Abstract
Fermentation is a crucial technology to improve the nutritional and functional properties of food materials. In this study, edible grass was processed by spontaneous fermentation. Changes in physicochemical properties, metabolites, and antioxidant activity of edible grass were investigated by colorimetric method and chromatography mass spectrometry-based non-targeted metabolomics approach during fermentation. The highest total polyphenol and total flavonoid contents, and free radical scavenging abilities were observed on the 17th day of fermentation. The maximum activity of superoxide dismutase was maintained stable in the fermentation time range of 7–70 days. In total, 16 differential metabolites were identified with fermentation duration up to 124 days. Fermented edible grass exerted protection from H2O2-induced cytotoxicity on HepG2 cells, regulating by the reduction in reactive oxygen species level and the increase in antioxidant enzyme activities. Overall, this study confirms that fermented edible grass obtained by spontaneous fermentation presented favorable nutritional and functional quality, and is expected to be a kind of food with antioxidant function.
1. Introduction
Edible grass (Rumex patientia L. × Rumex tianschanicus A. LOS) is a perennial food plant that can grow under different climatic and pedologic conditions in China and has attracted significant attention due to its abundant protein content and high superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity [1]. Previous work confirmed that the water extract of edible grass had the benefits of scavenging free radicals and inhibiting α-glucosidase activity, thus indicating its antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities [2]. However, the content of oxalic acid (considered as an anti-nutrition factor) in edible grass was high [3], which is a limitation in the development and utilization of edible grass in food product. Therefore, the development of technology for processing edible grass may provide an important scientific basis to reduce the oxalic acid content and enrich the product variety.
As is known to all, fermentation is one of the effective biological treatments to improve the flavor and nutritional quality of food materials [4,5,6]. Some macromolecular compounds that existed in raw food materials could be biotransformed into small molecular compounds with higher bioactivity by microorganisms, and levels of antinutritional compounds can be reduced during fermentation, which was beneficial for improving the health and nutritional properties of products [7,8,9]. In previous work, edible grass was fermented with two commercial lactic acid bacteria (LAB) to improve its functional properties [1]. The results have indicated that fermented edible grass with binary mixture strains showed a significant effect on increasing SOD activity and soluble protein content, as well as reducing the oxalic acid content compared to unfermented edible grass, and further improving antioxidant activity. In addition to LAB fermentation, spontaneous fermentation is also suitable for food processing and is widely used in the production of chocolate [10], vinegar [11], and wine [12]. Spontaneous fermentation is generally conducted by the natural inoculation of microorganisms from raw materials and environment [13]. However, research on spontaneous fermentation applied to edible grass processing has been unreported. Additionally, the changes in some small bioactive metabolites need to be analyzed in depth to clarify the promotion mechanism for edible grass by fermentation.
Consequently, spontaneous fermentation was used to process edible grass, and the dynamics of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity were evaluated in the present study. At the same time, non-targeted metabolomics was performed using gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to reveal the comprehensive changes of the main metabolites of fermented edible grass, and to further define the relationship of the metabolizing compounds and antioxidant activity. The results would be helpful to shed light on the spontaneous fermentation process of edible grass and provide useful information for the production of functional fermented edible grass products.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
Edible grass was purchased from Zhejiang Edible Grass Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd., (Shaoxing, China). Folin and Ciocalteu's phenol reagent, gallic acid, and rutin were obtained from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). Further, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (MSTFA), pyridine, 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS), and methoxyamine hydrochloride were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The assay kits used for determining protein concentration, reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, SOD, catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities were obtained from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China). Ribitol was acquired from Shanghai Yuanye Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). HepG2 cells were purchased from Procell Life Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China).
2.2. Spontaneous Fermentation of Edible Grass
One and a half kilograms of fresh and chopped edible grass was mixed with sucrose and deionized water at a weight ratio of 1:1:2 to carry out spontaneous fermentation in a stainless steel tank at 25 °C for 124 days. The fermentation tank was sealed and placed in the dark. The fermentation process was performed in triplicate, and the supernatant of fermentation broth (one sample, 30 mL) was collected after 1, 7, 17, 27, 37, 70, 106, and 124 days of fermentation. The collected samples were stored at −80 °C to ensure that the following experiments were conducted at the same time.
2.3. Determination of Physicochemical Properties of Fermented Edible Grass
pH values of the collected fermentation samples were measured by pH meter supplied by Hangzhou Qiwei Instrument Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China).
The determination of total polyphenol content (TPC) followed the method described previously [1,2]. In brief, 100 μL of diluted sample solution was mixed with 500 μL of 10% (w/v) Folin–Ciocalteu solution. After 3 min, 400 μL of 7.5% (w/v) Na2CO3 was added to the mixture, and they were incubated in the dark for 1 h. Absorbance was measured at 765 nm. The total polyphenol content was calculated using gallic acid as standard.
The determination of total flavonoid content (TFC) was referenced by previous reports [1,2]. Firstly, 500 μL of diluted sample solution was mixed with 30 μL of 5% (w/v) NaNO2, and the mixture was left to stand still for 6 min. Then, 30 μL of 10% (w/v) Al(NO3)3, 400 μL of NaOH (1 mol/L), and 40 μL of deionized water were added to the mixture and stand still for 15 min. Absorbance was measured at 510 nm. The total flavonoid content was calculated using rutin as standard.
Total sugar content was measured using the anthrone–sulphuric acid method [14] with some modifications. 800 μL of anthrone–sulphuric acid solution (2 mg/mL) was added to 200 μL of diluted sample solution at 0 °C, and they were incubated in a boiling water bath for 10 min. After the solution was cooled down to room temperature, its absorbance was measured at 620 nm. The total sugar content was calculated using glucose as standard.
SOD activity was determined by the assay kit supplied by Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China).
2.4. Metabolite Profiling Analysis
Samples containing 100 μL of fermentation broth, 300 μL of methanol, and 5 μL of ribitol water solution (2 mg/mL) were vortex mixed for 30 s. The mixture was prepared by ultrasonic treatment (ultrasonic power = 400 W) at 0 °C for 10 min and then centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 15 min to collect the supernatant. The partial supernatant (10 μL) from every sample constituted quality control (QC) samples. The samples were dried in the vacuum concentrator to prepare for derivatization. The dried samples were redissolved in methoxyamine hydrochloride in pyridine (100 μL, 20 mg/mL) at 80 °C for 30 min, and then incubated with 100 μL of MSTFA at 70 °C for 1.5 h. After being cooled to room temperature, the mixture was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min to obtain the supernatant for GC-MS analysis.
The analysis was performed using a HP-5MS capillary column (30 m × 250 μm, 0.25 μm). The injection temperature was 280 °C, and the transfer line and ion source temperatures were 280 °C and 250 °C, respectively. The carrier gas was helium with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, and the injection volume of the sample was 1 μL. In the heating process, the starting temperature of 40 °C was maintained for 1 min, then the temperature was reached at 310 °C with a heating rate of 8 °C/min and kept for 10 min. An ionization source in the single-ion monitoring scan mode was used to proceed full sweep electron bombardment with an electron energy of 70 eV. The scan range was from 50 to 500 m/z. The metabolites were identified by comparing them with the NIST 14 standard mass spectral database.
2.5. Free Radical Scavenging Activity
DPPH radical scavenging activity and ABTS radical scavenging activity were used to evaluate the antioxidant activity of fermented edible grass, and they were measured according to the methods previously reported [1].
2.6. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
HepG2 cells were cultured in DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% streptomycin-penicillin, and incubated at 37 °C in an incubator containing 5% CO2.
HepG2 was cultured for 24 h, after which HepG2 cells were seeded in 96-well plates (100 μL, 1 × 105 cells/well). Then, the control group and the experimental group of fermented edible grass were established. The control group was obtained by adding 100 μL DMEM medium to the cells seeded in 96-well plates and incubated for 24 h. The experimental group was prepared by adding 100 μL of fermented edible grass with different diluted times (20–160) and incubated for 24 h. Subsequently, the MTT assay was used to determine cell viability [15]. Non-toxic concentration was defined as the concentration of fermented edible grass that showed no significant difference compared to the control group in cell viability. Further experiments were conducted on the basis of the nontoxic concentration for fermented edible grass.
2.7. Induction of the H2O2-Mediated Oxidative Damaged HepG2 Cells Model
After HepG2 cells were cultured for 24 h, the cell suspension was absorbed and inoculated into 96-well plates (100 μL, 1 × 104 cells/well). Then, the control group, protective group, and oxidative damaged group were established as described below. 100 μL of fermented edible grass with nontoxic diluted times (DMEM dissolved) was added to each well containing HepG2 cells and incubated for 24 h, then 100 μL of H2O2 (0.3 mmol/L) was added to each well and then incubated for 2 h to prepare the protective group. 100 μL of DMEM medium was added to each well containing HepG2 cells and incubated for 24 h, then 100 μL of H2O2 (0.3 mmol/L) was added and then incubated for 2 h to prepare the oxidative damaged group. The control group was prepared by adding 200 μL DMEM medium to each well containing HepG2 cells and incubated for 24 h. The MTT assay was used to determine cell viability [15].
2.8. Determination of ROS Level and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
HepG2 cells from the control group, the protective group, and the oxidation damage group in 2.7 were collected and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min to acquire cell deposits. The ROS level of HepG2 cells was determined in terms of the instructions of the ROS assay kit. Protein concentration was measured using BCA protein concentration assay kit. The SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px activities in HepG2 cells were measured according to the manufacturers’ instructions for the SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px assay kits, respectively.
2.9. Data Analysis
All metabolite data was normalized using SIMCA-P 14.0 software (Umetrics, Umea, Sweden) before principal component analysis (PCA). The data of all samples were tested by PCA and projections to latent structure-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) models. Differential metabolites were defined at the variable importance in the projection values (VIP) of the OPLS-DA model (VIP > 1) combined with Student’s t-test (p < 0.05).
Statistical analysis was performed using Origin 2022 software (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA) and IBM SPSS Statistics 26 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Significant differences among means of samples were tested using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) at p < 0.05. Results were expressed as the average value with its standard deviation. The correlations between biochemical compositions and antioxidant activities were analyzed using the Pearson method.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Physicochemical Properties of Edible Grass during Spontaneous Fermentation
3.1.1. Total Polyphenol Content and Total Flavonoid Content
As shown in Figure 1a, the TPC of edible grass increased significantly (p < 0.05) during the first 17 days of fermentation, and the highest TPC (~246.52 μg/mL) was achieved on the 17th day. Then, the TPC decreased from 243.36 to 129.49 μg/mL with the increase in fermentation time from the 27th to the 37th day, and was subsequently kept almost unchanged until the fermentation time reached the 106th day. On the 124th day, the TPC was reduced to 97.39 μg/mL, which was only 40% of that on the 17th day. The increase-then-decrease trend was also reported in the spontaneous fermentation of black wolfberry vinegar, whose TPC increased significantly during the first 15 days and rapidly decreased from the 20th to the 25th day to the minimum [16]. The increase in TPC in prior fermentation stage can be explained by the gradual release of polyphenols caused by the destruction of cellular structures by enzymes and carboxylic acids and the generation of simple soluble phenolic compounds resulting from the hydrolysis of large polymeric phenolics by microorganisms [17,18,19]. The decrease observed in TPC could be due to phenolics oxidation caused by polyphenol oxidase [20] and/or the combination of phenolic compounds with other macromolecules [21].
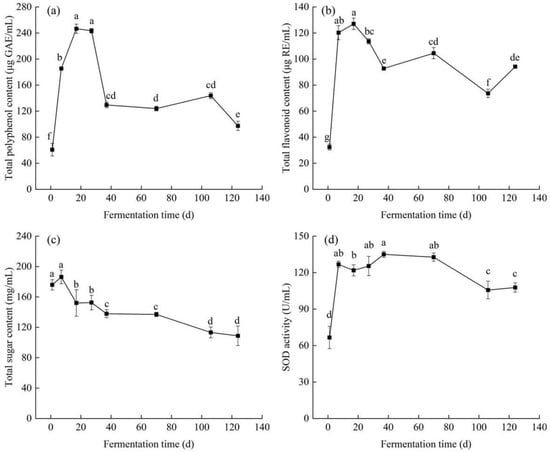
Figure 1.
Changes in (a) total polyphenol content, (b) total flavonoid content, (c) total sugar content and (d) SOD activity of edible grass during fermentation. The bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
As shown in Figure 1b, the TFC of fermented edible grass increased significantly (p < 0.05) from the first to the 17th day, and subsequently decreased from the 17th to the 106th day to the minimum (~73.61 μg/mL). Similar phenomena were also found in the fermentation processes of black beans and mung beans, which exhibited significant increase in TFC during the first 5 days of fermentation and then began to decline until the end of fermentation [22]. The peak value of TFC (~126.97 μg/mL) arrived on the 17th day, which was about 4 times higher than that on the first day. The increase in TFC for the first 17 days of fermentation could be as a result of debonding of flavonoids those were bound to proteins and carbohydrates in the cell wall [23]. At the end of fermentation, the TFC value was 94.17 μg/mL, decreasing by 26% compared to the maximum. The reason for the reduction was mainly due to the catalyzed oxidation of flavonoids caused by polyphenol oxidases [24] and the transformation of flavonoids to other compounds [25]. Although the highest TPC of fermented edible grass in this study was lower than that of edible grass fermented by lactic acid bacteria, the highest TFC was more than 1.32 times higher than that of edible grass fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum [1].
3.1.2. Total Sugar Content and Superoxide Dismutase Activity
The total sugar content of edible grass showed a downward trend during spontaneous fermentation, decreasing from an initial 204.23 to 108.74 mg/mL in the end (Figure 1c). Similar findings were discovered in green olive fermentation [26] and Aspergillus-type douchi fermentation [27], where the total sugar content decreased by 71%–79% and 26% throughout the fermentation process, respectively. The decrease in total sugars was possibly due to microorganisms consumption to produce small bioactive molecules [27,28] and utilization for microbial growth [29].
SOD is an important antioxidant enzyme responsible for scavenging superoxide anion free radicals [30,31]. As shown in Figure 1d, SOD activity increased significantly (p < 0.05) during the first 7 days of fermentation, followed by the unchanged level up to the 70th day, with the SOD activity ranging from 66.61 to 135.01 U/mL, and reduced to 107.75 U/mL at the end. The increase in SOD activity was probably due to microbial growth. Furthermore, the amount of SOD that originally existed in edible grass could also be continuously released from plant cells with fermentation, resulting in the increased SOD activity. With the increase in fermentation time, some fermentation products such as organic acids could lead to the low pH value (Figure S1), and the changes of nutrients used by microorganisms tend to be stable [32]. The phenomena resulted in the inhibition of microbial growth, and further led to the reduction of SOD produced by microorganisms. Therefore, the constant SOD activity was probably attributed to the counterbalance of the reduction of SOD produced by microorganisms and the release of SOD from plant cells. However, the fermentation temperatures and chemical compounds existed in the raw material and/or produced by microorganisms as a reaction to the acidic, stressful environment can lead to the instability and inactivation of SOD [33], giving rise to the reduction in SOD activity.
3.2. Metabolomics Analysis in the Fermentation Process of Edible Grass
3.2.1. Multivariate Analysis of Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics Data
The metabolites at the first day, the 17th day and the 124th day were analyzed with the metabolomics approach using GC-MS. A total of 48 compounds were detected, including sugars, organic acids, fatty acids, amino acids, and polyols (Table S1).
PCA was used to simplify the datasets and retain important information. The ellipse in the score plots of the models represents Hotelling’s T2 region and defines the 95% confidence interval of the modeled variation [34]. As shown in Figure S2, all samples were listed in the ellipse, indicating that no outlier was found in the analyzed samples. Clear separation was found in fermented edible grasses with different fermentation times in the PCA score plot, indicating that the metabolites in each group with different fermentation times had significant difference. The statistical value of R2X (0.755) was close to the value of Q2 (0.612), revealing good fitness and predictability of the PCA model.
Subsequently, supervised PLS-DA was applied to extract significant metabolites that discriminate fermented edible grass groups. In the PLS-DA model, the values of R2Y and Q2 are often used to estimate the stability of the model and the degree of confidence of the raw data [35]. The values of R2Y (0.989) and Q2 (0.957) are close to 1, respectively, indicating good fitness of the PLS-DA model (Figure S3). To avoid overfitting problem, the response permutation testing (RPT) was used to verify the PLS-DA model. Based on the result of the permutation (n = 200, intercept of Q2 = −0.141), the PLS-DA model was available for subsequent analysis (Figure S4).
3.2.2. Metabolite Differences in Fermented Edible Grass at Different Fermentation Times
According to the screening of PLS-DA model, a total of 16 metabolites with VIP score > 1.0 and p < 0.05 were selected as factors contributing to the discrimination among groups. The relative abundance of metabolites at various fermentation times from the first day to the 124th day is shown in Figure 2.
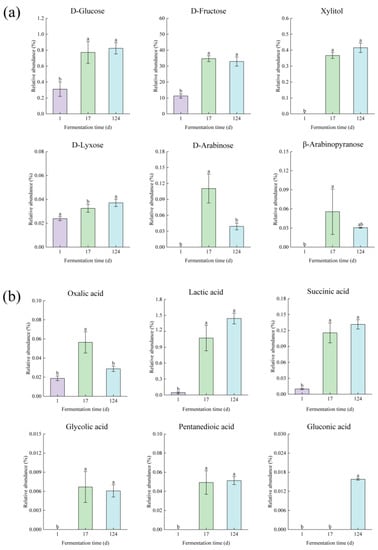
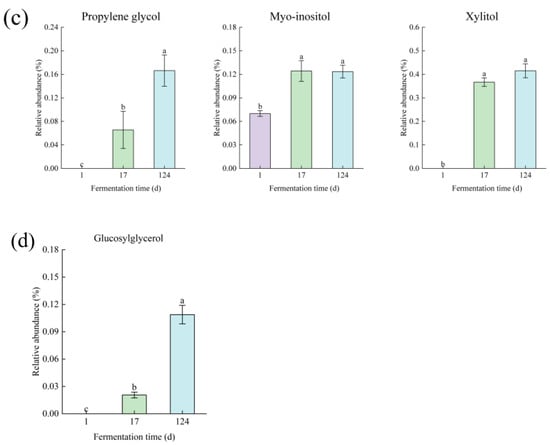
Figure 2.
Metabolite changes in (a) sugars, (b) organic acids, (c) polyols, and (d) glycoside of edible grass during fermentation. The bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
The levels of most sugars in fermented edible grass on the 17th day were higher than those on the first day (Figure 2a). Both D-glucose and D-fructose showed a significant relative content variation on the 17th day, attributing to the metabolism and hydrolysis of sucrose caused by microorganisms and hydrolytic enzymes [36]. With a further increase in fermentation time, sugar levels exhibited a downward or unchanged trend, resulting from the consumption for the microorganisms surviving [7].
Organic acids are common components of vegetables and fruits that have influence on sensory properties and nutritional stability of food, and can be intermediate or final products that affect biological processes through their participation in metabolic pathways [37]. Changes in organic acid levels were related to the dissolution of organic acids existing in edible grass and the metabolic activities of microorganisms. Some organic acids, including oxalic acid, lactic acid, succinic acid, glycolic acid, and pentanedioic acid were observed to increase significantly from the first day to the 17th day (Figure 2b). On the 124th day, the levels of pentanedioic acid, lactic acid, glycolic acid, and succinic acid kept almost unchanged compared to the 17th day, while the oxalic acid level was lower than that on the 17th day. Edible grass is a plant that is rich in oxalic acid [1]. With the gradual dissolution of oxalic acid in edible grass caused by the destruction of the cellular structure by the high osmotic pressure system formed by the high sugar concentration and the enzyme hydrolysis of cellulase and pectinase produced by microorganisms, the oxalic acid level on the 17th day was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than that on the first day. However, lactic acid bacteria could exhibit oxalate-degrading activity through the transportation of oxalate by permease into cells [1], leading to a low level of oxalic acid on the 124th day. Furthermore, gluconic acid was only identified on the 124th day, which was the result of glucose oxidation [38].
The production of propylene glycol can be accomplished through the glycerol and glucose pathways [39,40]. As shown in Figure 2c, an increased level of propylene glycol was observed during fermentation, suggesting that fermented edible grass can provide sufficient glycerol, glucose, and strains for the production of propylene glycol. The levels of myo-inositol and xylitol increased during the early stage of fermentation, and then maintained stable as fermentation progressed. Myo-inositol is a kind of cyclic sugar alcohol that has optical and biological activity, and can be synthetized by glucose-6-phosphate which can be transformed by glucose [41]. Therefore, the increase in myo-inositol level was consistent with the increased glucose level. D-xylose can be converted to xylitol by D-xylose reductase conversions in the D-xylose pathway [42], so the increase in xylitol level was probably related to the promoted transformation of D-xylose by its increased level. In addition, glucosylglycerol is the only differential metabolite of glycosides in the fermentation process, and its level increased with increasing fermentation time (Figure 2d).
3.3. Antioxidant Activity
3.3.1. Free Radical Scavenging Activity
In this study, the antioxidant property of fermented edible grass was characterized by the DPPH radical scavenging activity and the ABTS radical scavenging activity. Figure 3 shows the changes in the DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activities of edible grass during fermentation. The DPPH radical scavenging activity increased significantly (p < 0.05) with increasing fermentation time in the range of 1–17 days with the highest value achieved on the 17th day, and then decreased to a stable level on the 37th day until the end. The maximum DPPH radical scavenging activity of fermented edible grass was higher than that of black wolfberry vinegar (~64%) produced by spontaneous fermentation [16]. Changes in ABTS radical scavenging activity were similar to those in DPPH radical scavenging activity, presenting a maximum of 41% on the 17th day. Some functional compounds such as polyphenol compounds and SOD are abundant in fermented edible grass, which were the primary reasons for the improvement in antioxidant activity [43]. Therefore, increases in the DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activities in the early fermentation stage were considered due to the increased contents of functional compounds, while reductions in free radical scavenging activities were probably caused by the oxidative degradation of antioxidant compounds [44].
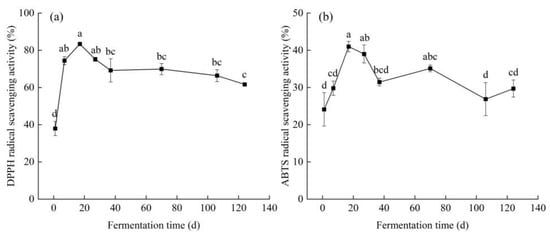
Figure 3.
(a) DPPH radical scavenging activity and (b) ABTS radical scavenging activity of edible grass during fermentation. The bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
The correlations between biochemical compositions and antioxidant activities have been analyzed, and the results are given in Figure 4. A highly significant positive correlation (p < 0.001) was found between DPPH radical scavenging activity and xylitol. Moreover, Pearson correlation coefficients (R2) between DPPH radical scavenging activity and total polyphenols, total flavonoids, SOD, oxalic acid, and pentanedioic acid were greater than 0.9. Other metabolites, including succinic acid, glycolic acid, and D-arabinose, were also significantly (p < 0.05) related to DPPH radical scavenging activity. Total polyphenols, D-arabinose, oxalic acid, glycolic acid, pentanedioic acid, and xylitol had significant (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01) positive correlations with ABTS radical scavenging activity, respectively, whose Pearson correlation coefficients were in the range of 0.85–0.93. It was worth noting that oxalic acid had positive correlation with both DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activities, which was different from the results observed in edible grass fermented with lactic acid bacteria [1]. The differences demonstrated that the changes in antioxidant activity of fermented edible grass were mainly attributed to the complex interplay of metabolites instead of the effect produced by a certain compound.
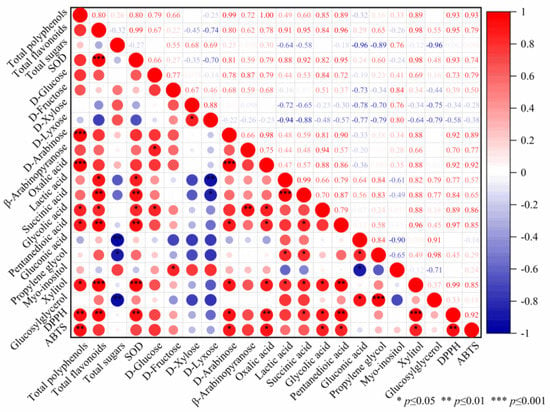
Figure 4.
Pearson correlation coefficients between biochemical compositions and antioxidant activities.
3.3.2. Protective Effect of Fermented Edible Grass on the H2O2-Mediated Oxidative Injured HepG2 Cells
H2O2 is a non-free radical kind of ROS that can easily cross the cell membrane and injure the cell [45]. In order to study the protection of fermented edible grass against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells, the cytotoxicity of fermented edible grass on the fermentation time of 17th day was measured using the MTT method. No significant difference in cell viability was found (p > 0.05) between the fermented edible grass with diluted times of 40, 80, 160, and the control group, while the fermented edible grass with diluted time of 20 was effective in lowering cell viability (Figure S5a). Therefore, fermented edible grasses in the diluted range of 40–160 were selected for further cell experiments. The viability of HepG2 cells incubated with 0.1–0.5 mmol/L of H2O2 for 2 h was then explored. Cell viability decreased with increasing H2O2 concentration, which was close to 50% at the H2O2 concentration of 0.3 mmol/L (Figure S5b). Thus, the oxidative damage model of HepG2 cells was established at the H2O2 concentration of 0.3 mmol/L. According to the above results, HepG2 cells were pretreated with fermented edible grass at diluted times of 40–160 for 24 h and then cultured with H2O2 for 2 h to evaluate cell viability. When HepG2 cells were pretreated with the three fermented edible grasses at different diluted times, the viability was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than in the oxidation damage group (Figure 5). The phenomenon indicated that fermented edible grass played a protective role against H2O2-induced oxidative stress injury in HepG2 cells.
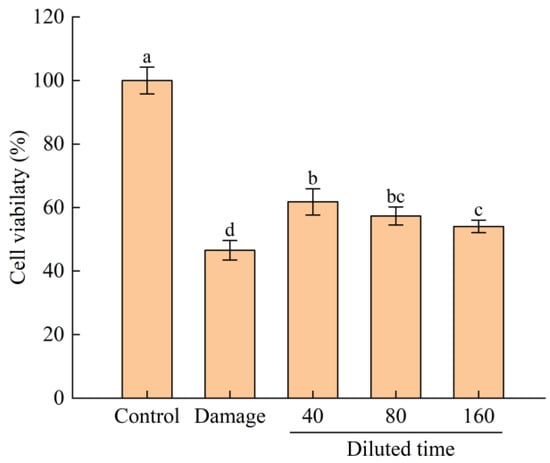
Figure 5.
The viabilities of HepG2 cells treated with fermented edible grass of different diluted times and H2O2. The bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
ROS level and antioxidant enzyme (SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px) activities in cells were generally used to explore the protection mechanism of antioxidants in H2O2-induced oxidative stress injury to HepG2 cells [46,47,48]. As shown in Figure 6a, HepG2 cells treated with H2O2 exhibited higher ROS level compared to the control group. However, the ROS level in HepG2 cells pretreated with fermented edible grass for 24 h was significantly (p < 0.05) decreased compared to that of the oxidation damage group. When treated with 0.3 mmol/L of H2O2 for 2 h, the activities of SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px in HepG2 cells (Figure 6b–d) were all drastically decreased from 109.09, 175.50 and 267.72 to 36.01, 125.07 and 178.40 U/mg protein, respectively (p < 0.05). Compared to the oxidation damage group, fermented edible grass protective groups with diluted times of 40 and 80 presented significantly higher (p < 0.05) activities of SOD, CAT and GSH-Px. The findings proved that the protective ability of fermented edible grass for HepG2 cells from H2O2-induced oxidative stress injury was partially explained by the ability to weaken intracellular oxidative stress reflected by the decreased ROS level and the positive effects on improving the activities of intracellular antioxidant enzymes.
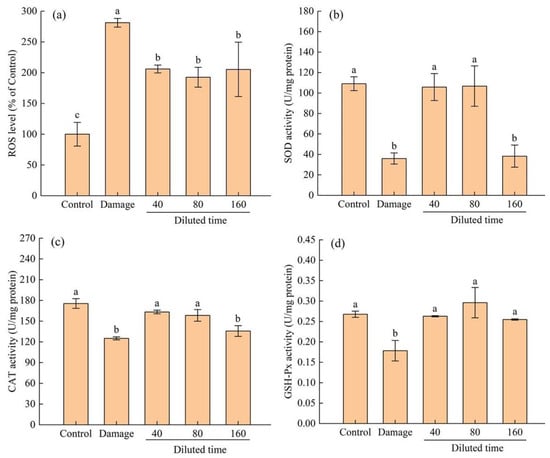
Figure 6.
Fermented edible grasses of different diluted times on (a) ROS level, (b) SOD activity, (c) CAT activity, and (d) GSH-Px activity in HepG2 cells. The bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
4. Conclusions
Changes in the physicochemical properties, metabolites and antioxidant activity of edible grass during spontaneous fermentation were studied in this work. Marked increases in the contents of total polyphenol, total flavonoid and SOD activity of edible grass were found in the initial stage of fermentation, while the total sugar content was reduced with the prolongation of the fermentation time. A total of 16 metabolites, including sugars, organic acids, polyols, and glycosides were identified as differential metabolites during edible grass fermentation. Increased DPPH radical scavenging activity and ABTS radical scavenging activity were found during the first 17 days of fermentation, which was correlated with the comprehensive effects of total polyphenols, total flavonoids, SOD, D-arabinose, oxalic acid, succinic acid, glycolic acid, pentanedioic acid, and xylitol. Furthermore, fermented edible grass showed cytoprotective effect in H2O2-mediated oxidative injured HepG2 cells. The protective effect was attributed to the reduction in ROS level and increase in SOD, CAT, and GPX activities. The results of this study can be applied as technical guidance and theoretical foundation for the high value utilization of edible grass. Further research on screening and identification of microbial community in the spontaneous fermentation of edible grass will help clarify the correlation among metabolites and microbial communities to monitor fermentation and improve the quality of fermented edible grass.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation9040377/s1, Figure S1: Changes in pH during edible grass fermentation; Figure S2: PCA score plot based on the GC-MS data of fermented edible grass samples from different fermentation times; Figure S3: PLS-DA score plot based on the GC-MS data of fermented edible grass samples from different fermentation times; Figure S4: Response permutation testing based on the GC-MS data of fermented edible grass samples from different fermentation times; Figure S5: The viabilities of HepG2 cells treated with (a) fermented edible grass and (b) H2O2 at different concentrations; Table S1: Identification of metabolites by GC-MS during fermentation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and writing—original draft, X.L. (Xianxiu Li); formal analysis, T.H.; data curation, Y.M.; project administration, J.M.; investigation, X.L. (Xiaojin Lai); methodology, H.T.; validation, Y.Z.; funding acquisition and writing—review and editing, R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. LGN22C200034), Science Foundation of Zhejiang University of Science and Technology (No. F701103K12) and Graduate Education and Teaching Reform Foundation of Zhejiang University of Science and Technology (No. F464103M11).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, X.; He, T.; Mao, J.; Sha, R. Effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on physicochemical properties, functional compounds and antioxidant activity of edible grass. Fermentation 2022, 8, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, T.; Yang, F.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Sha, R.; Mao, J. Analysis of nutritional components, functional components and bioactivity of edible grass. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 307–315. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, M.; Qu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y. Safety evaluation of edible grass as a new food raw material. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2021, 12, 3919–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Handa, C.L.; de Lima, F.S.; Guelfi, M.F.G.; da Silva Fernandes, M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Ida, E.I. Parameters of the fermentation of soybean flour by Monascus purpureus or Aspergillus oryzae on the production of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Fermentation and complex enzyme hydrolysis for improving the total soluble phenolic contents, flavonoid aglycones contents and bio-activities of guava leaves tea. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñaki, D.-O.; Juaristi, A.O. Fermented foods: An update on evidence-based health benefits and future perspectives. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, Z.; Eweys, A.S.; Zhou, H.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, X. Metabolomics strategy for revealing the components in fermented barley extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum dy-1. Food Res. Int. 2020, 139, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacrés, E.; Quelal, M.B.; Fernández, E.; Garcìa, G.; Cueva, G.; Rosell, C.M. Impact of debittering and fermentation processes on the antinutritional and antioxidant compounds in Lupinus mutabilis sweet. LWT 2020, 131, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sew, S.W.; Lu, Y.; Taniasuri, F.; Liu, S.Q. Chemical analysis and flavour compound changes of vegetable blend slurry fermented with selected probiotic bacteria. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar-Zumaeta, C.R.; Castro-Alayo, E.M.; Cayo-Colca, I.S.; Idrogo-Vásquez, G.; Muñoz-Astecker, L.D. Metabolomics during the spontaneous fermentation in cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.): An exploraty review. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniewicz, J.; Jakubczyk, K.; Kwiatkowski, P.; Maciejewska-Markiewicz, D.; Kochman, J.; Rebacz-Maron, E.; Janda-Milczarek, K. Analysis of antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial properties of selected polish grape vinegars obtained by spontaneous fermentation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Lv, J.W.; Ma, Y.L.; Guan, X.L. Changes in the physicochemical components, polyphenol profile, and flavor of persimmon wine during spontaneous and inoculated fermentation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, C.; Wijffels, R.H.; Xu, Y. Can we control microbiota in spontaneous food fermentation?–Chinese liquor as a case example. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, A.; Quintana, A.; Sánchez, M.; Rodríguez, E.N.; Cremata, J.; Sánchez, J.C. Rapid and sensitive anthrone–sulfuric acid assay in microplate format to quantify carbohydrate in biopharmaceutical products: Method development and validation. Biologicals 2007, 36, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Hu, Y.; Si, Q.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Ge, Q.; Sha, R. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity of sequentially extracted fractions from pingguoli pear fermentation broth and identification of bioactive compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Song, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chang, Y.; Ma, R.; Cao, X.; Wang, S. Dynamics of physicochemical properties, functional compounds and antioxidant capacity during spontaneous fermentation of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. (Qinghai-Tibet Plateau) natural vinegar. Foods 2022, 11, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaw, E.; Ma, Y.; Tchabo, W.; Apaliya, M.T.; Wu, M.; Sackey, A.S.; Xiao, L.; Tahir, H.E. Effect of lactobacillus strains on phenolic profile, color attributes and antioxidant activities of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.C.; Chen, C. Effects of origins and fermentation time on the antioxidant activities of kombucha. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, H.; Ma, R.; Ma, J.; Fang, H.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; McPhee, D.J. Fermentation by multiple bacterial strains improves the production of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of goji juice. Molecules 2019, 24, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, M.; Kang, W.H. Antioxidant activity, total polyphenol, flavonoid and tannin contents of fermented green coffee beans with selected yeasts. Fermentation 2019, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Njobeh, P.B.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Kayitesi, E. Co-influence of fermentation time and temperature on physicochemical properties, bioactive components and microstructure of ting (a Southern African food) from whole grain sorghum. Food Biosci. 2018, 25, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dun, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Ling, J. Effects on total phenolic and flavonoid content, antioxidant properties, and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of beans by solid-state fermentation with Cordyceps militaris. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopusiewicz, L.; Drozlowska, E.; Trocer, P.; Kwiatkowski, P.; Bartkowiak, A.; Gefrom, A.; Sienkiewicz, M. The effect of fermentation with kefir grains on the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of beverages from blue lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) seeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, G.-Y.; Kim, J.-K.; Gebru, Y.A.; Choi, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-K. Changes of phytochemical components (urushiols, polyphenols, gallotannins) and antioxidant capacity during fomitella fraxinea-mediated fermentation of Toxicodendron vernicifluum Bark. Molecules 2019, 24, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, R.; Luo, X. Effects of five different lactic acid bacteria on bioactive components and volatile compounds of oat. Foods 2022, 11, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiai, H.; Hafidi, A. Chemical composition changes in four green olive cultivars during spontaneous fermentation. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.W.; Li, H.; Zhao, W.P.; Xiong, K.; Wen, H.; Yang, H.L.; Wang, X.L. Dynamic analysis of physicochemical characteristics and microbial communities of Aspergillus-type douchi during fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo Brito, B.d.N.; Campos Chisté, R.; Santos Lopes, A.; Abreu Glória, M.B.; da Silva Pena, R. Influence of spontaneous fermentation of manipueira on bioactive amine and carotenoid profiles during tucupi production. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, J.; Ye, M.; Zhang, J. Effect of six lactic acid bacteria strains on physicochemical characteristics, antioxidant activities and sensory properties of fermented orange juices. Foods 2022, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, X.; Pan, D. Novel millet-based flavored yogurt enriched with superoxide dismutase. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 791886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.H.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Song, X.; Xia, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Ai, L.Z. Enhanced antioxidant activity in Streptococcus thermophilus by high-level expression of superoxide dismutase. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 579804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guan, Q.; Qin, Y.; Qin, Z.; Lin, D. Dynamic changes in physic-chemical properties and bacterial community during natural fermentation of tomatoes. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 63520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, J.; Fan, L.; Qin, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, L. Antioxidant properties of a vegetable-fruit beverage fermented with two Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-E.; Yoo, S.-A.; Seo, S.-H.; Lee, K.-I.; Na, C.-S.; Son, H.-S. GC–MS based metabolomics approach of Kimchi for the understanding of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation characteristics. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, W.; Li, D.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Selection of taste markers related to lactic acid bacteria microflora metabolism for Chinese traditional paocai: A gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2415–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Mu, Y.; Wei, S.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, C. Study on the dynamic changes and formation pathways of metabolites during the fermentation of black waxy rice wine. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2288–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitas, J.S.; Cvetanović, A.D.; Mašković, P.Z.; Švarc-Gajić, J.V.; Malbaša, R.V. Chemical composition and biological activity of novel types of kombucha beverages with yarrow. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 44, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Dai, L.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y. Efficient aerobic fermentation of gluconic acid by high tension oxygen supply strategy with reusable Gluconobacter oxydans HG19 cells. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Chuang, C.J.; Chang, J.S.; Wang, L.F.; Soo, P.C.; Wu, H.S.; Tsai, S.L.; Wei, Y.H. Exploring dual-substrate cultivation strategy of 1,3-propanediol production using Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 191, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Shentu, X.P.; Bian, Y.L.; Yu, X.P. 1,3-propanediol production from glucose by mixed-culture fermentation of Zygosacharomyces rouxii and Klebsiella pneumonia. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Wang, L.; Shi, C.R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.S.; Hu, M.R.; Tao, Y. Efficient production of myo-inositol in Escherichia coli through metabolic engineering. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Utsumi, Y.; Sawayama, S.; Watanabe, Y. Identification and characterization of d-arabinose reductase and d-arabinose transporters from Pichia stipitis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, N.; Chen, X.; Jiang, T.; Xu, H.; Lei, H. Insights into the improvement of bioactive phytochemicals, antioxidant activities and flavor profiles in Chinese wolfberry juice by select lactic acid bacteria. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCue, P.P.; Shetty, K. Phenolic antioxidant mobilization during yogurt production from soymilk using Kefir cultures. Process Biochem. 2004, 40, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-m.; Lu, S.-z.; Li, Y.-s.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tu, Z.-c. Protective effect of antioxidant peptides from grass carp scale gelatin on the H2O2-mediated oxidative injured HepG2 cells. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Lai, F.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Min, T.; Wu, H. Antioxidant mechanism of betaine without free radical scavenging ability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7921–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, Q.; Mao, J.; Sha, R. Hemicellulosic polysaccharides from bamboo leaves promoted by phosphotungstic acids and its attenuation of oxidative stress in HepG2 Cells. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 917432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Wu, L.; Zhong, W.; Zheng, Q.; Tan, W.; Feng, K.; Feng, X.; Meng, F. Cellular antioxidant properties of ischnoderma resinosum polysaccharide. Molecules 2022, 27, 7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).