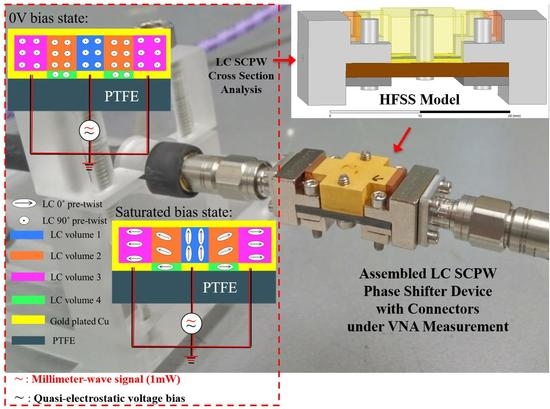
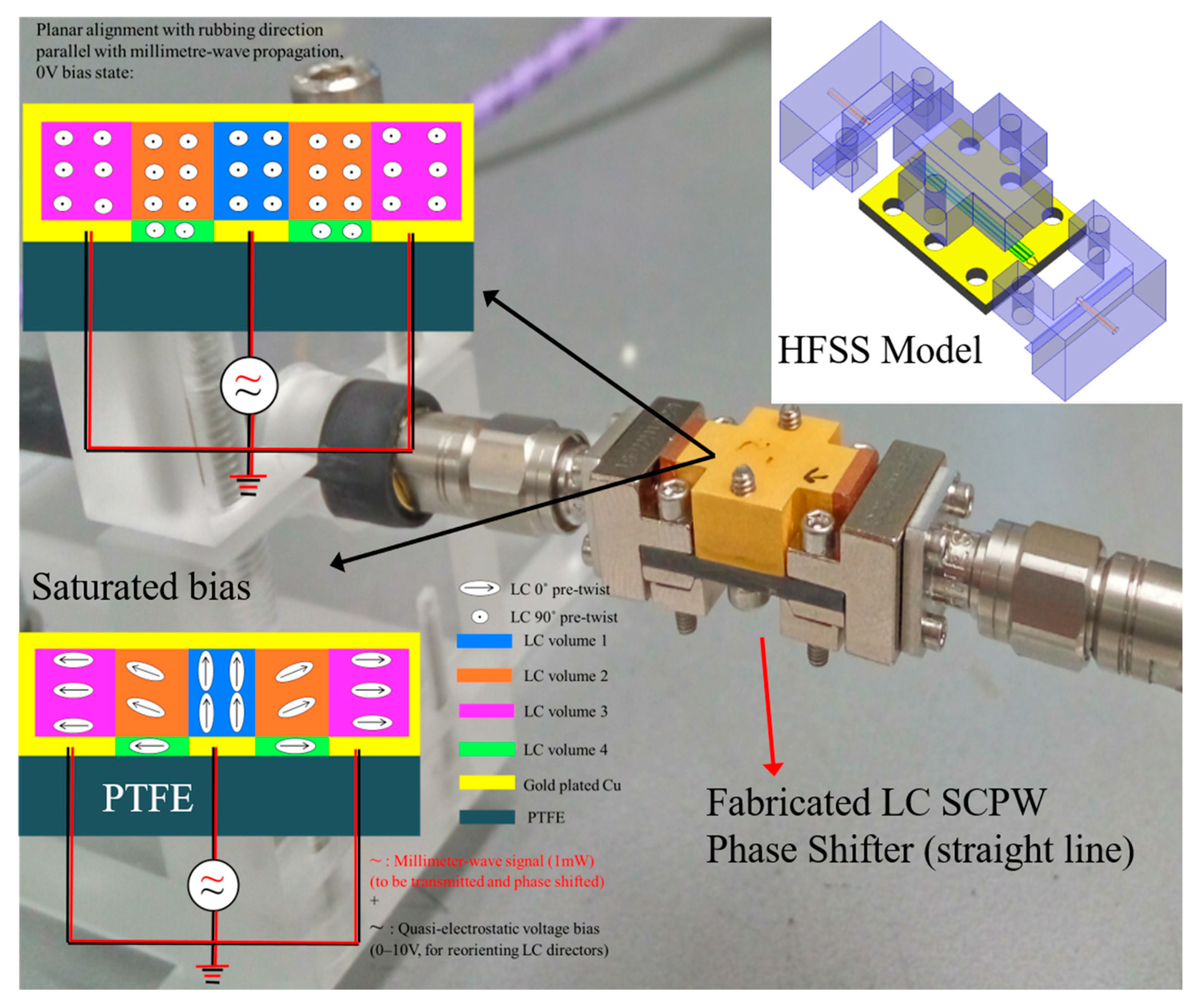
Rethinking Figure-of-Merits of Liquid Crystals Shielded Coplanar Waveguide Phase Shifters at 60 GHz
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
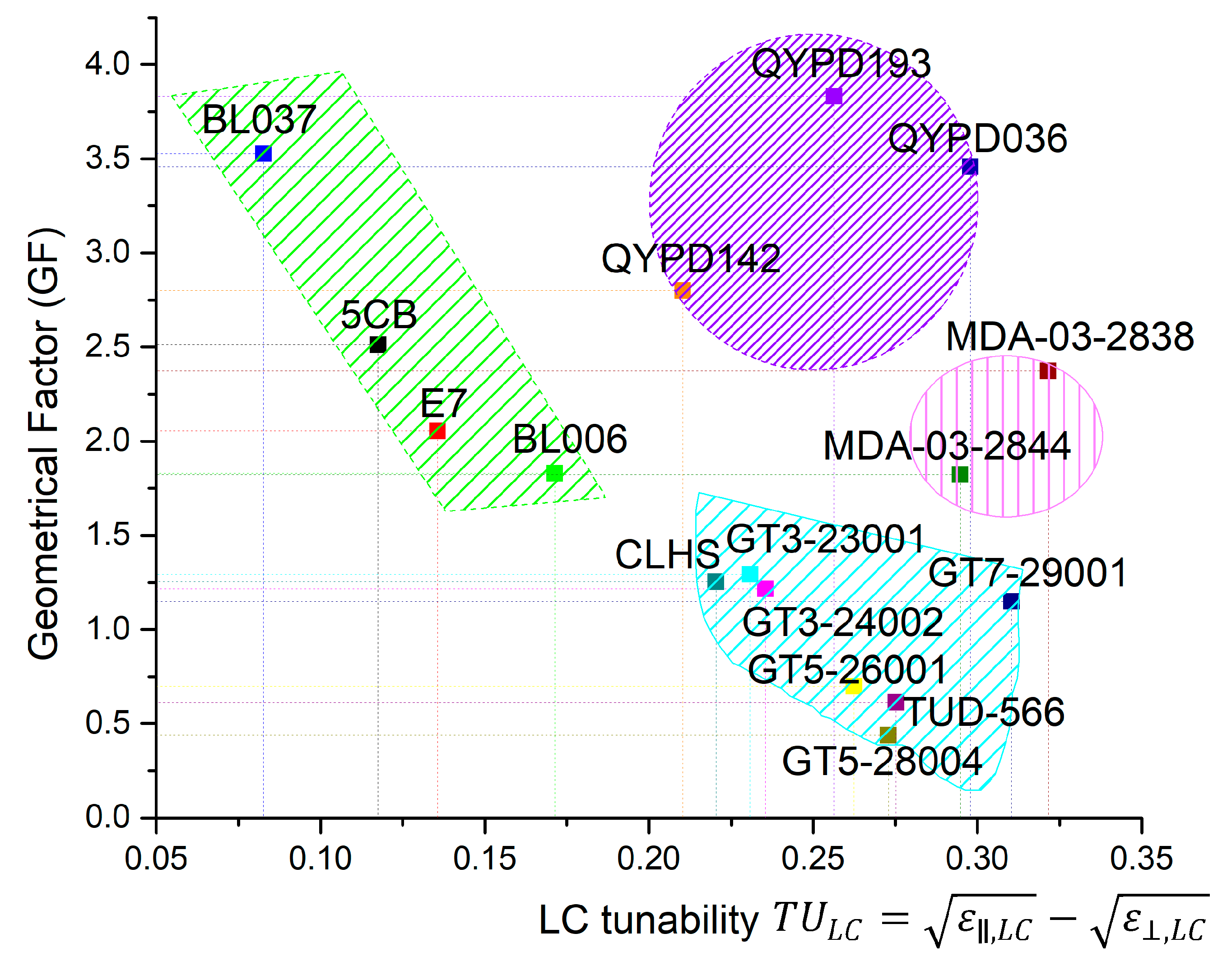
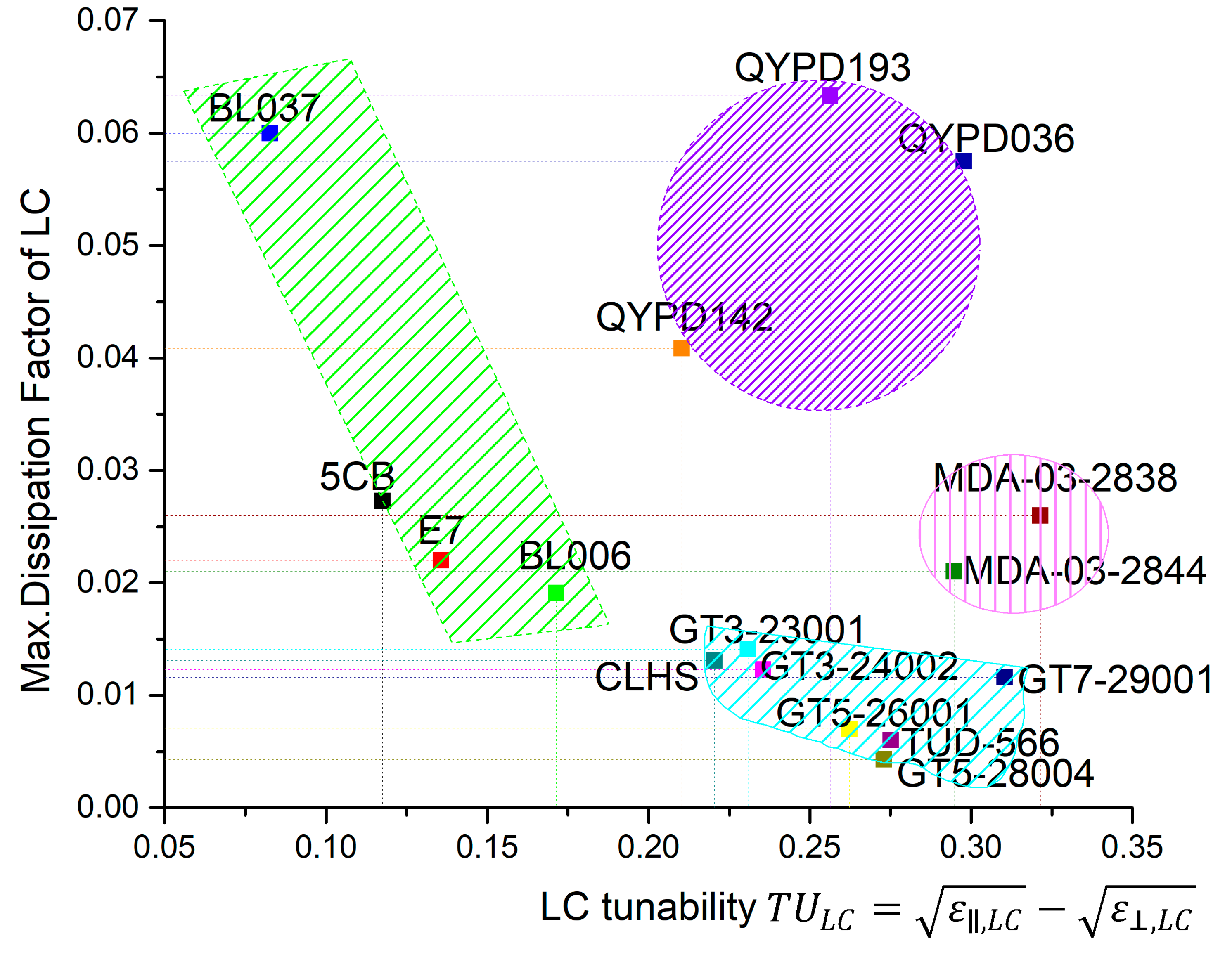
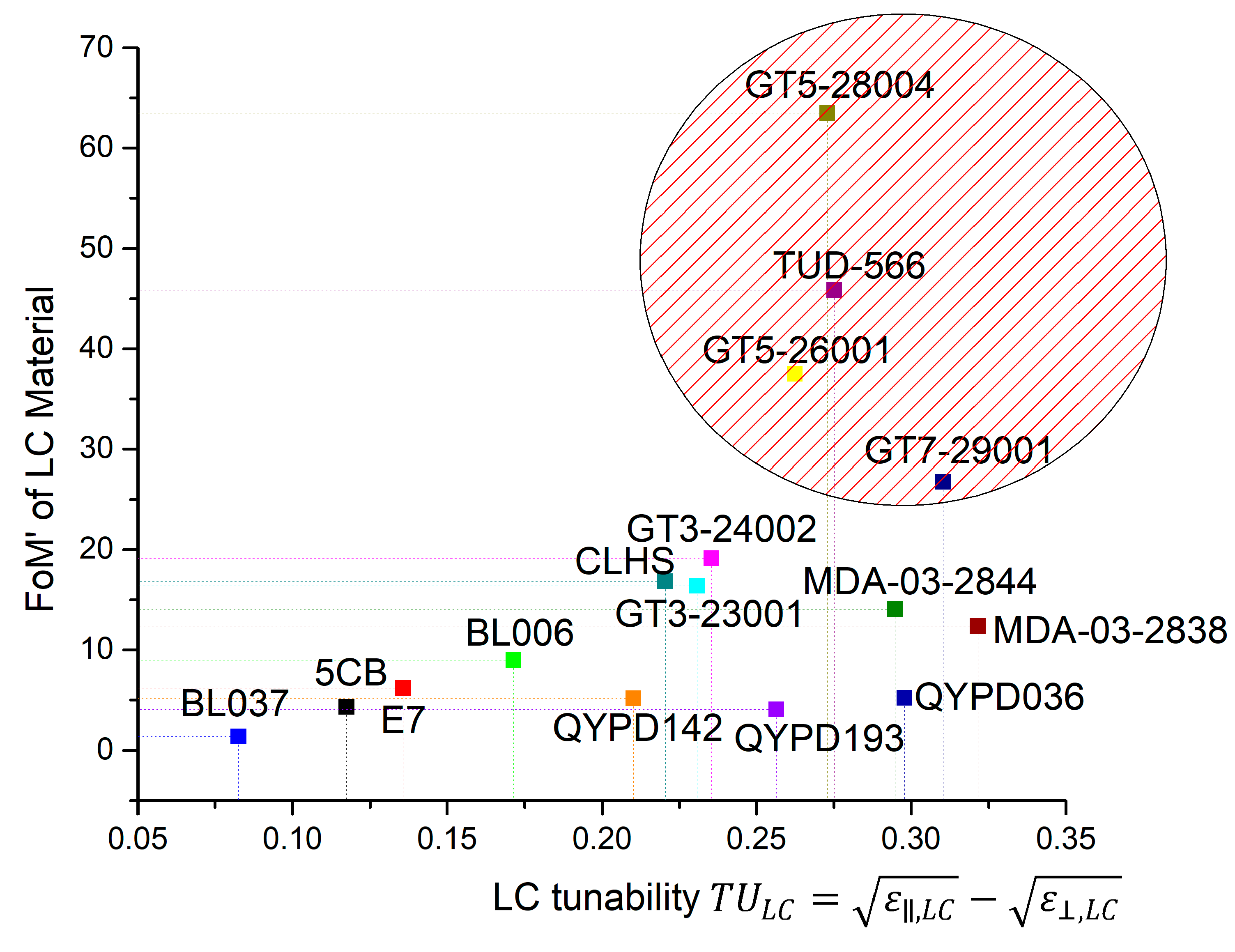
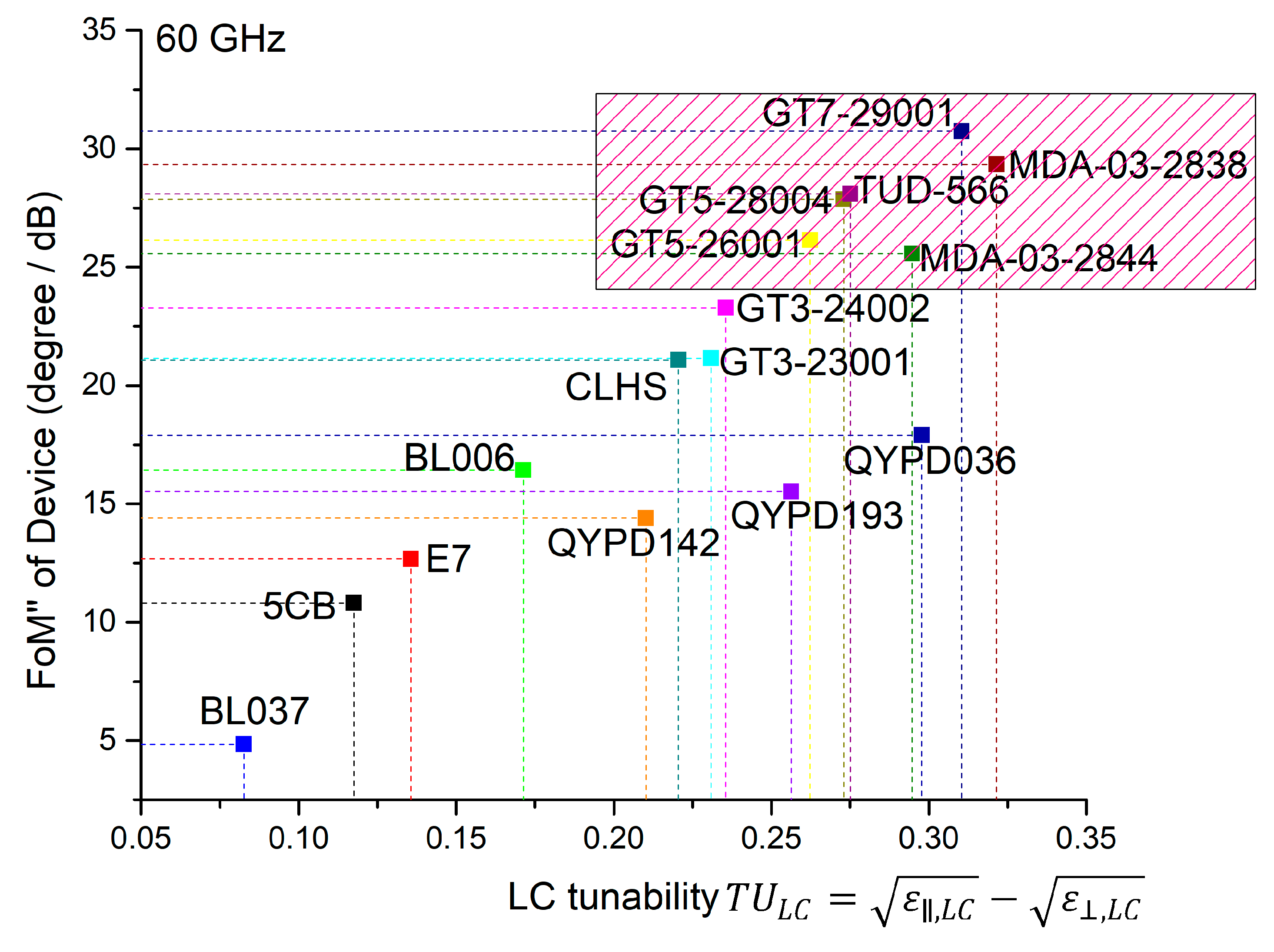
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koul, S.K.; Karthikeya, G.S. Millimetre Wave Antennas for 5G Mobile Terminals and Base Stations, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Attaran, M. The impact of 5G on the evolution of intelligent automation and industry digitization. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Maune, H.; Jost, M.; Wiens, A.; Weickhmann, C.; Reese, R.; Nikfalazar, M.; Schuster, C.; Franke, T.; Hu, W.; Nickel, M.; et al. Tunable Microwave Component Technologies for SatCom-Platforms. Frequenz 2017, 71, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiurkowska-Delaporte, M.; Kolek, Ł. Nematic Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2021, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulja, S.; Mirshekar-Syahkal, D.; Yazdanpanahi, M.; James, R.; Day, S.E.; Fernández, F.A. Liquid Crystal Based Phase Shifters in 60 GHz Band. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Wireless Technology Conference, Paris, France, 27–28 September 2010; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Maune, H.; Jost, M.; Reese, R.; Polat, E.; Nickel, M.; Jakoby, R. Microwave Liquid Crystal Technology. Crystals 2018, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chu, D. Liquid Crystal-Based Enclosed Coplanar Waveguide Phase Shifter for 54–66 GHz Applications. Crystals 2019, 9, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakoby, R.; Gaebler, A.; Weickhmann, C. Microwave Liquid Crystal Enabling Technology for Electronically Steerable Antennas in SATCOM and 5G Millimeter-Wave Systems. Crystals 2020, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, X. Rotating parabolic-reflector antenna target in SAR data: Model, characteristics, and parameter estimation. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2013, 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, M.; Weickhmann, C.; Strunck, S.; Gäbler, A.; Fritzsch, C.; Karabey, O.H.; Jakoby, R. Liquid crystal based low-loss phase shifter for W-band frequencies. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 1460–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goelden, F.; Gaebler, A.; Goebel, M.; Manabe, A.; Mueller, S.; Jakoby, R. Tunable liquid crystal phase shifter for microwave frequencies. Electron. Lett. 2009, 45, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nova, V.; Bachiller, C.; Villacampa, B.; Kronberger, R.; Boria, V.E. Characterization of Nematic Liquid Crystals at Microwave Frequencies. Crystals 2020, 10, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesmer, H.; Razzouk, R.; Polat, E.; Wang, D.; Jakoby, R.; Maune, H. Temperature Characterization of Liquid Crystal Dielectric Image Line Phase Shifter for Millimeter-Wave Applications. Crystals 2021, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.B.; Inoue, Y.; Moritake, H. NRD waveguide-type terahertz phase shifter using nematic liquid crystal. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Kuo, C.; Chen, P.H.; Wu, W.T.; Pan, R.P.; Yu, P.; Pan, C.L. High-Transmittance 2π Electrically Tunable Terahertz Phase Shifter with CMOS-Compatible Driving Voltage Enabled by Liquid Crystals. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Kumagai, T.; Yoshida, H.; Takeya, K.; Ozaki, M.; Tonouch, M.; Nose, T. THz Nematic Liquid Crystal Devices Using Stacked Membrane Film Layers. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 543, 77–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuscaldo, W.; Tofani, S.; Zografopoulos, D.C.; Baccarelli, P.; Burghignoli, P.; Beccherelli, R.; Galli, A. Tunable Fabry-Perot cavity THz antenna based on leaky-wave propagation in nematic liquid crystals. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2046–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, V.; Chigrinov, V. Figure of merit of liquid-crystal materials for optically addressed spatial modulators. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Chu, D. High Figure-of-merit compact phase shifters based on liquid crystal material for 1–10 GHz applications. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 56, 011701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I. Textures of Liquid Crystals; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dierking, I. Handbook of liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. Today 2015, 24, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagantsev, A.; Sherman, V.; Astafiev, K.; Venkatesh, J.; Setter, N. Ferroelectric Materials for Microwave Tunable Applications. J. Electroceramics 2003, 11, 5–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auciello, O.; Saha, S.; Kaufman, D.; Streiffer, S.; Fan, W.; Kabius, B.; Im, J.; Baumann, P. Science and technology of high dielectric constant thin films and materials integration for application to high frequency devices. J. Electroceramics 2004, 12, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendik, I.B.; Vendik, O.G.; Kollberg, E.L. Commutation quality factor of two-state switchable devices. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2000, 48, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zografopoulos, D.C.; Ferraro, A.; Beccherelli, R. Liquid-crystal high-frequency microwave technology: Materials and Characterization. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, T. Technology of liquid crystal based antenna. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 17138–17153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. 60 GHz optimised nickel-free gold-plated enclosed coplanar waveguide liquid crystal phase shifter. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications, Suzhou, China, 29–31 July 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. An efficient mixed-signal dielectric-partitioning model of liquid crystals based shielded coplanar waveguide for electronically reconfigurable delay lines design. Proc. SPIE 2021, 11775, 1177519. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Millimetre-wave beam steering with analog-resolution and minimised distortion based on liquid crystals tunable delay lines with enhanced signal-to-noise ratios. Proc. SPIE 2020, 11541, 115410H. [Google Scholar]
- Garbovskiy, Y.; Zagorodnii, V.; Krivosik, P.; Lovejoy, J.; Camley, R.E.; Celinski1, Z.; Glushchenko, A.; Dziaduszek, J.; Dąbrowski, R. Liquid crystal phase shifters at millimetre wave frequencies. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 054504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbe, M.; Hoehn, A.; Nathrath, N.; Weickhmann, C. Manufacturing and testing of liquid crystal phase shifters for an electronically steerable array. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wittek, M.; Fritzsch, C.; Schroth, D. Employing Liquid Crystal-Based Smart Antennas for Satellite and Terrestrial Communication. Inf. Disp. 2021, 37, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J. Rethinking Figure-of-Merits of Liquid Crystals Shielded Coplanar Waveguide Phase Shifters at 60 GHz. J 2021, 4, 444-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030034
Li J. Rethinking Figure-of-Merits of Liquid Crystals Shielded Coplanar Waveguide Phase Shifters at 60 GHz. J. 2021; 4(3):444-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinfeng. 2021. "Rethinking Figure-of-Merits of Liquid Crystals Shielded Coplanar Waveguide Phase Shifters at 60 GHz" J 4, no. 3: 444-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030034
APA StyleLi, J. (2021). Rethinking Figure-of-Merits of Liquid Crystals Shielded Coplanar Waveguide Phase Shifters at 60 GHz. J, 4(3), 444-451. https://doi.org/10.3390/j4030034