Contribution of EBSD for the Microstructural Study of Archaeological Iron Alloy Artefacts from the Archaeological Site of Loiola (Biscay, Northern Spain)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
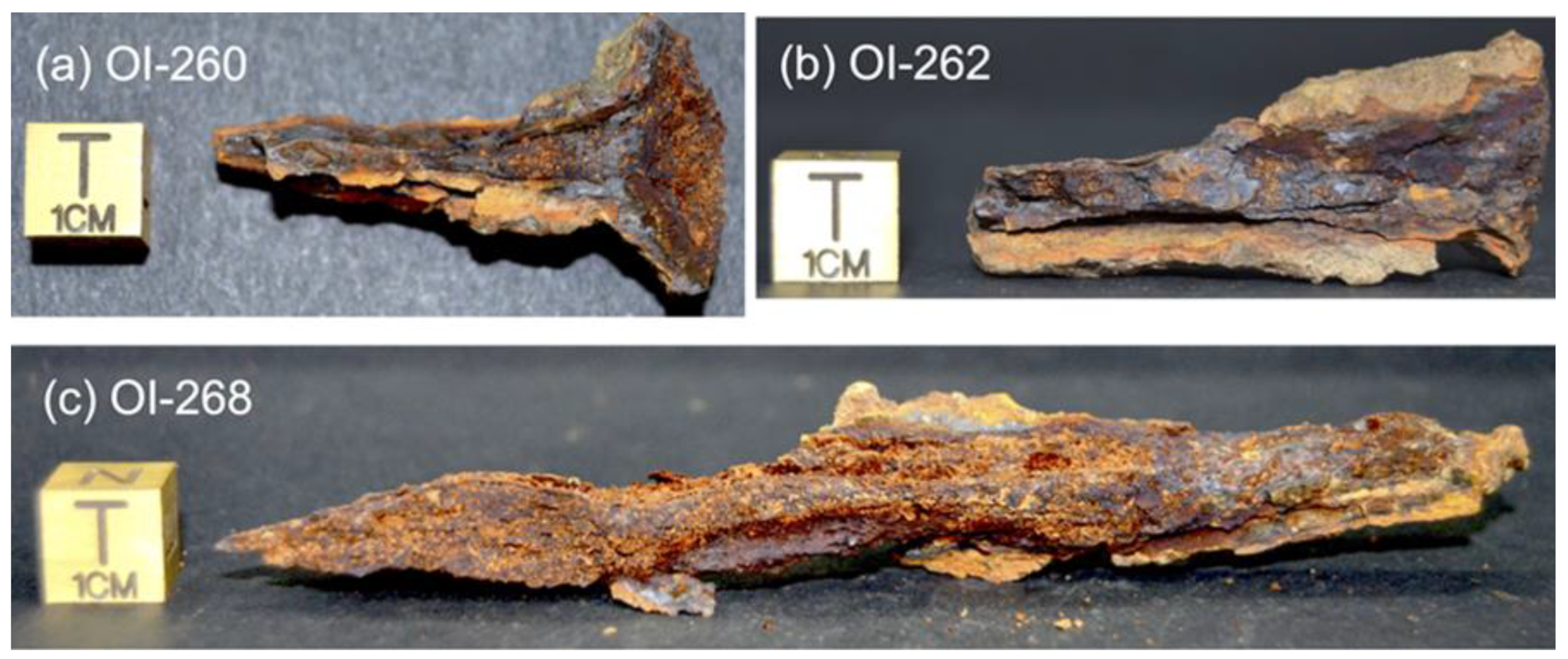
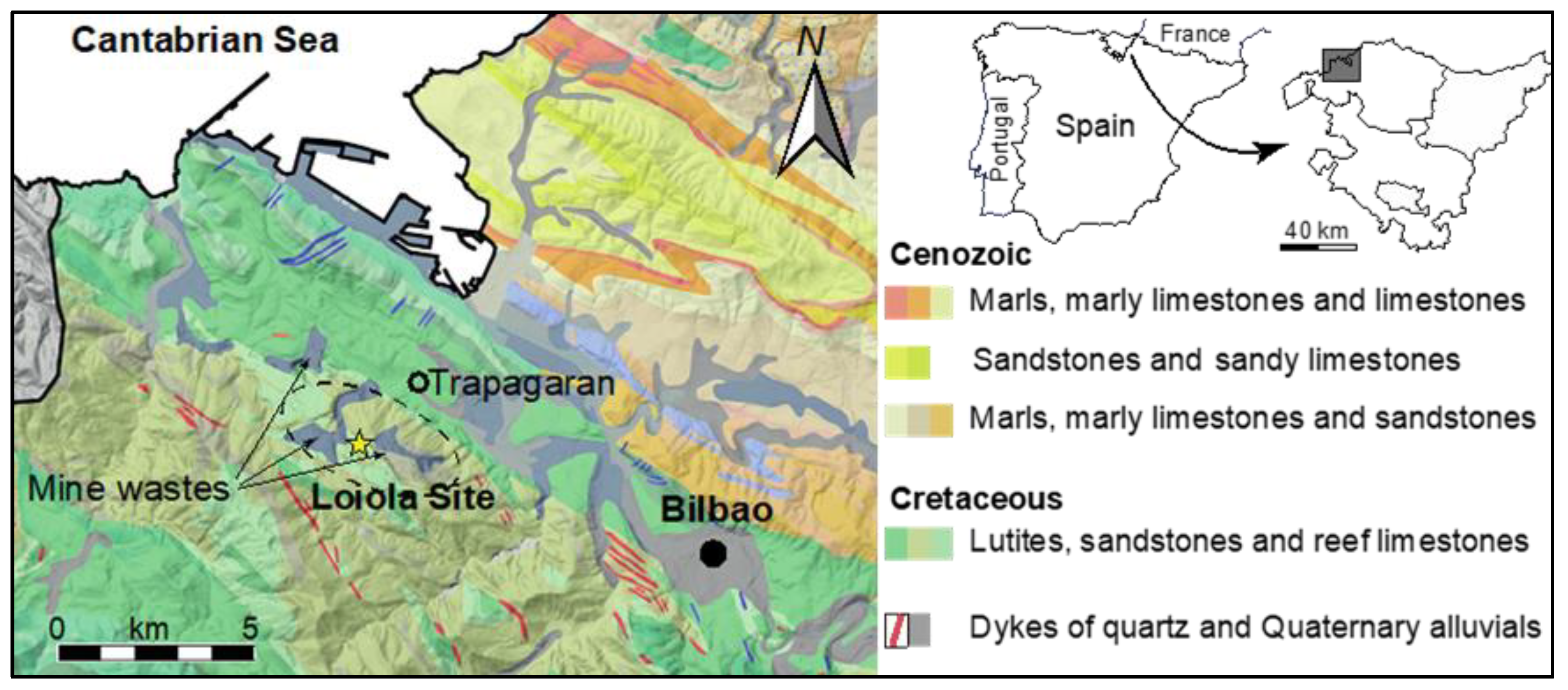
2.1. Corpus and Archaeological Context
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Analytical Procedure and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Microstructural Study
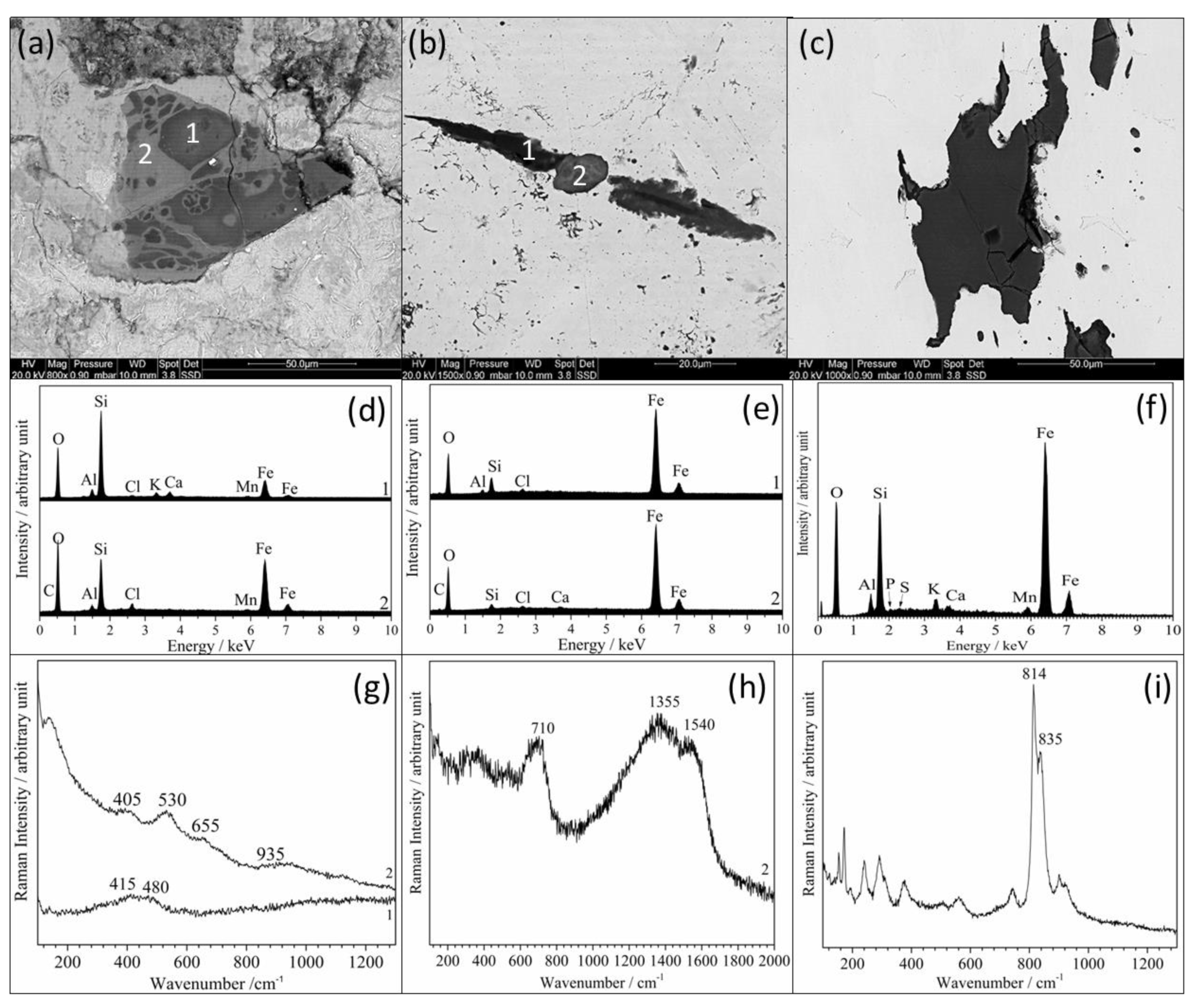
3.2. Inclusion Analysis
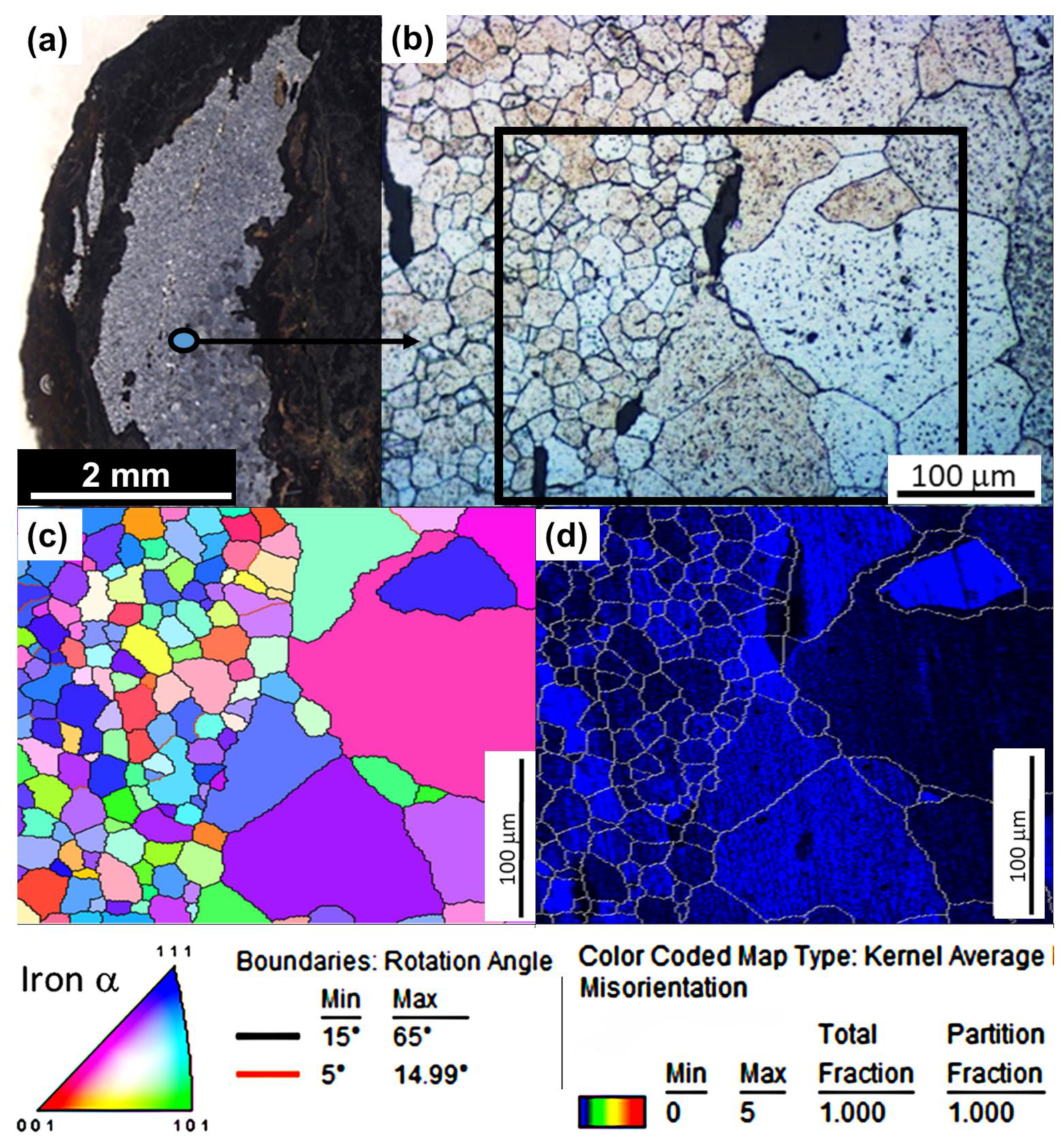
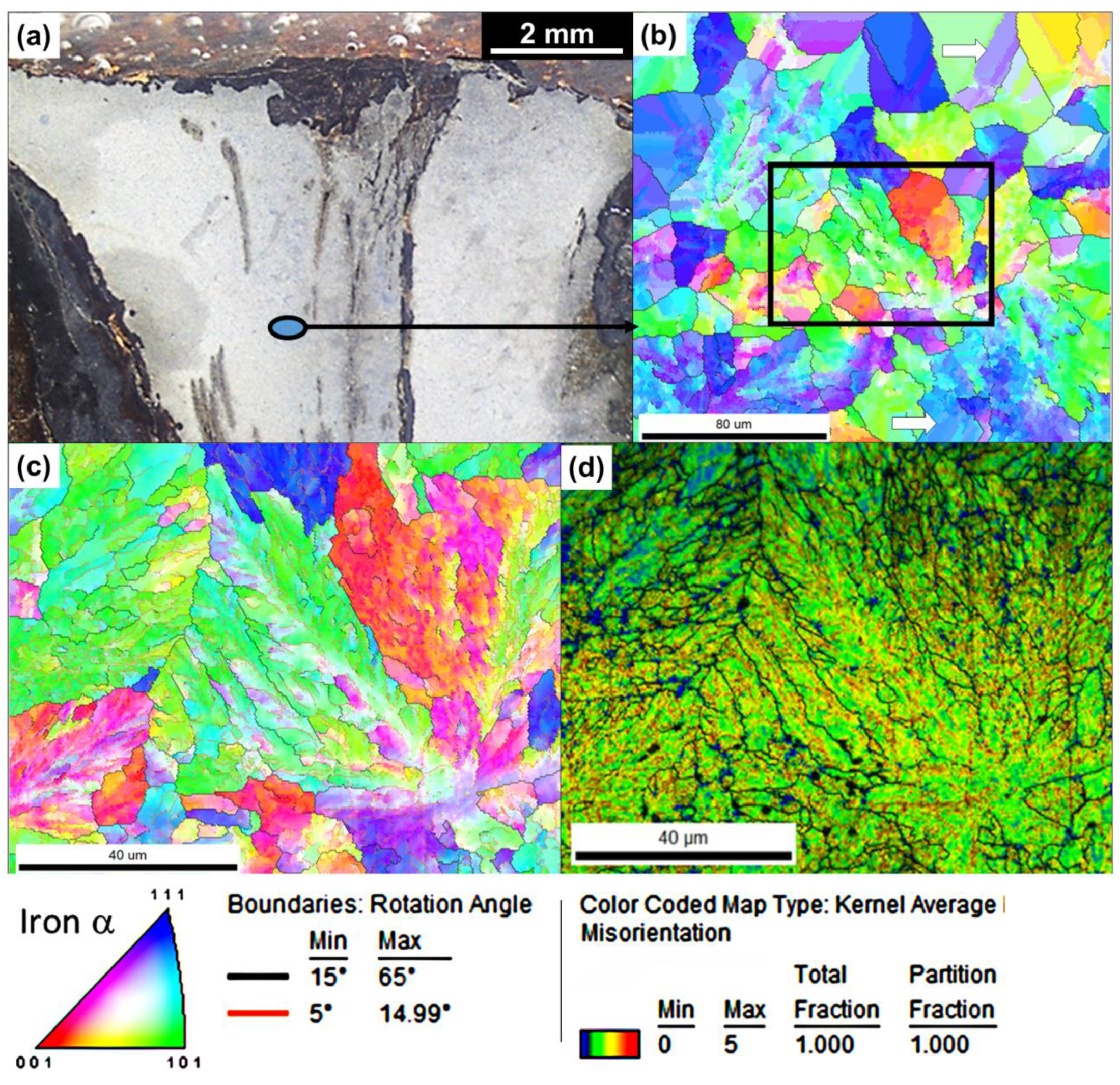
3.3. Microstructural Investigations Using EBSD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giumlia-Mair, A.; Maddin, R. The Origins of Iron. In The Civilisation of Iron: From Prehistory to the Third Millennium; Nicodemi, W., Ed.; Edizioni Olivares: Milan, Italy, 2004; pp. 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, E.; Van Nie, M. A Germanic ultrahigh carbon steel punch of the Late Roman-Iron Age. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, V.F. Iron and Steel in Ancient Times; Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pleiner, R. Iron in Archaeology: Early European Blacksmiths; Archeologický Ústav AV ČR: Praha, Czech Republic, 2006; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, Y.; Oudbashi, O.; Eid, D. Characterization of the microstructural features and the rust layers of an archaeological iron sword in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo (380–500 A.D.). Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxezarraga Ortuondo, I. Paleometalurgia del hierro en el País Vasco Cantábrico: Las haizeolak. Un estado de la cuestión. Munibe Antropol. Arkeol. 2004, 56, 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, J.G. The Classification of Early Ironworking Slags; Engineering and Physical Sciences; Aston University: Birmingham, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Pleiner, R. Iron in Archaeology: The European Bloomery Smelters; Archeologický Ústav AVČR: Praha, Czech Republic, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Portillo-Blanco, H.; Zuluaga, M.C.; Ortega, L.A.; Alonso-Olazabal, A.; Cepeda-Ocampo, J.J.; Martínez Salcedo, A. Mineralogical Characterization of Slags from the Oiola Site (Biscay Spain) to Assess the Development in Bloomery Iron Smelting Technology from the Roman Period to the Middle Ages. Minerals 2020, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giumlia-Mair, A.; Maddin, R. Iron Steel in the Roman Period in Late Antiquity. In The Civilisation of Iron: From Prehistory to the Third Millennium; Nicodemi, W., Ed.; Edizioni Olivares: Milan, Italy, 2004; pp. 113–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, J. Roman iron and steel: A review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pense, A.W. Iron through the ages. Mater. Charact. 2000, 45, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, G.; Dillmann, P.; Fluzin, P.; Long, L. A study of the Roman iron bars of Saintes-Maries-de-la-Mer (Bouches-du-Rhône, France). A proposal for a comprehensive metallographic approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 1234–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluzin, P.; Berranger, M.; Bauvais, S.; Pagès, G.; Dillmann, P. An archaeological archaeometrical approach of ferrous semi-product: A diachronic qualitative typology (VIIth c BC-IInd c, A.D.). In Acta mineraria et metallurgica: Studi in onore di Marco Tizzoni; Tizzoni, C.C., Ed.; Comune di Bergamo: Bergamo, Italy, 2012; pp. 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ingoglia, C.; Triscari, M.; Sabatino, G. Archaeometallurgy in Messina: Iron slag from a dig at block P, laboratory analyses and interpretation. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2008, 8, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Starley, D. Determining the Technological Origins of Iron and Steel. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1999, 26, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Chunag, A.; Gelegdorj, E. A technological transition in Mongolia evident in microstructure, chemical composition and radiocarbon age of cast iron artifacts. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 2465–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Gelegdorj, E.; Chimiddorj, Y.-E. Technological traditions inferred from iron artefacts of the Xiongnu Empire in Mongolia. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S. A preliminary study on the role and implication of plate-type iron artifacts in the ancient iron technology of Korea. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehren, T.; Belgya, T.; Jambon, A.; Káli, G.; Kasztovszky, Z.; Kis, Z.; Kovács, I.; Maróti, B.; Martinón-Torres, M.; Miniaci, G.; et al. 5,000 years old Egyptian iron beads made from hammered meteoritic iron. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 4785–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.-C.; Lee, H.-Y.; Lee, J.-G. Microstructure and heat treatment of Early Iron Age cast iron axes excavated from the Sinpung site, Wanju, Jeonbuk, in the Korean Peninsula. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2019, 11, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotten-Hallel, V.; Ashkenazi, D.; Tal, O. Archaeometallurgical Analysis of Thirteenth-Century Bronze and Iron Construction Implements from the Walls of the Frankish Castle at Arsuf/Arsur. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2022, 11, 255–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocchino, E.; Telloli, C.; Finotti, S.; Facchi, A.; Eftekhari, N.; De Vito, C. Microstructure, Chemistry and Mineralogy Approach for the Diagnostics of Metallic Finds of the Tomba della Biga (Adria, Italy). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Singh, A.K.; Kanungo, A.K.; Arora, A.; Rajan, K.; Selvakumar, V. Comparative microstructural and elemental analysis of iron artefacts from Kaveri valley archaeological sites. Archaeometry 2023, 65, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.W.; Charles, J.A.; Wallach, E.R. Iron–phosphorus–carbon system: Part 1—Mechanical properties of low carbon iron–phosphorus alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, A.; Hošek, J. Estimation of Phosphorus Content in Archaeological Iron Objects by Means of Optical Metallography and Hardness Measurements. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2015, 12, 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nicodemi, W.; Mapelli, C.; Venturini, R.; Riva, R. Metallurgical Investigations on Two Sword Blades of 7th 3rd Century, B.C. Found in Central Italy. ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mapelli, C.; Nicodemi, W.; Riva, R.F.; Vedani, M. Analysis of the nails from the roman legionary at Inchtuthil. Steel Res. Int. 2008, 79, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.R.; Sullivan, A.; Balasubramaniam, R. Electron backscattering diffraction analysis of an ancient wootz steel blade from central India. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, I.; Conforto, E.; Refait, P.; Rémazeilles, C. Study of ferrous corrosion products on iron archaeological objects by electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD). Appl. Phys. A 2013, 110, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grevey, A.L.; Vignal, V.; Krawiec, H.; Ozga, P.; Peche-Quilichini, K.; Rivalan, A.; Mazière, F. Microstructure and long-term corrosion of archaeological iron alloy artefacts. Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northover, S.; Northover, J.P. Applications of electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) in archaeology. In Historical Technology, Materials and Conservation: SEM and Microanalysis; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Arantegui, J.; Larrea, A. Electron backscattering diffraction as a complementary analytical approach to the microstructural characterization of ancient materials by electron microscopy. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 72, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudriss, A.; Creus, J.; Bouhattate, J.; Conforto, E.; Berziou, C.; Savall, C.; Feaugas, X. Grain size and grain-boundary effects on diffusion and trapping of hydrogen in pure nickel. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 6814–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudriss, A.; Le Guernic, S.; Wang, Z.; Osman Hoch, B.; Bouhattate, J.; Conforto, E.; Zhu, Z.; Li, D.S.; Feaugas, X. Meso-scale anisotropic hydrogen segregation near grain-boundaries in polycrystalline nickel characterized by EBSD/SIMS. Mater. Lett. 2016, 165, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, P. Adaptive domain misorientation approach for the EBSD measurement of deformation induced dislocation sub-structures. Ultramicroscopy 2021, 222, 113203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós Castillo, J. Golpeando mientras el hierro esté caliente. Paleosiderurgia en el Norte peninsular. Kobie Ser. Anejo 2014, 13, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Franco Pérez, F.J.; Etxezarraga Ortuondo, I.; Alberdi Lonbide, X. Los orígenes de la tecnología del hierro en el País Vasco: Ferrerías de monte o haizeolak. Kobie. Paleoantropol. 2015, 34, 267–282. [Google Scholar]
- Franco Pérez, F.J. Arqueología y Paleosiderurgia Prehidráulica en Bizkaia (Siglos III-XIII). Tras las Huellas de los Antiguos Ferrones, Geografía, Prehistoria y Arqueología; Universidad del País Vasco, Vitoria-Gasteiz: Gasteiz, Spain, 2017; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- García-Mondéjar, J.; Fernández-Mendiola, P.; Agirrezabala, L.; Aranburu, A.; López-Horgue, M.; Iriarte, E.; Martinez de Rituerto, S. El Aptiense-Albiense de la Cuenca Vasco-Cantábrica. In Geología de España; Vera, J.A., Ancochea, A., Sorando, J.P.C., Cortinas, A.B., Carredo, F.B., Eds.; IGME: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Gil Crespo, P.P. Las Mineralizaciones de Hierro en el Anticlinal de Bilbao: Mineralogía, Geoquímica y Metalogenia, Mineralogía y Petrología; Universidad del País Vasco: Leioa, Spain, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gil Crespo, P.P. Introducción a la geología y mineralogía de los yacimientos de hierro de Bilbao. In Historia del Hierro en Bizkaia y su Entorno; Urkitza, X.O.-E., Ingunza, M.E.A., Crespo, P.P.G., Eds.; Universidad del País Vasco (UPV/EHU): Bilbao, Spain, 2016; pp. 19–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pereda García, I. La metalurgia prehidráulica del hierro en Bizkaia: El caso de los alrededores del pantano de Oiola (Trapagarán, Bizkaia). Kobie. Paleoantropol. 1992, 20, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Pereda García, I. Aportación al conocimiento de la metalurgia del hierro en los s. XI-XIII en Bizkaia: El yacimiento de Oiola-IV (Trapagaran-Bizkaia). Kobie. Paleoantropol. 1997, 24, 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Cepeda Ocampo, J.J.; Unzueta Portilla, M. Ferrería romana de Loiola. Arkeoikuska: Investig. Arqueol. 2014, 2014, 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Franco Pérez, F.J.; Gener Moret, M. Early ironwork in Biscay: Survey, excavation, experimentation and materials characterization. An integral study of the mountainside ironworks (ferrerías de monte or “haizeolak”). Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrazábal Galarza, J. Análisis de muestras siderometalúrgicas procedentes de los yacimientos Oiola II y Oiola IV (Trapagaran, Bizkaia). Kobie. Paleoantropol. 1997, 24, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Cornacchia, G.; Roberti, R.; Faccoli, M. Characterization and Technological Origin Identification of Ancient Iron Nails. JOM 2020, 72, 3224–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galai, L.; Marchetti, L.; Miserque, F.; Frugier, P.; Godon, N.; Brackx, E.; Remazeilles, C.; Refait, P. Effect of dissolved Si on the corrosion of iron in deaerated and slightly alkaline solutions (pH ≈ 8.1) at 50 °C. Corros. Sci. 2023, 210, 110790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Ponge, D.; Raabe, D. Investigation of Orientation Gradients in Pearlite in Hypoeutectoid Steel by use of Orientation Imaging Microscopy. Steel Res. Int. 2007, 78, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenik, E.J. A study of cast iron nails. Hist. Archaeol. 1977, 11, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rémazeilles, C.; Zuluaga, M.C.; Portillo-Blanco, H.; Conforto, E.; Oudriss, A.; Ortega, L.À.; Alonso-Olazabal, A.; Cepeda-Ocampo, J.J. Contribution of EBSD for the Microstructural Study of Archaeological Iron Alloy Artefacts from the Archaeological Site of Loiola (Biscay, Northern Spain). Heritage 2024, 7, 3179-3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7060150
Rémazeilles C, Zuluaga MC, Portillo-Blanco H, Conforto E, Oudriss A, Ortega LÀ, Alonso-Olazabal A, Cepeda-Ocampo JJ. Contribution of EBSD for the Microstructural Study of Archaeological Iron Alloy Artefacts from the Archaeological Site of Loiola (Biscay, Northern Spain). Heritage. 2024; 7(6):3179-3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7060150
Chicago/Turabian StyleRémazeilles, Céline, Maria Cruz Zuluaga, Haizea Portillo-Blanco, Egle Conforto, Abdelali Oudriss, Luis Àngel Ortega, Ainhoa Alonso-Olazabal, and Juan José Cepeda-Ocampo. 2024. "Contribution of EBSD for the Microstructural Study of Archaeological Iron Alloy Artefacts from the Archaeological Site of Loiola (Biscay, Northern Spain)" Heritage 7, no. 6: 3179-3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7060150
APA StyleRémazeilles, C., Zuluaga, M. C., Portillo-Blanco, H., Conforto, E., Oudriss, A., Ortega, L. À., Alonso-Olazabal, A., & Cepeda-Ocampo, J. J. (2024). Contribution of EBSD for the Microstructural Study of Archaeological Iron Alloy Artefacts from the Archaeological Site of Loiola (Biscay, Northern Spain). Heritage, 7(6), 3179-3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage7060150






