Monte Carlo Simulations of ED-XRF Spectra as an Authentication Tool for Nuragic Bronzes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
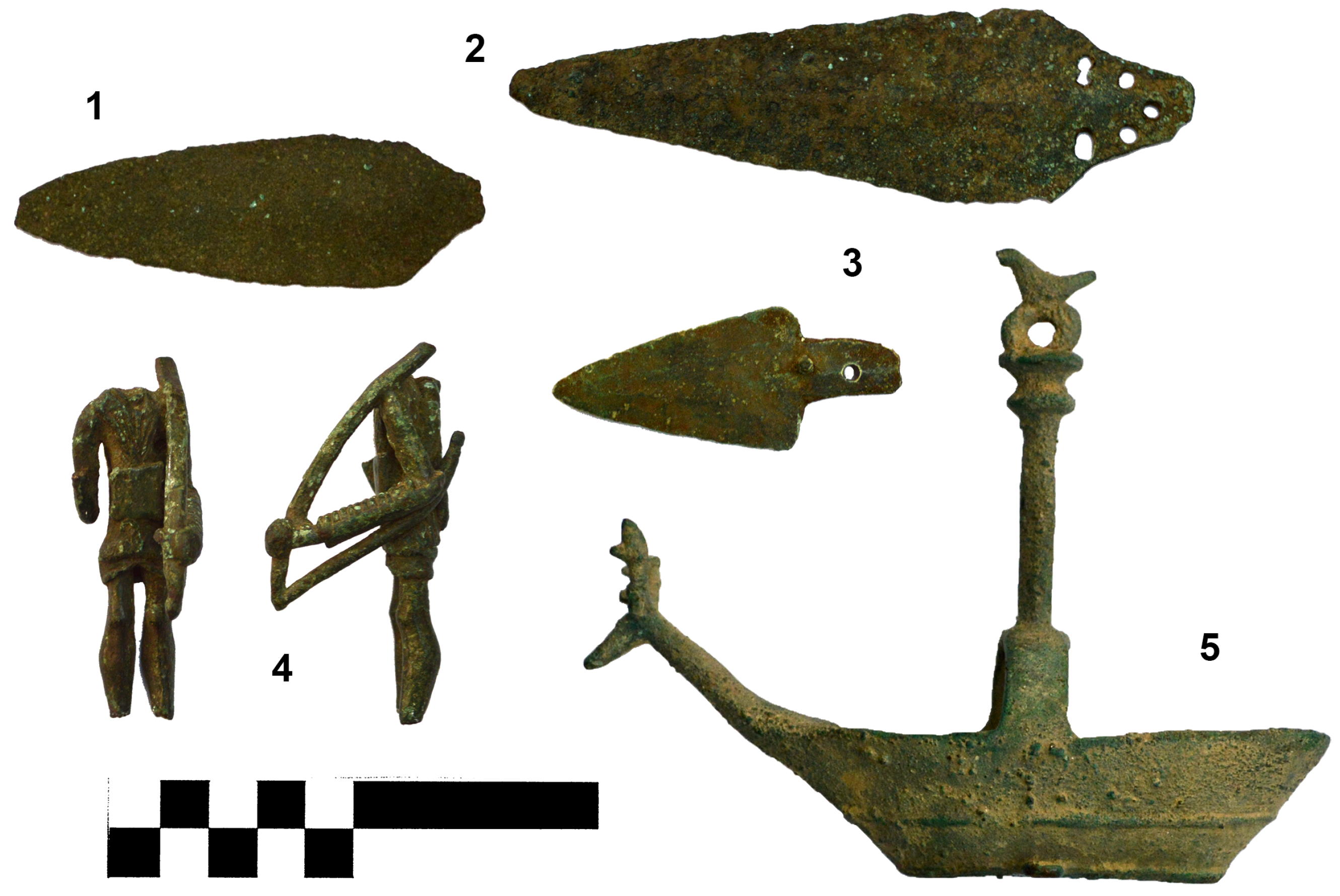
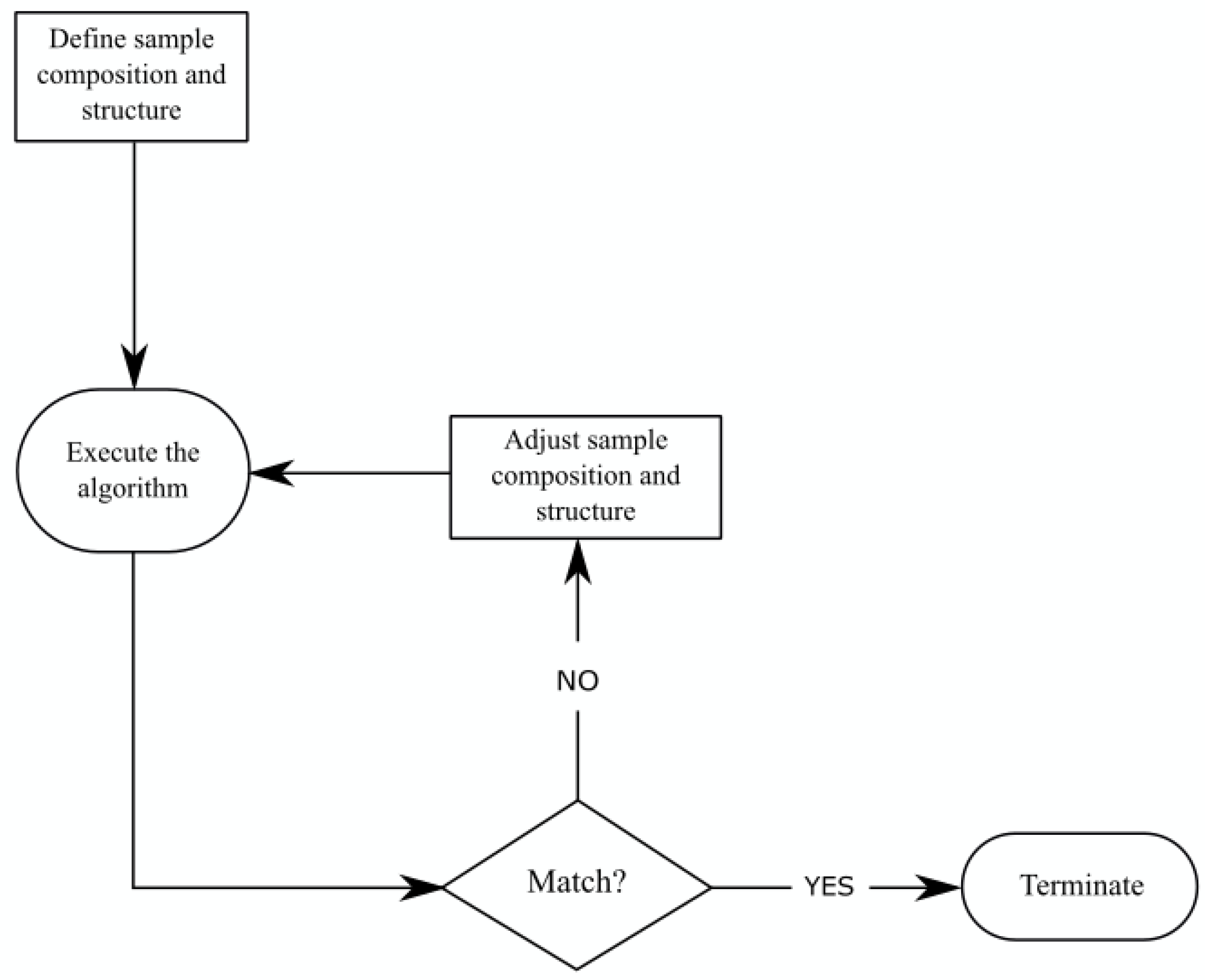
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
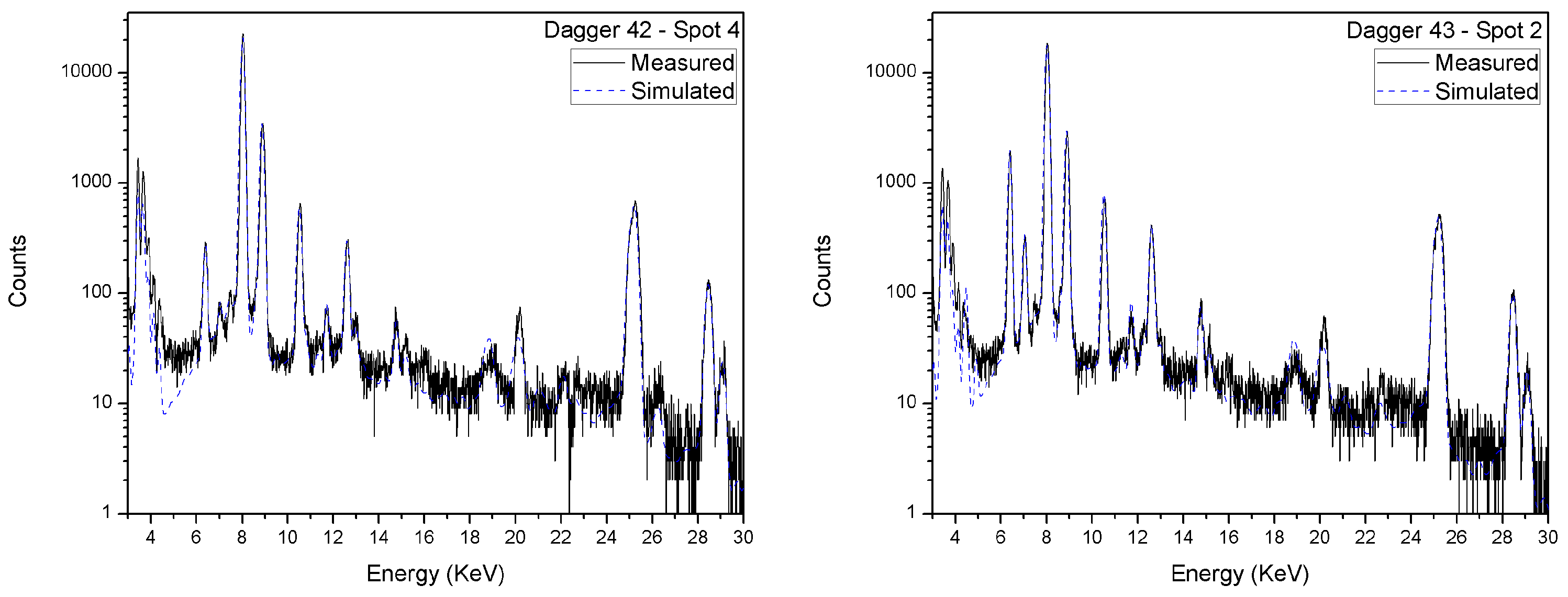
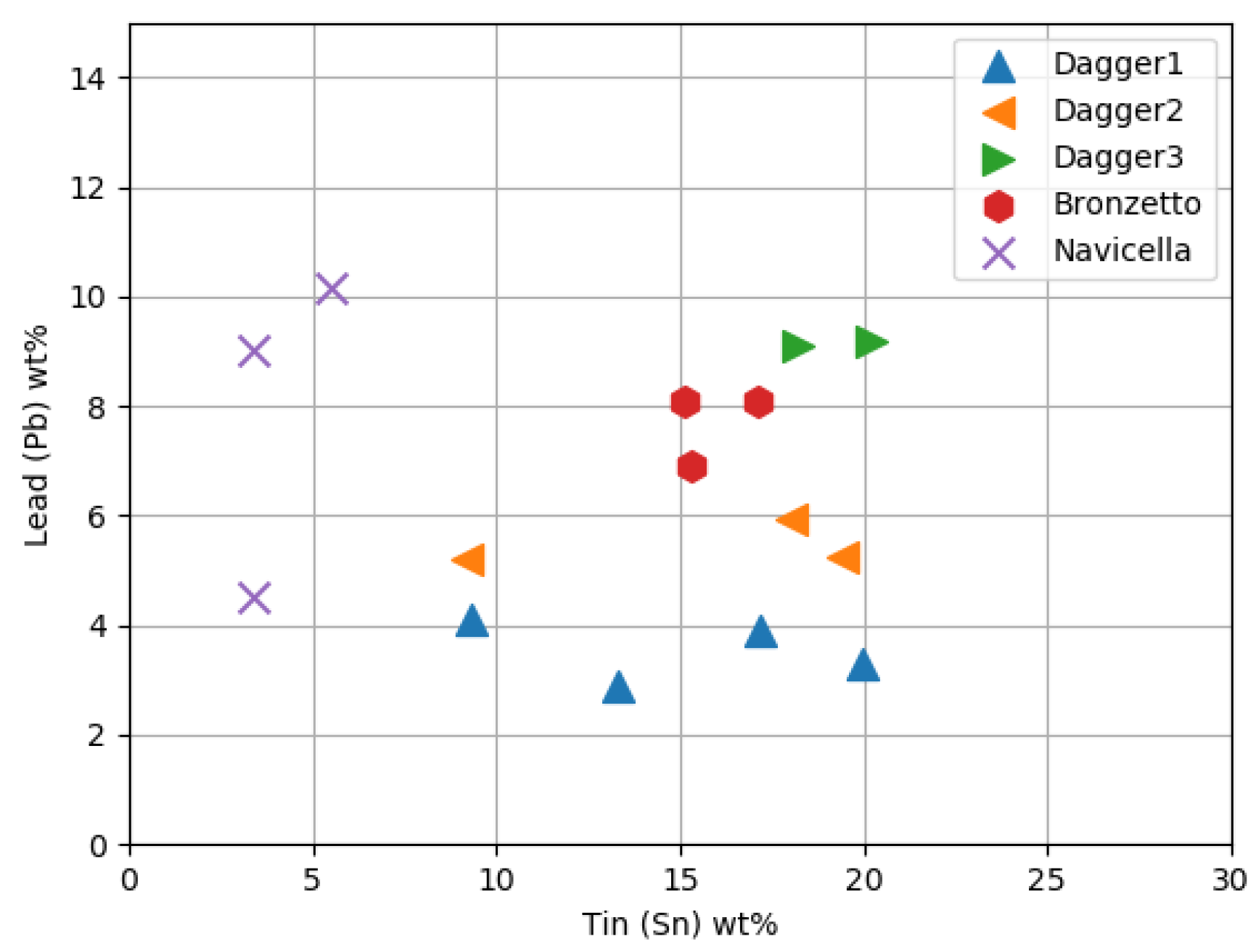
3.1. Daggers
3.2. Bronzetto
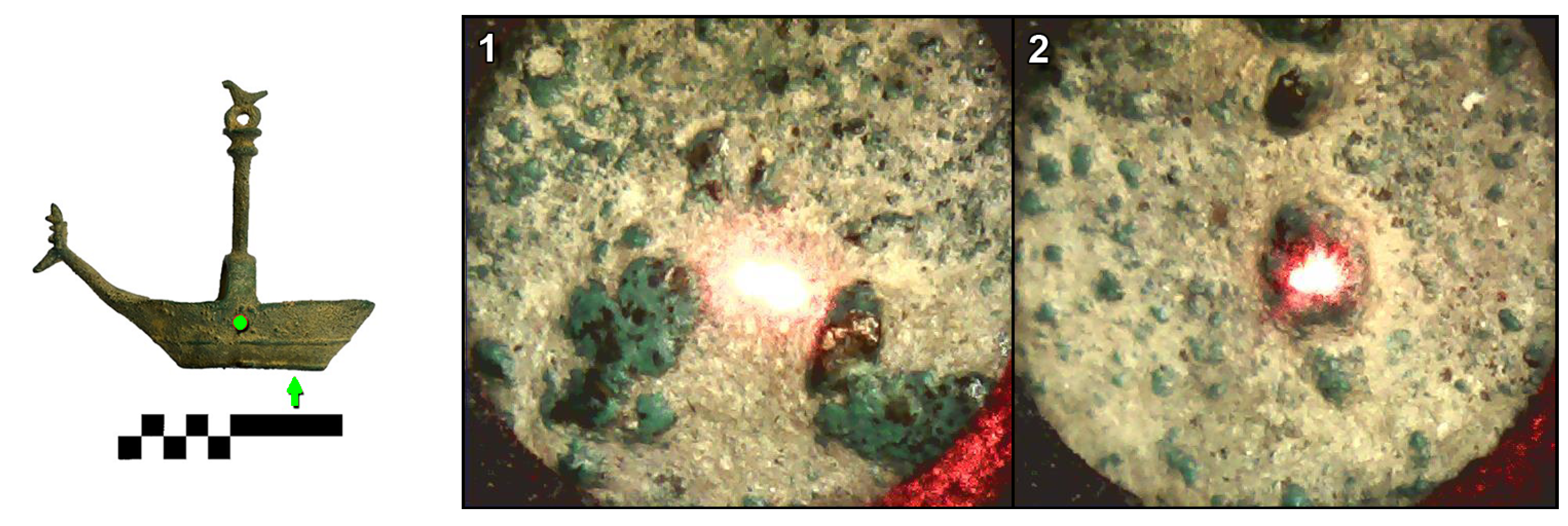
3.3. Navicella
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becker, M.J. Sardinia and the Mediterranean copper trade: Political development and colonialism in the Bronze Age. Anthropology 1980, 4, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Balmuth, M.S.; Tylecote, R. Ancient Copper and Bronze in Sardinia: Excavation and Analysis. J. Field Archaeol. 1976, 3, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depalmas, A.; Melis, R.T. The Nuragic People: Their Settlements, Economic Activities and Use of the Land, Sardinia, Italy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, T.M.A.; Mauro, P.; Alessandro, U. Il Tempo dei Nuraghi. La Sardegna dal XVIII all’VIII Secolo aC; Ilisso: Nuoro, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Schiavo, F.; Atzeni, C.; Nazionale Delle Ricerche, C.; di Cagliari, U. Archaeometallurgy in Sardinia: From the Origins to the Beginning of the Early Iron Age; Monographies Instrumentum; Edition M. Mergoil: Drémil-Lafage, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moravetti, A.; Alba, E.; Foddai, L. La Sardegna Nuragica: Storia e Materiali; Regione Autonoma della Sardegna C. Delfino: Cagliari, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavon, N.; de Palmas, A.; Bulla, C.; Piga, G.; Brunetti, A. An Energy-Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry and Monte Carlo simulation study of Iron-Age Nuragic small bronzes (“Navicelle”) from Sardinia, Italy. Spectrochim. Acta Part At. Spectrosc. 2016, 123, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stos-Gale, Z.A.; Maliotis, G.; Gale, N.H.; Annetts, N. Lead isotope characteristics of the cyprus copper ore deposits applied to provenance studies of copper oxide ingots. Archaeometry 1997, 39, 83–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.F. The Study of the Characterisation and Provenance of Coins and Other Metalwork Using XRF, PIXE and Activation Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 378–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, E.; Araújo, M.F.; Silva, R.J.; Vilaça, R. Characterisation of a Proto-historic bronze collection by micro-EDXRF. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2013, 296, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiola, L.; Blengino, J.M.; Fiaud, C. Morphology and mechanisms of formation of natural patinas on archaeological Cu–Sn alloys. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 2083–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesareo, R.; Rizzutto, M.A.; Brunetti, A.; Rao, D.V. Metal location and thickness in a multilayered sheet by measuring kα/Kβ, Lα/Lβ and Lα/Lγ X-ray ratios. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2009, 267, 2890–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesareo, R.; Brunetti, A.; D’Oriano, R.; Canu, A.; Demontis, G.M.; Celauro, A. A Roman bronze statuette with gilded silver mask from Sardinia: An EDXRF study. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos Lins, S.A.; Gigante, G.E.; Cesareo, R.; Ridolfi, S.; Brunetti, A. Testing the Accuracy of the Calculation of Gold Leaf Thickness by MC Simulations and MA-XRF Scanning. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottigli, U.; Brunetti, A.; Golosio, B.; Oliva, P.; Stumbo, S.; Vincze, L.; Randaccio, P.; Bleuet, P.; Simionovici, A.; Somogyi, A. Voxel-based Monte Carlo simulation of X-ray imaging and spectroscopy experiments. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2004, 59, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosio, B.; Schoonjans, T.; De Nolf, W. XRMC Source Code. Available online: https://github.com/golosio/xrmc/wiki (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Brunetti, A.; Sanchez Del Rio, M.; Golosio, B.; Simionovici, A.; Somogyi, A. A library for X-ray-matter interaction cross sections for X-ray fluorescence applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2004, 59, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Fabian, J.; La Torre, C.W.; Schiavon, N. A combined XRF/Monte Carlo simulation study of multilayered Peruvian metal artifacts from the tomb of the Priestess of Chornancap. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Depalmas, A.; di Gennaro, F.; Serges, A.; Schiavon, N. X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and Monte Carlo characterization of a unique nuragic artifact (Sardinia, Italy). Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2016, 121, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessanha, S.; Manso, M.; Antunes, V.; Carvalho, M.; Sampaio, J. Monte Carlo simulation of portable X-ray fluorescence setup: Non-invasive determination of gold leaf thickness in indo-Portuguese panel paintings. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2019, 156, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonjans, T.; Solé, V.A.; Vincze, L.; Sanchez del Rio, M.; Appel, K.; Ferrero, C. A general Monte Carlo simulation of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometers—Part 6. Quantification through iterative simulations. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2013, 82, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottaini, C.; Brunetti, A.; Bordalo, R.; Valera, A.; Schiavon, N. Non-destructive characterization of archeological Cu-based artifacts from the early metallurgy of southern Portugal. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2018, 10, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craddock, P.T. The composition of the copper alloys used by the Greek, etruscan and Roman civilisations: 2. The Archaic, Classical and Hellenistic Greeks. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1977, 4, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingo, G.M.; de Caro, T.; Riccucci, C.; Angelini, E.; Grassini, S.; Balbi, S.; Bernardini, P.; Salvi, D.; Bousselmi, L.; Çilingiroglu, A.; et al. Large scale investigation of chemical composition, structure and corrosion mechanism of bronze archeological artefacts from Mediterranean basin. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 83, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, N.; Celauro, A.; Manso, M.; Brunetti, A.; Susanna, F. Iron-Age bronze statuettes in Southern Portugal: Combining archaeological data with EDXRF and BSEM + EDS to assess provenance and production technology. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Golosio, B.; Schoonjans, T.; Oliva, P. Use of Monte Carlo simulations for cultural heritage X-ray fluorescence analysis. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2015, 108, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilliu, G. Sculture Della SARDEGNA Nuragica; Ilisso: Nuoro, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Minoja, M.; Salis, G.; Usai, L. L’isola Delle Torri: Giovanni Lilliu e La Sardegna Nuragica: Catalogo Della Mostra; Carlo Delfino Editore: Cagliari, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Melis, P. The Nuragic Civilization; Carlo Delfino Editore: Sassari, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Depalmas, A. Le Navicelle di Bronzo Della Sardegna Nuragica; Ettore Gasperini Editore Società Poligrafica Sarda: Cagliari, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta, M.; Catelli, E.; Prati, S.; Sciutto, G.; Mazzeo, R. Chinese archaeological artefacts: Microstructure and corrosion behaviour of high-leaded bronzes. J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, A. A diachronic study of Cypriot copper alloy artefacts. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 7, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caro, T. The ancient metallurgy in Sardinia (Italy) through a study of pyrometallurgical materials found in the archaeological sites of Tharros and Montevecchio (West Coast of Sardinia). J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 28, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nocco, C.; Brunetti, A.; Barcellos Lins, S.A. Monte Carlo Simulations of ED-XRF Spectra as an Authentication Tool for Nuragic Bronzes. Heritage 2021, 4, 1912-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030108
Nocco C, Brunetti A, Barcellos Lins SA. Monte Carlo Simulations of ED-XRF Spectra as an Authentication Tool for Nuragic Bronzes. Heritage. 2021; 4(3):1912-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030108
Chicago/Turabian StyleNocco, Carlo, Antonio Brunetti, and Sergio Augusto Barcellos Lins. 2021. "Monte Carlo Simulations of ED-XRF Spectra as an Authentication Tool for Nuragic Bronzes" Heritage 4, no. 3: 1912-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030108
APA StyleNocco, C., Brunetti, A., & Barcellos Lins, S. A. (2021). Monte Carlo Simulations of ED-XRF Spectra as an Authentication Tool for Nuragic Bronzes. Heritage, 4(3), 1912-1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage4030108







