Evaluation of a Prototype Variable-Frequency Soil-Moisture and EC Probe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
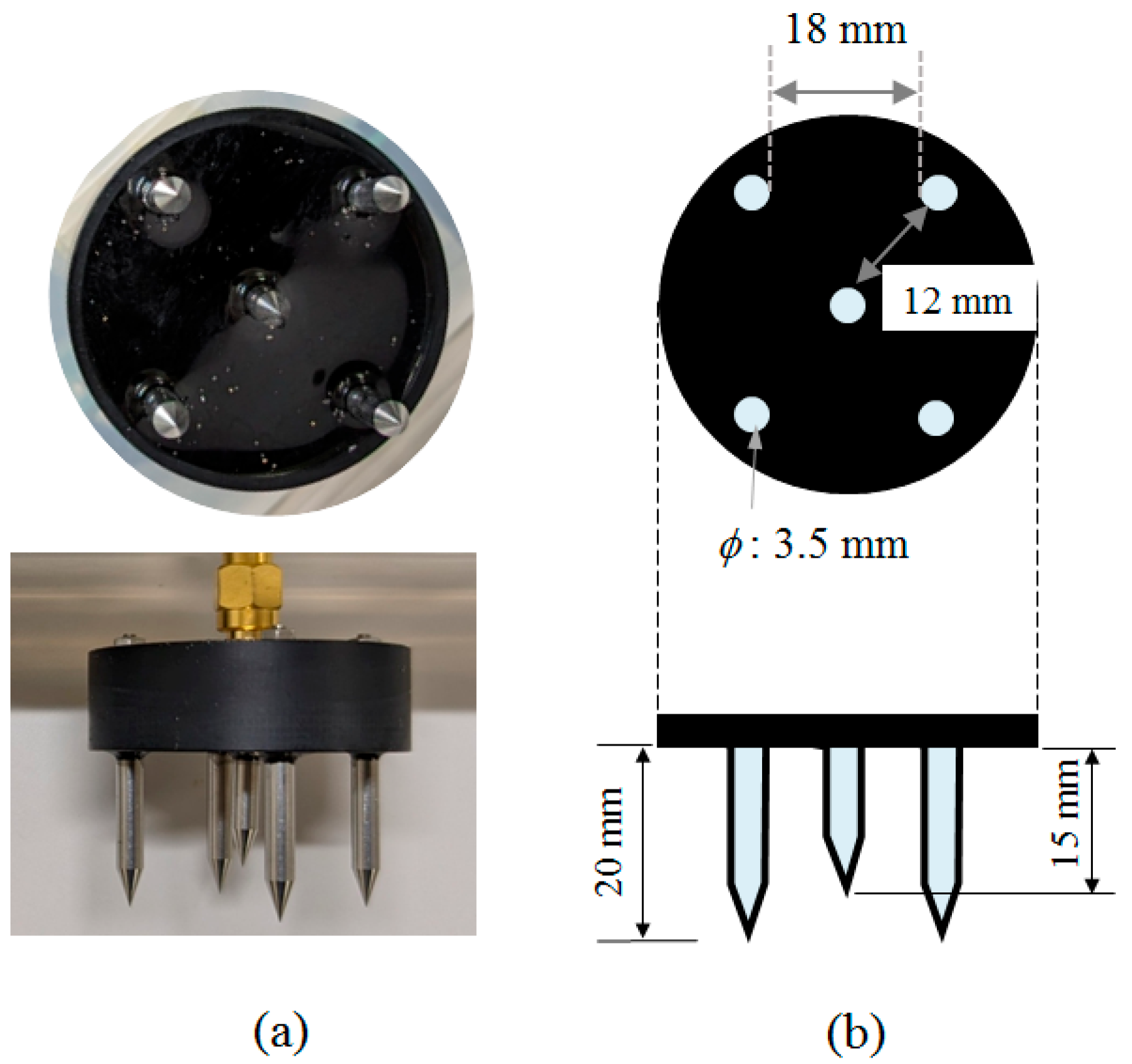
3. Description of the Probe
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Volume Measurement
4.2. Dielectric Permittivity Measurement in Oil–Ethanol and Ethanol–Water Mixtures
4.3. Dielectric Permittivity Measurement in Electrolyte Solutions
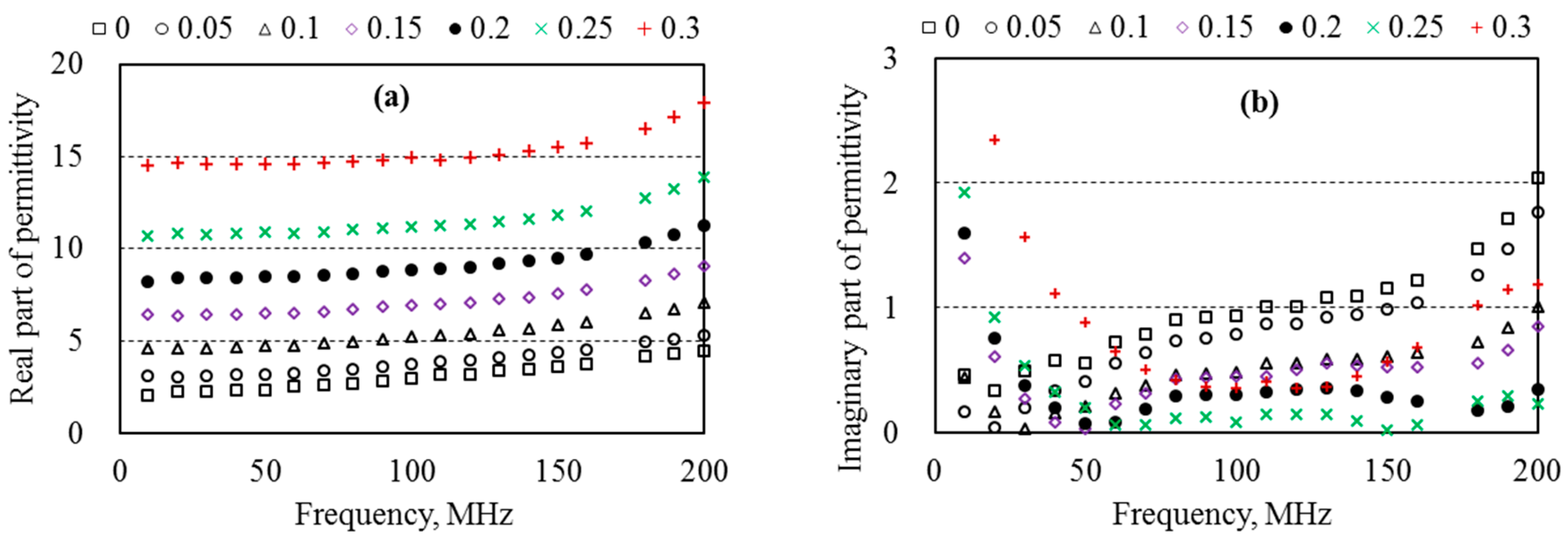
4.4. Dielectric Permittivity Measurement in Sand
4.5. Data Analyses
- (a)
- EC estimation from the imaginary part of dielectric permittivity
- (b)
- Soil-moisture content determination
- (c)
- MBE, RMSE, and % error calculations
5. Results
5.1. Probe Outputs
5.2. Sampling Volume of the Probe
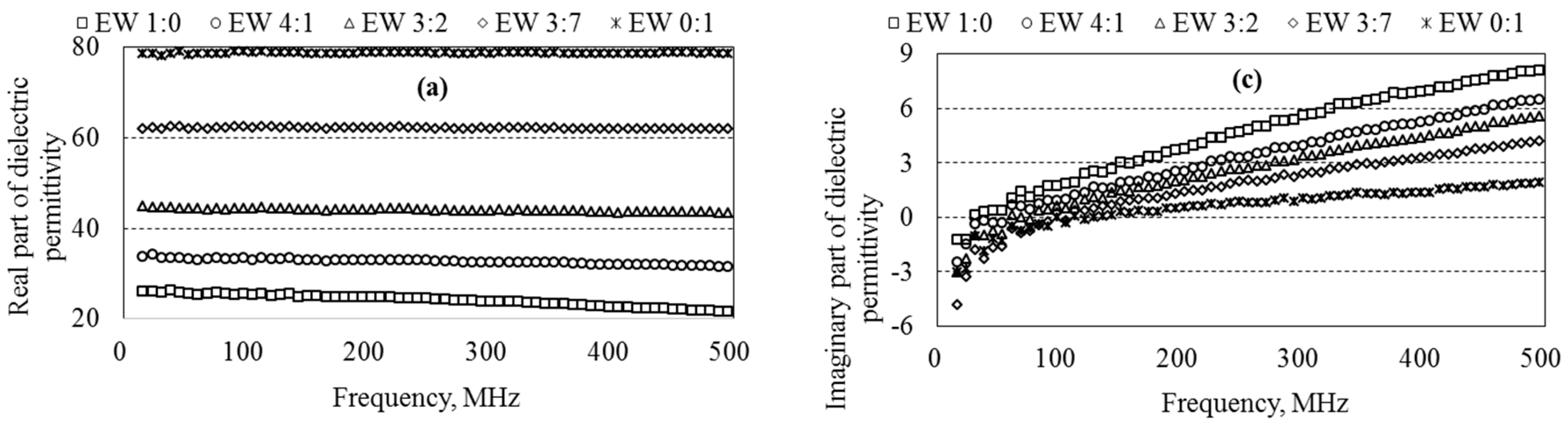
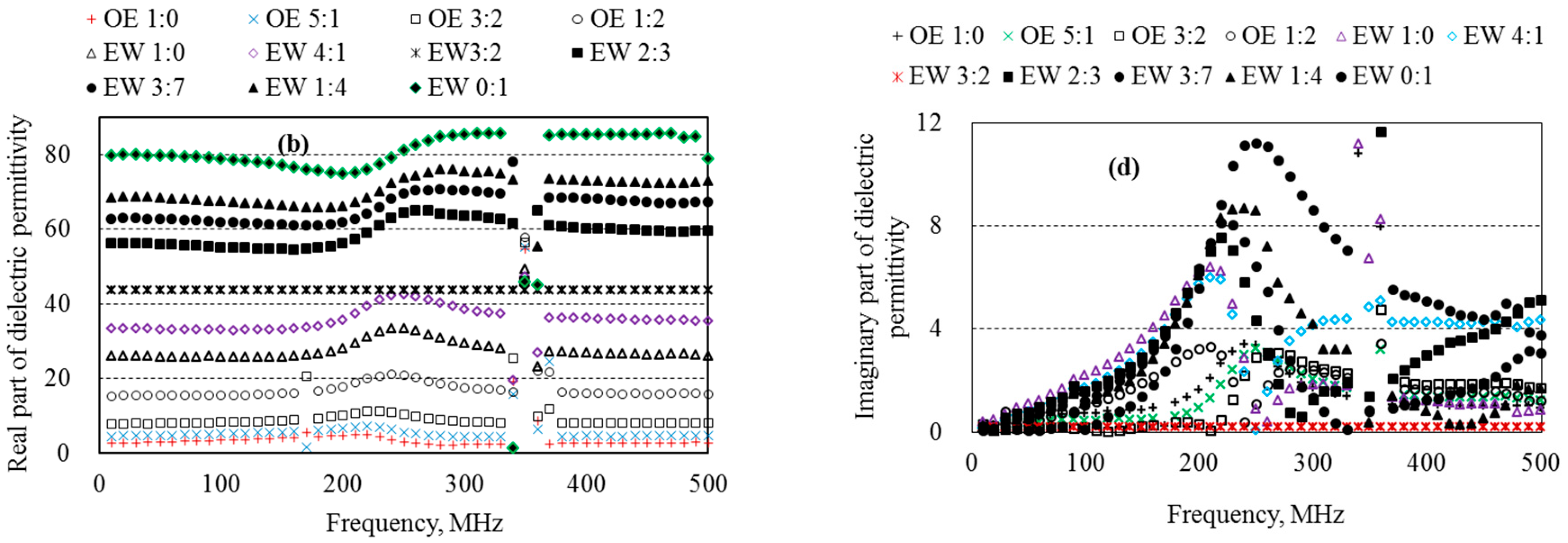
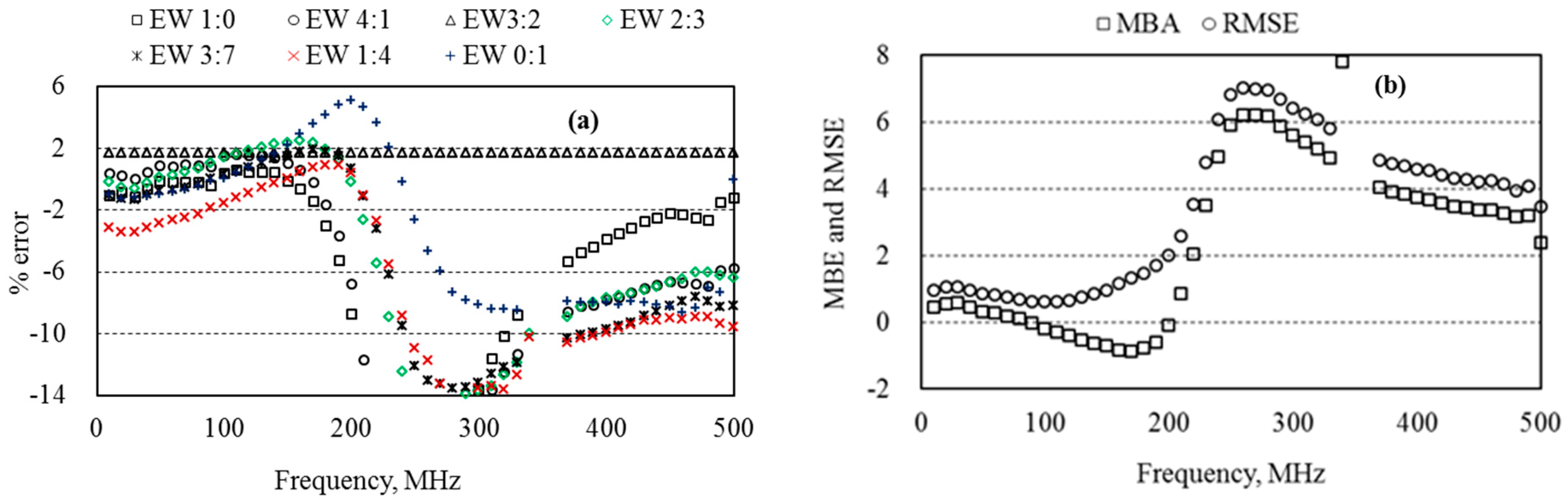
5.3. Dielectric Permittivity of Ethanol–Water Mixtures
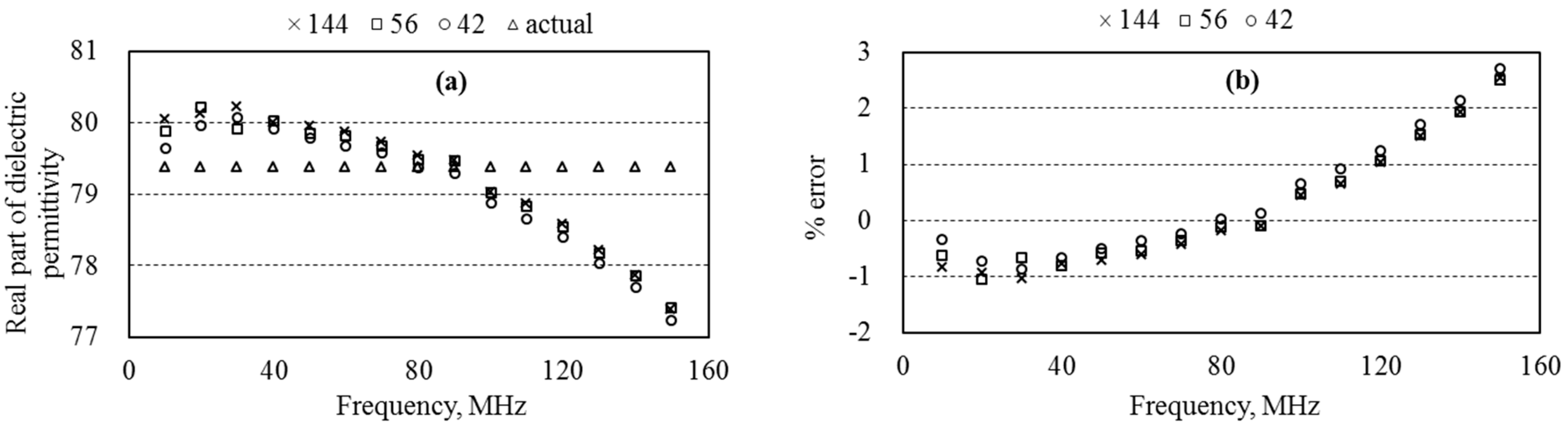
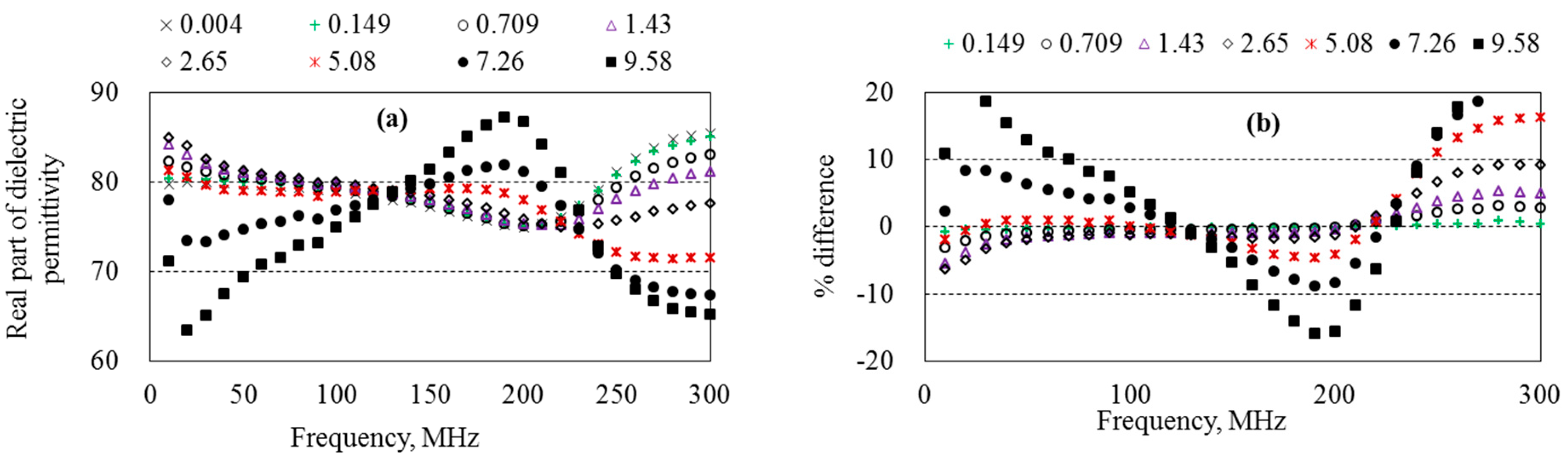
5.4. Dielectric Permittivity of Aqueous Solutions
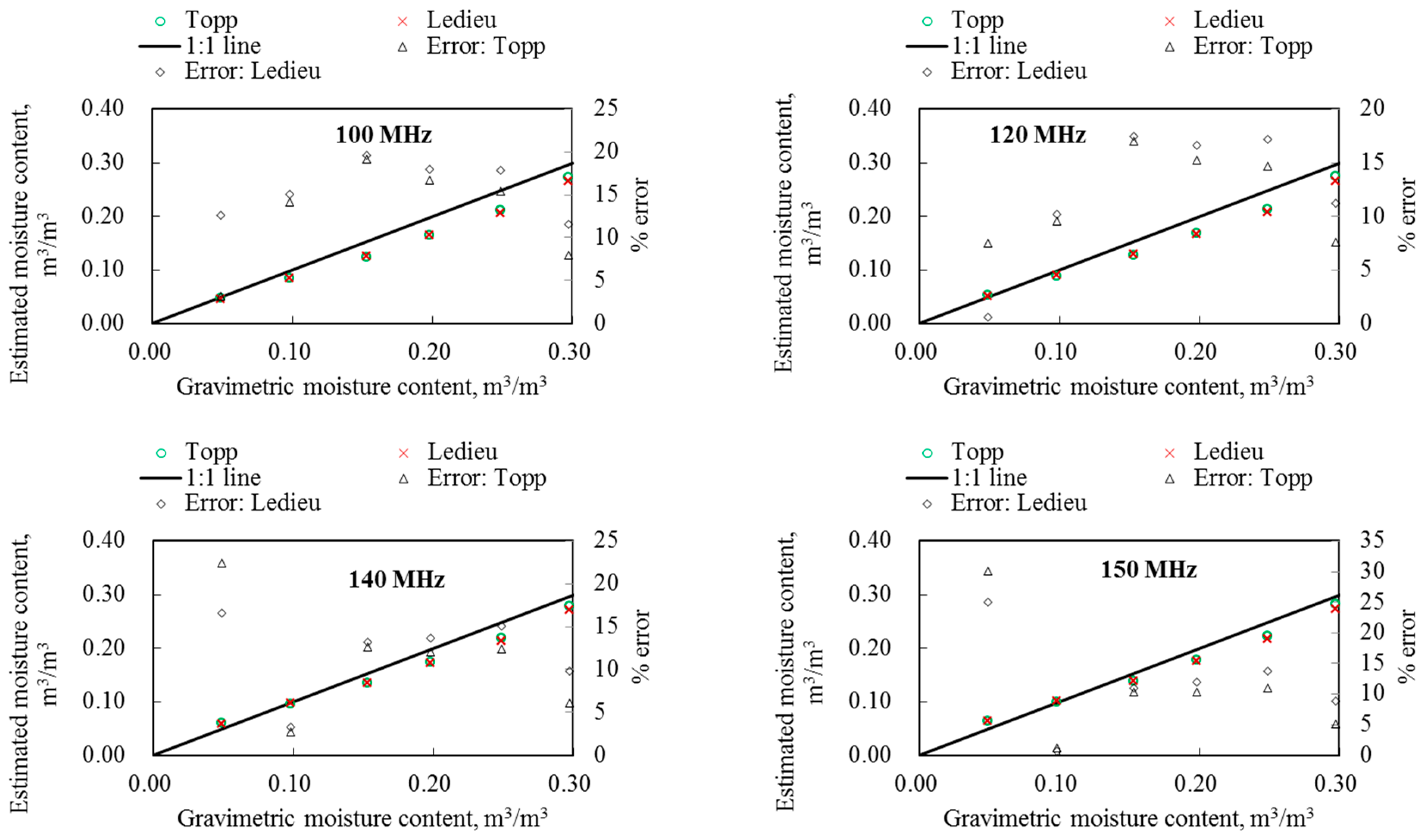
5.5. Dielectric Permittivity and Water Content of Sand
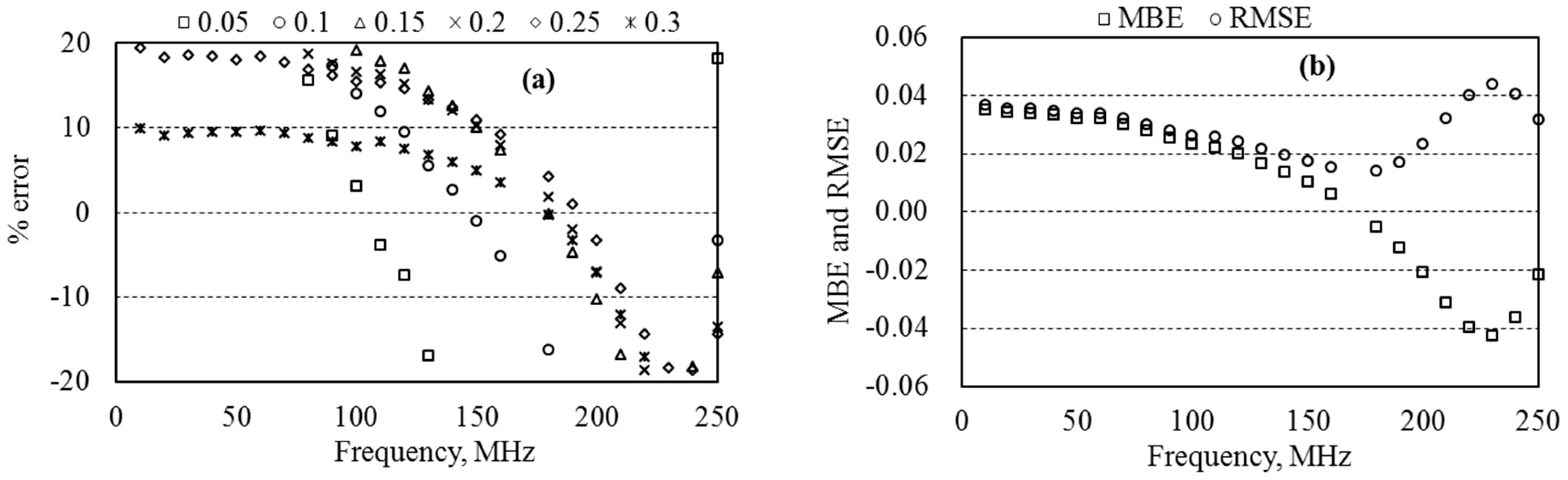
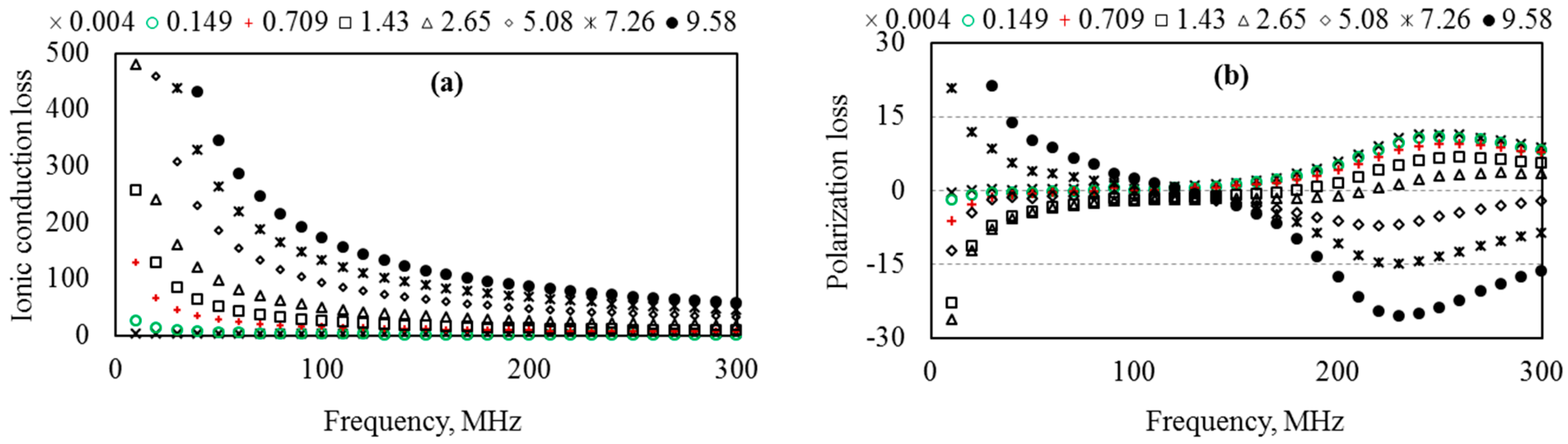
5.6. Energy Loss in Aqueous Solutions
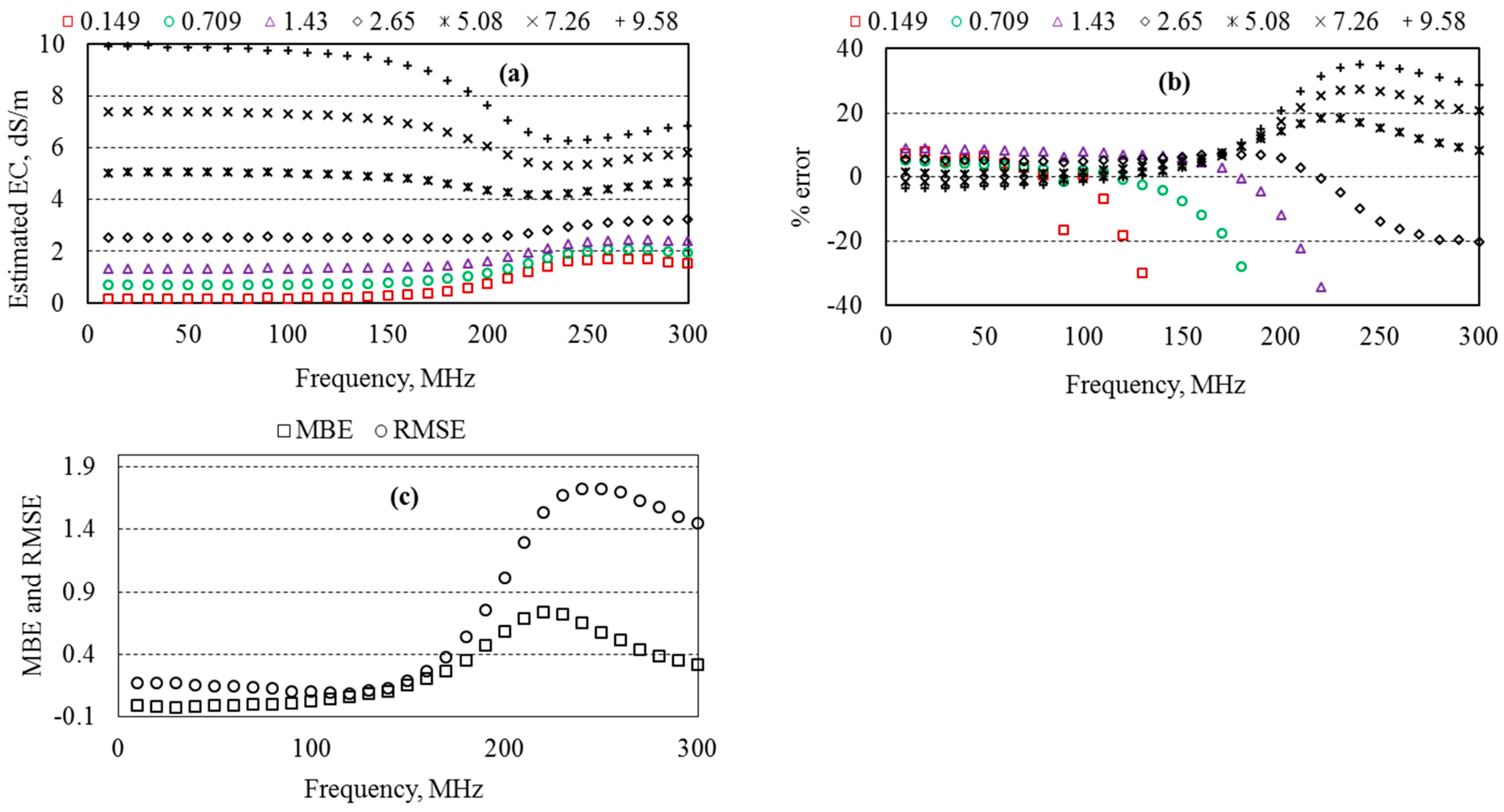
5.7. Estimated EC of Aqueous Solutions
6. Discussion
6.1. Important Features of the Probe
6.2. Optimum Measurement Frequency of the Probe
6.3. Measurement Accuracy
6.4. Further Development of the Probe
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, L.; Long, D.; Yan, L. Estimation of surface soil moisture with downscaled land surface temperatures using a data fusion approach for heterogeneous agricultural land. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 1105–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A.; Koven, C.D. Perspectives on the future of land surface models and the challenges of representing complex terrestrial systems. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2018MS001453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, E.W.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Reventos, V.J.; Álvarez Pérez, E.; Uwakweh, S.S.; Adorno García, C. Water and energy balance model GOES-PRWEB: Development and validation. Hydrology 2021, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, A.; McDonough, K.R.; Rahmani, V.; Hutchinson, S.L.; Hutchinson, J.S. The soil moisture data bank: The ground-based, model-based, and satellite-based soil moisture data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.W.; Tang, J.; Sarwar, A.; Shah, S.; Saddique, N.; Khan, M.U.; Imran Khan, M.; Nawaz, S.; Shamshiri, R.R.; Aziz, M.; et al. Soil moisture measuring techniques and factors affecting the moisture dynamics: A comprehensive review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.K.; Nghiem, S.V. Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; de Jeu, R.; Holmes, T. Multisensor historical climatology of satellite-derived global land surface moisture. J. Geophys. Res.—Earth Surf. 2008, 113, F01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Zheng, S.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X. The application and improvement of soil–water characteristic curves through in situ monitoring data in the plains. Water 2022, 14, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.D.; Foster, T.; Schultz, D.M.; Mieno, T. The effect of soil-moisture uncertainty on irrigation water use and farm profits. Adv. Water Resour. 2021, 154, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Her, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Smyth, A.; Martens-Habbena, W. Effect of information-driven irrigation scheduling on water use efficiency, nutrient leaching, greenhouse gas emission, and plant growth in South Florida. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 333, 107954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, R.W.; Fuentes, I.; Brombacher, J.; Degen, J.; Chambel-Leitão, P.; Santos, F. Progress in developing scale-able approaches to field-scale water accounting based on remote sensing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanova, A.; Hesse, C.; Krysanova, V.; Volk, M. Assessment of socio-economic and climate change impacts on water resources in Four European Lagoon Catchments. Environ. Manag. 2019, 64, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukal, M.S.; Irmak, S.; Sharma, K. Development and application of a performance and operational feasibility guide to facilitate adoption of soil moisture sensors. Sustainability 2019, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrov, P.P.; Belyaeva, T.A.; Kroshka, E.S.; Rodionova, O.V. Soil moisture measurement by the dielectric method. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargas, G.; Soulis, K.X. Performance evaluation of a recently developed soil water content, dielectric permittivity, and bulk electrical conductivity electromagnetic sensor. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, I.A.; Wang, M.; Ren, Y.; Shi, Q.; Malik, M.H.; Tao, S.; Cai, Q.; Gao, W. Performance analysis of dielectric soil moisture sensor. Soil Water Res. 2019, 14, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szerement, J.; Woszczyk, A.; Szypłowska, A.; Kafarski, M.; Lewandowski, A.; Wilczek, A.; Skierucha, W. A seven-rod dielectric sensor for determination of soil moisture in well-defined sample volumes. Sensors 2019, 19, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonquist, J.M.; Jones, S.B.; Robinson, D.A. A time domain transmission sensor with TDR performance characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringo, M.Q.; Martinez, C.G.; Martinez, O.G.; Ella, V.B. Development of low-cost soil moisture monitoring system for efficient irrigation water management of upland crops. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1038, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisso, R.; Alley, M.; Holshouser, D.; Thomason, W. Precision Farming Tools: Soil Electrical Conductivity; Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Walthert, L.; Schleppi, P. Equations to compensate for the temperature effect on readings from dielectric DecagonMPS-2 andMPS-6 water potential sensors in soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, M. Review of novel and emerging proximal soil moisture sensors for use in agriculture. Sensors 2020, 20, 6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.A.; Campbell, C.S.; Hopmans, J.W.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Jones, S.B.; Knight, R.; Ogden, F.; Selker, J.; Wendroth, O. Soil moisture measurement for ecological and hydrological watershed-scale observatories: A review. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyseure, G.C.L.; Mojid, M.A.; Malik, M.A. Measurement of volumetric water content by TDR in saline soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 48, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, K.; Wagner, N.; Felix-Henningsen, P. A new technique for measuring broadband dielectric spectra of undisturbed soil samples. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiwei, Z.; Zainuddin, M.F.; Ahmad, A.F.; Obays, S.J.; Abbas, Z. Development of an affordable soil moisture sensor system with Mini-VNA tiny and smartphone. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Moret-Fernández, D.; Lera, F.; Latorre, B.; Tormo, J.; Revilla, J. Testing of a commercial vector network analyzer as low-cost TDR device to measure soil moisture and electrical conductivity. CATENA 2022, 218, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, A.; Szypłowska, A.; Wilczek, A.; Kafarski, M.; Szerement, J.; Skierucha, W. One-port vector network analyzer characterization of soil dielectric spectrum. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3661–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, A.; Szypłowska, A.; Kafarski, M.; Wilczek, A.; Barmuta, P.; Skierucha, W. 0.05–3 GHz VNA characterization of soil dielectric properties based on the multiline TRL calibration. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 024007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrov, P.P.; Repin, A.V.; Rodionova, O.V. Wideband frequency domain method of soil dielectric property measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limsuwat, A.; Sakaki, T.; Illangasekare, T.H. Experimental Quantification of Bulk Sampling Volume of ECH2O Soil Moisture Sensors. Doctoral Dissertation, Colorado State University, Libraries, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, S.O. Electronic Materials and Devices; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.K. Field and Wave Electromagnetics; Addison & Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Topp, G.C.; Zegelin, S.; White, I. Impacts of the real and imaginary components of relative permittivity on time domain reflectometry measurements in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, S.; Umehara, T.; Redlin, H. Structures of water and primary alcohol studied by microwave dielectric analyses. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 95, 6257–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhlisin, M.; Saputra, A. Performance evaluation of volumetric water content and relative permittivity models. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 421762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.; Schulin, R.; Fluhler, H.; Attinger, W. Calibration of time domain reflectometry for water content measurement using a composite dielectric approach. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2267–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Jones, S.B.; Blonquist, J.M., Jr.; Friedman, S.P. A physically derived water content/permittivity calibration model for coarse-textured, layered soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledieu, J.; De Ridder, P.; De Clerck, P.; Dautrebande, S. A method of measuring soil moisture by time-domain reflectometry. J. Hydrol. 1986, 88, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gao, W.R.; Shamshiri, R.; Tao, S.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, G. Review of research progress on soil moisture sensor technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szypłowska, A.; Szerement, J.; Lewandowski, A.; Kafarski, M.; Wilczek, A.; Skierucha, W. Impact of soil salinity on the relation between soil moisture and dielectric permittivity. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Conference on: Electromagnetic Wave Interaction with Water and Moist Substances (ISEMA), Lublin, Poland, 4–7 June 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawilski, B.M.; Granouillac, F.; Claverie, N.; Lemaire, B.; Brut, A.; Tallec, T. Calculation of soil water content using dielectric-permittivity-based sensors–benefits of soil-specific calibration. Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2023, 12, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyamoto, H.; Masuda, N.; Hirashima, Y.; Mojid, M.A.; Mainuddin, M. Evaluation of a Prototype Variable-Frequency Soil-Moisture and EC Probe. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030050
Miyamoto H, Masuda N, Hirashima Y, Mojid MA, Mainuddin M. Evaluation of a Prototype Variable-Frequency Soil-Moisture and EC Probe. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(3):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyamoto, Hideki, Naoki Masuda, Yuta Hirashima, Mohammad A. Mojid, and Mohammed Mainuddin. 2025. "Evaluation of a Prototype Variable-Frequency Soil-Moisture and EC Probe" AgriEngineering 7, no. 3: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030050
APA StyleMiyamoto, H., Masuda, N., Hirashima, Y., Mojid, M. A., & Mainuddin, M. (2025). Evaluation of a Prototype Variable-Frequency Soil-Moisture and EC Probe. AgriEngineering, 7(3), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030050










