Physiological and Nutritional Responses of Ungrafted Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon Vines or Grafted to 101-14 Mgt and 1103P Rootstocks Exposed to an Excess of Boron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
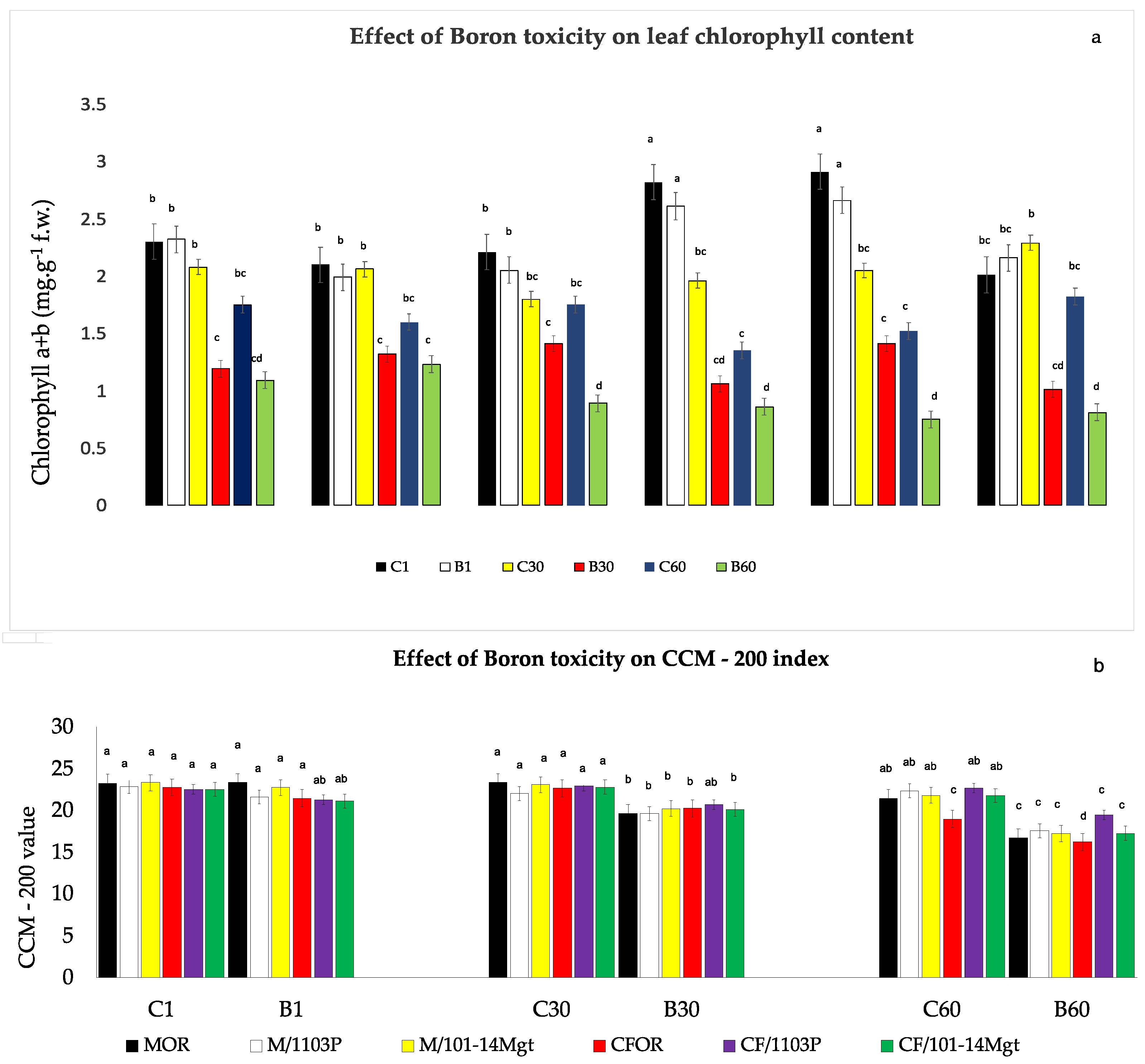
2.1. Chlorophyll Content
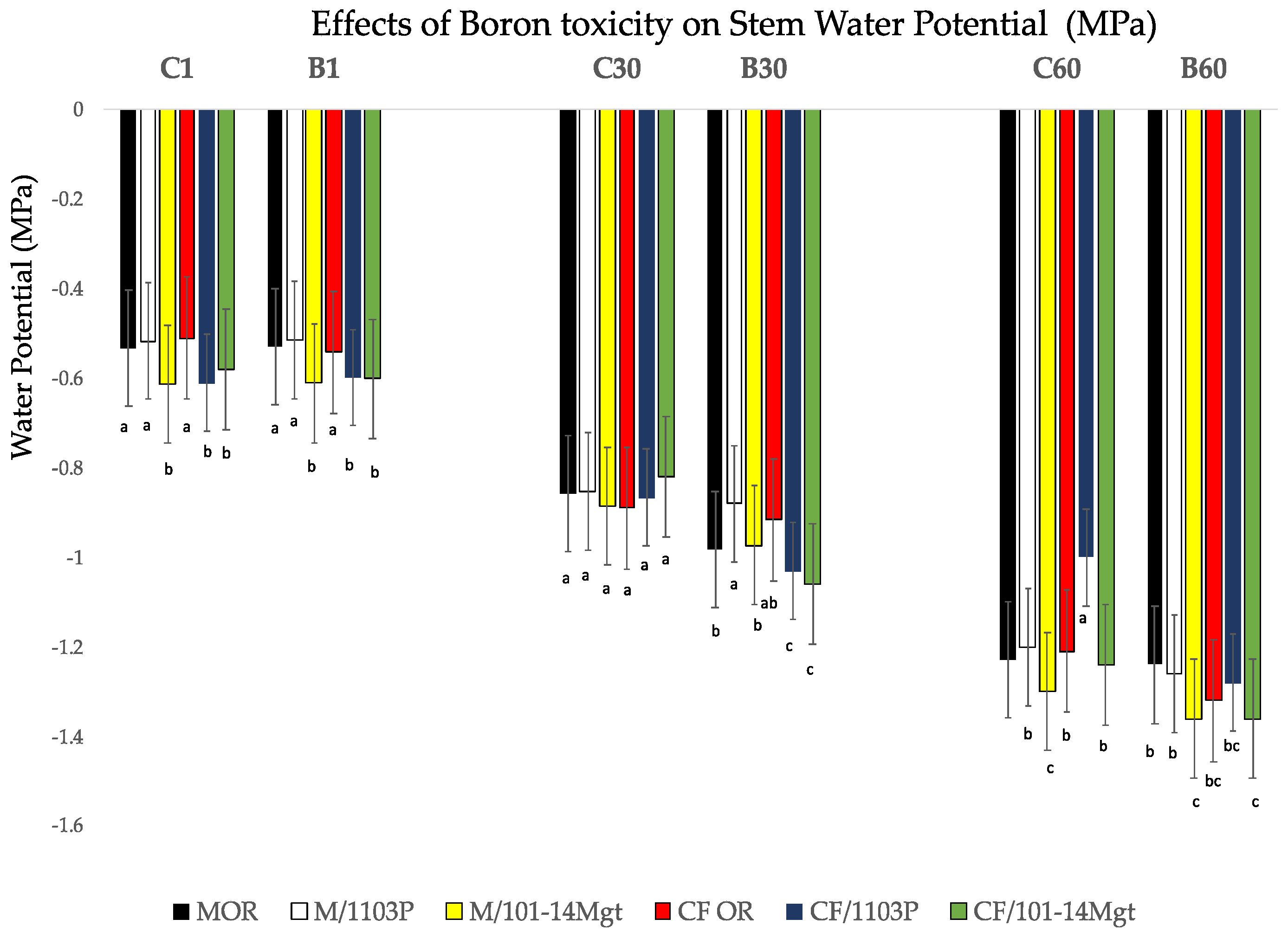
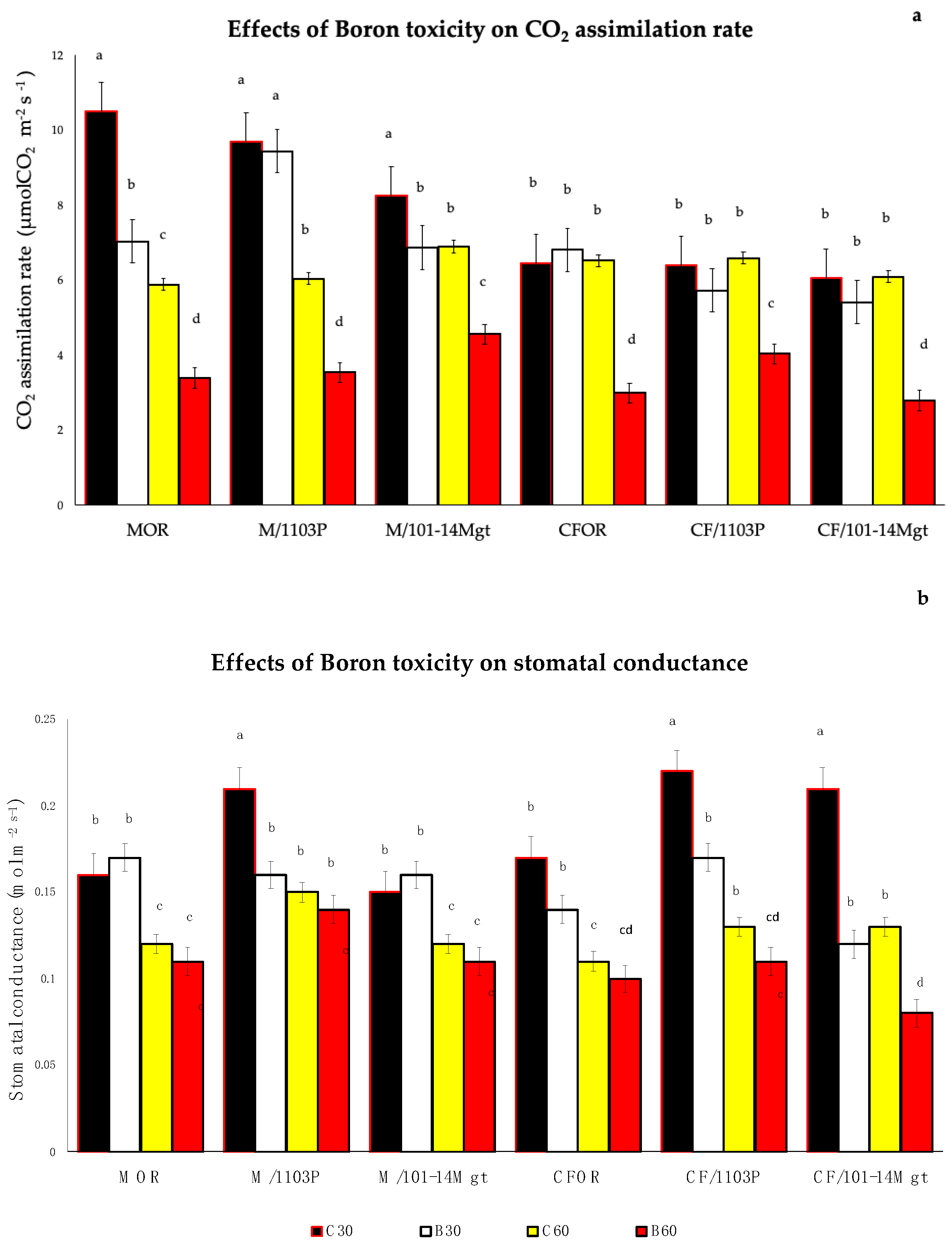
2.2. Stem Water Potential and Gas Exchange
2.3. Tissue Nutrient Concentrations and Growth Parameters
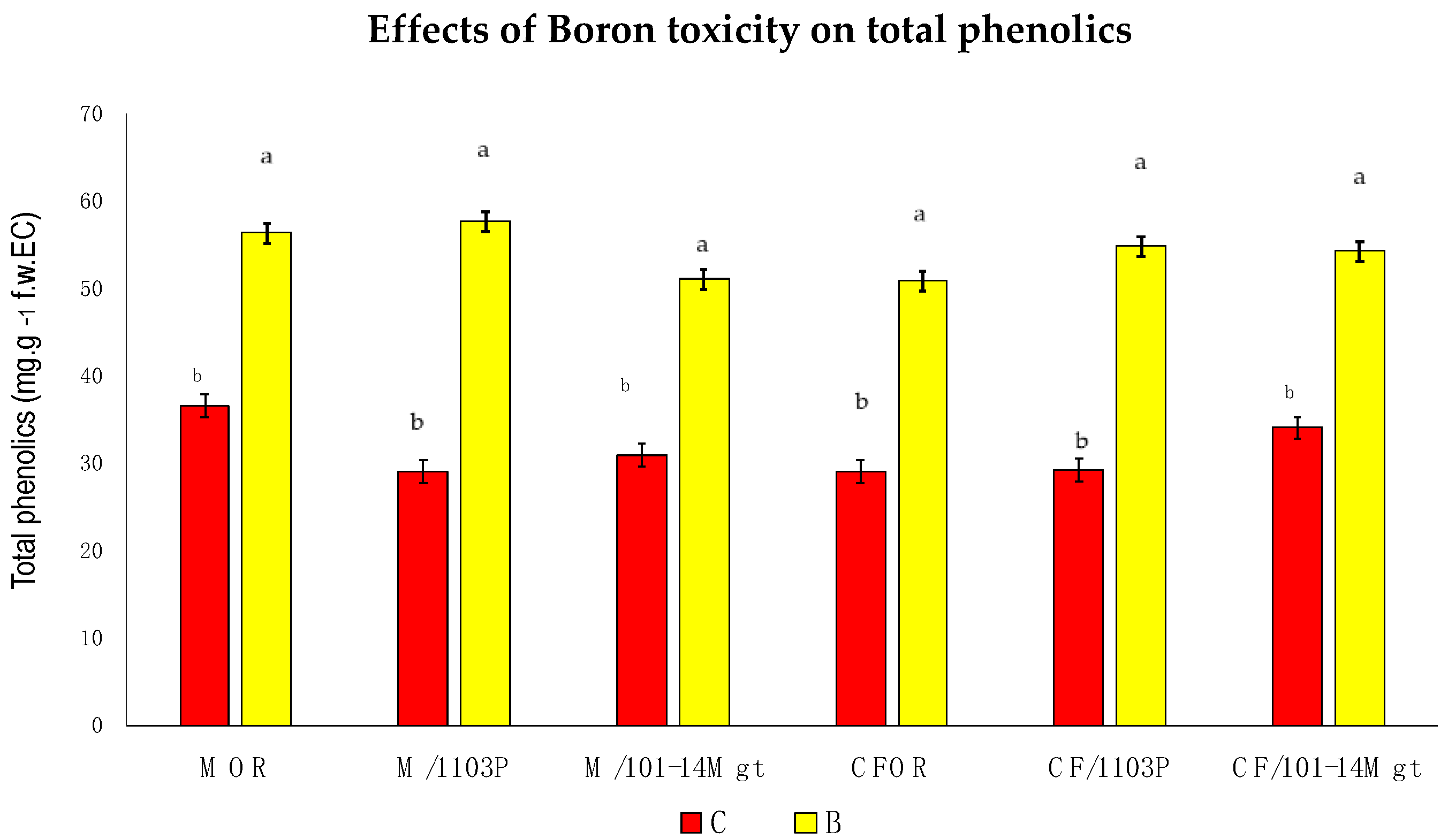
2.4. Total Phenolics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Climate Data
3. Results
3.1. Boron Distribution in Different Vine Parts
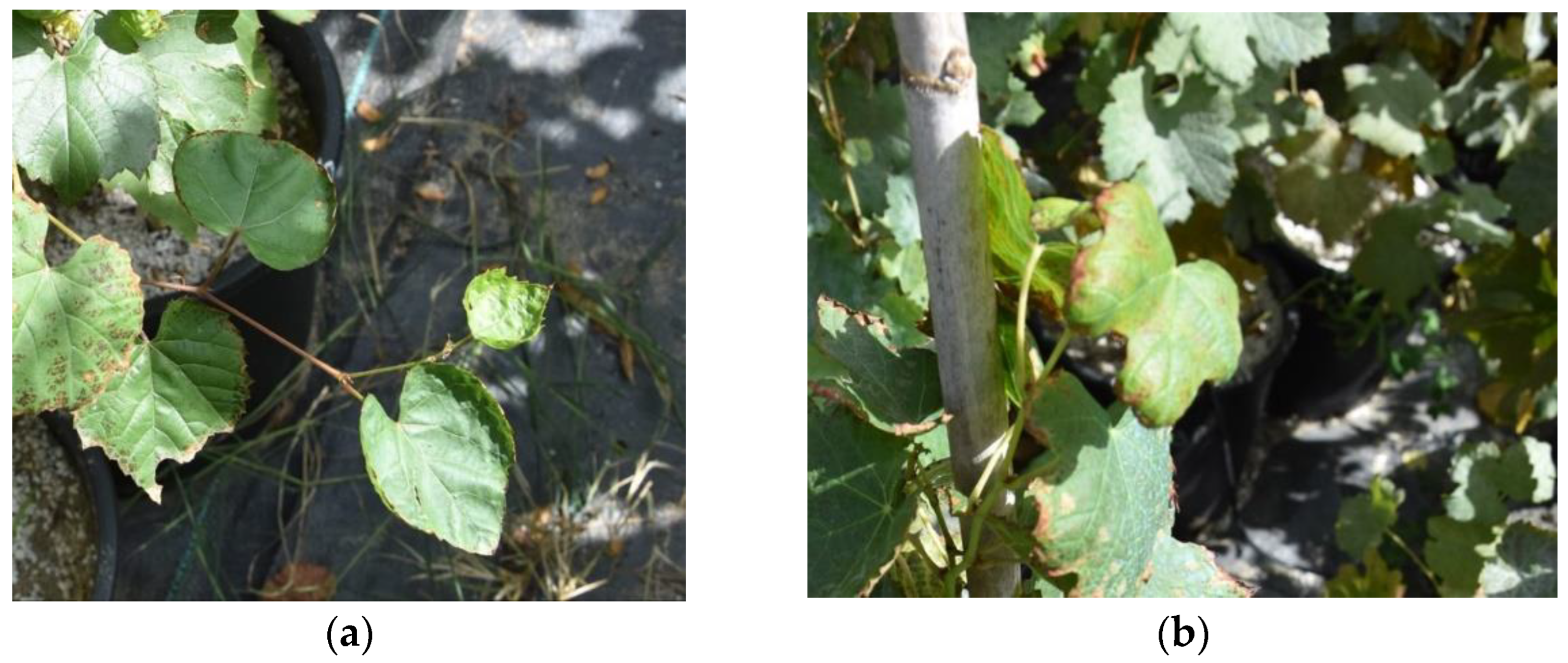
3.2. Plant Growth Parameters and Toxicity Symptoms
3.3. Tissue Nutrient Concentrations
3.4. Chlorophyll Content
3.5. Total Phenolics
3.6. Water Status and Photosynthetic Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. Vine Growth and Nutrient Concentrations in Plant Tissues
4.2. Photosynthetic Activity, Water Status, and Chlorophyll Pigments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, G.V.; Fixen, P.E. Testing Soils for Sulfur, Boron, Molybdenum, and Chlorine; SSSA Book Series; Westerman, R.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Pandita, S.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, A.; Bhardwaj, R. Biogeochemical Cycling, Tolerance Mechanism and Phytoremediation Strategies of Boron in Plants: A Critical Review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Princi, M.P.; Lupini, A.; Araniti, F.; Longo, C.; Mauceri, A.; Sunseri, F.; Abenavoli, M.R. Boron Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants. In Plant Metal Interaction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabu, M.; Akosman, M.S. Biological Effects of Boron. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 225, pp. 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhaken, R. Cell Wall Remodeling under Abiotic Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voxeur, A.; Fry, S.C. Glycosylinositol Phosphorylceramides from Rosa Cell Cultures Are Boron-Bridged in the Plasma Membrane and Form Complexes with Rhamnogalacturonan II. Plant J. 2014, 79, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, M.; Lehner, A.; Bouton, S.; Kiefer-Meyer, M.C.; Voxeur, A.; Pelloux, J.; Lerouge, P.; Mollet, J.-C. The Cell Wall Pectic Polymer Rhamnogalacturonan-II Is Required for Proper Pollen Tube Elongation: Implications of a Putative Sialyltransferase-like Protein. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, P.P.; Woods, W.G. The Chemistry of Boron and Its Speciation in Plants. Plant Soil 1997, 193, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paull, J.G.; Rathjen, A.J.; Cartwright, B. Major Gene Control of Tolerance of Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to High Concentrations of Soil Boron. Euphytica 1991, 55, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, W.; Christensen, L. Drip Irrigation Can Effectively Apply Boron to San Joaquin Valley Vineyards. Calif. Agric. 2005, 59, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.; Degl’Innocenti, E.; Pardossi, A.; Guidi, L. Antioxidant and Photosynthetic Responses in Plants under Boron Toxicity: A Review. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2012, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, R.J.; Hayes, J.E.; Post, A.; Stangoulis, J.C.R.; Graham, R.D. A Critical Analysis of the Causes of Boron Toxicity in Plants: Boron Toxicity in Plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2004, 27, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, I.; Díaz-López, L.; Gimeno, V.; Nieves, M.; Pereira, W.E.; Martínez, V.; Lidon, V.; García-Sánchez, F. Effects of Boron Excess in Nutrient Solution on Growth, Mineral Nutrition, and Physiological Parameters of Jatropha curcas Seedlings. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 2013, 176, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangoulis, J.C.R.; Reid, R.J. Boron Toxicity in Plants and Animals. In Boron in Plant and Animal Nutrition; Goldbach, H.E., Brown, P.H., Rerkasem, B., Thellier, M., Wimmer, M.A., Bell, R.W., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.P.S.; Powar, S.L. Tolerance of Wheat and Pea to Boron in Irrigation Water. Plant Soil 1978, 50, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppmann, W.; Bianchini, G.; Charalambides, A.; Dotsika, E.; Guerrot, C.; Klose, P.; Marei, A.; Pennisi, M.; Vengosh, A.; Voutsa, D. Boron contamination of Mediterranean groundwater resources: Extent, sources and pathways elucidated by environmental isotopes. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2005, 7, 10162. [Google Scholar]
- Sarafi, E.; Siomos, A.; Tsouvaltzis, P.; Chatzissavvidis, C.; Therios, I. Boron Toxicity Effects on Grafted and Non-Grafted Pepper (Capsicum annuum) Plants. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 441–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Grao, S.; Nieves, M.; Martínez-Nicolás, J.J.; Cámara-Zapata, J.M.; Alfosea-Simón, M.; García-Sánchez, F. Response of Three Citrus Genotypes Used as Rootstocks Grown under Boron Excess Conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, E.V. Crop Salt Tolerance. In Agricultural Salinity Assessment and Management; Tanji, K., Ed.; ASCE Manuals & Reports on Engineering Practice No. 71; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1990; pp. 262–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gunes, A.; Soylemezoglu, G.; Inal, A.; Bagci, E.G.; Coban, S.; Sahin, O. Antioxidant and Stomatal Responses of Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) to Boron Toxicity. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 110, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, N.; Mattheou, A.; Karagiannidis, N. Boron toxicity in grapevines as a result of irrigation: Effect of rain on leaching. Le Porgres Agric. Vitic. 1995, 112, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, D.R.; Arnon, D.I. The Water-Culture Method for Growing Plants without Soil. Circ. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. 1950, 347, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Wintermans, J.; De Mots, A. Spectrophotometric Characteristics of Chlorophylls a and b and Their Phenophytins in Ethanol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biophys. Incl. Photosynth. 1965, 109, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choné, X. Stem Water Potential Is a Sensitive Indicator of Grapevine Water Status. Ann. Bot. 2001, 87, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.D.; Pratt, P.F. Methods of Analysis for Soils, Plants and Waters; Division of Agricultural Sciences, University of California: Riverside, CA, USA, 1961; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Gaines, T.P.; Mitchell, G.A. Boron Determination in Plant Tissue by the Azomethine H Method. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1979, 10, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, R.; Cravero, M.; Gentilini, N. Metodi per Lo Studio Dei Polifenoli Dei Vini. L’enotecnico 1989, 25, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, R. Understanding the Boron Transport Network in Plants. Plant Soil 2014, 385, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannel, F.; Pfeffer, H.; Römheld, V. Compartmentation of Boron in Roots and Leaves of Sunflower as Affected by Boron Supply. J. Plant Physiol. 1998, 153, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.C. Deficiency, Sufficiency, and Toxicity Levels of Boron in Crops. Boron Its Role Crop Prod. 1993, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, J.; Noguchi, K.; Yasumori, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Gajdos, Z.; Miwa, K.; Hayashi, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Fujiwara, T. Arabidopsis Boron Transporter for Xylem Loading. Nature 2002, 420, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, K.; Fujiwara, T. Boron Transport in Plants: Co-Ordinated Regulation of Transporters. Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Castro, R.; Kasai, K.; Gainza-Cortes, F.; Ruiz-Lara, S.; Casaretto, J.A.; Pena-Cortes, H.; Tapia, J.; Fujiwara, T.; Gonzalez, E. VvBOR1, the Grapevine Ortholog of AtBOR1, Encodes an Efflux Boron Transporter That Is Differentially Expressed Throughout Reproductive Development of Vitis vinifera L. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, M.; Farokhzad, A.; Mandoulakani, B.A.; Ghasemzadeh, R. Biochemical and Gene Expression Responses of Two Iranian Grape Cultivars to Foliar Application of Methyl Jasmonate under Boron Toxicity Conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 249, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, I.E.; Dimassi, K.N.; Therios, I.N. Response of Two Citrus Genotypes to Six Boron Concentrations: Concentration and Distribution of Nutrients, Total Absorption, and Nutrient Use Efficiency. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 54, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, I.E.; Dimassi, K.N.; Bosabalidis, A.M.; Therios, I.N.; Patakas, A.; Giannakoula, A. Boron Toxicity in ‘Clementine’ Mandarin Plants Grafted on Two Rootstocks. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzissavvidis, C.; Therios, I. The Effect of Different B Concentrations on the Nutrient Concentrations of One Olive (Olea europaea L.) Cultivar and Two Olive Rootstocks; 2003; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Sotiropoulos, T.E.; Therios, I.N.; Dimassi, K.N. Calcium Application as a Means to Improve Tolerance of Kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa L.) to Boron Toxicity. Sci. Hortic. 1999, 81, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Tuna, A.L.; Dikilitas, M.; Ashraf, M.; Koskeroglu, S.; Guneri, M. Supplementary Phosphorus Can Alleviate Boron Toxicity in Tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 121, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, S.; Bethke, P.C.; Jones, R.L. Calcium Homeostasis in Plants. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 106, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Aung, M.S.; Maeda, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Takata, N.; Taniguchi, T.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron-Deficiency Response and Expression of Genes Related to Iron Homeostasis in Poplars. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2018, 64, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsch, R.; Mendel, R.R. Physiological Functions of Mineral Micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.P.; Dahiya, D.J.; Narwal, R.P. Boron Uptake and Toxicity in Wheat in Relation to Zinc Supply. Fertil. Res. 1990, 24, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelp, B. Boron Mobility and Nutrition in Broccoli (Brassica oleracea Var. Italica). Ann. Bot. 1988, 61, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparnakis, A.; Chatzissavvidis, C.; Antoniadis, V. How Apple Responds to Boron Excess in Acidic and Limed Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 13, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzissavvidis, C.; Therios, I. Response of Four Olive (Olea europaea L.) Cultivars to Six B Concentrations: Growth Performance, Nutrient Status and Gas Exchange Parameters. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 127, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelp, B.J.; Marentes, E.; Kitheka, A.M.; Vivekanandan, P. Boron Mobility in Plants. Physiol. Plant 1995, 94, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessner, U.; Patterson, J.H.; Forbes, M.G.; Fincher, G.B.; Langridge, P.; Bacic, A. An Investigation of Boron Toxicity in Barley Using Metabolomics. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nable, R.A.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Paull, J.G. Boron toxicity. Plant Soil 1997, 193, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaslan, M.; Gunes, A. Interactive Effects of Boron and Salinity Stress on the Growth, Membrane Permeability and Mineral Composition of Tomato and Cucumber Plants. Plant Soil 2001, 236, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, W.; Durst, R. Chemistry and Biology of Boron. Biofactors 1992, 3, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Cervilla, L.M.; Blasco, B.; Ríos, J.J.; Rosales, M.A.; Rubio-Wilhelmi, M.M.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.; Romero, L.; Ruiz, J.M. Response of Nitrogen Metabolism to Boron Toxicity in Tomato Plants. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.A.; Taban, N.; Taban, S. Effect of Calcium on the Alleviation of Boron Toxicity and Localization of Boron and Calcium in Cell Wall of Wheat. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2009, 37, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Aquea, F.; Federici, F.; Moscoso, C.; Vega, A.; Jullian, P.; Haseloff, J.; Arce-Johnson, P. A Molecular Framework for the Inhibition of Arabidopsis Root Growth in Response to Boron Toxicity: The Arabidopsis Root Response to Boron Toxicity. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Tang, N.; Jiang, H.-X.; Yang, L.-T.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.-S. CO2 Assimilation, Photosystem II Photochemistry, Carbohydrate Metabolism and Antioxidant System of Citrus Leaves in Response to Boron Stress. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Mishra, S.; Heckathorn, S.A.; Frantz, J.M.; Krause, C. Proteomic Analysis of Arabidopsis Thaliana Leaves in Response to Acute Boron Deficiency and Toxicity Reveals Effects on Photosynthesis, Carbohydrate Metabolism, and Protein Synthesis. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraslan, F.; Inal, A.; Gunes, A.; Alpaslan, M. Impact of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on the Growth, Antioxidant Activity and Physiology of Carrot Plants Subjected to Combined Salinity and Boron Toxicity. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 113, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani-Pouya, A.; Rasouli, F. The Potential of Leaf Chlorophyll Content to Screen Bread-Wheat Genotypes in Saline Condition. Photosynthetica 2014, 52, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Ramirez, A.I.; van Ieperen, W.; Vreugdenhil, D.; Millenaar, F.F. Plants under Continuous Light. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, L.; Degl’Innocenti, E.; Carmassi, G.; Massa, D.; Pardossi, A. Effects of Boron on Leaf Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Greenhouse Tomato Grown with Saline Water. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 73, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, T.E.; Therios, I.N.; Dimassi, K.N.; Bosabalidis, A.; Kofidis, G. Nutritional status, growth, CO2 assimilation, and leaf anatomical responses in two kiwifruit species under boron toxicity. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, W.E.; de Siqueira, D.L.; Martínez, C.A.; Puiatti, M. Gas Exchange and Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Four Citrus Rootstocks under Aluminium Stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2000, 157, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agati, G.; Tattini, M. Multiple Functional Roles of Flavonoids in Photoprotection. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Monthly Climate Data during Treatments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Tmean | Tmin | Tmax | Precipitation | Sunshine |
| July | 28.2 | 21.1 | 32.1 | 48 | 355 |
| August | 29.1 | 21.8 | 33.4 | 0 | 357 |
| Leaves | Shoots | Trunks | Roots | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments | M | CF | M | CF | M | CF | M | CF | |
| Control | OR | 47.56 d | 56.89 d | 15.81 c | 13.53 c | 11.13 b | 11.45 b | 33.09 c | 34.88 c |
| 1103P | 62.93 d | 59.76 d | 14.32 c | 13.09 d | 9.97 b | 10.71 b | 22.62 d | 34.17 c | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 53.15 d | 54.17 d | 15.24 c | 12.97 d | 10.46 b | 10.03 b | 35.23 c | 30.79 c | |
| 0.5 mM B | OR | 1021.30 b | 1064.37 a | 20.69 b | 16.40 c | 23.51 a | 18.49 a | 52.84 b | 59.70 a |
| 1103P | 980.67 c | 990.31 c | 26.32 a | 19.82 b | 27.46 a | 27.87 a | 52.21 b | 51.87 b | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 1011.70 b | 1033.18 b | 21.97 b | 17.87 c | 23.88 a | 19.67 a | 55.71 a | 62.72 a | |
| LSD: p < 0.05 | 19.60 | 3.529 | 11.06 | 3.17 | |||||
| F < 0.001 | 634.86 | 9.399 | 24.42 | 45.008 | |||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot | Trunk | Root | Shoot | Trunk | Root | ||
| Control | Own roots | 47.88 b | 60.51 a | 49.73 a | 38.91 d | 53.11 c | 44.98 b |
| 1103P | 52.15 a | 57.76 b | 50.93 a | 42.45 c | 61.01 a | 49.30 a | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 42.56 c | 58.52 b | 41.38 b | 38.46 d | 61.28 a | 39.86 b | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 44.24 bc | 59.45 a | 42.39 b | 36.89 d | 54.59 c | 34.94 c |
| 1103P | 46.21 b | 57.40 b | 42.44 b | 38.83 d | 69.48 a | 32.39 d | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 38.46 d | 57.62 b | 32.39 d | 34.08 d | 58.39 bc | 29.68 d | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 3.091 | 2.041 | 2.597 | 3.091 | 2.041 | 2.597 | |
| F < 0.001 | 16.101 | 41.171 | 42.566 | 16.101 | 41.171 | 42.566 | |
| Leaves | |||||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||||
| Treatments | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | |
| Control | Own roots | 2.16 a | 0.30 b | 2.35 a | 0.61 a | 2.88 a | 2.23 a | 0.33 a | 2.24 a | 0.62 a | 2.96 a |
| 1103P | 2.44 a | 0.32 a | 1.33 c | 0.72 a | 2.67 a | 1.95 b | 0.32 a | 1.65 c | 0.63 a | 2.88 a | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 1.77 b | 0.27 b | 1.56 c | 0.56 b | 2.63 ab | 1.94 b | 0.29 b | 1.96 b | 0.55 b | 2.70 a | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 1.83 ab | 0.23 c | 0.97 d | 0.42 c | 2.45 bc | 1.89 b | 0.28 b | 1.42 c | 0.44b c | 2.63 ab |
| 1103P | 1.81 ab | 0.20 c | 1.26 c | 0.49 b | 2.29 c | 1.77 b | 0.27 b | 1.47 c | 0.45 bc | 2.46 b | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 1.68 b | 0.25b c | 1.75 bc | 0.31 d | 1.96 c | 1.74 b | 0.22 c | 1.71 bc | 0.39 c | 2.37 b | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 0.177 | 0.024 | 0.249 | 0.122 | 0.158 | 0.177 | 0.024 | 0.249 | 0.122 | 0.158 | |
| F < 0.001 | 4.845 | 7.398 | 10.73 | 10.227 | 8.558 | 4.845 | 7.398 | 10.73 | 10.227 | 8.558 | |
| Roots | |||||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||||
| Treatments | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | |
| Control | Own roots | 1.14 a | 0.29 a | 0.58 a | 0.28 a | 1.18 | 1.16 a | 0.27 a | 0.65 a | 0.32 a | 1.16 |
| 1103P | 1.12 a | 0.30 a | 0.50 a | 0.31 a | 1.29 | 1.17 a | 0.29 a | 0.48 a | 0.31 a | 1.11 | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 1.20 a | 0.29 a | 0.52 a | 0.32 a | 1.03 | 1.12 a | 0.28 a | 0.42 b | 0.38 a | 1.05 | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 0.79 b | 0.18 b | 0.30 b | 0.21 b | 1.24 | 0.90 a | 0.20 b | 0.39 b | 0.21 b | 0.94 |
| 1103P | 0.88 ab | 0.20 b | 0.31 b | 0.20 b | 0.95 | 0.83 b | 0.19 b | 0.36 b | 0.23 b | 0.98 | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 0.83 b | 0.22 ab | 0.26 b | 0.23 b | 0.97 | 0.88 ab | 0.23 ab | 0.24 b | 0.19 b | 0.90 | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 0.321 | 0.094 | 0.069 | 0.106 | ns | 0.321 | 0.094 | 0.069 | 0.106 | ns | |
| F< 0.001 | 9.950 | 22.627 | 8.755 | 8.825 | 9.950 | 22.627 | 8.755 | 8.825 | |||
| Shoots | |||||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||||
| Treatments | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | |
| Control | Own roots | 1.06 a | 0.23 | 0.66 a | 0.22 b | 0.76 a | 0.95 b | 0.19 | 0.61 b | 0.18 c | 0.67 ab |
| 1103P | 1.07 a | 0.18 | 0.59 b | 0.19 c | 0.77 a | 1.05 a | 0.20 | 0.67 a | 0.24 a | 0.70 a | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 1.09 a | 0.18 | 0.60 b | 0.25 a | 0.70 a | 0.98 b | 0.21 | 0.52 c | 0.21 b | 0.76 a | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 0.96 b | 0.19 | 0.34 d | 0.14 c | 0.65 b | 0.86 c | 0.16 | 0.40 c | 0.15 c | 0.61 b |
| 1103P | 0.89 c | 0.15 | 0.45 c | 0.16 c | 0.64 b | 0.79 c | 0.20 | 0.29 d | 0.16 c | 0.59 b | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 0.79 c | 0.16 | 0.36 d | 0.15 c | 0.60 b | 0.75 c | 0.17 | 0.28 d | 0.14 c | 0.66 b | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 0.071 | ns | 0.058 | 0.029 | 0.10 | 0.071 | ns | 0.058 | 0.029 | 0.10 | |
| F < 0.001 | 5.752 | 23.831 | 16.85 | 7.360 | 5.752 | 23.831 | 16.85 | 7.360 | |||
| Trunks | |||||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||||
| Treatments | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | |
| Control | Own roots | 0.78 a | 0.25 a | 0.25 a | 0.15 b | 0.86 | 0.76 a | 0.24 a | 0.27 a | 0.16 b | 0.80 |
| 1103P | 0.81 a | 0.22 a | 0.28 a | 0.16 b | 1.52 | 0.80 a | 0.14 ab | 0.25 a | 0.14 b | 0.82 | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 0.55 b | 0.16 ab | 0.27 a | 0.18 a | 0.70 | 0.74 a | 0.25 a | 0.24 a | 0.16 b | 0.85 | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 0.62 ab | 0.08 b | 0.17 b | 0.12 c | 0.62 | 0.58 b | 0.11 b | 0.18 b | 0.13 c | 0.64 |
| 1103P | 0.57 b | 0.10 b | 0.18 b | 0.13 c | 0.70 | 0.54 b | 0.09 b | 0.17 b | 0.11 c | 0.72 | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 0.60 b | 0.09 b | 0.16 b | 0.12 c | 0.61 | 0.64 ab | 0.11 b | 0.16 b | 0.12 c | 0.58 | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 0.197 | 0.088 | 0.091 | 0.013 | ns | 0.197 | 0.088 | 0.091 | 0.013 | ns | |
| F < 0.001 | 8.053 | 2.460 | 8.061 | 17.916 | 8.053 | 2.460 | 8.061 | 17.916 | |||
| Leaves | |||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||
| Treatments | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | |
| Control | Own roots | 97.70 a | 16.25 b | 114.34 a | 10.60 a | 68.02 b | 14.06 b | 112.26 b | 9.15 a |
| 1103P | 96.03 a | 19.03 a | 106.21 b | 8.98 a | 54.19 b | 15.05 b | 135.68 a | 7.61 a | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 55.03 b | 14.31 b | 125.10 a | 7.51 ab | 50.09 b | 15.43 b | 121.26 a | 7.01 ab | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 59.54 b | 13.51 b | 95.94 b | 6.78 b | 57.01 b | 10.92 bc | 99.14 b | 5.67 b |
| 1103P | 56.85 b | 15.29 b | 95.66 b | 5.98 b | 47.59 bc | 14.32 b | 96.34 b | 5.45 b | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 41.94 bc | 12.80 b | 99.18 b | 5.02 c | 37.13 c | 10.39 c | 89.01 b | 5.87 b | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 17.619 | 1.988 | 22.03 | 2.11 | 17.619 | 1.988 | 22.03 | 2.11 | |
| F < 0.001 | 30.316 | 14.816 | 10.907 | 10.712 | 30.316 | 14.816 | 10.907 | 10.712 | |
| Roots | |||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||
| Treatments | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | |
| Control | Own roots | 32.68 a | 28.77 b | 243.28 a | 28.13 a | 35.14 a | 26.12 b | 238.91 a | 30.60 ab |
| 1103P | 31.90 a | 37.76 a | 276.31 a | 32.68 a | 34.18 a | 25.10 b | 251.01 a | 33.45 abc | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 34.96 a | 35.83 a | 302.65 a | 30.71 a | 31.61 a | 32.31 b | 246.51 a | 35.01 a | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 21.43 b | 15.19 c | 159.88 b | 19.50 ab | 24.30 a | 14.94 c | 160.74 b | 19.20 c |
| 1103P | 22.95 b | 18.96 c | 138.36 b | 18.04 b | 23.24 b | 17.93 c | 176.11 b | 18.58 c | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 19.98 b | 16.12 c | 146.35 b | 20.81 ab | 24.73 b | 16.75 c | 170.57 b | 17.82 bc | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 10.63 | 3.93 | 100.56 | 12.97 | 10.63 | 3.93 | 100.56 | 12.97 | |
| F < 0.001 | 17.38 | 16.945 | 7.313 | 9.942 | 17.38 | 16.945 | 7.313 | 9.942 | |
| Shoots | |||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||
| Treatments | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | |
| Control | Own roots | 39.57 a | 26.80 a | 24.87 a | 11.51 a | 29.01 b | 23.09 a | 25.16 a | 10.32 a |
| 1103P | 38.92 a | 20.52 a | 25.15 a | 10.55 a | 37.71 b | 30.14 a | 23.42 a | 11.35 a | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 40.20 a | 27.71 a | 23.89 a | 11.57 a | 35.13 ab | 19.12 b | 23.81 a | 10.74 a | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 24.29 b | 14.15 b | 16.50 b | 8.28 b | 26.24 b | 13.62 b | 21.31 a | 8.48 b |
| 1103P | 31.62 ab | 13.16 b | 16.28 b | 8.10 b | 27.81 b | 15.57 b | 15.24 b | 8.84 b | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 37.50 a | 15.60 b | 15.24 b | 7.31 b | 21.24 b | 11.66 b | 16.87 b | 7.36 b | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 4.239 | 10.68 | 7.62 | 3.26 | 4.239 | 10.68 | 7.62 | 3.26 | |
| F < 0.001 | 16.976 | 31.49 | 7.851 | 12.921 | 16.976 | 31.49 | 7.851 | 12.921 | |
| Trunks | |||||||||
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||||||
| Treatments | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | Mn | Zn | Fe | Cu | |
| Control | Own roots | 26.21 a | 17.08 a | 85.11 b | 8.83 ab | 20.49 b | 19.10 a | 81.23 b | 10.15 a |
| 1103P | 26.02 a | 15.97 a | 106.88 a | 10.28 a | 24.88 a | 17.55 a | 94.13 ab | 10.12 a | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 24.16 a | 17.71 a | 97.31 a | 9.41 a | 24.20 a | 18.08 ab | 95.51 a | 9.83 a | |
| 0.5 mM B | Own roots | 17.97 b | 11.01 b | 60.58 cd | 6.25 b | 17.97 b | 10.76 b | 49.93 d | 8.90 ab |
| 1103P | 18.57 b | 10.85 b | 83.40 b | 6.23 b | 18.56 b | 11.51 b | 60.63 c | 6.98 b | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 19.87 b | 10.07 b | 71.10 c | 5.85 b | 19.08 b | 13.51 ab | 70.03 c | 7.10 b | |
| LSD (p < 0.05) | 1.69 | 4.683 | 10.046 | 3.09 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 10.046 | 3.09 | |
| F < 0.001 | 17.694 | 1.242 | 18.406 | 11.204 | 17.694 | 17.694 | 18.406 | 11.204 | |
| Merlot | Cabernet Franc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day Thirty | Day Sixty | Day Thirty | Day Sixty | ||
| Control | Own roots | 0.758 b | 0.725 b | 0.780 ab | 0.661 c |
| 1103P | 0.815 ab | 0.722 b | 0.774 ab | 0.705 bc | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 0.828 a | 0.788 ab | 0.818 a | 0.727 b | |
| 0.5 mMB | Own roots | 0.768 b | 0.505 d | 0.783 ab | 0.489 d |
| 1103P | 0.796 ab | 0.729 b | 0.788 ab | 0.593 c | |
| 101-14 Mgt | 0.790 ab | 0.644 c | 0.729 b | 0.543 c | |
| LSD (p < 0.05): 0.044, F < 0.001: 19.057 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaou, K.-E.; Chatzistathis, T.; Theocharis, S.; Argiriou, A.; Koundouras, S. Physiological and Nutritional Responses of Ungrafted Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon Vines or Grafted to 101-14 Mgt and 1103P Rootstocks Exposed to an Excess of Boron. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040508
Nikolaou K-E, Chatzistathis T, Theocharis S, Argiriou A, Koundouras S. Physiological and Nutritional Responses of Ungrafted Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon Vines or Grafted to 101-14 Mgt and 1103P Rootstocks Exposed to an Excess of Boron. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(4):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040508
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaou, Kleopatra-Eleni, Theocharis Chatzistathis, Serafeim Theocharis, Anagnostis Argiriou, and Stefanos Koundouras. 2023. "Physiological and Nutritional Responses of Ungrafted Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon Vines or Grafted to 101-14 Mgt and 1103P Rootstocks Exposed to an Excess of Boron" Horticulturae 9, no. 4: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040508
APA StyleNikolaou, K.-E., Chatzistathis, T., Theocharis, S., Argiriou, A., & Koundouras, S. (2023). Physiological and Nutritional Responses of Ungrafted Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon Vines or Grafted to 101-14 Mgt and 1103P Rootstocks Exposed to an Excess of Boron. Horticulturae, 9(4), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9040508









