Co-Effect of pH Control Agent and pH Value on the Physical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Bath Deposition for Potential Application in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
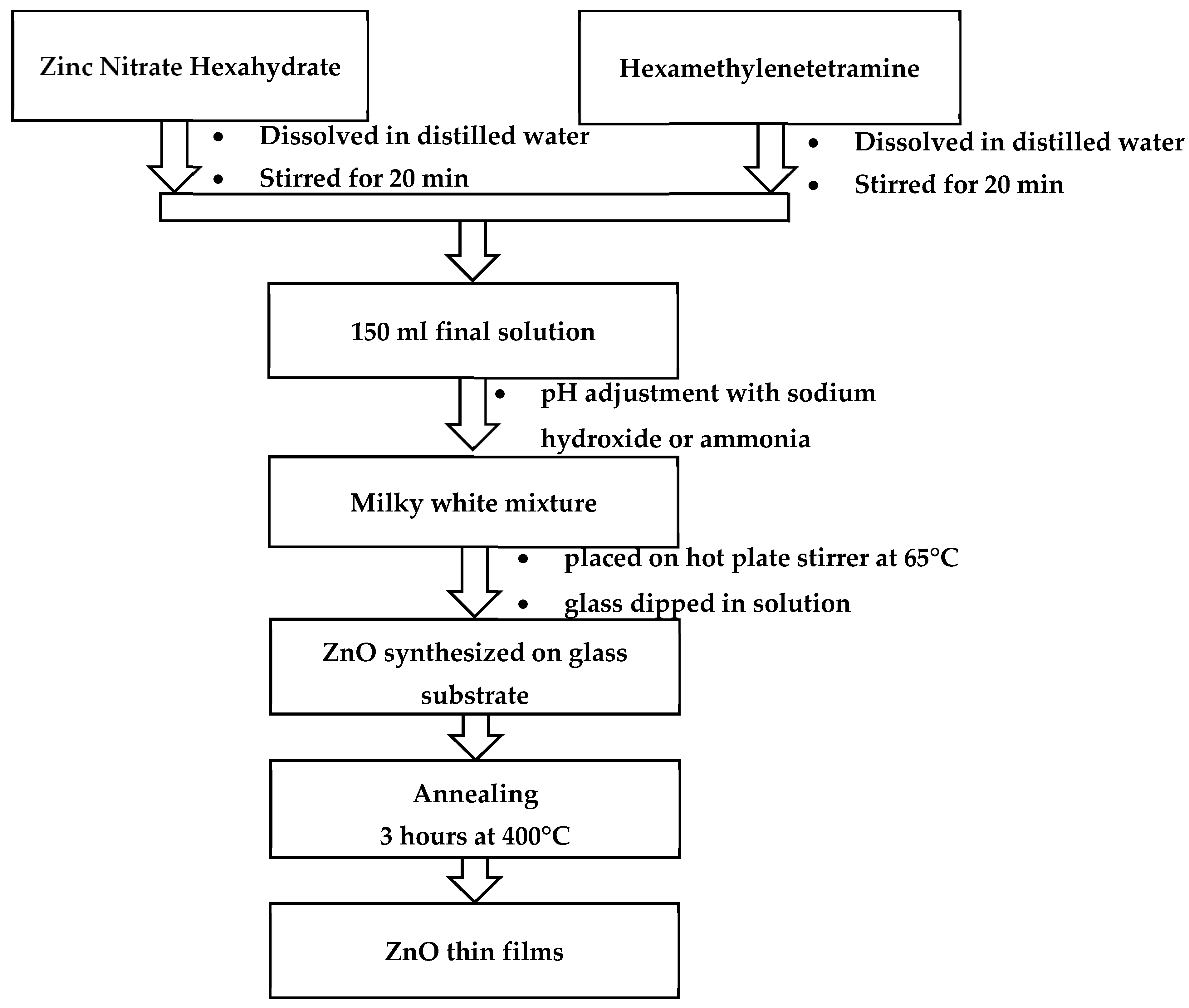
2.2. Synthesis of ZnO Thin Films
2.3. ZnO Thin Films Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
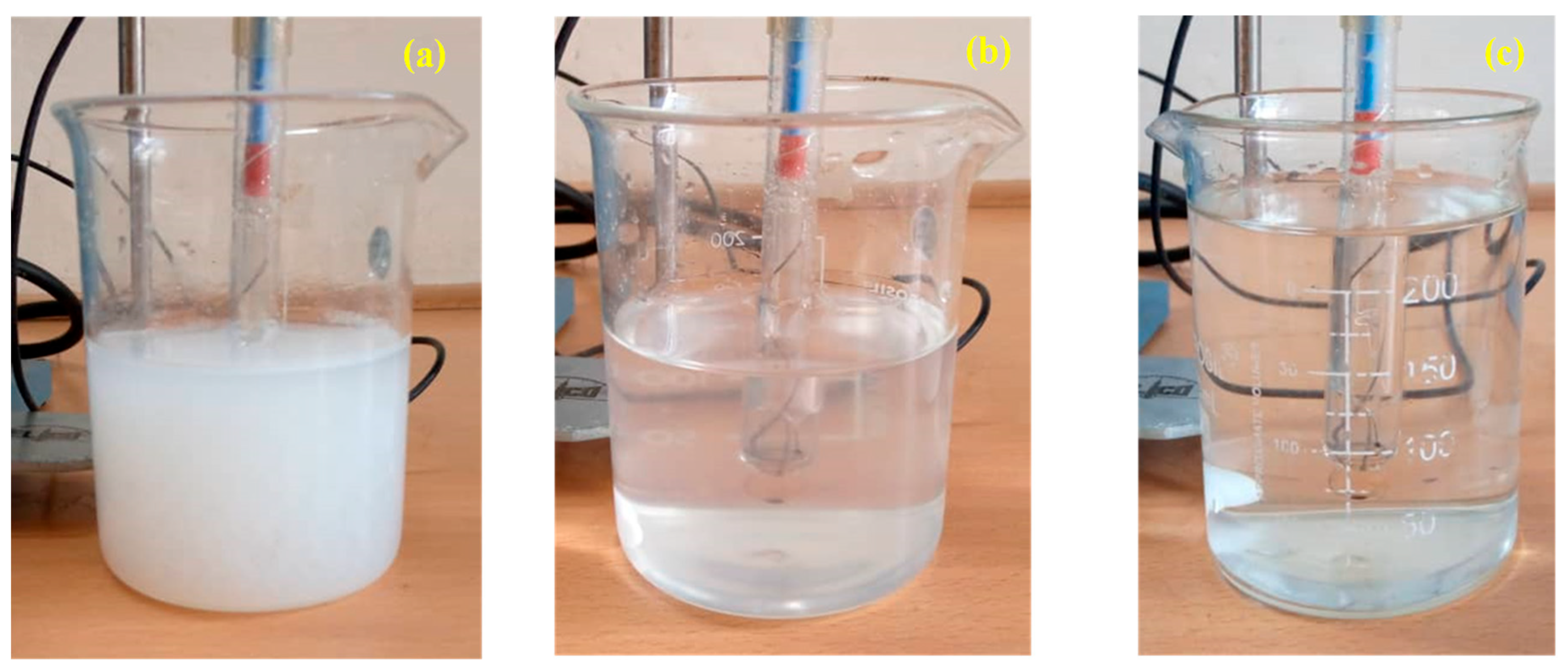
3.1. Impact of Ammonia on pH Adjustment
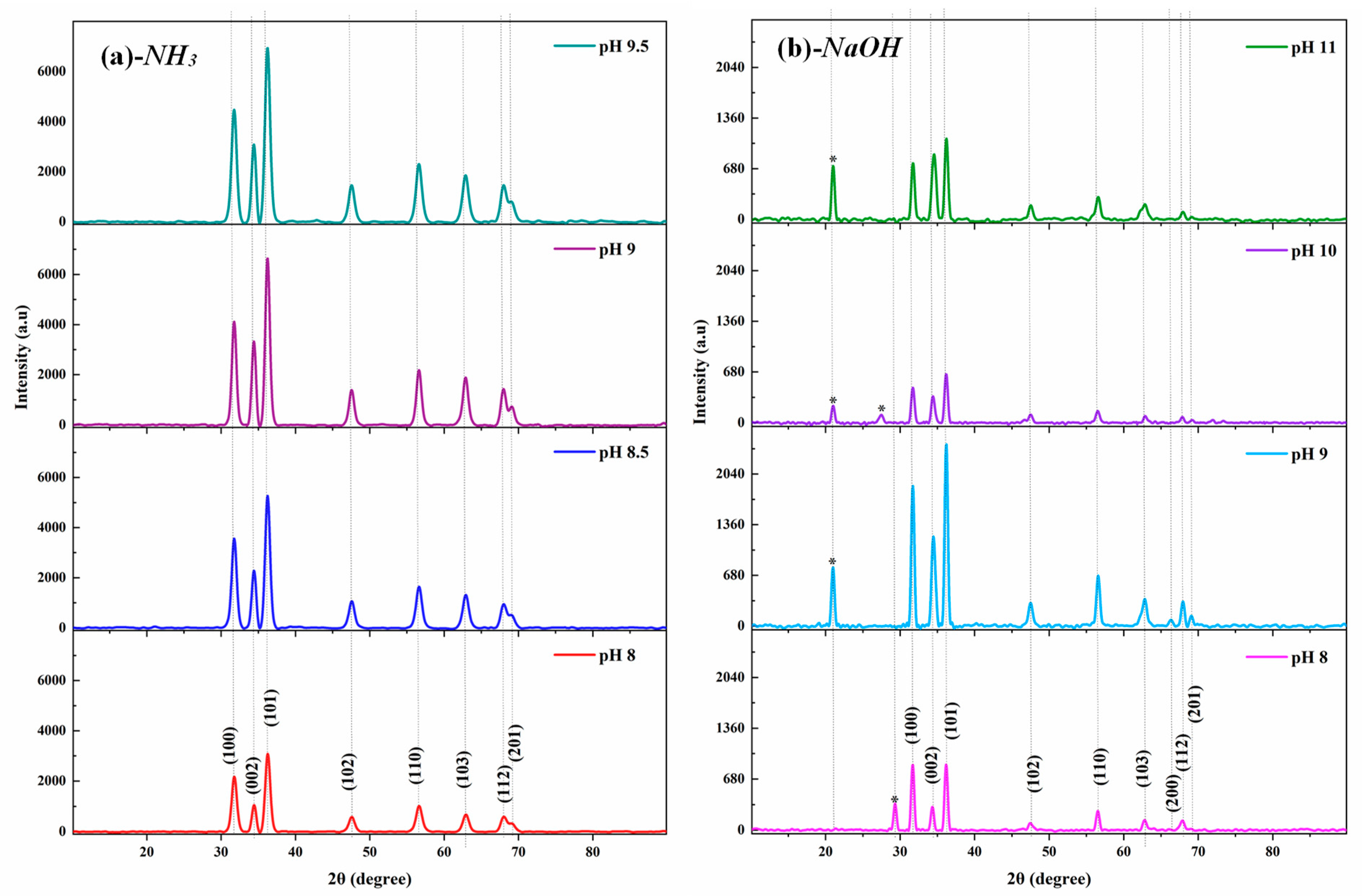
3.2. Structural Characterization
3.3. Morphological Properties
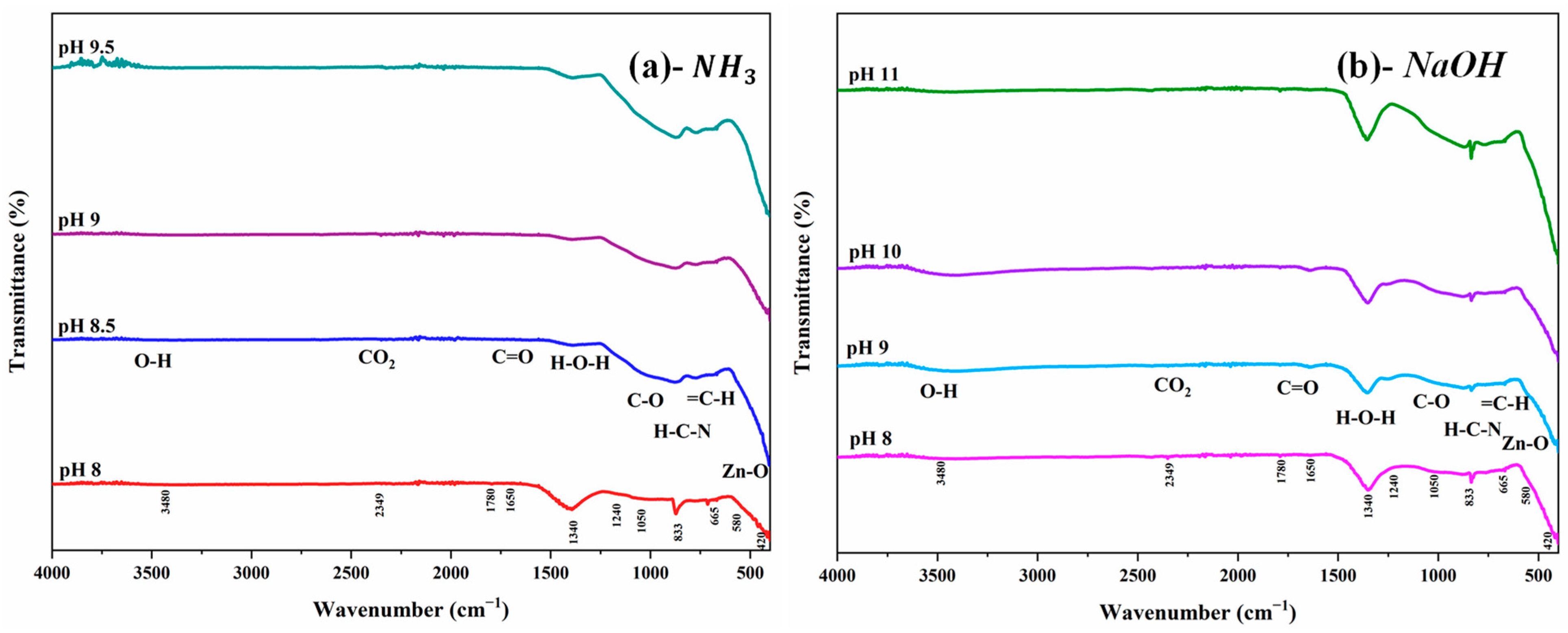
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
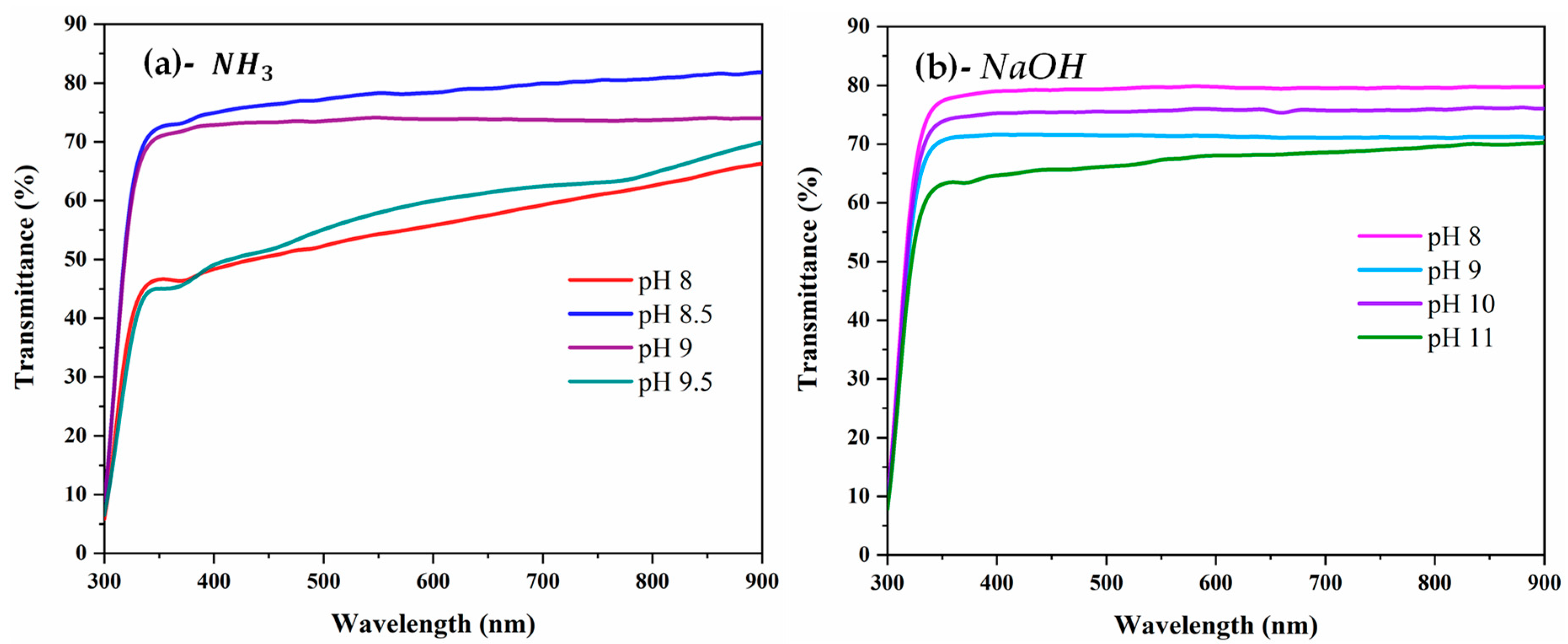
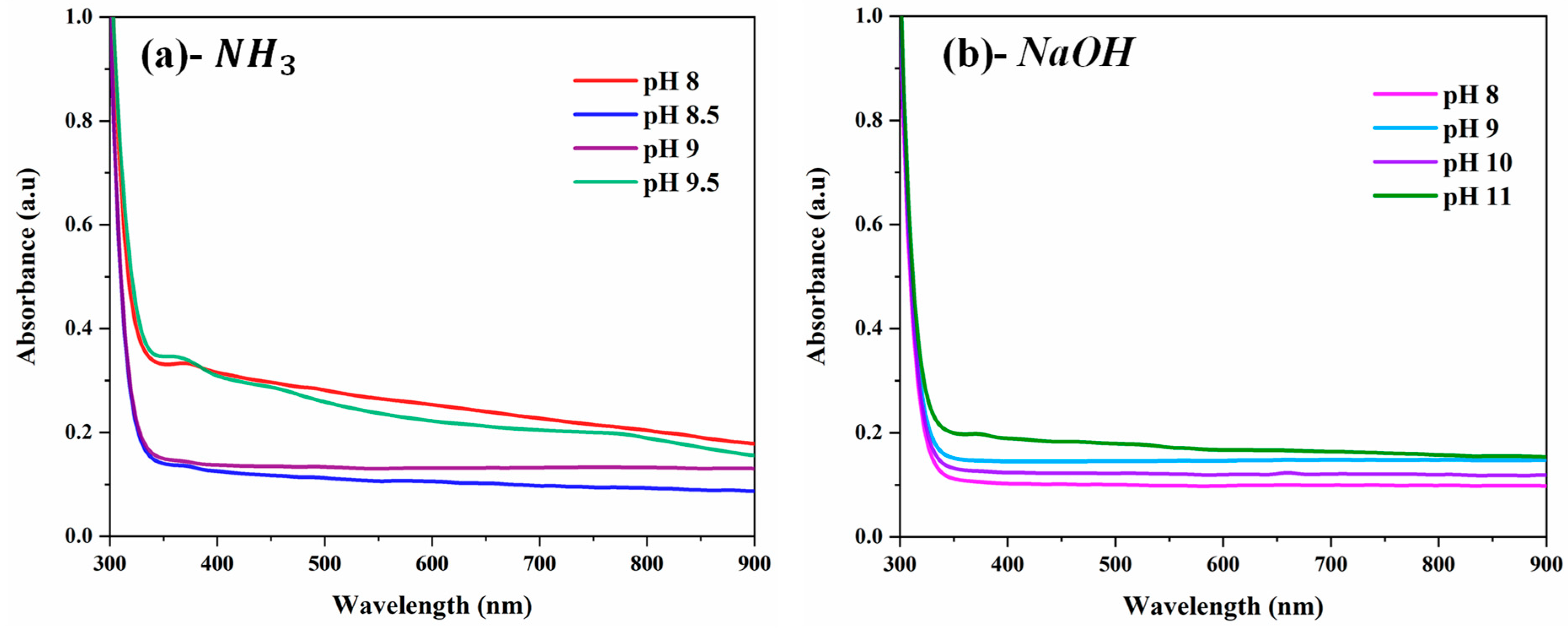
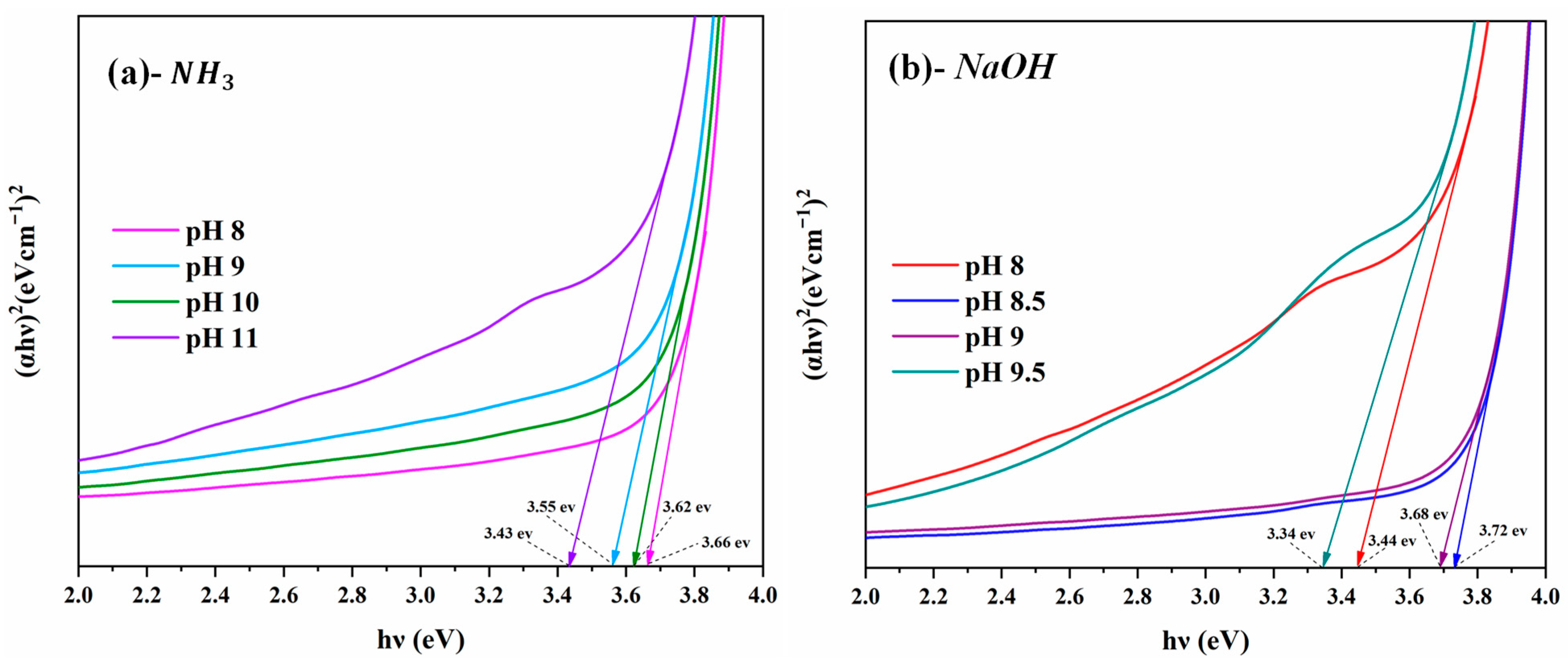
3.5. Optical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Baranoff, E.; Grätzel, M. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: A Brief Overview. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, S.S. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: Fundamentals and Current Status. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, P.; Marimuthu, R. A Review on Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSSCs), Materials and Applications. Iran. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 20, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, A.; Mesguich, F.; Hérissan, A.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Yanpeng, X.; Dubot, P. Optimized TiO2 Nanoparticle Packing for DSSC Photovoltaic Applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 148, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.H.; Lee, M.W.; Wang, G.-J.; Tai, M.F. Photovoltaic Performance of New-Structure ZnO-Nanorod Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.Y.; Sun, X.W.; Lo, G.Q.; Kwong, D.L.; Wang, J.X. Improved Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells with a ZnO-Nanoflower Photoanode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 263501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, C.; Abd-lefdil, S.; Sayah, D.; Cadene, M. ZnO Layers Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis. Eur. Phys. J. AP 1998, 1, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beula, R.J.; Suganthi, D.; Abiram, A. TiO2 Photo-Electrode with Gold Capping for Improved Observation in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, P.S.; Jose, R.; Vijila, C.; Ramakrishna, S. Improved Electron Diffusion Coefficient in Electrospun TiO2 Nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 21538–21542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Look, D.C.; Reynolds, D.C.; Sizelove, J.R.; Jones, R.L.; Litton, C.W.; Cantwell, G.; Harsch, W.C. Electrical Properties of Bulk ZnO. Solid State Commun. 1998, 105, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, K.; Anbazhagan, A.; Baneto, M.; Dineshbabu, N.; Ravidhas, C.; Muruganandam, G. Enhancement of the Hackee’s Quality Factor of Sol–Gel Spin Coated ZnO Thin Films by MO Doping. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 41, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.K.; Hashim, M.R.; Al-Douri, Y. Morphology and Optical Investigations of ZnO Pyramids and Nanoflakes for Optoelectronic Applications. Optik 2014, 125, 2560–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.; Abbas, M.A.; Lee, L.; Kang, B.; Kim, H.; Bang, J.H. Control of Morphology and Defect Density in Zinc Oxide for Improved Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 30475–30483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.-Y.; Yang, J.-F.; Lai, F.-I. Improved Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell with a ZnO Nanotree Photoanode by Hydrothermal Method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.-I.; Yang, J.-F.; Chen, W.-C.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Kuo, S.-Y. Enhancing Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Performance with Different Sizes of ZnO Nanorods Grown Using Multi-Step Growth. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, W.-R.; Jeong, H.-T.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, H.-G.; Choi, W.-Y. Fabrication of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells by Transplanting Highly Ordered TiO2 Nanotube Arrays. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittal, R.; Ho, K.-C. Zinc Oxide Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 920–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Kumari, P.; Soin, N.; Roy, S.S.; McLaughlin, J.A. Microstructure and Field Emission Characteristics of ZnO Nanoneedles Grown by Physical Vapor Deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 123, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, O.; Guérin, V.M.; Ghimpu, L.; Tiginyanu, I.M.; Pauporté, T. Nanofibrous-like ZnO Layers Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering and Their Integration in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 550, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, N.; Alameri, D.; Kim, Y.; Thomas, B.; McCormack, K.; Chan, M.; Divan, R.; Gosztola, D.J.; Liu, Y.; Kuljanishvili, I. Controlled Fabrication of Quality ZnO NWs/CNTs and ZnO NWs/Gr Heterostructures via Direct Two-Step CVD Method. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elen, K.; Van Den Rul, H.; Hardy, A.; Van Bael, M.K.; D’Haen, J.; Peeters, R.; Franco, D.; Mullens, J. Hydrothermal Synthesis of ZnO Nanorods: A Statistical Determination of the Significant Parameters in View of Reducing the Diameter. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiswaran, K.; Norizan, M.N.; Mahmed, N.; Mohamad, I.S.; Idris, S.N.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Amin, N.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P.; Nabiałek, M.; et al. Controlling the Layer Thickness of Zinc Oxide Photoanode and the Dye-Soaking Time for an Optimal-Efficiency Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. Coatings 2022, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.B.; Shen, H.L.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.B. Optical Properties of Nanosized ZnO Films Prepared by Sol-Gel Process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 100, 200. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Fang, D.; Xiong, F.; Ren, Y.; Bai, C.; Mi, B.; Gao, Z. Electrophoretic Deposition of Double-Layer ZnO Porous Films for DSSC Photoanode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2023, 28, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.K.; Majid, W.H.; Wang, H.Z.; Yousefi, R.; Moradi Golsheikh, A.; Ren, Z.F. Sonochemical Synthesis of Hierarchical ZnO Nanostructures. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2013, 20, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, A.B.B.; Hamid, N.H.B.; Bin Zulkefle, M.A.; Shariffudin, S.S.B.; Abdullah, W.F.H.B.; Herman, S.H. Post-Deposition Heat Treatment Effect on pH Sensing Behavior of Chemical Bath Deposited Nanostructured Zinc Oxide. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2023, 48, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.A.; Zulkefle, M.A.; Herman, S.H.; Alip, R.I. Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanostructure by Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) Method: Influence of Growth Time towards Nanostructure Characteristics. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 6891–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, R.S.; Lokhande, C.D. Chemical Deposition Method for Metal Chalcogenide Thin Films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2000, 65, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, M.N.; Sreelatha, C.J.; Ravinder, G.; Anusha, S. The Effect of Solution pH on the Structural, Surface Morphological, and Optical Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Synthesized by the Chemical Bath Deposition Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 54, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, R.; Riaz, S.; Hussain, S.S.; Naseem, S. Effect of pH on Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 5754–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernardou, D.; Kenanakis, G.; Couris, S.; Koudoumas, E.; Kymakis, E.; Katsarakis, N. pH Effect on the Morphology of ZnO Nanostructures Grown with Aqueous Chemical Growth. Thin Solid Film. 2007, 515, 8764–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Hamad, S.M.; Almessiere, M.A.; Ahmed, N.M.; Sajadi, S.M. Effect of Different pH Values on Growth Solutions for the ZnO Nanostructures. Chin. J. Phys. 2021, 71, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barrientos, A.; Ambrosio-Lazaro, R.C.; Ramirez-Bone, R.; Garcia-Ramirez, M.A.; Perez-Cortes, O.; Tapia-Olvera, R.; Plaza-Castillo, J. pH-Effect in the Fabrication of ZnO Nanostructured Thin Films by Chemical Bath Deposition for Increasing the Efficiency of Solar Cells. Materials 2023, 16, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.B.; Huang, S.M.; Zhang, D.W.; Bian, Z.Q.; Li, X.D.; Sun, Z.; Yin, X.J. Nanostructured ZnO Thin Films by Chemical Bath Deposition in Basic Aqueous Ammonia Solutions for Photovoltaic Applications. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 95, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Song, M.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Song, H.-M.; Yu, Y.-T. Effect of Ammonia Water on the Morphology of Monoethanolamine-Assisted Sonochemicaly Synthesized ZnO Nanostructures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.; Jo, J.-N.; Wu, X.-F.; Yoon, J.-M.; Yu, Y.-T. Synthesis of Well Dispersed, Regular Shape ZnO Nanorods: Effect of pH, Time and Temperature. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, H.F.; Morris, M.C.; Evans, E.H.; Paretzkin, B.; Wong-Ng, W.; Ettlinger, L.; Hubbard, C.R. Standard X-Ray Diffraction Powder Patterns from the JCPDS Research Associateship. Powder Diffr. 1986, 1, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliverdov, V.F. Relation between the Temperature Coefficient of Surface Tension and Phase Diagrams. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 2010, 84, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, J.A. Contribution à l’étude cristallochimique des hydrates de soude. I.—Méthodes expérimentales et les structures cristallines de NaOH.H2O et de 2 NaOH.7 H2O. Bull. Minéralogie 1958, 81, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemily, P.W. Structures cristallines des hydrates de la soude. I. Structure cristalline de NaOH.4H2O. Acta Cryst. 1957, 10, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, R.; Leinen, D.; Dalchiele, E.A.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R.; Martín, F. The Effects of Zinc Acetate and Zinc Chloride Precursors on the Preferred Crystalline Orientation of ZnO and Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Spray Pyrolysis. Thin Solid Film. 2006, 515, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano-Cortaza, M.; Ramírez-Morales, E.; Pal, U.; Pérez-Hernández, G.; Rojas-Blanco, L. pH Dependent Morphology and Texture Evolution of ZnO Nanoparticles Fabricated by Microwave-Assisted Chemical Synthesis and Their Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Activities. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 27469–27478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, K.; Shalini, R.; Ayyanar, M.; Kavitha, P.; Baneto, M.; Karunakaran, M.; Praseetha, P.K.; Pushpa, K.C.S.; Anuradha, N. Effect of pH of the Precursor Solution on the Photocatalytic and Biomedical Applications of Enzyme Coupled ZnO and SnO2 Nanomaterials: A Comparative Study. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.K.; Srivastav, A.; Güell, F.; John, T.T. pH-Controlled Synthesis of ZnO Nanoflowers: A Correlation Study among the Optoelectronic Properties and Improved Photodegradation Efficiency. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 172993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drici, A.; Djeteli, G.; Tchangbedji, G.; Derouiche, H.; Jondo, K.; Napo, K.; Bernède, J.C.; Ouro-Djobo, S.; Gbagba, M. Structured ZnO Thin Films Grown by Chemical Bath Deposition for Photovoltaic Applications. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2004, 201, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, M.; Hashim, U.; Ali, M.E.; Ali, S.M.U.; Rusop, M.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Willander, M. Effect of Different Seed Solutions on the Morphology and Electrooptical Properties of ZnO Nanorods. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 452407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Enhancement of ZnO Nanorods Properties Using Modified Chemical Bath Deposition Method: Effect of Precursor Concentration. Crystals 2020, 10, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.; Halim, M.M.; Hashim, M.R. Effect of CBD Growth Times on the ZnO Microrods Prepared on Macroporous Silicon. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Tijani, J.O.; Shuaib, D.T.; Mohammed, A.K.; Sumaila, A. Comparative Study of Crystallite Size Using Williamson-Hall and Debye-Scherrer Plots for ZnO Nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, Y. Preparation of Cauliflower-like ZnO Films by Chemical Bath Deposition: Photovoltaic Performance and Equivalent Circuit of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Mittal, S.; Leeladevi, V.; De, D. Nanoflower Shaped ZnO Photoanode and Natural Dye Sensitizer Based Solar Cell Fabrication. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneto, M.; Enesca, A.; Lare, Y.; Jondo, K.; Napo, K.; Duta, A. Effect of Precursor Concentration on Structural, Morphological and Opto-Electric Properties of ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 8397–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, S.S.; Ramachandran, K. Role of Aqueous Ammonia on the Growth of ZnO Nanostructures and Its Influence on Solid-State Dye Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 2076–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizama-Tzec, F.I.; García-Rodríguez, R.; Rodríguez-Gattorno, G.; Canto-Aguilar, E.J.; Vega-Poot, A.G.; Heredia-Cervera, B.E.; Villanueva-Cab, J.; Morales-Flores, N.; Pal, U.; Oskam, G. Influence of Morphology on the Performance of ZnO-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 37424–37433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvapriya, R.; Mayandi, J.; Ragavendran, V.; Sasirekha, V.; Vinodhini, J.; Pearce, J.M. Dual Morphology Titanium Dioxide for Dye Sensitized Solar Cells. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7268–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan Tamanna, N.; Hossain, S.; Mohammed Bahadur, N.; Ahmed, S. Green Synthesis of Ag2O & Facile Synthesis of ZnO and Characterization Using FTIR, Bandgap Energy & XRD (Scherrer Equation, Williamson-Hall, Size-Train Plot, Monshi- Scherrer Model). Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idiawati, R.; Mufti, N.; Taufiq, A.; Wisodo, H.; Laila, I.K.R.; Fuad, A. Sunaryono Effect of Growth Time on the Characteristics of ZnO Nanorods. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 202, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, E.; Slimani, Y.; Nawaz, M.; Trabelsi, Z.; Yasin, G.; Bilal, M.; Almessiere, M.A.; Baykal, A.; Thakur, A.; Thakur, P. Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of the Photocatalytic Properties of Zinc Oxide Co-Doped with Lanthanides Elements. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 170, 110910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumaran, S.; Gopalakrishnan, R. Structural, FTIR and Photoluminescence Studies of Cu Doped ZnO Nanopowders by Co-Precipitation Method. Opt. Mater. 2012, 34, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulst, H.C.; van de Hendrik, C. Light Scattering by Small Particles; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1981; ISBN 978-0-486-64228-4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Dai, M.; Lu, Y.; Sun, L. Hierarchical ZnO Nanowire−Nanosheet Architectures for High Power Conversion Efficiency in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2776–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, A.; Mostafa, M.S.; Yakout, H.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Shaaban, E.R. Determination of Optical Bandgap Energy and Optical Characteristics of Cd30Se50S20 Thin Film at Various Thicknesses. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 148, 107770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, J.P.; Noble, B.B.; Blinco, J.P.; Barner-Kowollik, C. Predicting Wavelength-Dependent Photochemical Reactivity and Selectivity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Menth, A. States in the Gap. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1972, 8–10, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.M.; Searson, P.C. ZnO Quantum Particle Thin Films Fabricated by Electrophoretic Deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 2939–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyaegbunam, F.N.C.; Augustine, C. A Study of Optical Band Gap and Associated Urbach Energy Tail of Chemically Deposited Metal Oxides Binary Thin Films. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2018, 13, 847–856. [Google Scholar]
- Marotti, R. Bandgap Energy Tuning of Electrochemically Grown ZnO Thin Films by Thickness and Electrodeposition Potential. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2004, 82, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.L.; Hashim, U.; Muhammad, K.; Voon, C.H. Sol–Gel Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanorods and Their Structural and Optical Investigation for Optoelectronic Application. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (a) | (b) NaOH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | pH | ||||||
| (100) | (002) | (101) | (100) | (002) | (101) | ||
| 8 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 8 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| 8.5 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 9 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 |
| 9 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 10 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.9 |
| 9.5 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 11 | 8.0 | 1.4 | 0.7 |
| pH | 2θ (°) | FWHM (°) | D (nm) | 1015 Lines/m2) | Lattice Parameters (Å) | Ratio | The Internal Strains Along a and c Axes | d (Å) | V (Å3) | L (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | c | (%) | (%) | |||||||||
| 8 | 36.282 | 0.773 | 10.815 | 8.550 | 3.249 | 5.205 | 1.602 | −0.009 | −0.024 | 2.474 | 47.572 | 1.977 |
| 8.5 | 36.261 | 0.764 | 10.942 | 8.353 | 3.251 | 5.207 | 1.602 | 0.049 | 0.018 | 2.475 | 47.647 | 1.978 |
| 9 | 36.253 | 0.715 | 11.691 | 7.316 | 3.251 | 5.209 | 1.602 | 0.058 | 0.049 | 2.476 | 47.671 | 1.978 |
| 9.5 | 36.254 | 0.796 | 10.501 | 9.068 | 3.251 | 5.210 | 1.602 | 0.077 | 0.069 | 2.476 | 47.698 | 1.979 |
| JCPDS card 36-1451 | 36.253 | - | - | - | 3.250 | 5.207 | 1.602 | - | - | 2.476 | 47.622 | - |
| pH | 2θ (°) | FWHM (°) | D (nm) | 1015 Lines/m2) | Lattice Parameters (Å) | Ratio | The Internal Strains Along a and c Axes | d (Å) | V (Å3) | L (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | c | (%) | (%) | |||||||||
| 8 | 36.179 | 0.310 | 26.959 | 1.376 | 3.258 | 5.219 | 1.602 | 0.277 | 0.252 | 2.481 | 47.977 | 1.983 |
| 9 | 36.198 | 0.301 | 27.767 | 1.297 | 3.256 | 5.215 | 1.602 | 0.215 | 0.176 | 2.480 | 47.881 | 1.981 |
| 10 | 36.193 | 0.354 | 23.609 | 1.794 | 3.256 | 5.210 | 1.600 | 0.206 | 0.069 | 2.480 | 47.821 | 1.981 |
| 11 | 36.218 | 0.402 | 20.792 | 2.313 | 3.254 | 5.186 | 1.594 | 0.147 | −0.381 | 2.478 | 47.551 | 1.977 |
| JCPDS card 36-1451 | 36.253 | - | - | - | 3.250 | 5.207 | 1.602 | - | - | 2.476 | 47.622 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gboglo, A.D.; Baneto, M.; Gadedjisso-Tossou, K.S.; Ako, O.; Ahyi, A.C.; Haris, M.; Senthilkumar, M.; N’konou, K.; Grandidier, B.; Beltako, K.; et al. Co-Effect of pH Control Agent and pH Value on the Physical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Bath Deposition for Potential Application in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Surfaces 2025, 8, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030046
Gboglo AD, Baneto M, Gadedjisso-Tossou KS, Ako O, Ahyi AC, Haris M, Senthilkumar M, N’konou K, Grandidier B, Beltako K, et al. Co-Effect of pH Control Agent and pH Value on the Physical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Bath Deposition for Potential Application in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Surfaces. 2025; 8(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleGboglo, Alphonse Déssoudji, Mazabalo Baneto, Komlan Segbéya Gadedjisso-Tossou, Ognanmi Ako, Ayayi Claude Ahyi, Muthiah Haris, Muthusamy Senthilkumar, Kekeli N’konou, Bruno Grandidier, Katawoura Beltako, and et al. 2025. "Co-Effect of pH Control Agent and pH Value on the Physical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Bath Deposition for Potential Application in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells" Surfaces 8, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030046
APA StyleGboglo, A. D., Baneto, M., Gadedjisso-Tossou, K. S., Ako, O., Ahyi, A. C., Haris, M., Senthilkumar, M., N’konou, K., Grandidier, B., Beltako, K., Amou, K. A., & Dzagli, M. M. (2025). Co-Effect of pH Control Agent and pH Value on the Physical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Bath Deposition for Potential Application in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Surfaces, 8(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/surfaces8030046






