Rutting Performance of Nano-Silica-Modified C320 Bitumen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nano-Silica in Bitumen Modification
3. Experimental Program
3.1. Materials
3.1.1. Bitumen
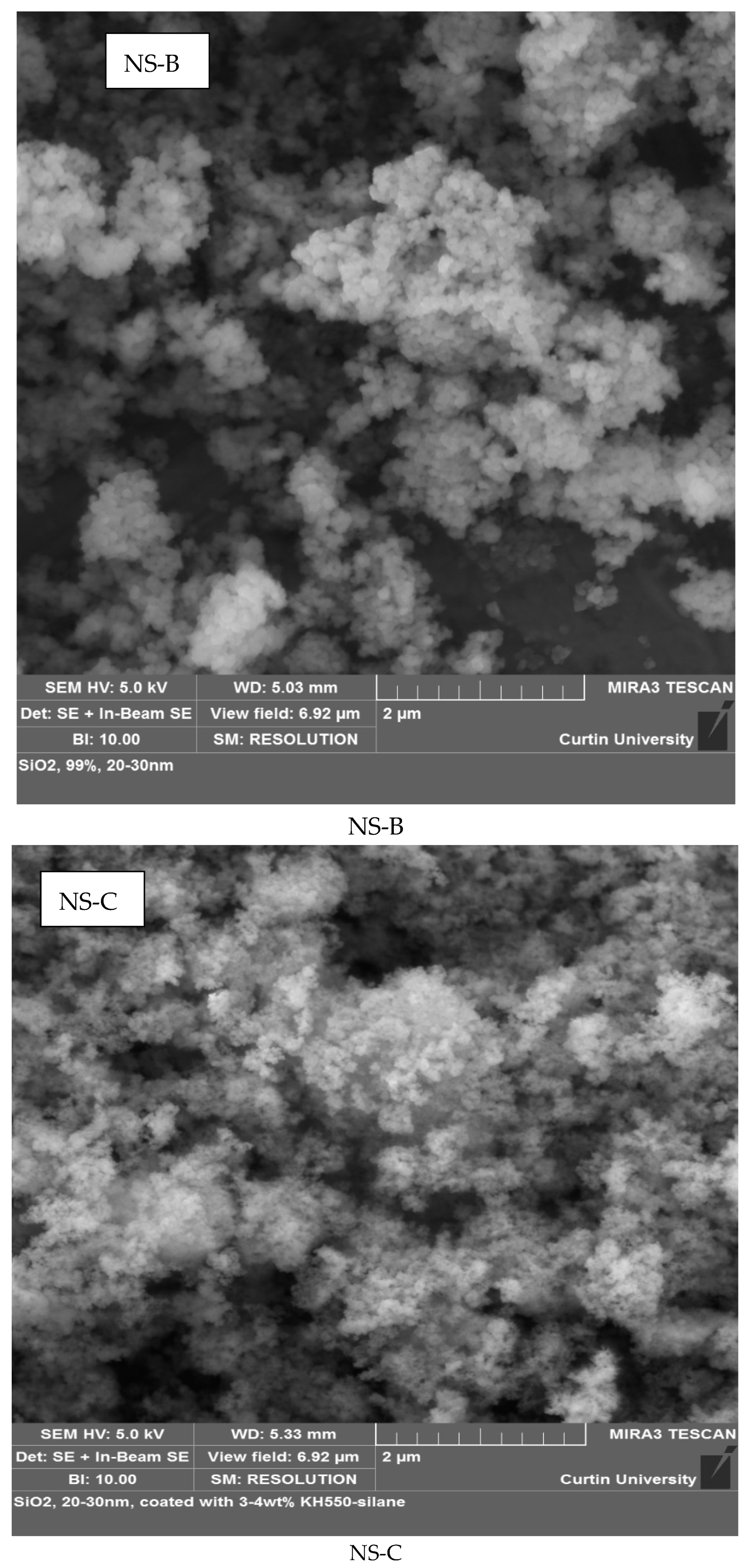
3.1.2. Nano-Silica
3.2. Sample Preparations
3.3. Testing Methods
3.3.1. Penetration Test
3.3.2. Softening Point Test
3.3.3. Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR)
3.3.4. Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Physical Properties
4.2. Rheological Properties of Nano-Silica Modified C320 Bitumen
4.3. DSR Rutting of Nano-Silica Modified C320 Bitumen
4.4. MSCR Rutting of Nano-Silica-Modified C320 Bitumen
5. Conclusions
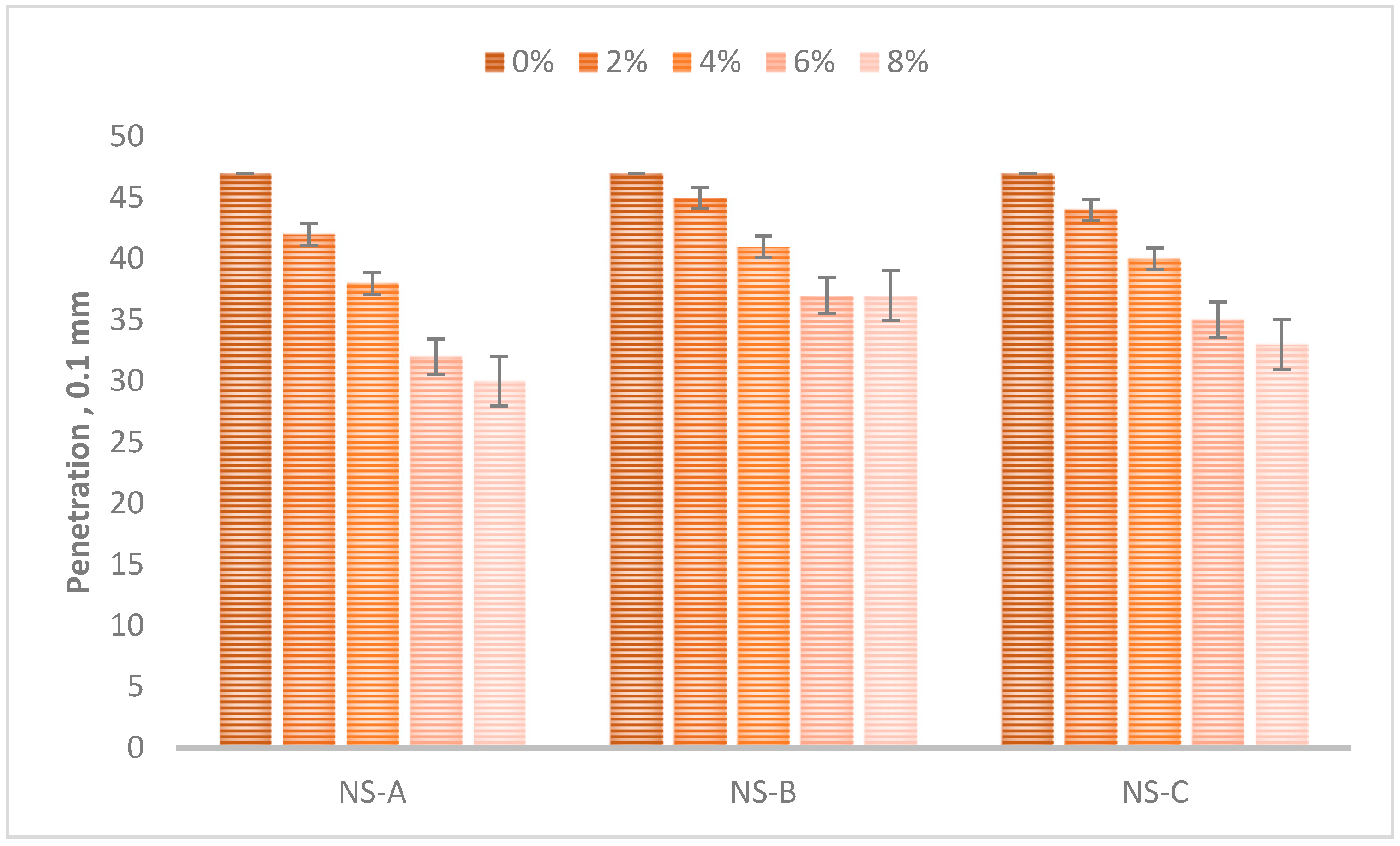
- The results show an improvement in the resistance to temperature sustainability in terms of the better penetration and the softening points results of the modified samples. Thus, the modified bitumen can significantly improve the stiffness of the modified bitumen and enhance the asphalt mixtures’ resistance to rutting deformation.
- From the results, an increase in the stiffness properties was observed by lowering the penetration. Moreover, the mechanical strength was enhanced, in terms of the complex shear modulus of all nano-silica-modified bitumen samples. The incorporation of relatively high percentages of nano-silica (6% and 8%) led to increased rutting resistance. Nevertheless, the trend followed by the rutting factor was not consistent as the rutting resistance was also affected by the size of the nano-silica coated with the silane coupling agent.
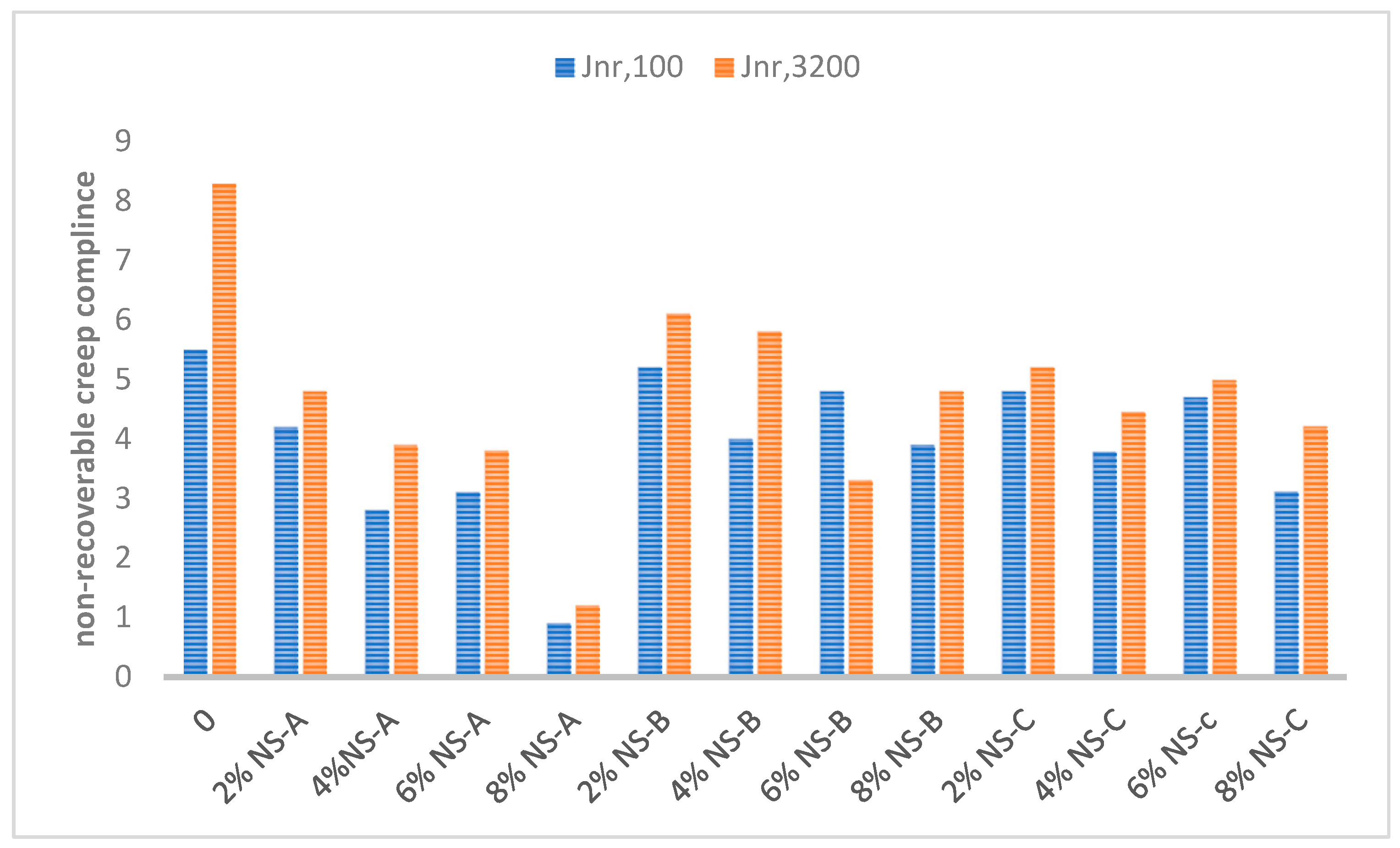
- The non-recovered strain for the nano-silica-modified bitumen C320 and the non-modified bitumen at three different nano-silica sizes for high- and low-stress levels was found. Most modified samples exhibited a decrease in Jnr under the application of high-stress loads. Therefore, the utilization of NS-A leads to a reduction in the levels of rutting deformation.
- Based on the results of this work, the implementation of NS of 15 nm coated with the silane coupling agent was selected for further research in the next work on producing the hybrid polymer–nano–silica-modified C320 bitumen. Numerous tests, including rutting, durability, and fatigue, on both binders and asphalt mixtures, will be conducted.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mashaan, N.S.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H. A comparison on physical and rheological properties of three different waste-plastic-modified bitumen. Recycling 2022, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H. Evaluation of the Performance of Two Australian Waste-Plastic-modified Hot Mix asphalt. Recycling 2022, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H. Laboratory Properties of Waste PET Plastic-Modified Asphalt Mixes. Recycling 2021, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moein, H.; Haddadi, F. The characteristics of hot mixed asphalt modified by nanosilica. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, T.; Afroozi, S. The Properties of Nanosilica-Modified Asphalt Cement. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaan, N.; Chegenizadeh, A.; Nikraz, H. Performance of PET and Nano-silica Modified Stone Mastic Asphalt Mixtures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.; You, Z.; Huang, J. Development of nano materials and technologies on asphalt materials—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, A.N.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Long-Term Ageing Influence on Rheological Characteristics of Asphalt Binders Containing Carbon Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2011, 12, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, A.N.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Influence of Carbon Nanoparticles on the Rheological Characteristics of Short-Term Aged Asphalt Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkhanian, A.N.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Characterization of Unaged Asphalt Binder with Carbon Nano Particle. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2011, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Su, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. High and Low Temperature Properties of Nano-Particles/Polymer Modified Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.E. Examining the Performance of Hot Mix Asphalt Using Nano-Materials. J. Eng. 2016, 6, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yusoff, N.I.M.; Breem, A.A.S.; Alattug, H.N.; Hamim, A.; Ahmad, J. The Effects of Moisture Susceptibility and Ageing Conditions on Nano-Silica/Polymer-Modified Asphalt Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 72, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; You, Z.; Li, L.; Lee, C.H.; Wingard, D.; Yap, Y.K.; Shi, X.; Goh, S.W. Rheological Properties and Chemical Bonding of Asphalt Modified with Nanosilica. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.; Diab, A. Characteristics of Asphalt Binder and Mixture Containing Nanosilica. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestani, B.; Nam, B.H.; Nejad, F.M.; Fallah, S. Nanoclay application to asphalt concrete: Characterization of polymer and linear nanocomposite-modified asphalt binder and mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Napiah, M.; Kamaruddin, I. Effect of nanosilica particles on polypropylene polymer modified asphalt mixture performance. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2018, 8, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xin, X.; Ren, J. Asphalt Modification Using Nano-Materials and Polymers Composite Considering High and Low Temperature Performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet, S.; Terzi, S.; Karahancer, S. Performance Analysis of Nano Modified Bitumen and Hot Mix Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.A.; Badiei, A.; Rashidi, A.M. Effect of Nanosilica Morphology on Modification of Asphalt Binder. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 2230–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuha, M. Engineering Characterisation of Wearing Course Materials Modified with Waste Plastic. Recycling 2022, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, N.; Pakshir, A.H. Rheology and storage stability of modified binders with waste polymers composites. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 20, 773–792. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas, H.; Ahmad, N.; Mashaan, N. Effect of Quartz Nano-Particles on the Performance Characteristics of Asphalt Mixture. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Reference | Asphalt | Nano-Silica (%) |
|---|---|---|
| [11] | 60/80 | 1.86 and 1.98 |
| [13] | PG-76 | 2 and 4 |
| [14] | PG 58–34 | 4 and 6 |
| [15] | 60/70 | 2, 4 and 6 |
| [18] | AH-70 | 3, 5 and 7 |
| Reference | Nano Silica Purity (%) | Size/Dia. (nm) | Surface Area (m²/g) | Density g/cm³ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] | SiO₂ > 99 | 10 | 600 | 2.4 |
| [5] | SiO₂ > 99 | 11–13 | 200 | 2.4 |
| [19] | SiO2 + carbon nanotube > 95 | 10–12 | Not Given | 2.64 |
| [20] | SiO₂ > 99 | Not Given | 195 | Not Given |
| Authors | % Nano-Silica | Time | Temperature | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] | 2, 4, 6, and 8 | 2 h | 135 °C | 4000 rpm |
| [5] | 1, 3, and 5 | 1 h | 160 °C | 3000 rpm |
| [19] | 1, 3, and 5 | 2 h | 160 °C | 4000 rpm |
| Properties | Value | Australian Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration at 25 °C | 42 mm | A2341.12 |
| Brookfield Viscosity at 135 °C | 0.502 Pa.s | AS 2341.2 |
| Flash point | 248 °C | AS 2341.14 |
| Nano Name | Sample Name | Area | Size | Colour | True Density | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2, 15 nm, coated with 2 wt% KH550-silane coupling agent. | NS-A | 600 m2/g | 15 nm | White powder | 2.4 g/cm3 | 97.3% |
| SiO2, 99+%, 20–30 nm (no coating agent) | NS-B | 180–600 m2/g | 20–30 mm | White powder | 2.4 g/cm3 | 99% |
| SiO2, 30 mm coated with 3–4 wt% KH550-silane coupling agent. | NS-C | 130–600 m2/g | 30 mm | White powder | 2.4 g/cm3 | 96.3% |
| 50 °C | 58 °C | 60 °C | 64 °C | 70 °C | 76 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 14.2 | 3.87 | 3.2 | 2.76 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 4% | 15.89 | 7.6 | 5.4 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 0.42 |
| 6% | 16.66 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 2.1 | 0.5 |
| 8% | 18.6 | 7.1 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 2.78 | 0.5 |
| 50 °C | 58 °C | 60 °C | 64 °C | 70 °C | 76 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 14.2 | 3.87 | 3.2 | 2.76 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 4% | 14.89 | 5.6 | 4.4 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 0.42 |
| 6% | 16.66 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 0.5 |
| 8% | 18.6 | 9.1 | 5.8 | 1.2 | 0.78 | 0.15 |
| 50 °C | 58 °C | 60 °C | 64 °C | 70 °C | 76 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 14.2 | 3.87 | 3.2 | 1.76 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 4% | 16.89 | 5.6 | 4.4 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 0.42 |
| 6% | 16.66 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 2.1 | 0.5 |
| 8% | 19.6 | 6.1 | 4.8 | 3.2 | 2.78 | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mashaan, N.S. Rutting Performance of Nano-Silica-Modified C320 Bitumen. Eng 2022, 3, 635-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng3040043
Mashaan NS. Rutting Performance of Nano-Silica-Modified C320 Bitumen. Eng. 2022; 3(4):635-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng3040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleMashaan, Nuha S. 2022. "Rutting Performance of Nano-Silica-Modified C320 Bitumen" Eng 3, no. 4: 635-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng3040043
APA StyleMashaan, N. S. (2022). Rutting Performance of Nano-Silica-Modified C320 Bitumen. Eng, 3(4), 635-645. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng3040043











