Abstract
Two strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc01 and Sc02) and one strain of Wickerhamomyces anomalus (Wa) were isolated from organic Verdejo spontaneous fermentations and used for the development of experimental winemaking. Sc01 and Sc02 represented 52.7% of the population of the Saccharomyces strains isolated throughout the fermentation process. W. anomalus appeared as the predominant species among the non-Saccharomyces yeasts. Wa turned out to be the strain of this species with the shortest lag phase and positive enzymatic activities, and it was selected for white wine production. Fermentations with unique inoculation of S. cerevisiae strains were compared with sequential inoculation with W. anomalus. The results showed that the sequential inoculations did not affect the fermentation kinetics or physicochemical characteristics of the wines compared with the unique inoculations. However, this study identified a significant impact on the aromatic profiles of the produced wines due to the sequential inoculations. This modification resulted in a similar new aromatic profile in both sequential inoculations, demonstrating common characteristics related to the contribution of W. anomalus. In general, the sequential fermentations were mainly characterized by lower levels of acetate esters and an increase in ethyl acetate levels, whereas lower levels of ethyl octanoate and ethyl dec-9-enoate were detected. Propan-1-ol and butan-1-ol showed an increase in the sequential fermentations, while 4-methylpentan-1-ol and 2-phenylethanol were found in lower concentrations. These results highlight the great influence that the presence of specific strains of native non-Saccharomyces yeasts exerts on the characteristics of elaborate wines.
1. Introduction
Spontaneous fermentation of grapes must begin with the development of non-Saccharomyces yeasts, which is limited to the first stages of alcoholic fermentation due to the harsh environmental conditions. As these species are disappearing, high-fermentative strains of S. cerevisiae multiply and finally lead to fermentation [1]. Despite surviving for only a few days, several studies of non-Saccharomyces yeasts have shown the ability of these species to influence the organoleptic characteristics of wines in distinct ways and to contribute positively to the winemaking process [2,3,4,5]. Moreover, the persistence of certain strains surviving at high ethanol concentrations influences the quality of the wine across the fermentation process [5,6,7].
W. anomalus, formerly known as Pichia anomala and its synonym Hansenula anomala, was reclassified in the genus Wickerhamomyces due to multigene phylogenetic analysis [8,9]. This ubiquitous species in the winemaking environment forms part of the grape microbiota and is normally present at early stages of fermentation [5]. Traditionally, W. anomalus has been considered to be a spoilage agent due to its ability to grow under harsh environmental conditions in food products and its tolerance to stressful grape and wine conditions such as low pH, ethanol content, or high osmotic pressure [10]. Its ability to produce significant amounts of ethyl acetate and acetic acid in wines has also been described, imparting negative sensory attributes [11,12].
However, W. anomalus is becoming an interesting species in oenological biotechnology, among others, due to its contribution to the production of aromatic compounds and exoenzymes [13,14,15]. Recent studies have focused on mixed cultures with S. cerevisiae and outlined the potential of certain W. anomalus strains to enhance wine quality by producing a unique aroma and flavor profile [15]. Although it is a major producer of ethyl acetate, its ability to produce fruity acetate esters and other positive aromatic compounds has also been reported [5,10,16]. W. anomalus has also been described as a good producer of oenologically relevant enzymes. Several forms of glucosidase activity have been identified in selected strains, such as β-glucosidase, which is involved in the release of aromatic compounds from their precursors in the grape [4]. Proteolytic enzymes of interest to prevent protein haze are also produced by W. anomalus strains [5,17].
The screening of oenologically relevant strains of W. anomalus in terms of their enzymatic activity and aromatic profile is a key step for selecting good candidates to improve wine quality. The individual effect of certain strains has been reported [6,18]; however, it is noteworthy that the modulation of the final organoleptic profile in wines occurs in the presence of mixed cultures, including S. cerevisiae [5,19]. Some detrimental compounds that are present at elevated concentrations in unique non-Saccharomyces cultures do not reach the threshold taste levels in mixed cultures [20]. In this sense, several studies address the improvement in the quality of wines through fermentation with mixed cultures. These wines are characterized by higher concentrations of acetate esters, which are correlated with fruity and floral notes [11,20,21,22,23].
Previous research by our group has focused on the study of the population dynamics of yeasts during spontaneous fermentation of the Verdejo grape variety from organic vineyards from the Appellation of Origin Rueda (AO Rueda, Spain). The results enabled us to select strains of S. cerevisiae and non-Saccharomyces yeasts with potential oenological characteristics of interest to be used in unique or sequential inoculations [24,25].
To advance this research, in the present study, we mixed cultures with sequential inoculation of selected indigenous W. anomalus and S. cerevisiae strains to obtain candidates to modulate and maintain the singularity of the elaborated wines. Trial fermentations were carried out in an experimental winery, monitoring the implantation and development of the strains in the fermentation tanks. The oenological characteristics and aroma profile of the resulting wines were evaluated to examine the impact of the sequential inoculation of isolated indigenous strains on the quality of Verdejo wines. The contribution of W. anomalus in the mixed fermentations resulted in fully differentiated experimental wines associated with a singular and characteristic volatile compound profile compared to S. cerevisiae single-fermentation wines. These results highlighted the importance of native non-Saccharomyces yeasts in fermentation processes and their workability in the winemaking of the Verdejo grape variety.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Yeast Strains and Culture Conditions
Two S. cerevisiae yeast strains (Sc01 and Sc02) and one non-Saccharomyces yeast strain of the species W. anomalus (Wa) were used in this study. The strains were obtained from previous studies of yeast ecology [24,25]. Briefly, yeasts were isolated during spontaneous fermentation processes of organic Verdejo grapes from the vineyards of the Belondrade Winery (La Seca, Valladolid, Spain), located in the AO Rueda. The criteria applied for the selection of the yeast strains for this study were based on their optimal fermentative behavior, their predominant abundance throughout the fermentation stages, and their positive enzymatic characteristics related to the release of aromas (β-lyase and β-glucosidase) and finning operations (β-glucanase and protease) in the winemaking process. The two S. cerevisiae strains represented 52.7% of the population of Saccharomyces strains isolated throughout the entire fermentation process. The analysis of the non-Saccharomyces yeast species revealed that W. anomalus appears to be the predominant species and is present in all stages of the fermentation process. Consequently, a strain with the shortest lag phase and positive enzymatic activities (β-glucosidase, protease, and β-lyase) for white wine production was selected among all W. anomalus isolates. The yeast strains were cultured on YPD medium, containing 1% (w/v) yeast extract (Biolife, Milano, Italy), 2% (w/v) peptone (Panreac, Barcelona, Spain), 2% (w/v) dextrose (Scharlab, Barcelona, Spain) and 2% (w/v) agar (Scharlab). The yeast stock strains were maintained frozen in 20% (v/v) glycerol and YPD broth at −80 °C.
2.2. Kinetic Parameters of S. cerevisiae Strains
Microfermentations were carried out in triplicate in 100 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 50 mL of Verdejo must, sterilized for 20 min at 121 °C. S. cerevisiae strains were cultured in YPD broth overnight, and the flask was inoculated with 106 CFU/mL, sealed with a fermentation cap, and fermented at 20 °C. The loss of weight was monitored to estimate the CO2 production until the end of fermentation. Kinetic curves were fitted to a model in which a linear phase is followed by a stationary phase [26] using the DMFit web edition (Institute of Food Research, Norwich, UK). Potential maximum rate (µmax), lag phase (lag), maximum CO2 production (yEnd), and fermenting power (FP) were determined.
2.3. Trial Fermentations in the Winery
Verdejo grapes were processed in the experimental winery of the Higher Technical School of Agrarian Engineering of Palencia (University of Valladolid). The grapes were destemmed preserving the berries whole. Then, they were lightly crushed and pressed, applying a pressure of 1.6 bar. The physicochemical characteristics of the initial must were as follows: density of 1190 g/L, 24 º°Brix (240.1 g/L of sugar), pH 3.33, and total acidity of 4.1 g/L (expressed as tartaric acid). Finally, the must was sulfited to 20 mg/L of free sulfur dioxide and decanted statically for 24 h at 4 °C.
To ensure enough biomass from the strains used for the inoculation of the must, a 2-step scale-up fermentation process was performed, maintaining the ratio of inoculation at 1:10. In this procedure, sterile Verdejo must was used to increase the fermentation volume 10-fold in each step. The racked must was divided into fermentation bottles, adding 4 L of must for each fermentation trial before the inoculation of 106 CFU/mL of the required strains. The sequential fermentations of W. anomalus/S. cerevisiae Sc01 and W. anomalus/S. cerevisiae Sc02 were initially inoculated with W. anomalus and, 48 h later, with the Sc01 and Sc02 strains, respectively. The unique fermentations were carried out for each S. cerevisiae strain (Sc01 and Sc02), which were inoculated from the beginning. All the fermentations were developed in duplicate.
2.3.1. Population Dynamic
The density and temperature of all the fermentations were monitored throughout the alcoholic fermentation. To avoid cross-contamination between the tanks, the density was established by weighing 10 mL volume samples extracted from the fermentation tanks at regular intervals during the fermentative process. The average fermentation temperature was 16 °C.
The analysis of the yeast strains taking part in the fermentation processes was carried out by plating serial dilutions of the tank samples onto YPD medium using peptone saline as diluent 0.1% (w/v) peptone (Panreac, Barcelona, Spain) and 0.85% (w/v) NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA; pH 7.0 ± 0.2) [27]. Fermentation samples were taken throughout the fermentation processes, specifically at the beginning of fermentation (48 h) and the end of fermentation (EF). The plates were incubated at 25 °C for 72 h, and the resulting colonies were used to confirm the presence of S. cerevisiae Sc01 and Sc02 strains and W. anomalus strain.
2.3.2. Implantation Studies
The implantation studies of W. anomalus populations were carried out before inoculating S. cerevisiae strains (48 h) and at the end of fermentation (EF). On the one hand, the colonies analyzed were subjected to new cultures on lysine agar medium containing 1.2% (w/v) yeast carbon base (Panreac), 0.25% (w/v) L-lysine-HCl (Panreac) and 2% (w/v) agar (BD Bacto™ Agar; Difco, MI, USA), in order to distinguish between Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces species. On the other hand, the colonies were confirmed at species level by sequencing the D1/D2 region of the 28S RNA gene before inoculating S. cerevisiae strains.
For the development of the molecular studies of implantation of the Sc01 and Sc02 strains, six colonies were picked up from the fermentation trials at the beginning of the fermentation stage, and three colonies were collected at the end of fermentation. Each colony was analyzed separately.
The implantation of S. cerevisiae Sc01 and Sc02 populations was determined by the interdelta PCR method, which is based on the pair primer delta12 (5′-TCAACAATGGAATCCCAAC-3′)/delta21 (5′-CATCTTAACACCGTATATGA-3′) [28]. PCR interdelta assays were performed in a 25 µL reaction volume containing 1 × PCR DreamTaq buffer, with MgCl2 (Fisher Scientific, Madrid, Spain), 200 mM of each dNTP (Fisher Scientific), 1 µM for each primer (Fisher Scientific) and 1 U of DreamTaq DNA polymerase (Fisher Scientific). As a template solution, suspensions of single yeast colonies were prepared in 30 µL of 10 mM Tris-HCl solution, pH 8.0 (Sigma-Aldrich). A total of 5 μL of the suspension was added to the PCR reaction mix without previous DNA extraction.
Reactions were run following the program: 4 min at 95 °C, 35 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 46 °C and 90 s at 72 °C, and finally a step of 10 min at 72 °C. The PCR amplification products were analyzed by 2% (w/v) agarose gel electrophoresis (D1 Low EEO agarose, Pronadisa, Madrid, Spain) in 1 × TAE buffer (Fisher Scientific), applying a current of 120 V for 2 h, over a gel distance of 5 cm. The gels were post-electrophoresis stained with a 1 × GelRed solution (Biotium, Fremont, CA, USA). All electrophoresis assays included PCR positive controls for each S. cerevisiae strain and GeneRuler 100 bp DNA ladder (Fisher Scientific) per each well line.
2.3.3. Wine Chemical Composition
The physicochemical characteristics of the trial wines were determined at the end of the alcoholic fermentation. All chemicals and reagents were analytical quality grade. All measurements were carried out in duplicate in each tank. Total acidity (expressed as g tartaric acid/L), volatile acidity (expressed as g acetic acid/L), reducing sugars (expressed as g residual sugar/L), and pH were determined following the methods recommended by the International Organization of Vine and Wine [27]. The alcoholic degree was determined by the ebulliometry method (expressed as % alcohol (v/v)) and free and total sulfur dioxide (expressed as mg SO2/L) using an automatic analyzer (SO2-Matic 23, Crison, Barcelona, Spain).
2.3.4. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
All the chemicals used for VOC analysis were analytical quality grade. Analysis of VOCs in wine samples was determined in duplicate by headspace-solid-phase gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The analysis was performed using a CombiPal RSI 120 autosampler (CTC Analytics AG, Zwingen, Switzerland) connected with a 7890A gas chromatograph (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and a 5977 mass selective detector (Agilent Technologies) [29]. For the extraction of VOCs, 5 mL of wine was placed in a 20 mL vial along with 50 μL of methyl nonanoate (0.059 mg/L) as an internal standard and 3 g of NaCl. After sealing the vial, it was incubated at 40 °C for 15 min with agitation at 250 rpm. A pre-conditioned 50/30 μm DVB/CAR/PDMS fiber (Supelco, Inc., Bellefonte, PA, USA) was exposed to the headspace of the vial at 40 °C for 30 min. Then, the fiber was injected into the chromatograph injector at 250 °C in splitless mode for 1 min. Volatiles were separated using an HP-Innowax column (60 m, 0.250 mm, 0.5 μm) (J&W Scientific, Folsom, CA, USA). The oven temperature program began at 40 °C for 5 min, followed by an increase to 230 °C at a rate of 2.5 °C/min, and then was maintained at 230 °C for 20 min. Helium gas, flowing at a rate of 1.2 mL/min under a pressure of 22.4 psi, was employed as the carrier gas. The mass spectrometer (MS) detector was operated in full scan mode within a mass range of m/z 30–500. Identification of compounds was achieved by comparing their mass spectra with those of pure standards and/or spectral data from the NIST08 v. 2.4 and Wiley7 libraries. Quantification was carried out using the internal standard quantification method as equivalents of 2-octanol [30].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and principal component analysis (PCA) were computed using the programs IBM SPSS Statistics version 26.0 (IBM Corp., Armok, NY, USA) and Statgraphics Centurion version 19 (Statgraphics Technologies, Inc., The Plains, VA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Kinetic Aptitude of Native S. cerevisiae Strains
Ecological studies in spontaneous fermentations of Verdejo organic grapes carried out previously by our research group revealed the presence of two predominant strains of S. cerevisiae, Sc01 and Sc02. The presence of these strains was independent of the vineyard, the vintage, or the fermentation stage analyzed [24]. Considering that a strain with a relative abundance higher than 10% is considered dominant [31], Sc01 and Sc02 were found to be dominant strains during spontaneous fermentation. Their relative abundances were 30% and 19%, respectively, of the total population of yeasts isolated. These results suggest a prevailing role of these strains in the final profile of Verdejo wines, as well as their ability to adapt to the physicochemical characteristics of this variety, making them candidates for use as starter cultures. To ensure a correct fermentative process, the fermentation kinetics of both strains were analyzed in triplicate (Figure 1). A commercial S. cerevisiae strain, previously isolated in AO Rueda (Uvaferm WAM, Lallemand, Blagnac, France), was used as a control to assess adequate fermentation parameters of the strains of interest. Both strains showed a regular kinetic curve and stood up for a high fermenting power (FP). No statistically significant differences were found in the kinetic parameters in comparison with the control strain of S. cerevisiae. This indicates the ability of these strains to carry out and complete the fermentative process.
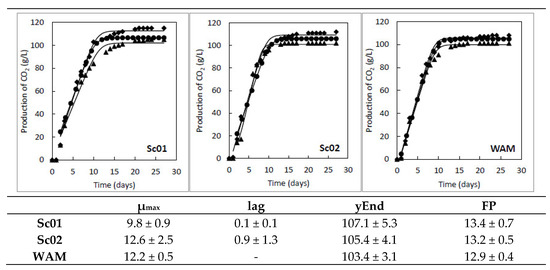
Figure 1.
Microvinifications kinetics. Evaluation of the optimal fermentative kinetic of Sc01 and Sc02 strains in comparison with a commercial strain (WAM) isolated from Verdejo grapes. Kinetics of each strain were performed in triplicate (rhombuses, circles, and triangles). Potential maximum rate, µmax (days−1), lag phase, lag (days), maximum CO2 production, and yEnd (g of total CO2 produced) were estimated with DMFit software version 3.5. Fermenting power, FP (% vol. ethanol), was calculated using yEnd data.
3.2. Trial Fermentations in the Winery
Previous studies by our group have shown the predominance of W. anomalus in the non-Saccharomyces yeast population in organic Verdejo wine [25]. Its presence at all the stages of alcoholic fermentation, as well as in different vineyards and vintages, suggests that this species may exert a relevant role in the final characteristics of the wine. The failure of W. anomalus to achieve dryness in wines has been previously reported [6], requiring an S. cerevisiae strain to complete alcoholic fermentation. Therefore, among the isolated W. anomalus yeasts, trial fermentations were carried out in the winery through sequential inoculation of the strain with the shortest lag phase and with positive enzymatic activities to produce Verdejo white wine (β-glucosidase, protease, and β-lyase) with native strain of S. cerevisiae Sc01 and Sc02.
As shown in Figure 2, the kinetics of fermentation were followed by density along the alcoholic fermentation process. No significant differences were found between unique and sequential inoculations with Sc01 and Sc02, showing the same profile of density decrease throughout the fermentation process. In addition, no significant delay in the onset of fermentation, sluggish or stuck alcoholic fermentation was observed in trials inoculated with W. anomalus compared to unique inoculations of Sc01 and Sc02.
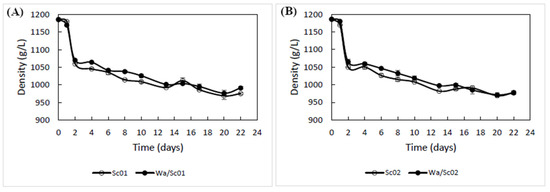
Figure 2.
Fermentation kinetics by density monitorization of winery vinifications in unique (Sc01 and Sc02) and sequential (Wa/Sc01 and Wa/Sc02) inoculation regimes. (A) Sc01 density monitorization in unique and sequential inoculation. (B) Sc02 density monitorization in unique and sequential inoculation.
Regarding the final physicochemical characteristics of the wines produced (Table 1), the unique and sequential inoculations led to dry wines with no significant differences in alcohol content, residual sugars, and pH. According to this, similar results have been recently reported in co-inoculated wines, as these parameters remained unchanged compared to S. cerevisiae unique inoculation [7]. Contrary to our data, W. anomalus has been described by other authors as a Crabtree-negative yeast that may be able to produce wines with a lower final alcoholic degree [32], as well as an increase in the pH of the wines subjected to sequential inoculation [23]. These results suggest that the effect on the final characteristics of the wine is strain-dependent. Although no significant differences were found in total and volatile acidity, both increased in the sequential inoculations. A high variability in volatile acidity in sequential inoculations compared to pure cultures has been previously described [22,23].

Table 1.
Basic chemical analysis of trial wines.
The molecular studies confirmed an adequate implantation of W. anomalus in sequential fermentations. As shown in Table 2, in the first stages of alcoholic fermentation, 100% of the colonies isolated from trial tanks after 48 h of fermentation were positively identified as W. anomalus. Interestingly, the lack of a lag phase and the predominance of this selected strain in the microbiota of the Verdejo must were achieved, confirming the appropriate adaptation and implantation of isolated and selected native strains to be used as starters in a particular variety. As expected, the predominant strains in the sequential fermentations at the end of the fermentation were Sc01 and Sc02, respectively. Similarly, unique fermentations were carried out by Sc01 and Sc02 strains, confirmed by the interdelta method at the beginning and the end of fermentation (Table 2), as well as in the tumultuous fermentation. These results confirmed the ability of these native strains to displace the microbiota coming from the grapes and the winery and to perform a complete and efficient alcoholic fermentation in this variety.

Table 2.
Implantation of the strains in trial fermentations.
3.3. VOCs Analysis
The organoleptic characteristics of wines are linked to the presence of certain volatile chemical compounds whose concentration, interaction, and balance in the wines give rise to a complex profile that determines their quality and uniqueness. The yeasts involved in the fermentation processes, through their metabolic activity and the release of extracellular enzymes, are one of the factors that modulate the profiles of volatile compounds [33]. In total, 32 volatile compounds were identified (Table 3). These compounds belonged to five chemical families: 4 acetate esters, 11 ethyl esters, 6 acids, 9 alcohols, and 2 aldehydes. Considering the sum of the average concentrations of the components of each group, alcohols and esters were the main volatile components, accounting for 52.0–62.4% and 34.6–45.5% of the total concentrations, respectively. However, the acid and aldehyde groups showed reduced concentrations (2.4–3.4% and 0.1–0.2%, respectively). This chemical profile of the volatile compounds was in accordance with the distribution scheme of the major wine components previously reported [33].

Table 3.
VOC analysis (mg/L) of the wines elaborated.
The production of esters during alcoholic fermentation is linked to the fruity aroma of the wine, and their enzymatic synthesis depends on the metabolic activity of the fermentative yeasts [33]. The formation of wine esters involves the condensation of an acid and an alcohol group, and according to their composition, esters are divided into 2 groups: acetate esters formed by acetyl-CoA and ethanol or higher alcohols, and ethyl esters formed by medium-chain fatty acids and ethanol [34].
Overall, acetate ester concentrations were lower in the Wa/Sc01 and Wa/Sc02 sequential fermentations compared to the unique fermentations, although without statistically significant differences except for hexyl acetate (A3). However, the Wa/Sc fermentations had different effects on the ethyl ester levels. Ethyl acetate is one of the most significant esters in wine, providing complexity and fruity character at levels of concentration below 100 mg/L [33,35], but it can induce negative effects on wine aroma (solvent/nail varnish-like aroma) when its concentration reaches levels of 150–200 mg/L [22]. The concentration of ethyl acetate (Et1) was higher in the two sequential fermentations (Wa/Sc01 and Wa/Sc02) than in the unique fermentations (Sc01 and Sc02), although its increase was only relevant (2.8-fold) in the first one. Regardless of the increase in concentration, the ethyl acetate levels accounted for 50% of the total ethyl esters in both mixed fermentations, underlining the quantitative significance of this compound. Interestingly, thresholds with undesirable effects were not reached in any of the fermentation processes. These results highlight the influence of this W. anomalus strain on the ester composition of the final product. Similar results were obtained in the evaluation of autochthonous W. anomalus strains from the Castilla–La Mancha region by developing sequential fermentations with a commercial S. cerevisiae strain from Airén white grape and Mazuela red grape musts [22,23].
In the same way, other ethyl esters showed higher concentrations in the sequential fermentations. On the one hand, ethyl propanoate ester (Et2) and ethyl 2-methylpropanoate (or ethyl isobutyrate, Et3) showed a moderate increase in their concentrations (until 1.1-fold to 1.7-fold) for both sequential fermentations when compared to the unique fermentations. Interestingly, ethyl 2-methylpropanoate (Et3) is associated with lemon, strawberry, and fruity odor descriptors [33]. On the other hand, ethyl heptanoate ester (Et7), which is associated with fruity and cognac odor descriptors [36], showed a marked increase in concentration (3.2-fold) in the Wa/Sc01 fermentation process, but its concentration did not increase in the Wa/Sc02 fermentation. Considering the sum of ethyl esters, the Wa/Sc01 fermentation showed different changes in the individual ester concentrations, which did not affect the final ethyl ester concentration compared to the unique Sc01 fermentation. However, the Wa/Sc02 fermentation revealed a decrease in the sum of ethyl esters compared to the Sc02 fermentation due to the decrease in the concentrations of some ethyl ester compounds such as ethyl hexanoate (Et6), ethyl octanoate (Et8), ethyl decanoate (Et09) and ethyl dec-9-enoate (Et10). Taken together, these results confirm that the evaluation of yeast as a starter must be assessed at the strain level, taking into account the specific differences in the metabolic activity of yeast strains and their impact on the chemical profile of the wine [4,6,18,20,37,38,39,40,41]. In the same way, the relationships established between the different species and strains used as inoculum in a multistarter fermentation should also be analyzed from a microbial community approach, expressed as antagonistic or synergistic interactions between yeasts throughout the fermentation processes [42].
Acid compounds showed no significant differences between sequential and control fermentations. Total acid concentrations below 20 mg/mL are associated with pleasant aromas and with complexity in the wine because the esterification of fatty acids in the presence of alcohols results in the formation of ethyl esters [35]. Only 3-methylbutanoic acid (or isovaleric acid, Ac2) showed a relevant increase in both sequential Wa/Sc01 and Wa/Sc02 fermentations (4.9-fold and 6.8-fold, respectively), although no significant differences were found. This acid is associated with candy odor descriptors [43]. The sum of the acid showed a reduced increase in the total concentrations in the Wa/Sc01 sequential fermentation and a slight decrease in the Wa/Sc02 fermentation compared to the controls. In no case did the sum of the acid concentrations exceed the limit value of 20 mg/L, which is linked with unpleasant aromas in wine and is related to odor descriptors such as rancidity, cheese, butter, and animal [43].
Higher alcohols or fusel alcohols, together with esters, are one of the main volatile compounds in wine. Their composition and concentration depend on the yeast metabolism and determine different effects on the wine’s flavor profile. Alcohol concentrations below 300 mg/L have a positive effect on the wine, providing fruity aromas either as precursors of esters or directly due to the presence of some aromatic alcohols, such as 2-phenylethyl ethanol [36]. However, the negative impact of the alcohol in the wine is expressed when their total concentration reaches values higher than 400 mg/L [34,35]. 3-methylbutan-1-ol (Alc4) and 2-phenylethanol (Alc8) were quantitatively the most important alcohol compounds, accounting for 80.1–85.2% and 8.0–14.3% of the higher alcohols determined in both sequential and unique fermentations, respectively. Four alcohol compounds showed significant differences in the ANOVA analysis comparing sequential and unique fermentations but with different behaviors (Table 3). Propan-1-ol and butan-1-ol showed an increase in their concentrations in the Wa/Sc01 and Wa/Sc02 sequential fermentations, while 4-methylpentan-1-ol (Alc6) and 2-phenylethanol (Alc8) showed lower concentrations in the sequential fermentations. Considering the sum of all alcoholic compounds, a slight decrease in the concentration of higher alcohols was observed in both sequential fermentations compared to the control fermentations. A new ratio of higher alcohols was established in the sequential fermentations depending on the yeast strains used, as described by Swiegers et al., (2005). Therefore, the balance between the positive and negative effects of the higher alcohols associated with the balance of their concentrations was ensured by the development of the sequential fermentations Wa/Sc. Similar results were reported by Izquierdo-Cañas et al., (2011) in the development of sequential Wa/Sc fermentations from white grape must. However, an increase in the higher alcohol concentrations was described by the same authors in a similar sequence of fermentation experiments from red grape must [22].
Aldehydes can be associated with bruised apple, nutty, and almond aromas but can also contribute to woody aromas and oxidation notes, especially in white wines. These oxidation notes are mainly related to the acetaldehyde concentration in the wine, which can reach values close to its sensory threshold value of 100 mg/L [35]. The concentrations of aldehydes obtained were very low for each type of fermentation considered in our experiments. Both benzaldehyde (Ald1) and acetaldehyde (Ald2) showed a slight increase in their concentrations in the two sequential fermentations, but they did not exceed the value of 0.501 mg/L. Izquierdo-Cañas et al., (2011) reported the same trend of increasing in the acetaldehyde concentrations but with final values 100-fold higher than those obtained in our study. Probably, an important source of variability is the difference in the fermentation conditions, but another factor to consider is the variability in acetaldehyde production related to the different W. anomalus strains tested [35].
The effects of the yeast combinations used on the volatile composition of the wines were analyzed using principal component analysis (PCA). All the 32 volatile compounds were included in the analysis (Figure 3). The first two principal components (PC) accounted for 90.6% of the total variance of the volatile compounds, describing the relationship between these compounds and the two yeast sequences compared to the unique fermentations. PC1 accounted for 67.6% of the variance and separated both sequential (Wa/Sc01, Wa/Sc02) and unique fermentations (Sc01, Sc02). PC2 explained 23.0% of the variance and determined a different distribution between the two sequential and the two unique fermentations. The sequential fermentations were grouped at negative values of the PC1 and between the 0.5 and −0.5 coordinates of the PC2, while the unique fermentations Sc01 and Sc02 were separated across the PC2 at the extreme and opposite coordinates. The distribution of the fermentations along the PC1 was mainly related to the concentrations of the volatile compounds, which showed significant differences by ANOVA analysis (Table 3). The increase in the concentrations of propan-1-ol (Alc1) and butan-1-ol (Alc3) was associated with the Wa/Sc01 and Wa/Sc02 sequential fermentations, and the higher values of hexyl acetate (A3), ethyl octanoate (Et8), ethyl dec-9-enoate (Et10), 4-methylpentan-1-ol (Alc6) and 2-phenylethanol (Alc8) were associated with the Sc02 control fermentation. The low (1.01 to 1.74-fold) or moderate (2.78 to 6.76-fold) increase in the concentration of other compounds such as ethyl acetate (Et1), ethyl propanoate (Et2), ethyl 2-methylpropanoate (Et3), ethyl heptanoate (Et7), 2-methylpropanoic acid (Ac1), 3-methylbutanoic acid (Ac2), hexan-1-ol (C6-1), 2-methylpropan-1-ol (Alc2), 3-methylbutan-1-ol (Alc4), benzaldehyde (Ald1) and acetaldehyde (Ald2) contributed to the clustering of the sequential Wa/Sc fermentations.
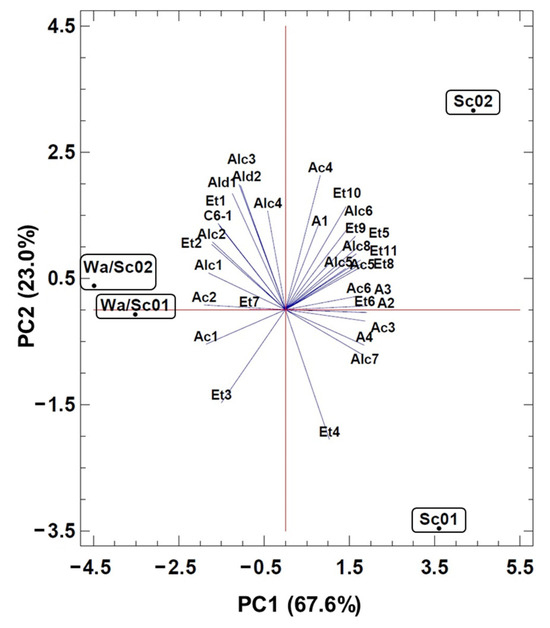
Figure 3.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of the volatile composition of Verdejo wines to evaluate the effect of the unique (Sc01, Sc02) and sequential (Wa/Sc01, Wa/Sc02) yeast starters. Symbols of VOCS (see Table 3).
The volatile compound profile of the sequential fermentations Wa/Sc01 and Wa/Sc02 showed common characteristics related to the contribution of W. anomalus to the alcoholic fermentation of Verdejo musts. These characteristics defined a differentiated product, as opposed to the Verdejo fermentation products obtained from fermentations using only S. cerevisiae strains (Sc01, Sc02). It is important to note that, despite the differences observed in the volatile compound profile of the two unique fermentations, the presence of the W. anomalus strain modulated these profiles and unified them into a new profile as a result of the specific metabolic activity of the W. anomalus strain. In this regard, the contribution of two W. anomalus strains to the characteristic volatile compound profiles in the development of sequential fermentation experiments of Viognier musts has been previously reported [18].
4. Conclusions
One of the major trends in the wine industry is based on using biotechnological tools to overcome the challenges that affect this sector. The use of mixed cultures with non-Saccharomyces yeasts in wineries offers winemakers many possibilities. On the one hand, the knowledge of the influence of the native microbiota to obtain more complex and distinctive wines may lead to the implementation of viticultural practices to maintain this biodiversity. On the other hand, the use of selected native non-Saccharomyces yeasts as starter cultures may be a useful tool for winemakers to manage the fermentation processes and obtain the desired specific aromatic profile in wines. Our contribution underlines the potential of microbial resources for the identification of adequate strains for a given variety to produce distinctive wines. Our results confirm the appropriate adaptation and implantation of selected native strains in Verdejo wine. The ability of the W. anomalus strain to overcome the influence of the S. cerevisiae strains, driving the aromatic profile of the final wines to obtain a similar profile in both fermentations, is noteworthy. In general, the sequential fermentations were mainly characterized by lower levels of acetate esters, the increase of ethyl acetate levels, propan-1-ol, and butan-1-ol, whereas lower levels of ethyl octanoate, ethyl dec-9-enoate, 4-methylpentan-1-ol, and 2-phenylethanol were detected. Looking to the future, sensory analysis is a key step in validating the use of these strains under real winemaking conditions. Moreover, the growing demand for unique wines could be met by new isolations of strains from spontaneous fermentations to be used as mixed starter cultures to produce a specific type of wine with the desired aromatic profile.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, and formal analysis L.L.-E., J.V.-C., J.M.R.-N., E.F.-F. and V.R.; software, L.L.-E.; investigation and data curation, L.L.-E., J.V.-C., J.M.R.-N., E.F.-F. and V.R.; writing—original draft preparation, L.L.-E., J.V.-C., J.M.R.-N., E.F.-F. and V.R.; writing—review and editing, L.L.-E., J.V.-C., J.M.R.-N., E.F.-F. and V.R.; supervision and project administration, J.V.-C., J.M.R.-N., E.F.-F. and V.R.; funding acquisition, J.V.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We thank Belondrade S. L. for providing funding, grapes, and samples for yeast isolation through the development of a collaboration agreement (061/100671) with the University of Valladolid.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Marta Baquerizo Mesonero-Romanos, winemaker at Belondrade Winery, for all her enthusiastic work and her expertise and assistance. We also thank Irene Fernández Estévez for contributing to the analytical work of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fleet, G.H. Yeast Interactions and Wine Flavour. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 86, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, N.P.; Varela, C.; Pretorius, I.S. Not Your Ordinary Yeast: Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts in Wine Production Uncovered. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comitini, F.; Capece, A.; Ciani, M.; Romano, P. New Insights on the Use of Wine Yeasts. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, B.; Gil, J.V.; Manzanares, P. Past and Future of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts: From Spoilage Microorganisms to Biotechnological Tools for Improving Wine Aroma Complexity. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, B.; Gil, J.V.; Manzanares, P. Challenges of the Non-Conventional Yeast Wickerhamomyces anomalus in Winemaking. Fermentation 2018, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, B.; Zambelli, P.; Vigentini, I.; Bauer, F.F.; Setati, M.E. Investigating the Effect of Selected Non-Saccharomyces Species on Wine Ecosystem Function and Major Volatiles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-B.; Park, H.-D. Isolation and Investigation of Potential Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts to Improve the Volatile Terpene Compounds in Korean Muscat Bailey A Wine. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzman, C.P. Phylogeny of the Ascomycetous Yeasts and the Renaming of Pichia anomala to Wickerhamomyces anomalus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2011, 99, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzman, C.P.; Robnett, C.J.; Basehoar-Powers, E. Phylogenetic Relationships among Species of Pichia, Issatchenkia and Williopsis Determined from Multigene Sequence Analysis, and the Proposal of Barnettozyma Gen. Nov., Lindnera Gen. Nov. and Wickerhamomyces Gen. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passoth, V.; Fredlund, E.; Druvefors, U.A.; Schnürer, J. Biotechnology, Physiology and Genetics of the Yeast Pichia anomala. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006, 6, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, O. Increase of Acetate Ester-Hydrolysing Esterase Activity in Mixed Cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia anomala. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, V.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M. Spoilage Yeasts in the Wine Industry. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 86, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabel, A.; Martens, S.; Petri, A.; Konig, H.; Claus, H. Wickerhamomyces anomalus AS1: A New Strain with Potential to Improve Wine Aroma. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwentke, J.; Sabel, A.; Petri, A.; König, H.; Claus, H. The Yeast Wickerhamomyces anomalus AS1 Secretes a Multifunctional Exo-β-1, 3-Glucanase with Implications for Winemaking. Yeast 2014, 31, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yan, J.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Dong, Z.G.; Luo, H.; Liu, M.; Su, J. Comparison of Potential Wickerhamomyces anomalus to Improve the Quality of Cabernet Sauvignon Wines by Mixed Fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 173, 114285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, F.; Gil, J.V.; Genovés, S.; Vallés, S.; Manzanares, P. Rational Selection of Non-Saccharomyces Wine Yeasts for Mixed Starters Based on Ester Formation and Enological Traits. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlander, M.; Distler, U.; Tenzer, S.; Thines, E.; Claus, H. Purification and Properties of Yeast Proteases Secreted by Wickerhamomyces anomalus 227 and Metschnikovia pulcherrima 446 during Growth in a White Grape Juice. Fermentation 2017, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Boss, P.; Walker, M.; Sumby, K.; Grbin, P.; Jiranek, V. Evaluation of Indigenous Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts Isolated from a South Australian Vineyard for Their Potential as Wine Starter Cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 312, 108373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzi, L.; Capozzi, V.; Berbegal, C.; Corbo, M.R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Spano, G.; Sinigaglia, M. Microbial Resources and Enological Significance: Opportunities and Benefits. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domizio, P.; Romani, C.; Lencioni, L.; Comitini, F.; Gobbi, M.; Mannazzu, I.; Ciani, M. Outlining a Future for Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts: Selection of Putative Spoilage Wine Strains to Be Used in Association with Saccharomyces cerevisiae for Grape Juice Fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 147, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, V.; Gil, J.V.; Piñaga, F.; Manzanares, P. Acetate Ester Formation in Wine by Mixed Cultures in Laboratory Fermentations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 86, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Cañas, P.M.; García-Romero, E.; Heras Manso, J.M.; Fernández-González, M. Influence of Sequential Inoculation of Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Quality of Red Wines. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Cañas, P.M.; Palacios García, A.T.; García Romero, E.G. Enhancement of Flavour Properties in Wines Using Sequential Inoculations of Non-Saccharomyces (Hansenula and Torulaspora) and Saccharomyces Yeast Starter. VITIS J. Grapevine Res. 2011, 50, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- López-Enríquez, L.; Vila-Crespo, J.; Rodríguez-Nogales, J.M.; Fernández-Fernández, E.; Ruipérez, V. Screening and Enzymatic Evaluation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Populations from Spontaneous Fermentation of Organic Verdejo Wines. Foods 2022, 11, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Enríquez, L.; Vila-Crespo, J.; Rodríguez-Nogales, J.M.; Fernández-Fernández, E.; Ruipérez, V. Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts from Organic Vineyards as Spontaneous Fermentation Agents. Foods 2023, 12, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranyi, J.; Roberts, T.A. A Dynamic Approach to Predicting Bacterial Growth in Food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1994, 23, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIV. Compendium of International Methods of Wine and Must Analysis; International Organisation of Vine and Wine: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 978-2-85038-016-7. [Google Scholar]
- Legras, J.-L.; Karst, F. Optimisation of Interdelta Analysis for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strain Characterisation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 221, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Huerta, C.; Fernández-Fernández, E.; Vila-Crespo, J.; Ruipérez, V.; Moyano, R.; Rodríguez-Nogales, J.M. Impact of Ageing on Ultrasound-Treated Lees on Volatile Composition and Sensory Properties of Red Sparkling Base Wine. Beverages 2023, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayestaran, B.; Martinez-Lapuente, L.; Guadalupe, Z.; Canals, C.; Adell, E.; Vilanova, M. Effect of the Winemaking Process on the Volatile Composition and Aromatic Profile of Tempranillo Blanco Wines. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillo, D.; Neira, N.; Blanco, P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strain Diversity Associated with Spontaneous Fermentations in Organic Wineries from Galicia (NW Spain). Fermentation 2020, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Quirós, M.; Morales, P. Yeast Respiration of Sugars by Non-Saccharomyces Yeast Species: A Promising and Barely Explored Approach to Lowering Alcohol Content of Wines. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumby, K.M.; Grbin, P.R.; Jiranek, V. Microbial Modulation of Aromatic Esters in Wine: Current Knowledge and Future Prospects. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzialo, M.C.; Park, R.; Steensels, J.; Lievens, B.; Verstrepen, K.J. Physiology, Ecology and Industrial Applications of Aroma Formation in Yeast. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, S95–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiegers, J.H.; Pretorius, I.S. Yeast Modulation of Wine Flavor. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Laskin, A.I., Bennett, J.W., Gadd, G.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 57, pp. 131–175. ISBN 0065-2164. [Google Scholar]
- Englezos, V.; Rantsiou, K.; Cravero, F.; Torchio, F.; Pollon, M.; Fracassetti, D.; Ortiz-Julien, A.; Gerbi, V.; Rolle, L.; Cocolin, L. Volatile Profile of White Wines Fermented with Sequential Inoculation of Starmerella bacillaris and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, A.; Calderón, F.; Benito, S. The Influence of Non-Saccharomyces Species on Wine Fermentation Quality Parameters. Fermentation 2019, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binati, R.L.; Lemos Junior, W.J.F.; Luzzini, G.; Slaghenaufi, D.; Ugliano, M.; Torriani, S. Contribution of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts to Wine Volatile and Sensory Diversity: A Study on Lachancea thermotolerans, Metschnikowia spp. and Starmerella bacillaris Strains Isolated in Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 318, 108470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borren, E.; Tian, B. The Important Contribution of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts to the Aroma Complexity of Wine: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, R.; González-Arenzana, L.; Portu, J.; Garijo, P.; López-Alfaro, I.; López, R.; Santamaría, P.; Gutiérrez, A.R. Wine Aromatic Compound Production and Fermentative Behaviour within Different Non-Saccharomyces Species and Clones. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, M.; Comitini, F.; Mannazzu, I.; Domizio, P. Controlled Mixed Culture Fermentation: A Newperspective on the Use of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts in Winemaking. FEMS Yeast Res. 2010, 10, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, M.; Capece, A.; Comitini, F.; Canonico, L.; Siesto, G.; Romano, P. Yeast Interactions in Inoculated Wine Fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcari, S.G.; Caliari, V.; Sganzerla, M.; Godoy, H.T. Volatile Composition of Merlot Red Wine and Its Contribution to the Aroma: Optimization and Validation of Analytical Method. Talanta 2017, 174, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).