Exergo-Economic Analysis of Solar-Driven Ammonia Production System for a Sustainable Energy Carrier †
Abstract
1. Introduction
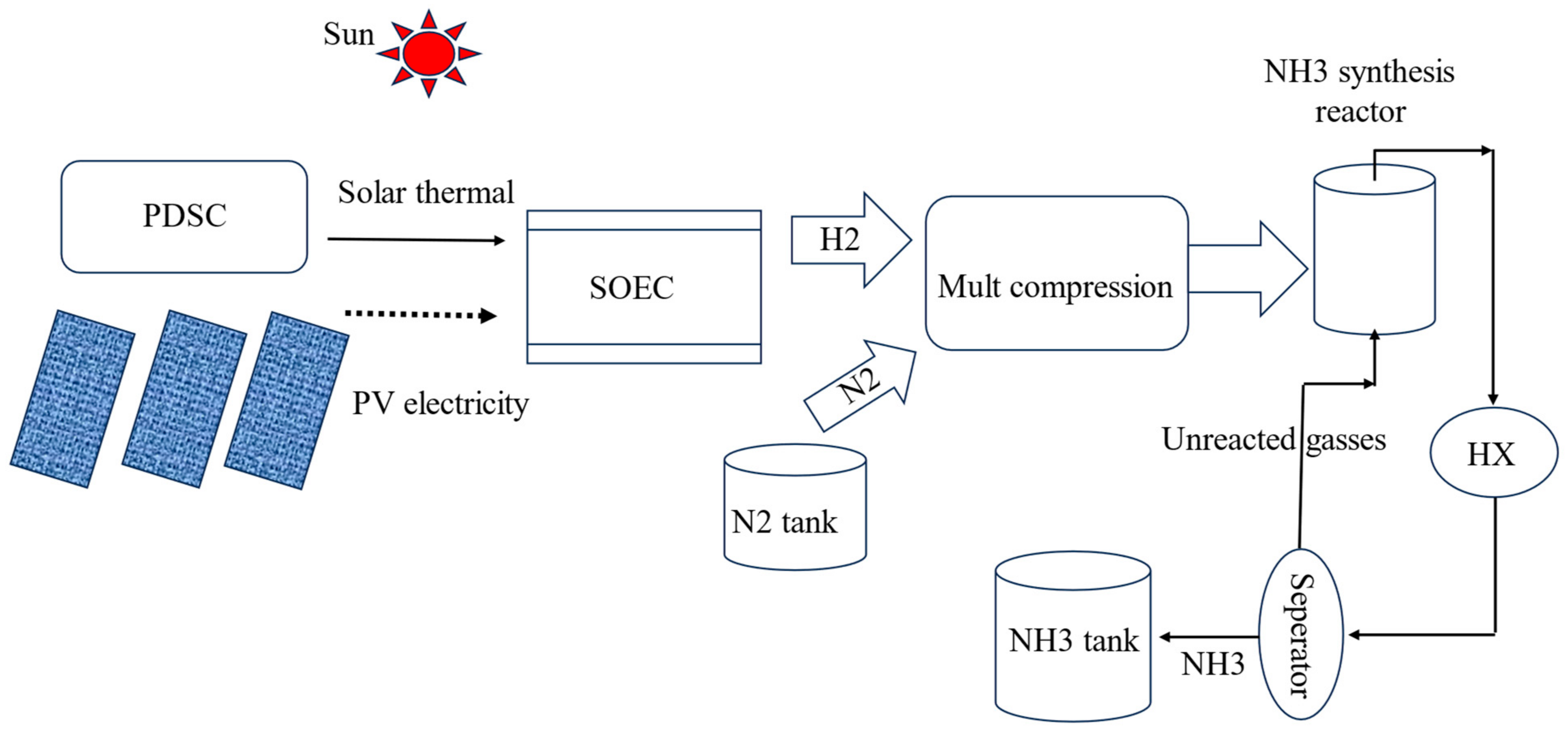
- This is a pure solar thermal and PV-based system for hydrogen and ammonia utilizing high-temperature SOEC.
- This system supplies freshwater from reverse osmosis desalination for the community and supports SOEC for hydrogen production.
- This study conducts a comprehensive exergy and exergy destruction analysis for the whole system.
- This study performs sensitivity analysis to investigate the impact of more efficient parameters.
2. System Description
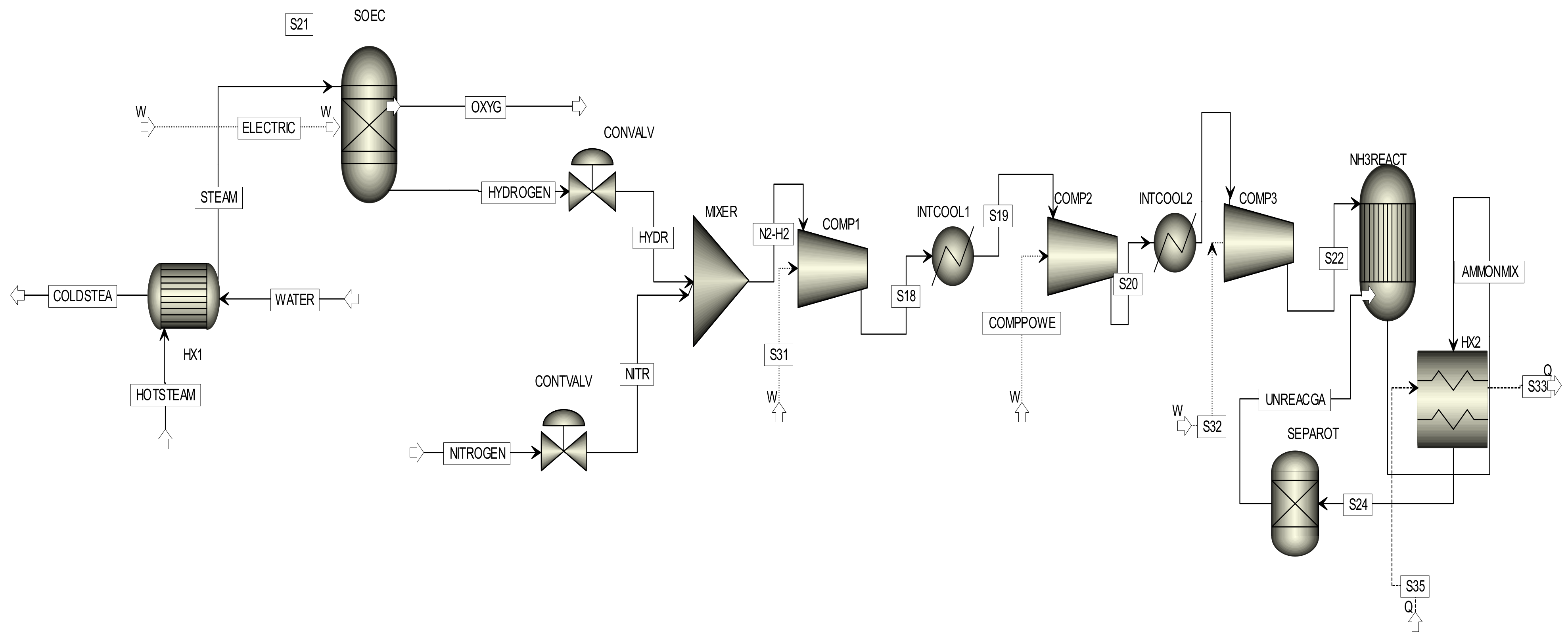
3. Methodology and Thermodynamic Analysis
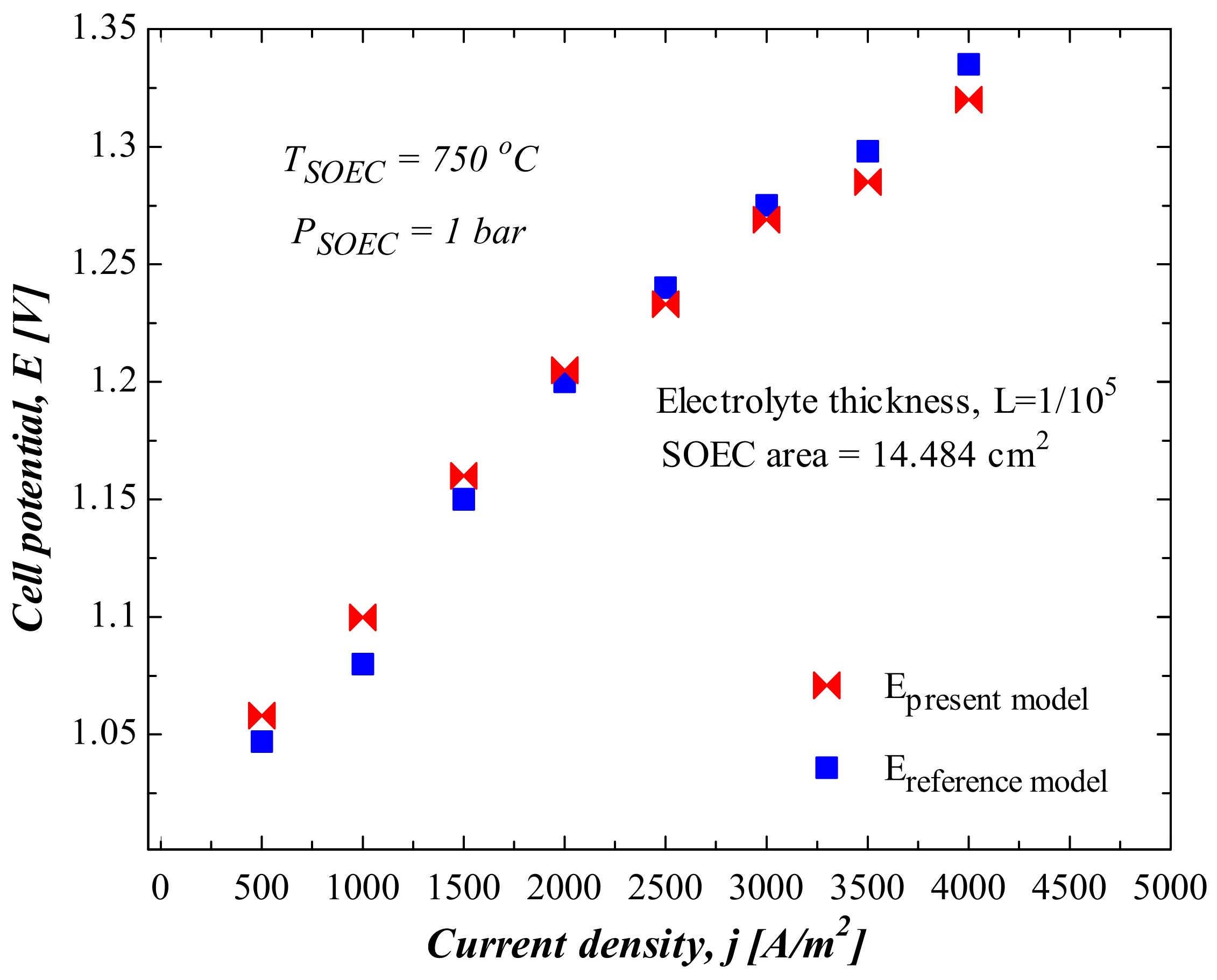
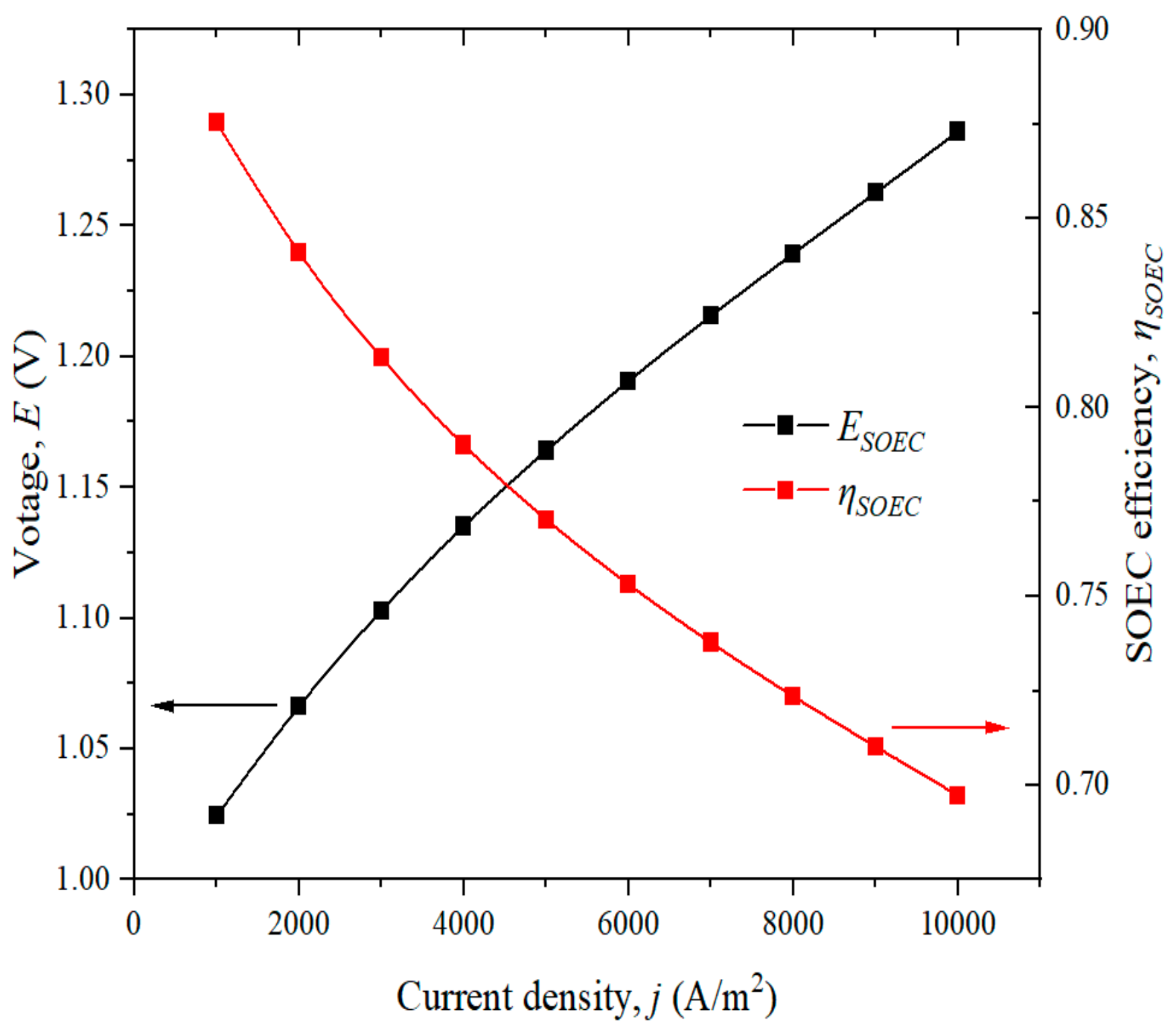
4. Model Validation, Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kakavand, A.; Sayadi, S.; Tsatsaronis, G.; Behbahaninia, A. Techno-economic assessment of green hydrogen and ammonia production from wind and solar energy in Iran. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 14170–14191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.A. Renaissance of ammonia synthesis for sustainable production of energy and fertilizers. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. 2021, 29, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedipour, S.; Gharehghani, A.; Ahbabi, S.J.; Andwari, A.M.; Mikulski, M. Proposing a hybrid thermal management system based on phase change material/metal foam for lithium-ion batteries. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Liu, S.; Li, G.R.; Gao, X.P. Strategy of enhancing the volumetric energy density for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2003955. [Google Scholar]
- Tukenmez, N.; Koc, M.; Ozturk, M. A novel combined biomass and solar energy conversion-based multigeneration system with hydrogen and ammonia generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 46, 16319–16343. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo, C.A.; Cloete, S. Techno-economic assessment of blue and green ammonia as energy carriers in a low-carbon future. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 255, 115312. [Google Scholar]
- Rivarolo, M.; Riveros-Godoy, G.; Magistri, L.; Massardo, A.F. Clean hydrogen and ammonia synthesis in Paraguay from the Itaipu 14 GW hydroelectric plant. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 3, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Ikäheimo, J.; Kiviluoma, J.; Weiss, R.; Holttinen, H. Power-to-ammonia in future North European 100% renewable power and heat system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 17295–17308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgulu, F.; Dincer, I. A renewable source based hydrogen energy system for residential applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 5842–5851. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Abid, M.; Ali, H.M.; Amber, K.P.; Bashir, M.A.; Javed, S. Comparative performance assessment of solar dish assisted s-CO2 Brayton cycle using nanofluids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 148, 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Abid, M.; Bashir, M.A.; Amber, K.P.; Khanmohammadi, S.; Yan, M. Thermodynamic and exergoeconomic analysis of a novel solar-assisted multigenerational system utilizing high temperature phase change material and hybrid nanofluid. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 113948. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Xia, Q.; Feng, S.; Liu, Q. A novel solar hydrogen production system integrating high temperature electrolysis with ammonia based thermochemical energy storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 237, 114143. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Chen, B.; Irvine, J.; Ni, M. Modeling of CH4-assisted SOEC for H2O/CO2 co-electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21839–21849. [Google Scholar]



| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Direct normal irradiance (DNI) | 1000 | W/m2 |
| Dish aperture area | 300 | m2 |
| Area of PV module | 800 | m2 |
| Normal cell temperature | 317.5 | K |
| TSOEC | 750 | °C |
| PSOEC | 1 | bar |
| Operating current density, J | 5000 | A/m2 |
| Area of SOEC | 0.530660 | m2 |
| Ammonia synthesis reaction pressure | 100 | bar |
| Ammonia synthesis reaction temperature | 665 | K |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.S.; Chen, C. Exergo-Economic Analysis of Solar-Driven Ammonia Production System for a Sustainable Energy Carrier. Eng. Proc. 2024, 76, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024076106
Khan MS, Chen C. Exergo-Economic Analysis of Solar-Driven Ammonia Production System for a Sustainable Energy Carrier. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 76(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024076106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Muhammad Sajid, and Chen Chen. 2024. "Exergo-Economic Analysis of Solar-Driven Ammonia Production System for a Sustainable Energy Carrier" Engineering Proceedings 76, no. 1: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024076106
APA StyleKhan, M. S., & Chen, C. (2024). Exergo-Economic Analysis of Solar-Driven Ammonia Production System for a Sustainable Energy Carrier. Engineering Proceedings, 76(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024076106





