Polysaccharide Paint Binding Media at Two Pharaonic Settlements in Nubia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Aims
1.2. The Sites
1.3. Approach
2. Samples
3. Method
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, L.; Quirke, S. Painting materials. In Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology; Nicholson, P.T., Shaw, I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 104–120. [Google Scholar]
- Pagès-Camagna, S.; Guichard, H. Egyptian colours and pigments in French collections: Physicochemical analyses on 300 objects. In Decorated Surfaces on Ancient Egyptian Objects: Technology, Deterioration and Conservation Proceedings of a Conference Held in Cambridge, UK on 7-8 September 2007; Dawson, J., Rozeik, C., Wright, M.M., Eds.; Archetype in Association with the Fitzwilliam Museum and Icon Archaeology Group: London, UK, 2010; pp. 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.; Dennis, M.; Khandekar, N.; Keeney, J.; Carson, D.; Swartz Dodd, L. An Egyptian cartonnage of the Graeco-Roman period: Examination and discoveries. Stud. Conserv. 2003, 48, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A.; Swartz Dodd, L.; Furihata, J.; Tanimoto, S.; Keeney, J.; Schilling, M.R.; Cowan, E. An ancient Egyptian cartonnage broad collar: Technical examination of pigments and binding media. Stud. Conserv. 2004, 49, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Warmlander, S.; Mazurek, J.; Quirke, S. Examination of some pigments, grounds and media from Egyptian cartonnage fragments in the Petrie Museum, University College London. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, R. Paint media and varnishes. In The Nebamun Wall Paintings: Conservation, Scientific Analysis and Display at the British Museum; Middleton, A., Uprichard, K., Eds.; Archetype in Association with the British Museum: London, UK, 2008; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Budka, J. Introduction. In AcrossBorders II: Living in New Kingdom Sai; Austrian Academy of Science Press: Vienna, Austria, 2020; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Budka, J. AcrossBorders: Five seasons of work in the Pharaonic town. In From Microcosm to Macrocosm Individual Households and Cities in Ancient Egypt and Nubia; Budka, J., Auenmüller, J., Eds.; Sidestone Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher, K.; Budka, J. Pigments, incense, and bitumen from the New Kingdom town and cemetery on Sai Island in Nubia. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 33, 102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, N. Building on new ground: The foundation of a colonial town at Amara West. In Nubia in the New Kingdom: Lived Experience, Pharaonic Control and Indigenous Traditions British Museum Publications on Egypt and Sudan 3; Spencer, N., Stevens, A., Binder, M., Eds.; Peeters: Leuven, Belgium, 2017; pp. 323–355. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher, K. Painting Amara West: The Technology and Experience of Colour in New Kingdom Nubia. British Museum Publications on Egypt and Sudan 13; Peeters: Leuven, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher, K.; Siddall, R.; Emmett, T.F.; Spencer, N. Multi-Scale Characterization of Unusual Green and Blue Pigments from the Pharaonic Town of Amara West, Nubia. Heritage 2021, 4, 2563–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcher, K.; Stacey, R.; Spencer, N. Bitumen from the Dead Sea in Early Iron Age Nubia. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, V. Analyses of copper- and beeswax- containing green paint on Egyptian antiquities. Stud. Conserv. 2007, 52, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleton, J.; Mejanelle, P.; Sansoulet, J.; Goursaud, S.; Tchapla, A. Characterization of neutral sugars and uronic acids after methanolysis and trimethylsilylation for recognition of plant gums. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 720, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinach, C.; Papillon, M.-C.; Pepe, C. Identification of binding media in works of art by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D. Ancient Egyptian pigments: The examination of some coffins from the San Diego Museum of Man. MRS Bull. 2010, 35, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallance, S.L.; Singer, B.W.; Hitchen, S.M.; Townsend, J.H. The development and initial application of a gas chromatographic method for the characterization of gum media. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 1998, 37, 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.W.; Karamalla, K.A. Studies on uronic acid materials. Part XII. The composition of acacia gum exudates. J. Chem. Soc. C Org. 1966, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.P.; Farooqi, M.I.H.; Taravel, F.R.; Joseleau, J.P. Studies on Acacia nilotica gum exudates. Structural variation due to different habitats. Carbohydr. Res. 1991, 222, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, P. Amara West I: The Architectural Report. EES Excavation Memoir 63; Egypt Exploration Society: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, S.S.; Rabah, A.A.; Ali, H.I.; Mahmoud, T.E. Acacia Seyal Gums in Sudan: A review. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual Conference for Postgraduate Studies and Scientific Research Basic Sciences and Engineering Studies, Khartoum, Sudan, 20–23 February 2016; Volume 6, pp. 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- POMO. Vachellia nilotica. Plants of the World Online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Available online: http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Cartwright, C.R.; Ryan, P. Archaeobotanical research at Amara West in New Kingdom Nubia. In Nubia in the New Kingdom: Lived Experience, Pharaonic Control and Indigenous Traditions British Museum Publications on Egypt and Sudan 3; Spencer, N., Stevens, A., Binder, M., Eds.; Peeters: Leuven, Belgium, 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, F.; Hansen, A.M. The enviromental remains. In AcrossBorders II: Living in New Kingdom Sai; Austrian Academy of Science Press: Vienna, Austria, 2020; pp. 275–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kamerling, J.P.; Gerwig, G.J. Strategies for the Structural Analysis of Carbohydrates. In Comprehensive Glycoscience Volume 2: Analysis of Glycans; Polysaccharide Functional Properties; Kamerling, H., Boons, G.-J., Lee, Y.C., Suzuki, A., Taniguchi, N., Vorage, A.G.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, J.P.M. Manual on Taxonomy of Acacia Species; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1983; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/Q2934E/Q2934E00.htm (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Mills, J.S.; White, R. The Organic Chemistry of Museum Objects, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hazmi, M.I.; Stauffer, K.R. Gas chromatographic determination of hydrolyzed sugars in commercial gums. J. Food Sci. 1986, 51, 1091–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.W. Chemotaxonomic aspects of the chemistry of acacia gum exudates. Kew Bull. 1978, 32, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Mazurek, J.; Restivo, A.; Colombini, M.P.; Bonaduce, I. Analysis of plant gums and saccharide materials in paint samples: Comparison of GC-MS analytical procedures and databases. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aspinall, G.; Baillie, J. Gum tragacanth. Part, I. Fractionation of the gum and the structure of tragacanthic acid. J. Chem. Soc. 1963, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twilley, J.W. The analysis of exudate plant gums in their artistic applications: An interim report. In Archaeological Chemistry III; Lambert, J.B., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 357–394. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, P. From raw resources to food processing. Archaeobotanical and ethnographic insights from New Kingdom Amara West and present-day Ernetta Island in Northern Sudan. In Exploring the Materiality of Food “Stuffs”: Archaeological and Anthropological Perspectives; Steel, L., Zinn, K., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, R.; Serpico, M. Adhesives and binders. In Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology; Nicholson, P.T., Shaw, I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 475–494. [Google Scholar]
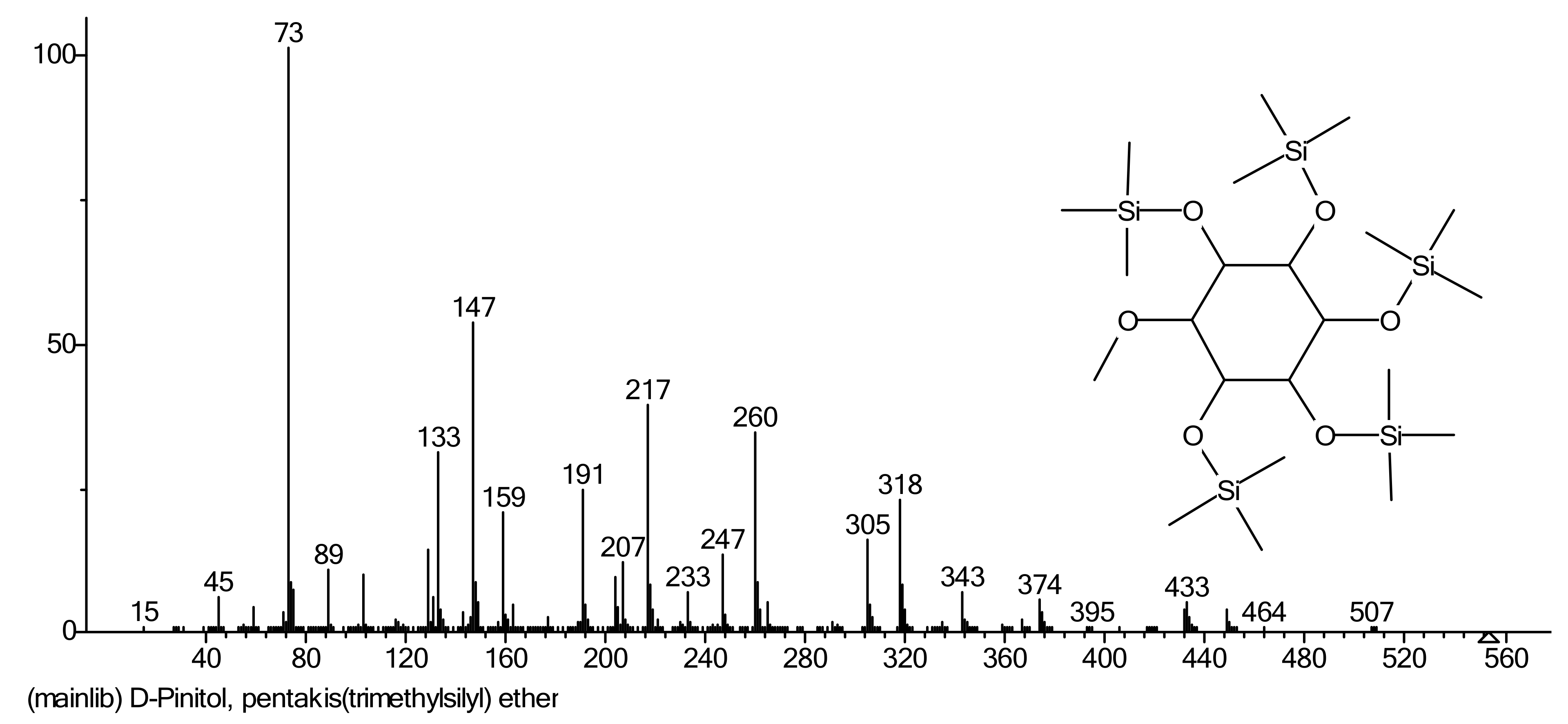
- Chaubal, R.; Pawar, P.V.; Hebbalkar, G.D.; Tungikar, V.B.; Puranik, V.G.; Deshpande, V.H.; Deshpande, N.R. Larvicidal activity of Acacia nilotica extracts and isolation of D-pinitol—A bioactive carbohydrate. Chem. Biodivers. 2005, 2, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaduce, I.; Brecoulaki, H.; Colombini, M.P.; Lluveras, A.; Restivo, V.; Ribechini, E. Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric characterisation of plant gums in samples from painted works of art. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1175, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejanelle, P.; Bleton, J.; Goursaud, S.; Tchapla, A. Identification of phenolic acids and inositols in balms and tissues from an Egyptian mummy. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 767, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, R.; Halpine, S.M. The binding media of ancient Egyptian painting. In Colour and Painting in Ancient Egypt; Davies, W.V., Ed.; British Museum Press: London, UK, 2001; pp. 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, R. Analysis of red paint and filling material from the sarcophagus of Queen Hatshepsut and King Thutmose, I. J. Mus. Fine Arts Boston 1993, 5, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Serpico, M.; White, R. Oil, fat and wax. In Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology; Nicholson, P.T., Shaw, I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 390–429. [Google Scholar]
- Budka, J. (Ed.) Pottery from SAV1 North. In AcrossBorders I, The New Kingdom Town of Sai Island, Sector SAV1 North Contributions to the Archeology of Egypt, Nubia and the Levant, 4; Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften: Vienna, Austria, 2017; pp. 119–156. [Google Scholar]
- Spataro, M.; Garnett, A.; Shapland, A.; Spencer, N.; Mommsen, H. Mycenaean pottery from Amara West (Nubia, Sudan). Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2017, 11, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, V.; Stacey, R.; Middleton, A. The blackening of paint containing Egyptian blue. Stud. Conserv. 2004, 49, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fur, D. La Conservation des Peintures Murales des Temples de Karnak; Editions Recherche sur les Civilisations: Paris, France, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, B. Technical analysis of reds and yellows in the tomb of Suemniwet, Theban Tomb 92. In Colour and Painting in Ancient Egypt; Davies, W.V., Ed.; British Museum Press: London, UK, 2001; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Stulik, D.; Porta, E.; Palet, A. Analyses of pigments, binding media and varnishes. In Art and Eternity: The Nefertari Wall Paintings Conservation Project 1986–1992; Corzo, M.A., Afshar, M., Eds.; Getty Conservation Institute: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 55–65. [Google Scholar]
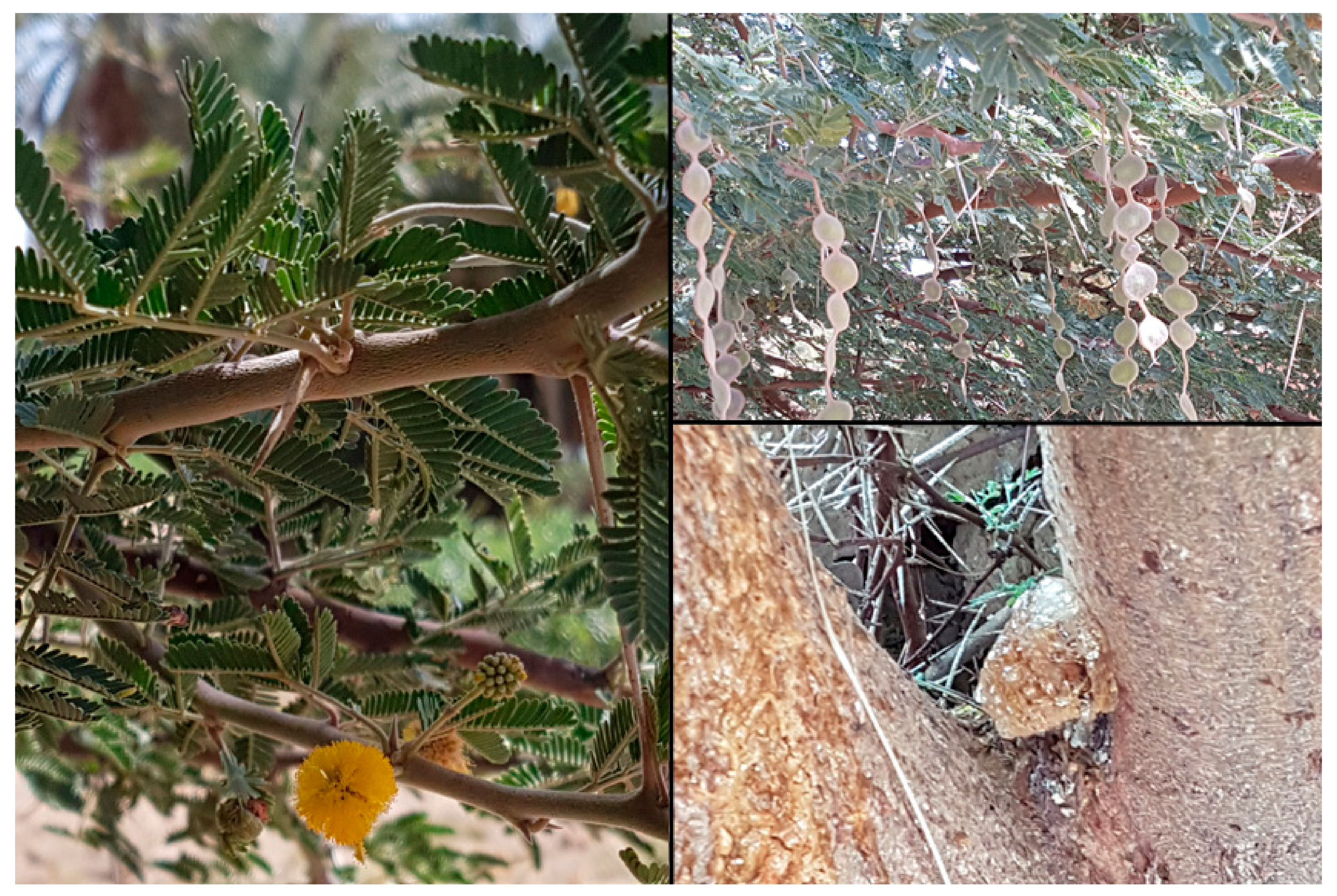
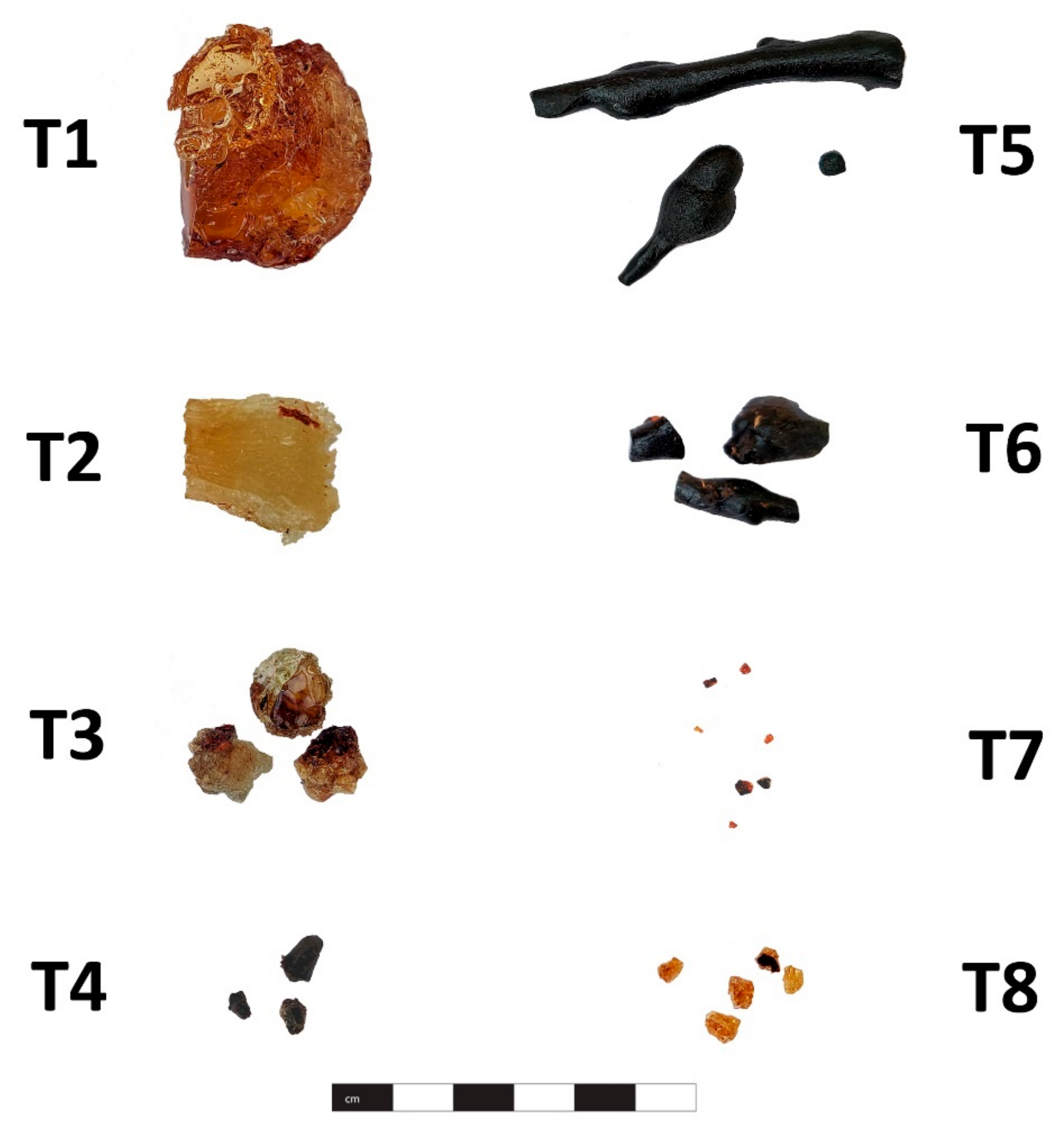
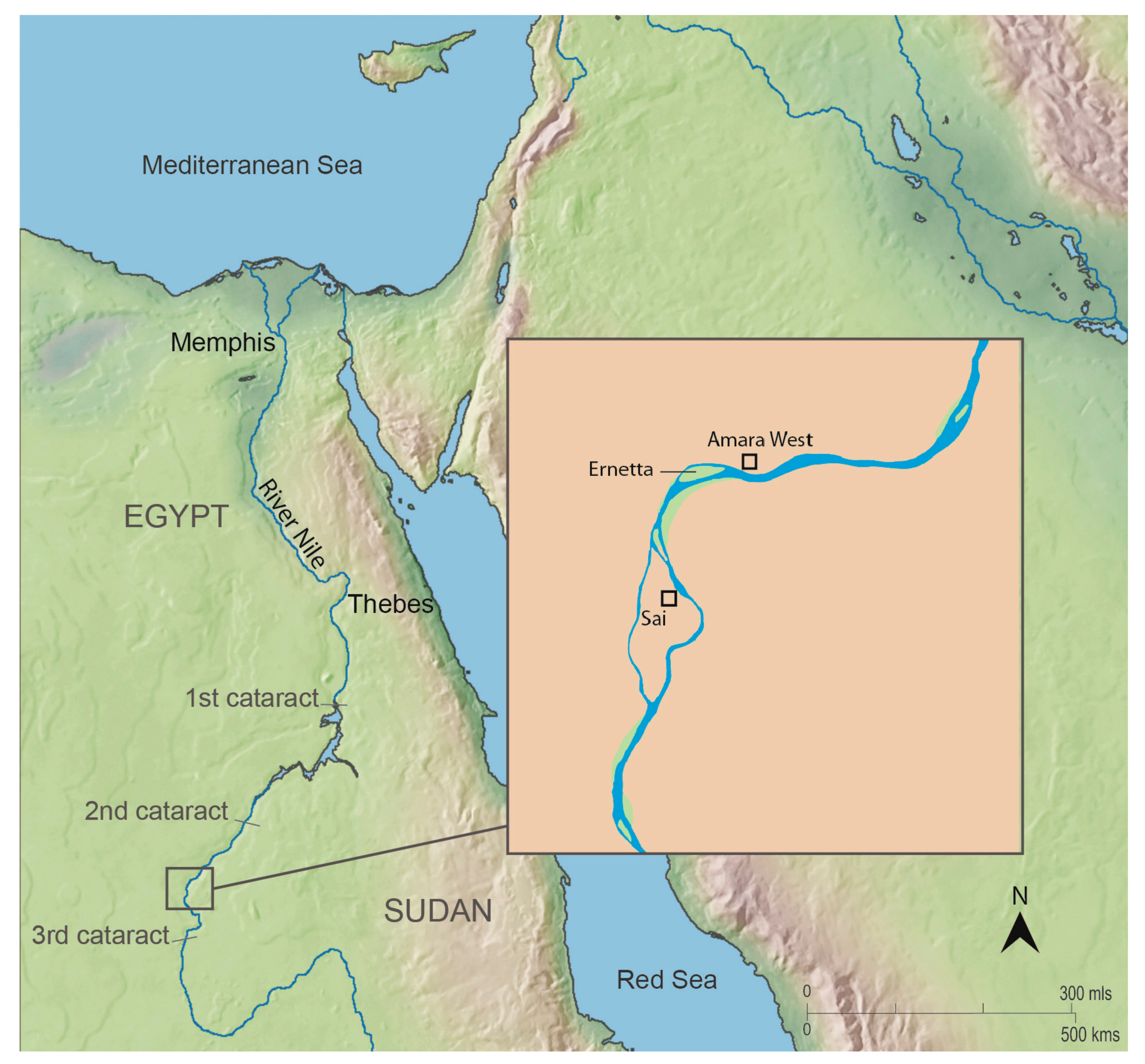


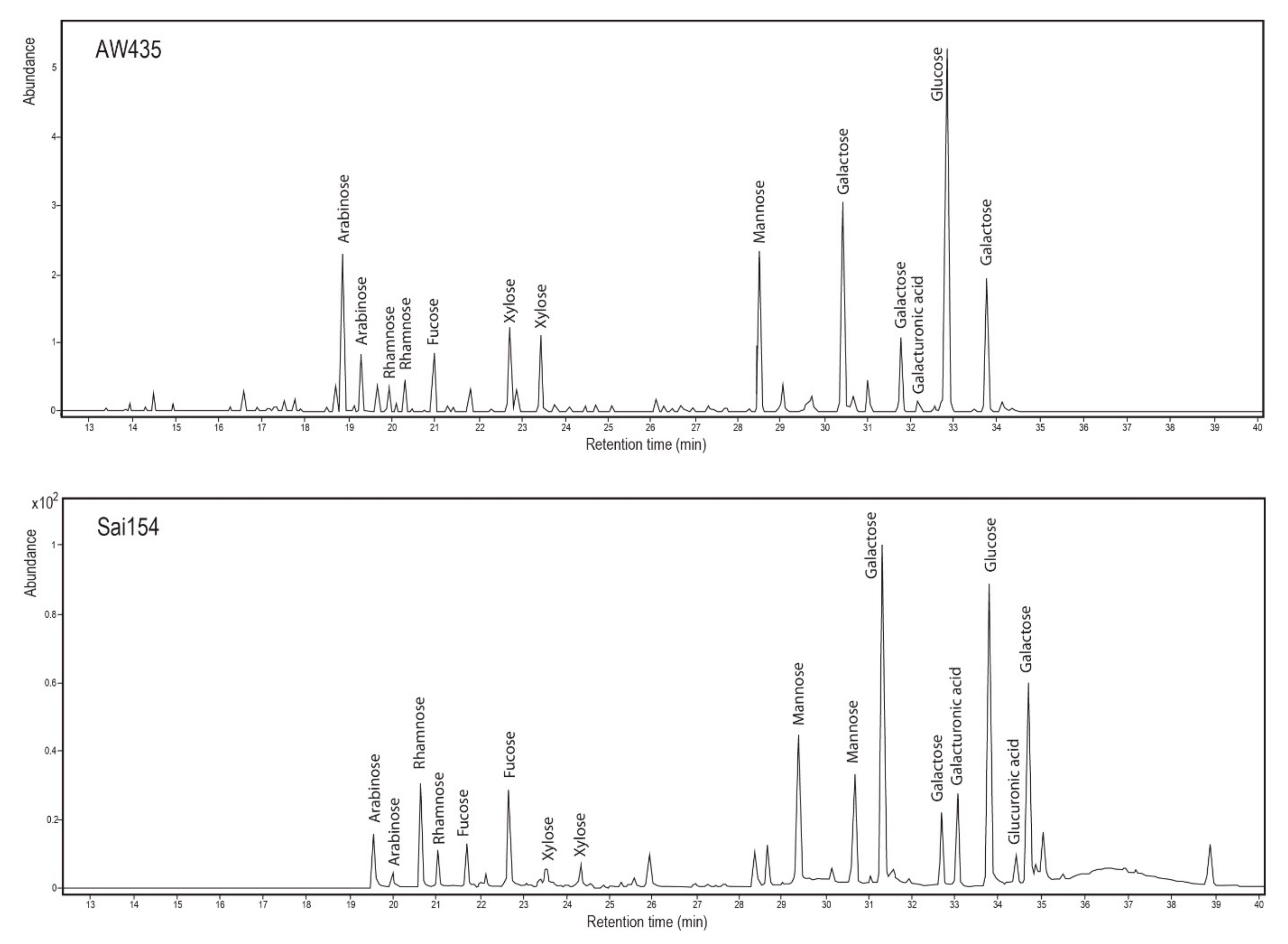
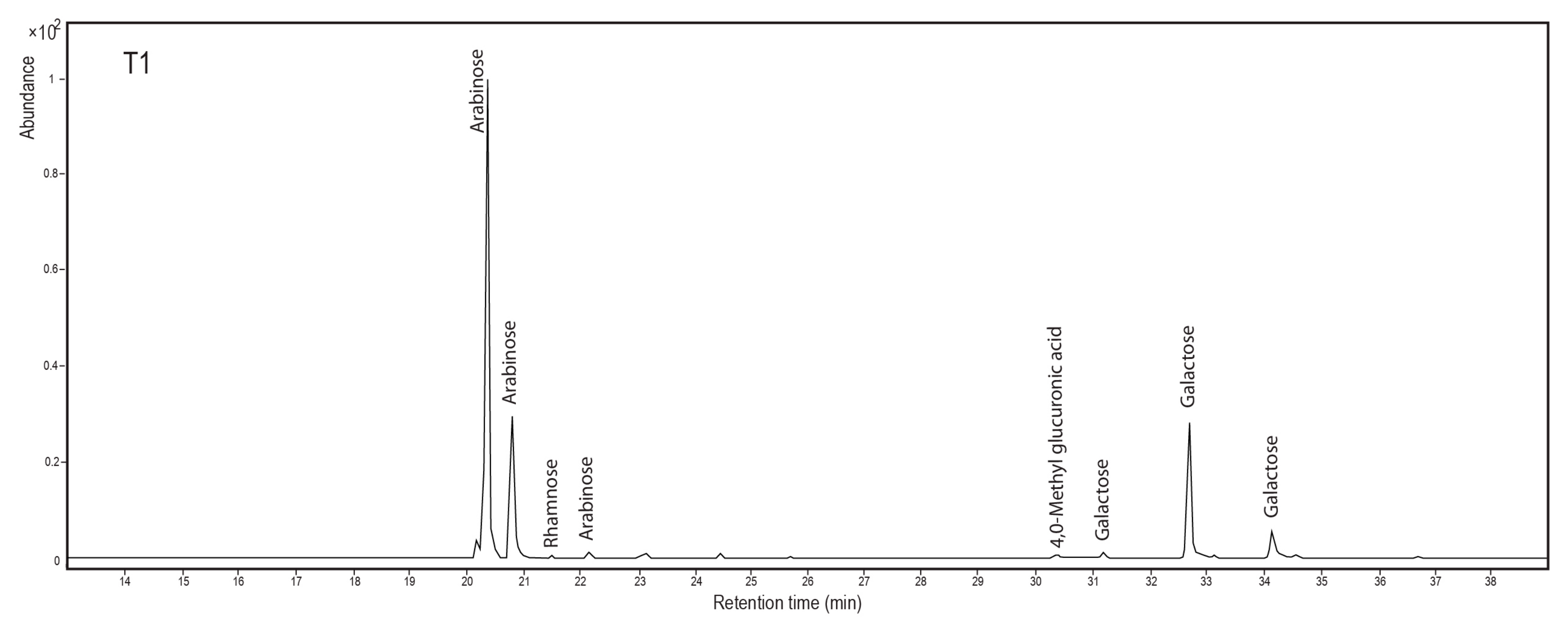

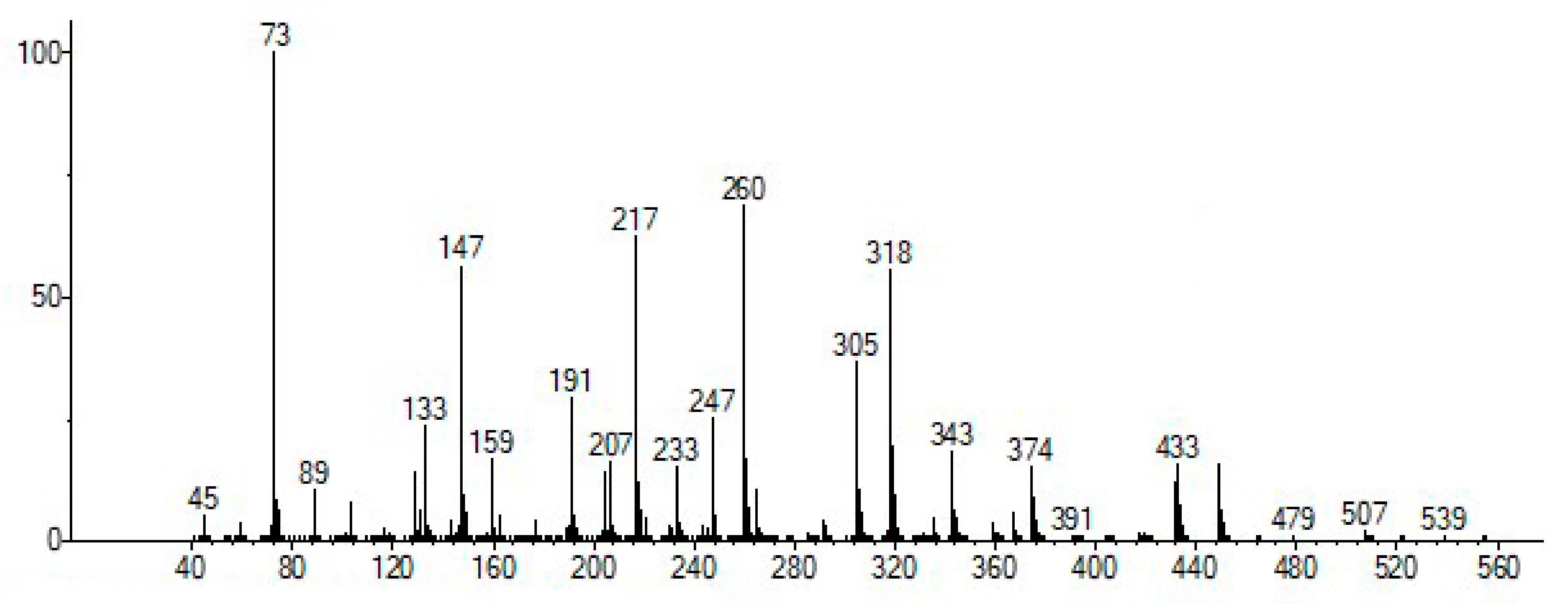
| Sample Number | Find Number | Provenance | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sai | ||||
| Sai130 | SAV1W 0550/2015 | SAV1W, Sq. 1S, SU 679 | c. 1400 BC | Palette with red ochre |
| Sai133 | SAV1W 0650/2015 | SAV1W, Sq. 1S, SU 698 | c. 1400–1300 BC | Palette with huntite |
| Sai150 | SAV1W 0230/2015 | SAV1W, Sq. 1S, SU 630 | c. 1540–1300 BC | Palette with Egyptian blue |
| Sai153 | SAV1W P045 | SAV1W, Sq. 1, SU 537 | c. 1400–1300 BC | Palette with yellow ochre, gypsum, calcite |
| Sai154 | SAV1W P048 | SAV1W, Sq. 1, SU 507 | c. 1540–1300 BC | Palette with yellow ochre, gypsum, calcite |
| Sai155 | SAV1W P051 | SAV1W, Sq. 1, SU 585 | c. 1540–1400 BC | Palette with anhydrite |
| Sai163 | SAV1W P069.1 | SAV1W, Sq. 1, SU 507 | c. 1540–1300 BC | Palette with red and yellow ochre, gypsum |
| Amara West | ||||
| AW119 | F17310 | E13.29.1 ((5230) | c. 1200 BC | Palette with bitumen |
| AW121 | F17311 | E13.29.4 (5243) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with bitumen, carbon |
| AW122 | F6190 | E13.31.2 (5332) | c. 1200 BC | Palette with gypsum, calcite |
| AW127 | F6170 | E13.6.4 (5341) | c. 1200 BC | Palette with Egyptian blue, gypsum |
| AW129 | F6079 | E13.29.4 (5222) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with yellow ochre, calcite |
| AW130 | F6147 | E13.31.1 (5325) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with red ochre |
| AW132y | F6147 | E13.31.1 (5325) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with yellow ochre, anhydrite |
| AW132b | F6147 | E13.31.1 (5325) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with Egyptian blue |
| AW133 | F6147 | E13.31.1 (5325) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with anhydrite |
| AW139 | F6281 | E13.29.3 (5246) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with carbon |
| AW141 | F6408 | E13.31.2 (5334) | c. 1200 BC | Palette red ochre, calcite |
| AW256 | E13.7.6 (4566) | c. 1200 BC | Gypsum wall plaster | |
| AW259 | E13.3.24 (4068) | c. 1200–1180 BC | Gypsum wall plaster | |
| AW323 | F7278 | D12.5.12 (2538) | c. 1200–1100 BC | Palette with yellow ochre |
| AW435 | F6264 | E13.29.2 (5261) | c. 1180 BC | Palette with red ochre, calcite |
| AW440 | F6493 | E13.14.1 (5361) | c. 1190 BC | Palette yellow ochre |
| AW445 | F6446 | E13.31.3 (5339) | c. 1200 BC | Palette with gypsum |
| Arabinose | Rhamnose | Galactose | Glucose | Mannose | Xylose | Fucose | Glucuronic Acid | Galacturonic Acid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples from Sai | |||||||||
| Sai130 | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | |
| Sai133 | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | |
| Sai150 | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | ||||
| Sai153 | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ |
| Sai154 | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + |
| Sai155 | ++ | + | + | + | + | ||||
| Samples from Amara West | |||||||||
| AW121 | ++ | + | + | ||||||
| AW129 | + | + | + | + | (+) | ||||
| AW132b | + | + | + | (+) | |||||
| AW139 | + | + | + | ||||||
| AW256 | + | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | |
| AW323 | + | + | |||||||
| AW435 | + | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ||
| AW445 | + | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + |
| Samples from Ernetta Island | |||||||||
| T1–3, T7–8 (amber) | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | ||||
| T4–6 (black) | + | + | |||||||
| Modern samples from the British Museum Reference Collection | |||||||||
| Acacia arabica 1 | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ||||
| Gum tragacanth 2 | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | + | ||
| Prunus gum 3 | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Examples from literature (modern) | |||||||||
| Acacia arabica a | ++ | + | ++ | + | + | ||||
| Acacia arabica b | + | + | + | + | |||||
| Acacia nilotica c | ++ | (+) | ++ | + | |||||
| Acacia nilotica d | ++ | + | ++ | + | |||||
| Acacia Senegal e | ++ | + | ++ | + | |||||
| Gum tragacanth f | ++ | (+) | + | + | ++ | + | ++ | ||
| Gum tragacanth b | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| Apricot gum g | ++ | ++ | + | + | |||||
| Cherry gum a | ++ | + | + | + | + | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fulcher, K.; Spencer, N.; Budka, J.; Stacey, R.J. Polysaccharide Paint Binding Media at Two Pharaonic Settlements in Nubia. Heritage 2022, 5, 2028-2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030106
Fulcher K, Spencer N, Budka J, Stacey RJ. Polysaccharide Paint Binding Media at Two Pharaonic Settlements in Nubia. Heritage. 2022; 5(3):2028-2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030106
Chicago/Turabian StyleFulcher, Kate, Neal Spencer, Julia Budka, and Rebecca J. Stacey. 2022. "Polysaccharide Paint Binding Media at Two Pharaonic Settlements in Nubia" Heritage 5, no. 3: 2028-2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030106
APA StyleFulcher, K., Spencer, N., Budka, J., & Stacey, R. J. (2022). Polysaccharide Paint Binding Media at Two Pharaonic Settlements in Nubia. Heritage, 5(3), 2028-2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5030106






