Abstract
Aloe Vera leaves have great potential as an economic supplement with an adequate nutritional profile. The current study aimed to fortify plain (loaf) cakes with Aloe Vera leaf gel (AVG) powder. AVG was freeze-dried to produce Aloe Vera powder (ALP), and four plain (loaf) cakes were prepared with different proportions of ALP (0, 4, 6, and 8%). ALP contained significantly (p < 0.05) more protein (22.23 vs. 12.24), ash (19.83 vs. 0.64), and iron (175 vs. 3.05) than refined wheat flour (RWF). Along with total polyphenols and total flavonoids, ALP demonstrated good antioxidant activity. ALP-cakes and RWF-cakes were also evaluated for their nutritional and functional properties. The addition of 6 and 8% ALP to the formulation increased total polyphenols, total flavonoids, and antioxidant activity in plain (loaf) cakes. Hardness and chewiness increased in ALP-cakes but decreased in RWF-cakes, while cohesiveness and springiness decreased in ALP-cakes. In conclusion, the best formulation was a 4% ALP incorporated cake, and ALP can be supplemented in plain cakes at a rate of up to 8% to improve nutrient value. This is the first study to evaluate the quality characteristics of fortified plain (loaf) cakes using ALP.
1. Introduction
Aloe Vera has long been recognized as a natural product and has been well known for its herbal, medicinal, beauty, and skin care properties for centuries [1]. The plant has three-sided fleshy leaves, yellow flowers, and fruits containing many seeds. The Aloe Vera leaf contains 75 potentially active elements, including vitamins, minerals, enzymes, lignin, saponins and amino acids, etc. [2]. Because of these characteristics, it is one of the most nutrient-dense plants ever discovered. For this variety of benefits, it is widely used in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. It can also be used as natural additives and preservatives in foods [3,4].
Bakery items such as bread, cakes, cookies, etc., are consumed on a daily basis in vast amounts across the world and play an important role in human nutrition [5]. Among the different bakery products, cake is a popular and palatable item that is consumed and favored by people of all ages. Cakes have different shapes, colors, flavors, and sizes. Products have been made using a few basic ingredients, including flour, sugar, baking powder, eggs, butter, etc. [5]. Aloe Vera has the potential to be used as a biopreservative in a variety of food products such as bakery, beverage, confectionary, and dairy, among others. It acts as an enhancer of food quality parameters. It also acts as a hydrocolloid that further helps to confirm the rheological properties and texture of food products [6]. A study mentioned the use of Aloe Vera gel as a fat substitute in the preparation of low fat cream cakes as a healthy option for overweight and obese people [7].
Wheat flour is one of the main ingredients used for the production of cake. The use and fortification of wheat flour is of great importance to modern food science and technology. When wheat flour is replaced with other functional ingredients, the quantitative and qualitative properties of the final baked product change, influencing functional properties such as increased water holding, thickening, texturizing, gel forming, and stabilizing capacities [8,9,10,11,12]. The partial or complete substitution of wheat flour is always desirable to improve the nutritional value of the product as well as health concern. Wheat flour contains gluten, and this gluten is responsible for celiac disease [13]. Celiac disease is caused by the presence of highly immunogenic gliadins in gluten. Nonceliac gluten sensitivity, such as innate immune response, disappears in patients after gluten is removed from their diets [13]. Celiac disease patients are advised to limit or avoid gluten consumption. Substituting Aloe Vera powder for wheat flour reduces gluten content while increasing nutrient content in cakes. The current study aimed to partially replace wheat flour with Aloe Vera leaves powder (ALP) due to the presence of several potential active elements in the ALP. Aloe Vera leaves have an abundance of catechin, lignin, saponins, sinapic acid and quercitrin. Research revealed that Aloe Vera leaves showed antioxidant, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities along with anticancer effect of aloe-emodin (anthroquinone) compound [14,15,16]. Substitution of wheat flour with Aloe Vera leaves powder (ALP) boosts the functional and nutritional properties of bakery products such as cakes. Aloe Vera leaves powder (ALP) can be obtained after the grinding of the aloe gel [17]. Considering all nutritional components, ALP can be considered a fine substitute for a small proportion of wheat flour in the production and manufacturing of plain cakes. Ayo-Omogie and Odekunle [18] suggested that maximum 10% substitution of wheat flour with banana flour during donut for good consumer acceptability. Similarly, some other studies [12,19] found that replacing wheat flour in cookies and cakes with 1–6 percent and 4–6 percent banana blossom flour, respectively, increased the mineral and protein content of the bakery products. In addition, a thin coating of Aloe Vera gel can function as a regular food preservative. Hence, the purpose of this study was to investigate the nutritional, textural, and sensory properties of ALP-incorporated plain (loaf) cakes. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the nutritional, sensory, and textural properties of ALP-fortified plain (loaf) cakes. This research also assists researchers in considering the use of ALP in the formulation of various bakery items.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
Aloe Vera was collected from M/S Kawser’s Horticulture farm, Natore, Bangladesh. Refined wheat flour was purchased from supermarket, Mymensngh, Bangladesh, and Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) was prepared in the laboratory.
2.2. Preparation of ALP
Fresh, undamaged leaves of the Aloe Vera were sorted and washed thoroughly with clean water to remove all dirt. The water was drained to remove all latex because an excessive intake of latex could cause the adverse effect. All the latex (middle layer) was removed by making a cross sectional-cut in the bottom side of the leave and was kept for 30 min. Outer layer of the leave was removed by knife. The Aloe Vera gel was soaked in 100 mL of 2% citric acid solution for 10 min and washed accordingly using running water. To avoid enzymatic browning, the gel was soaked in 100 mL of 2% ascorbic acid solution for 15 min again. Aloe Vera powder was prepared by freeze-drying process. The gel was pre-frozen at −20 °C for 2 h followed by lyophilized at −88 °C and 0.01 mm Hg pressure and 0.01 mm Hg pressure for 60 h to obtain dried gel fillet. Next, it was grounded (Panasonic Mixer Grinder MX-AC555, Haryana, India) to obtain aloe Vera powder (ALP) with moisture content 4% [17].
2.3. Functional Properties of ALP and Refined Wheat Flour (RWF)
2.3.1. Bulk Density (g/cm3) of ALP and RWF
Five (5) g of each sample was placed in a 100 mL measuring cylinder and calculated by dividing the mass of the flour by volume occupied in the cylinder [19].
2.3.2. Foaming Capacity of ALP and RWF
Fifty (50) ml of distilled water was mixed with 2 g of sample and shaken thoroughly to form foam. Foaming capacity is known as the formation and elevation of foam (ml) after mixing of ALP and RWF and distilled water [19].
2.3.3. Water Absorption Capacity (WAC) of ALP and RWF
Ten (10) g of sample and water was mixed to obtain stiff consistent dough. The amount of water required was noted as water absorption capacity [20].
2.3.4. Oil Absorption Capacity (OAC) of ALP and RWF
Oil absorption capacity was determined following the procedure of Tasnim et al. [12]. Oil absorption capacity was calculated as follows:
2.3.5. Swelling of Flour and Solubility of ALP and RWF
One (1) g sample was taken in a 50 mL centrifuge tube. Ten (10) ml of distilled water was added to the tube and thoroughly mixed. The mixer was heated at 80 °C for 30 min in a shaking water bath (Schufzart, MembartGmBH + Co., Bϋchenbach, Germany). The tubes were dried and cooled at room temperature (30 ± 2 °C) after removing from the water bath. The mixer was centrifuged at 542× g force for 15 min. Finally, the supernatant was evaporated, and the dried residue was weighted in order to determine the solubility.
The swelling power of ALP was determined by decanting and weighting the supernatant.
2.3.6. Particle Size Analysis of Mix Flour (ALP and RWF) and RWF
The analysis of particle size was determined by adopting modified method of Agrahar-Murugkar et al. [21]. Average particle size (d3,2—surface-weighted mean diameter—Sauter mean diameter and d4,3—volume weighted mean diameter—De Brouckere mean diameter) of 2, 4, and 6% Aloe Vera flour plus refined wheat flour were determined by particle size analyzer (Malvern Zetasizer Nano Zs, Malvern, UK).
2.4. Preparation of ALP-fortified Plain (Loaf) Cakes
The basic formulation for plain (loaf) cakes (multistage mixing) and ALP-fortified cakes is the same except for wheat and ALP percentage, as shown in Table 1. Four cake samples were prepared by partial substitution of RWF with different percentage of ALP (0, 4, 6, and 8%) in the basic formulation of cake [12]. Each cake sample’s RWF, ALP, and other ingredients were precisely weighed. The RWF and various percentages of ALP were combined. To prepare the batter for cake, first, one egg (60 g) was taken and beaten in a beater bowl until forming the foam. Sugar-shortening mixture was prepared by mixing sugar (90 g), oil (60 g), and butter (20 g) for 20 min in a cake mixer. Again, this mixture was added into the beater bowl and again beaten to mix all ingredients properly. After that, flour (RWF and/or mixed flour), baking powder, milk powder, and salt were added into the beater bowl. All the ingredients were mixed properly at a low rotational speed (150 rpm) for 10 min to ensure proper mixing of the ingredients. Then, another 60 g of egg and vanilla essence (2 drops) were added to the mixer and stirred at medium speed (250 rpm) for 5 min to make proper cake batter. A portion of butter (3 g) was then scaled to a pre-oiled cake bowl. All cakes were baked in the oven at 170 °C for 45 min. It is a common industrial practice all over the world to use oil and butter for pound cakes. By combining these two, a mixture with the flavor of butter but the ability to sear at higher temperatures was created. Moreover, butter helps to raise the dough better. Oil in the mixing process helps to mix the ingredients and form the dough as it remains in liquid form, while butter remains solid at room temperature.

Table 1.
Basic formulation for the preparation of plain cakes (on 100 g flour basis).
2.5. Proximate Composition Analysis
Moisture and proximate composition of RWF, ALP, and plain (loaf) cakes were determined using 2019 published guidelines and methods of AOAC: moisture content 950.46 [22], crude protein 981.10 [23], crude fat 922.06 [24], and ash 920.153 [25]. Total carbohydrate content of ALP and cake samples was determined according to methods of FAO [26]. Mineral content of ALP and cakes was determined according to the modified method describe by Poitevin [27]. Mineral content of ALF and cakes was also determined according to the modified method as described by Poitevin [27]. The solution (30 mL) of HNO3 and HCLO4 was prepared in a mass ratio of 2:1 to 1.5 g Achetadomesticus powder in a Kjedhal flask. The solution kept at rest for 24 h. Water (H2O) and HNO3 were removed by boiling of the solutions slowly. Perchloric acid (HClO4) was added to solution after cessation of the effervescent reaction. The test portion was then cooled at room temperature (28 ± 2 °C). The solution was transferred to a volumetric flask (50 mL), and the volume was made by distilled water. Iron (Fe), potassium (k), and calcium (Ca) were analyzed inductively with an ICP (inductively coupled plasma) emission spectrophotometer.
2.6. Total Polyphenol Assay
The total polyphenol content of the RWF, ALP, and plain (loaf) cakes were determined using the Folin–Ciocalteu method [28]. Ten (10) mg of ALP and finely ground plain cakes was dissolved in 200 µL of H2O. Next, 1 mL of Folin–Ciocalteu’s reagent was added to the mixer and allows standing for 10 min at room temperature. In total, 0.8 mL of Na2CO3 (7.5% w/v) was added to the mixer and mixed properly. The mixer was allowed to stand for 30 min. Absorption (PerkinElmer, Lambda 25, UV/VIS spectrophotometer) was measured at 765 nm. The total phenolic content was measured as mg of gallic acid equivalents per 100 g of wet and dry mass [29].
2.7. Total Flavonoid Assay
Total flavonoid content of RWF and ALP was measured using modified method described by Marinova et al. [30]. In total, 10 mg of ALP was dissolved in 1 mL of distilled water and mixed. Next, 60 µL NaNO2 (5% w/v) was added to the mixer and rested for 5 min. In total, 60 µL AlCl3 (10% w/v) was added and settled for 6 min. A total of 400 µL NaOH (1 M) was added, and the volume was made up to 2 mL with distilled water. The solution was mixed thoroughly and absorption (PerkinElmer, Lambda 25, UV/VIS spectrophotometer) was measured at 510 nm against reagent blank. Concentrations were measured using catechin stand curve. On the other hand, total flavonoid was expressed as mg of catechin equivalent (CE) per 100 g of wet and dry mass [29].
2.8. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC)
In 200 µL methylated β-cyclodextrin solution, 56 nM fluorescein was added followed by addition of 240 nM 2,2′-azobis (2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride. A Microplate reader (TECAN Austria GmbH, Austria) was used to measure fluorescence of fluorescein (485 nm excitation and 520 nm emission) at every 10 min for 2 h at temperature 37 °C. Antioxidant capacity (ORAC) was expressed as micromoles of Torolox equivalents (TE) per germ of wet and dry mass [29].
2.9. Physical Properties of Control (Only RWF) and ALP-fortified Plain (Loaf) Cakes
Physical properties of control (only RWF) and ALP-fortified plain (loaf) cakes such as height (cm), weight (g), volume (cm3), and baking loss (%) were determined following the method of Bilgen et al. [31]. Cake symmetry was determined one day after baking by AACC Baking Quality Method 10–91 [32]. Color attributes of product were analyzed with the help of a colorimeter (Chroma Meter CR400, Konica Minolta, Japan) under specific condition (Illuminant: *C, D65, space: LAB). The color was determined in L*, a*, b* system, where L* = lightness (100: white, 0: black), a* = redness (+), or greenness (−), and b* = yellowness (+), or blueness (−).
2.10. Textural Properties of Control (Only RWF) and ALP Powder Incorporated plain (Loaf) Cakes
Textural properties of control (only RWF) and ALP supplemented cakes were determined from the middle (2.0 cm × 2.0 cm × 2.0 cm) of the cakes using a texture analyzer (TA-XT plus, Stable Micro Systems, Godalming, Surrey, UK). It has 36 mm diameter cylindrical probe and 50% compression with test speed 1.0 mm/s. Operational conditions were: 2.0 mm/s pretest speed, 2.0 mm/s post-test speed, and 5 g trigger force. Hardness, cohesiveness, adhesiveness, springiness, resilience, gumminess, and chewiness were determined accordingly. The Texture Expert 1.05 software (Stable Microsystems, Godalming, Surrey, UK) was used to find out all the textural properties of the cake samples by programming a double cycle.
2.11. Determination of Sensory Attributes
Plain (loaf) cakes were assessed for color, flavor, texture, and overall acceptability. A 1–9 point hedonic rating test was also performed to determine the degree of acceptability of cakes containing different ALP levels. One slice from each lot of cakes was presented to semitrained 10 panelists of Department of Food Technology and Rural Industries, Bangladesh Agricultural University as randomly coded samples. The taste panelists were requested to rank the sample for color, flavor, texture, and overall acceptability on a 1–9 point scale [33]. Each panelist was asked to provide informed written consent before progressing with the process.
2.12. Changes in Weight during Storage Condition
Plain cakes were analyzed for moisture gain or loss at various storage conditions in terms of weight changes over a 10 day period. Samples were vacuum-packed in single-layer polythene and kept at room temperature (30 ± 2 °C) as well as at refrigeration temperature (5 ± 1 °C). Every day, the weight gain or loss of control and ALP-fortified samples was monitored.
2.13. Statistical Analysis
The plain cake samples were analyzed by Fischer’s LSD multiple comparison test to view the differences. A single-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to find the significant differences [34]. STATA v15 was used to carry out all the analysis.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Comparison of Nutritional and Functional Properties of ALP and RWF
Table 2 shows the comparative study between ALP and RWF for their nutritional composition and functional properties. It is noticeable that ALP is a good source of protein and ash. Moisture, fat, and total carbohydrate content were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in RWF. Moisture, ash, protein, fat, and total carbohydrate of ALP were almost similar to that reported by Hamman [35]. In the case of RWF, the results were in agreement with [36,37,38].

Table 2.
Nutritional and functional properties of Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) and refined wheat flour (RWF).
Different functional properties of ALP was compared with RWF and shown in Table 2. Functional properties of powder/flour reflect endogenous physical and chemical properties that influence food properties during handling, storage, processing, and analysis, among other things [39]. The bulk density of RWF (0.65 ± 0.05 g/mL) was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than ALP (0.48 ± 0.04 g/mL). Table 2 suggested that WAC (g water/g sample) were significantly (p < 0.05) higher in ALP than RWF. WAC plays a very important role in the textural quality of food products such as soups, ground meat, dressing, sauces, and bakery products. High WAC leads to swelling properties which provide consistency, thickening, viscosity, adherence properties, increasing weight and decreasing of height, specific volume, and volume of the cakes [40,41]. Therefore, higher WAC of ALP/RWF might cause an increase in weight, height, and volume of the cakes. The study also suggested that OAC (g/g) and swelling power (%) was significantly (p < 0.05) higher in ALP than RWF. Comparative analysis for mineral content shows that ALP contains significantly higher amount of iron (Fe) than RWF; whereas RWF contains higher amount of calcium (Ca) and potassium (K). Total polyphenols and total flavonoids content of ALP were found to be 75.01 ± 3.22 mg of GAE/100 g and 6.87 ± 0.18 mg of CE/100 g, respectively. However, antioxidant capacity of ALP (measured as ORAC hydrophilic and total) was found to be 49.55 ± 1.2 µmol of TE/g. Plain (loaf) cakes fortified with ALP are high in antioxidants and a viable option for making healthy baked goods.
3.2. Particle Size Analysis of Mix Flour (ALP and RWF) and RWF
Figure 1 illustrates the particle size distribution of mixed flour (4, 6, and 8% ALP mixed with RWF) and control flour (RWF). Bimodal particle size distribution was observed for all flours, with two distinct peaks for mixed flour and no distinct peak for RWF. The results are in agreement with [11,21,42]. Figure 1 also indicated that most of the flour tested had particle sizes ~100 µm, indicating a higher volume of flour. Particle size distribution of mixed flour and RWF was ranged from 0.1–100 µm. However, volume of particles for all mixed flour was at ~140 µm and for control (RWF) at 88 µm. This result suggested that RWF has lower protein and fiber content as smaller particle size (SPZ) flour suggests low protein and fiber content [43]. SPZ flour gave hard dough with higher density results in less development of biscuits, cake, and bread [11,44]. Hence, coarser particle size flour from composite or mixed flour is the most desirable for cake preparation. Mean volume diameter (MVD) (d4,3: 68.85 µm) and surface mean diameter (SMD) of RWF (d3,2: 25.75 µm) were less than (p < 0.5) all mixed flour (d4,3: 78.15 µm; d3,2: 30.55 µm, respectively). There was no significant difference (p > 0.5) among 4, 6, and 8% mixed flour. The particle size of flour often affects the water absorption capacity, swelling power, and density of cakes. Flour with fine particle size has a higher density and less effective baking properties [11]. Therefore, coarser composite flour is desired for the preparation of cake.
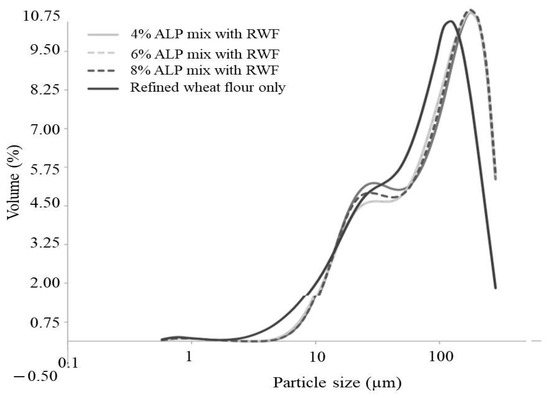
Figure 1.
Particle size of mix flour (Aloe Vera powder and refined wheat flour) and refined wheat flour.
3.3. Physical Properties, Proximate Composition, and Mineral Content of Control Cake and Cake-fortified with ALP
Table 3 shows different physical properties of the developed cakes. Weight of the ALP-fortified cakes (225.5–250.8 g) was higher than control cake (216.6 g) due to the higher water absorption capacity of ALP (4.76 ± 0.06) than RWF (4.15 ± 0.05) [36]. As a result, ALP supplementation increased the weight of the cakes. It was also noticeable that weight of cakes (from S3 to S1) gradually increased with the increasing percentage of ALP due to the lower baking loss and higher WAC of ALP [12]. Cakes with varying percentages of ALP had lower volumes (300–310 cm3) than the control cake (327 cm3). This might be due to a reduction in gluten content due to supplementation. Research also revealed that substituting nonglutinous flour for wheat flour resulted in lower product volumes [45]. It was also observed that the volume of the cakes decreased with an increasing percentage of ALP (from S3 to S1) due to the absorption of air, oil, and fiber components [46]. Specific volume of the cakes (from S3 to S1) gradually decreased with an increasing level of ALP in the formulation. This could be due to a reduction in gluten content due to supplementation. Previous research also revealed that the specific volume of the developed cakes gradually decreased with increasing levels of nonglutinous flour substitution [47]. The height of the control cake (6.70 cm) was found to be higher than that of the cakes containing ALP (6.50–5.65 cm). The decrease in height from 6.70 to 5.65 cm of the cake could be the result of reduction in gluten content of the blends due to supplementation with ALP [38]. When the ALP in the dough was increased, the cake weight increased while the weight loss decreased. Baking loss (%) of the ALP supplemented cakes (S3 = 47.03%, S2 = 45.92% and S1 = 42.66%) were lower than control cakes (50.52%). ALP supplementation of RWF reduced weight loss due to ALP’s higher protein and fiber content than RWF [12]. Table 3 shows that L* of crumb decreased with increasing ALP percentage (from 67.90 to 53.28). S2 (6%) and S1 (8%) did not show any significant difference (p > 0.05) for L*-values. a*-value of cake crumb increased with ALP supplementation in dough. However, as ALP concentration was increased, the b*-values of cake crumb decreased. ALP used for cake processing was less light, less yellow, and more reddish in color (Table 2) than RWF, resulting in lower L*, b*, and higher a*-values.

Table 3.
Effect of addition of Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) on physical and nutritional properties of plain (loaf) cakes.
The ALP supplemented cakes were analyzed for their nutritional composition (Table 3). Moisture content analysis showed that replacing RWF with ALP results in a gradual increase in moisture content in cakes. This might be due to low water-binding capacity of ALP protein, high fiber content of ALP, and lower baking loss of supplemented cakes. However, research revealed that non-wheat proteins increased the water absorption of dough due to high water-binding capacity [48]. This could be due to ALP’s higher fiber content than RWF, which helps to retain moisture and contributes to the higher moisture content of composite loaf cakes [49]. Lower baking loss, on the other hand, is responsible for the higher moisture content of the ALP-supplemented plain cakes. Furthermore, higher initial moisture content may result in an increase in the moisture content of the final products. Protein content of all samples was higher than the control sample, as ALP is a rich source of protein. For instance, dietary protein is required for functional needs such as improving health, muscle, and growth [44]. Consumption of cakes enriched with 8% ALP can easily supplied recommended dietary allowance (RDA) of protein for healthy people. Fat content of S4 was the maximum (22.24%) among all samples though it is not significantly different (p > 0.05) from S3. Sample S2 and S1 were not significantly different (p > 0.05) with each other. It was observed that ash content cake increased gradually with the addition of ALP. 8% ALP (S1) cake had the highest ash content (2.95%) and revealed a significant amount of minerals present in the ALP.
For an adult aged 19–50 years, 100 g plain cake enriched with 8% ALP contribute more than 15% RDA for iron, compared to 8% iron contribution from control cakes. The result suggested that 100 g plain cake enriched with 8% ALP contributes more than 6% RDA for calcium, compared to 8% iron contribution from control cake for an adult aged 19–50 years based on Institution of Medicine, Food, and Nutrition Board [50]. The results suggested that ALP could be used as an alternative protein source in bakery products. Total carbohydrate content decreased in ALP-enriched cake (from S3 to S1) with increasing amount of ALP in dough. This may be due to the lower percentage of carbohydrate present in ALP determined in the present study (49.37%) than that of wheat flour (72.46%) [36]. Total polyphenols and antioxidant activity (measured as ORAC) increased in ALP enriched cake (from S3 to S1) with increasing amount of ALP in dough, as ALP is a rich source of polyphenols and flavonoids.
Evenness and edges are symmetrical parameters. Evenness is classified as even, medium even, or uneven. According to subjective analysis, the crust color of the control cake was brown, whereas the crust color of the 8% ALP enriched cake was brownish dark and the consistency changed from tender to medium tender. Crum color of the cakes was brownish yellow, less brownish yellow, less darkish brown, and darkish for control, 4, 6 and 8% ALP supplemented cakes, respectively (Table 4). Control sample (S4) and 4% ALP (S3) showed appetizing flavor though 6 and 8% ALP-enriched cake shows slight bitter flavor. Subjective analysis also suggested that closely bounded grain was noticed for control (S4) and 4% ALP (S3), whereas less airy for both S2 (6% ALP) and S1 (8% ALP). Because of the increase in ALP, the size and shape of the grain of the crumb lost their uniformity (Table 4).

Table 4.
Effect of addition of Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) on symmetry, crust, and crumb characteristics of plain cakes.
3.4. Effect of ALP on the Textural Properties of Cakes
Textural profile of plain cake samples is shown in Table 5. It can be observed that the hardness of the plain cake samples increased with the increasing percentage of ALP from 0 to 8%. Hardness of ALP-enriched cakes was directly correlated to the volume of the testing materials. This was due to higher protein content and a better water absorption capacity in the mixed flour [11]. Decreasing the volume increased the hardness due to lack of gluten in the mix. Elasticity represents the springiness which determines the extent of recovery between the first and second compression. Springiness value of plain cake was in the range 0.79–0.92. 8% ALP-fortified cake (S1) had significantly lower springiness than the other cake samples. There was no significant difference among the three samples (S2, S3, and S4). Again, cohesiveness, gumminess, chewiness, and resilience of plain cake samples are 0.68–0.77, 4.87–5.12, 4.09–4.48, and 0.37–0.38, respectively. Lower cohesiveness and springiness found in this study are related to the water absorption capacity, low gluten, and higher fat content of the dough. However, the result indicated that that only sample S1 (8% ALP) was significantly different with other plain (loaf) cake samples in cake resilience values. These findings were not surprising given that the lack of gluten structure results in a crumbly, brittle crumb texture [51]. It was noticeable that all textural parameters decreased due to addition of ALP and differed significantly (p < 0.05) from the control cake. This reduction in loaf textural parameters could be attributed to the higher fat content in the formulations, which disrupts the gluten network development while lubricating and hydrating the entire mix [52,53].

Table 5.
Effect of addition of Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) on textural properties plain cakes.
3.5. Organoleptic Parameters of ALP Supplemented Cakes
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) suggested that there was a significant (p < 0.05) difference in color acceptability among the plain (loaf) cakes. Sample S3 was most acceptable by the panelist than other cakes. In case of flavor preferences, one-way ANOVA showed that there was significant (p < 0.05) difference in flavor acceptability. Sample S1 was most preferred, and S3 was least preferred relative to other sample at 5% level of significance. ANOVA analysis suggested that there was significant texture difference (p < 0.05) between control loaf cake and loaf cakes containing ALP. Control cake (S4) was more acceptable and significantly different from the other cake samples. For overall acceptability, ANOVA analysis suggested that Sample S3 (4% ALP) was the most preferable relative to others (Table 6). The sample with 4% ALP showed the finest sensory characteristics in terms of color, texture, flavor, and overall acceptability. However, the other samples were also found acceptable. A DMRT analysis revealed that 4% ALP loaf cakes were significantly better in color, texture, flavor, and overall acceptability than other plain (loaf) containing 0, 4, 6, and 8% ALP. However, increasing the amount of ALP decreased the level of overall acceptability.

Table 6.
Effect of addition of Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) on sensory attributes of plain cakes.
3.6. Changes in Weight during Storage of Developed Cakes
During the storage period, the weights of cakes gradually decreased at room temperature (30 ± 2 °C) due to the moisture removal from cakes (Figure 2). On the other hand, a weight gain was also observed in the refrigerated condition (5 ± 1 °C) (Figure 3). This could be because of the high humidity in refrigerated conditions. The weight differences between control and ALP-enriched cakes were found to be minimal. This was most likely due to the vacuum packing of samples, which almost completely stopped moisture gain or loss [36].
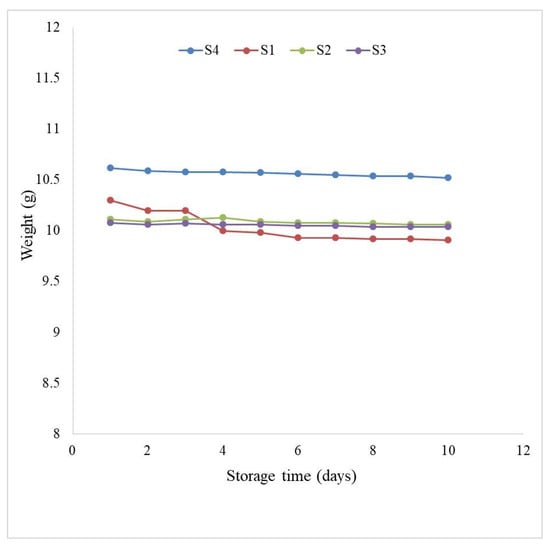
Figure 2.
Changes in weight of control and Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) incorporated plain cakes during storage period at room temperature (30 ± 2 °C).
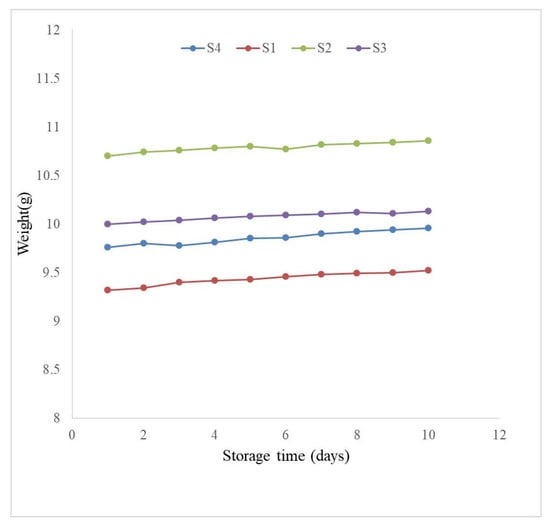
Figure 3.
Changes in weight of control and Aloe Vera leaf powder (ALP) incorporated plain cakes during storage period at refrigeration temperature (5 ± 1 °C).
4. Conclusions
Cakes are one of the useful food items for fortifying the human diet with various nutritionally rich functional ingredients. The addition of polyphenol, antioxidant, and protein-rich ingredients to bakery products increases consumer acceptance and protein intake while lowering calorie density and total carbohydrate in the diet. This research studied the physicochemical, nutritional, and functional properties of Aloe Vera powder and substituted wheat flour by Aloe Vera powder. It was observed that ALP is a good source of protein, mineral, flavonoid, and anti-oxidant. In the processed plain (loaf) cakes, there was an increase in weight, moisture, ash, protein, crude fiber, iron, and calcium with increasing of ALP percentage. However, the specific volume, volume, and baking loss was deceased due to the addition of different percentage (4, 6, and 8%) of ALP. The amount of total polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidant capacity in ALP-fortified plain (loaf) cakes was higher than in wheat flour loaf cakes alone. However, physical and sensory quality was inversely correlated with ALP incorporation, though 4% incorporation did not affect the quality significantly. This study concludes that plain (loaf) cakes may be supplemented with up to 4% Aloe Vera powder to improve its nutritional and functional properties, without any change in the physical characteristics and consumer acceptability. Further research can be conducted to determine the restrictions on the processing and use of aloe powder, as well as in vitro and in vivo analyses on the reduction of negative health effects of baked goods by using ALP. Moreover, a nutritional profiling could be a suitable option for additional research. Moreover, nutritional profiling may be a viable option for additional research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.R.M., D.S. and M.F.J.; methodology, D.S., K.D. and D.A.; software, D.S. and M.T.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.F.J., M.A.R.M. and T.V.R.; writing—review and editing, T.V.R. and M.A.R.M.; supervision, M.A.R.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All of the data used to generate the results is included in the article, and no additional source data is required.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge department of Food Technology and Rural Industries, Bangladesh Agriculture University for technical support and assistance in this MS research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Surjushe, A.; Vasani, R.; Saple, D.G. Aloe Vera: A short review. Indian J. Darmatol. 2008, 53, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, P. Aloe Vera revisited. Br. J. Photother. 1998, 4, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaili, S.; Hosseini, M.; Shojaee Aliabadi, S.; Mirmoghtadaie, L. Improving Qualitative and Texture Characteristics of Fat-Free Sponge Cake Using Aloe Vera Gel Powder. Iran. J. Nutr. Sci. Food Technol. 2018, 12, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Khaing, T.A. Evaluation of the antifungal and antioxidant activities of the leaf extract of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller). World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 75, 610–612. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Shin, G.M. Studies on quality characteristics of sponge cake made with aloe Vera powder. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2018, 24, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, S.K.; Gokhale, J.S.; Mulla, M.Z.; Kandu, V.R.; Patil, S. A comprehensive overview of functional and rheological properties of aloe Vera and its application in foods. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.A.R. Use of Aloe Vera gel as a fat replacer in the preparation of cakes. Int. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2017, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dikeman, C.L.; Fahey, G.C.; Murphy, M.R. Dietary fibers affect viscosity of solutions and simulated human gastric and small intestinal digesta. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunzek, H.; Muller, S.; Vetter, S.; Godeck, R. The significance of physicochemical properties of plant cell wall materials for the development of innovative food products. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2002, 214, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucky, A.R.; Al-Mamun, A.; Hosen, A.; Toma, M.A.; Mazumder, M.A.R. Nutritional and sensory quality assessment of plain cake enriched with beetroot powder. Food Res. 2020, 4, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, M.A.; Jubayer, M.F.; Begum, A.A.; Nupur, A.H.; Ranganathan, T.V.; Mazumder, M.A.R. Substituting wheat flour with okara flour in biscuit production. Foods Raw Mater. 2020, 8, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, T.; Das, P.C.; Begum, A.A.; Nupur, A.H.; Mazumder, M.A.R. Nutritional, textural and sensory quality of plain cake enriched with rice rinsed water treated banana blossom flour. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Bhatia, S.; Chunduri, V.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, S.; Kapoor, P.; Kumari, A.; Garg, M. Pathogenesis of celiac disease and other gluten related disorders in wheat and strategies for mitigating them. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ah, Y.E.; Dae, K.S.; Min, L.W.; Jin, P.H.; Keun, K.S.; Youl, C.J.; Wongi, M.; Hee, R.M. Evaluation of antioxidant, antinociceptive, and anti-inflamatory activities of ethanol extracts from Aloe saponaria. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.H.; Jin, C.; Xin, M.; Jian-Min, H. Effect of Aloe vera polysaccharides on immunity and antioxidant activities in oral ulcer animal models. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.L.; Lu, Y.C.; Chung, J.G.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, S.G.; NG, S.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Su, H.L.; Chen, S.S. Aloe-emodin induces apoptosis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via caspase-8-mediated activation of the mitochondrial death pathway. Cancer Lett. 2010, 291, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, K.S.; Khatkar, B.S. Processing, food applications and safety of aloe vera products: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayo-Omogie, H.N.; Odekunle, O.Y. Substituting wheat flour with banana flour: Effects on the quality attributes of doughnut and cookies. Appl. Trop. Agric. 2017, 22, 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Elaveniya, E.; Jayamuthunagai, J. Functional, physicochemical and anti-oxidant properties of dehydrated banana blossom powder and its incorporation in biscuits. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2014, 6, 4446–4454. [Google Scholar]
- Khetarpaul, N.; Grewal, R.B.; Jood, S. Quality Control in Bread Making, Bakery Science and Cereal Technology; Daya Publishing House: New Delhi, India, 2005; p. 171. [Google Scholar]
- Agrahar-Murugkar, D.; Gulati, P.; Kotwaliwale, N.; Gupta, C. Evaluation of nutritional, textural and particle size characteristics of dough and biscuits made from composite flours containing sprouted and malted ingredients. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5129–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AOAC. Official Methods 950.46 Moisture in Meat and Meat Products, 21st ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods 981.10 Crude Protein in Meat and Meat Products, 21st ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods 922.06 Fat in Grain and Flour, 21st ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods 920.153 Ash in Meat and Meat Products, 21st ed.; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Food Energy Methods of Analysis and Conversion Factors. 2003. Available online: http://www.fao.org/uploads/media/FAO_2003_Food_Energy_02.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Poitevin, E. Determination of calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, phosphorus, sodium, and zinc in fortified food products by microwave digestion and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry: Single-laboratory validation and ring trial. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nejatzadeh-Barandozi, F. Antibacterial activities and antioxidant capacity of Aloe Vera. Org. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinova, D.; Ribarova, F.; Atanassova, M. Total phenolics and total flavonoids in Bulgarian fruits and vegetables. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2005, 40, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgen, S.; Coşkuner, Y.; Karababa, E. Effects of baking parameters on the white layer cake quality by combined use of conventional and microwave ovens. J. Food Proc. Preserv. 2004, 28, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th ed.; AACC: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- SAS. SAS Users Guide: Statistics, 5th ed.; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984; pp. 187–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hamman, J.H. Composition and applications of Aloe Vera leaf gel. Molecules 2008, 13, 1599–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huq, S.; Das, P.C.; Islam, M.A.; Jubayer, M.F.; Ranganathan, T.V.; Mazumder, M.A.R. Nutritional, textural, and sensory quality of oil fried donut enriched with extracted dietary fiber and okara flour. J. Food Proc. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.C.; Khan, M.J.; Rahman, M.S.; Majumder, S.; Islam, M.N. Comparison of the physico-chemical and functional properties of mango kernel flour with wheat flour and development of mango kernel flour based composite cakes. NFS J. 2019, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marufa, M.A.; Das, P.C.; Iqbal, A. Utilization of Jamun seed powder in composite cake formulation. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2019, 17, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menon, L.; Majumdar, S.D.; Ravi, U. Mango (Mangiferaindica L.) kernel flour as a potential ingredient in the development of composite flour bread. Indian J. Natl. Prod. Resour. 2014, 5, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik, D.R.; Porcel, M.V.O.; González, U.; Zaritzky, N.; Campderrós, M.E. Recovery of caprine whey protein and its application in a food protein formulation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ahmedna, M.; Goektepe, I. Peanut protein concentrate: Production and functional properties as affected by processing. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.D.; Bechtel, D.B.; Todd, T.C.; Seib, P.A. Measurement of wheat starch granule size distribution using image analysis and laser diffraction technology. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaines, C.S.; Donelson, J.R.; Finney, P.L. Holding Time and Temperature on Cookie Dough Handling Properties and Cookie Size. Cereal Chem. 1988, 65, 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Manley, D. Technology of Biscuits, Crackers and Cookies; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gernah, D.I.; Chinma, C.E. Breadmaking potentials of cassava-maize-soyabean flour blends. J. Sustain. Agric. Environ. 2006, 8, 196–206. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Saqib, M.N.; Alim, M.A. Evaluation of quality characteristics of composite cake prepared from mixed jackfruit seed flour and wheat flour. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2016, 14, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akter, N.; Alim, M.A. Preparation of wheat-potato-peanut composite flour cakes. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2018, 16, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Attabi, Z.H.; Merghani, T.M.; Ali, A.; Rahman, M.S. Effect of barley flour addition on the physico-chemical properties of dough and structure of bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauvain, S.P.; Cyster, J. Sponge Cake Technology; CCFRA Review No. 2; CCFRA: Chipping Campden, UK, 1996; pp. 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluorid; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, E.; Gormley, T.R.; Arendt, E.K. Recent advances in the formulation of gluten-free cereal-based products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.M.; Chapman, D.; Neville, D.P.; Keogh, M.K.; Arendt, E.K. Effect of varying the microencapsulation process on the functionality of hydrogenated vegetable fat in short dough biscuits. Food Res. Int. 2003, 6, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, J.; Laguna, L.; Puig, A.; Salvador, A.; Hernando, I. Effect of fat replacement by inulin on textural and structural properties of short dough biscuits. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 2739–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).