Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein Enhances PMN Phagocytosis by Binding to Cell Surface-Expressed Lactoferrin and Cathepsin G That Activates MAP Kinase Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. PMN phagocytosis-enhancing activity of THP is initiated by binding to PMN surface that depolarizes membrane potentials
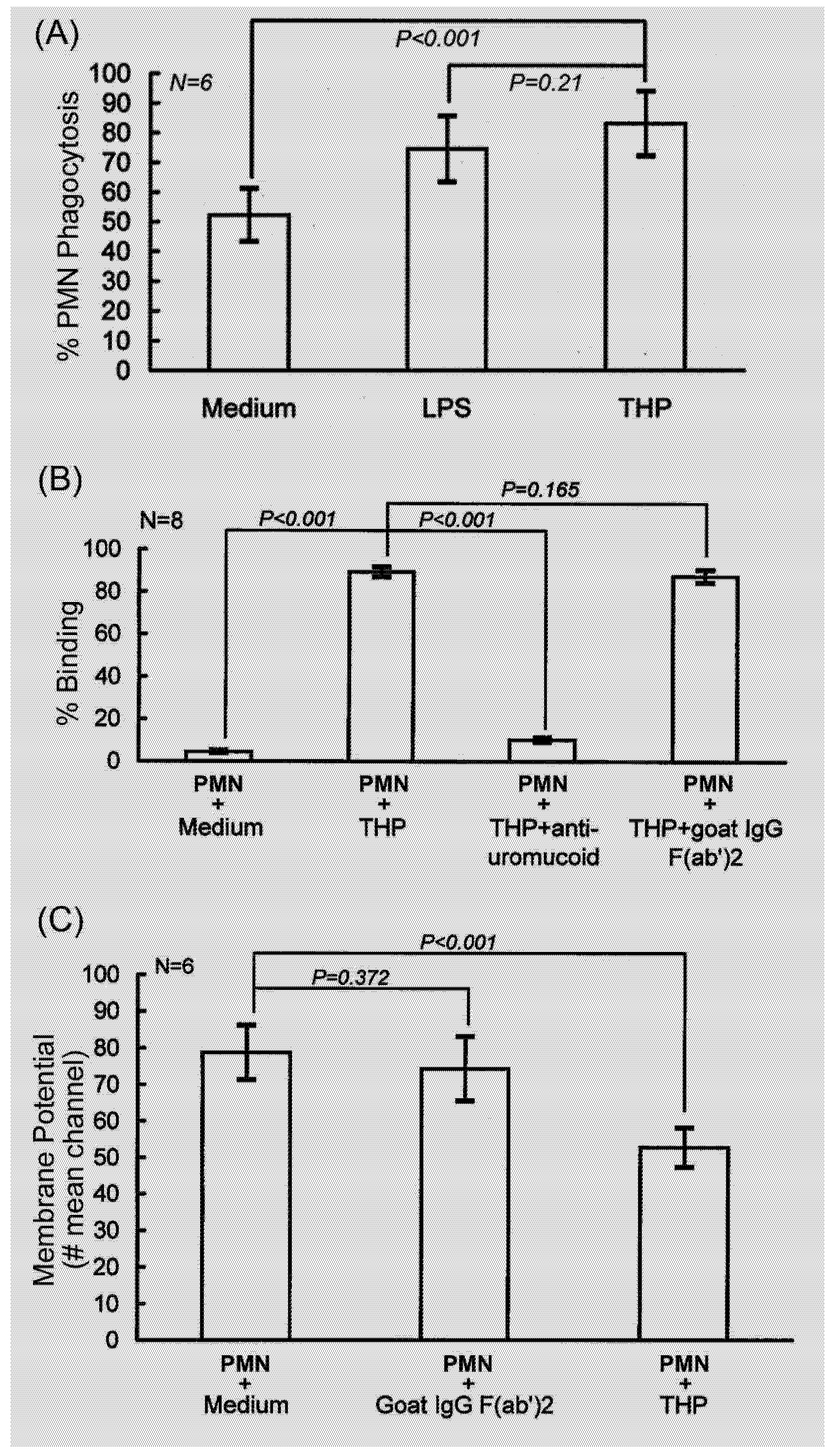
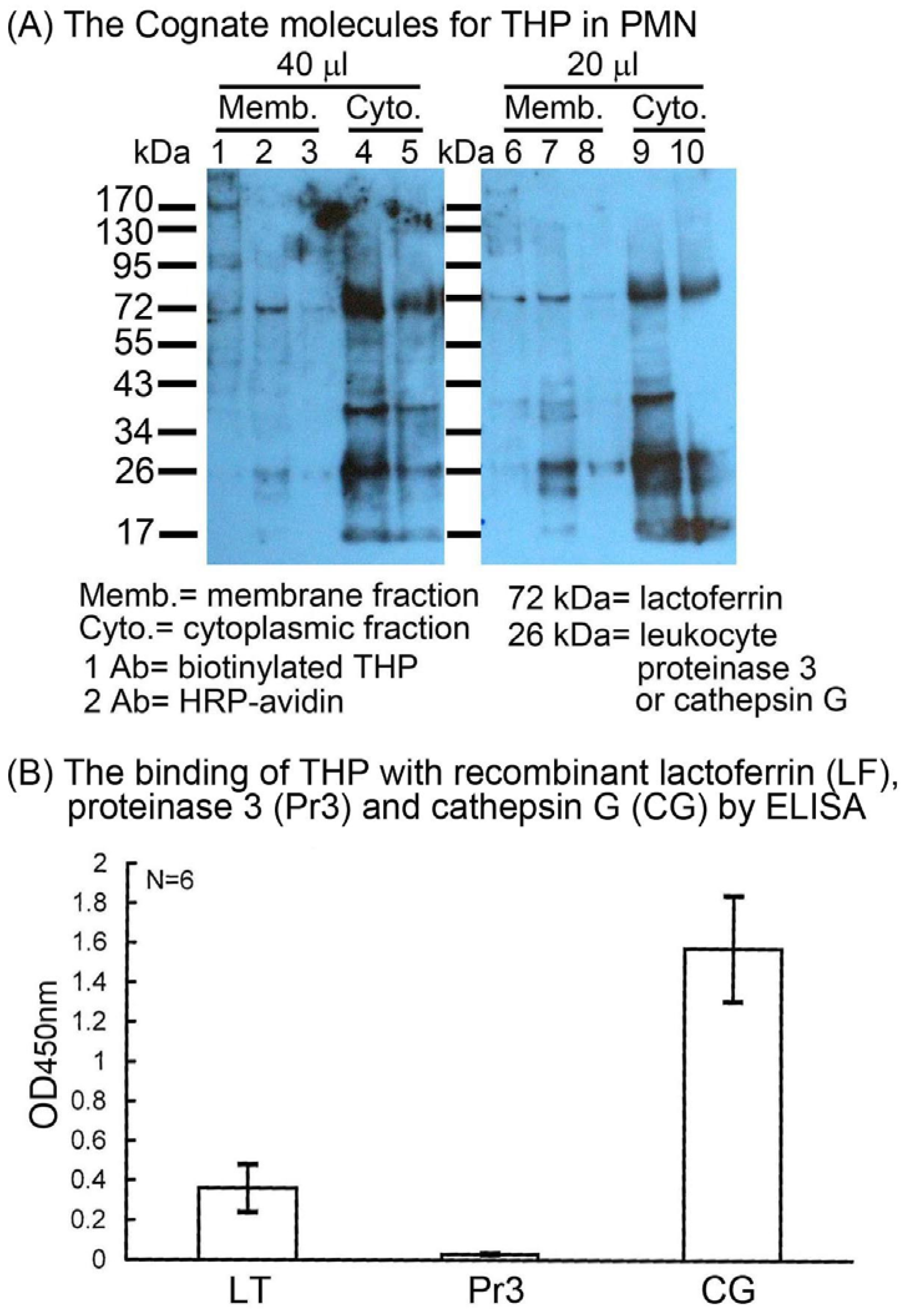
2.2. Identification of the binding molecule(s) of THP on PMN surface

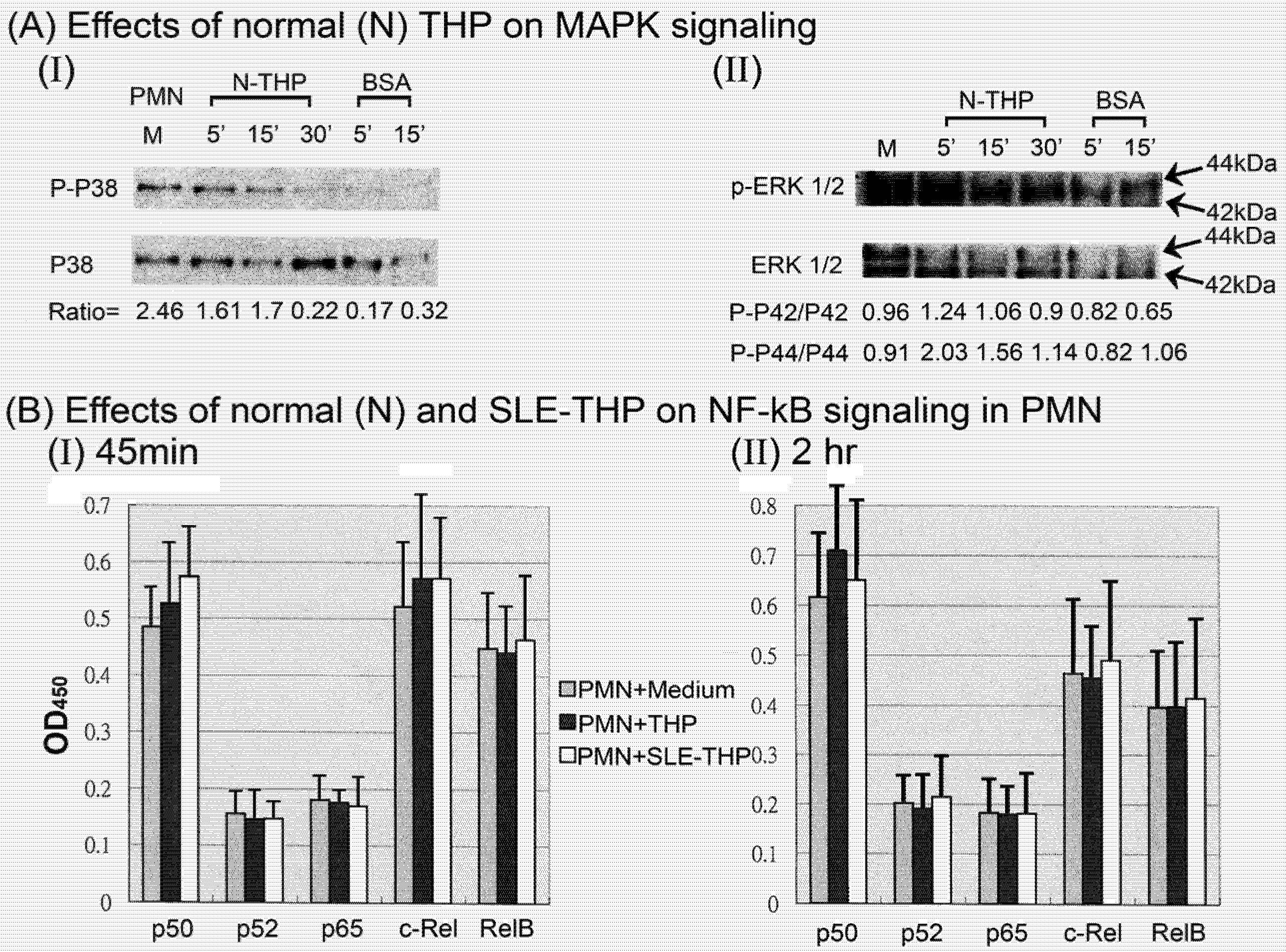
2.3. THP-induced phosphorylation of MAP kinase signaling pathways in PMN
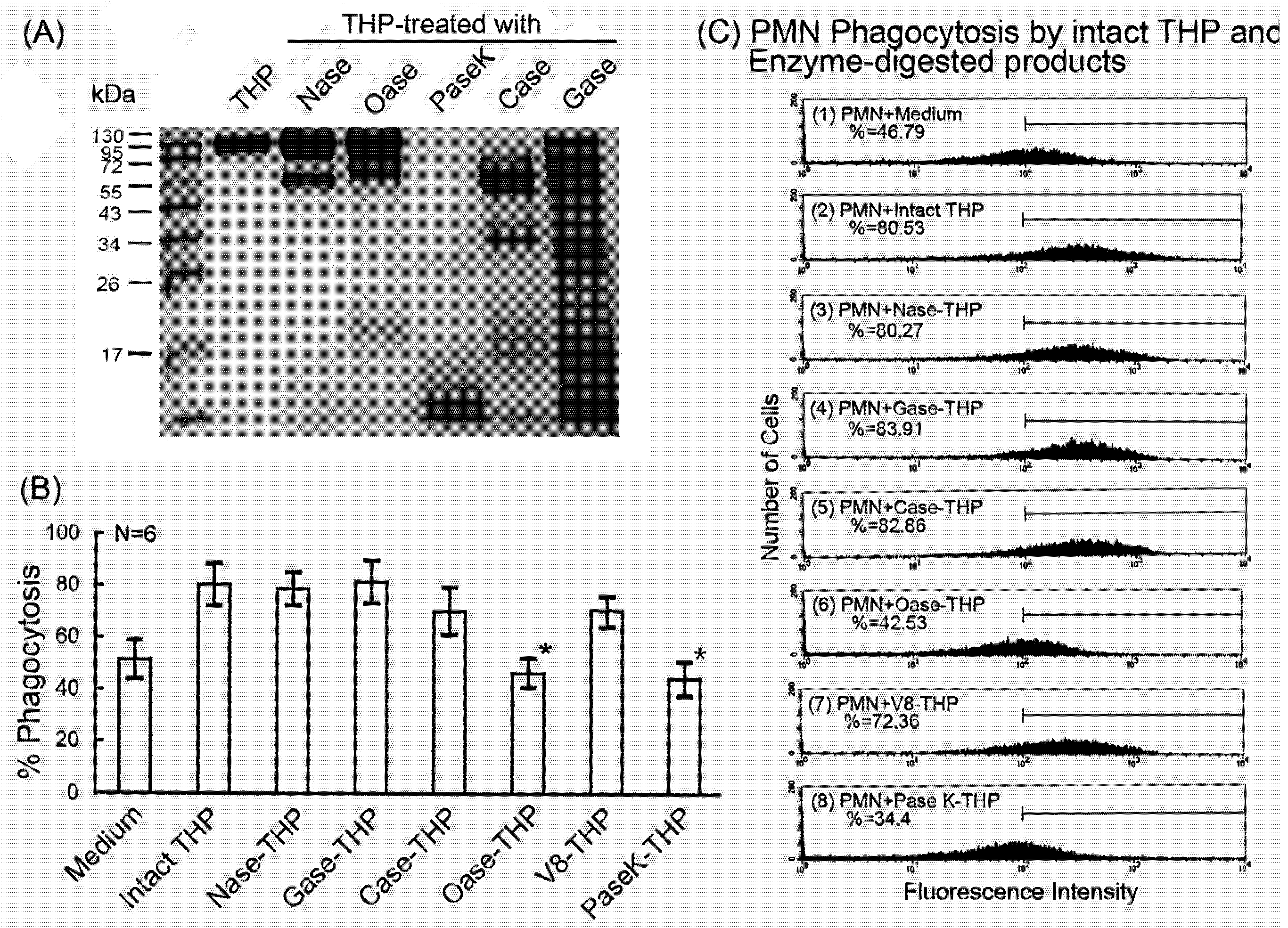
2.4. Comparison of intact THP molecule and its enzyme-digested products on PMN phagocytosis
3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents and antibodies
3.2. Purification of THP from urine of normal human individuals and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
3.3. Biotinylation of THP
3.4. Isolation of PMN from human peripheral blood
3.5. Detectionof PMN phagocytosis by flow cytometry
3.6. Detection of the binding between THG and PMN by flow cytometry
3.7. Estimation of membrane potentials of individual cell by flow cytometry
3.8. Extraction of membranous and cytosolic proteins from PMN
3.9. Detection of THP-binding molecules on surface membrane and cytosolic molecules of PMN after 10% SDS-PAGE analysis
3.10. Measurement of binding capacity between LF, Pr3 or CG and biotinylated THP by ELISA
3.11. Detection of p38 and ERK1/2 MAP kinase phosphorylation in PMN lysates by Western blot
3.12. Detection of DNA binding activity of the five NF-κB family members in PMN nuclear extracts after incubation with THP
3.13. Statistical analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Tamm, I.; Horsfall, F.L. A mucoprotein derived from human urine which reacts with influenza, mumps, and Newcastle viruse. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1950, 74, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Pak, J.; Pu, Y.; Zhong, Z.-T.; Hasty, D.L.; Wu, X.-R. Tamm-Horsfall protein binds to type I fimbriated Escherichia coli and prevents E. coli binding to uroplakin Ia and Ib receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 9924–9930. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, A.P.; Neuberger, A.; Ratcliffee, W.A. Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein: The chemical composition. Biochem. J. 1970, 120, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, F.K.; Kent, P.W. Subunits of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Biochem. J. 1970, 116, 791–796. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, D.C. Binding of Tamm-Horsfall protein to complement 1q measured by ELISA and resonant mirror biosensor techniques under various ionic-strength conditions. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.C. Binding of Tamm-Horsfall protein to complement 1q and complement 1, including influence of hydrogen-ion concentration. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-Q.; Sanders, P.W. Localization of a single-binding site for immunoglobulin-light chains on human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. J. Clin. Invest. 1997, 99, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-H.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Lee, Y.-F.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Yu, C.-L. Intact protein core structure is essential for protein-binding, mononuclear cell proliferating, and neutrophil phagocytosis-enhancing activities of normal human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchmore, A.V.; Decker, J.M. Evidence that recombinant IL-1α exhibits lectin-like specificity and binds to homogeneous uromodulin via N-linked oligosaccharide. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Sherblom, A.P.; Sathyamoorthy, N.; Decker, J.M.; Muchmore, A.V. IL-2, a lectin with specificity for high mannose glycopeptides. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 939–944. [Google Scholar]
- Sherblom, A.P.; Decker, J.M.; Muchmore, A.V. The lectin-like interaction between recombinant tumor necrosis factor and uromodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 5418–5424. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.B.; Davies, M.; Peters, J.R.; Williams, J.D. Tamm-Horsfall pretein binds to a single class of carbohydrate specific receptor on human neurophils. Kidney Int. 1993, 44, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-L.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Sun, K.-H.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Tsai, Y.-Y.; Tsai, S.-T.; Yu, H.-S.; Han, S.-H. Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein (THG) is a binder for surface membrane proteins on blood cells and glomerular mesangial cells. Immunopharmacolgy 1997, 35, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.-J.; Chang, K.-L.; Lin, T.-M.; Huang, Y.-H.; Yeh, T.-M. Uromodulin and Tamm- Horsfall protein induce human monocytes to secrete TNF and express tissue factor. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3449–3456. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.-L.; Lin, W.-M.; Liao, T.-S.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Sun, K.-H.; Chen, K.-H. Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein (THG) purified from normal human pregnancy urine increases phagocytosis complement receptor expression and arachidonic acid metabolism of polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Immunopharmacolgy 1992, 24, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Zhu, X.-H.; Huang, H.-Y.; Shapiro, E.; Hasty, D.L.; Wu, X.-R. Ablation of the Tamm-Horsfall protein gene increases susceptibility of mice to bladder colonization by type 1-fimbriated Escherichia coli. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2004, 286, F795–F802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfistershammer, K.; Christoph, K.; Leitner, F.; Stockl, J.; Majdic, O.; Weichhart, T.; Sobanov, Y.; Bochkov, V.; Saemann, M.; Zlabinger, G..; Steinberger, P. Identification of the scavenger receptors SREC-1, Cla-1 (SR-B1) and SR-A1 as cellular receptor for Tamm-Horsfall protein. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Saemann, M.D.; Weichhart, T.; Zeyda, M.; Stuhlmeier, G.; Schunn, M.; Stuhlmeier, K.M.; Sobanov, Y.; Stulnig, T.M.; Akira, S.; von Ahsen, U.; Hori, W.H.; Zlabinger, G.J. Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein links innate immune cell activation with adaptive immunity via a Toll-like receptor-4-dependent mechanism. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 468–475. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, S.; Metzger, R.; Bunnemann, B. Tamm-Horsfall protein-mRNA synthesis is located to the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop in rat kidney. Histochemistry 1990, 94, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolari, F.; Caridi, G.; Rampoldi, L.; Tardanico, R.; Izzi, C.; Pirulli, D.; Amoroso, A.; Casari, G.; Ghiggeri, G.M. Uromodulin storage disease: clinical aspects and mechanisms. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 44, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinschert, S.; Ruf, N.; Bernascone, I.; Sacherer, K.; Lamorte, G.; Neumayer, H.H.; Nurnberg, P.; Luft, F.C.; Rampoldi, L. Functional consequences of a novel uromodulin mutation in a family with familial juvenile hyperuricaemic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 3150–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleyer, A.J.; Hart, T.C. Familial juvenile hyperuricaemic nephropathy. Q. J. Med. 2003, 96, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-L.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Lin, W.-M.; Liao, T.-S.; Chen, H.-L.; Sun, K.-H.; Chen, K.-H. Tamm-Horsfall Urinary glycoprotein enhances monokine releases and augments lymphocyte proliferation. Immunopharmacology 1993, 26, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonen, P.; Gaffiner, R.; Wingfield, P. Native cytokines do not bind to uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein). FEBS 1988, 226, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afeltra, A.; Caccavo, D.; Ferri, G.M.; Addessi, M.A.; De Rosa, F.G.; Moroso, A.A.; Bonomo, L. Expression of lactoferrin on human granulocytes: analysis with polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 109, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Derity, L.V.; Chor, J.; Thomas, L.L. Surface expression of lactoferrin by resting neutrophils. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attucci, S.; Korkmaz, B.; Juliano, L.; Hazouard, E.; Girardin, C.; Brillard-Bourdet, M.; Anthonioz, R.P.; Gauthier, F. Measurement of free and membrane-bound cathepsin G in human neutrophils using new sensitive fluorogenic substrates. Biochem. J. 2002, 366, 965–970. [Google Scholar]
- Bangalore, N.; Travis, J. Comparison of properties of membrane-bound versus soluble forms of human leukocytes elastase and cathepsin G. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 1994, 375, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, A.H.; Heeringa, P.; Brourver, E.; Limburg, P.C.; Kallember, C.G. Activation of granulocytes by anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA): A FcγRII-dependent process. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 98, 270–278. [Google Scholar]
- Daley, J.M.; Reichner, J.S.; Mahoney, E.J.; Manfield, L.; Henry, W.L., Jr.; Masrofrancesco, B.; Albina, J.E. Modulation of macrophage phenotype by soluble product(s) release from neurophils. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar]
- Borregaad, N.; Cowland, J.B. Granules of the human neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Blood 1997, 89, 3503–3521. [Google Scholar]
- Balazovich, K.J.; Fernandez, R.; Hinkovska-Galcheva, V.; Suchard, S.J.; Boxer, L.A. Transforming growth factor-β1 stimulated degranulation and oxidant release by adherent human neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 60, 772–777. [Google Scholar]
- Elbim, C.; Reglier, H.; Fay, M.; Delarche, C.; Andrieu, V.; El Benna, J.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A. Intracellular poor of IL-10 receptors in specific granules of human neutrophils: differential mobilization by proinflammatory mediators. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5201–5207. [Google Scholar]
- Na, Y.J.; Han, S.B.; Kang, J.S.; Yoon, T.D.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.M.; Yang, K.H.; Joe, C.O. Lactoferrin works as a new LPS-binding protein in inflammatory activation of macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.M.M.; Charlwood, P.A.; Marshall, R.D. Isolation and characterization of glycopeptides from digests of human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 89, 303–319. [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi, F.; Malagolin, N.; Dall’olis, F. A tetra-antennary glycopeptides from human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein inhibits agglutination of desialylated erythrocytes induced by leukoagglutinin. Biosoc. Rep. 1984, 4, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini-Cessi, F.; Dall’olis, F.; Malagolin, N. High mannose oligosaccharides from human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Biosci. Res. 1984, 4, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooijen, L.L.M.; Voskamp, A.F.; Kamerling, J.P.; Vliegenthart, J.F.G. Glycosylation sites and site specific glycosylation in human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Glycobiology 1999, 9, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firon, N.; Ofek, I.; Sharon, N. Carbohydrate binding site of the mannose-specific fimbrial lectins of enterbacteria. Infect. Immun. 1984, 43, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore, A.V.; Decker, J.M. Evidence that recombinant IL-1α exhibits lectin-like specificity and binds to homogenous uromodulin via N-linked oligosaccharides. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Olio, F.; Chiricole, M.; Molagalin, N.; Franceschi, C.; Serafini-Cessi, F. Immuno-suppressive activity of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein oligosaccharides: effect of removal of outer sugars and conjugation with a protein carries. Cell. Immunol. 1991, 137, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.L.; Rajasekaran, M.; Arsanjani, A.H.; Chanoweth, M.; Stein, P. Role of sialic acid in urinary cytoprotective activity of Tamm-Horsfall protein. Urology 2007, 69, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.S.; McGiven, A.R. Stimulation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes by Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Immunology 1978, 35, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.-J.; Lu, M.-C.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Yu, H.-S.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Yu, C.-L. Release of surface-expressed lactoferrin from polymorphonuclear neutrophils after contact with CD4+T cells and its modulation on Th1/Th2 cytokine production. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.R.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Rinderknecht, E.; Svedersky, L.P.; Finkle, B.S.; Palladino, M.A., Jr. Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon- gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 2069–2073. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, H.M.; Natale, P.J.; Kamentsky, L.M. Estimation of membrane potentials of individual lymphocytes by flow cytometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5728–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Siao, S.-C.; Li, K.-J.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Yu, C.-L. Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein Enhances PMN Phagocytosis by Binding to Cell Surface-Expressed Lactoferrin and Cathepsin G That Activates MAP Kinase Pathway. Molecules 2011, 16, 2119-2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16032119
Siao S-C, Li K-J, Hsieh S-C, Wu C-H, Lu M-C, Tsai C-Y, Yu C-L. Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein Enhances PMN Phagocytosis by Binding to Cell Surface-Expressed Lactoferrin and Cathepsin G That Activates MAP Kinase Pathway. Molecules. 2011; 16(3):2119-2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16032119
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiao, Syue-Cian, Ko-Jen Li, Song-Chou Hsieh, Cheng-Han Wu, Ming-Chi Lu, Chang-Youh Tsai, and Chia-Li Yu. 2011. "Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein Enhances PMN Phagocytosis by Binding to Cell Surface-Expressed Lactoferrin and Cathepsin G That Activates MAP Kinase Pathway" Molecules 16, no. 3: 2119-2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16032119
APA StyleSiao, S.-C., Li, K.-J., Hsieh, S.-C., Wu, C.-H., Lu, M.-C., Tsai, C.-Y., & Yu, C.-L. (2011). Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein Enhances PMN Phagocytosis by Binding to Cell Surface-Expressed Lactoferrin and Cathepsin G That Activates MAP Kinase Pathway. Molecules, 16(3), 2119-2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16032119





