Textile Dyes from Gokstad Viking Ship’s Grave
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Analytical Procedures
2.2.1. EDTA/DMF Procedure
2.2.2. DMSO Extraction
2.2.3. HCl/MeOH Procedure
2.3. Instrumentation
2.3.1. HPLC-DAD
2.3.2. HPLC-ESI-Q-ToF System
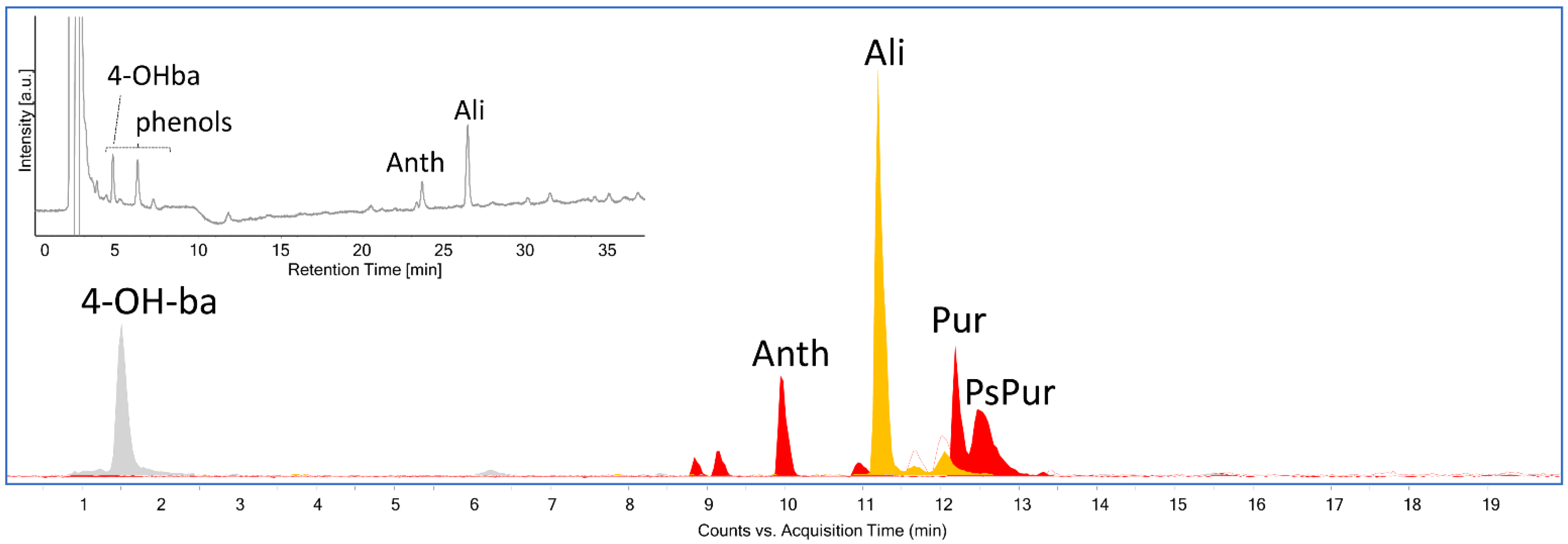
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardon, D. Natural Dyes. In Sources, Tradition, Technology and Science; Archetype: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Skre, D. Viking-Age Economic Transformations. The West-Scandinavian Case. In Viking-Age Transformations: Trade, Craft and Resources in Western Scandinavia; Glørstad, Z.T., Loftsgarden, K., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sindbæk, S. Urbanism and Exchange in the North Atlantic/Baltic, 600–1000 ce. In The Routledge Handbook of Archaeology and Globalization; Hodos, T., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 553–565. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, E.A. Tools and Textiles—Production and Organisation in Birka and Hedeby. In Proceedings of the XVI Viking Congress, Reykjavík, Iceland, 14–23 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vedeler, M. Silk for the Vikings; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Berghe, I.; Gleba, M.; Mannering, U. Towards the Identification of Dyestuffs in Early Iron Age Scandinavian Peat Bog Textiles. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton Rogers, P. Dyes and Wools in Iron Age Textiles from Norway and Denmark. J. Dan. Archaeol. 1988, 7, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton Rogers, P. Dyes of the Viking Age: A Summary of Recent Work. In Dyes in History and Archaeology; Walton, P., Ed.; Pangur Press: York, UK, 1988; Volume 7, pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Walton Rogers, P. Cordage and Raw Fibre from 16–22 Coppergate; Addyman, P.V., Ed.; The Archaeology of York: York, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Berghe, I.; Gleba, M.; Mannering, U. Dyes: To Be or Not to Be. An Investigation of Early Iron Age Dyes in Danish Peat Bog Textiles. In Proceedings of the North European Symposium for Archaeological Textiles X, Copenhagen, Denmark, 14–17 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hofenk de Graaf, J. The Colourful Past: Origins, Chemistry and Identification of Natural Dyestuffs; Archetype Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2004.
- Nicolaysen, N. Langskibet Fra Gokstad Ved Sandefjord; Cammermeyer, A., Ed.; Kristiania: Oslo, Norway, 1882. [Google Scholar]
- Nockert, M. Silkebroderi. In Tekstilene, Osebergfunnet Bind Iv; Christensen, E.A., Nockert, M., Eds.; Kulturhistorisk: Oslo, Norway, 2006; pp. 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Vedeler, M. Golden Textiles from Gokstad. Archaeol. Text. Rev. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hougen, B. Gulltråd Fra Gokstadfunnet. Et Fragment. In Honos Ella Kivikoski; Sarvas, P., Kivikoski, E., Siiriäinen, A., Eds.; Finska Fornminnesföreningen; Suomen Muinaismuistoyhdistys: Helsinki, Finland, 1973; pp. 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ingstad, A.S. Archaeological Textiles: Textiles from Oseberg, Gokstad and Kaupang. In Archaeological Textiles: 2nd NESAT Symposium: Report; Københavns Universitet Arkaeologisk Institut: Kobenhavn, Denmark, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Vedeler, M. Reconstructing the Tunic from Lendbreen in Norway. Archaeol. Text. Rev. 2017, 59, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Vasileiadou, A.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Zotou, A. Development and Validation of a Liquid Chromatographic Method with Diode Array Detection for the Determination of Anthraquinones, Flavonoids and Other Natural Dyes in Aged Silk. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degano, I. Liquid Chromatography: Current Applications in Heritage Science and Recent Developments. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degano, I.; La Nasa, J. Trends in High Performance Liquid Chromatography for Cultural Heritage. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauk, V.; Barták, P.; Lemr, K. Characterization of Natural Organic Colorants in Historical and Art Objects by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3393–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, D. Investigating Asian Colourants in Chinese Textiles from Dunhuang (7th–10th Century Ad) by High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry—Towards the Creation of a Mass Spectra Database. Dyes Pigm. 2019, 163, 454–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lech, K.; Fornal, E. A Mass Spectrometry-Based Approach for Characterization of Red, Blue, and Purple Natural Dyes. Molecules 2020, 25, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otłowska, O.; Ślebioda, M.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Karczewski, J.; Śliwka-Kaszyńska, M. Chromatographic and Spectroscopic Identification and Recognition of Natural Dyes, Uncommon Dyestuff Components, and Mordants: Case Study of a 16th Century Carpet with Chintamani Motifs. Molecules 2018, 23, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degano, I.; Mattonai, M.; Sabatini, F.; Colombini, M.P. A Mass Spectrometric Study on Tannin Degradation within Dyed Woolen Yarns. Molecules 2019, 24, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirok, J.B.W.; den Uijl, M.J.; Moro, G.; Berbers, S.V.J.; Croes, C.J.M.; van Bommel, M.R.; Schoenmakers, P.J. Characterization of Dye Extracts from Historical Cultural-Heritage Objects Using State-of-the-Art Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry with Active Modulation and Optimized Shifting Gradients. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3062–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valianou, L.; Karapanagiotis, I.; Chryssoulakis, Y. Comparison of Extraction Methods for the Analysis of Natural Dyes in Historical Textiles by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2175–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, J.; Grzywacz, C.M.; Claro, A. A Comparative Investigation of Hydrolysis Methods to Analyze Natural Organic Dyes by Hplc-Pda—Nine Methods, Twelve Biological Sources, Ten Dye Classes, Dyed Yarns, Pigments and Paints. Stud. Conserv. 2011, 56, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyova, J. Mild Extraction of Dyes by Hydrofluoric Acid in Routine Analysis of Historical Paint Micro-Samples. Microchim. Acta 2008, 162, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Laursen, R.A. Development of Mild Extraction Methods for the Analysis of Natural Dyes in Textiles of Historical Interest Using Lc-Diode Array Detector-Ms. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, Z.C. Archaeo-Chemical Analysis of Royal Purple on a Darius I Stone Jar. Microchim. Acta 2008, 162, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degano, I.; Lucejko, J.J.; Colombini, M.P. The Unprecedented Identification of Safflower Dyestuff in a 16th Century Tapestry through the Application of a New Reliable Diagnostic Procedure. J. Cult. Herit. 2011, 12, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhita, A.; Ferreira, T.; Candeias, A.; Dias, C.B. Extracting Natural Dyes from Wool—an Evaluation of Extraction Methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilillo, M.; Restivo, A.; Degano, I.; Ribechini, E.; Colombini, M.P. Gc/Ms Investigations of the Total Lipid Fraction of Wool: A New Approach for Modelling the Ageing Processes Induced by Iron-Gallic Dyestuffs on Historical and Archaeological Textiles. Microchem. J. 2015, 118, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serjeant, R.B. Material for a History of Islamic Textiles up to the Mongol Conquest. Ars Islamica 1942, 9, 54–92. [Google Scholar]
- Skals, I. Identifikation Af Textilfibre Fra Gokstad-Fundet; Nationalmuseet i København: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]

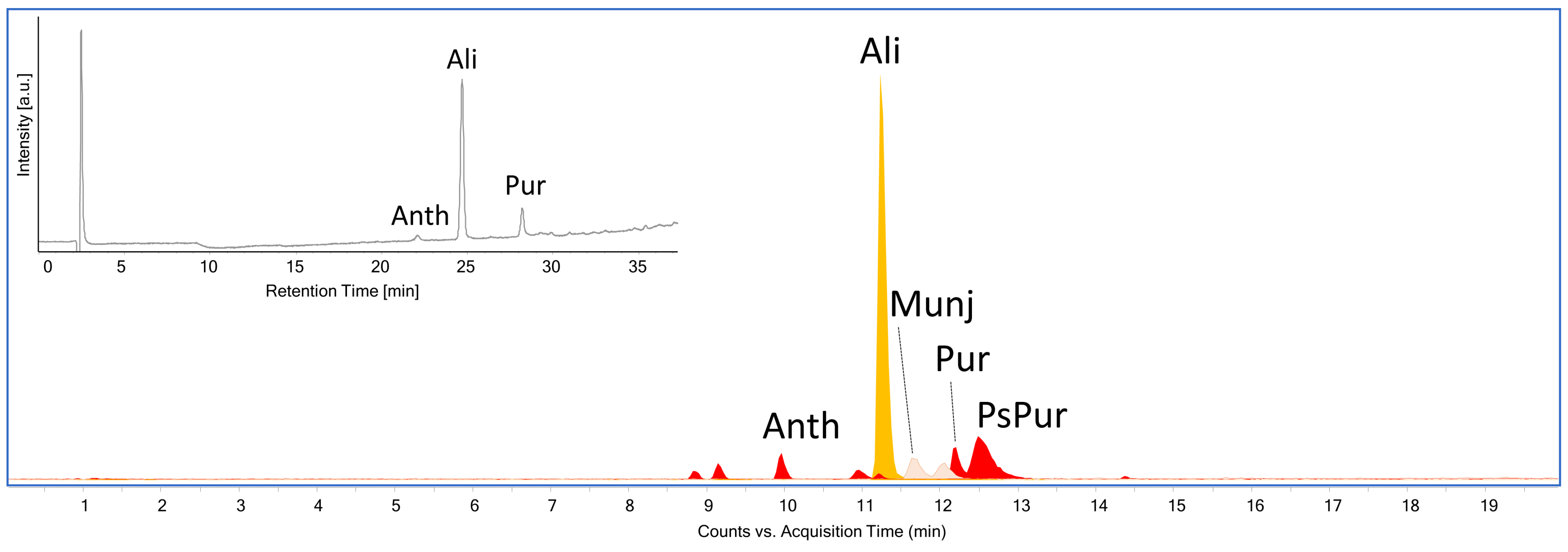
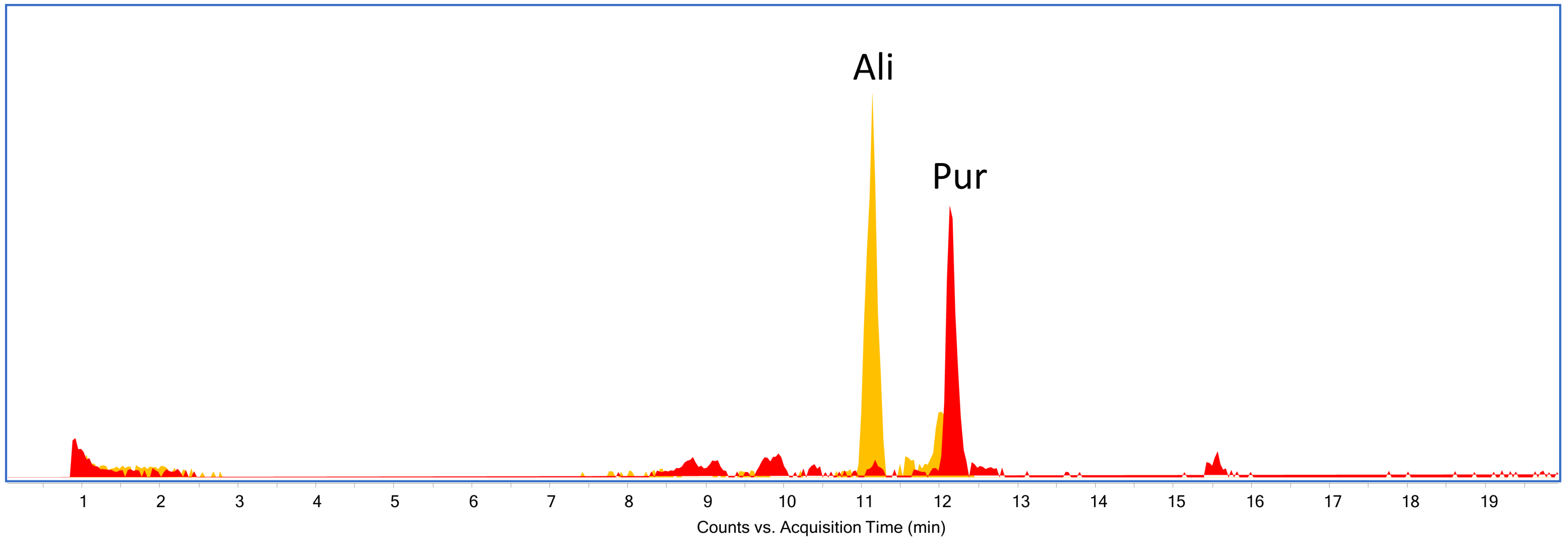
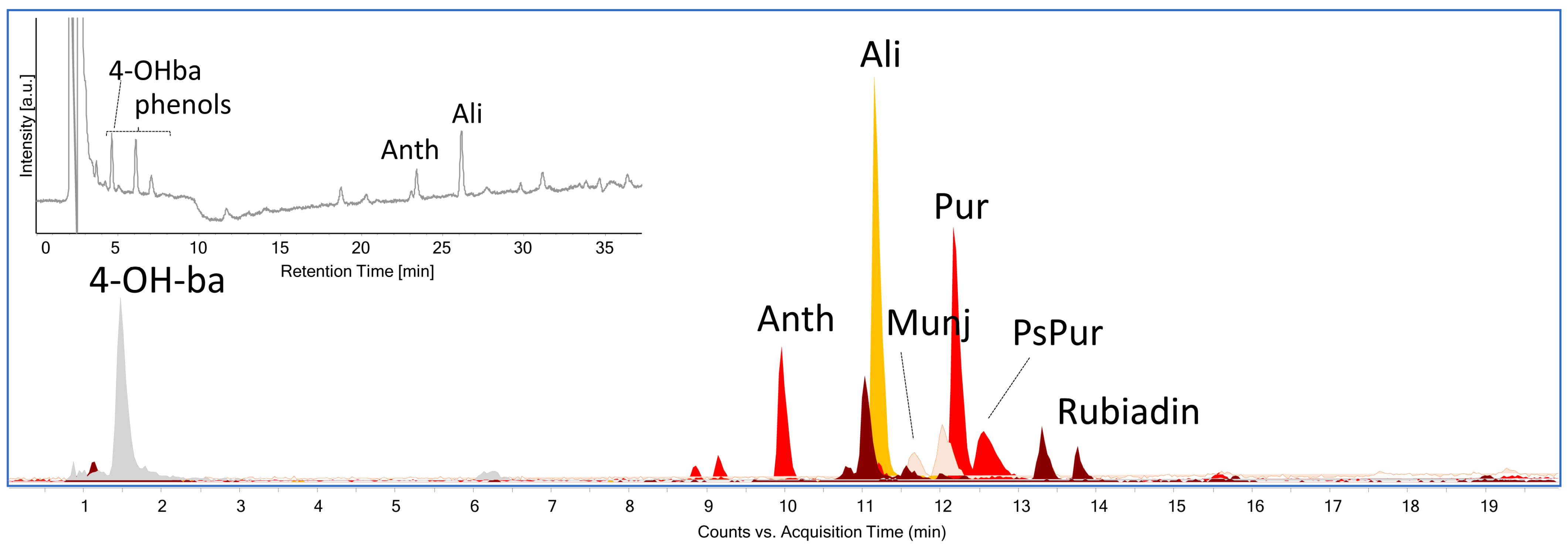
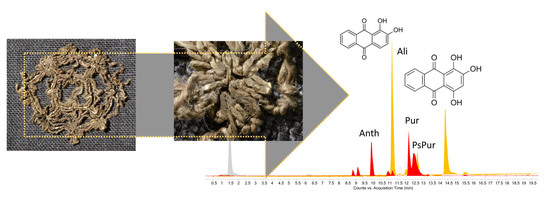
| Sample | Color | N° in Gokstad Collection | Description | Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Red/brown | C10389/37C | Ship’s tent | EDTA/DMF and HCl/MeOH + AcOEt extraction |
| S2 | Yellow (white?) | C10389/37C | Ship’s tent | DMSO and HCl/MeOH + AcOEt extraction |
| S3 | Red (red silk?) | C10459/b | Red thread silk embroidery | EDTA/DMF and HCl/MeOH + AcOEt on the residue (both fractions injected together) |
| S4 | Red (golden silk?) | C10459/b | Golden thread silk embroidery | EDTA/DMF and HCl/MeOH + AcOEt on the residue (both fractions injected together) |
| Sample | Molecular Markers Detected by HPLC-DAD | Molecular Markers Detected by HPLC-ESI-Q-ToF MS | Identified Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | alizarin, purpurin, anthragallol | alizarin, purpurin, pseudopurpurin, munjistin, anthragallol | madder-type dyestuff |
| S2 | no peak identified | alizarin, purpurin | madder-type dyestuff |
| S3 | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, phenols, anthragallol, alizarin | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, anthragallol, alizarin, purpurin, pseudopurpurin, rubiadin | madder-type dyestuff; degradation products of protein-based fibers |
| S4 | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, phenols, anthragallol, alizarin | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, anthragallol, alizarin, purpurin, pseudopurpurin | madder-type dyestuff; degradation products of protein-based fibers |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łucejko, J.J.; Vedeler, M.; Degano, I. Textile Dyes from Gokstad Viking Ship’s Grave. Heritage 2021, 4, 2278-2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030129
Łucejko JJ, Vedeler M, Degano I. Textile Dyes from Gokstad Viking Ship’s Grave. Heritage. 2021; 4(3):2278-2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030129
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁucejko, Jeannette Jacqueline, Marianne Vedeler, and Ilaria Degano. 2021. "Textile Dyes from Gokstad Viking Ship’s Grave" Heritage 4, no. 3: 2278-2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030129
APA StyleŁucejko, J. J., Vedeler, M., & Degano, I. (2021). Textile Dyes from Gokstad Viking Ship’s Grave. Heritage, 4(3), 2278-2286. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030129