The Present and Future of a Digital Montenegro: Analysis of C-ITS, Agriculture, and Healthcare
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cooperative Intelligent Transportation Systems
2.1. Introduction and Concepts
2.2. Current State in Montenegro
2.3. Technologies and Use Cases
- The communication parties are highly mobile. The relative speeds can easily exceed 250 km/h.
- The network topology changes frequently and rapidly.
- Message distribution has to be handled in a spatially aware way while the nodes are moving.
- The messages typically have broadcast destination addresses.
- The node density can be high. Channel contention needs to be avoided by appropriate countermeasures.
- The communication scheme has to support nomadic devices.
- ITS stations shall trust each other.
- Privacy protection methods need to be applied to avoid sensitive data collection.
- Distributed operation is favored over centralized due to the mission-critical use cases.
- Accurate absolute positioning is required.
2.4. Relevant Features and Attributes of Montenegro
2.5. Considerations and Implications
2.6. Summary
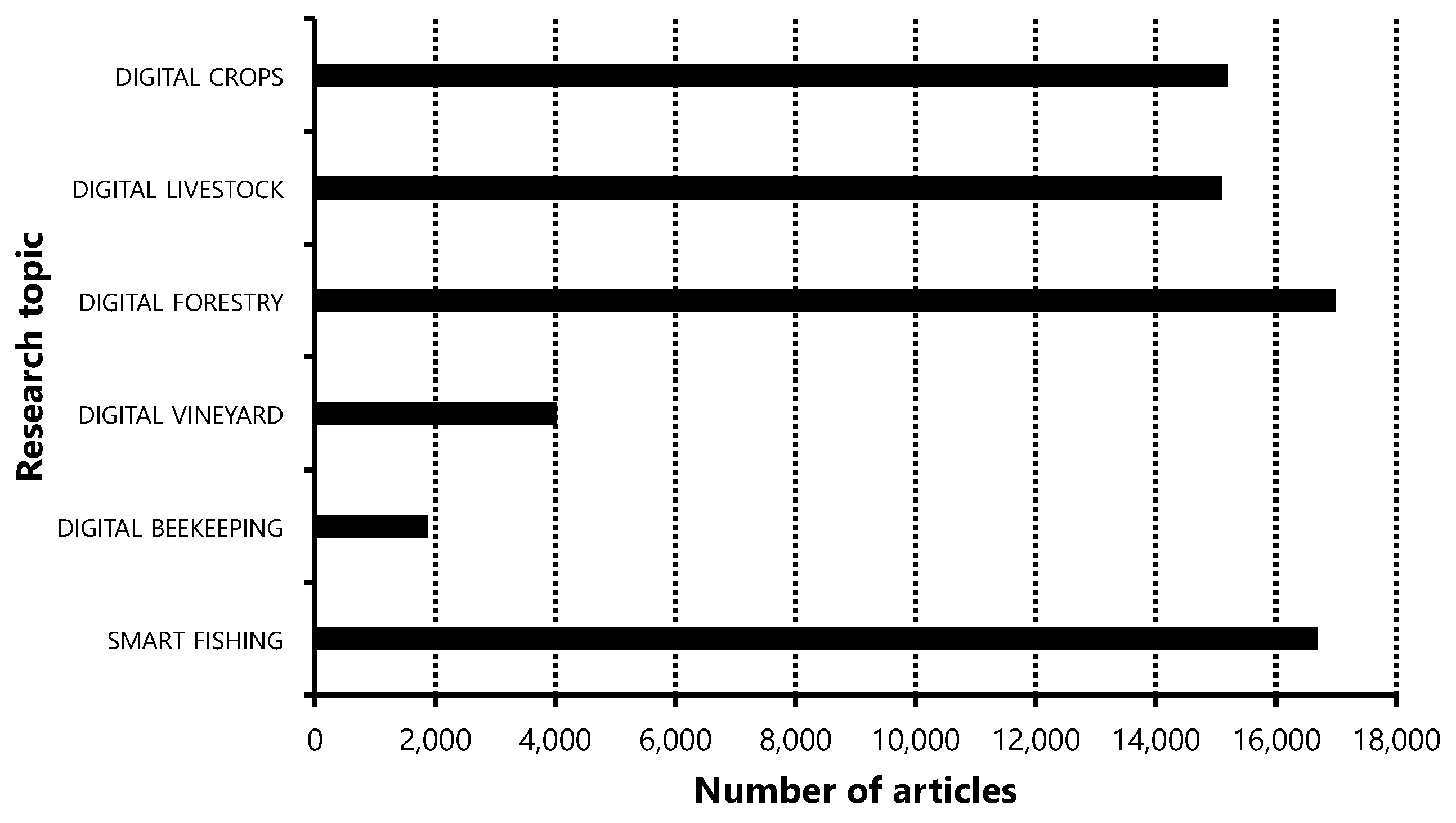
3. Digital Agriculture and Smart Farming
3.1. Introduction and Concepts
3.2. Current State in Montenegro
3.3. Technologies and Use Cases
3.4. Considerations and Implications
- Affordability is still a major challenge associated with the integration of expensive technologies on farms. Although studies show that PLF technologies make a farm more profitable, the diverse nature of each farm makes it a concern worth considering thoroughly before deciding to adopt PLF.
- The major risk of PLF is that since it is often integrated and automatic, a system failure can cause devastating impacts, especially if the system is fully automatic.
- Another associated risk is when the unit of animals is not individuals but a group of individuals such as poultry where flocks are measured. In such cases, special individual needs can be overlooked.
- The use of intrusive tags is a risk to animal welfare, which is still used in many PLF practices and technologies.
3.5. Summary
4. Digital Healthcare and eHealth
4.1. Introduction and Concepts
- Use of digital health technologies as a diagnostic tool—detection of heart rhythm disorders (e.g., atrial fibrillation), detection of retinopathy, metastases, metabolic disorders in tumor cells, etc.—today is possible with the use of digital technologies.
- Digital health as a disease management and decision support tool—several applications related to a specific disease or condition have been established so far. Some of them are more related to diagnostic approaches, but there are a lot of them that aid in treatment.
- Digital health to improve research recruitment—MyHeart Counts and Health eHeart [118] are examples of randomized clinical trials in which digital technologies were used as a recruitment tool.
- Political commitment;
- Normative and regulatory frameworks;
- Technical infrastructure;
- Economic investments;
- Training and education;
- Research;
- Monitoring and evaluation.
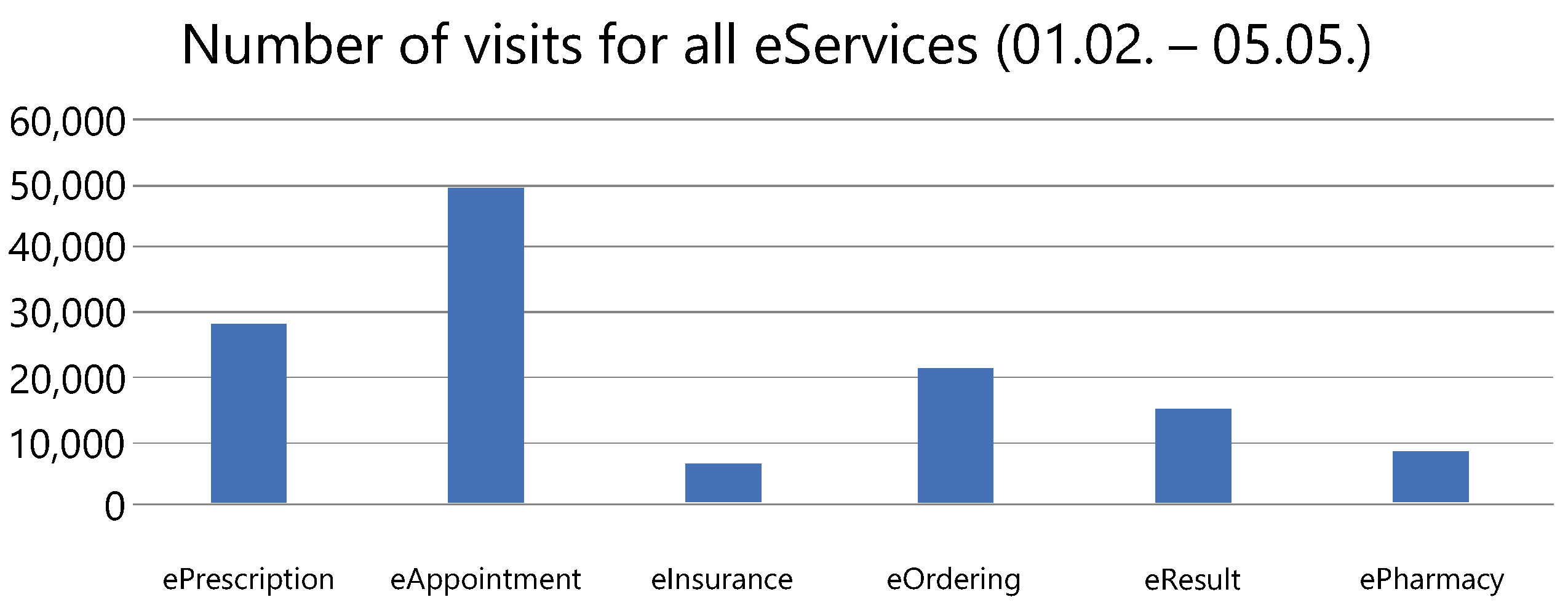
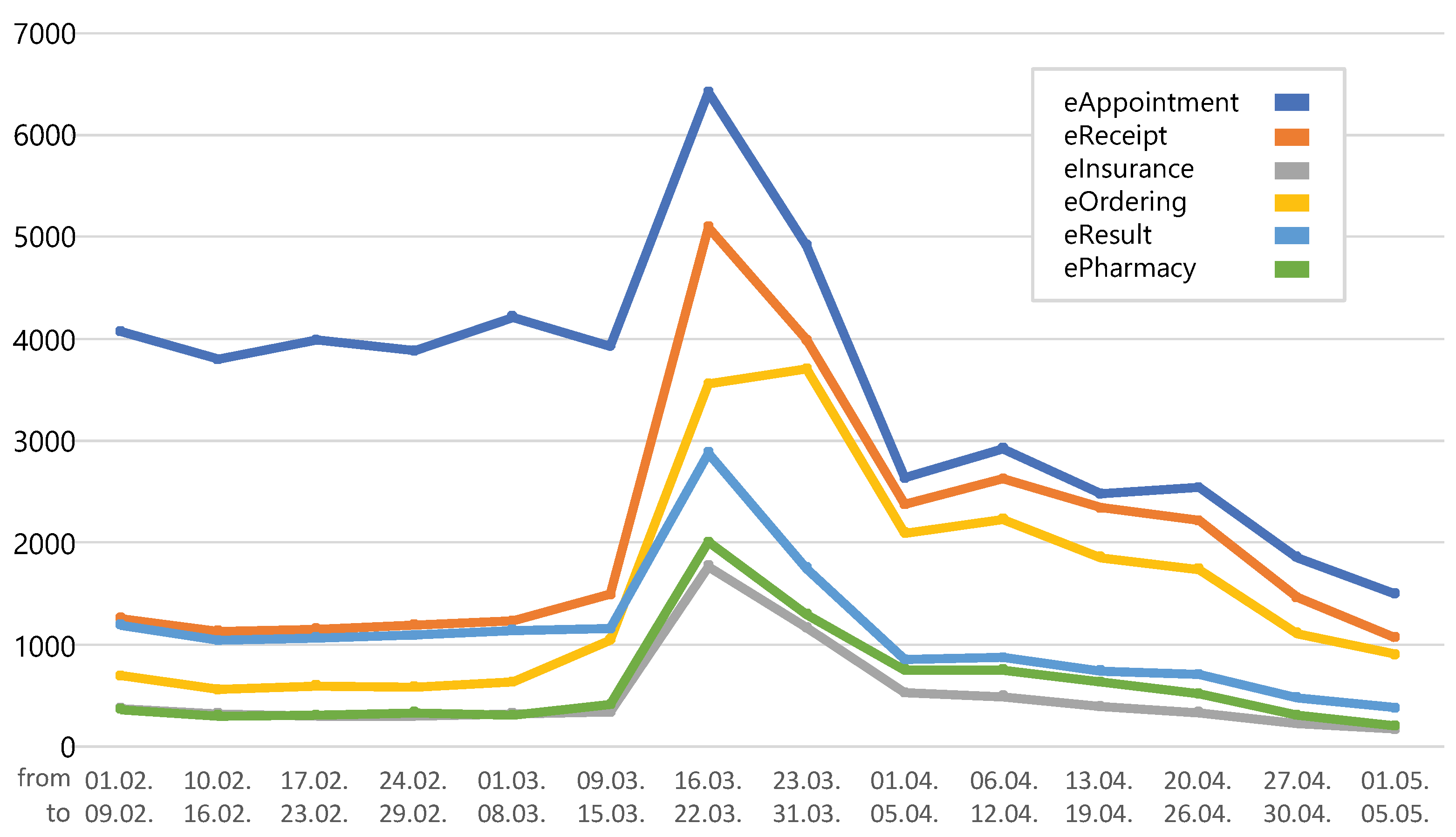
4.2. Current State in Montenegro
4.3. Technologies and Use Cases
4.4. Relevant Features and Attributes of Montenegro
4.5. Considerations and Implications
4.6. Summary
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3GPP | 3rd Generation Partnership Project |
| BSM | Basic Safety Message |
| BTP | Basic Transport Protocol |
| C2C-CC | CAR 2 CAR Communication Consortium |
| CALM | Communications Access for Land Mobiles |
| CAM | Cooperative Awareness Message |
| CEDR | Conference of European Directors of Roads |
| CICW | Cooperative Intersection Collision Warning |
| C-ITS | Cooperative Intelligent Transportation System |
| C-V2X | Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything |
| CSMA/CA | Carrier-Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance |
| DENM | Decentralized Environmental Notification Message |
| DG MOVE | Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport |
| ECRL | European Certificate Revocation List |
| ECTL | European Certificate Trust List |
| EHR | Electronic Health Record |
| ETSI | European Telecommunications Standards Institute |
| Euro NCAP | European New Car Assessment Programme |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| HCS | Healthcare service |
| I2V | Infrastructure-to-Vehicle |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| IoT | Internet-of-Things |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| ITS | Intelligent Transportation System |
| IVI | In-Vehicle Information |
| LTE | Long-Term Evolution |
| MAC | Media Access Control |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer |
| OSI | Open Systems Interconnection |
| PKI | Public Key Infrastructure |
| PLF | Precision Livestock Farming |
| RSU | Roadside Unit |
| RTTI | Real-time Traffic Information |
| SAE | System Architecture Evolution |
| SDSS | Spatial Decision Support Systems |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| V2I | Vehicle-to-Infrastructure |
| V2N | Vehicle-to-Network |
| V2V | Vehicle-to-Vehicle |
| V2X | Vehicle-to-Everything |
| WAVE | Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments |
| WEF | World Economic Forum |
References
- El Hamdi, S.; Abouabdellah, A.; Oudani, M. Industry 4.0: Fundamentals and main challenges. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Colloquium on Logistics and Supply Chain Management (LOGISTIQUA), Paris, France, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rainnie, A.; Dean, M. Industry 4.0 and the future of quality work in the global digital economy. Labour Ind. J. Soc. Econ. Relat. Work 2020, 30, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrapati, R. Industry 4.0: Prospects and challenges leading to smart manufacturing. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2022, 42, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, K. The Fourth Industrial Revolution; Crown Business: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, C. Industry 4.0: The digital German ideology. Triplec Commun. Capital. Crit. 2018, 16, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skobelev, P.; Borovik, S.Y. On the way from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0: From digital manufacturing to digital society. Ind. 4.0 2017, 2, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Callaghan, C.W. Transcending the threshold limitation: A fifth industrial revolution? Manag. Res. Rev. 2019, 43, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, Z.; Sarfraz, A.; Iftikar, H.M.; Akhund, R. Is COVID-19 pushing us to the fifth industrial revolution (society 5.0)? Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizic, M.C.; Mladineo, M.; Gjeldum, N.; Celent, L. From industry 4.0 towards industry 5.0: A review and analysis of paradigm shift for the people, organization and technology. Energies 2022, 15, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, I. The myth of the fourth industrial revolution. Theoria 2021, 68, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philbeck, T.; Davis, N. The fourth industrial revolution. J. Int. Aff. 2018, 72, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, J. Will we work in twenty-first century capitalism? A critique of the fourth industrial revolution literature. Econ. Soc. 2019, 48, 371–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avis, J. Post-Work, Post-Capitalism and the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In Vocational Education in the Fourth Industrial Revolution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 73–102. [Google Scholar]
- Avis, J. Education and Employment in a Post-Work Age. In Vocational Education in the Fourth Industrial Revolution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Giesen, K.G. The Transhumanist Ideology and the International Political Economy of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In Ideologies in World Politics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, P. Shared consciousness: Toward a world of transhuman relations. In Identity, Institutions and Governance in an AI World; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 247–264. [Google Scholar]
- Degtyareva, V.; Lyapina, S.; Tarasova, V.; Yeremyan, L. Development of the National Qualifications System: The Impact of Transhumanism. Wisdom 2022, 2, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, G.; Demestichas, P. Intelligent transportation systems. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2010, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamssaggad, A.; Benamar, N.; Hafid, A.S.; Msahli, M. A survey on the current security landscape of intelligent transportation systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 9180–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.; Deborah, L.J. An improved public transportation system for effective usage of vehicles in intelligent transportation system. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, 34, e4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kang, B.; Yu, K.; Qi, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Li, H.A. Contour-maintaining-based image adaption for an efficient ambulance service in intelligent transportation systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 12644–12654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gechter, F.; Aglzim, E.H.; Senouci, S.M.; Rodet-Kroichvili, N.; Cappelle, C.; Fass, D. Transportation of goods in inner-city centers: Can autonomous vehicles in platoon be a suitable solution? In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Belfort, France, 11–14 December 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dontu, A.; Gaiginschi, L.; Barsanescu, P. Reducing the urban pollution by integrating weigh-in-motion sensors into intelligent transportation systems. State of the art and future trends. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 591, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.A.; Havlík, P.; Schmid, E.; Valin, H.; Mosnier, A.; Obersteiner, M.; Böttcher, H.; Skalskỳ, R.; Balkovič, J.; Sauer, T.; et al. Impacts of population growth, economic development, and technical change on global food production and consumption. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L. Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Meena, R.S.; Jhariya, M.K. Resources Use Efficiency in Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, N.; Kumar, A.; Ramaswami, R. The Effect of National Healthcare Expenditure on Life Expectancy. 2014. Available online: https://smartech.gatech.edu/handle/1853/51648 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- van den Heuvel, W.J.; Olaroiu, M. How important are health care expenditures for life expectancy? A comparative, European analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 276.e9–276.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Loures, E.R.; Deschamps, F.; Brezinski, G.; Venâncio, A. The impact of the fourth industrial revolution: A cross-country/region comparison. Production 2018, 28, e20180061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, E. The fourth industrial revolution—The case of South Africa. Politikon 2020, 47, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankervis, A.; Connell, J.; Cameron, R.; Montague, A.; Prikshat, V. ‘Are we there yet?’Australian HR professionals and the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Asia Pac. J. Hum. Resour. 2021, 59, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DigNest: Digital Entrepreneurial Nest and Industry 4.0 in Montenegro. Available online: https://dignest.me/ (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Golubović, V.; Mirković, M.; Mićunović, N.; Srića, V. Digital Transformation in Montenegro–Current Status, Issues and Proposals for Improvement. J. Comput. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melović, B.; Jocović, M.; Dabić, M.; Vulić, T.B.; Dudic, B. The impact of digital transformation and digital marketing on the brand promotion, positioning and electronic business in Montenegro. Technol. Soc. 2020, 63, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bošković, B.; Nuhodžić, R.; Bugarinović, M. The Sustainability of Small Countries’ Railway Sector Institutions in Liberalized Market—Case Study Montenegro. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Railway Research (WCRR), Milan, Italy, 29 May–2 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jakovljevic, N.; Jonic, I.; Nesic, K. Design for rehabilitation of 7 steel railway bridges in Montenegro. Procedia Eng. 2016, 156, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramo, F.; Llaci, S. The impact of railway (corridor VIII and the line Albania-Montenegro) on the agribusiness development in Albania. Albanian J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 11, 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- Nikčević, J.; Škurić, M. A contribution to the sustainable development of maritime transport in the context of blue economy: The Case of Montenegro. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapidani, N.; Kočan, E. Implementation of national maritime single window in Montenegro. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd Telecommunications Forum Telfor (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 24–26 November 2015; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hasaj, A.; Krymbi, E.; Kruja, D. Cross-border cooperation on water transportation, between region of Shkodra and Montenegro. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Maritime Transport, Barcelona, Spain, 27–29 June 2016; pp. 535–544. [Google Scholar]
- Rajović, G.; Bulatović, J. Zoning as a condition of sustainable agriculture northeastern Montenegro: A case study. Rocz. Ochr. Środowiska 2016, 18, 65–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rajović, G. Important social factors for development of agriculture in North-Eastern Montenegro. Ekon. J. Econ. Theory Pract. Soc. Issues 2011, 57, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ćorić, D.; Popović, M. E-Agriculture: Montenegro Case. Entren. Enterp. Res. Innov. 2015, 1, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Radonjić, S.; Hrnčić, S. A review of new alien arthropod pests and their impact on agriculture crops in Montenegro. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2017, 9, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Hrncic, S. A survey of olive pests in Montenegro. In Acta Horticulturae; ISHS: Leuven, Belgium, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 819–821. [Google Scholar]
- Hrnčić, S.; Radonjić, S. A survey of raspberry pests in Montenegro. In Proceedings of the X International Rubus and Ribes Symposium 946, Zlatibor, Serbia, 22–26 June 2011; pp. 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanović, A.; Raković, P. E-health Card Information System: Case Study Health Insurance Fund of Montenegro. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 10–14 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lješnjanin, S. Management in healthcare institutions of Montenegro. Zdr. Zaštita 2019, 48, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantas, J.; Sendelj, R.; Ammenwerth, E. Multidisciplinary Approach for Education in Healthcare Management: Case Study from Montenegro. Importance Health Inform. Public Health Dur. Pandemic 2020, 272, 330. [Google Scholar]
- Vujanović, N. Technological Trends in the Manufacturing and Service Sectors. The Case of Montenegro. South East Eur. J. Econ. Bus. 2021, 16, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boban, M.; Slavica, M.; Stevan, M.; Radovan, P.; Ore, E. Research of consumption and competitiveness of homemade products for manufacturing improvement: A case study from Montenegro. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 3757–3764. [Google Scholar]
- Labović, S.B.; Joksimović, I.; Galić, I.; Knežević, M.; Mimović, M. Food Safety Behaviours among Food Handlers in Different Food Service Establishments in Montenegro. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajović, G.; Bulatović, J. Plant and Animal production in Montenegro with Overview of the Food Industry. Int. Lett. Soc. Humanist. Sci. 2015, 63, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinovic, A.; Mirecki, S. Food, nutrition, and health in Montenegro. In Nutritional and Health Aspects of Food in the Balkans; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 165–186. [Google Scholar]
- Jaksic-Stojanovic, A.; Jankovic, M.; Seric, N. Montenegro as high-quality sports tourism destination-trends and perspectives. Sport Mont. 2019, 17, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moric, I. Clusters as a factor of rural tourism competitiveness: Montenegro experiences. Bus. Syst. Res. Int. J. Soc. Adv. Innov. Res. Econ. 2013, 4, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moric, I.; Pekovic, S.; Janinovic, J.; Perovic, Đ.; Griesbeck, M. Cultural tourism and community engagement: Insight from Montenegro. Bus. Syst. Res. Int. J. Soc. Adv. Innov. Res. Econ. 2021, 12, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigović, M. Quantifying seasonality in tourism: A case study of Montenegro. Acad. Tur. Tour. Innov. J. 2011, 4, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- C-ROADS. The Platform of harmonised C-ITS deployment in Europe. 2022. Available online: https://www.c-roads.eu/platform.html (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Ministry of Capital Investments: Transport Development Strategy—Montenegro 2019–2035. 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.me/dokumenta/a080d54d-0b87-4d8c-bfbf-bdc8ae5dc8bb (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Directive 2010/40/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 7 July 2010 on the Framework for the Deployment of Intelligent Transport Systems in the Field of Road Transport and for Interfaces with Other Modes of Transport. 2010. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32010L0040 (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Prelevic, M. Management of Transport Processes with the use of Intelligent Transport Systems—A Case Study of the Company Vertigo Montenegro Ltd.-Podgorica. Glob. J. Res. Eng. 2020, 20, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, E.G. On Medium Access and Physical Layer Standards for Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems in Europe. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boban, M.; Manolakis, K.; Ibrahim, M.; Bazzi, S.; Xu, W. Design aspects for 5G V2X physical layer. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), Berlin, Germany, 31 October–2 November 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21217:2020; Intelligent Transport Systems—Station and Communication Architecture. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ISO/IEC 7498-1:1994; Information Technology–Open Systems Interconnection–Basic Reference Model: The Basic Model. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- IEEE Std 802.11-2016 (Revision of IEEE Std 802.11-2012); IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Telecommunications and Information Exchange between Systems Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–3534. [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.; Anwar, W.; Schwarzenberg, N.; Franchi, N.; Fettweis, G. System-level Performance Comparison of IEEE 802.11p and 802.11bd Draft in Highway Scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2020 27th International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT), Bali, Indonesia, 5–7 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP; Digital Cellular Telecommunications System (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; 5G. Release 14 Description; Summary of Rel-14 Work Items. Technical Specification (TS) 21.914, 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). 2018. Version 14.0.0. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=3179 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Dayal, A.; Shah, V.K.; Choudhury, B.; Marojevic, V.; Dietrich, C.; Reed, J.H. Adaptive Semi-Persistent Scheduling for Enhanced On-road Safety in Decentralized V2X Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IFIP Networking Conference (IFIP Networking), Espoo and Helsinki, Finland, 21–24 June 2021; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.H.C.; Molina-Galan, A.; Boban, M.; Gozalvez, J.; Coll-Perales, B.; Şahin, T.; Kousaridas, A. A Tutorial on 5G NR V2X Communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1972–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 1609.3-2020 (Revision of IEEE Std 1609.3-2016)—Redline; IEEE Standard for Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE)–Networking Services–Redline. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–344. [CrossRef]
- ETSI EN 302 636-4-1 V1.4.1; Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; GeoNetworking; Part 4: Geographical Addressing and Forwarding for Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Communications; Sub-Part 1: Media-Independent Functionality. European Telecommunications Standards Institute: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2020. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_en/302600_302699/3026360401/01.04.01_60/en_3026360401v010401p.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- ETSI EN 302 636-5-1 V2.2.1 (2019-05); Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; GeoNetworking; Part 5: Transport Protocols; Sub-Part 1: Basic Transport Protocol. European Telecommunications Standards Institute: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2019. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_en/302600_302699/3026360501/02.02.01_60/en_3026360501v020201p.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- ETSI EN 302 637-2 V1.4.1 (2019-04); European Standard, Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 2: Specification of Cooperative Awareness Basic Service. 2019. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_en/302600_302699/30263702/01.04.01_60/en_30263702v010401p.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- ETSI EN 302 637-3 V1.3.1 (2019-04); Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 3: Specifications of Decentralized Environmental Notification Basic Service. 2019. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_en/302600_302699/30263703/01.03.01_60/en_30263703v010301p.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- ISO/TS 19321:2020; Intelligent Transport Systems—Cooperative ITS—Dictionary of in-Vehicle Information (IVI) Data Structures. Standard, International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/76974.html (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- SAE International. J2735_202211-V2X Communications Message Set Dictionary; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.sae.org/standards/content/j2735_202211/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- SAE International. On-Board System Requirements for V2V Safety Communications; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.sae.org/standards/content/j2945/1_202004/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- ETSI TS 102 941 V2.2.1 (2022-11); Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Security; Trust and Privacy Management. European Telecommunications Standards Institute: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2021. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/102900_102999/102941/02.02.01_60/ts_102941v020201p.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- ETSI TS 102 940 V2.1.1; Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Security; ITS Communications Security Architecture and Security Management; Release 2. European Telecommunications Standards Institute: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2021. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/102900_102999/102940/02.01.01_60/ts_102940v020101p.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- The European Commission. ANNEX III and IV to the Commission Delegated Regulation supplementing Directive 2010/40/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to the Deployment and Operational Use of Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems. 2019. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=PI_COM%3AC%282019%291789 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Car2Car Communication Consortium. Basic System Profile. 2022. Available online: https://www.car-2-car.org/documents/basic-system-profile (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- ISO/IEC 15408-1:2022; Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection—Evaluation Criteria for IT Security—Part 1: Introduction and General Model. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Ministry of Economic Development. Spatial Plan of Montenegro Until 2020. 2008. Available online: https://wapi.gov.me/download-preview/b57f5f50-6f9c-4c27-ba86-122f5166b126?version=1.0 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Preparation of the Transport Development Strategy–Montenegro (Contract No. 829-4147). Transport Development Strategy Report; 2017. Available online: https://va.mite.gov.it/File/Documento/228159 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- List of Cities in Montenegro by Population. 2022. Available online: https://all-populations.com/en/me/list-of-cities-in-montenegro-by-population.html (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- WHO. Death on the Roads–Based on the WHO Global Status Report on Road Safety 2018. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/roadsafety/death-on-the-roads/#country_or_area/MNE (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Level crossing–Current Situation in the Western Balkan Region, Statistics, Classification and Comparison on LCs within Western Balkan. Available online: https://www.transport-community.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Railroad-Level-Crossings-Current-State_TCS.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2022).
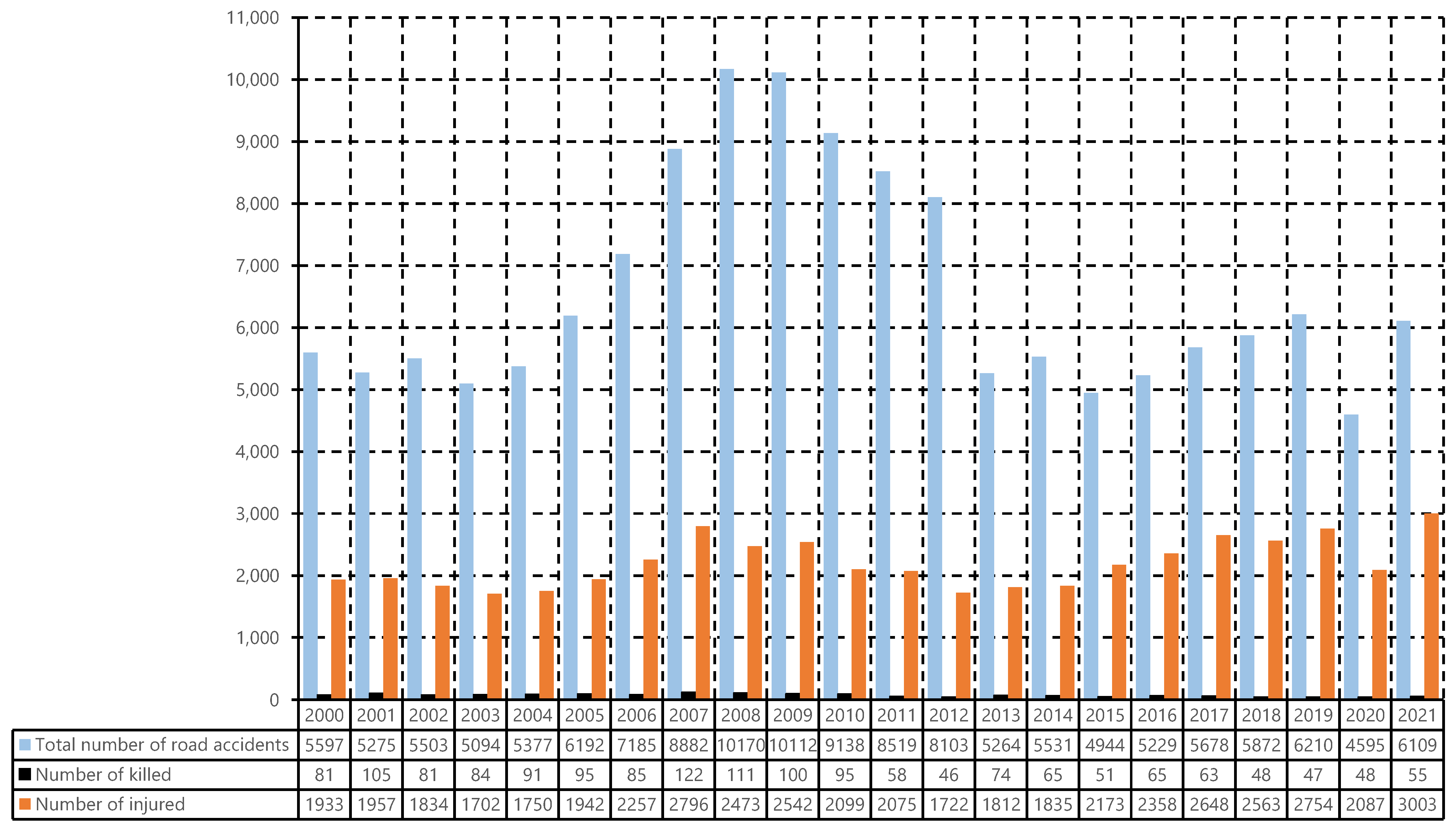
- Pajkovic, A.P.V.; Grdinic, M. Road traffic safety performance in Montenegro. Mach. Technol. Mater. 2014, 3, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lučić, M. Characteristics and state of road traffic safety in Montenegro. Trans Motauto World 2021, 6, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- MONSTAT. Annual Statistic of Transport Storage and Communications, 2021. 2022. Available online: https://www.monstat.org/eng/novosti.php?id=3487 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Brož, J.; Tichý, T.; Angelakis, V.; Bělinová, Z. Usage of V2X Applications in Road Tunnels. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Englund, C. Cooperative Intersection Management: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buinevich, M.; Spirkina, A.; Elagin, V.; Tarakanov, S.; Vladyko, A. V2X-based Intersection Priority Management. In Proceedings of the 2021 Systems of Signals Generating and Processing in the Field of on Board Communications, Moscow, Russia, 16–18 March 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, H.M.; Jang, J.A.; Oh, H.S. Effectiveness Analysis of Warning Service using V2X Communication Technology at Intersection. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 17–19 October 2018; pp. 1506–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Hirakawa, G.; Shibata, Y. Experimentation of V2X Communication in Real Environment for Road Alert Information Sharing System. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 30th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), Crans-Montana, Switzerland, 23–25 March 2016; pp. 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aissaoui, R.; Menouar, H.; Dhraief, A.; Filali, F.; Belghith, A.; Abu-Dayya, A. Advanced real-time traffic monitoring system based on V2X communications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 10–14 June 2014; pp. 2713–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billot, R.; El Faouzi, N.E.; Guériau, M.; Monteil, J. Can C-ITS lead to the emergence of Traffic Management 2.0? In Proceedings of the 17th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Qingdao, China, 8–11 October 2014; pp. 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susic-Radovanovic, B.; Vojinovic, N.; Remikovic, S. Montenegro in Figures 2021. Statistical Office of Montenegro-Monstat. 2021. Available online: http://monstat.org/uploads/files/publikacije/Monstat%20-%20CG%20u%20Brojkama%20ENG_WEB.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Smart Farming and the Future of Agriculture. Available online: https://www.lll.tum.de/interview-smart-farming-and-the-future-of-agriculture/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Publications Office of the European Union: Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishery Statistics—2020 Edition. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-statistical-books/-/ks-fk-20-001 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Statistical Office of Montenegro–Monstat. Statistical Yearbook 2022. Available online: http://monstat.org/eng/novosti.php?id=3646 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Stjepana Filipovića. Sustainable Agriculture for Sustainable Balkans. Available online: http://www.sasb-eu.org/en/nature/the-western-balkans/montenegro (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Maraš, V.; Popovic, T.; Gajinov, S.; Mugosa, M.; Popovic, V.; Savović, A.; Pavicevic, K.; Mirovic, V. Precision Viticulture Using Wireless Sensor Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 9th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 8–11 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, K. Association of Beekeeping Organizations of Montenegro. Available online: https://pcelarstvo.me/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Bee and Me. Available online: https://beeandme.com/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Smart Beehive: Species Protection with the Cloud and IoT. Available online: https://open-telekom-cloud.com/en/blog/references/magenta-bieneninitiative (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- IoBee. Available online: https://io-bee.eu/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- BeeLife. Available online: https://www.bee-life.eu/about (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Schillings, J.; Bennett, R.; Rose, D.C. Exploring the Potential of Precision Livestock Farming Technologies to Help Address Farm Animal Welfare. Front. Anim. Sci 2021, 2, 639678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilani, C.; Confessore, A.; Bozzi, R.; Sirtori, F.; Pugliese, C. Review: Precision Livestock Farming technologies in pasture-based livestock systems. Animal 2022, 16, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineview. Vineview: Monitoring the Wineyard by Drones. Available online: https://vineview.com/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Maraš, V.; Popović, T.; Gajinov, S.; Mugoša, M.; Popović, V.; Savović, A.; Pavićević, K.; Mirović, V. Optimal Irrigation as a tool of Precision Agriculture. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 10–14 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DigNest. WP1. Analysis and Road-Mapping: Supporting Digitization of Industry in Montenegro; DELIVERABLE 1.2 Cooperation between Higher Education Institutions (HEI) and Economics and Social Environment in EU Countries. 2021. Available online: https://dignest.me/#/page/wp1-analysis-and-road-mapping-supporting-digitization-of-industry-in-montenegro (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Watson, A.; Wilkinson, T.M. Digital healthcare in COPD management: A narrative review on the advantages, pitfalls, and need for further research. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2022, 16, 17534666221075493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Harrington, R.A.; McClellan, M.B.; Turakhia, M.P.; Eapen, Z.J.; Steinhubl, S.; Mault, J.R.; Majmudar, M.D.; Roessig, L.; Chandross, K.J.; et al. Using digital health technology to better generate evidence and deliver evidence-based care. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2680–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, M.V.; Shcherbina, A.; Pavlovic, A.; Homburger, J.R.; Goldfeder, R.L.; Waggot, D.; Cho, M.K.; Rosenberger, M.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Myers, J.; et al. Feasibility of obtaining measures of lifestyle from a smartphone app: The MyHeart Counts Cardiovascular Health Study. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabello, G.M.; Pêgo-Fernandes, P.M.; Jatene, F.B. Are We Preparing for the Digital Healthcare Era? Sao Paulo Med. J. 2022, 140, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmer, R.J.; Collins, N.M.; Collins, C.S.; West, C.P.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Digital health interventions for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. In The Mayo Clinic Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 90, pp. 469–480. [Google Scholar]
- Odone, A.; Buttigieg, S.; Ricciardi, W.; Azzopardi-Muscat, N.; Staines, A. Public health digitalization in Europe: EUPHA vision, action and role in digital public health. Eur. J. Public Health 2019, 29, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šćepanović, L.; Terzić, N. Changes in primary health care in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in Montenegro. Srp. Med. časopis Lek. Komore 2022, 3, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovic, A.; Jankovic, D.; Rajkovic, P. Extensions and adaptations of existing medical information system in order to reduce social contacts during COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2020, 141, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erakovic, J.; Milikic, D.; Radulovic, L.; Perunicic, S.; Idrizovic, Z.; Roganovic, M. Reorganization of multiple sclerosis health care system in Clinical Centre of Montenegro during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eneurologicalsci 2020, 21, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudrapati, R. Using industrial 4.0 technologies to combat the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 78, 103811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrović, D.; Peličić, D. Telemedicine in the COVID-19 pandemic. Zdr. Zaštita 2020, 49, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendelj, R.; Ognjanovic, I. Cybersecurity Challenges in Healthcare. In Achievements, Milestones and Challenges in Biomedical and Health Informatics; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 190–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kumpunen, S.; Webb, E.; Permanand, G.; Zheleznyakov, E.; Edwards, N.; van Ginneken, E.; Jakab, M. Transformations in the landscape of primary health care during COVID-19: Themes from the European region. Health Policy 2022, 126, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djurovic, G.; Djurovic, V.; Bojaj, M.M. The macroeconomic effects of COVID-19 in Montenegro: A Bayesian VARX approach. Financ. Innov. 2020, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart Specialization Strategy 2021–2024. Available online: https://s3.me/pametna-specijalizacija-u-crnoj-gori/ (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Roganović, M.; Ognjanović, I.; Šendelj, R.; Reich, C.; Bokor, L.; Mantas, J.; Golob, M.; Šimšić, N.; Orović, I.; Radusinović, T.; et al. Digital Entrepreneurial Nest: Supporting Digitization of Healthcare at National Level in Montenegro. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2022, 289, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic, S.; Pavlicic, M.; Stojanovic, R.; Krivokapic, S. “TeleCG”–Pilot Telemedicine Network of Montenegro. In Proceedings of the INFOFEST2004, Budva, Montenegro, 26 September–2 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ognjanović, I.; Šendelj, R.; Mantas, J.; Roganović, M. Development of ICT Enhanced Person-Centred Care Services for Stroke Outpatient Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 7–10 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
| Use Case | Type | Most Relevant Deployment Location | Expected Impact (1–5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do not pass warning | V2V | Rural main roads | 5 |
| Slow moving vehicle | V2V | Rural main roads | 3 |
| Roadworks warning | I2V | Rural main roads, Urban | 3 |
| Hazardous location notification | I2V | Rural main roads, Urban | 4 |
| In-vehicle signage | I2V | Rural main roads | 3 |
| Signalized intersections | I2V | Urban | 3 |
| Signalized intersections with preemption | I2V, V2I | Urban | 4 |
| Adverse weather conditions | I2V | Rural main roads | 4 |
| Probe vehicle data | V2I | Urban | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kara, P.A.; Ognjanovic, I.; Maindorfer, I.; Mantas, J.; Wippelhauser, A.; Šendelj, R.; Laković, L.; Roganović, M.; Reich, C.; Simon, A.; et al. The Present and Future of a Digital Montenegro: Analysis of C-ITS, Agriculture, and Healthcare. Eng 2023, 4, 341-366. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4010021
Kara PA, Ognjanovic I, Maindorfer I, Mantas J, Wippelhauser A, Šendelj R, Laković L, Roganović M, Reich C, Simon A, et al. The Present and Future of a Digital Montenegro: Analysis of C-ITS, Agriculture, and Healthcare. Eng. 2023; 4(1):341-366. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleKara, Peter A., Ivana Ognjanovic, Ingo Maindorfer, John Mantas, Andras Wippelhauser, Ramo Šendelj, Luka Laković, Milovan Roganović, Christoph Reich, Aniko Simon, and et al. 2023. "The Present and Future of a Digital Montenegro: Analysis of C-ITS, Agriculture, and Healthcare" Eng 4, no. 1: 341-366. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4010021
APA StyleKara, P. A., Ognjanovic, I., Maindorfer, I., Mantas, J., Wippelhauser, A., Šendelj, R., Laković, L., Roganović, M., Reich, C., Simon, A., & Bokor, L. (2023). The Present and Future of a Digital Montenegro: Analysis of C-ITS, Agriculture, and Healthcare. Eng, 4(1), 341-366. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4010021