Effects of Dietary Fermented Chinese Herbal Waste Compound on the Growth, Digestive Function, Antioxidative Capacity and Non-Specific Immunity of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Diets
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Growth Performance Measurement
2.5. Enzymatic Activity Assays
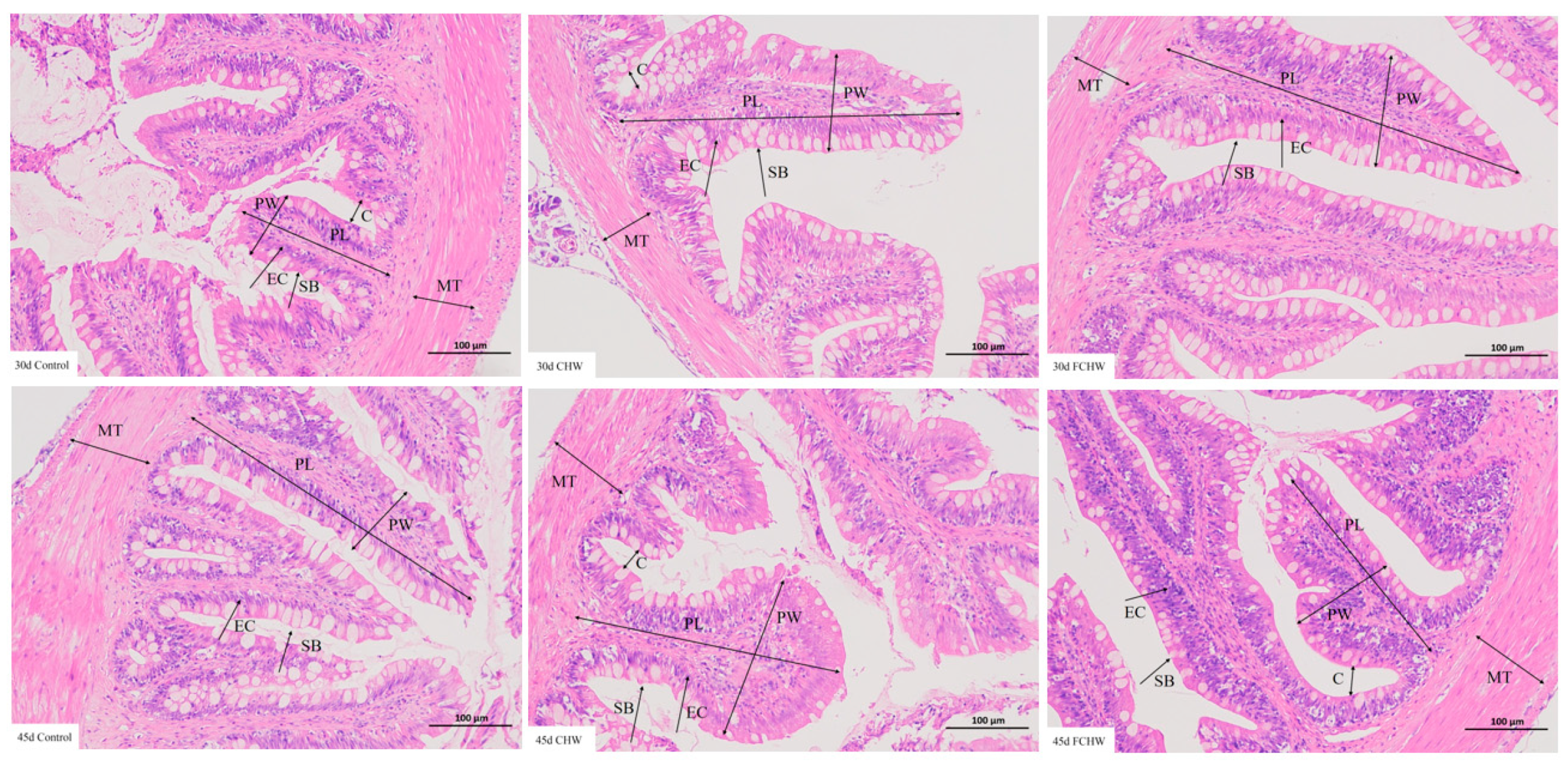
2.6. Intestinal Histology Observation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Dietary FHWC on the Growth Performance of M. salmoides
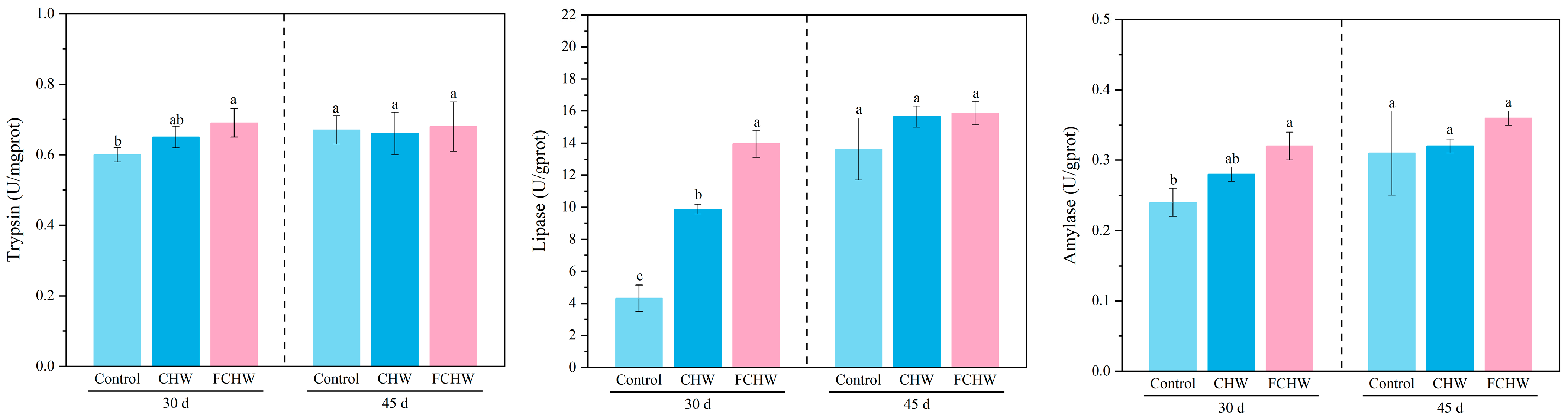
3.2. Effects of Dietary FHWC on Intestinal Digestive Function of M. salmoides
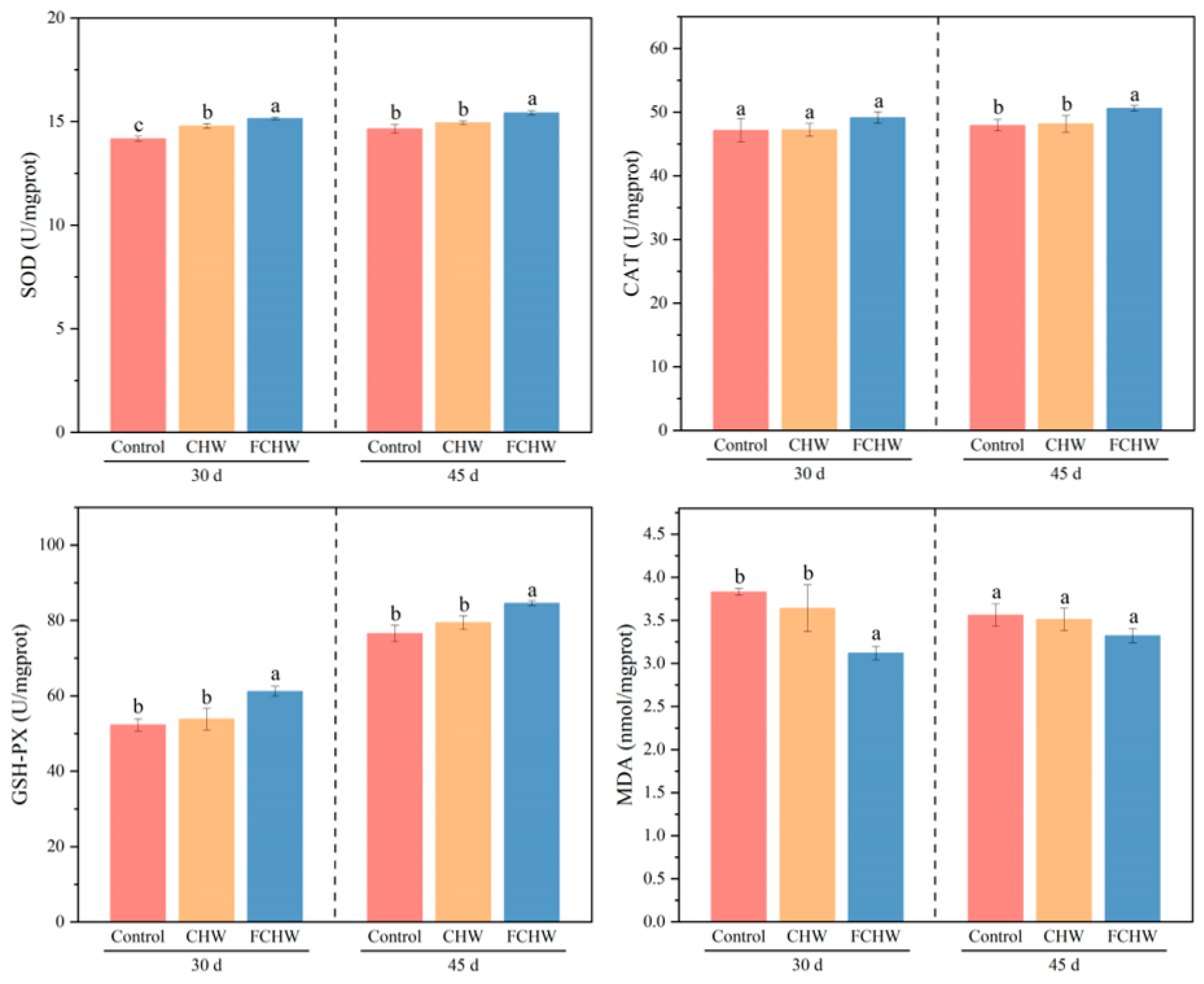
3.3. Effects of Dietary FHWC on Hepatic Antioxidative Capacity of M. salmoides
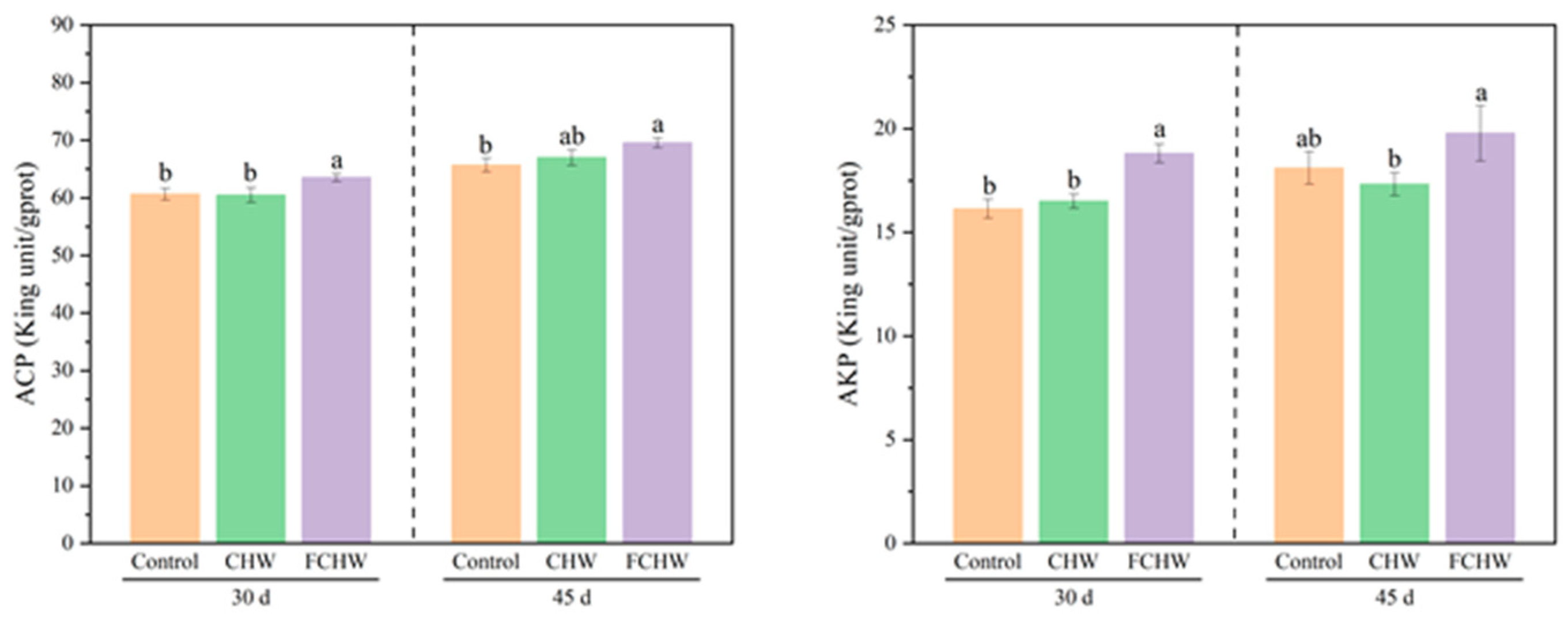
3.4. Effects of Dietary FHWC on Hepatic Non-Specific Immunity of M. salmoides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FCHW | Fermented Chinese herbal waste compound |
| CHW | Chinese herbal waste |
References
- Pu, H.; Li, X.; Du, Q.; Cui, H.; Xu, Y. Research progress in the application of Chinese herbal medicines in aquaculture: A Review. Engineering 2017, 3, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Jia, S.; Zhi-Nan, Y.; Shuang, L.; Yue-Hong, L.I. Research progress of Chinese herbal medicine in aquaculture. Feed Res. 2023, 46, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Bose, S.; Wang, J.-H.; Yadav, M.K.; Mahajan, G.B.; Kim, H. Fermentation, a feasible strategy for enhancing bioactivity of herbal medicines. Food Res. Int. 2016, 81, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.; Fan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. The Application of fermentation technology in traditional Chinese medicine: A review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 899–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, R.; Ma, F.; Jiang, W.; Han, C. Recycling utilization of Chinese medicine herbal residues resources: Systematic evaluation on industrializable treatment modes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 32153–32167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Z.-X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Gao, J. Treatment and bioresources utilization of traditional Chinese medicinal herb residues: Recent technological advances and industrial prospect. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Lutz-Carrillo, D.J.; Quan, Y.; Liang, S. Taxonomic status and genetic diversity of cultured largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides in China. Aquaculture 2008, 278, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Ramos, F. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: Current knowledge and alternatives to tackle the problem. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Bi, X.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Dai, W. Study on optimization of aerobic fermentation conditions for stems and leaves of compound Chinese herbs. Feed Res. 2024, 23, 119–124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Li, J.L.; Wu, T.T. Effects of exogenous enzyme and citric acid on activities of endogenous digestive enzyme of tilapia(Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus). J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2005, 28, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Xue, Y. Effects of chronic exposure of 2,4-dichlorophenol on the antioxidant system in liver of freshwater fish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenzado, C.; Hidalgo, M.C.; García-Gallego, M.; Morales, A.E.; Furné, M.; Domezain, A.; Domezain, J.; Sanz, A. Antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in sturgeon Acipenser naccarii and trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. A comparative study. Aquaculture 2006, 254, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Dogru, M.I.; Dogru, A.K.; Gul, M.; Esrefoglu, M.; Yurekli, M.; Erdogan, S.; Ates, B. The effect of adrenomedullin on rats exposed to lead. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhao, L.; Pan, Y.; Kang, Y.; Liu, Z. Chinese herbal medicines mixture improved antioxidant enzymes, immunity and disease resistance to infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 3217–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Chen, W.; Vong, C.T.; Yao, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Astragali Radix (Huangqi): A promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elabd, H.; Wang, H.-P.; Shaheen, A.; Matter, A. Astragalus membranaceus nanoparticles markedly improve immune and anti-oxidative responses; and protection against Aeromonas veronii in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.-T.; Zhao, S.-Z.; Wang, K.-L.; Fan, M.-X.; Han, Y.-Q.; Wang, H.-L. Effects of dietary Astragalus Membranaceus supplementation on growth performance, and intestinal morphology, microbiota and metabolism in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 100955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, H.; Wang, H.-P.; Shaheen, A.; Yao, H.; Abbass, A. Astragalus membranaceus (AM) enhances growth performance and antioxidant stress profiles in bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Wu, M.; Yang, Q.; Li, H. The extract of Astragalus membranaceus inhibits lipid oxidation in fish feed and enhances growth performance and antioxidant capacity in Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Fishes 2023, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Ahmed, H.A.; Shukry, M.; Chaklader, M.R.; Saleh, R.M.; Khallaf, M.A. Astragalus membranaceus Extract (AME) enhances growth, digestive enzymes, antioxidant capacity, and immunity of Pangasianodon hypophthalmus juveniles. Fishes 2022, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Pu, J.; Luo, L.; et al. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus by-product on pellet quality, mold growth and resistance of Crucian carp (Carassius auratus) against Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac. Rep. 2025, 43, 102820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, I.P.; Lee, P.-T.; Nan, F.-H. Rheum officinale extract promotes the innate immunity of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) and exerts strong bactericidal activity against six aquatic pathogens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 102, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.F.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, G.X. In vivo evaluation of anthelmintic potential of medicinal plant extracts against Dactylogyrus intermedius (Monogenea) in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, W.; Yin, S.; Long, X.; Zhao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y. Improvement effects and mechanism of compound Chinese herbal medicine on fatty liver in largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquaculture 2025, 598, 742075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.T.; Ding, Z.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, W.Q.; Xia, R.X.; Yang, S.; Fei, H. Combination of herbal extracts regulates growth performance, liver and intestinal morphology, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal microbiota in Acrossocheilus fasciatus. Aquaculture 2025, 594, 741428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liang, J.; Ling, J.; Chen, Y.; Tang, X.; et al. Application of fermented Chinese herbal medicines in food and medicine field: From an antioxidant perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 148, 104410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, F.J.; Díaz, M.; Alarcón, F.J.; Sarasquete, M.C. Characterization of digestive enzyme activity during larval development of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 1996, 15, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y. The effect of fermented Chinese herbal medicine extracts on the growth performance and intestinal digestive enzyme activity of Ictalurus punctatus. Feed China 2010, 15, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Schallmey, M.; Singh, A.; Ward, O.P. Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S. Application of fermentation strategy in aquafeed for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, X.M.; Shu, H.; Zhang, H.F.; Shi, H.R. The effects of two kinds of microecologics on body composition, intestinal digestive enzyme and histological structure of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀×E. lanceolatus ♂). Feed Ind. 2018, 39, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhong, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Effects of dietary andrographolide levels on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, intestinal immune function and microbioma of rice field eel (Monopterus Albus). Animals 2020, 10, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandalios, J.G. Oxidative stress: Molecular perception and transduction of signals triggering antioxidant gene defenses. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 995–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavas, L.; Tarhan, L. Glutathione redox system, GSH-Px activity and lipid peroxidation (LPO) levels in tadpoles of R.r.ridibunda and B.viridis. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2003, 21, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.; Bao, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, B. Effects of dietary fermented Chinese herbal medicines on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, liver antioxidant capacity, and intestinal inflammatory gene expression of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wei, L.; Zhai, H.; Ren, T.; Han, Y. An evaluation on betaine and trimethylammonium hydrochloride in the diet of Carassius auratus: Growth, immunity, and fat metabolism gene expression. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ayiku, S.; Liu, H.; Tan, B.; Dong, X.; Chi, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W. Effects of dietary ESTAQUA® yeast culture supplementation on growth, immunity, intestinal microbiota and disease-resistance against Vibrio harveyi in hybrid grouper (♀Epinephelus fuscoguttatus×♂E. lanceolatus). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 22, 100922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Nutrient Components | Proportion | Nutrient Components | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude protein, %≥ | 48.0 | Total phosphorus, %≥ | 1.0 |
| Crude fiber, %≥ | 4.0 | Sodium chloride, %≥ | 0.3–3.0 |
| Crude lipid, %≥ | 9.0 | Lysine, %≥ | 2.6 |
| Ash, %≤ | 12.0 | Moisture, %≤ | 12.0 |
| calcium, % | 1.0–3.0 |
| Time | Group | SGR (%) | WGR (%) | FCR | HI (%) | SR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 d | Control | 3.56 ± 0.14 b | 191.64 ± 12.72 b | 1.52 ± 0.02 a | 2.01 ± 0.09 b | 100 |
| CHW | 3.60 ± 0.26 b | 195.54 ± 23.32 b | 1.50 ± 0.02 a | 2.40 ± 0.15 a | 100 | |
| FCHW | 4.17 ± 0.08 a | 249.01 ± 8.30 a | 1.45 ± 0.04 a | 2.29 ± 0.05 ab | 100 | |
| 45 d | Control | 2.61 ± 0.08 b | 224.30 ± 11.73 b | 1.60 ± 0.11 a | 1.38 ± 0.11 a | 100 |
| CHW | 2.85 ± 0.11 b | 260.38 ± 17.66 b | 1.53 ± 0.06 a | 1.50 ± 0.06 a | 100 | |
| FCHW | 3.31 ± 0.11 a | 344.12 ± 21.17 a | 1.49 ± 0.02 a | 1.38 ± 0.17 a | 100 |
| Time | Group | Villus Height (mm) | Villus Width (mm) | Muscularis Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 d | Control | 0.55 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.02 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 b |
| CHW | 0.40 ± 0.01 c | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 c | |
| FCHW | 0.69 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 0.22 ± 0.01 a | |
| 45 d | Control | 0.63 ± 0.01 c | 0.14 ± 0.02 b | 0.19 ± 0.01 b |
| CHW | 0.67 ± 0.01 b | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | |
| FCHW | 0.74 ± 0.02 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Shi, Z.; Bi, X.; Dai, W. Effects of Dietary Fermented Chinese Herbal Waste Compound on the Growth, Digestive Function, Antioxidative Capacity and Non-Specific Immunity of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes 2025, 10, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120629
Zhang X, Zhao X, Shi Z, Bi X, Dai W. Effects of Dietary Fermented Chinese Herbal Waste Compound on the Growth, Digestive Function, Antioxidative Capacity and Non-Specific Immunity of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes. 2025; 10(12):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120629
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaolei, Xinye Zhao, Zecheng Shi, Xiangdong Bi, and Wei Dai. 2025. "Effects of Dietary Fermented Chinese Herbal Waste Compound on the Growth, Digestive Function, Antioxidative Capacity and Non-Specific Immunity of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides)" Fishes 10, no. 12: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120629
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhao, X., Shi, Z., Bi, X., & Dai, W. (2025). Effects of Dietary Fermented Chinese Herbal Waste Compound on the Growth, Digestive Function, Antioxidative Capacity and Non-Specific Immunity of Juvenile Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes, 10(12), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10120629







