Changes in the Quality and Nontargeted Metabolites of Salt-Fermented Shrimp (Saeu-jeot) Based on Fermentation Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Physicochemical Analysis
2.2.1. pH and Acidity
2.2.2. Total Nitrogen (TN), Amino-Nitrogen (AN), and Volatile Basic Nitrogen (VBN) Concentrations
2.2.3. Biogenic Amine (BA) Concentration
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.4. Nontargeted Metabolite Profiling
2.4.1. Preparation of Metabolite Extracts
2.4.2. LC-QTOF-MS Analysis
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Quality Indicators during Saeu-jeot Fermentation
3.2. Changes in Safety Factors during Saeu-jeot Fermentation
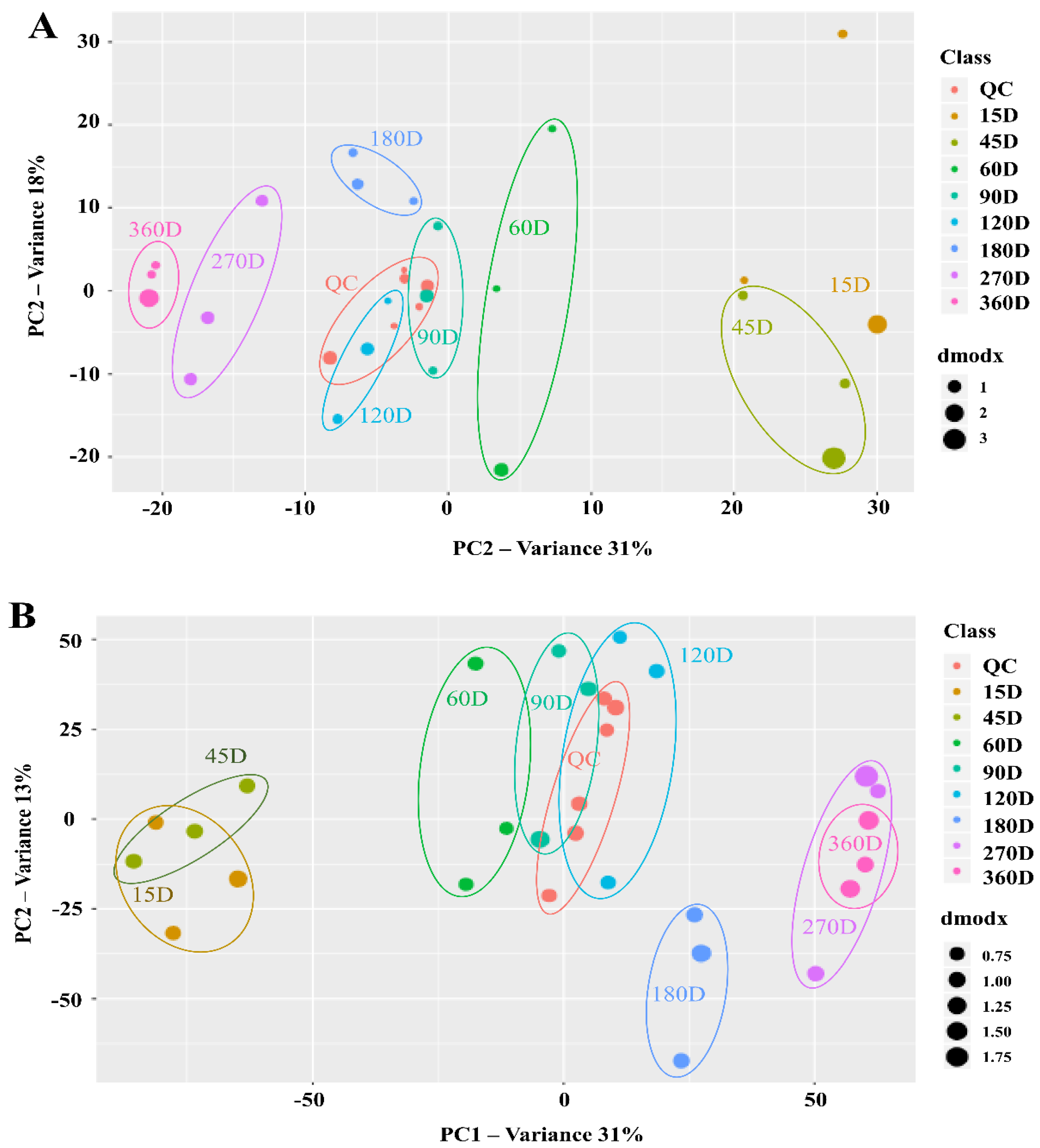
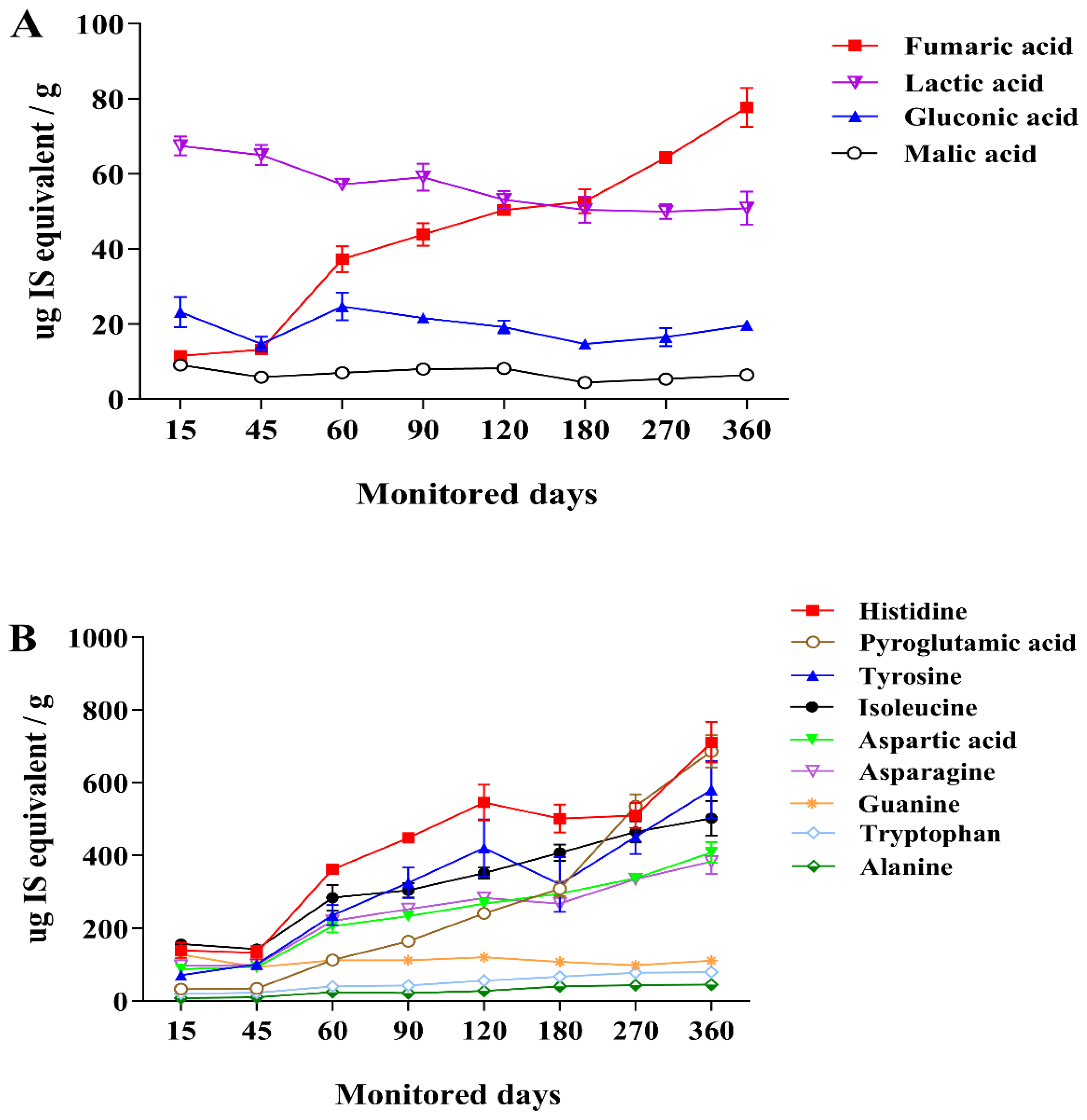
3.3. Changes in Metabolite Profiles during Saeu-jeot Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koo, O.K.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, K.R.; Jang, D.J.; Yang, H.J.; Kwon, D.Y. Korean traditional fermented fish products: Jeotgal. J. Ethn. Foods 2016, 3, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, J.H. Analysis of the cultivable bacterial community in jeotgal, a Korean salted and fermented seafood, and identification of its dominant bacteria. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, C.H. Importance of lactic acid bacteria in Asian fermented foods. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajeb, P.; Jinap, S. Fermented shrimp products as source of Umami in Southeast Asia. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, S10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jeon, C.O. Microbial succession and metabolite changes during fermentation of saeu-jeot: Traditional Korean salted seafood. Food Microbiol. 2013, 34, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-M.; Jung, Y.-J.; Jeong, E.-J.; Kim, S.-J. A nationwide survey on the preference characteristics of minor ingredients for winter Kimchi. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 32, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Jeon, C.O. Effects of temperature on microbial succession and metabolite change during saeu-jeot fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Mi, S.; Liu, X.; Sang, Y.; Sun, J. Variations in the physicochemical properties and bacterial community composition during fermentation of low-salt shrimp paste. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.J.; Lee, E.S.; Park, S.L.; Choi, H.J.; Roh, S.W.; Nam, Y.D. Bacterial community analysis in three types of the fermented seafood, jeotgal, produced in South Korea. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Hwang, S.; Cha, J. Transcriptome analysis of halotolerant Staphylococcus saprophyticus isolated from Korean fermented shrimp. Foods 2022, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, N.; Lee, S.H.; Jin, H.M.; Jung, J.Y.; Schumann, P.; Jeon, C.O. Garicola koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from saeu-jeot, traditional Korean fermented shrimp. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Jeon, C.O. Halomonas garicola sp. nov., isolated from saeu-jeot, a Korean salted and fermented shrimp sauce. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmi, H.; Astuti, D.I.; Putri, S.P.; Sato, A.; Laviña, W.A.; Fukusaki, E.; Aditiawati, P. Dynamic changes in the bacterial community and metabolic profile during fermentation of low-salt shrimp paste (Terasi). Metabolites 2022, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiller, K.; Metallo, C.M.; Kelleher, J.K.; Stephanopoulos, G. Nontargeted elucidation of metabolic pathways using stable-isotope tracers and mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6621–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumeh, E.A.; Hedemann, M.S.; Poulsen, H.D.; Corrent, E.; van Milgen, J.; Nørgaard, J.V. Nontargeted LC-MS metabolomics approach for metabolic profiling of plasma and urine from pigs fed branched chain amino acids for maximum growth performance. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 4195–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobus, J.R.; Wambaugh, J.F.; Isaacs, K.K.; Williams, A.J.; McEachran, A.D.; Richard, A.M.; Grulke, C.M.; Ulrich, E.M.; Rager, J.E.; Strynar, M.J.; et al. Integrating tools for non-targeted analysis research and chemical safety evaluations at the US EPA. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.M.; Chun, B.H.; Kim, H.M.; Jeon, C.O. Characterization and correlation of microbial communities and metabolite and volatile compounds in doenjang fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D.E.; Singh, D.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomics reveal optimal grain preprocessing (milling) toward rice Koji fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2694–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-E.; Yoo, S.-A.; Seo, S.-H.; Lee, K.-I.; Na, C.-S.; Son, H.-S. GC–MS based metabolomics approach of Kimchi for the understanding of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation characteristics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kwak, H.S.; Kim, S.S. Effects of salinity on bacterial communities, Maillard reactions, isoflavone composition, antioxidation and antiproliferation in Korean fermented soybean paste (doenjang). Food Chem. 2018, 245, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogg, C.L. Determination of nitrogen by the micro-Kjeldahl method. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 43, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Slyke, D.D.; Kirk, E. Comparison of gasometric, colorimetric, and titrimetric determinations of amino nitrogen in blood and urine. J. Biol. Chem. 1933, 102, 651–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, A.; Hwang, H.J.; Mah, J.H. Validation of an HPLC analytical method for determination of biogenic amines in agricultural products and monitoring of biogenic amines in Korean fermented agricultural products. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Patti, G.J.; Rinehart, D.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS Online: A web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.W.; Yang, J.H.; Hong, S.W.; Park, S.H.; Lee, M.A. Changes in quality properties of kimchi based on the nitrogen content of fermented anchovy sauce, Myeolchi Aekjeot, during fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.K.; Song, K.T. High hydrostatic pressure sterilization of putrefactive bacteria in salted and fermented shrimp with different salt content. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 598–603. [Google Scholar]
- Bekhit, A.E.A.; Duncan, A.; Bah, C.S.F.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Al-Juhaimi, F.Y.; Amin, H.F. Impact of fermentation conditions on the physicochemical properties, fatty acid and cholesterol contents in salted-fermented hoki roe. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behling, A.R.; Taylor, S.L. Bacterial histamine production as a function of temperature and time of incubation. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erna, K.H.; Rovina, K.; Mantihal, S. Current detection techniques for monitoring the freshness of meat-based products: A review. J. Packag. Technol. Res. 2021, 5, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.-H.; Moon, E.S.; Ha, S.D. Assessment of microbial contamination and safety of commercial shrimp jeotgal (salt fermented shrimp). J. Food Hyg. Saf. 2007, 22, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.A.; An, S.E.; Jeong, H.G.; Lee, S.H.; Mun, K.H.; Kim, J.B. Evaluation of microbiological safety in commercial Jeotgal. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2018, 25, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Lambropoulou, D.; Morrison, C.; Kłodzińska, E.; Namieśnik, J.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Literature update of analytical methods for biogenic amines determination in food and beverages. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.H.; Brown, W.D. Histamine (?) Toxicity from Fish Products. Adv. Food Res. 1978, 24, 113–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Kimura, B.; Yoshikawa, M.; Fujii, T. Cloning and sequencing of the histidine decarboxylase genes of gram-negative, histamine-producing bacteria and their application in detection and identification of these organisms in fish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2568–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Chun, B.H.; Jeong, S.E.; Jeon, C.O. Tetragenococcus halophilus MJ4 as a starter culture for repressing biogenic amine (cadaverine) formation during Saeu-jeot (salted shrimp) fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, T.; Kimizuka, A.; Ruddle, K.; Ishige, N. Chemical components of fermented fish products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1992, 5, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Schieber, A.; Gänzle, M.G. Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations—A review. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fermentation Period (Days) | pH | Acidity (%) | Total Nitrogen (%) | Amino-Nitrogen (mg/100 g) | Volatile Basic Nitrogen (mg/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 7.61 ± 0.03 a,* | 0.21 ± 0.02 a | 1.18 ± 0.01 a | 381.84 ± 0.00 a | 9.73 ± 0.35 a |
| 30 | 7.28 ± 0.00 b | 0.38 ± 0.01 b | 1.06 ± 0.04 b | 449.83 ± 0.00 a | 13.37 ± 0.03 b |
| 45 | 7.14 ± 0.03 bc | 0.50 ± 0.05 c | 1.21 ± 0.01 b | 559.14 ± 3.47 b | 24.54 ± 0.05 c |
| 60 | 6.98 ± 0.07 cd | 0.58 ± 0.03 cd | 1.32 ± 0.00 c | 578.77 ± 0.00 b | 25.79 ± 0.08 d |
| 90 | 6.94 ± 0.04 d | 0.61 ± 0.03 d | 1.36 ± 0.01 c | 638.56 ± 3.45 bc | 26.83 ± 0.09 e |
| 120 | 6.80 ± 0.06 d | 0.66 ± 0.03 d | 1.42 ± 0.01 d | 661.58 ± 3.46 cd | 27.05 ± 0.01 e |
| 180 | 6.83 ± 0.01 d | 0.65 ± 0.00 d | 1.45 ± 0.00 d | 684.63 ± 2.12 de | 28.62 ± 0.13 f |
| 270 | 6.89 ± 0.10 d | 0.64 ± 0.01 d | 1.56 ± 0.00 e | 755.46 ± 8.87 ef | 40.78 ± 0.28 g |
| 360 | 6.86 ± 0.05 d | 0.66 ± 0.01 d | 1.59 ± 0.01 e | 777.87 ± 8.34 f | 39.38 ± 0.24 h |
| Change during fermentation ** | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, K.; Jang, M.; Lee, H.; Sung, J.; Kim, J.-C. Changes in the Quality and Nontargeted Metabolites of Salt-Fermented Shrimp (Saeu-jeot) Based on Fermentation Time. Fermentation 2023, 9, 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100889
Park S, Kim K, Jang M, Lee H, Sung J, Kim J-C. Changes in the Quality and Nontargeted Metabolites of Salt-Fermented Shrimp (Saeu-jeot) Based on Fermentation Time. Fermentation. 2023; 9(10):889. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100889
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sunhyun, Keono Kim, Mi Jang, Heeyoung Lee, Jeehye Sung, and Jong-Chan Kim. 2023. "Changes in the Quality and Nontargeted Metabolites of Salt-Fermented Shrimp (Saeu-jeot) Based on Fermentation Time" Fermentation 9, no. 10: 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100889
APA StylePark, S., Kim, K., Jang, M., Lee, H., Sung, J., & Kim, J.-C. (2023). Changes in the Quality and Nontargeted Metabolites of Salt-Fermented Shrimp (Saeu-jeot) Based on Fermentation Time. Fermentation, 9(10), 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100889





