Ablefit: Development of an Advanced System for Rehabilitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
- Health professionals—minimum academic qualifications of a degree and clinical experience in a hospital setting of 2 or more years.
- Senior adults—aged 65 years or over with a healthy physical condition.
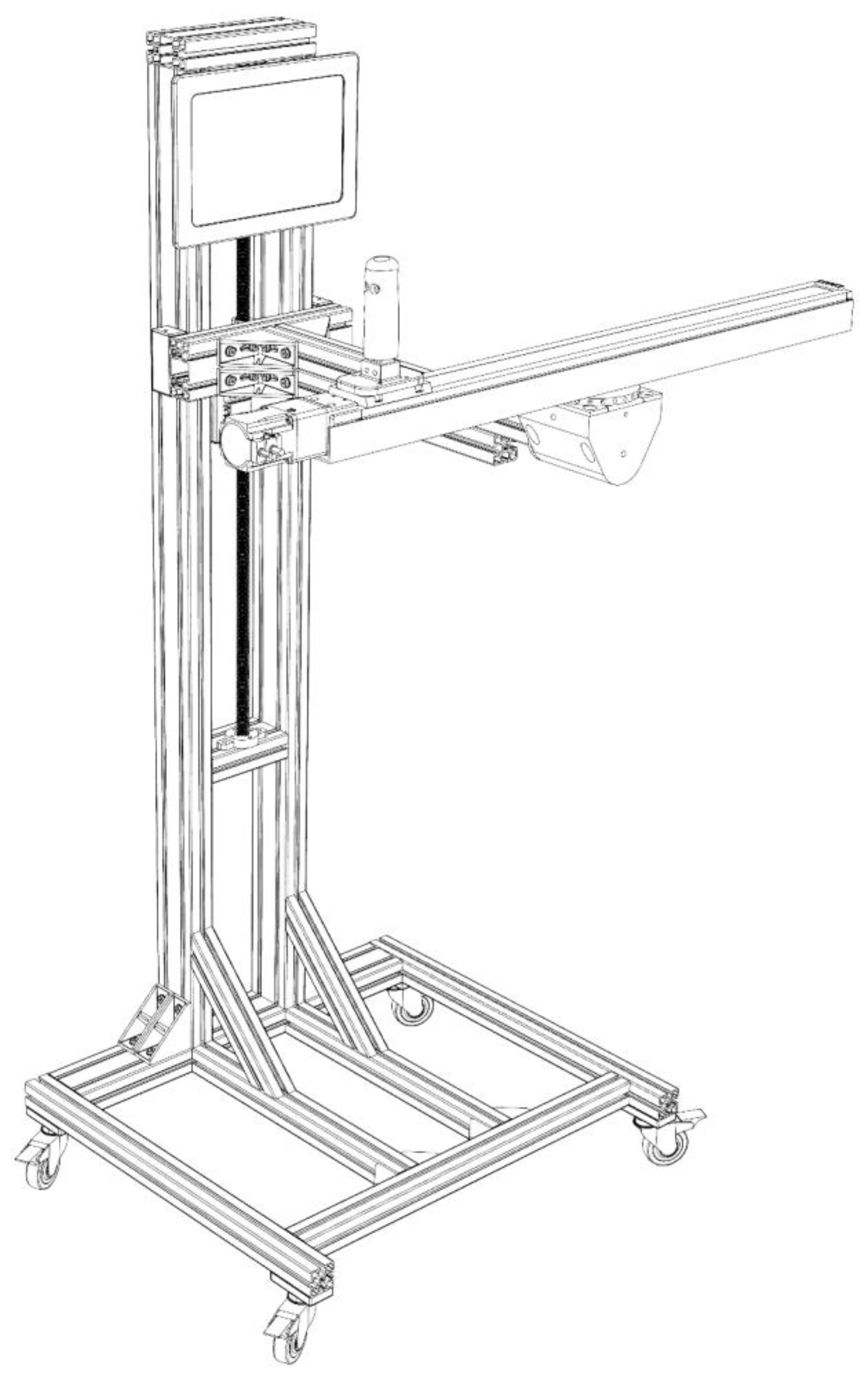
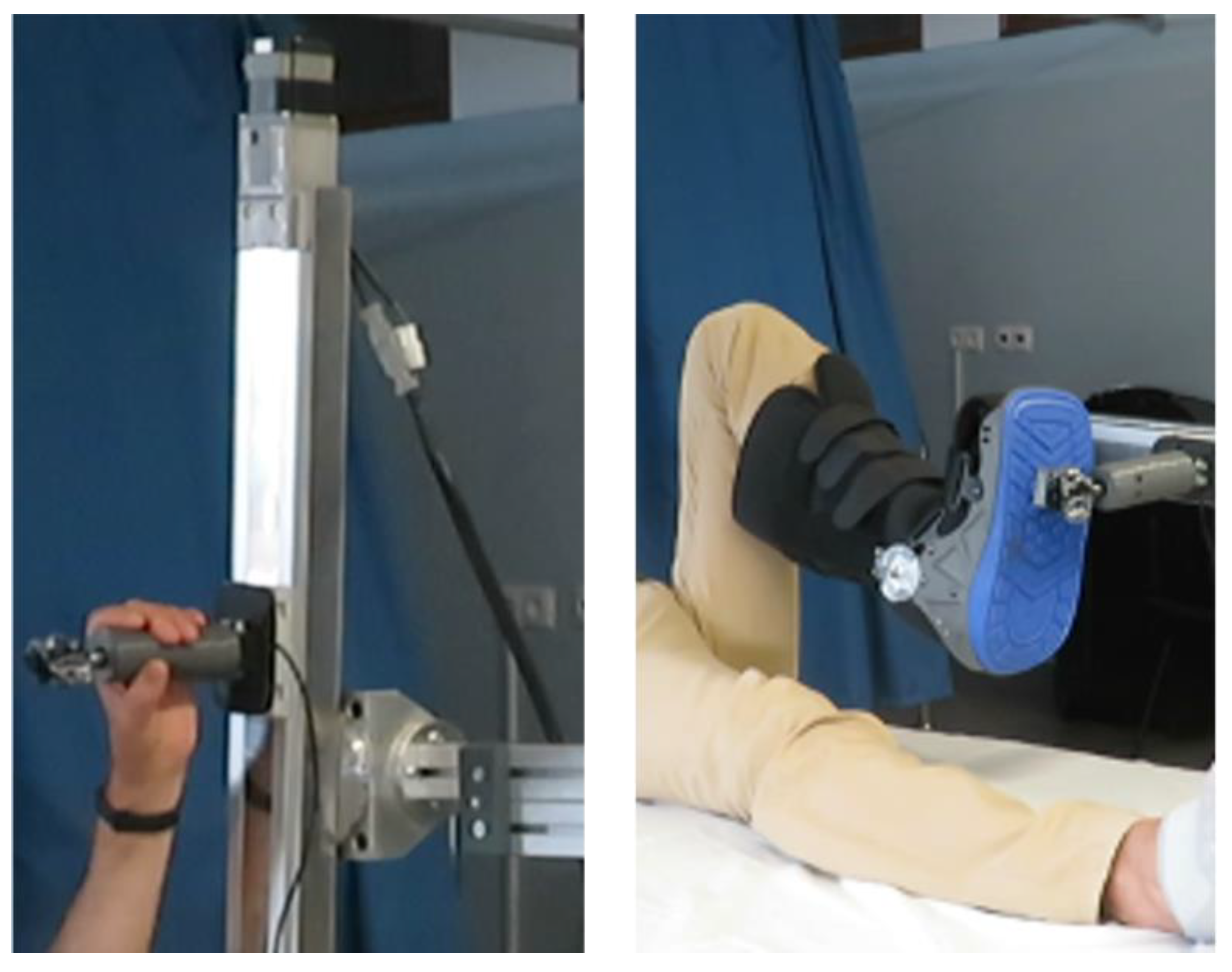
2.2. Medical Device (Ablefit)
2.3. Pre-Clinical Usability Study
2.3.1. Professionals
2.3.2. End-Users
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. End-Users/Senior Adult
3.1.1. Device Security
3.1.2. Ease of Use/Learning
3.1.3. Comfort
3.1.4. Movements
3.1.5. Benefits
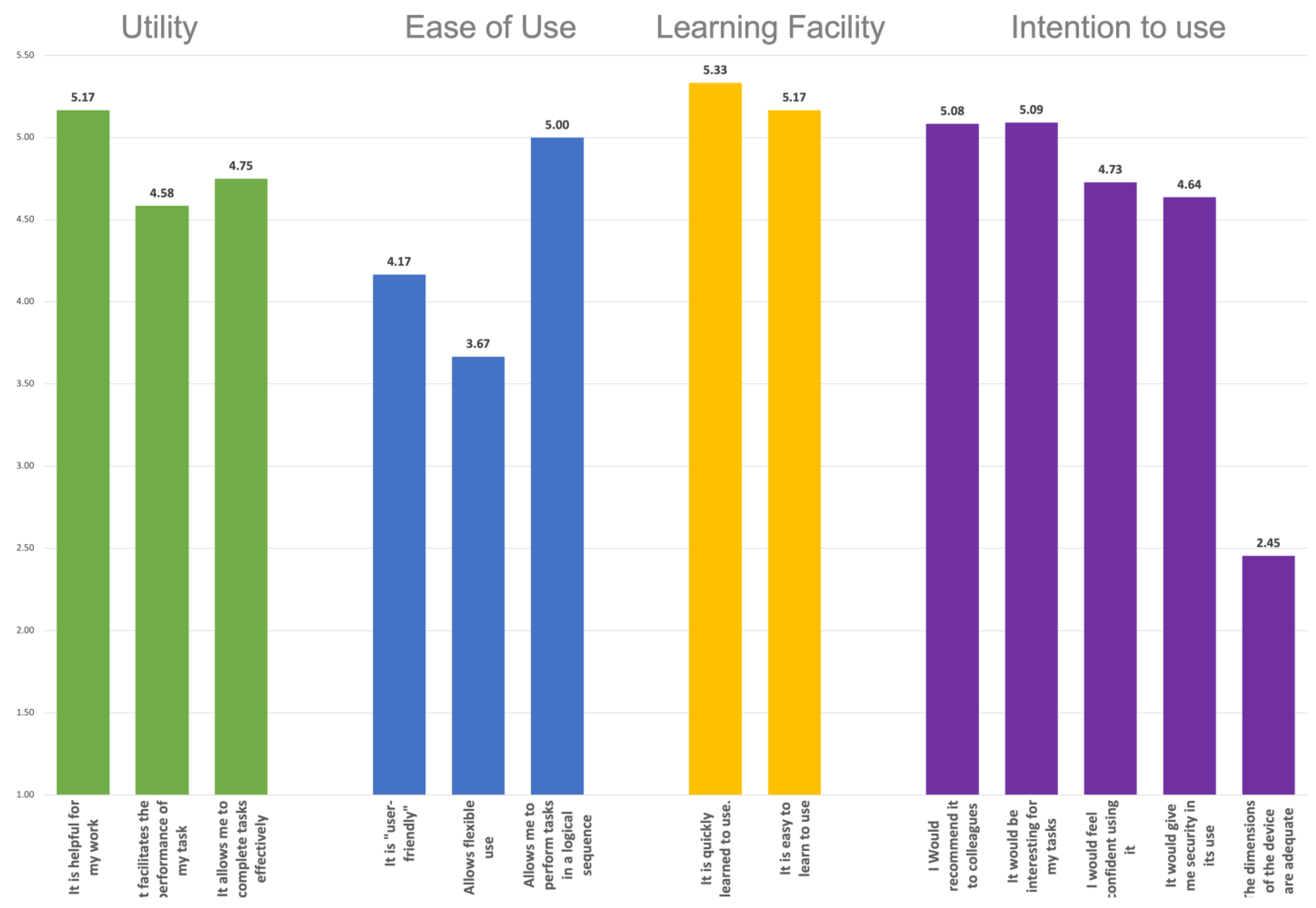
3.2. Professional User
4. Discussion
4.1. Safety
4.2. Functionality and Ergonomy
4.3. Benefits of Ablefit
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Future Directions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Cao, J.; Jiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Song, B.; Jin, J.; et al. The Association between Major Complications of Immobility during Hospitalization and Quality of Life among Bedridden Patients: A 3 Month Prospective Multi-Center Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Jiao, J.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; et al. Factors Associated with Death in Bedridden Patients in China: A Longitudinal Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Cao, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhu, C.; Song, B.; Jin, J.; et al. Risk Factors for 3-Month Mortality in Bedridden Patients with Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia: A Multicentre Prospective Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salz, I.W.; Carmeli, Y.; Levin, A.; Fallach, N.; Braun, T.; Amit, S. Elderly Bedridden Patients with Dementia Use over One Quarter of Resources in Internal Medicine Wards in an Israeli Hospital. Isr. J. Health Policy Res. 2020, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanejima, Y.; Shimogai, T.; Kitamura, M.; Ishihara, K.; Izawa, K.P. Effect of Early Mobilization on Physical Function in Patients after Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Deng, Y.; Yu, K.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Ma, J.; et al. Early Mobilization of Critically Ill Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coles, S.J.; Erdogan, M.; Higgins, S.D.; Green, R.S. Impact of an Early Mobilization Protocol on Outcomes in Trauma Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit: A Retrospective Pre-Post Study. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 88, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaparthi, G.K.; Gatty, A.; Samuel, S.R.; Amaravadi, S.K. Effectiveness, Safety, and Barriers to Early Mobilization in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 7840743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqel, M.O.A.; Brabazon, D.; Issa, A.; Elsharif, A.A.; Ghaben, S.; Alajerami, Y.S.M.; Khalaf, H.; Alrayyes, T.; Bratanov, D.; Debeljak, M. Review of Recent Research Trends in Assistive Technologies for Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Promising Electronic Technologies (ICPET), Gaza, Palestine, 23–24 October 2019; pp. 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, R.A.; Santos-Costa, P.; Sousa, L.B.; Graveto, J.; Salgueiro-Oliveira, A.; Serambeque, B.; Marques, I.; Cruz, A.; Parreira, P. Innovative Devices for Bedridden Older Adults Upper and Lower Limb Rehabilitation: Key Characteristics and Features; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1185, ISBN 9783030414931. [Google Scholar]
- Masengo, G.; Zhang, X.; Dong, R.; Alhassan, A.B.; Hamza, K.; Mudaheranwa, E. Lower Limb Exoskeleton Robot and Its Cooperative Control: A Review, Trends, and Challenges for Future Research. Front. Neurorobot. 2023, 16, 913748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Xue, Q. Lower Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton Robot: A Review. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2021, 13, 168781402110118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharififar, S.; Shuster, J.J.; Bishop, M.D. Adding Electrical Stimulation during Standard Rehabilitation after Stroke to Improve Motor Function. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, S.F.M.; Chia, P.F.; Fong, K.N.K. Effectiveness of Home-Based Upper Limb Rehabilitation in Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 964196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumaa, M.; Rehan Youssef, A. Is Virtual Reality Effective in Orthopedic Rehabilitation? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. 2019, 99, 1304–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsaki, I.; Dimitriadi, N.; Despoti, A.; Tzoumi, D.; Leventakis, N.; Roussou, G.; Papathanasiou, A.; Nanas, S.; Karatzanos, E. The Effectiveness of Immersive Virtual Reality in Physical Recovery of Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 880447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rooij, I.J.M.; van de Port, I.G.L.; Meijer, J.-W.G. Effect of Virtual Reality Training on Balance and Gait Ability in Patients With Stroke: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tyson, S.; Weightman, A. Professionals’ Views and Experiences of Using Rehabilitation Robotics With Stroke Survivors: A Mixed Methods Survey. Front. Med. Technol. 2021, 3, 780090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qassim, H.M.; Wan Hasan, W.Z. A Review on Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robots. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, C.; Sayer, A.A. Improving Muscle Strength and Physical Function in Older People Living with Sarcopenia and Physical Frailty: Not All Exercise Is Created Equal. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2022, 52, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bårdstu, H.B.; Andersen, V.; Fimland, M.S.; Aasdahl, L.; Raastad, T.; Cumming, K.T.; Sæterbakken, A.H. Effectiveness of a Resistance Training Program on Physical Function, Muscle Strength, and Body Composition in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Receiving Home Care: A Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, J.S.; Fox, J.E. Usability Testing. In Human Computer Interaction Handbook. Fundamentals, Evolving. Technologies, and Emerging Applications, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 1221–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.; Parola, V.; Neves, H.; Bernardes, R.A.; Duque, F.M.; Mendes, C.A.; Pimentel, M.; Caetano, P.; Petronilho, F.; Albuquerque, C.; et al. Physical Rehabilitation Programs for Bedridden Patients with Prolonged Immobility: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.G.; Potrebny, T.; Larun, L.; Ciliska, D.; Olsen, N.R. Usability Methods and Attributes Reported in Usability Studies of Mobile Apps for Health Care Education: Scoping Review. JMIR Med. Educ. 2022, 8, e38259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvain, F.; Chaniaud, N. Multi-User Centered Design: Acceptance, User Experience, User Research and User Testing. Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Council of the European Union Regulation (Eu) 2017/745 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Medical Device Regulation—Annex I, Section 23.1(D). Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 60, 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho, K.E.C.; Gois Júnior, M.B.; Sá, K.N. Tradução e Validação Do Quebec User Evaluation of Satisfaction with Assistive Technology (QUEST 2.0) Para o Idioma Português Do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2014, 54, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortum, P.T.; Bangor, A. Usability Ratings for Everyday Products Measured With the System Usability Scale. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2013, 29, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.R. Psychometric Evaluation of an After-Scenario Questionnaire for Computer Usability Studies. ACM SIGCHI Bull. 1991, 23, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.R. Psychometric Evaluation of the PSSUQ Using Data from Five Years of Usability Studies. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2002, 14, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.F.; Martins, A.I.; Costa, V.; Queiros, A.; Silva, A.; Rocha, N.P. European Portuguese Validation of the Post-Study System Usability Questionnaire (PSSUQ). In Proceedings of the 2015 10th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Aveiro, Portugal, 17–20 June 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbary Sartang, A.; Ashnagar, M.; Habibi, E.; Sadeghi, S. Evaluation of Rating Scale Mental Effort (RSME) Effectiveness for Mental Workload Assessment in Nurses. J. Occup. Health Epidemiol. 2016, 5, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.M.; Miskulin, R.G.S. Content Analysis as a Methodology. Cad. Pesqui. 2017, 47, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vears, D.F.; Gillam, L. Inductive Content Analysis: A Guide for Beginning Qualitative Researchers. Focus Health Prof. Educ. A Multi-Prof. J. 2022, 23, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitkina, O.V.; Kim, H.K.; Park, J. Usability and User Experience of Medical Devices: An Overview of the Current State, Analysis Methodologies, and Future Challenges. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2020, 76, 102932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppelaar, E. Use and Effect of Ergonomic Devices in Healthcare; Erasmus University Rotterdam: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 60, ISBN 9789461693518. [Google Scholar]
- Zamzam, A.H.; Abdul Wahab, A.K.; Azizan, M.M.; Satapathy, S.C.; Lai, K.W.; Hasikin, K. A Systematic Review of Medical Equipment Reliability Assessment in Improving the Quality of Healthcare Services. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 753951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnard, A.; Debuse, D.; Wilkinson, M.; Samson, L.; Weber, T.; Caplan, N. Movement Amplitude on the Functional Re-Adaptive Exercise Device: Deep Spinal Muscle Activity and Movement Control. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| OBSERVED PROBLEM | SOLUTION PROPOSAL |
|---|---|
| Software | Software |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Hardware | Hardware |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neves, H.; Cruz, A.; Bernardes, R.A.; Cardoso, R.; Pimentel, M.; Duque, F.M.; Lopes, E.; Veiga, D.; Malça, C.; Durães, R.; et al. Ablefit: Development of an Advanced System for Rehabilitation. BioMedInformatics 2023, 3, 164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3010012
Neves H, Cruz A, Bernardes RA, Cardoso R, Pimentel M, Duque FM, Lopes E, Veiga D, Malça C, Durães R, et al. Ablefit: Development of an Advanced System for Rehabilitation. BioMedInformatics. 2023; 3(1):164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeves, Hugo, Arménio Cruz, Rafael A. Bernardes, Remy Cardoso, Mónica Pimentel, Filipa Margarida Duque, Eliana Lopes, Daniela Veiga, Cândida Malça, Rúben Durães, and et al. 2023. "Ablefit: Development of an Advanced System for Rehabilitation" BioMedInformatics 3, no. 1: 164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3010012
APA StyleNeves, H., Cruz, A., Bernardes, R. A., Cardoso, R., Pimentel, M., Duque, F. M., Lopes, E., Veiga, D., Malça, C., Durães, R., Corrente, G., Parreira, P., Apóstolo, J., & Parola, V. (2023). Ablefit: Development of an Advanced System for Rehabilitation. BioMedInformatics, 3(1), 164-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics3010012







