Classification and Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases and Insect Pests Based on Improved ResNet-50 Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
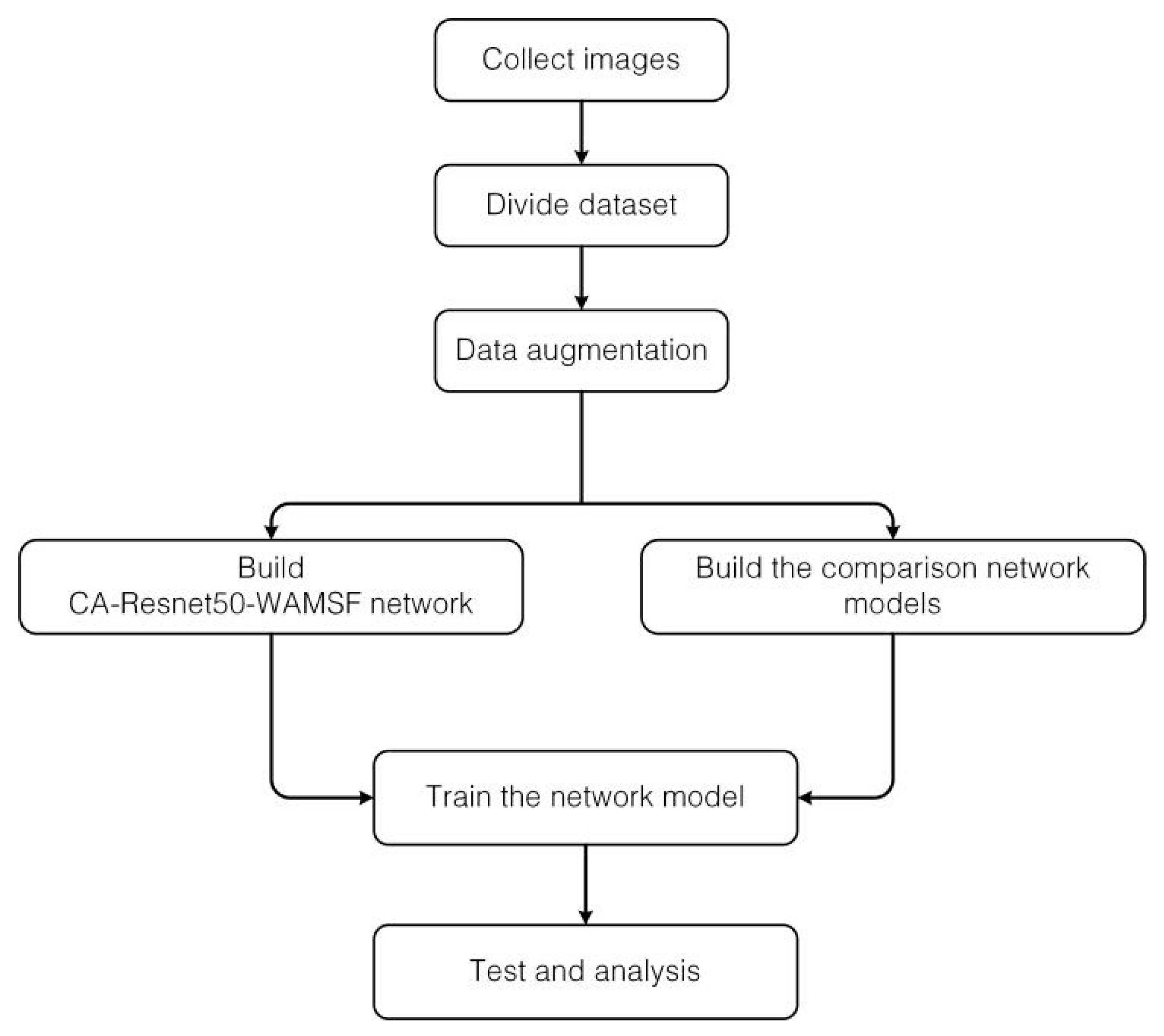
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials for Apple Tree Leaf Diseases and Insect Pests
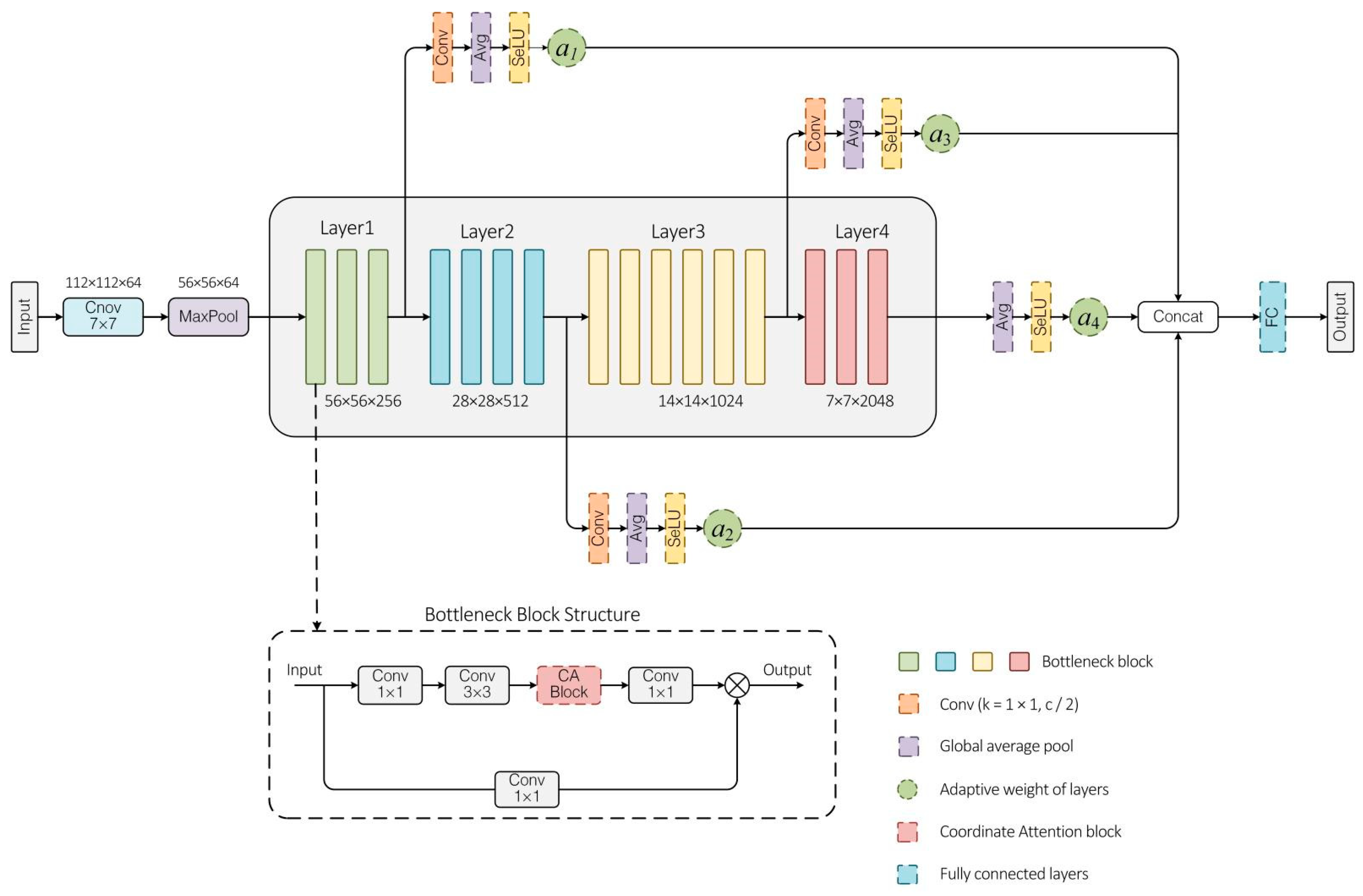
2.2. CA–ResNet-50–WAMSFF Network Model
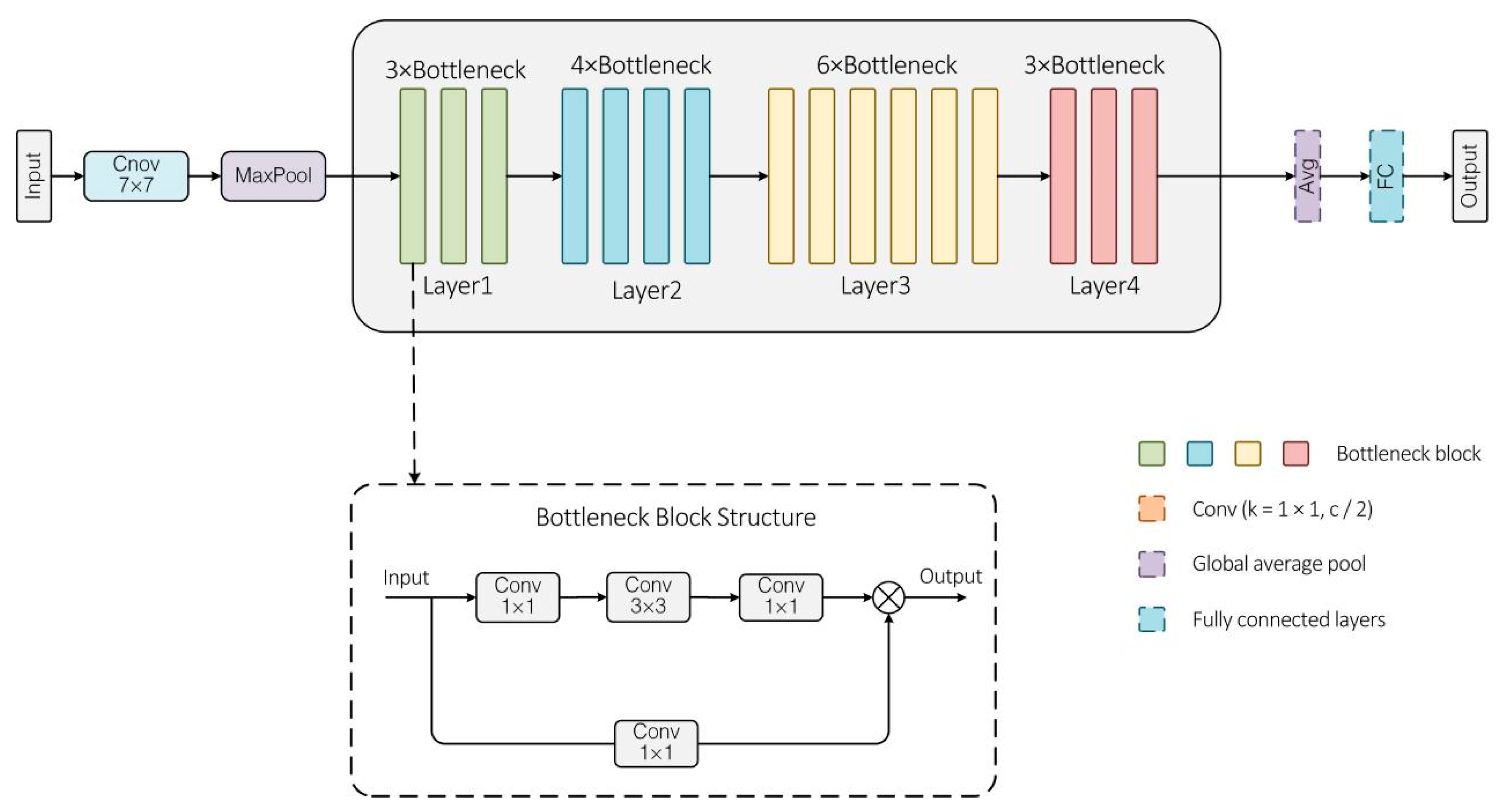
2.2.1. Model Network Analysis
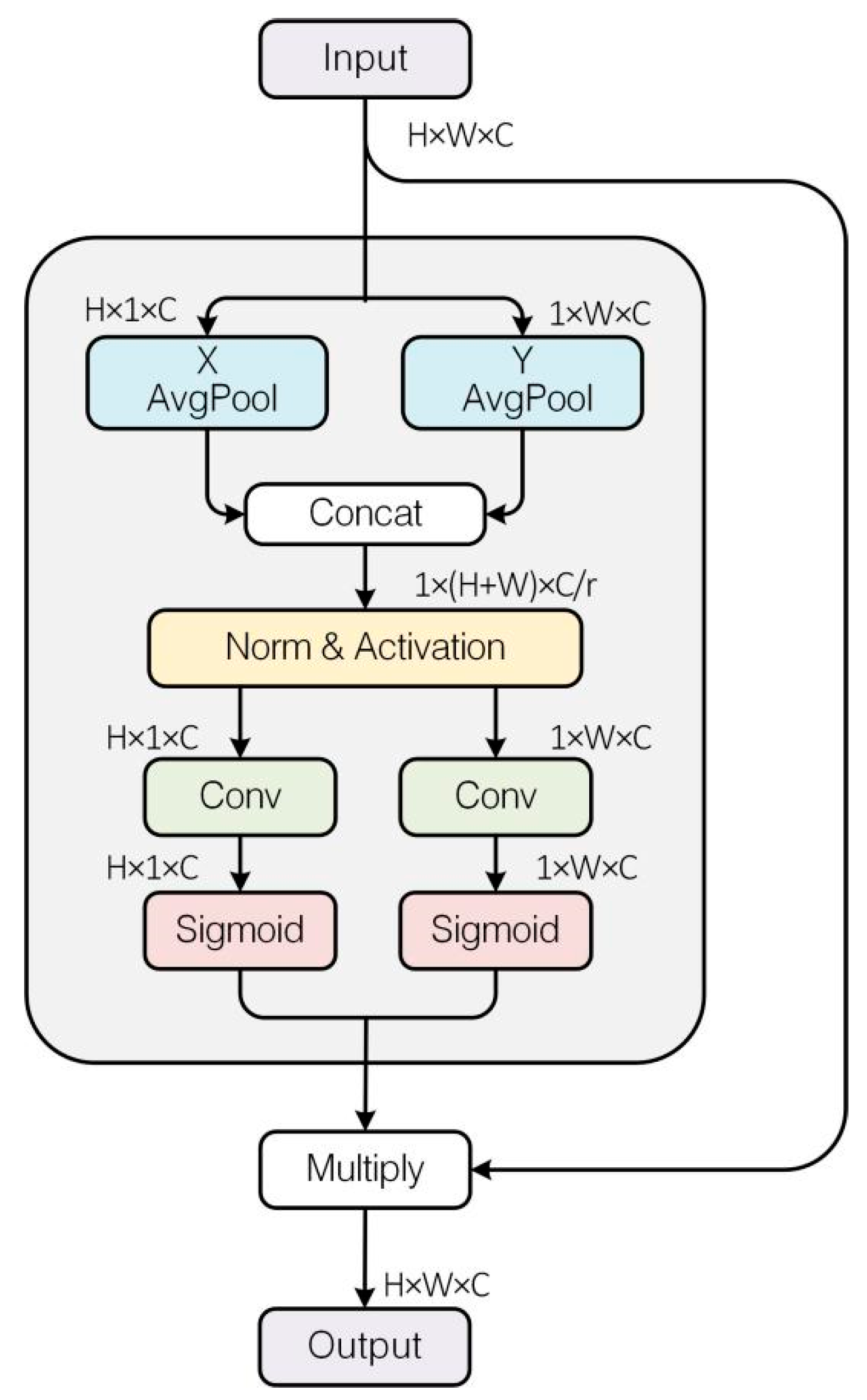
2.2.2. CA–ResNet-50–WAMSFF Model Improvement Analysis
2.3. Model Network Training Design
2.3.1. Training Method
2.3.2. Data Augmentation
2.3.3. Experimental Environment
2.3.4. Experimental Setting
3. Experimental Results
3.1. CA–ResNet-50–WAMSFF Model Loss Function Analysis
3.2. CA–ResNet-50–WAMSFF Model Ablation Test
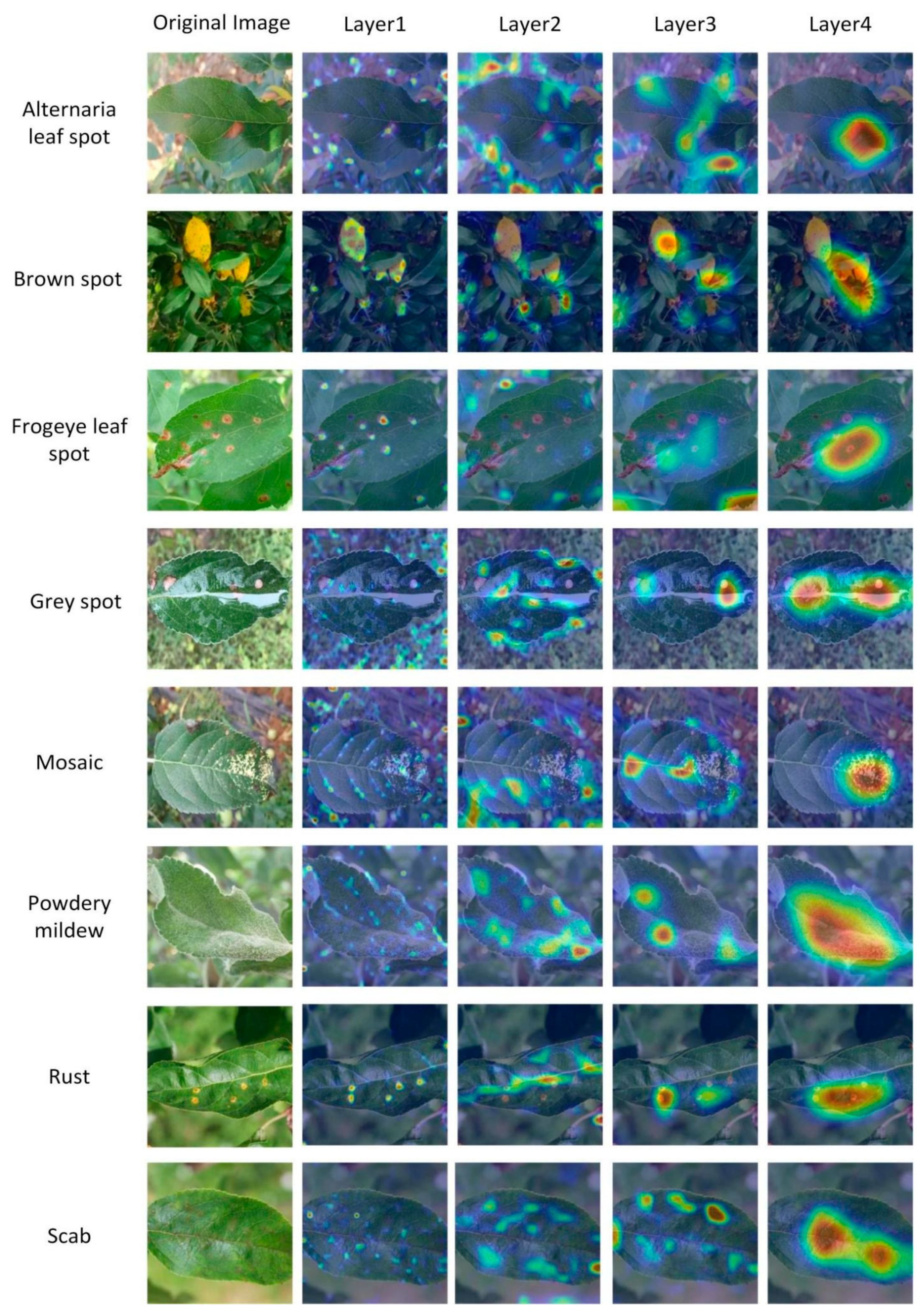
3.3. Categorical Heat Maps Analysis
4. Comparison and Discussion
4.1. Comparison and Discussion in Deep Neural Networks
4.2. Comparison and Discussion with Related Work in the AppleLeaf9 Datasets
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Wang, N.H.; Lan, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, F. Research on integrated prediction model of apple yield. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2022, 50, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Cheng, C.; Qiu, G.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Li, E. Technological innovation approaches for high-quality development of apples. China Fruit Tree 2021, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, L. Principles and Key Technologies of Pest Control in Apple. World Trop. Agric. Inf. 2021, 10, 3940. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.L. Discussion on green control technology of apple diseases and insect pests. South. Agric. 2022, 16, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Liu, C. Recognition System for Leaf Diseases of Ophiopogon japonicus Based on PCA-SVM. Res. Plant Dis. Insect Pests 2020, 11, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, H.; Shah, J.; Dabhi, V. Detection and classification of rice plant diseases. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2018, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.L.; Wu, D.X.; Hu, H.S.; Wei, P. Pose estimation-dependent identification method for field moth images using deep learning architecture. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 136, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; You, Z.; Wu, X. Fusion of superpixel, expectation maximization and PHOG for recognizing cucumber diseases. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 140, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, G. Research on pest image recognition based on cascade AdaBoost classifier. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2019, 40, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Javed, K.; Saba, T. An automated system for cucumber leaf diseased spot detection and classification using improved saliency method and deep features selection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 18627–18656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.X.; Zhang, D. Using deep transfer learning for image-based plant disease identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105393–105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Gao, Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, Z. Overview of Image Classification Algorithms Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Comput. Appl. 2021, 42, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Mou, X. A review of target detection algorithms based on deep learning. Comput. Eng. 2021, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Zeng, R.; Wu, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. A review of agricultural plant phenotypes based on deep learning. Sci. China 2019, 49, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanci, K.; Aslan, M.F.; Ropelewska, E.; Unlersen, M.F.; Durdu, A.A. Novel convolutional-recurrent hybrid network for sunn pest–damaged wheat grain detection. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 1748–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Toudeshki, A.; Ehsani, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Ma, R. Yield estimation of citrus fruit using rapid image processing in natural background. Smart Agric. Technol. 2021, 2, 10027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madec, S.; Jin, X.; Lu, H.; De Solan, B.; Liu, S.; Duyme, F.; Heritier, E.; Baret, F. Ear density estimation from high resolution RGB imagery using deep learning technique. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 264, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, M.P.; Atkinson, J.A.; Wells, D.M.; Pridmore, T.P.; French, A.P. Deep learning for multi-task plant phenotyping. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2055–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, H. Lightweight agricultural crops pest identification model using improved ShuffleNet V2. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 161–170, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Niu, T.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; He, D. Identification of apple leaf diseases by improved deep convolutional neural networks with an attention mechanism. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 723294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Qu, J.H. A detection method for apple leaf diseases based on Tiny-YOLO. Shandong Norm. Univ. 2020, 35, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Li, J.J.; Jia, R.C.; Liu, B.; Yao, Z.; Yuan, A.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, H. LAD-Net: A Novel Light Weight Model for Early Apple Leaf Pests and Diseases Classification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraju, Y.; Venkatesh, S.S.; Stalin, S. Apple andgrape leaf diseases classification using transfer learning viafine-tuned classifier. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and AppliedNetwork Technologies (ICMLANT), Hyderabad, India, 20–21 December2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.Z.; Chao, X.F. Apple Tree Leaf Disease Segmentation Dataset [DS/OL]. Sci. Data Bank 2022. Available online: https://cstr.cn/31253.11.sciencedb.01627 (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the 34th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; IEEE Computer Society: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ren, J.; Jing, J. Adaptive Feature Fusion Embedding Network for Few Shot Fine-Grained Image Classification. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2023, 59, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Chen, B.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Sandler, M.; Howard, A. Mnasnet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. In Proceedings of the 32th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 2820–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2017), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2015), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.; Hu, Q.; Dong, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, B. Axiom-based Grad-CAM: Towards Accurate Visualization and Explanation of CNNs. In Proceedings of the 33stBritish Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2020), Manchester, UK, 7–11 September 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Duan, S.; Wang, L. Efficient Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases in the Wild Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Types of Pests and Diseases | Number of Images | Dataset Partitioning | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Training Sets | Number of Validation Sets | Number of Test Sets | ||
| Alternaria leaf spot | 417 | 250 | 83 | 84 |
| Brown spot | 411 | 246 | 82 | 83 |
| Frogeye leaf | 3181 | 1908 | 636 | 637 |
| Grey spot | 339 | 1376 | 172 | 172 |
| Health | 516 | 309 | 103 | 104 |
| Mosaic | 371 | 222 | 74 | 75 |
| Powdery mildew | 1184 | 710 | 237 | 237 |
| Rust | 2753 | 1651 | 551 | 551 |
| Scab | 5410 | 3246 | 1082 | 1082 |
| Model No. | Model | Top-1 Accuracy | Average Recall | Average Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ResNet-50 | 95.31% | 95.62% | 95.31% |
| 2 | ResNet-50+CA | 97.89% | 97.68% | 97.21% |
| 3 | ResNet-50+WAMSFF | 97.77% | 97.97% | 97.78% |
| 4 | ResNet-50+CA+WAMSFF | 98.32% | 98.41% | 98.23% |
| No. | Model Type | Top-1 Accuracy | Average Recall | Average Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AlexNet | 91.02% | 91.23% | 91.06% |
| 2 | DenseNet | 95.01% | 95.34% | 95.21% |
| 3 | VGG16 | 93.34% | 93.56% | 93.81% |
| 4 | MNASNet | 92.28% | 92.13% | 92.45% |
| 5 | GoogLeNet | 94.45% | 94.67% | 94.71% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, W.; Shi, F.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Q. Classification and Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases and Insect Pests Based on Improved ResNet-50 Model. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9091046
Zhang X, Li H, Sun S, Zhang W, Shi F, Zhang R, Liu Q. Classification and Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases and Insect Pests Based on Improved ResNet-50 Model. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(9):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9091046
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaohua, Haolin Li, Sihai Sun, Wenfeng Zhang, Fuxi Shi, Ruihua Zhang, and Qin Liu. 2023. "Classification and Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases and Insect Pests Based on Improved ResNet-50 Model" Horticulturae 9, no. 9: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9091046
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, H., Sun, S., Zhang, W., Shi, F., Zhang, R., & Liu, Q. (2023). Classification and Identification of Apple Leaf Diseases and Insect Pests Based on Improved ResNet-50 Model. Horticulturae, 9(9), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9091046





