3D Reconstruction & Modeling of the Traditional Greek Trechadiri: “Aghia Varvara”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Greek Traditional Shipbuilding & Trechadiri
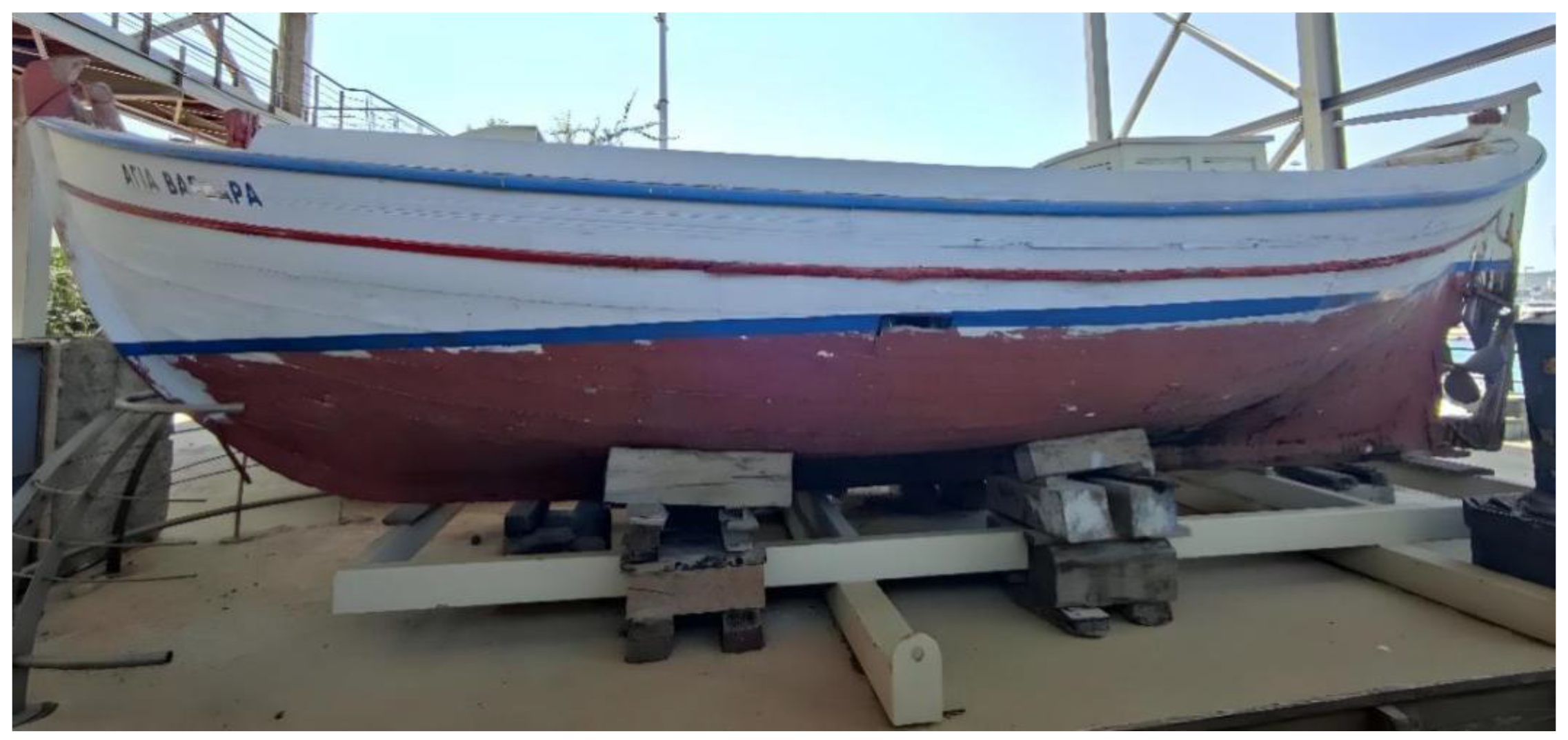
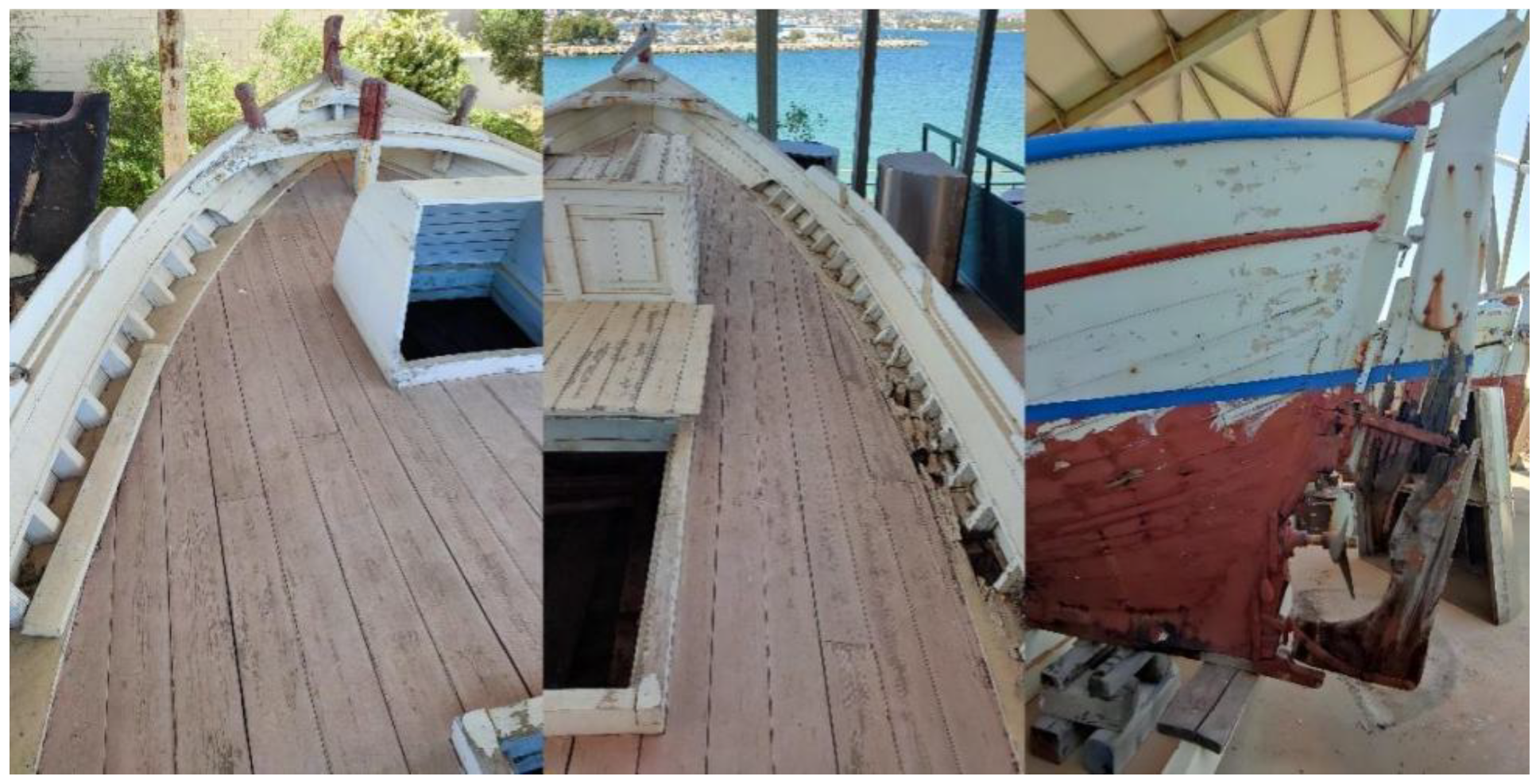
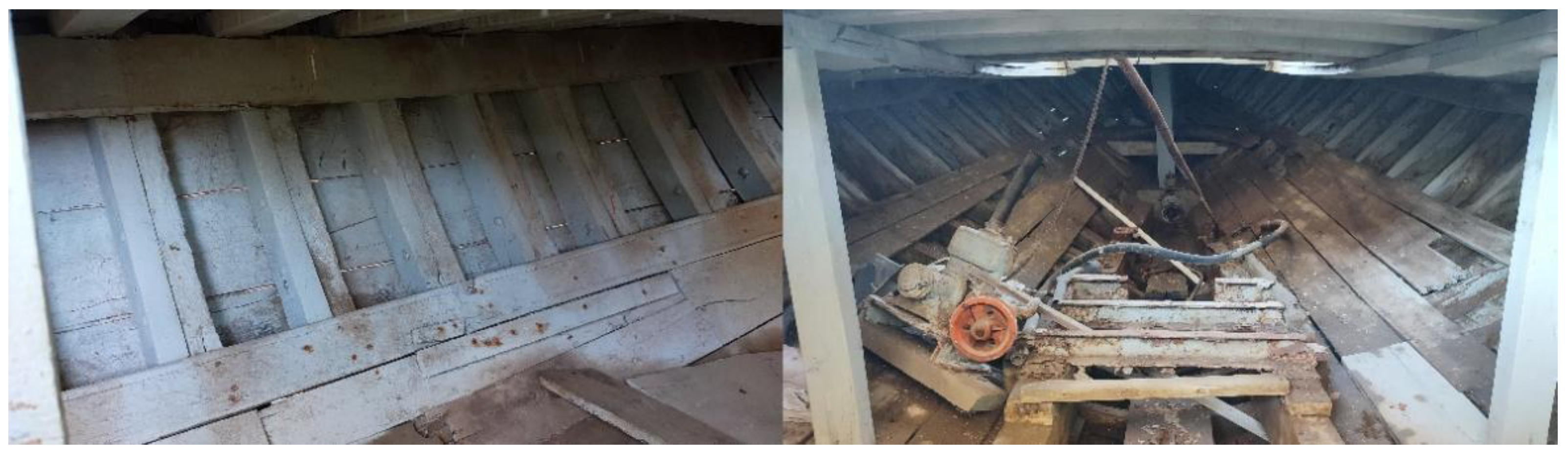
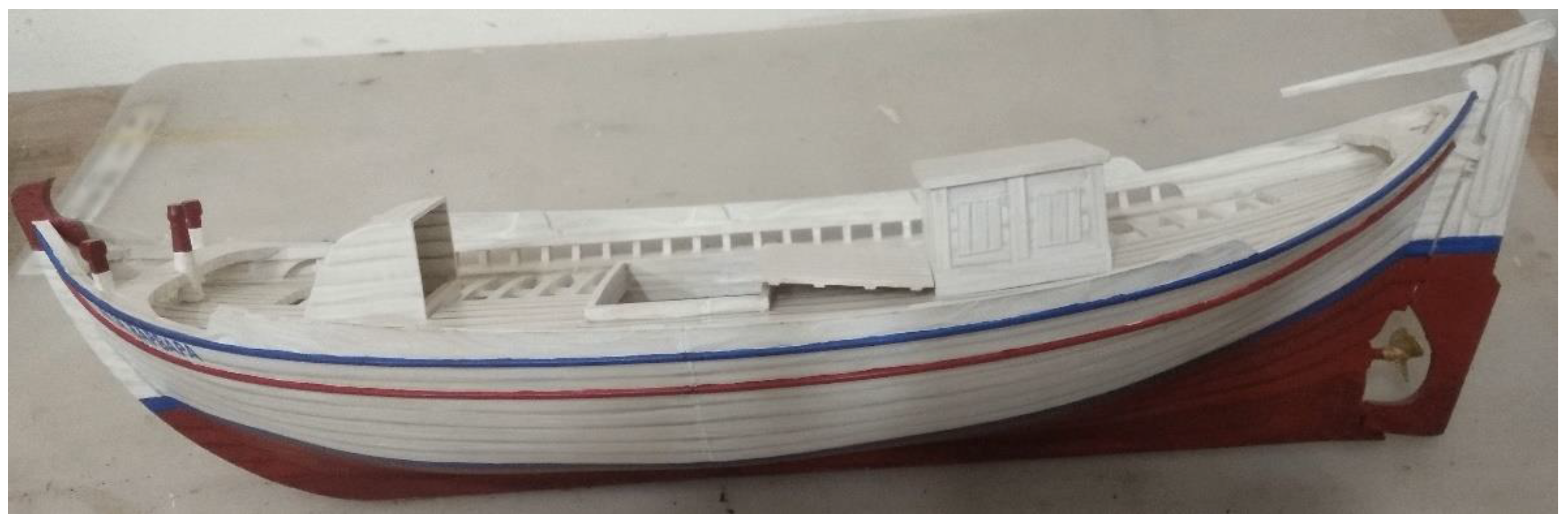
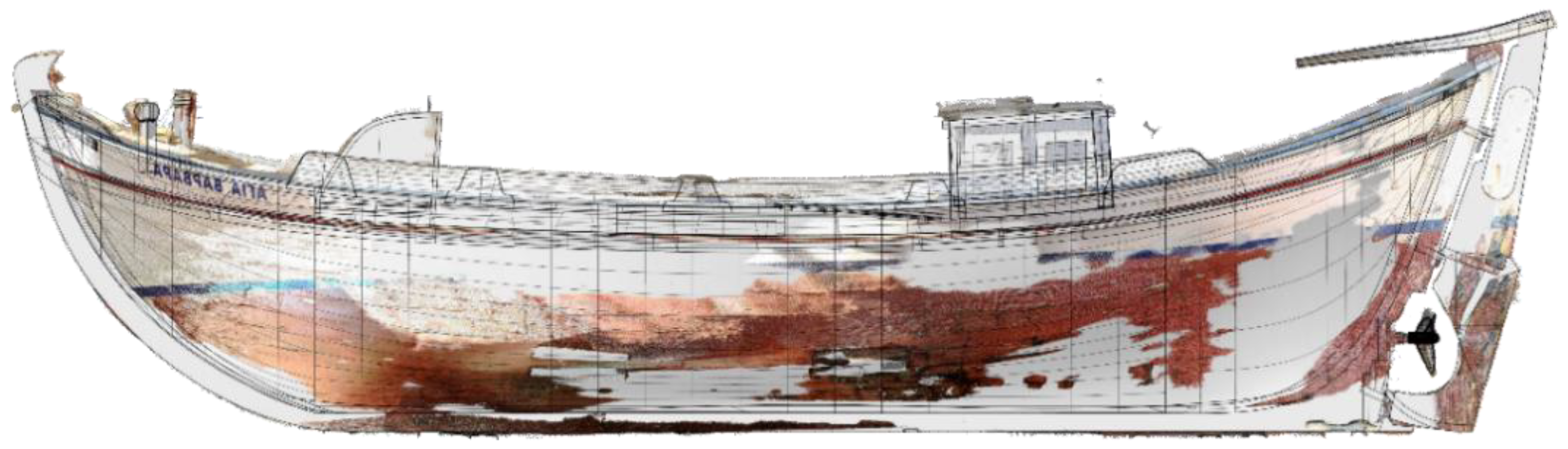
1.3. “Aghia Varvara”
- Type: Trechadiri,
- Place of Construction: Perama, Greece,
- Year of Construction: 1925
- Length Overall: 10.60 m, Beam: 4.55 m
1.4. Objectives
- to analyze and present the digital model reconstruction techniques using 3D technology: 3D laser scanning and editing of point clouds, Rhino3D Design, texturing, and 3D printing
- to contribute to culture preservation by recreating a digital model of a Trechadiri type boat with as much detailed and precise design information as feasible.
2. 3D Reconstruction Process
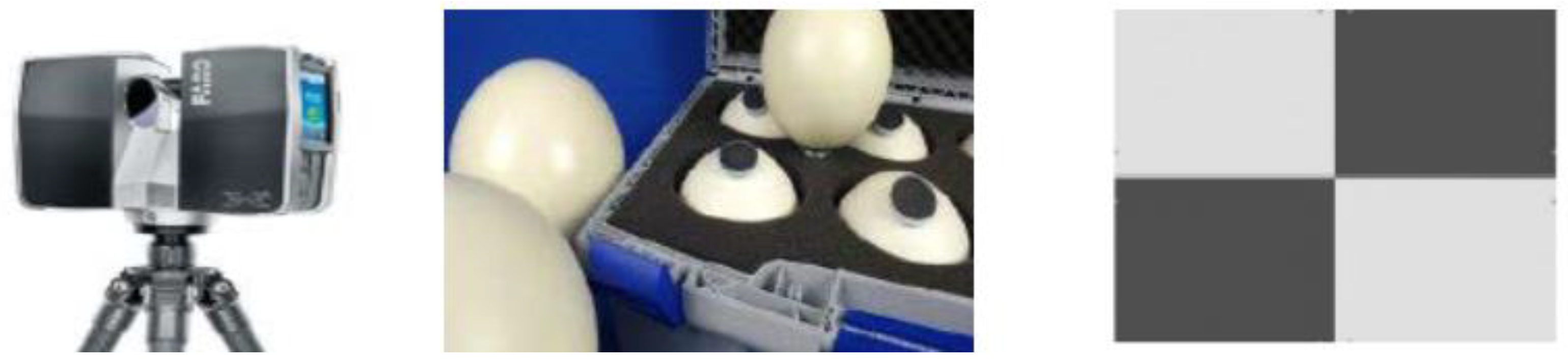
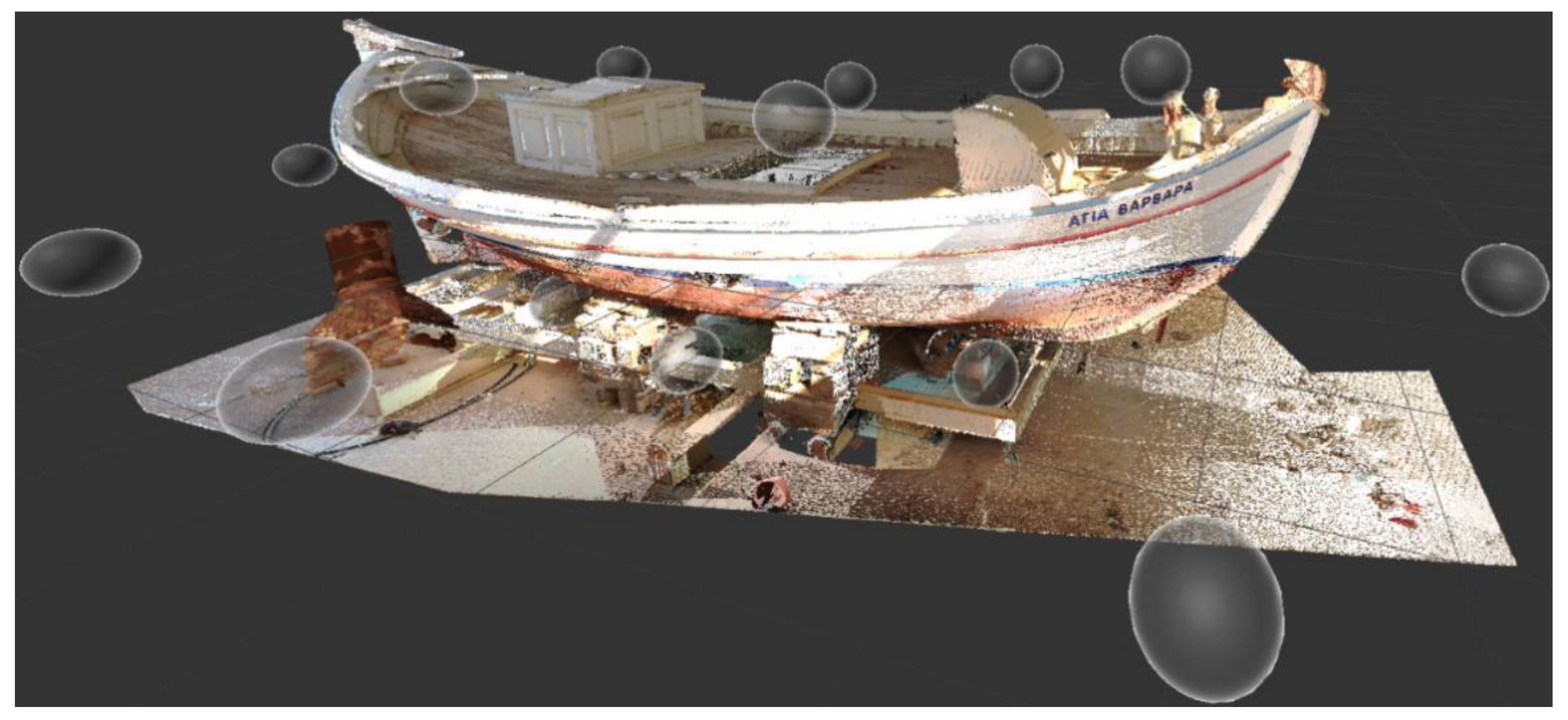
2.1. 3D Laser Scanning
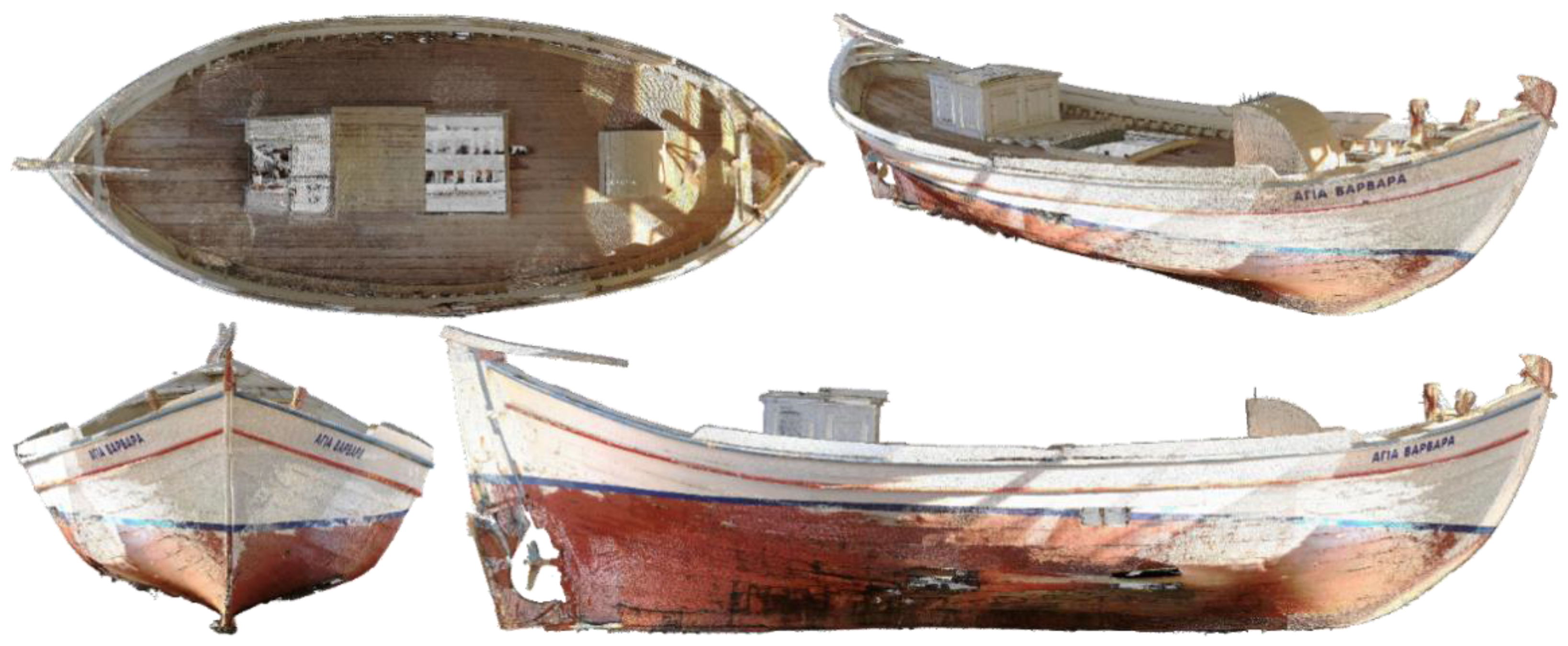
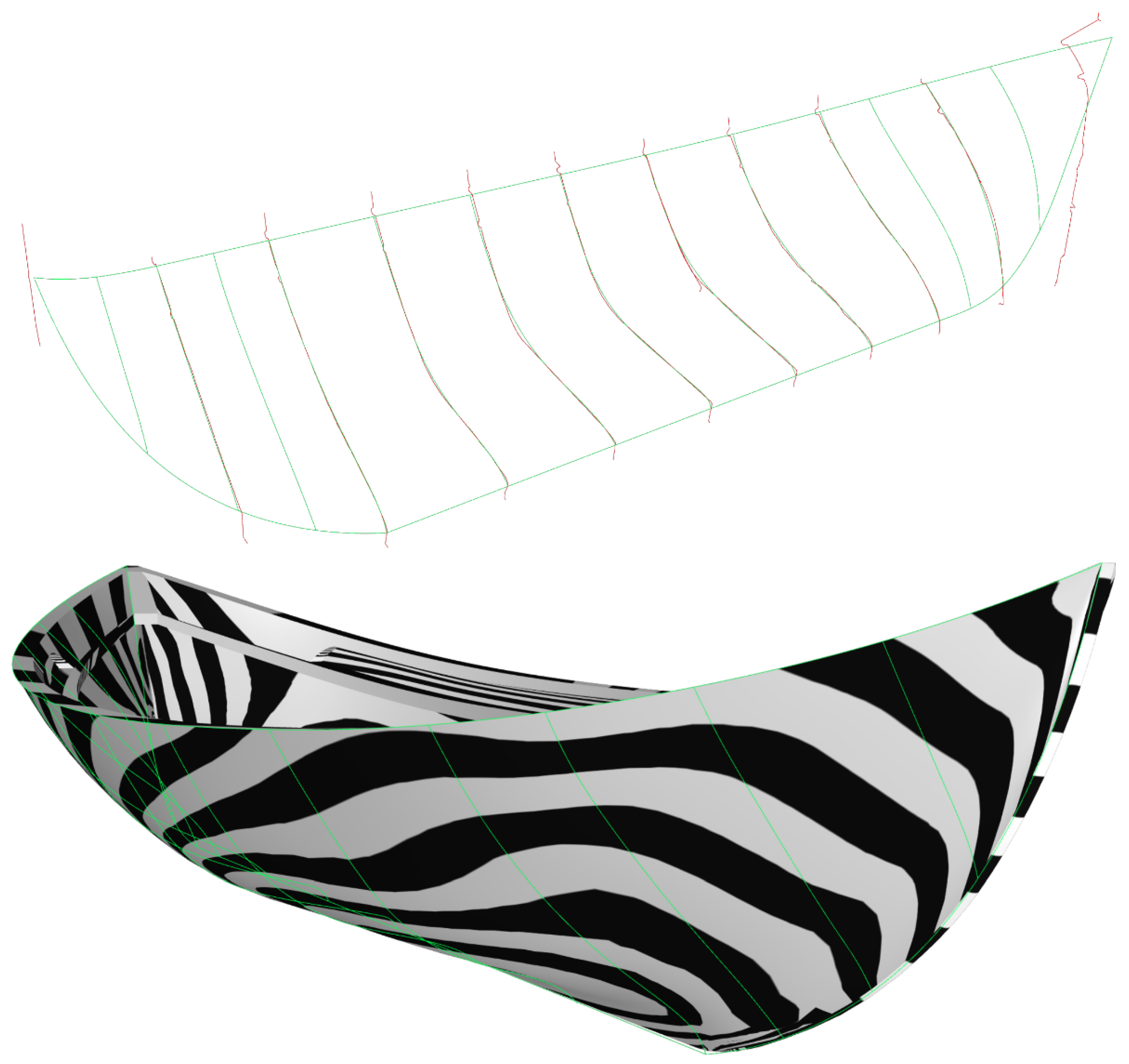
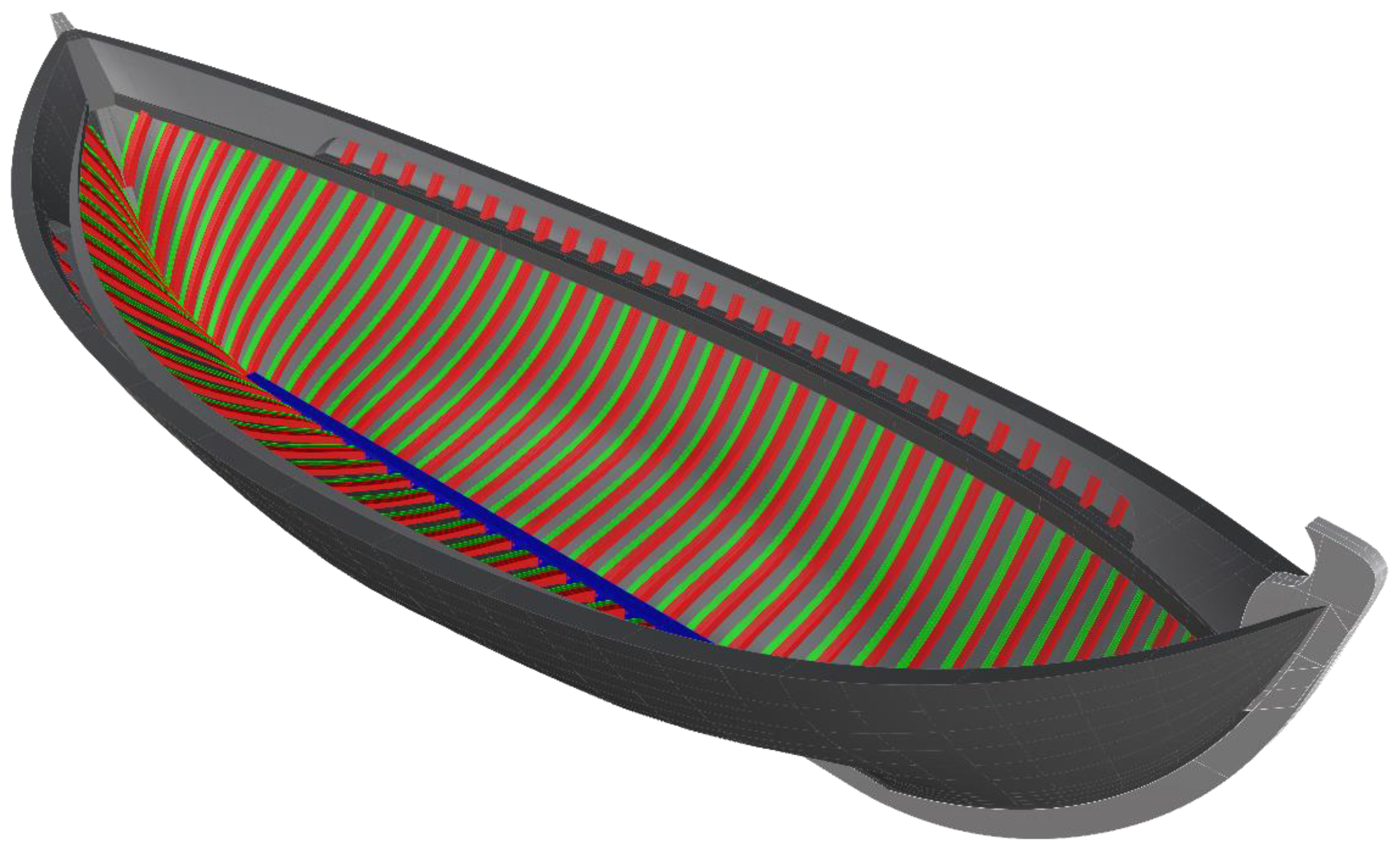
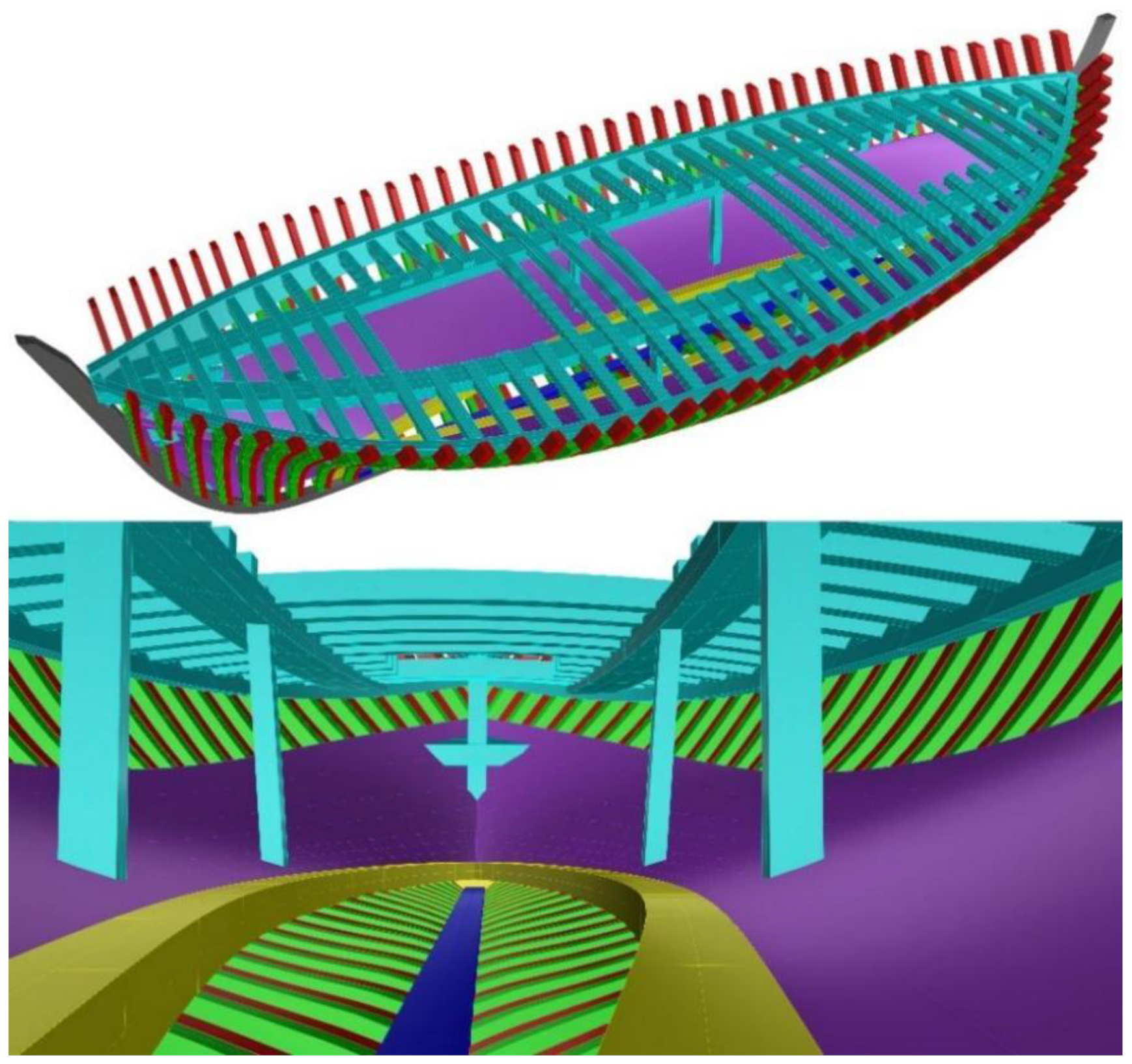
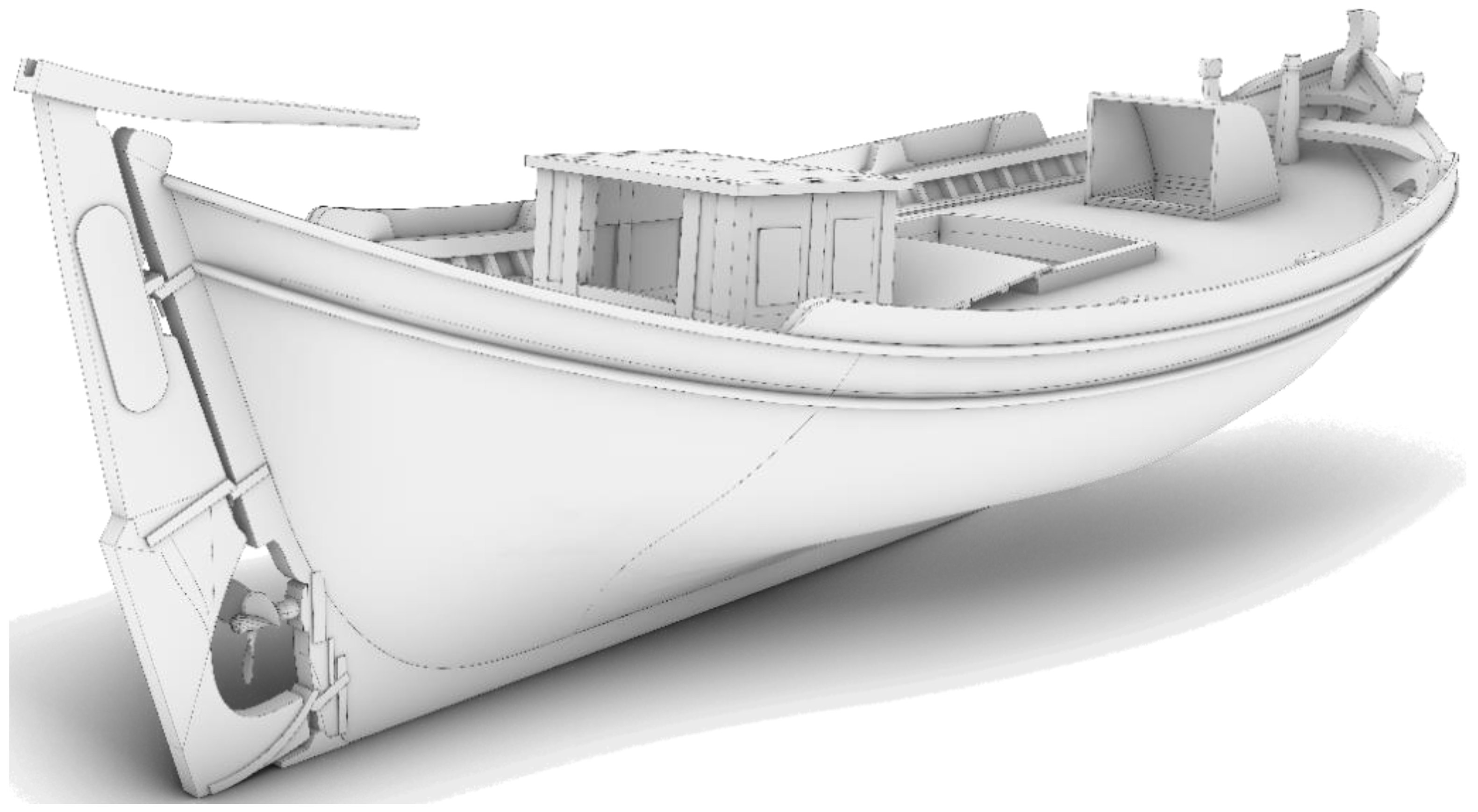
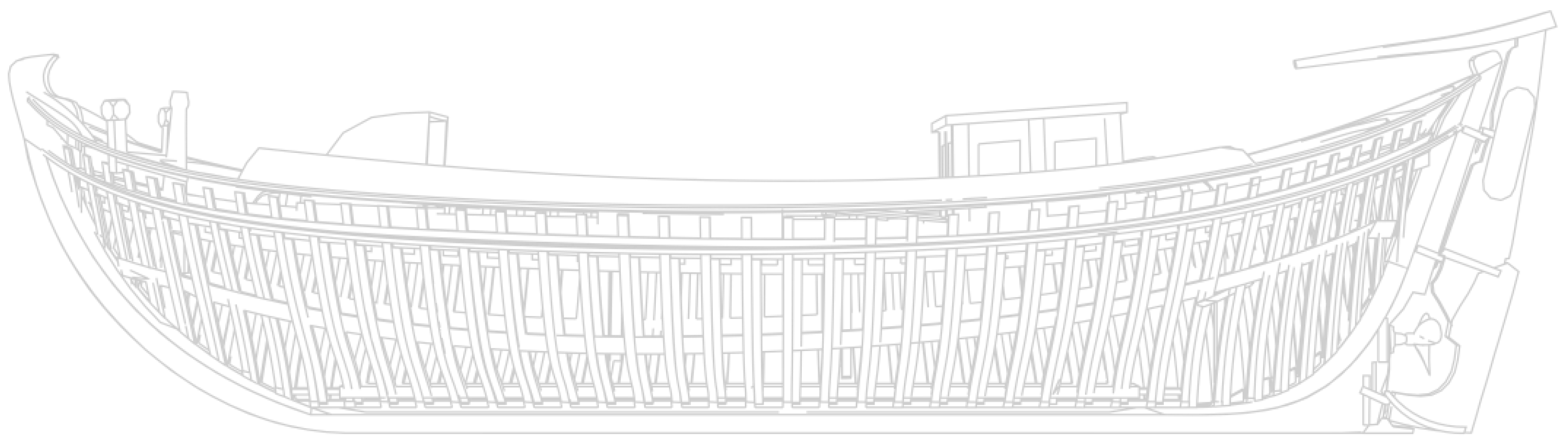
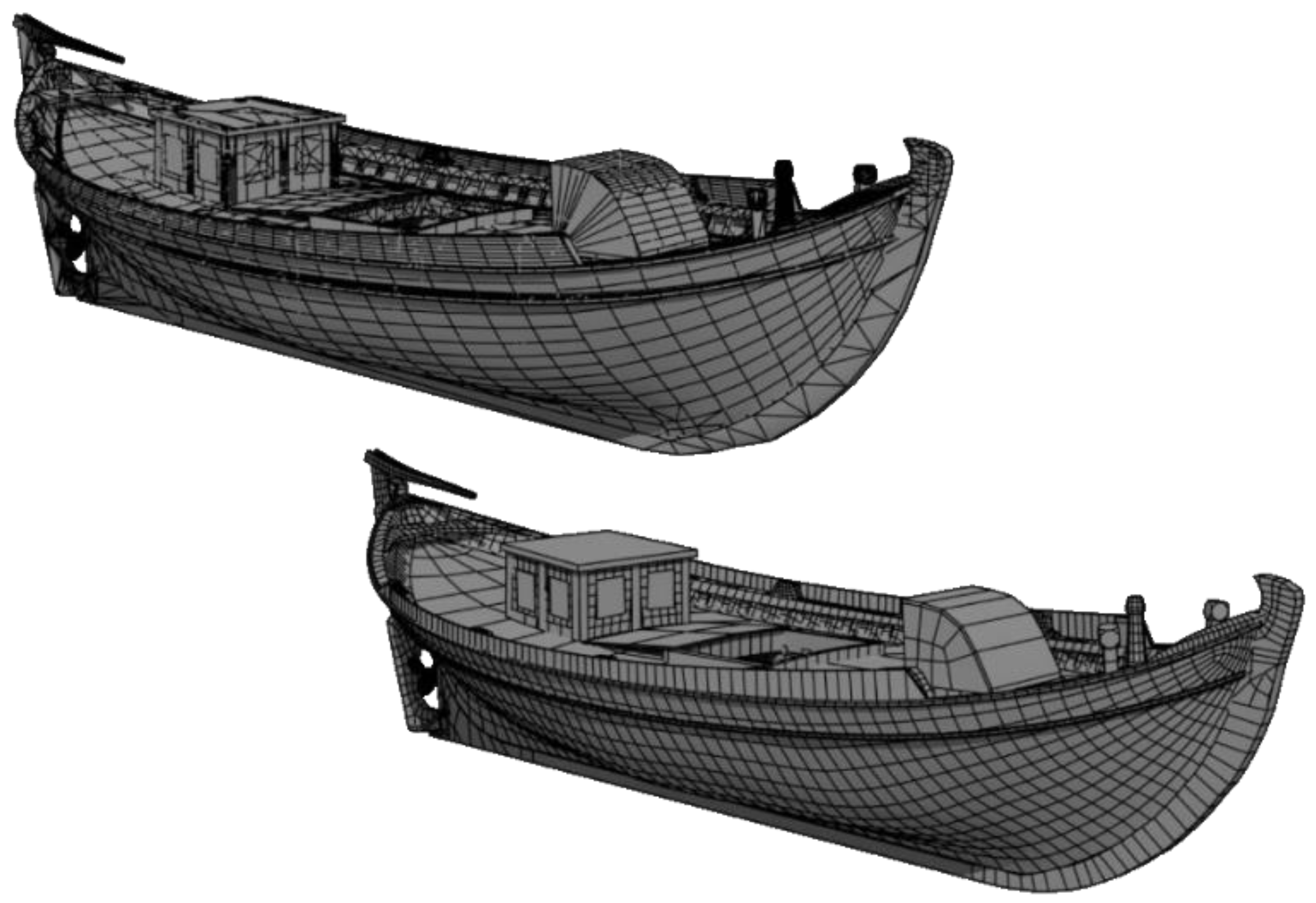
2.2. Design in Rhino3D
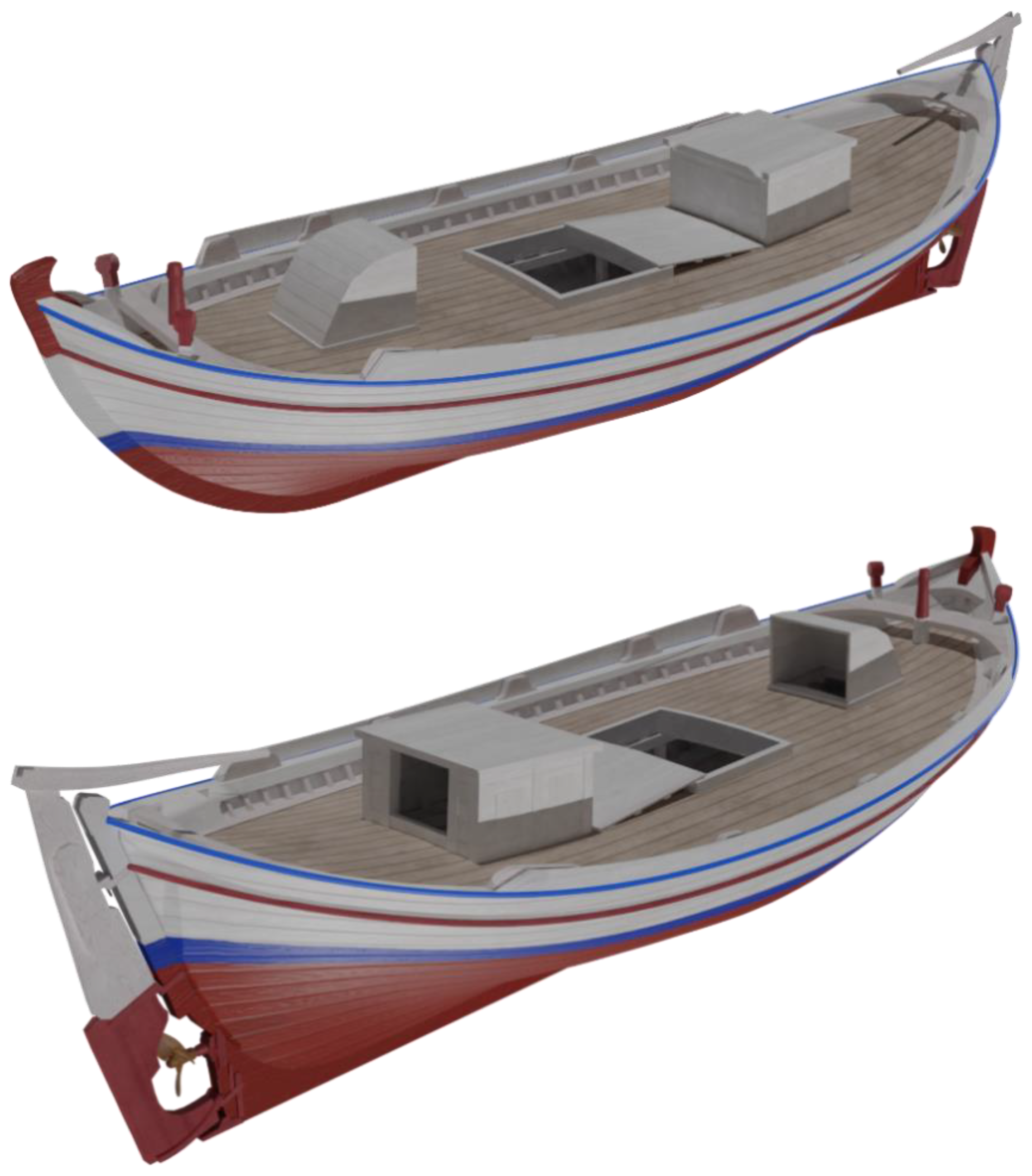
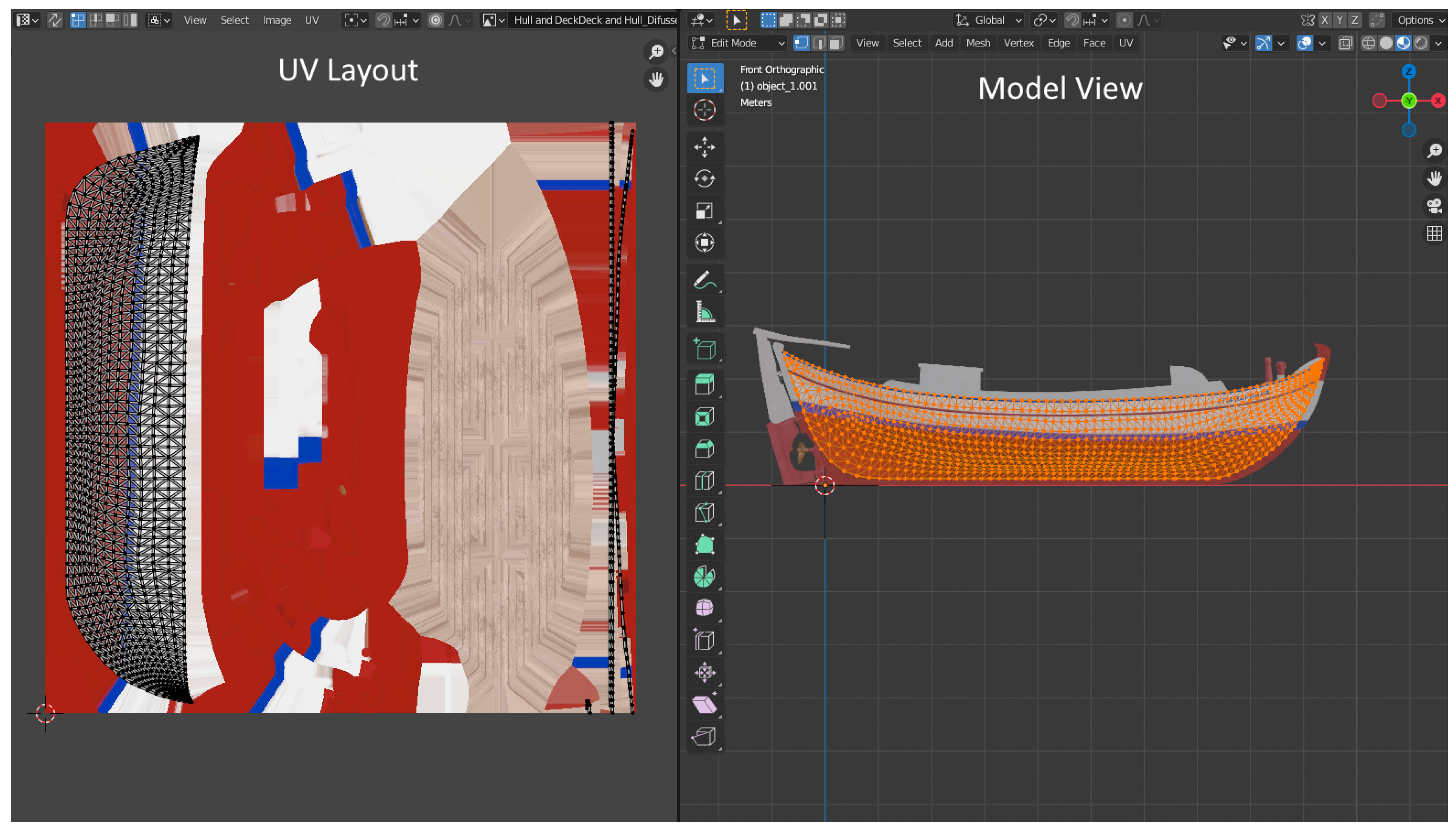
2.3. Texturing
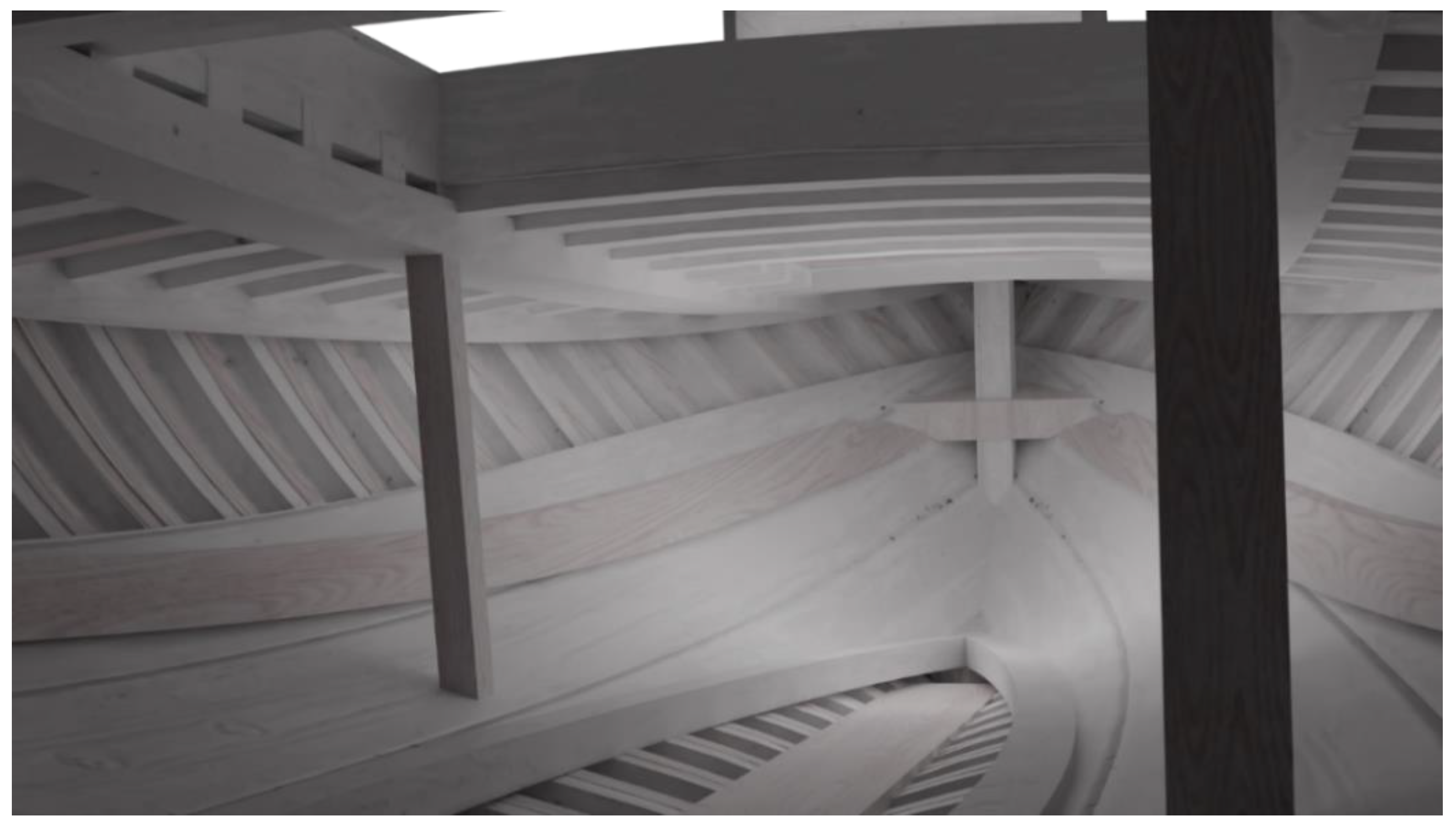
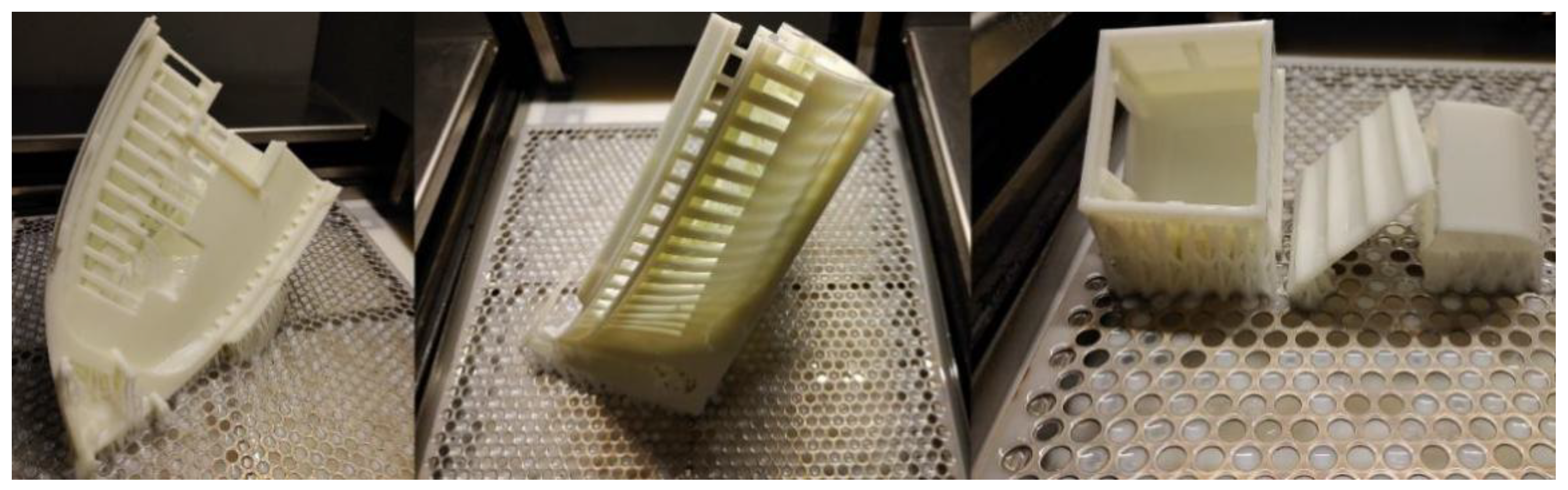
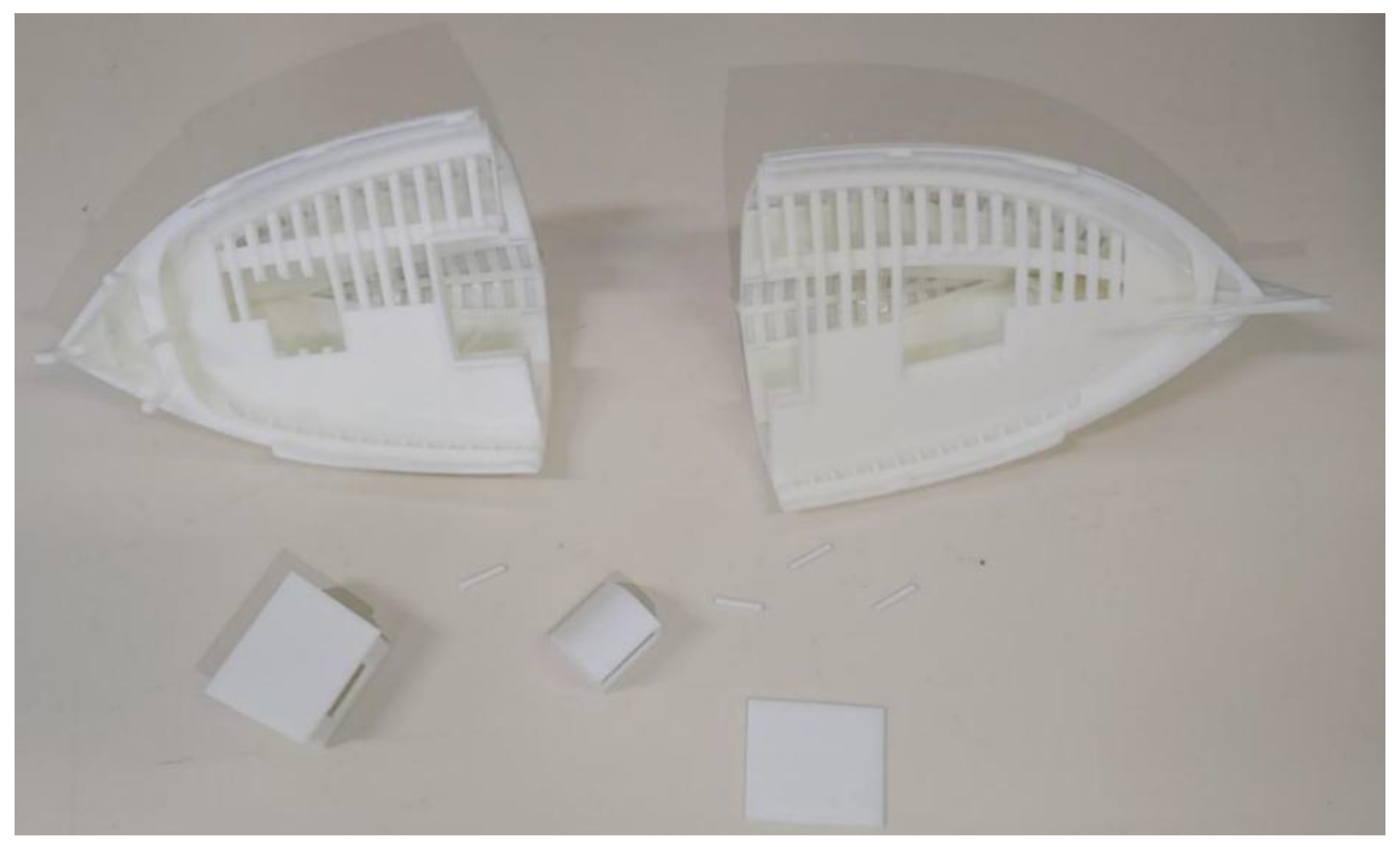
3. 3D Rendering & 3D Printing
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kadi, H.; Anouche, K. Knowledge-based parametric modeling for heritage interpretation and 3D reconstruction. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2020, 19, e00160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagrigorakis, M.J.; Maravelakis, E.; Kyparissi-Apostolika, N.; Stravopodi, E.; Konstantaras, A.; Apostolikas, O.; Toulas, P.; Potagas, C.; Papapolychroniou, T.; Mastoris, M.; et al. An Integrated Study of the Mesolithic Skeleton in Theopetra Cave, Greece: From the Skeleton Analysis to 3D Face Reconstruction. Heritage 2022, 5, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Muñoz, Ó.; Gabrielli, D.A.; Palacín, A.M.; Moga, E.S.; Sánchez-Ortiz, A. 3D Digital Technologies for the Elaboration of a Replica of a Dermatological Didactic Model Belonging to the Olavide Museum from the Original Mould. Heritage 2022, 5, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.F.; McLoughlin, L.; Liarokapis, F.; Peters, C.; Petridis, P.; De Freitas, S. Developing serious games for cultural heritage: A state-of-the-art review. Virtual Real. 2010, 14, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skublewska-Paszkowska, M.; Milosz, M.; Powroznik, P.; Lukasik, E. 3D technologies for intangible cultural heritage preservation—Literature review for selected databases. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remondino, F.; Girardi, S.; Rizzi, A.; Gonzo, L. 3D modeling of complex and detailed cultural heritage using multi-resolution data. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2009, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, E.; Rosen, B. Preserving the maritime cultural heritage of the Mediterranean, a cradle of cultures, religions and civilizations—The holy land perspective. J. Coast. Conserv. 2010, 14, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, G.M.; Fradley, M.; Blue, L.; Breen, C. Establishing a baseline for the study of maritime cultural heritage in the Gaza Strip. Palest. Explor. Q. 2022, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Lagudi, A.; Ritacco, G.; Agrafiotis, P.; Skarlatos, D.; Cejka, J.; Kouril, P.; Liarokapis, F.; Philpin-Briscoe, O.; Poullis, C.; et al. Development and Integration of Digital Technologies Addressed to Raise Awareness and Access to European Underwater Cultural Heritage. An Overview of the H2020 i-MARECULTURE Project. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2017, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Menna, F.; Nocerino, E.; Scamardella, A. Reverse Engineering and 3D Modelling for Digital Documentation of Maritime Heritage. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2011, XXXVIII-5/W16, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colson, A. Digital Documentation of Ships in Cultural Heritage: A European Review. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W5, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, J.P.; Wetherelt, A.; Zazzaro, C.; Eyre, M. From Boatyard to Museum: 3D laser scanning and digital modelling of the Qatar Museums watercraft collection, Doha, Qatar. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2018, 47, 419–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanner, P. 3D laser scanning for the digital reconstruction and analysis of a 16th century clinker built sailing vessel. In ACUA Underwater Archaeology Proceedings; Advisory Council on Underwater Archaeology: Pensacola, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 137–149. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/4948046/3D_Laser_Scanning_for_the_Digital_Reconstruction_and_Analysis_of_a_16th_century_Clinker_Built_Sailing_Vessel (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Afshar, R.; Alavyoon, N.; Ahlgren, A.; Gamstedt, E. Full scale finite element modelling and analysis of the 17th-century warship Vasa: A methodological approach and preliminary results. Eng. Struct. 2021, 231, 111765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlando, G.; Lamera, L.; Guidi, G. Temporary made permanent: Turning temporary exhibitions into fixed memories. In Proceedings of the 2012 18th International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia, Milan, Italy, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liritzis, I.; Volonakis, P.; Vosinakis, S. 3D Reconstruction of Cultural Heritage Sites as an Educational Approach. The Sanctuary of Delphi. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringas, C.; Tasiopoulou, E.; Kaplanidi, D.; Partarakis, N.; Zabulis, X.; Zidianakis, E.; Patakos, A.; Patsiouras, N.; Karuzaki, E.; Foukarakis, M.; et al. Traditional Craft Training and Demonstration in Museums. Heritage 2022, 5, 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Love, P. Digital reproduction of historical building ornamental components: From 3D scanning to 3D printing. Autom. Constr. 2017, 76, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabulis, X.; Partarakis, N.; Meghini, C.; Dubois, A.; Manitsaris, S.; Hauser, H.; Thalmann, N.M.; Ringas, C.; Panesse, L.; Cadi, N.; et al. A Representation Protocol for Traditional Crafts. Heritage 2022, 5, 716–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, G.; Fix, P.; Kennedy, C.; Herbst, J.; Shultz, L.; Borrero, R.; Dostal, C. Integrating digital and conventional recording techniques for the documentation and reconstruction of an 18th-Century wooden ship from Alexandria, VA. Digit. Appl. Archaeol. Cult. Herit. 2020, 16, e00136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragassa, C. Industrialising a Wooden Boat; NAUTECH: Auckland, New Zealand, 2015; Available online: https://www.academia.edu/25809719/Industrialising_a_Wooden_Boat (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Damianidis, K. Vernacular Boats and Boatbuilding in Greece. Ph.D. Thesis, University of St Andrews, St Andrews, UK, 1991. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10023/7116 (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Damianidis, K.; Zivas, A. Trehadiri Boat: An Example of The Greek Shipbuilding Tradition; HOMMEH Publications: Athens, Greece, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Damianidis, K. Greek Traditional Boatbuiding; Cultural Technological Institution ETBA Publications: Athens, Greece, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Intangible Cultural Heritage of Greece: The Craft of Wooden Shipbuilding. Available online: https://ayla.culture.gr/en/xilonaupigiki_wooden_shipbuilding/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Delis, A. Mediterranean Wooden Shipbuilding in the nineteenth century: Production, Productivity and Ship Types in Comparative Perspective. Cah. Méditerranée 2012, 84, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Regulation (EU) No 508/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 May 2014 on the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund and repealing Council Regulations (EC) No. 2328/2003, (EC) No. 861/2006, (EC) No. 1198/2006 and (EC) No. 791/2007 and Regulation (EU) No. 1255/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council; Article 34; European Parliament: Strasbourg, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hellenic Republic: Ministry of Rural Development and Food. Available online: http://www.minagric.gr/index.php/en/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Maritime Tradition Museum. Available online: https://www.maritime-museum.gr/index.php (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Indruszewski, G.; Farin, G.; Razdan, A.; Simon, A.; Van Alfen, D.; Rowe, J. Application of 3D Modeling in Ship Reconstruction and Analysis: Tools and Techniques. 2004. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/3270023/APPLICATION_OF_3D_MODELING_IN_SHIP_RECONSTRUCTION_AND_ANALYSIS_TOOLS_AND_TECHNIQUES (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- What Are Points Clouds? Available online: https://tech27.com/resources/point-clouds/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Green Maritime Technology—GMT. Available online: https://gmtech.gr/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- FARO Focus Premium. Available online: https://www.faro.com/en/Products/Hardware/Focus-Laser-Scanners/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Digital Capture of a Traditional Boat Maria Pagida. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHWqGUwXgiE (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- What Is Autodesk Recap? Available online: https://www.chetu.com/blogs/construction/what-is-autodesk-recap-digital-simulation-for-business.php (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Software Tools for Managing E57 Files. Available online: http://www.libe57.org/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Rhinoceros [Computer Software]. 2021. Available online: https://www.rhino3d.com (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Piegi, L.; Tiller, W. The NURBS Book; Springer Publications: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Are NURBS? Available online: https://www.rhino3d.com/features/nurbs/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Zebra|Rhino3D—Modeling. Available online: https://docs.mcneel.com/rhino/6/help/en-us/commands/zebra.htm (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Van Lammeren, W.P.A.; Van Manen, J.D.; Oosterveld, M.W.C. The Wageningen B-Screw Series; The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine: Washington, DC, USA, 1969; Volume 77, 43p, Available online: https://trid.trb.org/view/354 (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Arapakopoulos, A.; Polichshuk, R.; Segizbayev, Z.; Ospanov, S.; Ginnis, A.; Kostas, K. Parametric models for marine propellers. Ocean Eng. 2019, 192, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retopology. Available online: http://people.wku.edu/joon.sung/edu/anim/3d/modeling/retopology/retopology.html (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Rhinoceros Help—QuadRemesh. Available online: https://docs.mcneel.com/rhino/7/help/en-us/index.htm#commands/quadremesh.htm (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Blender. Available online: http://www.blender.org (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Adobe Substance 3D Painter. Available online: https://www.adobe.com/products/substance3d-painter.html (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Liaskos, O.; Mitsigkola, S.; Arapakopoulos, A.; Papatzanakis, G.; Ginnis, A.; Papadopoulos, C.; Peppa, S.; Remoundos, G. Development of the Virtual Reality Application: “The Ships of Navarino”. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycles Open Source Production Rendering. Available online: https://www.cycles-renderer.org/about/ (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Stereolithography/SLA 3D Printing—Simply Explained|All3DP. Available online: https://all3dp.com/2/stereolithography-3d-printing-simply-explained/ (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- ZRapid Tech-Innovator of 3D Printing Technologies. Available online: http://www.zero-tek.com/en/sla300.html (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Zguris, Z. How Mechanical Properties of Stereolithography 3D Prints Are Affected by UV Curing. Available online: https://formlabs.com/ (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- E-Navs.eu: Digital Repository. Available online: https://e-navs.eu/repository-2/?lang=en (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- WebGL: 2D and 3D Graphics for the Web. Available online: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebGL_API (accessed on 4 May 2022).









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arapakopoulos, A.; Liaskos, O.; Mitsigkola, S.; Papatzanakis, G.; Peppa, S.; Remoundos, G.; Ginnis, A.; Papadopoulos, C.; Mazis, D.; Tsilikidis, O.; et al. 3D Reconstruction & Modeling of the Traditional Greek Trechadiri: “Aghia Varvara”. Heritage 2022, 5, 1295-1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5020067
Arapakopoulos A, Liaskos O, Mitsigkola S, Papatzanakis G, Peppa S, Remoundos G, Ginnis A, Papadopoulos C, Mazis D, Tsilikidis O, et al. 3D Reconstruction & Modeling of the Traditional Greek Trechadiri: “Aghia Varvara”. Heritage. 2022; 5(2):1295-1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleArapakopoulos, Andreas, Orestis Liaskos, Sofia Mitsigkola, Georgios Papatzanakis, Sofia Peppa, Georgios Remoundos, Alexandros Ginnis, Christos Papadopoulos, Dimitrios Mazis, Odysseas Tsilikidis, and et al. 2022. "3D Reconstruction & Modeling of the Traditional Greek Trechadiri: “Aghia Varvara”" Heritage 5, no. 2: 1295-1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5020067
APA StyleArapakopoulos, A., Liaskos, O., Mitsigkola, S., Papatzanakis, G., Peppa, S., Remoundos, G., Ginnis, A., Papadopoulos, C., Mazis, D., Tsilikidis, O., & Yighourtakis, Y. (2022). 3D Reconstruction & Modeling of the Traditional Greek Trechadiri: “Aghia Varvara”. Heritage, 5(2), 1295-1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage5020067





