Abstract
The incorporation of the natural amino acid L-proline in the synthesis to vanadium-chromium Prussian blue derivatives results in materials exhibiting magnetic ordering including chiral magnetic centers. Although the amorphous nature of these materials makes difficult to assess the structural features of these proline-containing compounds, magnetic and spectroscopic data confirms their multifunctionality. They exhibit high-temperature magnetic ordering (Tc < 255 K) and a circular dichroic signal, representing the molecule-based chiral magnets with the highest ordering temperatures reported to date. In addition, the presence of chiral L-proline (or D-proline) has additional benefits, including higher redox stability and the appearance of magnetic hysteresis. The latter was not observed in the parent compounds, the series of room temperature molecule-based magnets V[Cr(CN)6]x.
Keywords:
molecule-based magnets; chirality; magnetic hysteresis; cyanide; vanadium; chromium; amino acid 1. Introduction
Molecule-based magnets [1] are particularly suited for the development of multifunctionality [2]. By design of functional molecules as building blocks, one can bring to a solid the desired combination properties. This is unparalleled by solid-state materials, where it is very difficult to tune or modify their physical properties by chemical methods. This powerful molecular strategy to yield unique multifunctional materials has been particularly successful in the development of magnetic materials with a second added value: sensing [3,4,5,6], porosity [7], superconductivity [8,9,10,11], electrochromism [12], or optical activity [13,14,15,16]. The latter is a very appealing possibility, since unique properties are expected in such materials, such as non-linear optical switching [17] or magneto-chiral dichroism and birefringence [18,19]. The unprecedented magneto-optical features proposed include the possibility to tune light-matter interactions via external magnetic stimuli. However, molecule-based magnets typically exhibit very low ordering temperatures, well below the boiling temperature of liquid nitrogen, precluding immediate or wide applications. This is due to the weak nature of magnetic super-exchange and dipolar interactions, both at the origin of their magnetic properties.
One significant exception is the family of Prussian blue analogs (PBAs). High temperature molecule-based magnets are available [20,21,22,23], just selecting the right combination of constitutive transition metal cations [24], with particular success in the Vanadium-Chromium series: V[Cr(CN)6]0.86 (Tc = 315 K), K0.058V[Cr(CN)6]0.79 (Tc = 372 K) or KVII[Cr(CN)6] (Tc = 376 K) [25,26,27]. Such high-temperature ordering above room temperature comes with a price in these materials, though. They all have in common an amorphous long-range structure containing non-stoichiometric amounts of V in low oxidation states (II and III). For this reason, these compounds must be prepared under an inert atmosphere, as they present an inherent instability to oxygen. If the VII/III centers are oxidized by air to the VIV vanadyl species (VO2+), the ordering temperature decreases down to 115 K in the corresponding (VO)[CrIII(CN)6]x analog [28].
Optically active materials based on Prussian blue coordination magnets have been obtained by the incorporation of ancillary chiral ligands in the construction of PBAs [29,30,31]. The chiral ligand typically coordinates the divalent metal cation, lowering connectivity and ordering temperatures, but providing optical activity. However, this strategy has not successfully applied to the high-temperature counterparts, due to the key participation of V in low oxidation states. These states are redox-unstable in reaction conditions, upon the presence of the chosen chiral ligands, typically chelating diamines [32,33,34]. These non-innocent ligands coordinate and destabilize the vanadium or chromium centers in low redox states, as needed for the formation of the extended network.
Here we describe the successful use of an enantiopure natural amino acid, L-proline (L-pro), as a chiral inductor in the preparation of cyanide-based magnets. Our target magnetic materials, prepared from the reaction of vanadium (II) and hexacyanochromate in the presence of this enantiopure zwitterion, exhibit optical activity, and spontaneous magnetization at temperatures as high as 260 K. Our strategy offers, for the first time, a successful rational strategy towards molecule-based high temperature optically active magnets.
2. Results and Discussion
From the different synthetic protocols, we followed a variation of the improved synthesis reported by Garde et al. [35] Vanadium(II) chloride and tetrabutylammonium hexacyanochromate were reacted in water in the presence of L-proline (Scheme 1), at a L-pro/V ratio = 0, 1 and 2, under nitrogen atmosphere. After 20 min, a solid was filtered and dried in a nitrogen stream. The stoichiometry for these compounds was determined by elemental analysis, and they will be referred according to the initial L-pro/V ratio during the reaction, for the sake of clarity, as VCr0, VCr1 and VCr2, respectively.
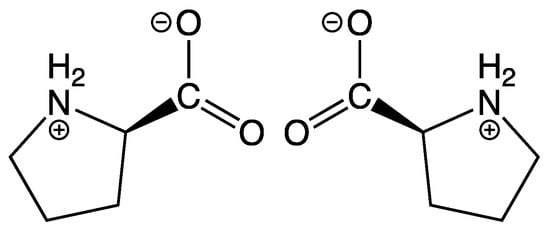
Scheme 1.
Zwitterionic structure of both proline enantiomers: (L)-proline (left) and (D)-proline (right).
These solids are amorphous, as expected, showing no powder diffraction pattern [10]. The incorporation of proline was confirmed and quantified by elemental analysis (ICP-MS). These also indicated the presence of sub-stoichiometric amounts of TBA+ and Cl−. According to the elemental data and thermogravimetry, the stoichiometries are (TBA)0.2V[Cr(CN)6]0.8Cl0.4·16H2O (VCr0), (TBA)0.6(L-pro)1.8V[Cr(CN)6]0.77Cl0.6·12H2O (VCr1), and (TBA)0.6(L-pro)2.8V[Cr(CN)6]0.66Cl0.50·8H2O (VCr2). The proline ratio in the products is higher than in the reagents. This, in addition to the uncertain redox state of the metals, the zwitterionic nature of the L-pro moieties, and the additional ionic content in the formulas, makes it difficult to derive any plausible hypothesis regarding the coordination environment of the V centers and of the L-pro molecules. Most certain, at least for VCr2, some L-pro molecules must be trapped inside the cyanide bridged network via supramolecular interactions, and not directly coordinated to metals (L-pro/V ≈ 3).
We also characterized the materials by IR spectroscopy in the search for some data regarding the latter. Although the materials were manipulated under an inert atmosphere, spectroscopic data were obtained in the open air, and partial oxidation was observed, not necessarily present in the as-prepared compounds. In the proline-free compound, VCr0, two bands were found corresponding to the cyanide stretching. One centered at 2118 cm−1, assigned to the VII-CrIII couple, and another one centered at 2175 cm−1, signature of the VIV-CrIII couple. The latter increases its intensity after air exposition, as expected (Figure S1). The presence of proline in VCr1 and VCr2 is confirmed in the IR spectra by its signature band at 2964 cm−1 (Figures S1 and S2), corresponding to the H–N stretching frequency. In the CN stretching region, we observed the same two bands, analogous to the parent compound, with only two major differences: the bands are weaker and, more importantly, the changes after air exposition are minimal. This suggests that redox stability increases when proline is present in the structure.
To characterize the magnetic behavior of these materials, we performed magnetic measurements in the 2–300 K range (Figure 1). In all cases, the magnetization (M) shows a sharp jump and tends to saturation as the temperature is decreased, the signature of the onset of spontaneous magnetization. Critical temperatures (Tc) were extracted from the slope of the initial increase in M projected to M = 0 cm3 mol−1 Oe. With this criteria, VCr0 shows a spontaneous magnetization below 275 K. This initial Tc indicates partial oxidation of the material, since it is lower than those typically reported for the V-Cr series, albeit strong variations depending on preparation [36]. After 24 h of air exposition, Tc decreases down to 120 K, the typical Tc for the all-vanadyl Prussian blue analogue [13].
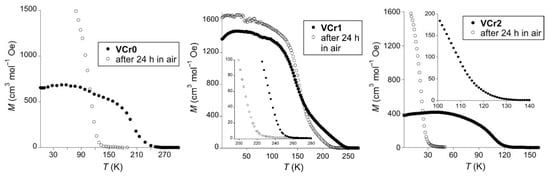
Figure 1.
Field-cooled magnetization for VCr0, VCr1 and VCr2: as prepared (full circles) and after 24 h of air exposition (empty circles).
VCr1 shows a very high ordering temperature of 255 K. The onset of spontaneous magnetization below this temperatures was confirmed by zero-field cooled/field cooled/remnant magnetization (ZFC/FC/RM) measurements (Figure S3), showing consistent temperatures for the deviation between ZFC and FC data, in agreement with the temperature where RM data becomes negligible. After 24 h exposed to air, Tc drops only by 30 K, down to 222 K, confirming the superior redox stability of this material, as already hinted by IR data.
At a higher L-pro/V ratio, this positive effect is lost. VCr2 shows a Tc of 122 K, and decreases down to 30 K once it is exposed to air. Thus, there is an optimum L-pro/V ratio to maximize the magnetic performance. This also suggests that the initial proline is mainly incorporated into the interstices of the material, with relatively low participation in direct binding to the V centers. This would agree with the high Tc of VCr1. At higher proline loading, the proline units may block a higher number of coordination sites, blocking magnetic connectivity. This reduces the overall magnetic dimensionality, and Tc decreases.
The field dependence of the magnetization and the corresponding hysteresis cycles were measured at 2 K (Figure 2). VCr0 exhibited no memory effect, in good agreement with previous literature [35]. Cyanide-based V-Cr materials are typically soft magnets, with irreversibility appearing well below 50 Oe [36,37]. In contrast, magnetic hysteresis loops open at 2 K for both proline-containing derivatives. Coercive field (Hc) increases with proline content, reaching Hc = 382 Oe for VCr2, and Hc = 155 Oe for VCr1, whereas total magnetization decreases. Both materials do not reach perfect saturation at high fields, indicating the presence of a paramagnetic contribution. At 3 T, M is 0.88 μB for VCr1 and 0.40 μB for VCr2. These low values are in good agreement with the presence of antiferromagnetic exchange between the chromium and vanadium networks, resulting in ferrimagnetic ordering. Using these values, we may estimate the approximate oxidation state of V centers. All chromium centers are in the S(CrIII) = 3/2 ground state, but vanadium can be in any state between S(VII) = 3/2, S(VIII) = 1 and even S(VIV) = ½, due to undesired oxidation during synthesis or during transfer into the magnetic measurements compartment. VCr1 magnetization data is in good agreement with an all VII compound, what would yield M ≈ 0.7 μB for an analogous magnetically isotropic system (g ≈ 2). On the contrary, VCr2 magnetization data suggests an equimolar VII/VIII ratio, which would require the presence of deprotonated L-proline, as already suggested by the formula. This is also in good agreement with the lower Tc found for this derivative. Remnant magnetizations (MR) are 0.11 and 0.08 μB, respectively, very similar for both materials, despite their very different ordering temperatures, different oxidation states, and different magnetization behavior.
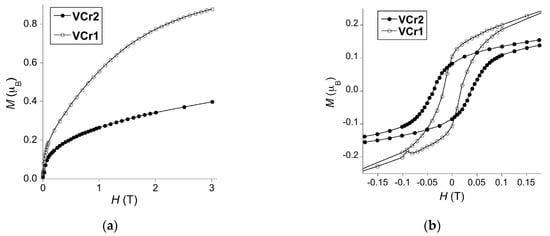
Figure 2.
(a) Magnetization data and (b) hysteresis cycle for VCr1 (empty circles) and VCr2 (full circles) at 2 K.
In order to confirm that the optical activity has been transferred to the magnetic skeleton, even when most prolinate ligands are occupying interstitial species without direct bond to the metal centers, we studied the appearance of circular dichroism (CD) in the absorption spectra of these materials in the visible range. Due to technical issues, these experiments were performed in air. Thus, oxidation to vanadyl is expected, but this should not affect the chirality of the materials. If the vanadyl derivative remains chiral, it must be due to the parent material being chiral itself, and optical activity should be preserved. It is also worthy to mention that proline only absorbs in the UV region. Therefore, all bands appearing in the visible must have contributions from the metal centers, the spin carriers. Indeed, we observed a negative Cotton effect in the CD spectra for both compounds (Figure 3). We also prepared the same materials starting with D-proline. The CD spectra for D-VCr1 and D-VCr2 are the corresponding specular images of the L-proline counterparts, showing the analogous positive Cotton effect, and confirming the optical activity of the magnetic V-Cr networks.
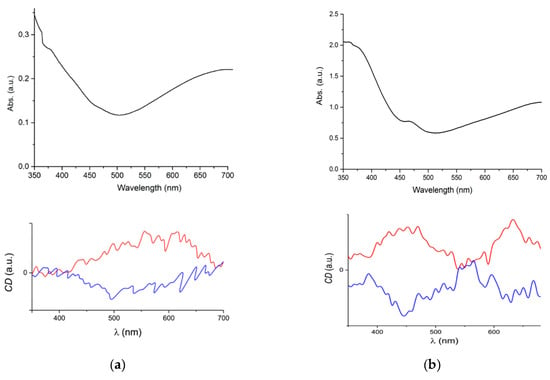
Figure 3.
CD signal for compounds VCr1 (a) and VCr2 (b): D enantiomer (red line), L enantiomer (blue line).
The different absorption and CD spectra indicate the presence of different chromophores in both materials. In the visible range, VCr1 shows a broad band centered around 680 nm, a minimum at 500 nm and then a second broad band with its maximum below 350 nm. Accordingly, the CD spectra must be associated to the first band. In the case of VCr2, there is a broad band centered above 700 nm, and below the minimum at 500 nm, two additional bands appear: a shoulder at 420 nm and another intense band centered at 360 nm. This high energy absorption, absent or negligible in VCr1, should be at the origin of the double Cotton effect observed in VCr2, with the corresponding dichroic signal remaining active well below 400 nm, and just disappearing below 450 nm in the other case.
3. Materials and Methods
Synthesis. All reagents and solvents were commercially available and used as received. All procedures were carried out in a nitrogen flushed glove box, to avoid the presence of oxygen. (TBA)3[Cr(CN)6] (TBA = tetrabutylammonium) was obtained by mixing ethanol solutions of K3[Cr(CN)6] and TBACl overnight.
VCr0: anhydrous VCl2 (0.9 mmol) was dispersed in 5 mL of deaerated water and left stirring for 20 h. (TBA)3[Cr(CN)6] (0.3 mmol), dissolved in 5 mL of deaerated water, were added dropwise to this green suspension. Immediately, a deep blue precipitate forms. The solid was centrifuged, and washed thoroughly with water and methanol. (TBA)0.2V[Cr(CN)6]0.8Cl0.4·16H2O (568.35): calcd. V 8.96, Cr 7.32, C 16.91, H 6.95, N 12.32, Cl 2.50; found: V 8.96, Cr 7.32, C 17.38, H 6.45, N 12.15; Cl 2.50.
VCr1: anhydrous VCl2 (0.9 mmol) was dispersed in 5 mL of reaerated water containing proline (0.9 mmol) and left stirring for 20 h. The initially green suspension turns into a brown solution. (TBA)3[Cr(CN)6] (0.3 mmol) were added dropwise, dissolved in 5 mL of deaerated water. Immediately, a deep blue precipitate forms. The solid was centrifuged, and washed thoroughly with water and methanol. Proposed stoichiometry for VCr1: (TBA)0.6(L-pro)1.8V[Cr(CN)6]0.77Cl0.6·12H2O (801.37): calcd. V 6.36, Cr 5.00, C 34,81, H 7.77, N 12.27, Cl 2.66; found V 6.36, Cr 5.00, C 35.05, H 7.50, N 12.30, Cl 2.66.
VCr2: this compound was prepared following the same procedure as for VCr1, but using 1.8 mmol of L-proline in the preparation. Proposed stoichiometry for VCr2: (TBA)0.6(L-pro)2.8V[Cr(CN)6]0.66Cl0.50·8H2O (818.00): calcd. V 6.23, Cr 4.20, C 40.47, H 7.74, N 12.60, Cl 2.17; found V 6.23, Cr 4.20, C 40.79, H 7.59, N 12.49, Cl 2.17.
Methods. elemental analysis (C, H, N and Cl) were carried out by the CAI Microanálisis Elemental (Universidad Complutense, Madrid). In all cases a non-magnetic impurity of TBACl was detected, up to 30%, probably co-precipitated/occluded during the fast precipitation process [35]. The corresponding elemental content was discarded for the correct estimation of the stoichiometry of the materials. Metal content analysis (V and Cr) were carried out by ICP-MS in the Laboratorio de Técnicas Instrumentles (UVa). Infrared spectra were recorded in the 4000–400 cm−1 range with a Bruker Optics FT-IR Alpha spectrometer using the ATR mode. Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA) were performed with a TGA/SDTA851 Mettler Toledo instrument with a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 in air. Magnetic measurements were carried out on polycrystalline powder samples. Each sample was secured inside a tight gel capsule in a nitrogen-purged glovebox, and transferred into the sample compartment of a Quantum Design MPMS-XL SQUID magnetometer (Quantum Design, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). ZFC/FC/RM measurements were carried out under an applied field of 50 Oe. After these initial measurements, the compounds were exposed to air for 24 h, and the magnetic measurements repeated to determine the effect of air instability. Circular dichroism data was collected on pressed pellets obtained from powder samples with an Applied Photophysics Chirascan spectrometer at room temperature.
4. Conclusions
We have demonstrated a simple strategy to incorporate enantiopure (L- or D-) proline in the preparation of high temperature cyanide-based V-Cr magnets in order to confer them optical activity. At low proline/V ratios, these materials maintain a very high ordering temperature, close to room temperature (≈255 K), and exhibit a remarkably high redox stability, when compared with the classic cyanide-based V–Cr magnets. Unfortunately, the structurally amorphous nature of these materials does not allow us to elucidate the structural environment of the proline molecules. At this point, it is uncertain if they occupy any of the vanadium open coordination sites, or if they are just incorporated via supramolecular interactions in the cavities of the cyanide-bridged extended network. Local structural techniques, such as X-ray absorption, will be helpful to determine the coordination modes. Either way, the optical activity of the ferrimagnetic network is confirmed by the UV-vis absorption spectra observed for the metal-based transitions, confirming the true multifunctionality of these cyanide-based materials, regardless of the structural participation of the amino acid.
Our simple strategy is powerful enough to develop room-temperature chiral magnets, while conferring superior magnetic performance: our proline-modified magnets are the first of their kind showing magnetic hysteresis. This should be related to a higher magnetic anisotropy in these systems, as induced by the presence of chiral centers. Further experiments in the search for synergy between spontaneous magnetization and optical activity are underway, including the search for the elusive magneto-chiral dichroism [38,39,40,41].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2312-7481/6/1/12/s1, Figure S1: FT-IR spectra of VCr0: as prepared (a), and after 24 h exposed to air (b); of VCr1, as prepared (c) and after 24 h exposed to air (d); and of L-proline (e), Figure S2: FT-IR spectra of VCr0: as prepared (a), and after 24 h exposed to air (b); of VCr2, as prepared (c) and after 24 h exposed to air (d); and of L-proline (e), Figure S3: UV-vis data for compounds VCr1 (a) and VCr2 (b).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R.G.-M.; Formal analysis, B.R.-G. and J.R.G.-M.; Funding acquisition, J.R.G.-M.; Investigation, B.R.-G. and J.R.G.-M.; Methodology, B.R.-G. and J.R.G.-M.; Resources, J.R.G.-M.; Supervision, J.R.G.-M.; Writing—original draft, B.R.-G. and J.R.G.-M.; Writing—review & editing, J.R.G.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union (project ERC StG grant CHEMCOMP no 279313); the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación/Agencia Estatal de Investigación/FEDER (RTI2018-095618-B-100); and the Generalitat de Catalunya (2017-SGR-1406 and the CERCA Programme).
Acknowledgments
We thank David Nieto-Castro for helpful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miller, J.S. Magnetically ordered molecule-based materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3266–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkowicz, D.; Czarnecki, B.; Reczynski, M.; Arczynski, M. Multifunctionality in molecular magnetism. Sci. Prog. 2015, 98, 346–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozumi, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Ohkoshi, S. Electrochemical synthesis, crystal structure, and photomagnetic properties of a three-dimensional cyano-bridged copper-molybdenum complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3864–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkoshi, S.; Imoto, K.; Tsunobuchi, Y.; Takano, S.; Tokoro, H. Light-induced spin-crossover magnet. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilà, D.; Prado, Y.; Koumousi, E.S.; Mathonière, C.; Clérac, R. Clerac, Switchable Fe/Co Prussian blue networks and molecular analogues. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magott, M.; Stefanczyk, O.; Sieklucka, B.; Pinkowicz, D. Octacyanidotungstate(IV) coordination chains demonstrate a light-induced excited spin state trapping behavior and magnetic exchange photoswitching. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13283–13287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darago, L.E.; Aubrey, M.L.; Yu, C.J.; Gonzalez, M.I.; Long, J.R. Electronic conductivity, ferrimagnetic ordering and reductive insertion mediated by organic mixed-valence in a ferric semiquinoid metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15703–15711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, P.; Kurmoo, M. Molecular magnetic semiconductors, metals and superconductors: BEDT-TTF salts with magnetic anions. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, E.; Fujiwara, H.; Kato, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Tokumoto, M.; Cassoux, P. Antiferromagnetic organic metal exhibiting superconducting transition, κ-(BETS)2FeBr4. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5581–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uji, S.; Shinagawa, H.; Terashima, T.; Yakabe, T.; Terai, Y.; Tokumoto, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Tanaka, H.; Kobayashi, H. Magnetic-field-induced superconductivity in a two-dimensional organic conductor. Nature 2001, 410, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, K.; Shan, H.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; Wu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, A.; et al. Molecule-confined engineering towards superconductivity and ferromagneticm in two-dimensional superlattice. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16398–16404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, L.; Robertson, N.; Johansson, J.O. Electrochromic thin films of the V-Cr Prussian blue analogue molecular magnet. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 236, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghidja, A.; Rogez, G.; Rabu, P.; Welter, R.; Drillon, M. An approach to chiral magnets using α-hydroxycarboxylates. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2715–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, Y.; Inoue, K.; Baranoc, N.; Kurmoo, M.; Kikuchi, K. Field-induced ferrimagnetic state in a molecule-based magnet consisting of a CoII ion and a chiral triplet bis(nitroxide) radical. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9902–9909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Mascarós, J.R.; Coronado, E.; Goddard, P.A.; Singleton, J.; Coldea, A.I.; Wallis, J.D.; Coles, S.J.; Alberola, A. A chiral ferromagnetic molecular metal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9271–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkowicz, D.; Podgajny, R.; Nitek, W.; Rams, M.; Majcher, A.M.; Nuida, T.; Ohkoshi, S.; Sieklucka, B. Multifunctional magentic molecular {[MnII(urea)2(H2O)]2[NbIV(CN)8]}n system: Magnetization-induced SHG in the chiral polymorph. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkoshi, S.; Takano, S.; Imoto, K.; Yoshikiyo, M.; Namai, A.; Tokoro, H. 90-degree optical switching of output second-harmonic light in chiral photomagnet. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, L.D.; Vrbancich, J. Magneto-chiral birefringence and dichroism. Mol. Phys. 1984, 51, 715–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikken, G.L.J.A.; Raupach, E. Observation of magnetochiral dichroism. Nature 1997, 390, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallah, T.; Thiébaut, S.; Verdaguer, M.; Veillet, P. High-TC molecular-based magnets: Ferrimagnetic mixed-valence chromium(III)-chromium(II) cyanides with TC at 240 and 190 K. Science 1993, 262, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, W.E.; Paulson, S.C.; Wynn, C.M.; Girtu, M.A.; Epstein, A.J.; White, H.S.; Miller, J.S. Magnetic field induced reversed (negative) magnetization for electrochemically deposited TC = 260 K oxidized films of chromium cyanide magnets. Adv. Mater. 1997, 9, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.O.; Kim, J.W.; Allwright, E.; Rogers, D.M.; Robertson, N.; Bigot, J.Y. Directly probing spin dynamics in a molecular magnet with femtosecond time-resolution. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 7061–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, W.; Imoto, K.; Tsunobuchi, Y.; Ohkoshi, S. Vanadium octacyanoniobate-based magnet with a Curie temperature of 138 K. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 4604–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.; Rodríguez-Fortea, A.; Álvarez, S.; Verdaguer, M. Is it possible to get high TC magnets with Prussian blue analogues? A theoretical prospect. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, S.T.; Mallah, T.; Ouahès, R.; Veillet, P.; Verdaguer, M. A room-temperature organometallic magnet based on Prussian blue. Nature 1995, 378, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatlevik, Ø.; Buschmann, W.E.; Zhang, J.; Manson, J.L.; Miller, J.S. Enhancement of the magnetic ordering temperature and air stability of a mixed valent vanadium hexacyanochromate(III) magnet to 99 °C (372 K). Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.M.; Girolami, G.S. Sol-gel synthesis of KVII[CrIII(CN)6]∙2H2O: A crystalline molecule-based magnet with a magnetic ordering temperature above 100 °C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5593–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, S.; Mallah, T.; Ouahès, R.; Veillet, P.; Verdaguer, M. A chromium-vanadyl ferrimagnetic molecule-based magnet: Structure, magnetism, and orbital interpretation. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Gimenez-Saiz, C.; Martinez-Agudo, J.M.; Nuez, A.; Romero, F.M.; Stoecklie-Evans, H. Design of chiral magnets: Cyanide-bridged bimetallic assemblies based on cyclohexane-1,2-diamine. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Gomez-Garcia, C.J.; Nuez, A.; Romero, F.M.; Waerenborgh, J.C. Synthesis, chirality, and magnetic properties of bimetallic cyanide-bridged two-dimensional ferromagnets. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2670–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millon, J.; Daniel, M.C.; Kaiba, A.; Guionneau, P.; Brandes, S.; Sutter, J.P. Nanoporous magnets of chiral and racemic [{Mn(HL)}2Mn{Mo(CN)7}2] with switchable ordering temperatures (TC = 85 K ↔ 106 K) driven by H2O sorption (L = N,N-dimethylalaninol). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13872–13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, E.; Gomez-Garcia, C.J.; Nuez, A.; Romero, F.M.; Rusanov, E.; Stoeckli-Evans, H. Ferromagnetism and chirality in two-dimensional cyanide-bridged bimetallic compounds. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 4615–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, W.; Kitagawa, S.; Ohba, M. Chiral cyanide-bridged MnIIMnIII ferrimagnets, [MnII(HL)(H2O)][MnIII(CN)6]∙2H2O (L = S- or R-1,2-diaminopropane): Syntheses, structures, and magnetic behaviors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Train, C.; Gruselle, M.; Verdaguer, M. The fruitful introduction of chirality and control of absolute configurations in molecular magnets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3297–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, R.; Herrera, J.M.; Villain, F.; Verdaguer, M. Molecule-based magnets with TC above room temperature: Improved synthesis of vanadium-chromium Prussian blue analogues with inserted alkali cations. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2008, 361, 3597–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, E.; Ferlay, S.; Phan, X.; Desplanches, C.; Cartier dit Moulin, C.; Sainctavit, P.; Baudelet, F.; Dartyge, E.; Veillet, P.; Verdaguer, M. Synthesis and magnetization of new room-temperature molecule-based magnets: Effect of stoichiometry on local magnetic structure by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 11347–11352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, R.; Villain, F.; Verdaguer, M. Molecule-based room-temperature magnets: Catalytic role of V(III) in the synthesis of vanadium–chromium Prussian blue analogues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10531–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Train, C.; Gheorghe, R.; Krstic, V.; Chamoreau, L.-M.; Ovanesyan, N.S.; Rikken, G.L.J.A.; Gruselle, M.; Verdaguer, M. Strong magneto-chiral dichroism in enantiopure chiral ferormagnets. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceolín, M.; Goberna-Ferrón, S.; Galan-Mascaros, J.R. Strong hard X-ray magnetochiral dichroism in paramagnetic enantiopure molecules. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3120–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessoli, R.; Boulon, M.-E.; Caneschi, A.; Mannini, M.; Poggini, L.; Wilhem, F.; Rogalev, A. Strong magneto-chiral dichroism in a paramagnetic molecular helix observed by hard X-rays. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, M.; Breslavetz, I.; Paillot, K.; Inoue, K.; Rikken, G.L.J.A.; Train, C. A chiral Prussian blue analogue pushes magneto-chiral dichroism limits. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20022–20025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).