Seasonal Development of Paeonia obovata and Paeonia oreogeton and Their Contents of Biologically Active and Reserve Substances in the Forest-Steppe Zone of Western Siberia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Seasonal Development Analysis
2.3. Extract Preparation
2.4. Determination of Flavonol Contents
2.5. Quantification of Catechins
2.6. Quantification of Tannins
2.7. Quantification of Saponins
2.8. Quantification of Ascorbic Acid
2.9. Quantification of Pectins and Protopectins
2.9.1. Extraction of Water-Soluble Pectin (Extract I)
2.9.2. Extraction of Protopectin (Extract II)
2.9.3. The Reaction with Thymol
2.10. Quantification of Carotenoids
2.11. Quantification of Sugar and Starch
3. Results
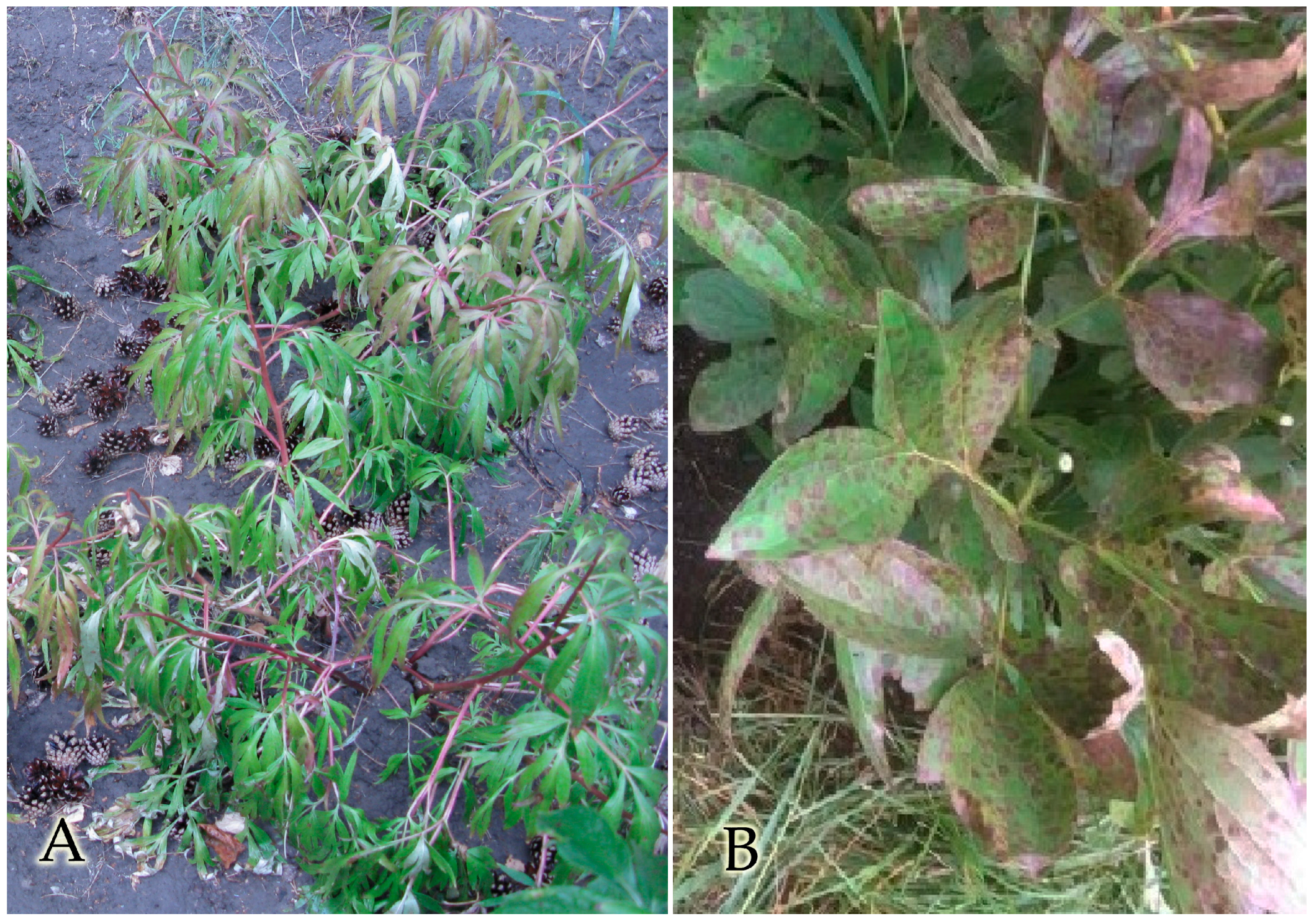
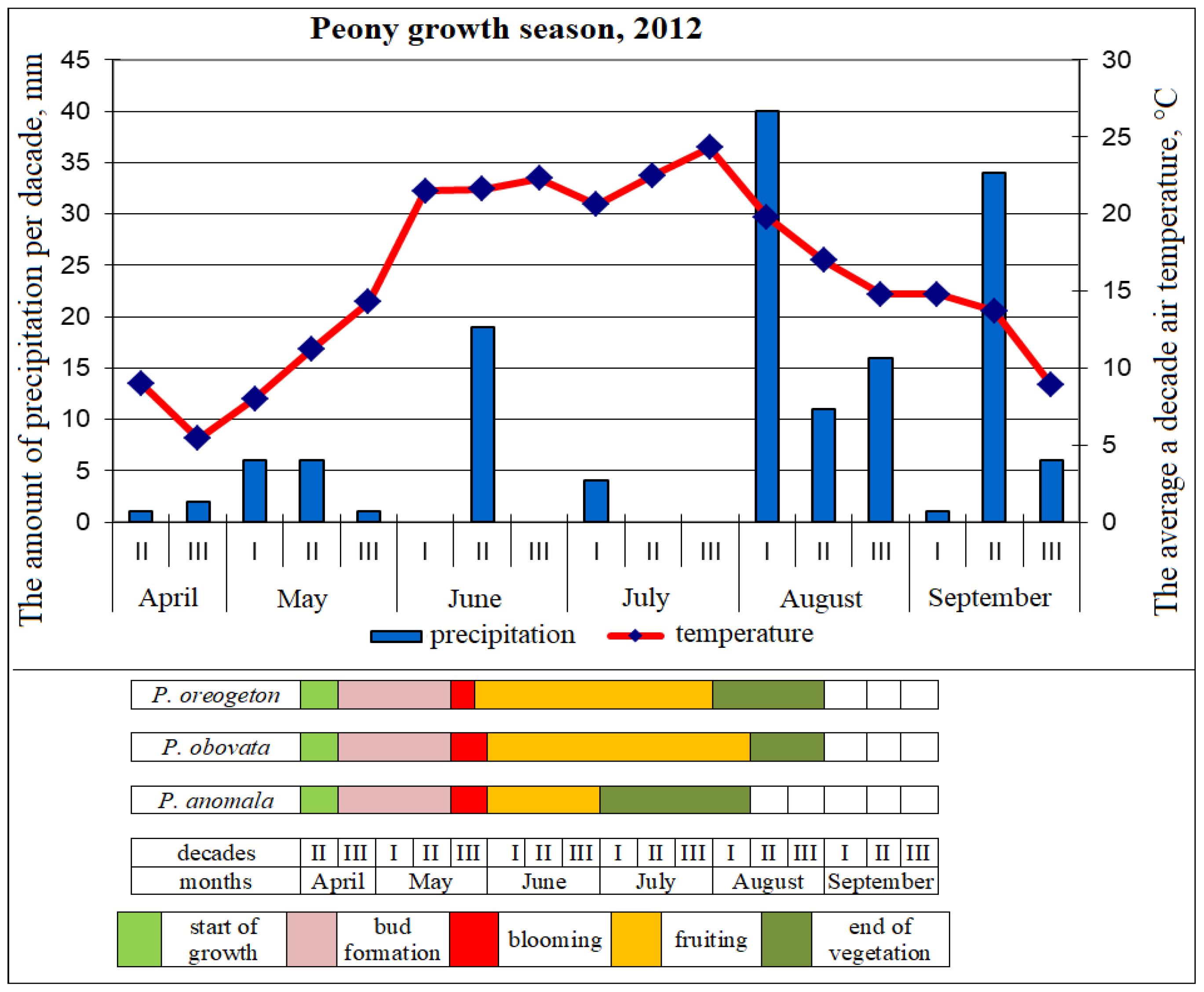
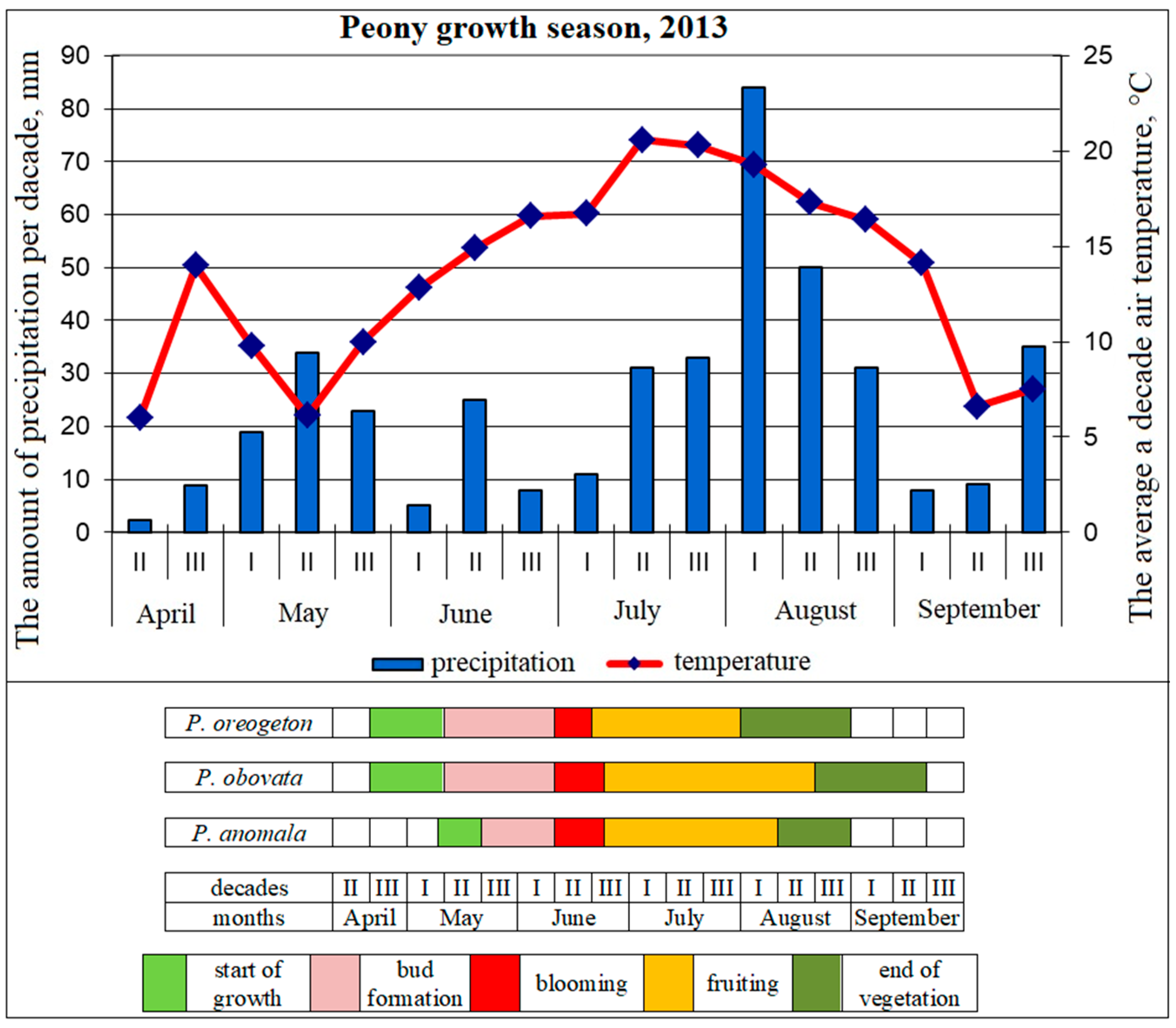
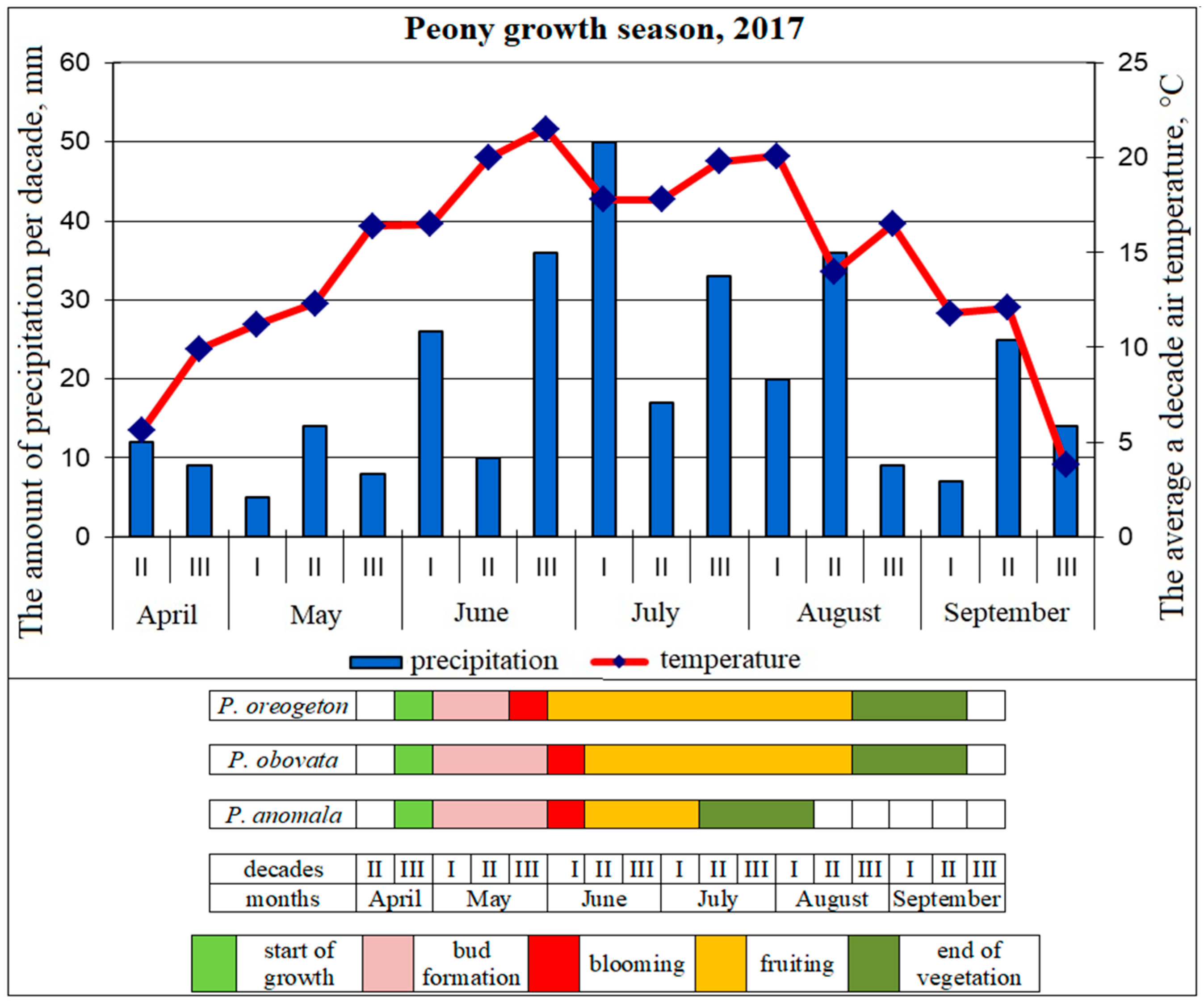
3.1. Seasonal Development of Paeonia in the Continental Climate
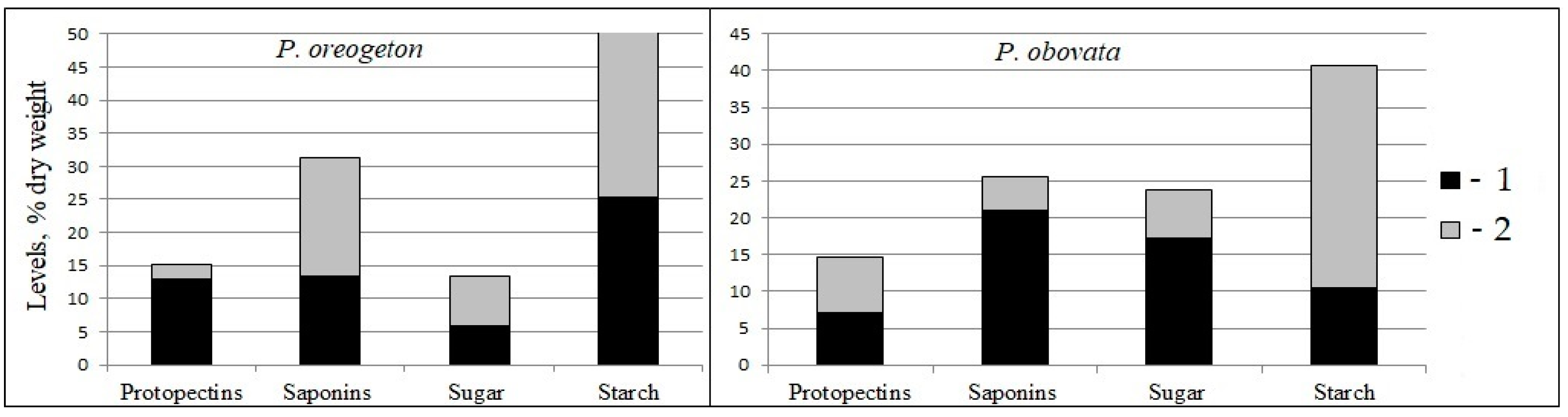
3.2. Contents of Biologically Active and Reserve Substances in the Leaves and Roots of Paeonia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kemularia-Natadze, L.M. On the position of the family Paeoniaceae in the system of angiosperms. Notes Syst. Geogr. Plants 1958, 20, 19–28. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.Y. Peonies of the world. In Taxonomy and Phytogeography; Pt. 1; Kew Publishing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.S.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Yu, X.N.; Wang, L.S. Characterization of phytochemicals in the roots of wild herbaceous peonies from China and screening for medicinal resources. Phytochemistry 2020, 174, 112331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reut, A.A.; Denisova, S.G.; Pupykina, K.A. Accumulation and distribution of biologically active substances in raw materials of some taxa of the genus Paeonia L. Chem. Plant Raw Mater. 2019, 4, 269–278. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Li, Y.Q.; Mo, H.Z.; He, J.X. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.) seed protein hydrolysates obtained with different proteases. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, N.N.; Zhou, X.Y.; Peng, L.P.; Liu, Z.A.; Shu, Q.Y. A comprehensive study of three species of Paeonia stem and leaf phytochemicals, and their antioxidant activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 273, 113985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Lee, M.M.; Fang, H.L.; Yang, J.G.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, H.Y. Paeoniflorin inhibits excitatory amino acid agonist-and high-dose morphine-induced nociceptive behavior in mice via modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. BMC Compl. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkhtuya, E.; Shimamura, T.; Kashiwagi, T.; Ukeda, H. Antioxidative constituents in the leaves of Paeonia anomala grown in Mongolia. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Song, T.; Hou, X.L.; Sui, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Hu, D.; Wang, X.H.; Xiao, Z.X.; Wang, R.R.; Wang, J.; et al. Anti-depressant effect of Paeonia lactiflora pall extract in rats. Trop. J. Pharmaceut. Res. 2017, 16, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; He, C.; Xiao, P. Genus Paeonia: A comprehensive review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, clinical application, and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, Part I; China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- Rhizomes and Rhizomata et Radices Paeonia Anomala; Pharmacopeial Article 42-531-98; Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Pharmacopoeial State Committee: Moscow, Russia, 2000. (In Russian)
- Peony Evasive Tincture 25 mL. Available online: https://www.rigla.ru/product/49409 (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Peony Extract, Coated Tablets. Available online: https://www.eapteka.ru/goods/id221531/ (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Degtjareva, G.; Efimov, S. The genetic diversity of Paeonia anomala (Paeoniaceae), as indicated by nuclear its and plastid ycf1 molecular markers. In Proceedings of the Northern Asia Plant Diversity: Current Trends in Research and Conservation: BIO Web of Conferences, Novosibirsk, Russia, 6–12 September 2021; Volume 38, p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Shulkina, T. Ornamental Plants from Russia and Adjacent States of the Former Soviet Union: A Botanical Guide for Travelers and Gardeners; Kew Publ.: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Malik, K.; Tariq, A.; Zhang, G.; Yaseen, G.; Rashid, N.; Sultana, S.; Zafar, M.; Ullah, K.; Khan, M.P.Z. Botany, ethnomedicines, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Himalayan paeony (Paeonia emodi Royle.). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wu, S.P. A review of the ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacology of tree peony (Sect. Moutan). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.-Y.; Pan, K.-Y.; Rao, G.-Y. Cytogeography and taxonomy of the Paeonia obovata polyploid complex (Paeoniaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2001, 227, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimov, S.V.; Degtyareva, G.V.; Terentyeva, Y.I.; Samigullin, T.H.; Skaptsov, M.V.; Valiejo-Roman, C.M. Species complex of Paeonia obovata Maxim. (Paeoniaceae): Five species or just one? Skvortsovia 2018, 4, 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- Halda, J.J.; Waddick, J.W. The Genus Paeonia; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.B.; Wang, D.Q.; Peng, H.S. Study on the relationship between classification, distribution and medicinal use of Sect. Moutan of the genus Paeonia in China. Res. Pract. Chin. Med. 2004, 18, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Kataoka, M.; Tsuboi, N.; Kouno, I. New monoterpene glycoside esters and phenolic constituents of Paeoniae Radix, and increase of water solubility of proanthocyanidins in the presence of paeoniflorin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Wu, D.G.; Chen, Y.W. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of plants from the genus Paeonia. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 41, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoki, T.; Mitsuhiro, S. Flower anthocyanins of herbaceous peony. Shimane Daigaku Nogakubu Kenkyu Hokoku 1991, 25, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Yu, Z.G. Analysis of Volatiles in Paeonia obovata Flowers by HS-SPME-GC-MS. Chem. Nat. Comp. 2016, 52, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, M.J. Differences in the chemical profiles and biological activities of Paeonia lactiflora and Paeonia obovata. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beideman, I.N. Methods of Studying the Phenology of Plants and Plant Communities; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1974. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Koch, E.; Bruns, E.; Chmielewski, F.M.; Defila, C.; Lipa, W.; Menzel, A. Guidelines for Plant Phenological Observations; WMO/TD No. 1484; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Uranov, A.A. Ontogenesis and Age Composition of Flowering Plant Populations; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1967; pp. 3–8. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zaugolnova, L.B.; Zhukova, A.A.; Komarova, A.S.; Smirnova, O.V. Plant Cenopopulations (Population Biology Essays); Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1988. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ermakov, A.I.; Arasimovich, V.V.; Yarosh, N.P.; Peruanskiy, Y.V.; Lukovnikova, G.A.; Ikonnikova, M.I. Methods of Biochemical Investigation of Plants; Leningrad: Agropromizdat, Russia, 1987. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Brighente, I.M.C.; Dias, M.; Verdi, L.G.; Pizzolatti, M.G. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of some Brazilian species. Pharm. Biol. 2007, 45, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Ricardo-da-Silva, J.M.; Spranger, I. Critical factors of vanillin assay for catechins and proanthocyanidins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4267–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukushkina, T.A.; Zykov, A.A.; Obukhova, L.A. Common cuff (Alchemia vulgaris L.) as a source of drugs of natural origin. In Proceedings of the Actual Problems of Creating New Drugs of Natural Origin: Materials of the VII International Congress, St. Petersburg, Russia, 3–5 July 2003; pp. 64–69. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Fedoseeva, L.M. The study of tannins of underground and aboveground vegetative organs of the Bergenia Crassifolia (L.) Fitsch., growing in Altai. Chem. Plant Raw Mater. 2005, 2, 45–50. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kiseleva, A.V.; Volkhonskaya, T.A.; Kiselev, V.E. Biologically Active Substances of Medicinal Plants of Southern Siberia; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1991. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kriventsov, V.I. Carbazole-free method for the quantitative spectrophotometric determination of pectin substances. Proc. Nikitsk. Bot. Gard. 1989, 109, 128–137. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kriventsov, V.I. Guidelines for the Analysis of Fruits for Biochemical Composition; GNBS: Yalta, Ukraine, 1982. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Borodova, V.Y.; Gorenkov, E.S.; Klyueva, O.A.; Malofeeva, L.N.; Megerdicheva, E.Y. Guidelines for Chemical-Technological Variety Testing of Vegetable, Fruit and Berry Crops for the Canning Industry; Russian Agricultural Academy: Moscow, Russia, 1993. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zaprometov, M.N. Fundamentals of Biochemistry of Phenolic Compounds; Vysshaya shkola: Moscow, Russia, 1974. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berezina, E.V.; Brilkina, A.A.; Veselov, A.P. Content of phenolic compounds, ascorbic acid, and photosynthetic pigments in Vaccinium macrocarpon Ait. dependent on seasonal plant development stages and age (the example of introduction in Russia). Sci. Hortic. 2017, 218, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M. Environmental factors on secondary metabolism of medicinal plants. Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 3, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.; Younas, M.; Arshad, B.; Zaman, W.; Ayaz, A.; Rasheed, S.; Shah, A.; Ullah, F.; Saqib, S. Bioactive potential of cultivated Mentha arvensis L. for preservation and production of health-oriented food. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2022, 32, 835–844. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolevskaya, K.A. Introduction of Plants in Siberia; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1991. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Canter, P.H.; Thomas, H.; Ernst, E. Bringing medicinal plants into cultivation: Opportunities and challenges for biotechnology. TRENDS Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komina, O.V. Biological Features of Some Species of the Genus paeonia L. When Introduced in the Forest-Steppe Zone of Western Siberia. Ph.D. Thesis, Central Siberian Botanical Garden SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia, 2014. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Makedonskaya, N.V. Rhythms of seasonal development and features of biology of Far Eastern pions in culture. In Rhythms of Seasonal Development of Plants in Primorye; DVNTS AN SSSR: Vladivostok, Russia, 1980; pp. 49–57. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gubanenko, G.A.; Morozova, E.V.; Rubchevskaya, L.P. The influence of climatic factors on the content of flavonoids in the Paeonia anomala L. biomass. Chem. Plant Raw Mater. 2014, 1, 165–170. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Oyungerel, S.; Batzaya, G.; Byamba-Yondon, G.; Lyankhua, B.; Ochgerel, N.; Usukhjargal, D. Seasonal variation of some bioactive compounds and physiological characteristics in peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). Mong. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 15, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.P.; Cheng, F.Y.; Hu, X.G.; Mao, J.F.; Xu, X.X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Xian, H.L. Modelling environmentally suitable areas for the potential introduction and cultivation of the emerging oil crop Paeonia ostii in China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calonghi, N.; Farruggia, G.; Boga, C.; Micheletti, G.; Fini, E.; Romani, L.; Telese, D.; Faraci, E.; Bergamini, C.; Cerini, S.; et al. Root Extracts of Two Cultivars of Paeonia Species: Lipid Composition and Biological Effects on Different Cell Lines: Preliminary Results. Molecules 2021, 26, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Hao, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, D. Anthocyanin Accumulation and Differential Expression of the Biosynthetic Genes Result in a Discrepancy in the Red Color of Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Flowers. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshenko, O.V.; Rudaya, O.A.; Efimov, S.V.; Kiris, Y.N. The transpiration rate of some species’ leaves of the genus Paeonia L., as one possible performance of their adaptation to the environment. For. Bull. 2017, 21, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kostikova, V.A.; Kalendar, O.V.; Tashev, N.A.; Erst, A.S.; Vasilyeva, O.Y. Biologically active and reserve substances of Siberian peonies. In Proceedings of the Northern Asia Plant Diversity: Current Trends in Research and Conservation: BIO Web of Conferences, Novosibirsk, Russia, 6–12 September 2021; Volume 38, p. 61. [Google Scholar]


| Substances | P. oreogeton | P. obovata | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhizomes | Leaves | Rhizomes | Leaves | |
| Moisture (% dry weight) | 66.86 | 80.39 | 78.17 | 74.63 |
| Flavonols (% dry weight) | no | 1.17 ± 0.04 b | no | 1.77 ± 0.05 a |
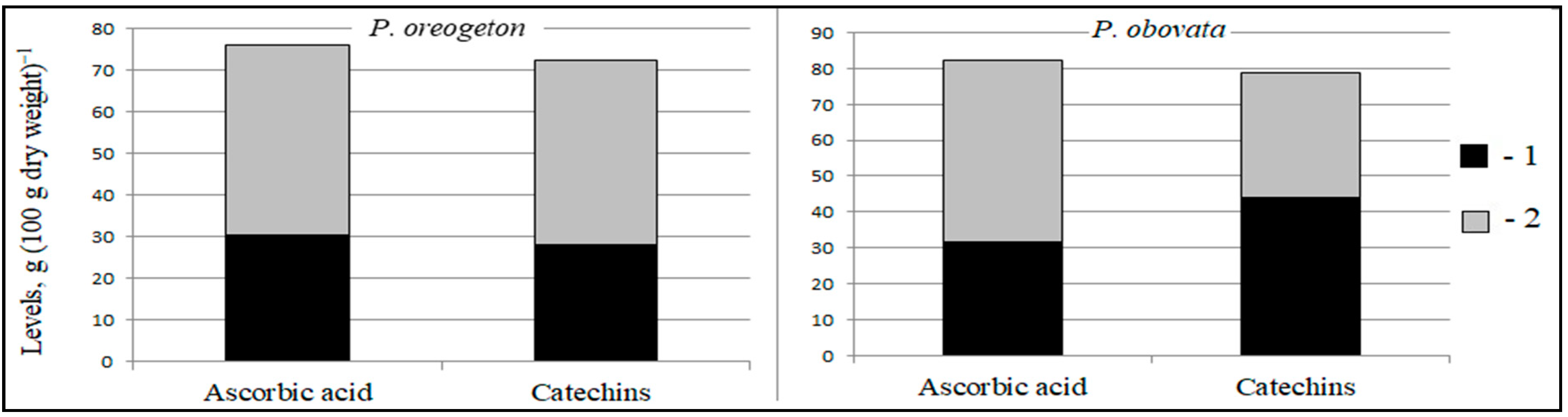
| Catechins (g (100 g dry weight)−1) | 28.1 ± 0.48 d | 68.3 ± 1.17 b | 44.0 ± 0.76 c | 84.4 ± 1.45 a |
| Tannins (% dry weight) | 2.56 ± 0.02 d | 16.42 ± 0.14 a | 11.59 ± 0.10 c | 12.81 ± 0.11 b |
| Ascorbic acid (g (100 g dry weight)−1) | 30.5 ± 1.22 b | 155.2 ± 6.21 a | 31.5 ± 1.26 b | 151.8 ± 6.07 a |
| Pectins (% dry weight) | 1.15 ± 0.01 b | 1.89 ± 0.06 a | 2.02 ± 0.10 a | 0.86 ± 0.01 c |
| Protopectins (% dry weight) | 13.03 ± 0.26 a | 5.99 ± 0.01 c | 7.02 ± 0.09 b | 3.96 ± 0.02 d |
| Saponins (% dry weight) | 13.37 ± 0.51 b | 11.25 ± 0.43 c | 21.06 ± 0.80 a | 12.94 ± 0.49 b |
| Carotenoids (g (100 g dry weight)−1) | no | 29.1 ± 0.29 b | no | 89.2 ± 0.87 a |
| Sugar (% dry weight) | 5.97 ± 0.21 c | 17.44 ± 0.61 b | 17.22 ± 0.60 b | 20.85 ± 0.73 a |
| Starch (% dry weight) | 25.31 ± 0.94 a | - | 10.51 ± 0.39 b | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalendar, O.V.; Kostikova, V.A.; Kukushkina, T.A.; Erst, A.S.; Kuznetsov, A.A.; Kulikovskiy, M.S.; Vasilyeva, O.Y. Seasonal Development of Paeonia obovata and Paeonia oreogeton and Their Contents of Biologically Active and Reserve Substances in the Forest-Steppe Zone of Western Siberia. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010102
Kalendar OV, Kostikova VA, Kukushkina TA, Erst AS, Kuznetsov AA, Kulikovskiy MS, Vasilyeva OY. Seasonal Development of Paeonia obovata and Paeonia oreogeton and Their Contents of Biologically Active and Reserve Substances in the Forest-Steppe Zone of Western Siberia. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalendar, Olga V., Vera A. Kostikova, Tatiana A. Kukushkina, Andrey S. Erst, Alexander A. Kuznetsov, Maxim S. Kulikovskiy, and Olga Y. Vasilyeva. 2023. "Seasonal Development of Paeonia obovata and Paeonia oreogeton and Their Contents of Biologically Active and Reserve Substances in the Forest-Steppe Zone of Western Siberia" Horticulturae 9, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010102
APA StyleKalendar, O. V., Kostikova, V. A., Kukushkina, T. A., Erst, A. S., Kuznetsov, A. A., Kulikovskiy, M. S., & Vasilyeva, O. Y. (2023). Seasonal Development of Paeonia obovata and Paeonia oreogeton and Their Contents of Biologically Active and Reserve Substances in the Forest-Steppe Zone of Western Siberia. Horticulturae, 9(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9010102







