Hybrid Framework of Fermi–Dirac Spin Hydrodynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Tensors of Perfect Spin Hydrodynamics
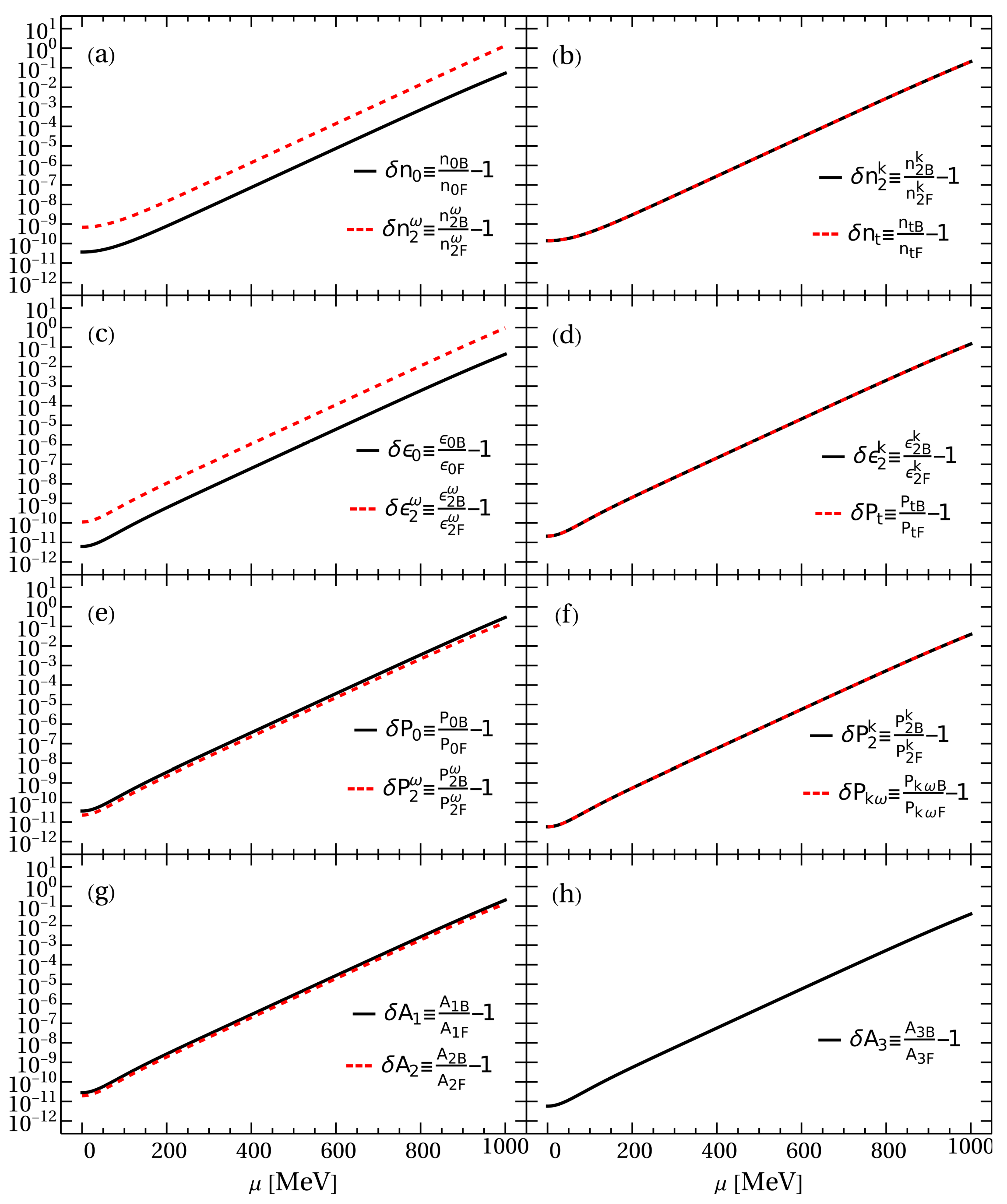
2.2. Tensors of Dissipative Spin Hydrodynamics
3. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamczyk, L. et al. [The STAR Collaboration] Global Λ hyperon polarization in nuclear collisions: Evidence for the most vortical fluid. Nature 2017, 548, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J. et al. [STAR Collaboration] Global polarization of Λ hyperons in Au + Au collisions at = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 98, 014910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J. et al. [STAR Collaboration] Polarization of Λ () hyperons along the beam direction in Au + Au collisions at = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 132301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, S. et al. [The ALICE Collaboration] Evidence of spin–orbital angular momentum interactions in relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 012301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niida, T.; Voloshin, S.A. Polarization phenomenon in heavy-ion collisions. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2024, 33, 2430010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, W. Phenomenology of Ultra-Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, W.; Heller, M.P.; Spalinski, M. New theories of relativistic hydrodynamics in the LHC era. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2018, 81, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, F.; Tinti, L. The ideal relativistic rotating gas as a perfect fluid with spin. Ann. Phys. 2010, 325, 1566–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, F. Hydrodynamics of fluids with spin. Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 2011, 8, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, F.; Chandra, V.; Del Zanna, L.; Grossi, E. Relativistic distribution function for particles with spin at local thermodynamical equilibrium. Ann. Phys. 2013, 338, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, A.; Grossi, E.; Karpenko, I.; Becattini, F. Λ polarization in very high energy heavy ion collisions as a probe of the quark–gluon plasma formation and properties. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, F.; Buzzegoli, M.; Inghirami, G.; Karpenko, I.; Palermo, A. Local Polarization and isothermal local equilibrium in relativistic heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 272302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florkowski, W.; Friman, B.; Jaiswal, A.; Speranza, E. Relativistic fluid dynamics with spin. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 97, 041901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, W.; Friman, B.; Jaiswal, A.; Ryblewski, R.; Speranza, E. Spin-dependent distribution functions for relativistic hydrodynamics of spin- particles. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 116017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, S.; Florkowski, W.; Jaiswal, A.; Kumar, A.; Ryblewski, R. Relativistic dissipative spin dynamics in the relaxation time approximation. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 814, 136096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, S.; Florkowski, W.; Jaiswal, A.; Kumar, A.; Ryblewski, R. Dissipative spin dynamics in relativistic matter. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 014030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, S.; Florkowski, W.; Jaiswal, A.; Kumar, A.; Ryblewski, R. Relativistic spin magnetohydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 192301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Shokri, M.; Mehr, S.M.A.T. Relativistic hydrodynamics with spin in the presence of electromagnetic fields. Nucl. Phys. A 2023, 1035, 122656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickgenannt, N.; Sheng, X.-L.; Speranza, E.; Wang, Q.; Rischke, D.H. Kinetic theory for massive spin-1/2 particles from the Wigner-function formalism. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 056018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickgenannt, N.; Speranza, E.; Sheng, X.-l.; Wang, Q.; Rischke, D.H. Derivation of the nonlocal collision term in the relativistic Boltzmann equation for massive spin-1/2 particles from quantum field theory. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 016022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickgenannt, N.; Speranza, E.; Sheng, X.l.; Wang, Q.; Rischke, D.H. Generating spin polarization from vorticity through nonlocal collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Weickgenannt, N.; Rischke, D.H. Lorentz-covariant nonlocal collision term for spin-1/2 particles. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 116021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickgenannt, N.; Wagner, D.; Speranza, E.; Rischke, D.H. Relativistic second-order dissipative spin hydrodynamics from the method of moments. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 096014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weickgenannt, N.; Blaizot, J.P. Chiral hydrodynamics of expanding systems. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 056012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Shokri, M.; Rischke, D.H. Damping of spin waves. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 043103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Relativistic first-order spin hydrodynamics via the Chapman–Enskog expansion. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 076009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Stephanov, M.A.; Yee, H.-U. Nondissipative second-order transport, spin, and pseudogauge transformations in hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 082302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Gale, C.; Jeon, S. From chiral kinetic theory to relativistic viscous spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. C 2021, 103, 044906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, W.; Stewart, J.M. Transient relativistic thermodynamics and kinetic theory. Ann. Phys. 1979, 118, 341–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Hongo, M.; Huang, X.G.; Matsuo, M.; Taya, H. Fate of spin polarization in a relativistic fluid: An entropy-current analysis. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 795, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Pu, S. Spin hydrodynamics and symmetric energy-momentum tensors—A current induced by the spin vorticity. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 817, 136346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, A.; Das, A.; Florkowski, W.; Ryblewski, R. Canonical and phenomenological formulations of spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. C 2023, 108, 024902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, A.; Das, A.; Ryblewski, R. Stability studies of first-order spin-hydrodynamic frameworks. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 054043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, G.; Hasanujjaman, M.; Bhatt, J.R.; Mishra, H.; Alam, J.-e. Causality and stability of relativistic spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 054031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-L.; Fang, S.; Pu, S. Analytic solutions of relativistic dissipative spin hydrodynamics with Bjorken expansion. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 114043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; Daher, A.; Das, A.; Florkowski, W.; Ryblewski, R. Boost invariant spin hydrodynamics within the first order in derivative expansion. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 094022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; Daher, A.; Das, A.; Florkowski, W.; Ryblewski, R. Relativistic second-order spin hydrodynamics: An entropy-current analysis. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 014024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-Q.; Wang, D.-L.; Yang, C.; Pu, S. Causality and stability analysis for the minimal causal spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 094031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, A.; Florkowski, W.; Ryblewski, R. Stability constraint for spin equation of state. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 110, 034029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, D.-L.; Pu, S. Thermodynamic stability in relativistic viscous and spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 110, 034010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, A.; Florkowski, W.; Ryblewski, R.; Taghinavaz, F. Stability and causality of rest frame modes in second-order spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, A.D.; Gürsoy, U.; Yarom, A. Hydrodynamics of spin currents. SciPost Phys. 2021, 11, 041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, M.; Huang, X.-G.; Kaminski, M.; Stephanov, M.; Yee, H.-U. Relativistic spin hydrodynamics with torsion and linear response theory for spin relaxation. J. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yang, D.-L.; Gubler, P. Spin alignment of vector mesons by second-order hydrodynamic gradients. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 054038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, D.; Huang, A.; Hou, D.; Liao, J. Relativistic viscous hydrodynamics with angular momentum. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2265–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, D.; Tinti, L.; Torrieri, G. Ideal relativistic fluid limit for a medium with polarization. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 056012, Addendum in Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 079901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, D.; Torrieri, G. Causality and dissipation in relativistic polarizable fluids. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 056011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, D.; Torrieri, G. Linear response theory and effective action of relativistic hydrodynamics with spin. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 036007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, W.; Hontarenko, M. Generalized thermodynamic relations for perfect spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2025, 134, 082302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drogosz, Z.; Florkowski, W.; Hontarenko, M. Hybrid approach to perfect and dissipative spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 110, 096018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, W. Spin hydrodynamics. J. Subat. Part. Cosmol. 2025, 3, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denicol, G.S.; Rischke, D.H. Microscopic Foundations of Relativistic Fluid Dynamics; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.R.; van Leeuwen, W.A.; van Weert, C.G. Relativistic Kinetic Theory. Principles and Applications; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; Available online: https://archive.org/details/relativistickine0000groo (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Speranza, E.; Weickgenannt, N. Spin tensor and pseudo-gauges: From nuclear collisions to gravitational physics. Eur. Phys. J. A 2021, 57, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becattini, F.; Daher, A.; Sheng, X.-L. Entropy current and entropy production in relativistic spin hydrodynamics. Phys. Lett. B 2024, 850, 138533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drogosz, Z.; Florkowski, W.; Hontarenko, M.; Ryblewski, R. Dynamical constraints on pseudo-gauge transformations. Phys. Lett. B 2025, 861, 139244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, W.; Kumar, A.; Ryblewski, R. Relativistic hydrodynamics for spin-polarized fluids. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2019, 108, 103709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quantum Field Theory. Lectures of Sidney Coleman; Chen, B.G.-g., Derbes, D., Griffiths, D., Hill, B., Sohn, R., Ting, Y.-S., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bhadury, S.; Florkowski, W.; Jaiswal, A.; Ryblewski, R. Longitudinal spin polarization in a thermal model with dissipative corrections. Phys. Rev. C 2024, 111, 064912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, J.I.; Rrapaj, E.; Rudaz, S. Relaxation time for strange quark Spin in rotating quark–gluon plasma. Phys. Rev. C 2020, 101, 024907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, J.I.; Rrapaj, E.; Rudaz, S. Spin versus helicity equilibration times and Lagrangian for strange quarks in rotating quark–gluon plasma. Phys. Rev. C 2020, 102, 064911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathisson, M. Neue Mechanik materieller Systeme. Acta Phys. Polon. 1937, 6, 163–200. Available online: https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/fulltext?series=T&vol=6&no=3&page=163 (accessed on 16 July 2025). English translation: Republication of: New mechanics of material systems. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2010, 42, 1011–1048. [CrossRef]
- Weyssenhoff, J.; Raabe, A. Relativistic dynamics of spin-fluids and spin-particles. Acta Phys. Polon. 1947, 9, 7–18. Available online: https://www.actaphys.uj.edu.pl/T.php?v=9 (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Drogosz, Z.; Florkowski, W.; Łygan, N.; Ryblewski, R. Boost-invariant spin hydrodynamics with spin feedback effects. Phys. Rev. C 2025, 111, 024909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Ryblewski, R.; Florkowski, W. Spin dynamics with realistic hydrodynamic background for relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2025, 111, 024907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapna; Singh, S.K.; Wagner, D. Spin polarization of Λ hyperons from dissipative spin hydrodynamics. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.22552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Coefficient | Fermi–Dirac Case | Boltzmann Case |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Fermi–Dirac Case | Boltzmann Case |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Fermi–Dirac Case | Boltzmann Case |
|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drogosz, Z. Hybrid Framework of Fermi–Dirac Spin Hydrodynamics. Physics 2025, 7, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030031
Drogosz Z. Hybrid Framework of Fermi–Dirac Spin Hydrodynamics. Physics. 2025; 7(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrogosz, Zbigniew. 2025. "Hybrid Framework of Fermi–Dirac Spin Hydrodynamics" Physics 7, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030031
APA StyleDrogosz, Z. (2025). Hybrid Framework of Fermi–Dirac Spin Hydrodynamics. Physics, 7(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7030031





