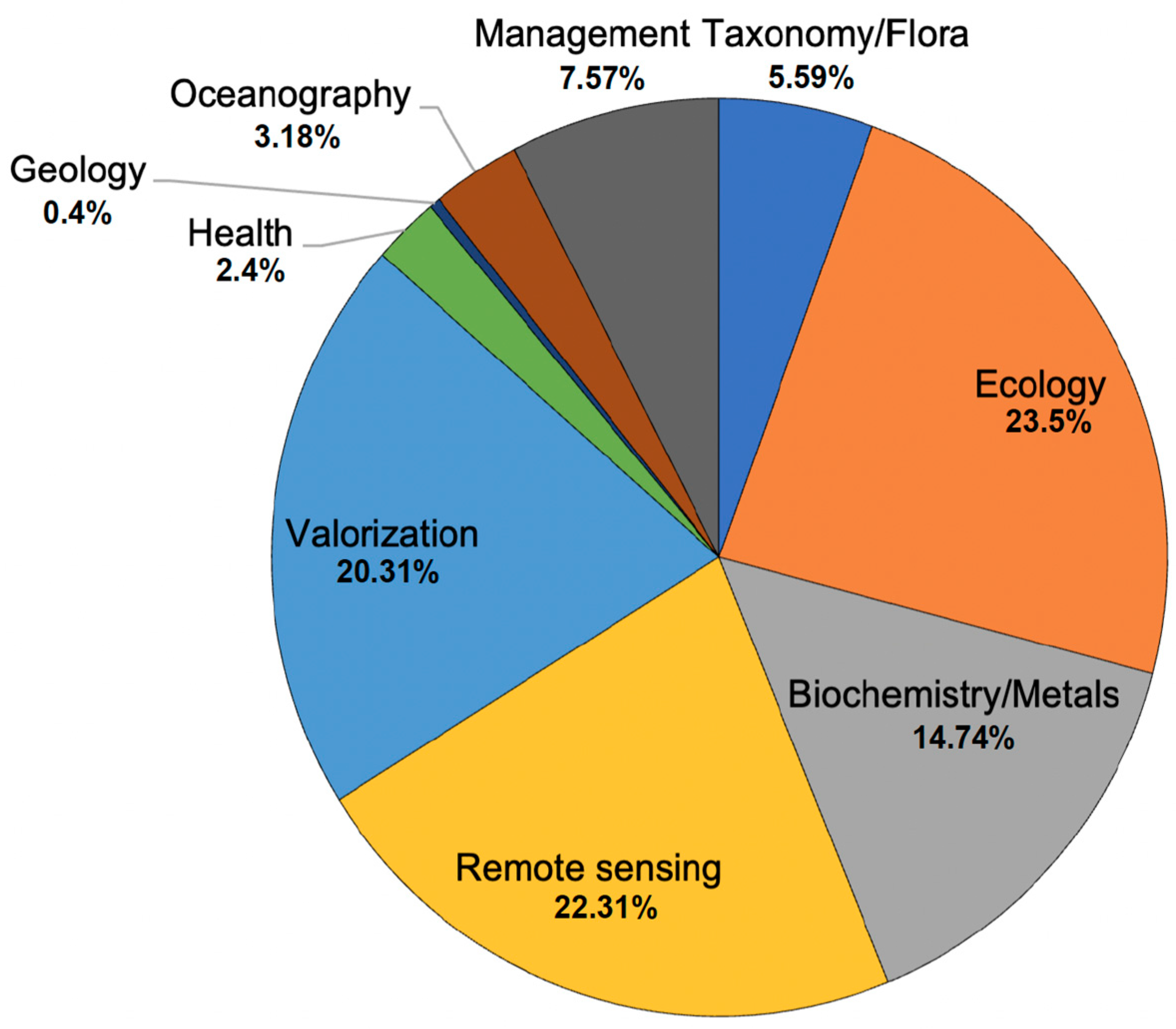
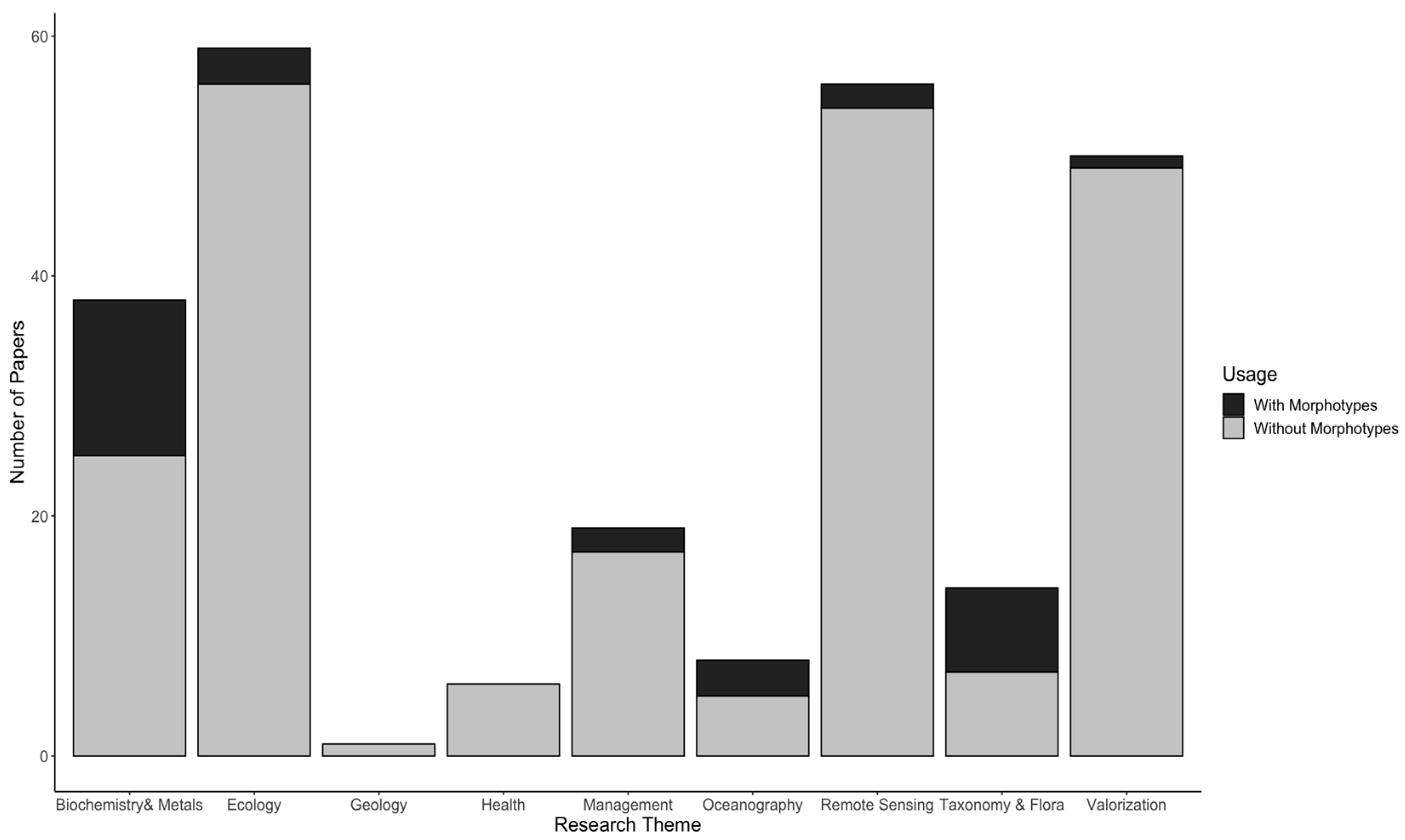
- Themes used to classify each type of study:
- Taxonomy: species molecular identification.
- Ecology: interaction with other species or impact on ecosystems.
- Biochemistry: nutrient, metals, and other chemicals’ tissue content.
- Remote sensing: satellite imagery and mapping.
- Valorization: raw material used in product development.
- Health: impacts on human health.
- Geology: climate changes at the geological scale.
- Oceanography: oceanic current impacts on sargasso transportation.
- Management: biomass influx management.
- Each publication was allocated to only one theme, and the distribution was determined from the keywords and objectives of the research conducted. If a publication applied multiple themes, only the more predominant theme would be considered.
- Type of Science: Studies were categorized into “basic science” and “applied science”. The allocation of each publication depended on the authors’ purpose of the study as determined in the introduction or abstract sections. “Applied science” articles were designated as those with the intention of creating a product or service, while “basic science” articles were designated as those with the intention of contributing to knowledge;
- Keywords: Provided in the article.
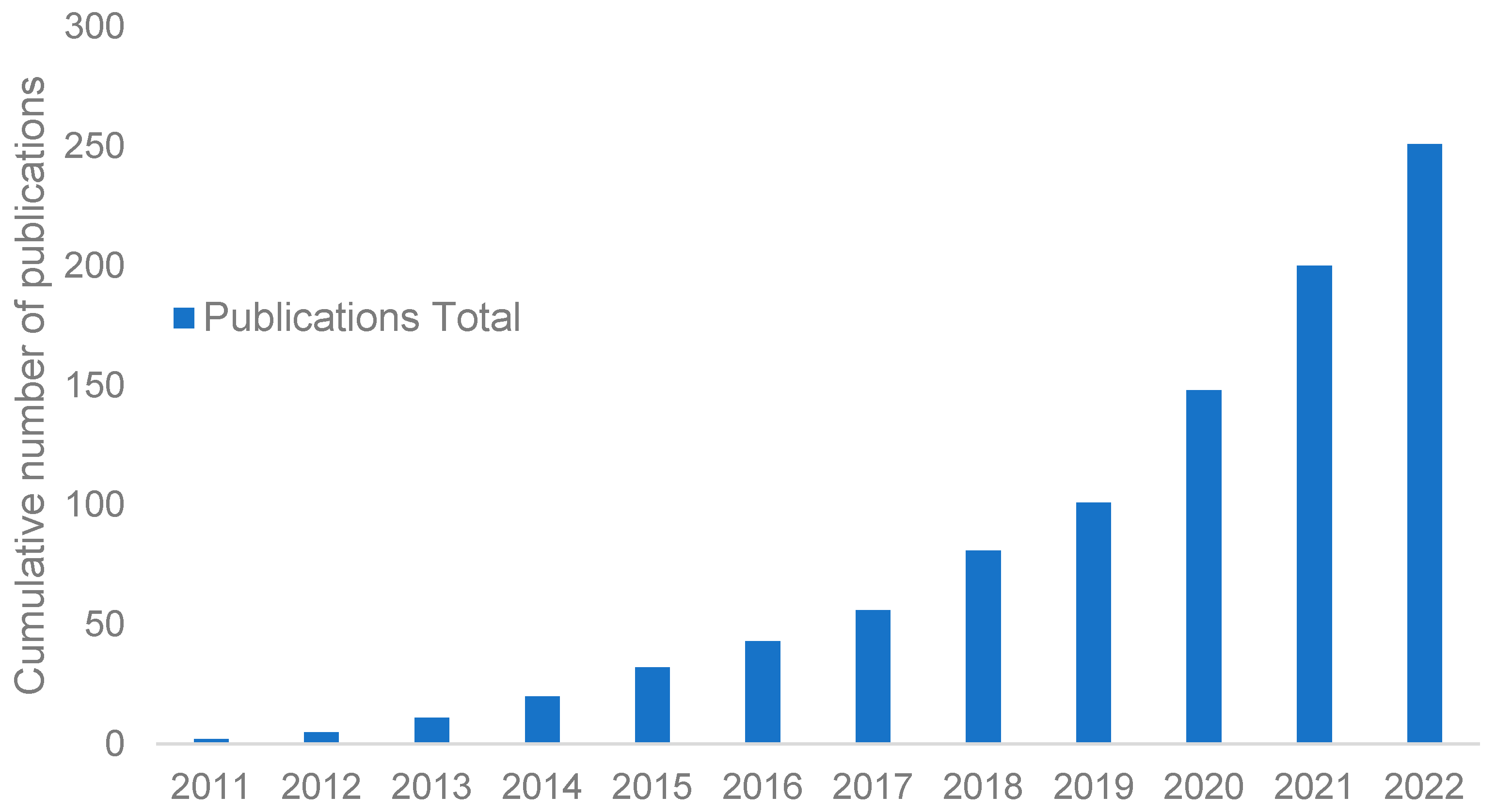
3. Results
Publications Per Subregion
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Addico, G.N.D.; de Graft-Johnson, K.A.A. Preliminary Investigation into the Chemical Composition of the Invasive Brown Seaweed Sargassum along the West Coast of Ghana. AJB 2016, 15, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Mitchum, G.; Lapointe, B.; Montoya, J.P. The Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt. Science 2019, 365, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milledge, J.; Harvey, P.; Milledge, J.J.; Harvey, P.J. Golden Tides: Problem or Golden Opportunity? The Valorisation of Sargassum from Beach Inundations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.M.; Ramin, P.; Udugama, I.; Young, B.R.; Gernaey, K.V.; Baroutian, S. Techno-Economic and Environmental Impact Assessment of Biogas Production and Fertiliser Recovery from Pelagic Sargassum: A Biorefinery Concept for Barbados. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 245, 114605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Hernández Arana, H.A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Espinoza-Avalos, J.; Canizales-Flores, H.M.; González-Godoy, C.E.; Barba-Santos, M.G.; Vega-Zepeda, A.; Collado-Vides, L. Severe Impacts of Brown Tides Caused by Sargassum Spp. on near-Shore Caribbean Seagrass Communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Medina-Valmaseda, A.E.; Blanchon, P.; Monroy-Velázquez, L.V.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Delgado-Pech, B.; Vásquez-Yeomans, L.; Francisco, V.; García-Rivas, M.C. Faunal Mortality Associated with Massive Beaching and Decomposition of Pelagic Sargassum. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, A.E. Quantitative Observations on the Pelagic Sargassum Vegetation of the Western North Atlantic. Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Coll. 1939, 6, 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Dragone, N.B.; Schell, J.; Slikas, B.; Murphy, L.G.; Morrall, C.E.; Zettler, E.R. Comparative Mitochondrial and Chloroplast Genomics of a Genetically Distinct Form of Sargassum Contributing to Recent “Golden Tides” in the Western Atlantic. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibner, S.; Martin, L.; Thibaut, T.; Aurelle, D.; Blanfuné, A.; Whittaker, K.; Cooney, L.; Schell, J.M.; Goodwin, D.S.; Siuda, A.N.S. Consistent Genetic Divergence Observed among Pelagic Sargassum Morphotypes in the Western North Atlantic. Mar. Ecol. 2022, 43, e12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winge, Ö. The Sargasso Sea, Its Boundaries and Vegetation; Carlsberg Physiological Laboratory: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1923; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Schell, J.; Goodwin, D.; Siuda, A. Recent Sargassum Inundation Events in the Caribbean: Shipboard Observations Reveal Dominance of a Previously Rare Form. Oceanography 2015, 28, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.N.; Morris, B.F.; Cadwallader, J.; Stoner, A.W. Studies of Sargassum and the Sargassum Community; Bermuda Biological Station Special Publication. No. 22, 1983; Bermuda Biological Station: Hamilton, Bermuda, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Stoner, A.W. Pelagic Sargassum: Evidence for a Major Decrease in Biomass. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1983, 30, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffoley, D.d’A.; Roe, H.S.; Angel, M.V.; Ardron, J.; Bates, N.R.; Boyd, I.L.; Brooke, S.; Buck, K.N.; Carlson, C.A.; Causey, B. The Protection and Management of the Sargasso Sea; Sargasso Sea Alliance: Hamilton, Bermuda, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.K.; Linton, T. Development and Implementation of Sargassum Early Advisory System (SEAS). Shore Beach 2013, 81, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, J.S.; Johnson, D.R.; Ko, D.S.; Sanchez-Rubio, G.; Hendon, J.R.; Lay, M. Unprecedented influx of pelagic Sargassum along Caribbean island coastlines during summer 2011. Proc. Gulf Caribb. Fish. Inst. 2011, 64, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, J.S.; Johnson, D.R.; Ko, D.S. Pelagic Sargassum in the Tropical North Atlantic. Gulf Caribb. Res. 2016, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, E.M.; Lumpkin, R.; Putman, N.F.; Smith, R.H.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Rueda-Roa, D.T.; Hu, C.; Wang, M.; Brooks, M.T.; Gramer, L.J.; et al. The Establishment of a Pelagic Sargassum Population in the Tropical Atlantic: Biological Consequences of a Basin-Scale Long Distance Dispersal Event. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 182, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.; Noriega, C.; Mascarenhas, A.; Costa, M.; Monteiro, S.; Santana, L.; Silva, I.; Prestes, Y.; Araujo, M.; Rollnic, M. Possible Amazonian Contribution to Sargassum Enhancement on the Amazon Continental Shelf. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Brewton, R.A.; Herren, L.W.; Wang, M.; Hu, C.; McGillicuddy, D.J.; Lindell, S.; Hernandez, F.J.; Morton, P.L. Nutrient Content and Stoichiometry of Pelagic Sargassum Reflects Increasing Nitrogen Availability in the Atlantic Basin. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu-Yang, Y.; Dessert, C.; Losno, R. Atmospheric Deposition over the Caribbean Region: Sea Salt and Saharan Dust Are Sources of Essential Elements on the Island of Guadeloupe. JGR Atmos. 2022, 127, e2022JD037175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.M. Connectivity and Management of Caribbean Coral Reefs. Science 1997, 278, 1454–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.R.; Cramer, K.L. Defining and Dividing the Greater Caribbean: Insights from the Biogeography of Shorefishes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-González, J.G.; Amador-Castro, F.; Gordillo-Sierra, A.R.; García-Cayuela, T.; Alper, H.S.; Carrillo-Nieves, D. Opportunities Surrounding the Use of Sargassum Biomass as Precursor of Biogas, Bioethanol, and Biodiesel Production. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; Young, E.; King, S. Satellite Images Suggest a New Sargassum Source Region in 2011. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniver, C.F.H.; Photiades, A.; Moore, P.J.; Winters, A.L.; Woolmer, A.; Adams, J.M.M. The Global Problem of Nuisance Macroalgal Blooms and Pathways to Its Use in the Circular Economy. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and Golden Seaweed Tides on the Rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosellón-Druker, J.; Calixto-Pérez, E.; Escobar-Briones, E.; González-Cano, J.; Masiá-Nebot, L.; Córdova-Tapia, F. A Review of a Decade of Local Projects, Studies and Initiatives of Atypical Influxes of Pelagic Sargassum on Mexican Caribbean Coasts. Phycology 2022, 2, 254–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidai, Y.A.; Dash, J.; Tompkins, E.L.; Tonon, T. A Systematic Review of Floating and Beach Landing Records of Sargassum beyond the Sargasso Sea. Environ. Res. Commun. 2020, 2, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iporac, L.A.R.; Hatt, D.C.; Bally, N.K.; Castro, A.; Cardet, E.; Mesidor, R.; Olszak, S.; Duran, A.; Burkholder, D.A.; Collado-Vides, L. Community-Based Monitoring Reveals Spatiotemporal Variation of Sargasso Inundation Levels and Morphotype Dominance across the Caribbean and South Florida. Aquat. Bot. 2022, 182, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattio, L.; Payri, C.E. 190 Years of Sargassum taxonomy, facing the advent of DNA phylogenies. Bot. Rev. 2011, 77, 31–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Simister, R.; Campbell, S.; Marston, M.; Bose, S.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; Gomez, L.D.; Gallimore, W.A.; Tonon, T. Biomass Composition of the Golden Tide Pelagic Seaweeds Sargassum Fluitans and S. Natans (Morphotypes I and VIII) to Inform Valorisation Pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 2020, 143134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sánchez, M.; Graham, C.; Vera, E.; Escalante-Mancera, E.; Álvarez-Filip, L.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. Temporal Changes in the Composition and Biomass of Beached Pelagic Sargassum Species in the Mexican Caribbean. Aquat. Bot. 2020, 167, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Delfín, E.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Salazar-Garibay, A.; Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Robledo, D. Species Composition and Chemical Characterization of Sargassum Influx at Six Different Locations along the Mexican Caribbean Coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Gutierrez, R.; Jouanno, J.; Berline, L.; Descloitres, J.; Chevalier, C. Impact of Tropical Cyclones on Pelagic Sargassum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.J.; Dierssen, H.M. Color Change in the Sargassum Crab, Portunus Sayi: Response to Diel Illumination Cycle and Background Albedo. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokina, K.I.; Keeling, P.J.; Tikhonenkov, D.V. Heterotrophic Flagellates and Centrohelid Heliozoans from Marine Waters of Curacao, the Netherlands Antilles. Eur. J. Protistol. 2021, 77, 125758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegwalt, F.; Jeantet, L.; Lelong, P.; Martin, J.; Girondot, M.; Bustamante, P.; Benhalilou, A.; Murgale, C.; Andreani, L.; Jacaria, F.; et al. Food Selection and Habitat Use Patterns of Immature Green Turtles (Chelonia Mydas) on Caribbean Seagrass Beds Dominated by the Alien Species Halophila Stipulacea. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 37, e02169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherington, B.; Hirama, S.; Hardy, R. Young Sea Turtles of the Pelagic Sargassum-Dominated Drift Community: Habitat Use, Population Density, and Threats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 463, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenería, F.A.M.; Labrada-Martagón, V.; Herrera-Pavón, R.L.; Work, T.M.; González-Ballesteros, E.; Negrete-Philippe, A.C.; Maldonado-Saldaña, G. Fibropapillomatosis Dynamics in Green Sea Turtles Chelonia Mydas over 15 Years of Monitoring in Akumal Bay, Quintana Roo, Mexico. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2022, 149, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Quintana-Pali, G.; Trujano-Rivera, K.I.; Herrera, R.; del Carmen García-Rivas, M.; Ortíz, A.; Castañeda, G.; Maldonado, G.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Sargassum Landings Have Not Compromised Nesting of Loggerhead and Green Sea Turtles in the Mexican Caribbean. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.E.; Torres-Conde, E.G.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E. Pelagic Sargassum Cleanup Cost in Mexico. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2023, 237, 106542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degia, A.K.; Small, M.; Oxenford, H.A. Applying Hazard Risk Assessment and Spatial Planning Tools to Sargassum Inundations in the Eastern Caribbean Small Island States as a Basis for Improving Response; University of West Indies: Cave Hill, Barbados, 2022; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Desrochers, A.; Cox, S.-A.; Oxenford, H.A.; van Tussenbroek, B. Pelagic Sargassum—A Guide to Current and Potential Uses in the Caribbean; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Papers; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Boggild, A.K.; Wilson, M.E. What Every Travel Medicine Practitioner Needs to Know about Sargassum Weed: Five Key Points. J. Travel Med. 2019, 26, taz048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lanlay, D.B.; Monthieux, A.; Banydeen, R.; Jean-Laurent, M.; Resiere, D.; Drame, M.; Neviere, R. Risk of Preeclampsia among Women Living in Coastal Areas Impacted by Sargassum Strandings on the French Caribbean Island of Martinique. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 94, 103894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, D.; Villalobos-Sánchez, E.; Alam-Escamilla, D.; Elizondo-Quiroga, D. In Vitro Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Dry Algae Powders. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merle, H.; Resière, D.; Mesnard, C.; Pierre, M.; Jean-Charles, A.; Béral, L.; Nevière, R. Case Report: Two Cases of Keratoconjunctivitis Tied to Sargassum Algae Emanations. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resiere, D.; Valentino, R.; Nevière, R.; Banydeen, R.; Gueye, P.; Florentin, J.; Cabié, A.; Lebrun, T.; Mégarbane, B.; Guerrier, G.; et al. Sargassum Seaweed on Caribbean Islands: An International Public Health Concern. Lancet 2018, 392, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resiere, D.; Mehdaoui, H.; Florentin, J.; Gueye, P.; Lebrun, T.; Blateau, A.; Viguier, J.; Valentino, R.; Brouste, Y.; Kallel, H.; et al. Sargassum Seaweed Health Menace in the Caribbean: Clinical Characteristics of a Population Exposed to Hydrogen Sulfide during the 2018 Massive Stranding. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 2020, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz Schiro, J.A.; Meyer-Arendt, K.J.; Schneider, S.K. Sargassum on Santa Rosa Island, Florida: Faunal Use and Beachgoer Perception. J. Coast Conserv. 2017, 21, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Environment Programme—Caribbean Environment Programme Sargassum White Paper—Turning the Crisis into an Opportunity; United Nations: Kingston, Jamaica, 2021; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.; Coles, V.; Hood, R.; Gower, J. Factors controlling the seasonal distribution of pelagic Sargassum. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 599, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinanes, J.; Putman, N.F.; Goni, G.; Hu, C.; Wang, M. Monitoring pelagic Sargassum inundation potential for coastal communities. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2021, 2021, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Gallegos, E.; García-Sánchez, M.; Graham, C.; Olivos-Ortiz, A.; Siuda, A.N.S.; van Tussenbroek, B.I. Growth Rates of Pelagic Sargassum Species in the Mexican Caribbean. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 185, 103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C. Automatic Extraction of Sargassum Features from Sentinel-2 MSI Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 2579–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beron-Vera, F.J.; Miron, P. A minimal Maxey–Riley model for the drift of Sargassum rafts. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 904, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hu, C. Satellite Remote Sensing of Pelagic Sargassum Macroalgae: The Power of High Resolution and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Murch, B.; Barnes, B.; Wang, M.; Maréchal, J.-P.; Franks, J.; Johnson, D.; Lapointe, B.; Goodwin, D.; Schell, J.; et al. Sargassum Watch Warns of Incoming Seaweed. Eos 2016, 97, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Feng, L.; Hardy, R.F.; Hochberg, E.J. Spectral and spatial requirements of remote measurements of pelagic Sargassum macroalgae. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyesiku, O.; Egunyomi, A. Identification and chemical studies of pelagic masses of Sargassum natans (Linnaeus) Gaillon and S. fluitans (Borgessen) Borgesen (brown algae), found offshore in Ondo State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
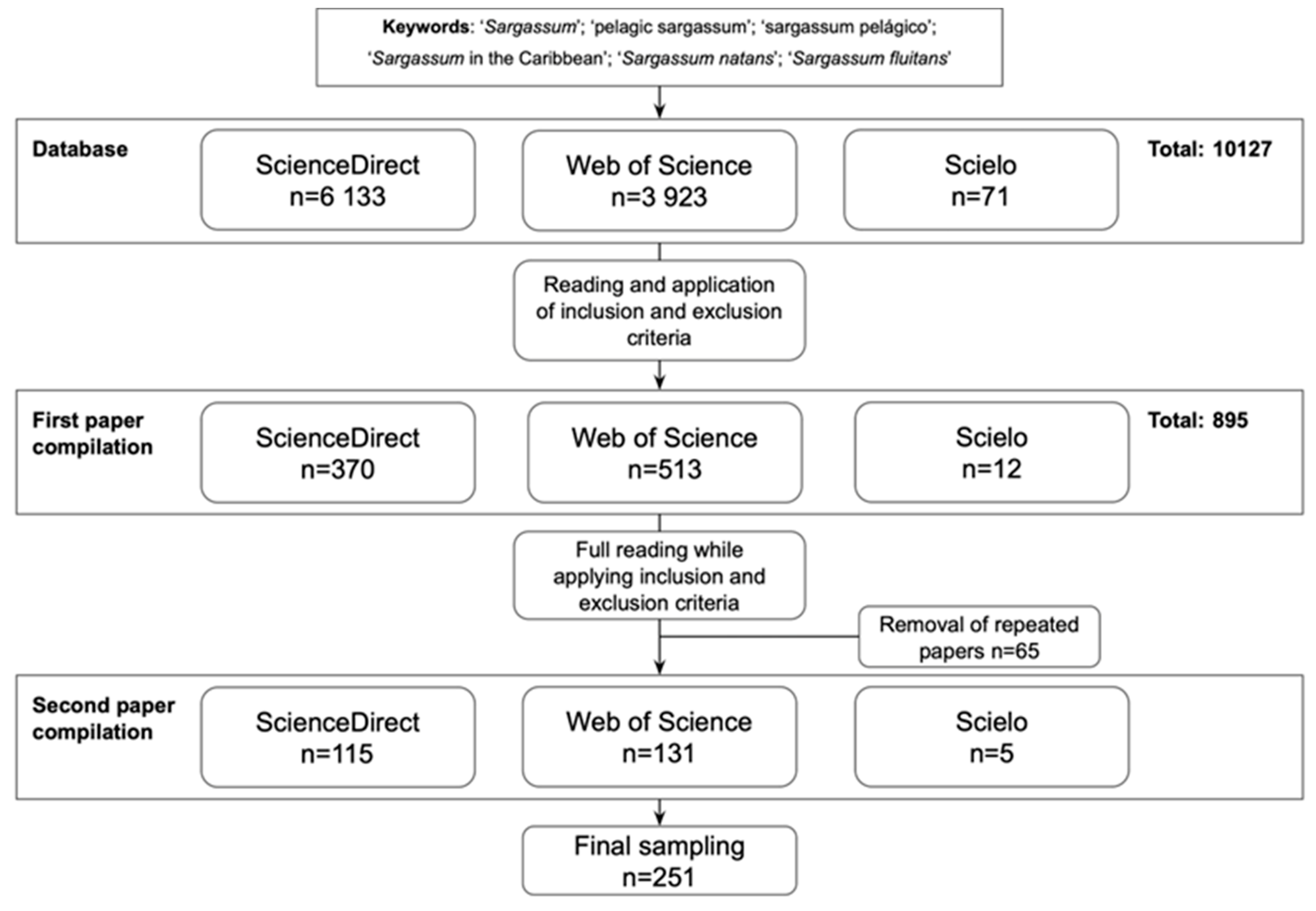


| Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arita, J.T.; Iporac, L.A.R.; Bally, N.K.; Fujii, M.T.; Collado-Vides, L. Integrative Literature Analysis of Holopelagic Sargassum (Sargasso) in the Western Atlantic (2011–2022): Status, Trends, and Gaps. Phycology 2023, 3, 447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040030
Arita JT, Iporac LAR, Bally NK, Fujii MT, Collado-Vides L. Integrative Literature Analysis of Holopelagic Sargassum (Sargasso) in the Western Atlantic (2011–2022): Status, Trends, and Gaps. Phycology. 2023; 3(4):447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleArita, Julianna T., Lowell Andrew R. Iporac, Natalie K. Bally, Mutue T. Fujii, and Ligia Collado-Vides. 2023. "Integrative Literature Analysis of Holopelagic Sargassum (Sargasso) in the Western Atlantic (2011–2022): Status, Trends, and Gaps" Phycology 3, no. 4: 447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040030
APA StyleArita, J. T., Iporac, L. A. R., Bally, N. K., Fujii, M. T., & Collado-Vides, L. (2023). Integrative Literature Analysis of Holopelagic Sargassum (Sargasso) in the Western Atlantic (2011–2022): Status, Trends, and Gaps. Phycology, 3(4), 447-458. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3040030







