PREFACE: A Search for Long-Lived Particles at the Large Hadron Collider
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. BSM Benchmark Models of a Dark Sector
1.2. Proposed Long-Lived Particle Search Experiments
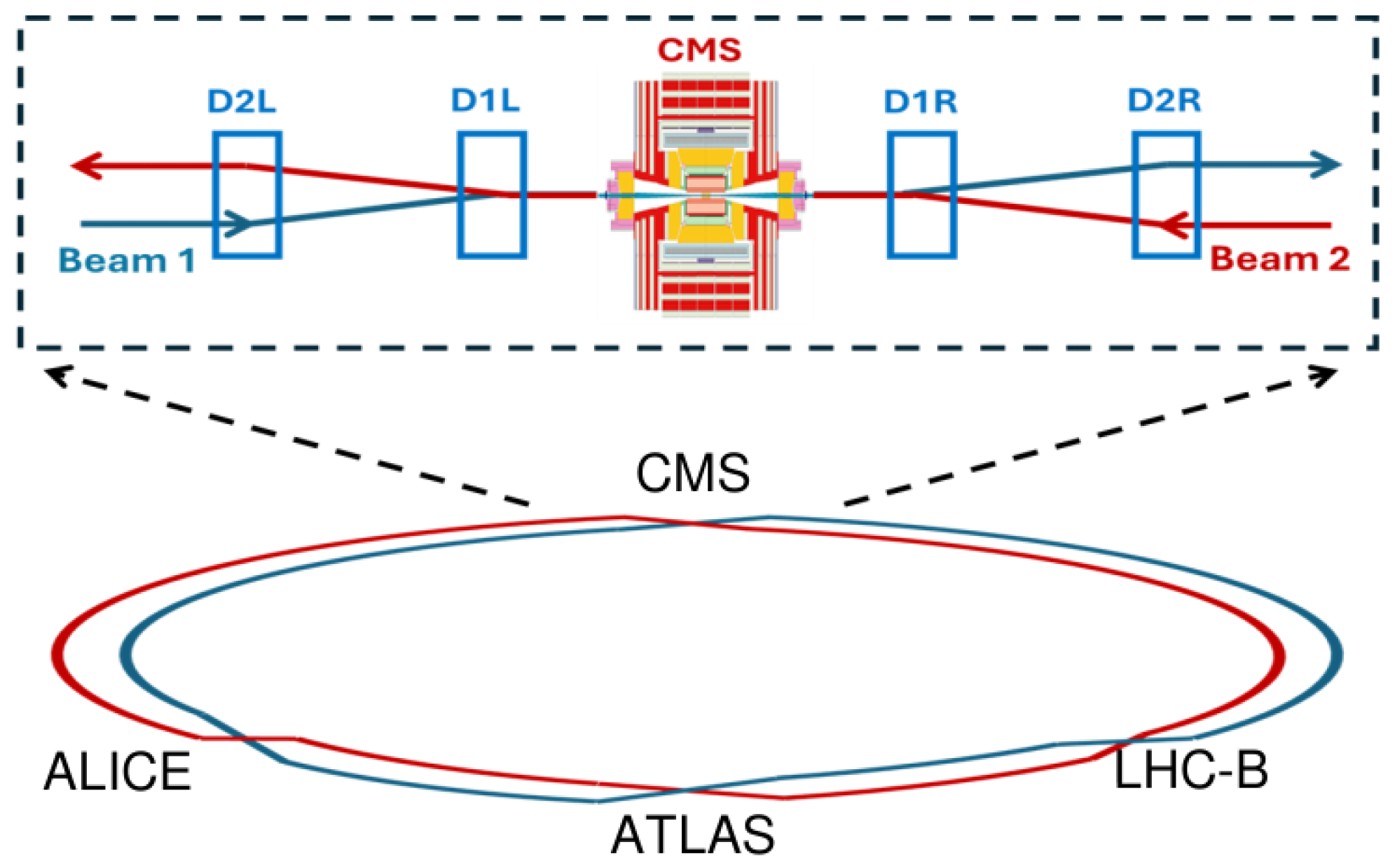
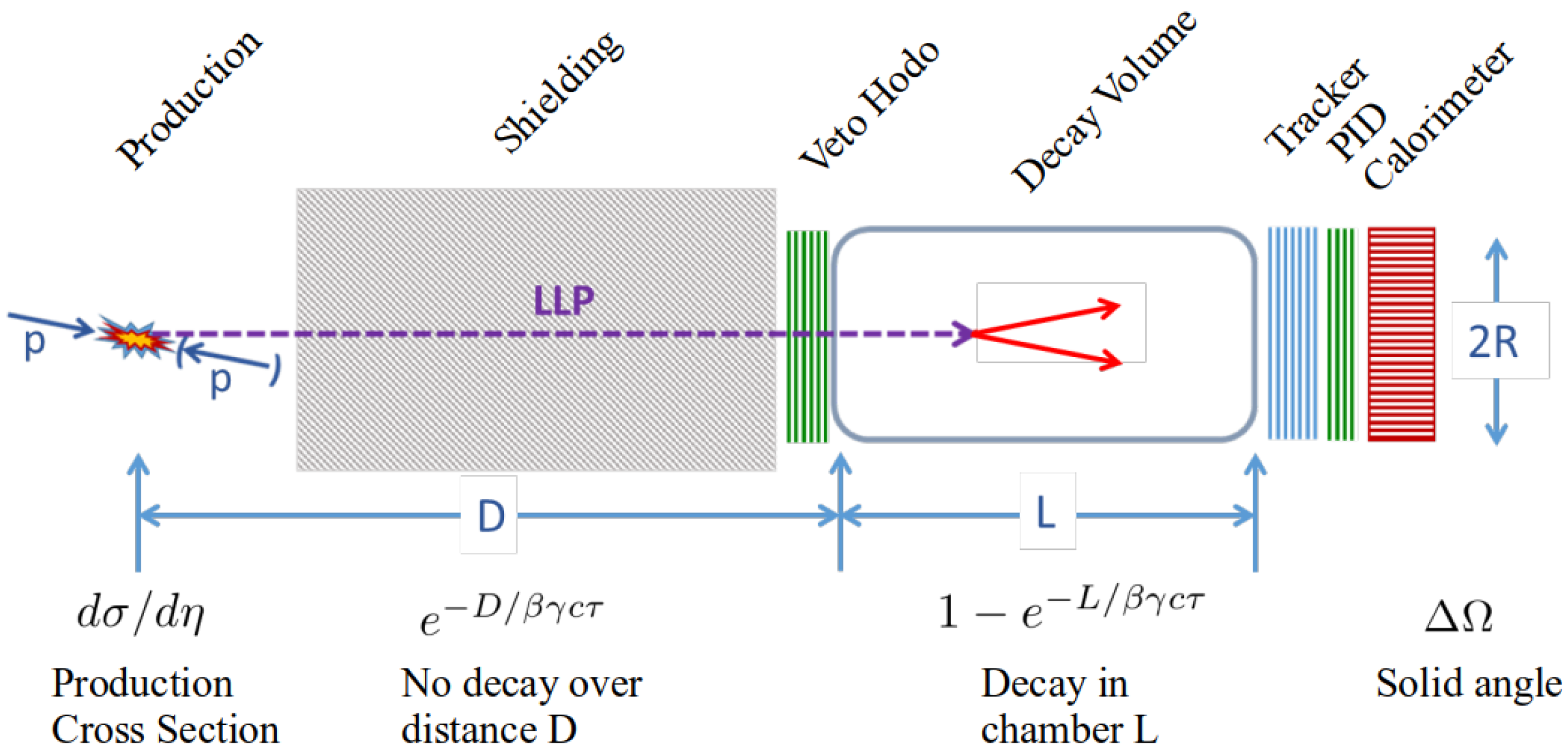
2. Long-Lived Particle Search at Long Straight Section 5 (LSS5)
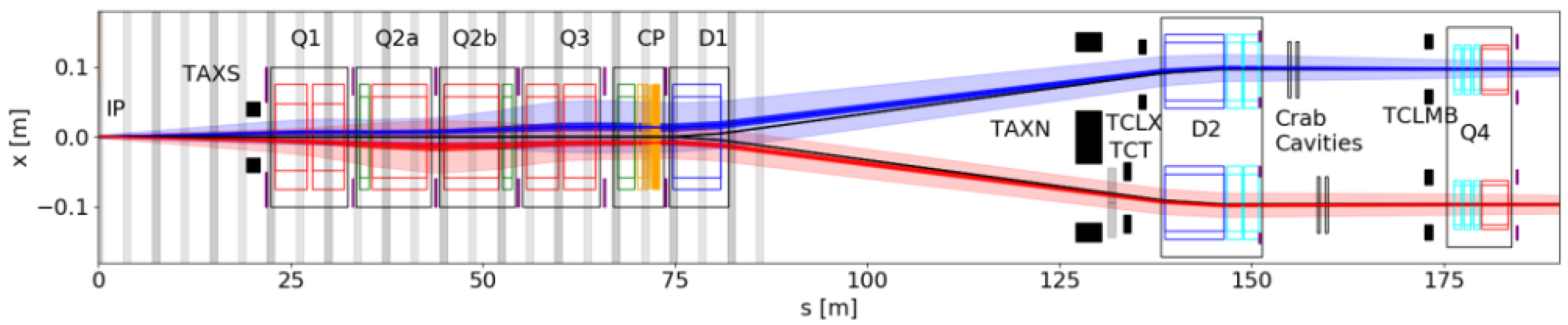
2.1. Experimental Conditions at LSS5
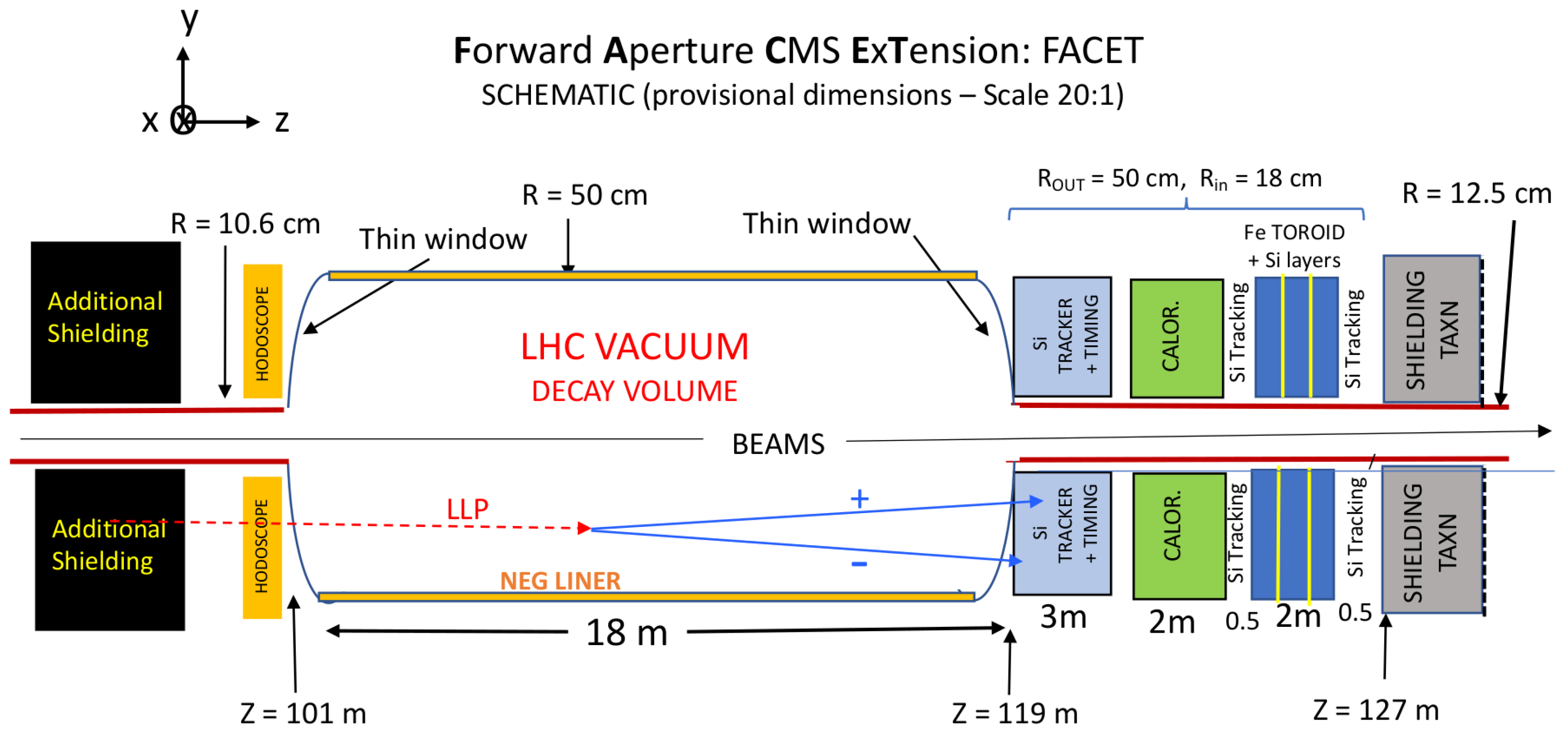
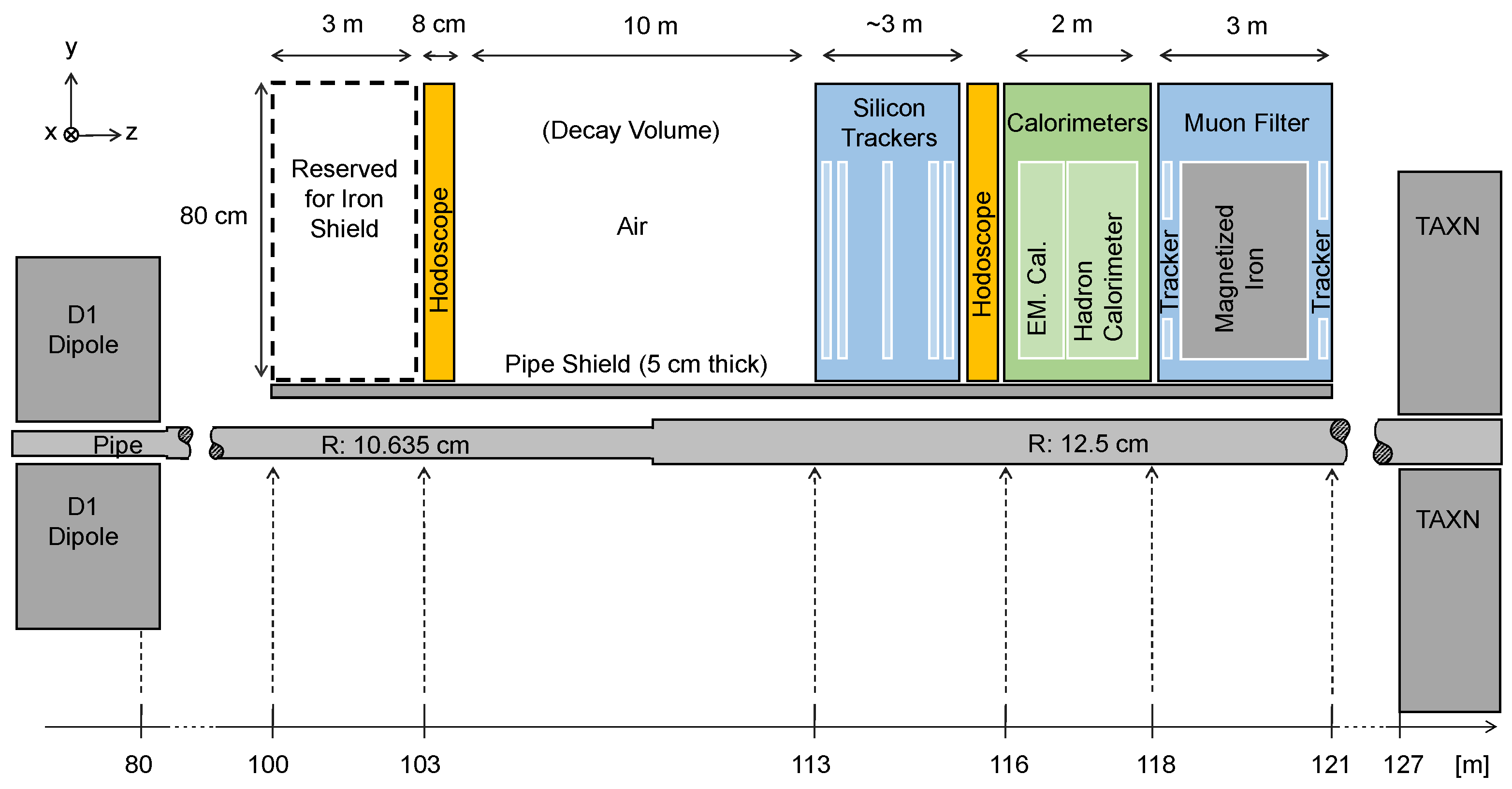
2.1.1. FACET Overview
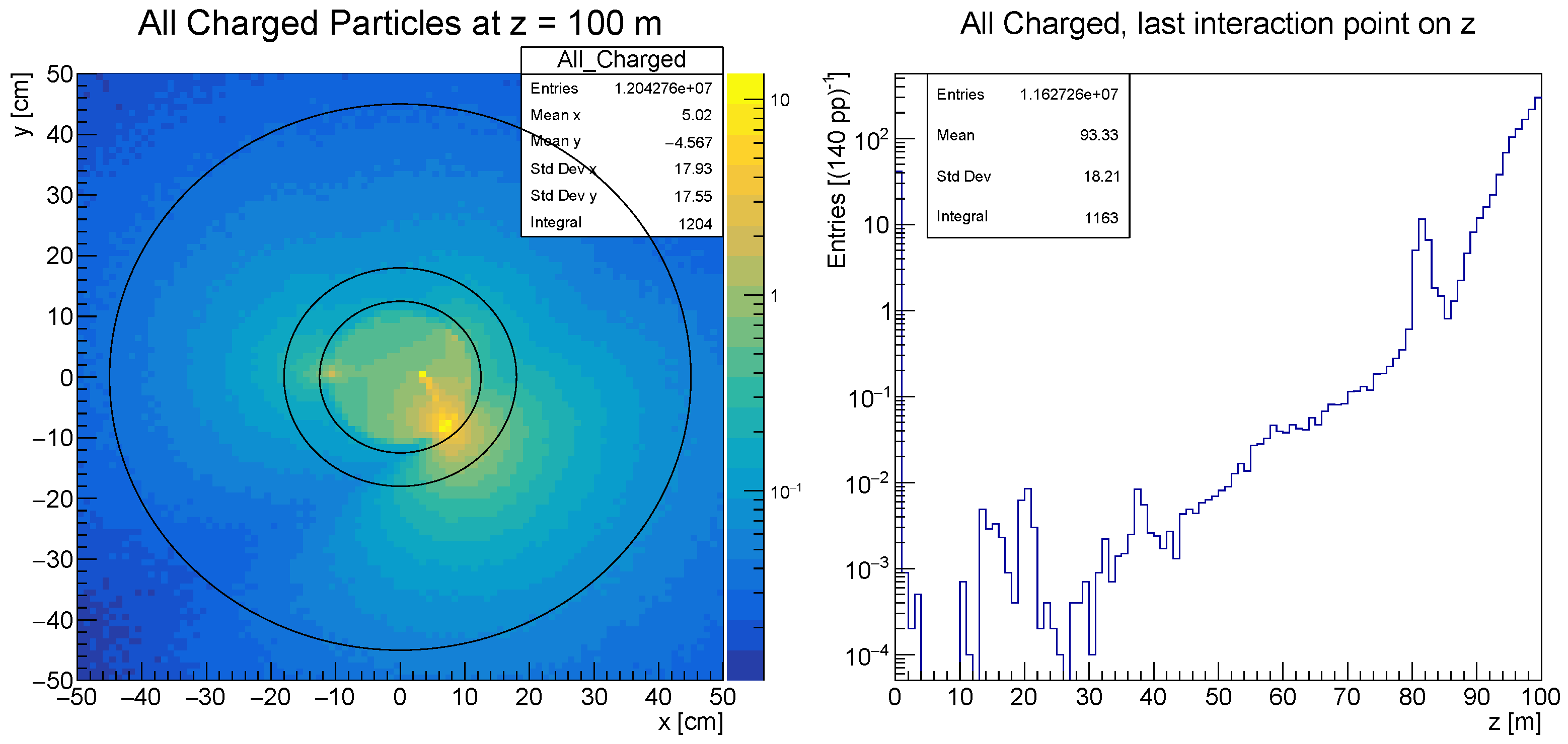
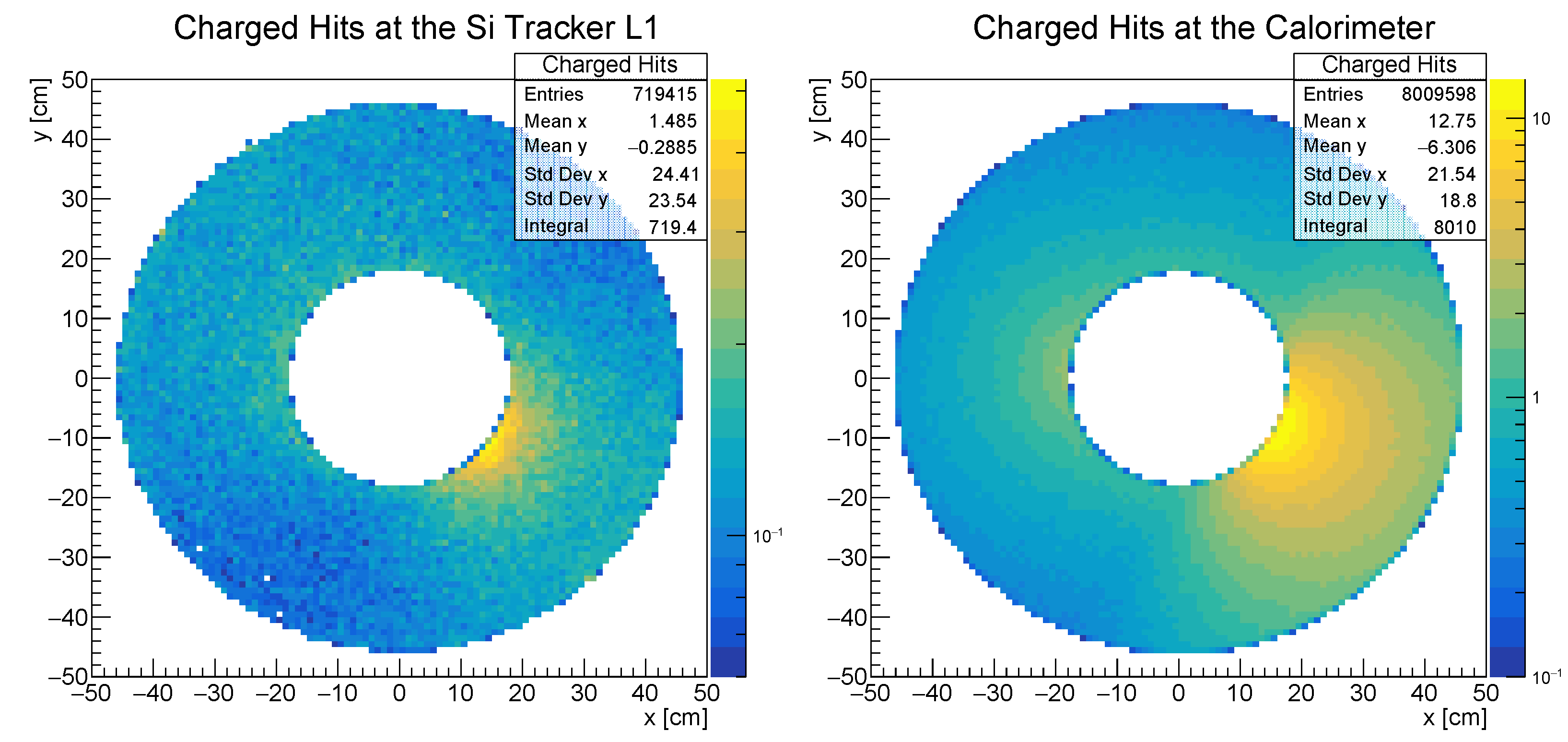
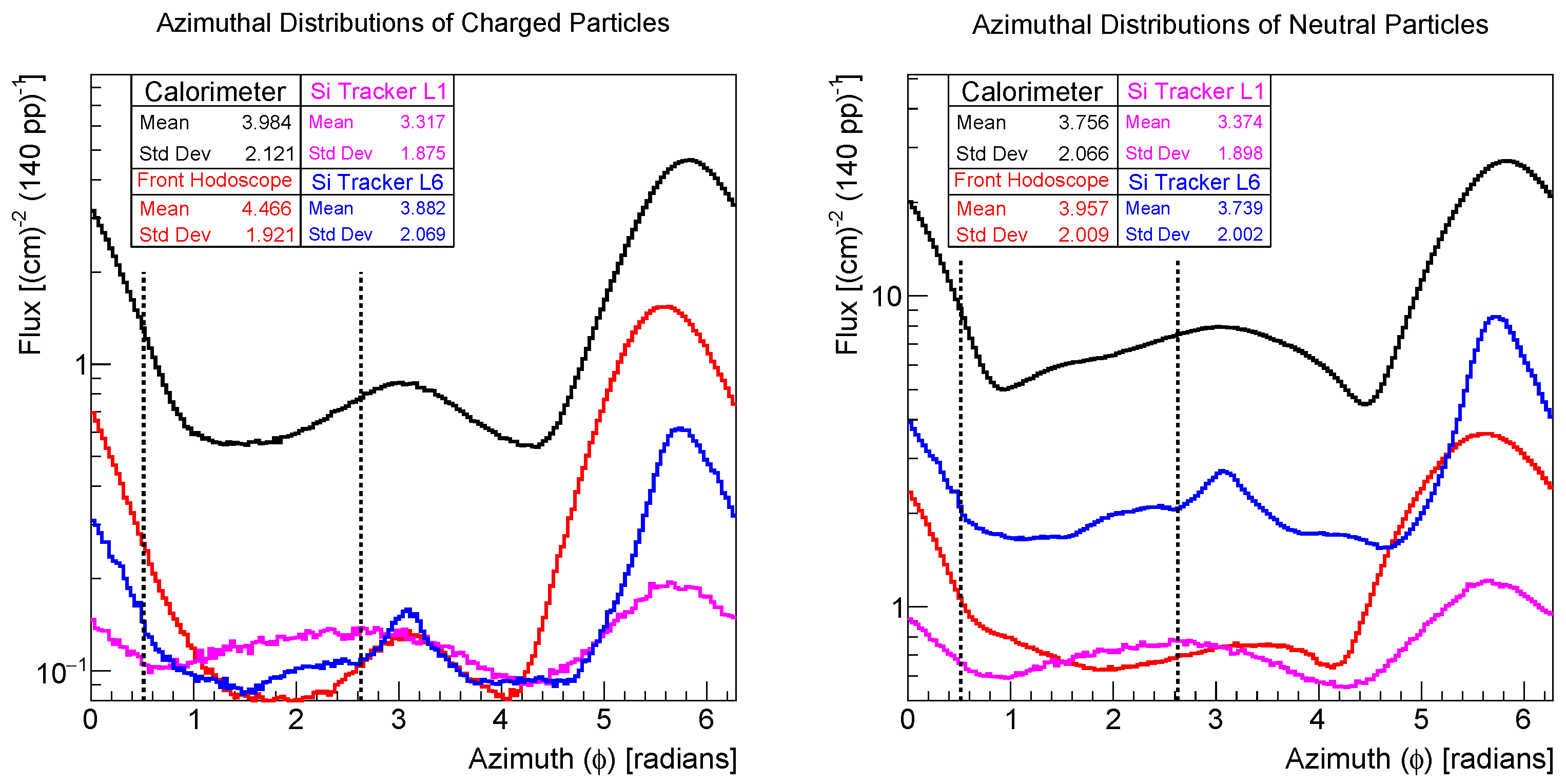
2.1.2. Backgrounds in FACET
2.1.3. Limitations Imposed for Run 4
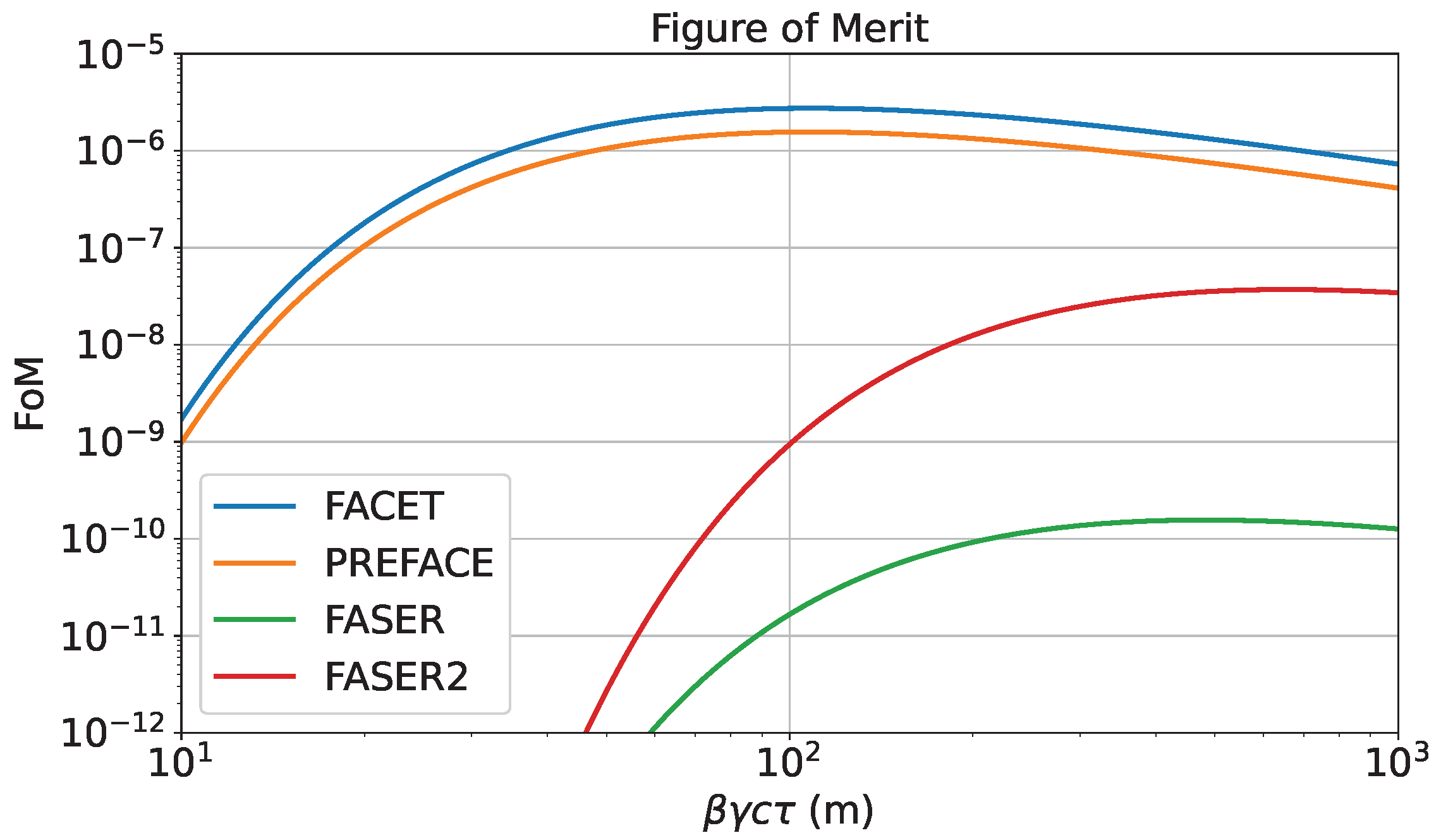
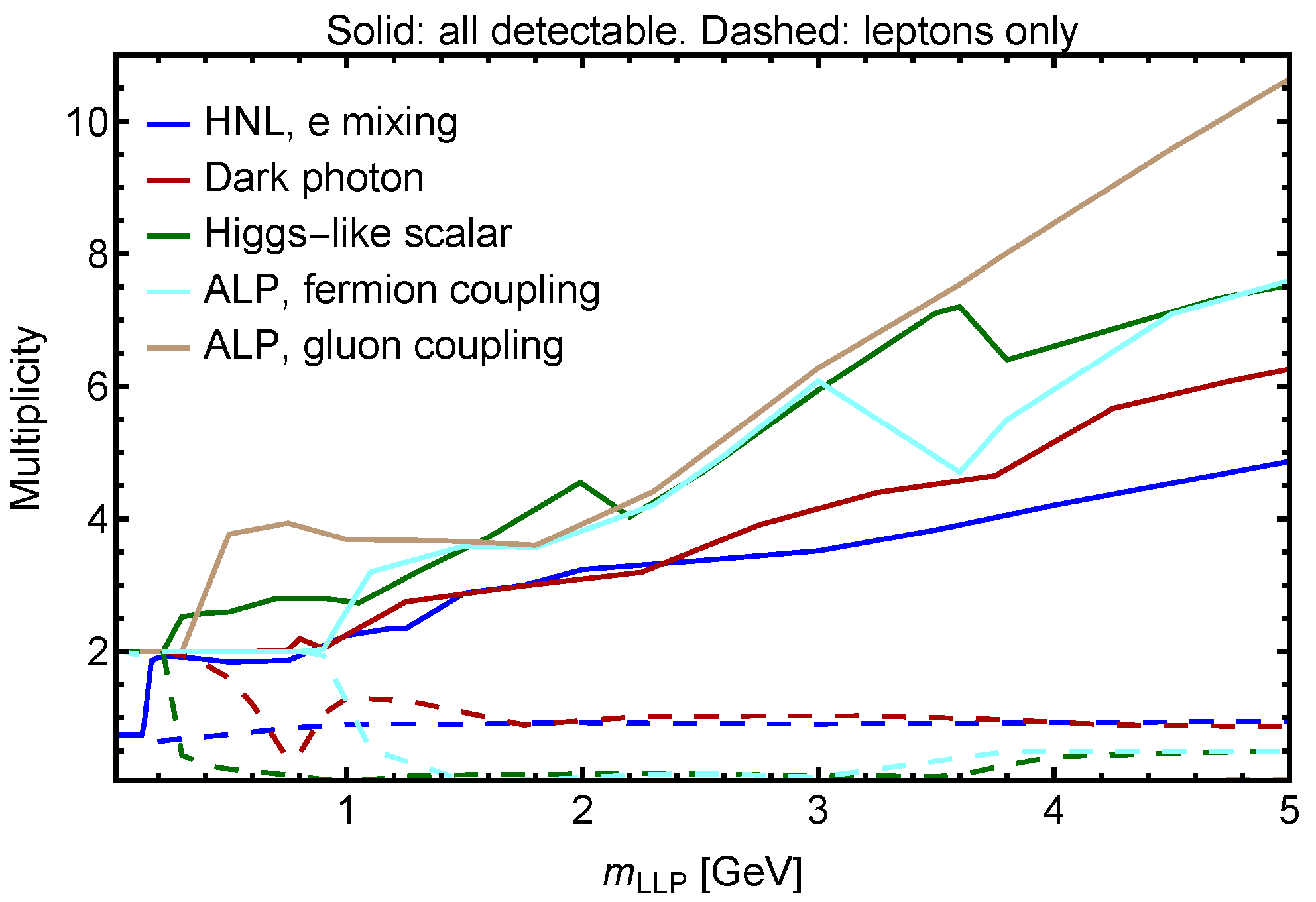
2.2. Figure of Merit for LLP Search Apparatus
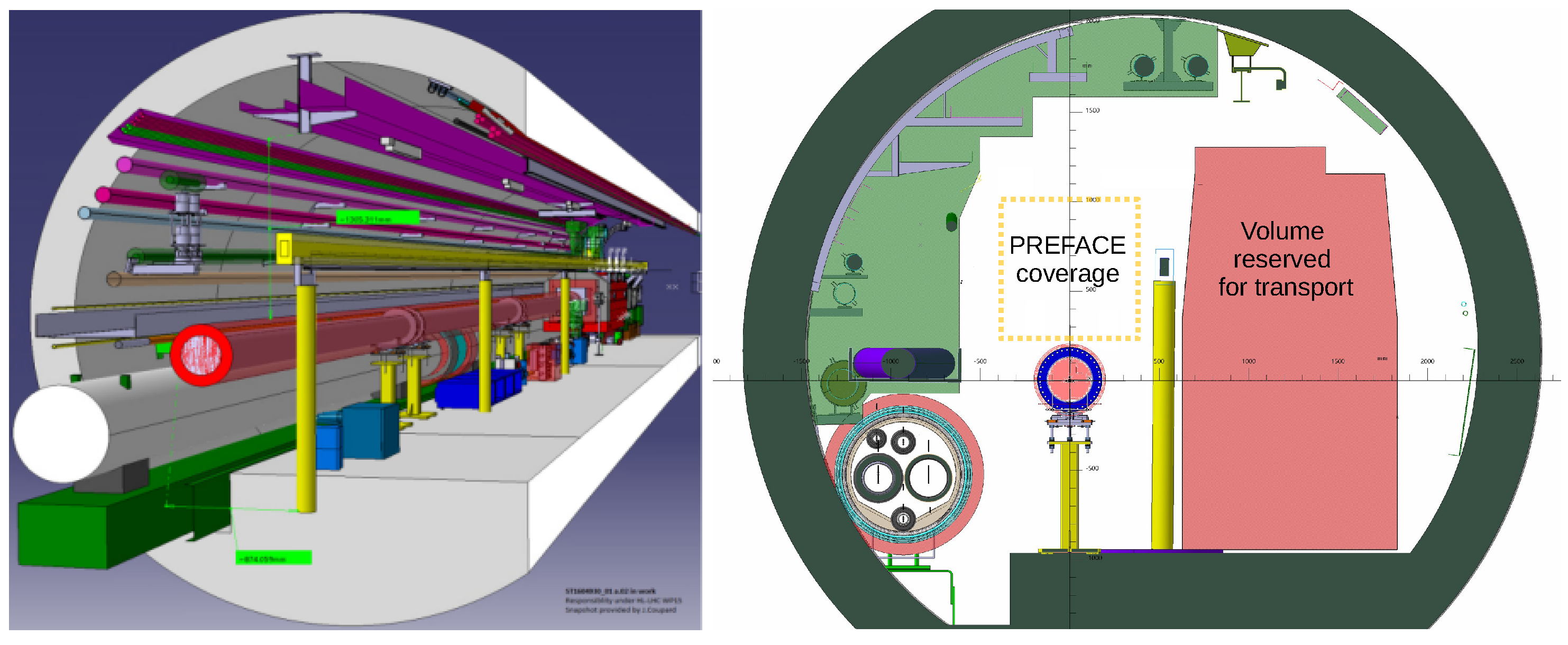
3. PREFACE Setup
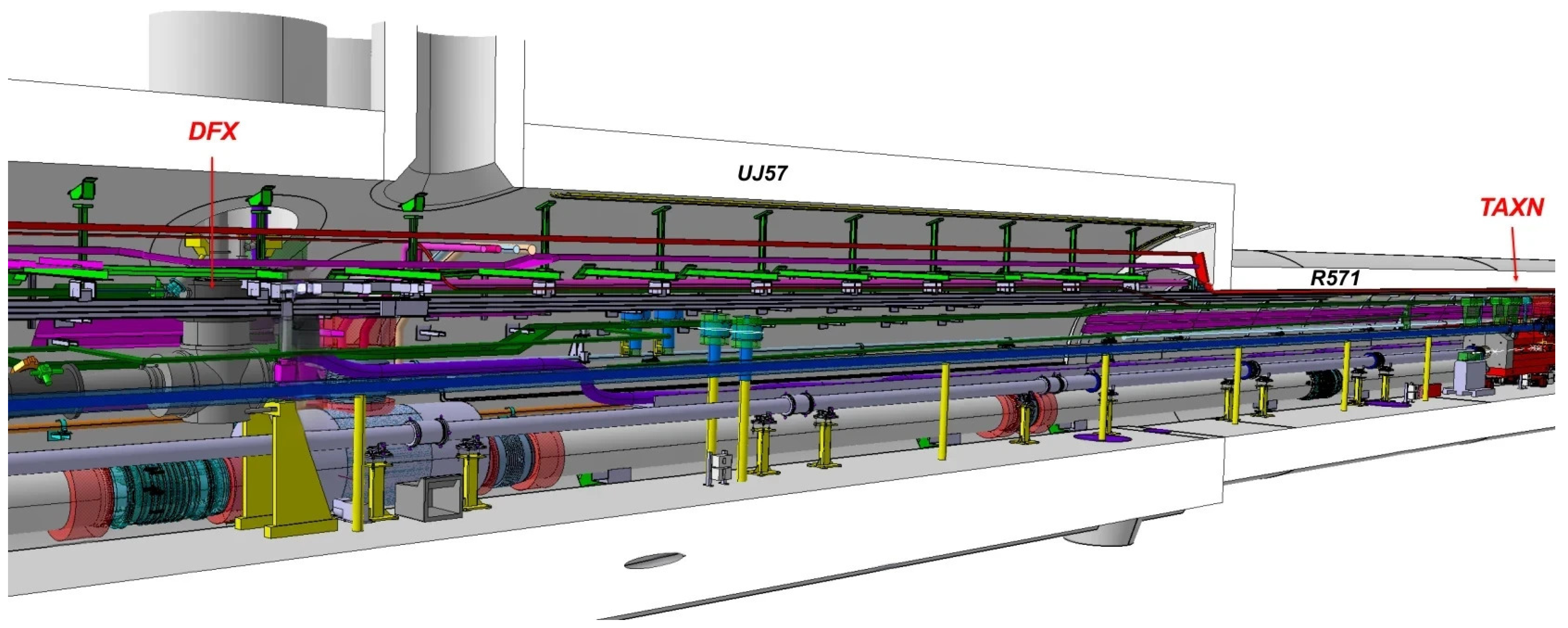
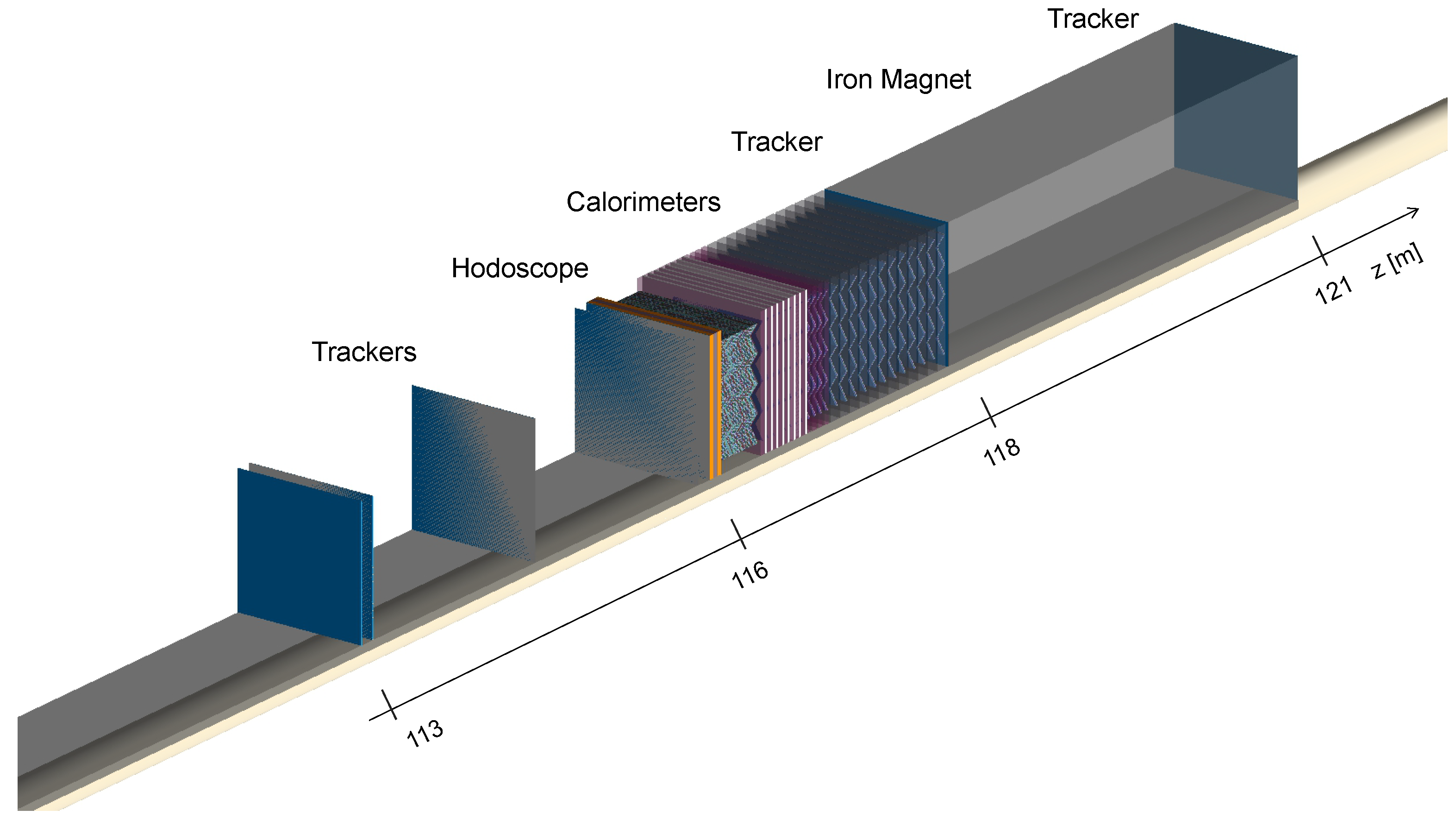
3.1. PREFACE Geometry
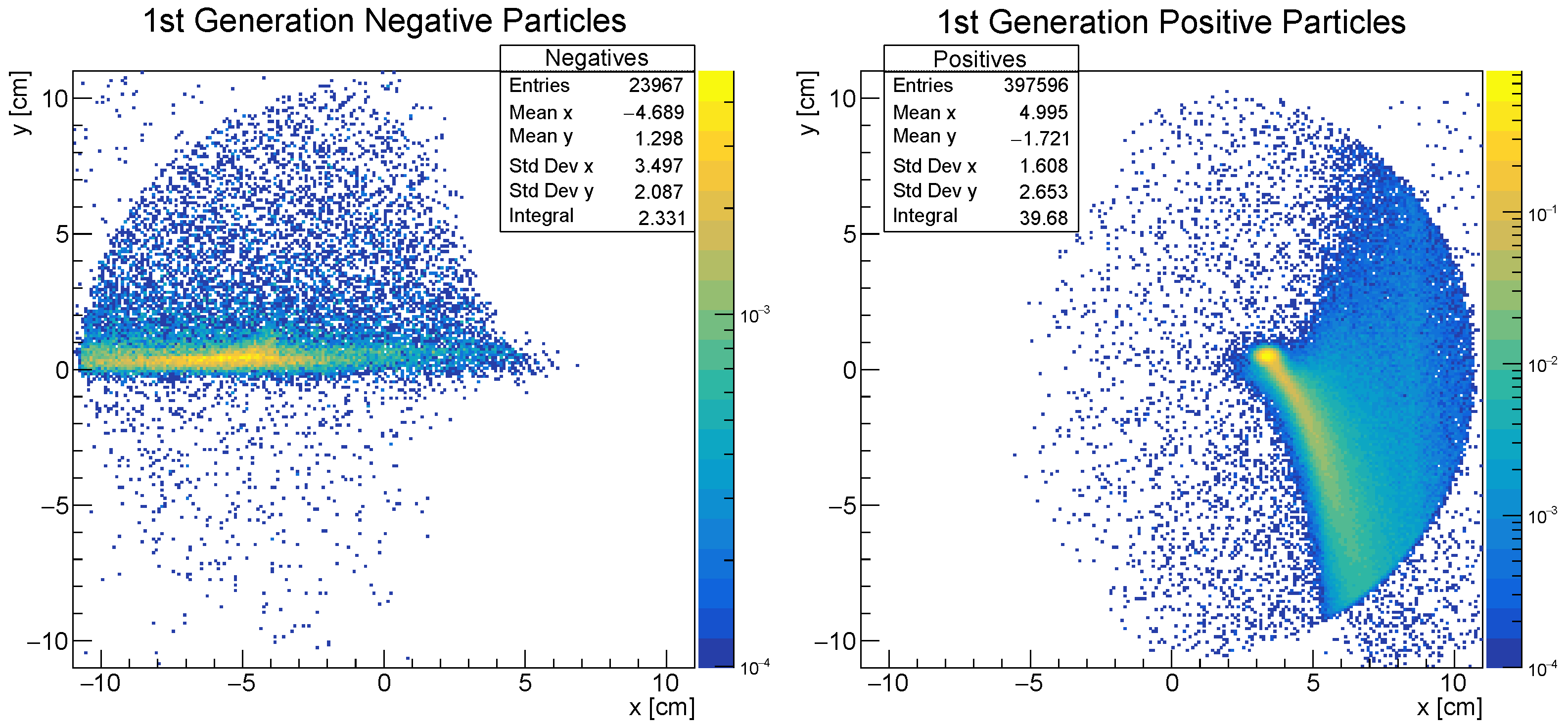
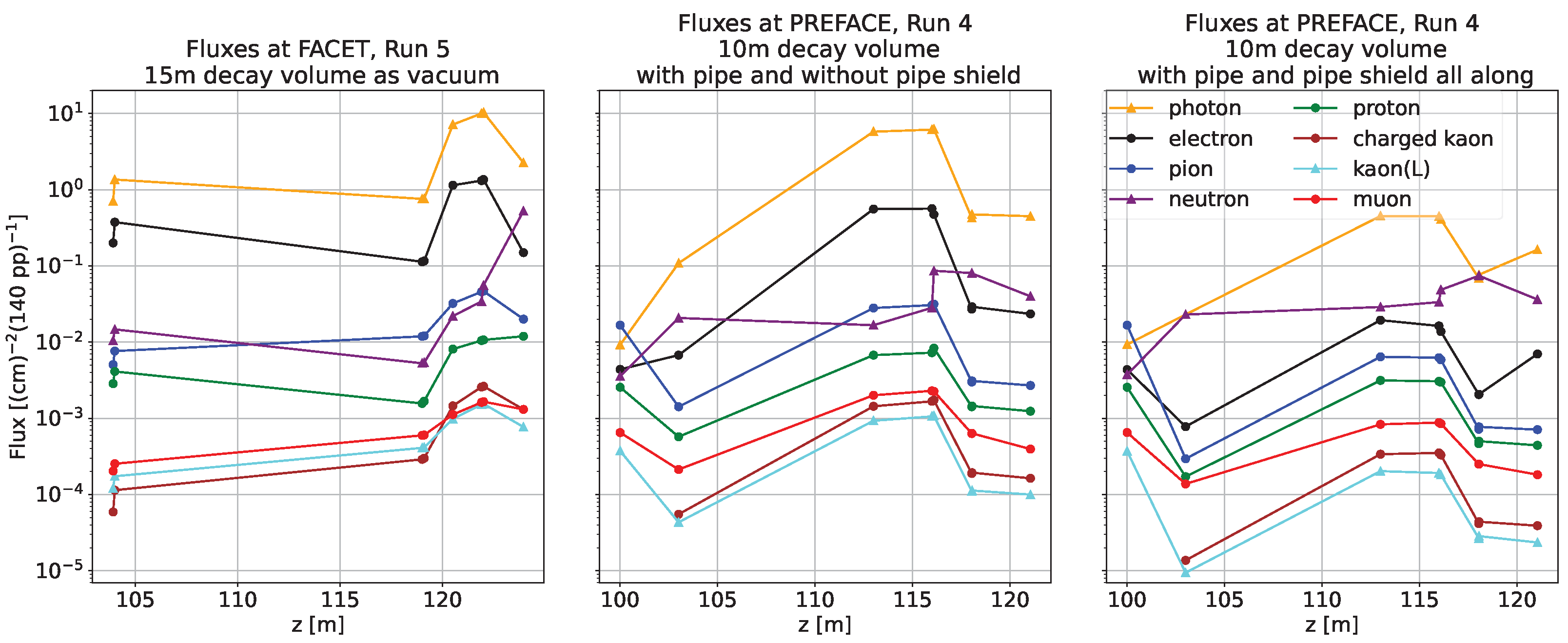
3.2. Background Estimates
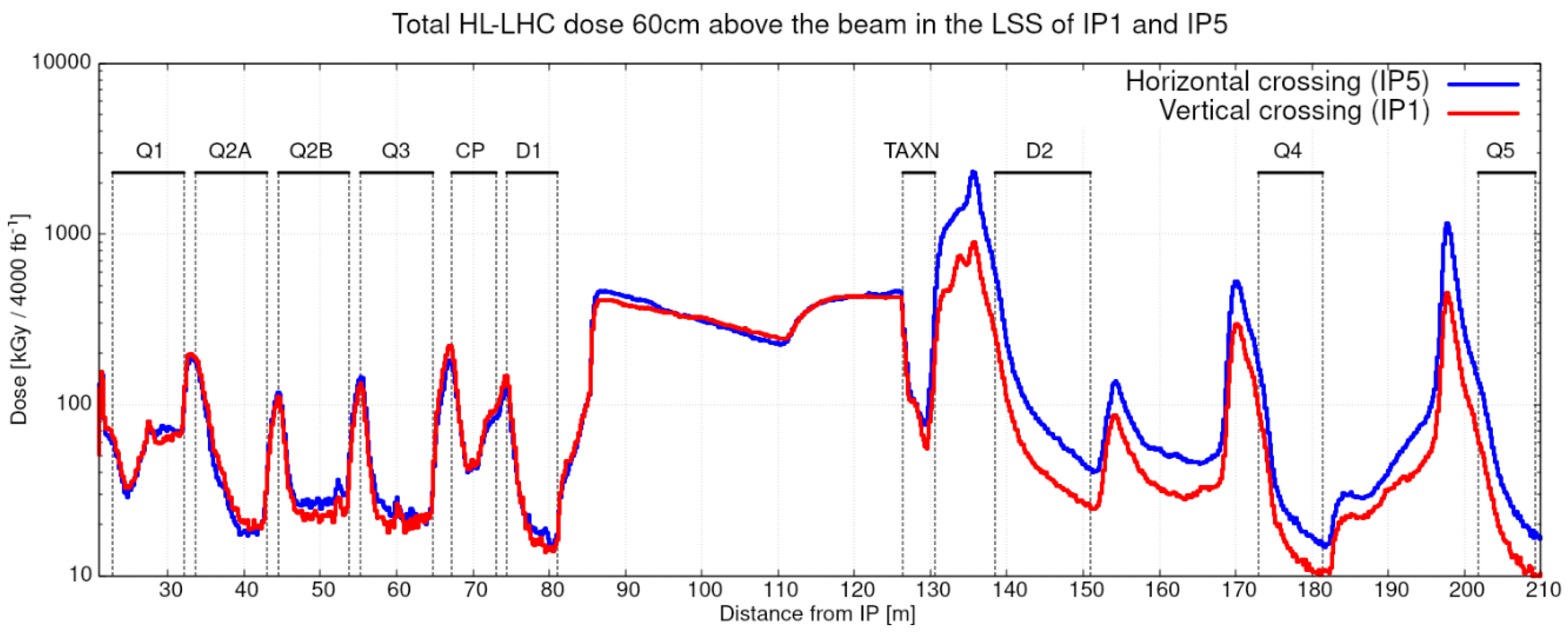
3.3. Radiation Levels in the Region Foreseen for PREFACE
4. Physics Case for PREFACE
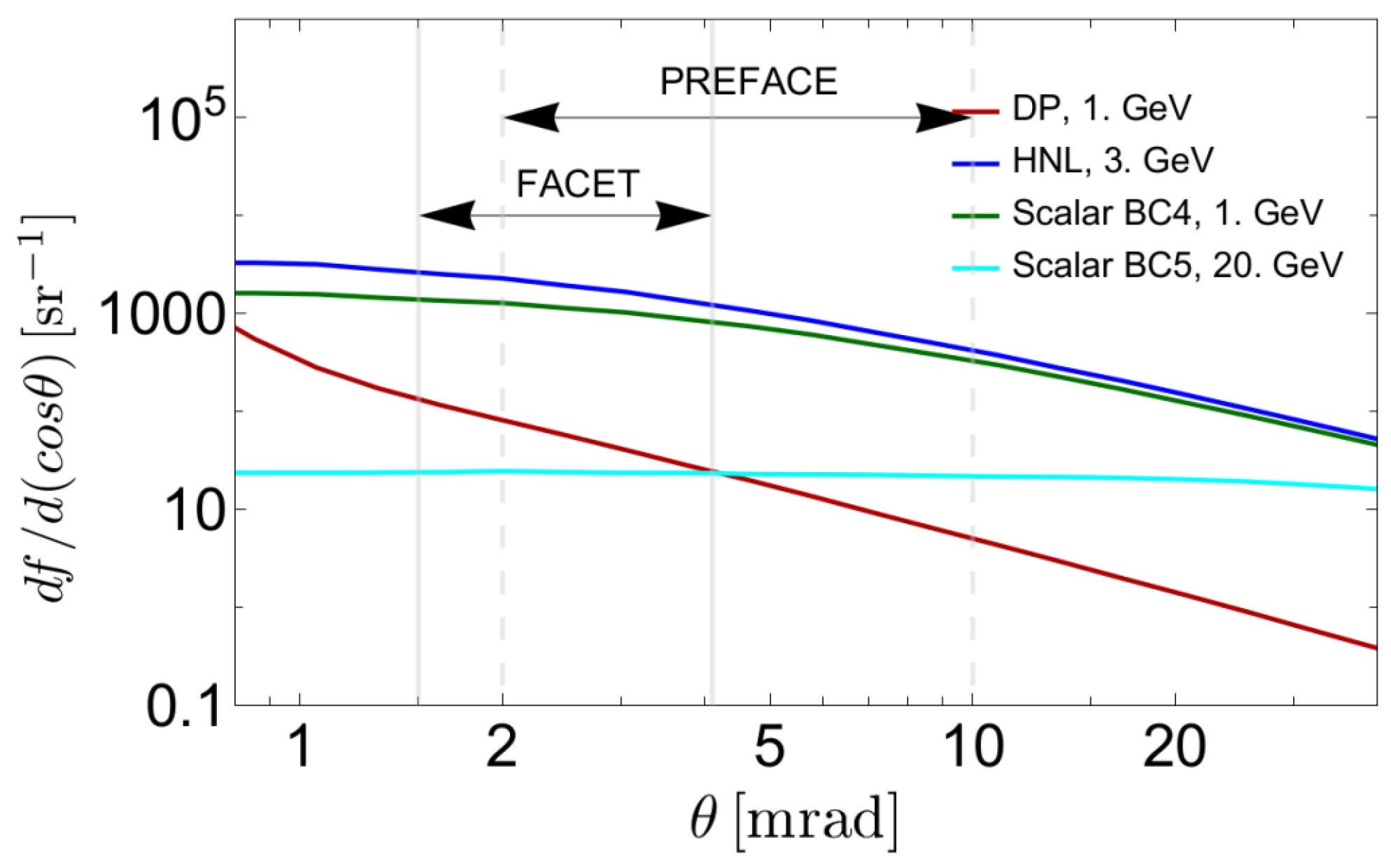
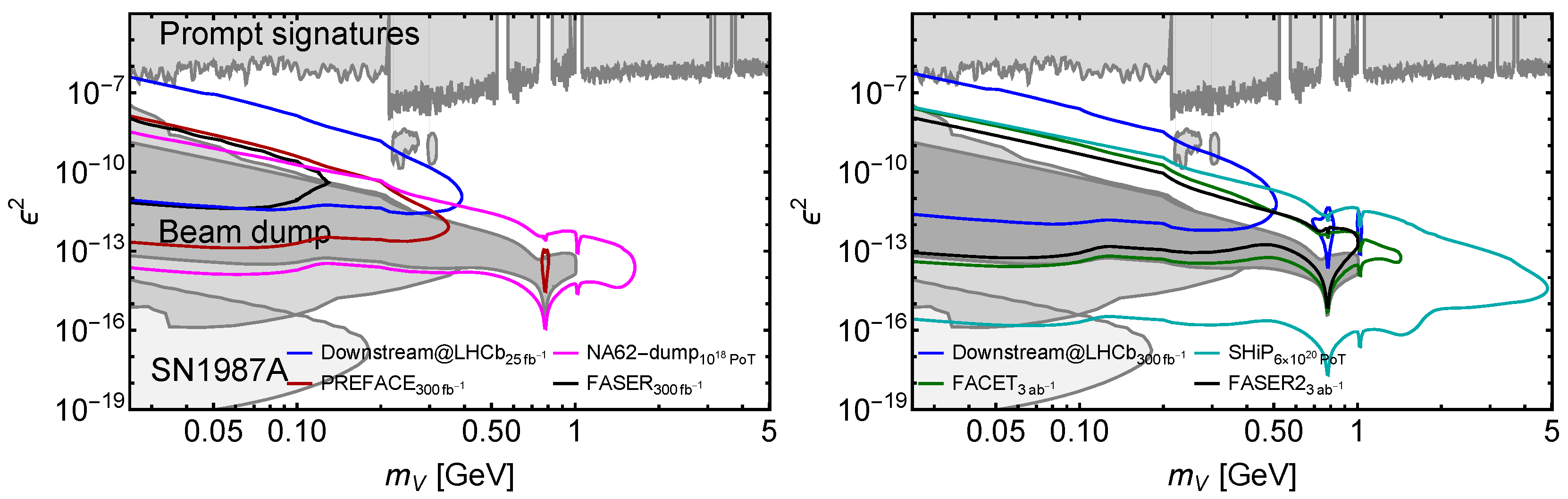
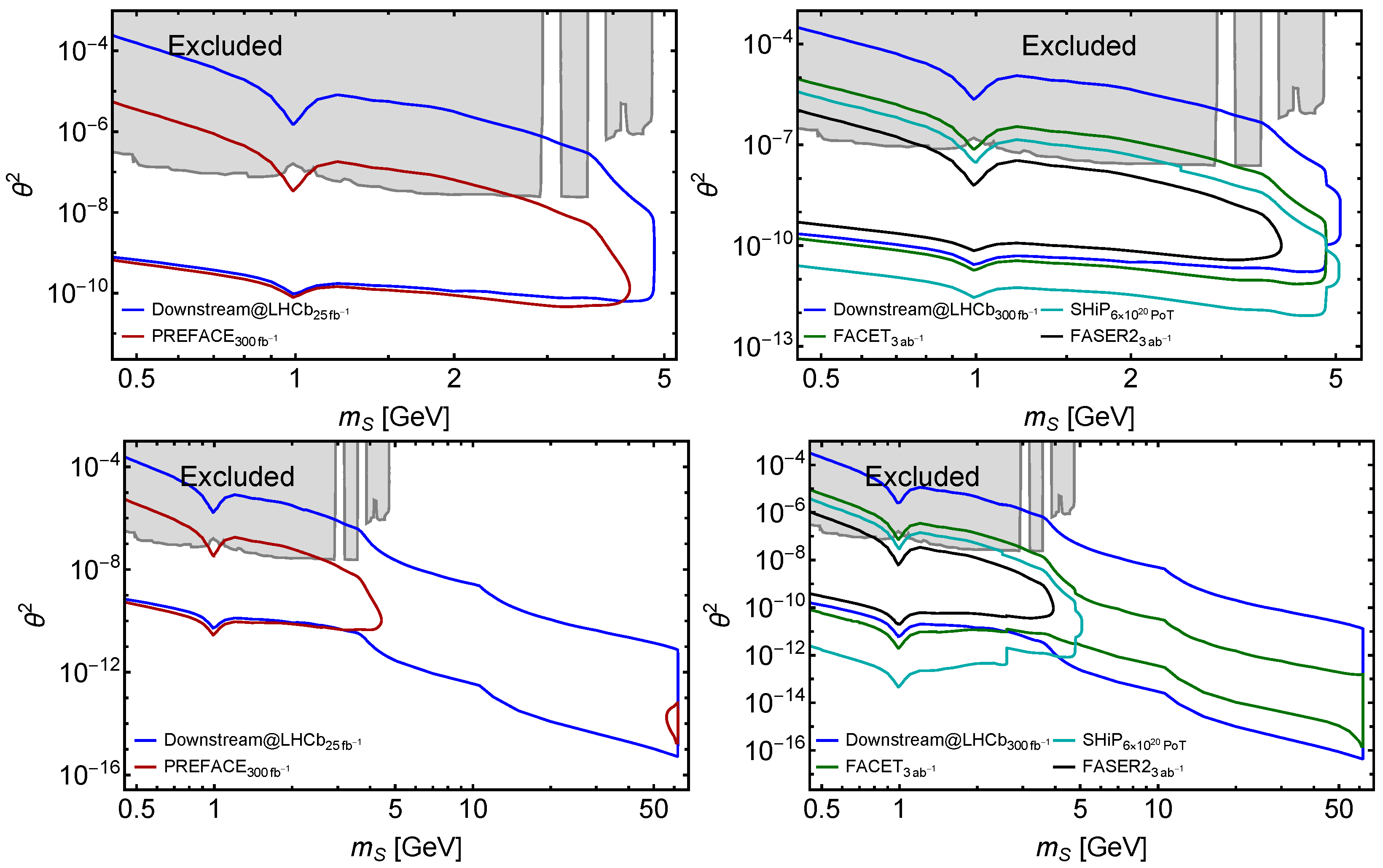
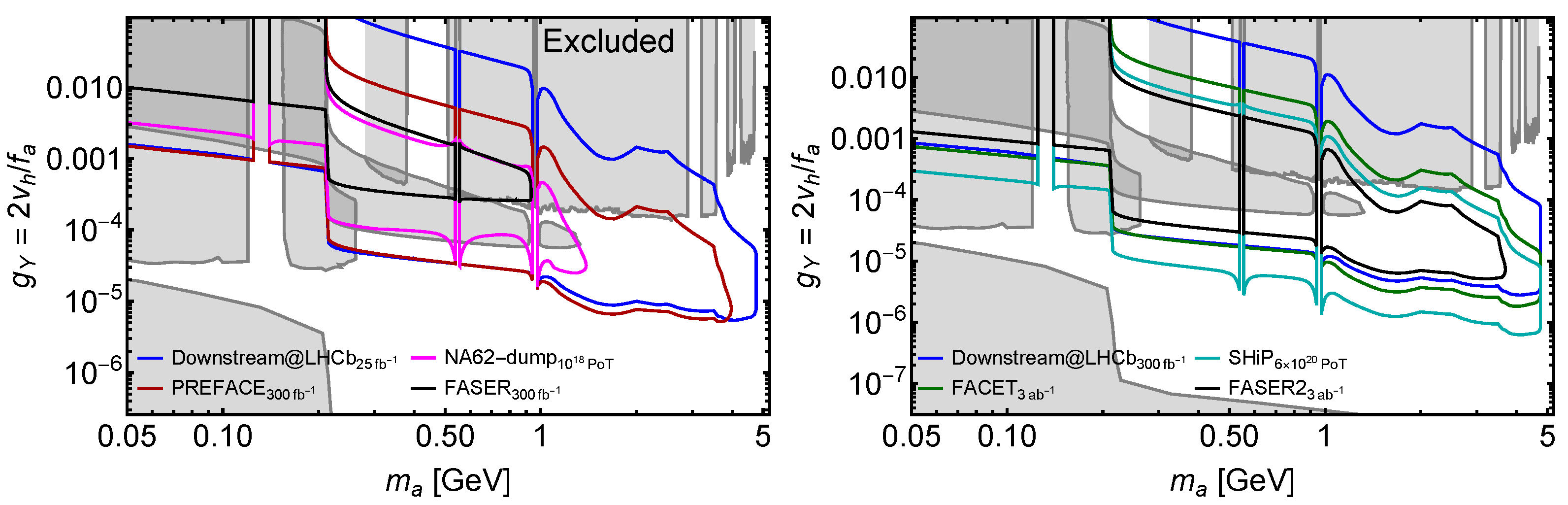
4.1. Comparison to FACET and Other LLP Projects
4.2. Sensitivity Calculations
4.2.1. Heavy Neutral Leptons
4.2.2. Dark Photons
4.2.3. Higgs-like Scalars
4.2.4. ALPs Coupled to Fermions
5. Experimental Program for PREFACE
5.1. Considerations on PREFACE Apparatus
5.1.1. Decay Analysis
5.1.2. Muon Spectrometer with Permanent Magnets
5.1.3. Alternative Air-Core Permanent Magnet
5.2. Remarks on the PREFACE Setup
5.3. Trigger Criteria
- The slope of particle tracks is a powerful diagnostic to reject hits on the beam pipes. Tracks with high polar angles, , can be ignored; those tracks are secondary particles, mostly from scattering in the beam pipes and the pipe shield.
- Any tracks extrapolated upstream to a hit in the front tracker to be ignored;
- We require at least two of the remaining charged particles to have a vertex in the decay volume.
- at least one high-momentum muon tracks and/or at least one high-energy electron showers with quite small angles with respect to the beams (“high” refers to means above 100 GeV but tuneable);
- at least two tracks in the tracker that were not detected in the front tracker at the beginning of the decay region, with a distance of closest approach below μm at a point inside the fiducial decay region; and
- a neural net (machine learning/AI) rejecting most interactions on the beam-pipe or shielding while selecting decay candidates.
5.4. Tracking, Timing, and Calorimetry
5.5. Search for
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| ALICE | A Large Ion Collider Experiment |
| ALP | axion-like particle |
| ATLAS | A Toroidal LHC ApparatuS |
| BC | benchmark case |
| BSM | beyond the SM |
| Bx | magnetic field vertical bend |
| B·L | magnetic field times length |
| CALICE | CAlorimeter for the LInear Collider Experiment |
| CERN | the European Organization for Nuclear Research |
| CL | confidence level |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| CP | corrector package |
| DAQ | data acquisition |
| DFX | Design, Fabrication, and eXamination (unit) |
| DP | dark photon |
| D1(2) | dipole magnet 1 (2) |
| D1(2)L/R | D1(2) left/right |
| Dx, Dy | x, y apertures |
| EM | electromagnetic |
| FACET | Forward-Aperture CMS ExTension |
| FASER | ForwArd Search ExpeRiment |
| Fluka | Fluktuierende Kaskade |
| FoM | figure-of-merit |
| FPF | Forward Physics Facility |
| Geant | GEometry ANd Tracking |
| HAD | hadronic (calorimeter) |
| HGCAL | High-Granualty CALorimeter |
| HL-LHC | high-luminocity LHC |
| HNL | heavy neutral lepton |
| ID | identity |
| IP | interaction point |
| LGAD | low gain avalanche diode |
| LHC | Large Hadron Collider |
| LHCb (LHC-B) | LHC beauty |
| LLP | long-lived particle |
| LSS5 | long straight section at IP5 |
| L1, L6 | first, sixth silicon tracker |
| MS | multiple scattering |
| NA | north area |
| PBC | physics beyond colliders |
| PID | particle identifier |
| PoT | proton-on-target |
| PREFACE | Pionner Rare-Event Apparatus for Collider Experiments |
| QCD | quantum chromodynamics |
| Q1–Q4 | quadrupole magnet 1–4 |
| R571 | LHC tunnel hall name |
| rms | root mean square |
| SHiP | Search for Hidden Particle |
| SM | Standard Model |
| Std Dev | standard deviation |
| TAXN | target neutral beam absorber |
| TAXS | target absorber for secondary particles |
| TCLX | target collimator long with increased cross section |
| TCLMB | targets collimators loss monitoring block |
| TCT | tertiary collimator |
| TID | total ionizing dose |
| TOF | time-of-flight |
| TR | tracking |
| UJ57 | LHC tunnel hall name |
| ZDC | Zero Degree Calorimeter |
Appendix A. Future Studies in Progress
- Optimize shielding design to minimize radiation doses and track multiplicity. Investigate available radiation-hard calorimeters and trackers with adequate performance. Design magnet optimizing length to minimize hadron track leakage. Design tracking in front of the fiducial decay region with (optional) timing for particle ID of backgrounds (and testing Fluka simulations).
- Calculate acceptance for (+ anything) decays as a function of . Calculate muon charge sign assignment and momentum resolution versus p, and use of calibration channels, for example, (from shielding).
- Design track-based trigger on vertices. Investigate AI trigger classifying events as X candidates, SM decays, or interactions.
- Design supports and infrastructure, including signals and DAQ, cables, etc. People, timeline, costs, etc.
References
- Alimena, J.; Beacham, J.; Borsato, M.; Cheng, Y.; Vidal, X.C.; Cottin, G.; Curtin, D.; De Roeck, A.; Desai, N.; Evans, J.A.; et al. Searching for long-lived particles beyond the Standard Model at the Large Hadron Collider. J. Phys. G 2020, 47, 090501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, H. [on behalf on the ATLAS and CMS Collaborations]. Recent results from Beyond Standard Model (BSM) searches at LHC. Nucl. Part. Phys. Proc. 2015, 267–269, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policicchio, A. [on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration]. BSM searches in ATLAS. PoS 2015, CORFU2014, 063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aberle, O.; Béjar Alonso, I.; Brüning, O.; Fessia, P.; Lamont, M.; Rossi, L.; Tavian, L.; Zerlauth, M. High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider (HL-LHC). Technical Design Report; CERN Report CERN-2020-010; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, O.; Rossi, L. The High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 1, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, A.; Mangano, M.; Meyer, A.B.; Nisati, A.; Salam, G.; Vesterinen, M.A. Report on the Physics at the HL-LHC, and Perspectives for the HE-LHC; CERN Report CERN-2019-007; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchutska, L. [on behalf of the CMS Collaboration]. Prospects for BSM searches at the high-luminosity LHC with the CMS detector. Nucl. Part. Phys. Proc. 2016, 273–275, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühr, F. [on behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration]. Prospects for BSM searches at the high-luminosity LHC with the ATLAS detector. Nucl. Part. Phys. Proc. 2016, 273–275, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, O.; Mellado, B.; Antusch, S.; Bagnaschi, E.; Banerjee, S.; Beck, G.; Belfatto, B.; Bellis, M.; Berezhiani, Z.; Blanke, M.; et al. Unveiling hidden physics at the LHC. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsou, V.A. Hunting new physics with ATLAS. EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 182, 02089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekhin, S.; Altmannshofer, W.; Asaka, T.; Batell, B.; Bezrukov, F.; Bondarenko, K.; Boyarsky, A.; Choi, K.-Y.; Corral, C.; Craig, N.; et al. A facility to search for hidden particles at the CERN SPS: The SHiP physics case. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 124201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beacham, J.; Burrage, C.; Curtin, D.; De Roeck, A.; Evans, J.; Feng, J.L.; Gatto, C.; Gninenko, S.; Hartin, A.; Irastorza, I.; et al. Physics beyond colliders at CERN: Beyond the Standard Model working group report. J. Phys. G 2020, 47, 010501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antel, C.; Battaglieri, M.; Beacham, J.; Boehm, C.; Buchmüller, O.; Calore, F.; Carenza, P.; Chauhan, B.; Cladè, P.; Coloma, P.; et al. Feebly-interacting particles: FIPs 2022 Workshop Report. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batell, B.; Blinov, N.; Hearty, C.; McGehee, R. Exploring dark sector portals with high intensity experiments. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.06905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-T.; Lv, H.; Shen, W.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J. Probing dark QCD sector through the Higgs portal with machine learning at the LHC. J. High Energy Phys. 2023, 2023, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, H.; et al. [FASER Collaboration] The FASER detector. J. Instrum. 2024, 19, P05066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Kling, F.; Reno, M.H.; Rojo, J.; Soldin, D.; Anchordoqui, L.A.; Boyd, J.; Ismail, A.; Harland-Lang, L.; Kelly, K.J.; et al. The Forward Physics Facility at the High-Luminosity LHC. J. Phys. G 2023, 50, 030501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerci, S.; Sunar Cerci, D.; Lazic, D.; Landsberg, G.; Cerutti, F.; Sabaté-Gilarte, M.; Albrow, M.G.; Berryhill, J.; Green, D.R.; Hirschauer, J.; et al. FACET: A new long-lived particle detector in the very forward region of the CMS experiment. J. High Energy Phys. 2022, 2022, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzo, A. [on behalf of FACET Team]. FACET: Forward Aperture CMS ExTension. Talk at the Thirteenth Workshop of the LLP Community (LLP13) on Searching for Long-Lived Particles at the LHC and Beyond, 19–23 June 2023, CERN, Geneva, Switerland. 2023. Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/1216822/timetable/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Feng, J.L.; Galon, I.; Kling, F.; Trojanowski, S. ForwArd Search ExpeRiment at the LHC. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, G.; Barranco, J.; Bertarelli, A.; Biancacci, N.; Bruce, R.; Brüning, O.; Buffat, X.; Cai, Y.; Carver, L.R.; Fartoukh, S.; et al. High Luminosity LHC: Challenges and plans. J. Instrum. 2016, 11, C12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grachov, O.; Murray, M.; Wood, J.; Onel, Y.; Sen, S.; Yetkin, T. [on behalf of HCAL-CMS Collaboration]. Commissioning of the CMS zero degree calorimeter using LHC beam. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 293, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrow, M.; et al. [The CMS and TOTEM Collaborations] CMS–TOTEM Precision Proton Spectrometer. Technical Design Report; CERN Report CERN-LHCC-2014-021; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://cds.cern.ch/record/1753795 (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Agostinelli, S.; et al. [Geant4 Collaboration] Geant4—A simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. Phys. Res. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2003, 506, 250–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballarini, F.; et al. [The FLUKA Collaboration] The FLUKA code: Overview and new developments. EPJ Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessia, P.; et al. [EN STI R2E Team] HL-LHC Integration Boundary Conditions at IR5 for Any Installation between DFX and TAXN. Talk at the FMS–LLP Search General Meeting, 1 October 2020; CERN, Geneva, Switerland. Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/959035/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Diwan, M.V.; et al. [FPF Working Groups] Forward Physics Facility; BNL Report BNL-224243-2023-COPA; Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL): Upton, NY, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1972463 (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Lerner, G.; Sabaté Gilarte, M.; Alía, R.G.; Cerutti, F.; Tsiganis, A. HL-LHC Radiation Levels on Alignment Systems in the LSS of IP1–IP5. Presentation at the Review of HL-LHC Alligment and Internal Metrology (WP15.4) Meeting, 26–28 August, 2019, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland. 2019. Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/831552/contributions/3484724/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Berlin, A.; Kling, F. Inelastic dark matter at the LHC lifetime frontier: ATLAS, CMS, LHCb, CODEX-b, FASER, and MATHUSLA. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 015021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchynnikov, M.; Tastet, J.-L.; Mikulenko, O.; Bondarenko, K. Sensitivities to feebly interacting particles: Public and unified calculations. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 075028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilten, P.; Soreq, Y.; Williams, M.; Xue, W. Serendipity in dark photon searches. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloni, D.; Soreq, Y.; Williams, M. Coupling QCD-scale axionlike particles to gluons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 031803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, K.; Boyarsky, A.; Gorbunov, D.; Ruchayskiy, O. Phenomenology of GeV-scale heavy neutral leptons. J. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiarska, I.; Bondarenko, K.; Boyarsky, A.; Gorkavenko, V.; Ovchynnikov, M.; Sokolenko, A. Phenomenology of GeV-scale scalar portal. J. High Energy Phys. 2019, 2019, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Valle Garcia, G.; Kahlhoefer, F.; Ovchynnikov, M.; Zaporozhchenko, A. Phenomenology of axionlike particles with universal fermion couplings revisited. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 055042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorkavenko, V.; Jashal, B.K.; Kholoimov, V.; Kyselov, Y.; Mendoza, D.; Ovchynnikov, M.; Oyanguren, A.; Svintozelskyi, V.; Zhuo, J. LHCb potential to discover long-lived new physics particles with lifetimes above 100 ps. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina Gil, E.; et al. [NA62 Collaboration] Search for leptonic decays of dark photons at NA62. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 111802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyselov, Y.; Ovchynnikov, M. Searches for long-lived dark photons at proton accelerator experiments. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 111, 015030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, R.; et al. [SHiP Collaboration]; Aberle, O.; et al. [BDF Working Group] BDF/SHiP at the ECN3 High-Intensity Beam Facility. Proposal; CERN Report CERN-SPSC-2023-033/SPSC-P-369; CERN: Geneva, Switerland, 2023; Available online: https://cds.cern.ch/record/2878604/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Foroughi-Abari, S.; Reimitz, P.; Ritz, A. A closer look at dark vector splitting functions in proton bremsstrahlung. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.09123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedziela, J. SHIFT@LHC: Searches for new physics with shifted interaction on a fixed target at the Large Hadron Collider. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackstone, P.J.; Tarrús Castellà, J.; Passemar, E.; Zupan, J. Hadronic decays of a Higgs-mixed scalar. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.W. Decay and detection of a light scalar boson mixing with the Higgs boson. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 015018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, T. Performance of the CALICE calorimeters. PoS 2013, ICHEP2012, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Halbach, K. Design of permanent multipole magnets with oriented rare earth cobalt material. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. 1980, 169, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümler, P.; Soltner, H. Practical concepts for design, construction and application of Halbach magnets in magnetic resonance. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2023, 54, 1701–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
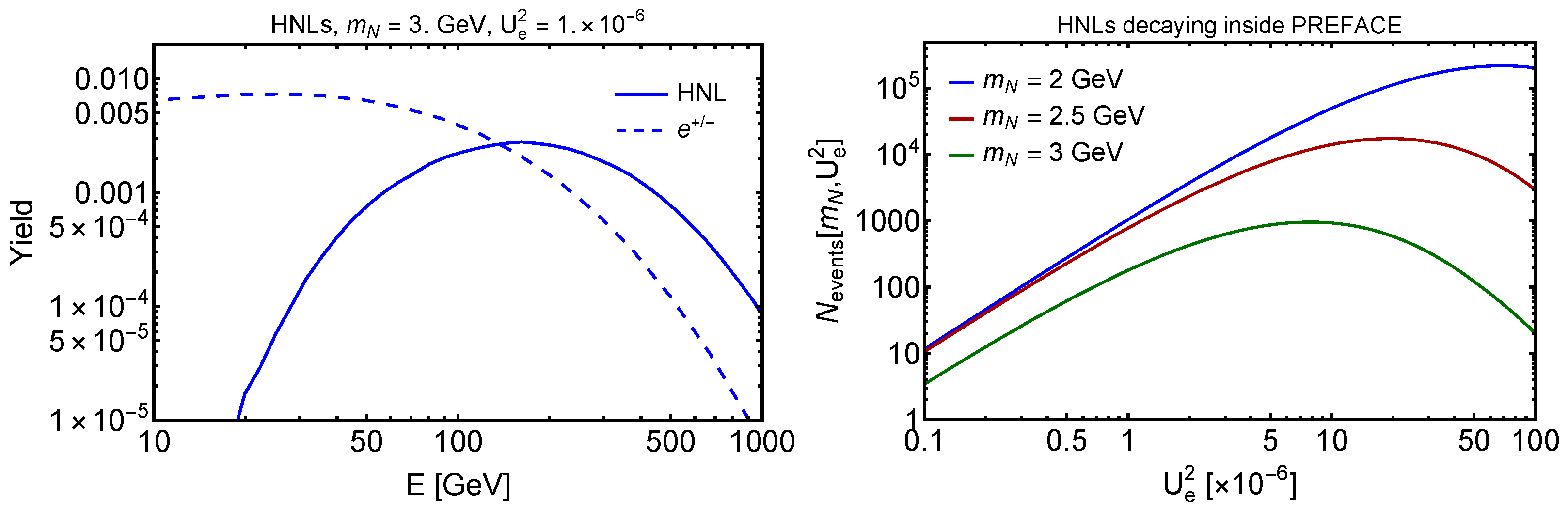
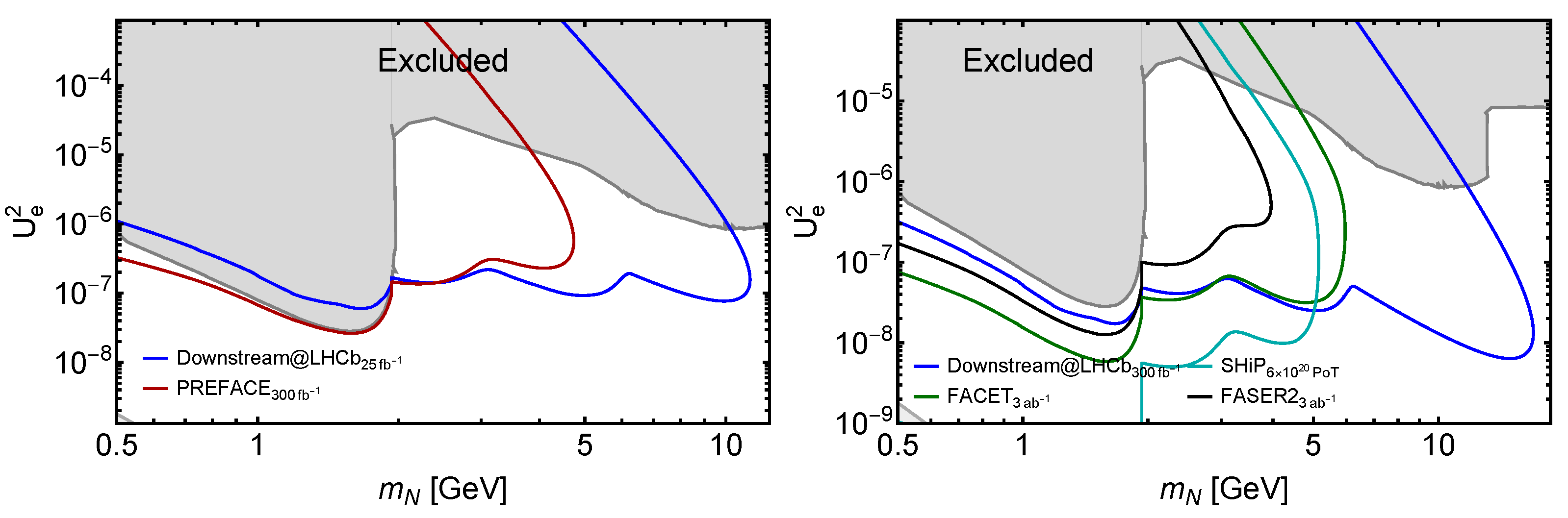
| Distance | Length of Decay Volume | Geometry | Luminosity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FACET | 100 m | 18 m | m | 3 |
| PREFACE | 100 m | 10 m | 0.8 m × 0.8 m | 300 |
| FASER | 480 m | 1.5 m | m | 300 |
| FASER2 | 650 m | 10 m | 3 m × 1 m | 3 |
| Model | (Effective) Lagrangian a | Mediator LLP a |
|---|---|---|
| HNL N | Heavy neutrino with interaction suppressed by | |
| Higgs-like scalar S | A light Higgs boson with interaction suppressed by | |
| Dark Photon V | A massive photon with interaction suppressed by | |
| ALP a | A -like particle with the interaction suppressed by |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hacisahinoglu, B.; Ozkorucuklu, S.; Ovchynnikov, M.; Albrow, M.G.; Penzo, A.; Aydilek, O. PREFACE: A Search for Long-Lived Particles at the Large Hadron Collider. Physics 2025, 7, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030033
Hacisahinoglu B, Ozkorucuklu S, Ovchynnikov M, Albrow MG, Penzo A, Aydilek O. PREFACE: A Search for Long-Lived Particles at the Large Hadron Collider. Physics. 2025; 7(3):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleHacisahinoglu, Burak, Suat Ozkorucuklu, Maksym Ovchynnikov, Michael G. Albrow, Aldo Penzo, and Orhan Aydilek. 2025. "PREFACE: A Search for Long-Lived Particles at the Large Hadron Collider" Physics 7, no. 3: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030033
APA StyleHacisahinoglu, B., Ozkorucuklu, S., Ovchynnikov, M., Albrow, M. G., Penzo, A., & Aydilek, O. (2025). PREFACE: A Search for Long-Lived Particles at the Large Hadron Collider. Physics, 7(3), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030033





