Abstract
Obesity is a prevalent chronic disease worldwide. In this study, we screened lactic acid bacteria (LAB) suitable for fermenting Shenheling extract (SHLE) to enhance its anti-obesity efficacy and improve flavor. Using SHLE as the medium, a single strain was inoculated and the lactic acid bacteria suitable for growth in SHLE were preliminarily screened through a growth curve. The growth of the initially screened LAB was characterized in detail by the pH value, titration acidity and viable bacteria count. At the same time, appropriate LAB were selected with the lipase activity inhibition rate, α-glucosidase activity inhibition rate and a sensory evaluation as the response indicators. As a result, 6 of the 12 strains of lactic acid bacteria grew well in SHLE. The fermentation of five representative LAB could significantly improve the inhibition rate of the lipase activity of SHLE and maintain the inhibition rate of the α-glucosidase activity at a high level. In addition, fermentation removed the original flavors of SHLE such as grass, bitterness and cassia and added a sour taste, fruity aroma and cool taste. Among them, Lactobacillus fermentum grx08 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus hsryfm1301 gave SHLE a soft sour taste after fermentation. L. fermentum grx08, L. rhamnosus grx10 and hsryfm1301 imparted a moderately fruity aroma to SHLE after fermentation. In summary, L. fermentum grx08 and L. rhamnosus hsryfm1301 were the candidate strains for fermenting SHLE to produce good-flavored slimming functional drinks.
1. Introduction
Obesity is a public health problem that is prevalent worldwide. It is a risk factor for chronic non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, non-alcoholic fatty liver and hypertension [1]. It is also disadvantageous to infectious diseases such as COVID-19 [2,3]. The main problem of obesity is the long-term positive energy balance; that is, the absorption of energy is longer than the consumption of energy. Therefore, inhibiting the digestion and absorption of energy substances is an important strategy for the treatment of obesity. Often, attempts are made to reduce fat and carbohydrate absorption [4]. Orlistat is a commonly used lipase inhibitor for weight loss, but it can cause side effects such as diarrhea, oily stools and the malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins [5]. Therefore, it is a new trend to find lipase inhibitors without side effects from natural raw materials such as herbal medicines and edible plants [6].
In the treatment strategy of complex diseases such as obesity, an increasing number of research results and a consensus show that compounds with multiple targets are better than drugs with single targets [7,8,9]. Natural herbal or botanical formulas have shown clinically better weight-loss effects. In countries such as China [10,11], Japan [12,13], South Korea [14] and Australia [15,16], clinical trials of herbal or plant compounds for weight loss have been carried out with the population as the research object. All showed that the compound was both safe and effective. However, herbal or botanical compounds often have unpleasant odors and tastes, which limit their promotion and application in obese people. Recently, Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) published a 2022 nutritional and dietary supplement consumption trend forecast report, showing that, in the context of the global epidemic, consumers are increasingly demanding plant-based functional products. Fifty-eight percent of global consumers require functional products to have a good flavor and taste and put forward the requirements of convenience and compliance with daily dietary habits in dosage forms such as functional food and beverages that are absolutely attractive [17].
Just as obesity is formed over time, losing weight is also a long-term behavior. Therefore, for obese people, there is an urgent need for safe and effective plant-based weight-loss products that conform with dietary habits and have good flavors. Fermented products are generally preferred flavor products. Gil-Rodríguez et al. [18] found that lactic acid bacteria (LAB) fermentation could improve the lipase inhibitory activity of milk. Jeong et al. [19] found that LAB (Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus MG4502, Lactobacillus gasseri MG4524, Limosilactobacillus reuteri MG5149 and Weissella cibaria MG5285) exhibited α-glucosidase inhibitory activities (>60.3%). Yi et al. [20] found that fermented ginseng could block adipogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells. Pan et al. [21] showed that a lemon peel fermentation supernatant could inhibit the weight gain of mice and improve the lesions of the liver and epididymal adipose tissue. However, the current studies on the anti-obesity effects of fermented herbs mainly focus on a single raw material; there are very few reports on fermented compounds. A multinational international study found that worldwide, the consumption habits of consumers and the consumption of beverages are increasing [22]. Other studies have found that controlling or replacing the consumption of sugary drinks can effectively reduce the incidence of obesity [23]. Shi et al. [24] found that LAB fermentation could remove the bad flavors (such as grass) of peas. Turmeric has shown an anti-obesity efficacy in high-fat-diet rats after fermentation [25,26]. It can also improve flavors; thus, it has the potential to be developed into an anti-obesity functional drink [27]. To the best of our knowledge, there are few reports about LAB-fermenting plant-based compound slimming drinks. Therefore, the development of plant-based drinks with weight-loss effects to replace sugary drinks is necessary and feasible for the treatment of obese individuals and the prevention and control of obese groups.
In this study, we used Shenheling extract (SHLE), a plant formula extract used for weight loss in China, as the culture substrate to screen LAB suitable for fermentation. With the lipase inhibitory activity, the α-glucosidase inhibitory activity and a sensory evaluation as the response indicators, lactic acid bacteria that improved the flavor of SHLE and improved the anti-obesity efficacy properties were preferred. In this study, we provide basic research experience for the development of LAB-fermented botanical beverages with a good flavor and weight-loss effects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
p-Nitrophenyl palmitate, p-nitrophenyl α-D-glucopyranoside (p-NPG), pancreatic lipase, orlistat and acarbose were all purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. α-Glucosidase, gallic acid, rutin and anhydrous glucose were obtained from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China. A Folin–Ciocâlteu reagent was purchased from Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., China. The rest of the chemicals, reagents, consumables and culture media were purchased from National Pharmaceutical Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
2.2. Preparation and Fermentation of SHLE
SHLE was prepared according to our previous study [28]. The raw materials and proportions of SHL are shown in Table 1. The fully crushed SHL powder and ultrapure water were mixed evenly at a ratio of 1:10 (g/mL), soaked at room temperature for 30 min, heated at 100 °C for 30 min and cooled and centrifuged at 4000× g for 10 min. The supernatant was taken as SHLE.

Table 1.
The composition and proportions of SHL.
In this study, 12 LAB strains belonging to the Dairy Experimental Center (Jiangsu Provincial Key Lab of Dairy Biotechnology and Safety Control, Yangzhou University, China) were used (Table 2).

Table 2.
Species and strain names used in this study.
The strains of Lactobacillus were inoculated into a conventional MRS medium and cultured at 37 °C for 18 h. The cells were then centrifuged at 5000× g for 1 min, the supernatant was poured out, sterile normal saline was added to wash the precipitated bacteria and washing was repeated twice. Finally, the bacterial suspension was obtained by resuspending the bacteria in sterile physiological saline and adjusting the OD600 to 1.0. The above bacterial suspension was inoculated into SHLE at a ratio of 3% (v/v) and then cultured under anaerobic conditions at 37 °C for 72 h. After inoculation, 20 mL was sampled immediately, of which 2 mL was used to count the living bacteria and the rest was centrifuged at 5000× g for 5 min. The supernatant was taken as the fermentation broth for 0 h and stored at −80 °C until use. After that, the samples were obtained and treated according to the above method every 6 h until the end of fermentation at 72 h. Freshly inoculated SHLE was aspirated (300 µL) into a honeycomb plate, placed into a preheated automatic growth curve instrument and cultivated at 37 °C for 72 h. The OD600 value was measured and recorded every 2 h and used to draw the growth curves.
2.3. Determination of Live Bacterial Count, pH and Titratable Acidity
The number of living bacteria in the sample was determined by the plate colony counting method. The pH value was measured by an FE20 pH meter (METTLER TOLEDO Int. Ltd., Zurich, Switzerland). The pH meter was calibrated with pH 4.01 and 6.86 standard buffer solutions before use. The determination method of titratable acidity was as follows: 5 g of the sample was weighed and titrated by a 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution until a pH value up to 7.0 was reached [28]. The volume of the NaOH solution consumed by the above process was recorded as V mL.
Titratable acidity value (°T) = V × 20.
2.4. Determination of Total Polysaccharide Content (TPSC)
The TPSC in the sample was determined by the phenol–sulfuric acid method and slightly modified according to the method of Nazeam et al. [29]; anhydrous glucose was used as the standard. First, the samples were diluted 50-fold with distilled water. A total of 0.5 mL of the diluted sample, 0.5 mL of a 6% phenol solution and 2.5 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid were then added, mixed well and allowed to stand at 25 °C for 30 min. Finally, 200 µL was pipetted into a 96-well plate and the absorbance at 490 nm was measured by a spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA) [28]. The data were expressed as mg of the glucose equivalent (GlcE) per mL of SHLE.
2.5. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
The TFC was determined by the aluminum nitrate colorimetric method with rutin as the standard and slightly modified according to the method of Chen et al. [30]. The sample (0.5 mL) was mixed with 0.05 g/mL NaNO2 (1 mL) and allowed to stand for 6 min. An amount of 0.1 g/mL Al (NO3)3 (1 mL) was then added, mixed evenly and allowed to rest for 6 min. Next, 0.04 g/mL NaOH (3 mL) was added, mixed evenly and allowed to rest for 15 min. Finally, 200 µL was pipetted into a 96-well plate and the absorbance at 510 nm was measured by a spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA). The data were expressed as milligrams of rutin equivalent (RE) per milliliter of SHLE [28].
2.6. Determination of Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
The TPC was slightly modified according to the research of Derakhshan et al. [31]. As determined by the Folin–Ciocâlteu method, a standard curve was prepared with gallic acid as the standard. A total of 400 µL of Folin–Ciocâlteu reagent was added to 100 µL of the standard or sample and mixed well. After 1 min, 300 µL of 10% sodium carbonate was added to the mixture, mixed well, brought to a volume of 5 mL with ultrapure water and incubated at room temperature for 60 min. Finally, 200 µL was pipetted into a 96-well plate. The absorbance was measured at 765 nm by a spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA) [28]. The data were expressed as mg of the gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per mL of SHLE.
2.7. Determination of Pancreatic Lipase Activity Inhibition
The method mentioned in the study of Kim et al. was slightly modified [32]. In a 280 µL reaction system, 180 µL of pH 7.2 phosphate buffer, 40 µL of the sample and 20 µL of 10 mM p-NPP (p-nitrophenyl palmitate) were added in succession and incubated at 37 °C for 10 min. A total of 40 µL of 10 mg/mL pancrelipase solution was then added, fully mixed and incubated at 37 °C for 15 min, followed by the immediate addition of 200 μL of absolute alcohol to terminate the reaction. The mixture was centrifuged at 10,000× g for 2 min and the supernatant was taken. The absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 405 nm by a spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA) and recorded as B1. The sample was replaced with a phosphate buffer as the sample blank control and recorded as B0. The sample without inhibitors was taken to measure the inhibitor-free activity and denoted as A1; the corresponding negative control without an enzyme was used as a negative control without an inhibitor and denoted as A0 [28]. Orlistat was used as a positive control:
Lipase activity inhibition (%) = (1 − (B1 − B0)/(A1 − A0)) × 100.
2.8. Determination of α-Glucosidase Activity Inhibition
The method mentioned in the literature by Silva et al. was slightly modified [33]. A total of 100 μL of a pH 6.8 phosphate buffer, 20 μL of the sample and 20 μL of 20 mM p-NPG were added to a 96-well plate and incubated at 37 °C for 10 min; 20 μL of a 1 U/mL α-glucosidase solution was then added, mixed well and incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. A spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Co., Ltd., Waltham, MA, USA) was immediately used to measure the absorbance at a wavelength of 405 nm and the absorbance was recorded as B1. The sample was replaced with a phosphate buffer as a sample blank control and recorded as B0. The sample without an inhibitor was used to measure the inhibitor-free activity and was recorded as A1. Correspondingly, the negative control without an inhibitor lacked an enzyme and was recorded as A0 [28]. Acarbose was used as a positive control:
Inhibition of α-glucosidase activity (%) = (1 − (B1 − B0)/(A1 − A0)) × 100.
2.9. Sensory Evaluation
Ten students who received professional sensory analysis training were selected to form an evaluation group and a sensory evaluation of the fermentation broth was conducted according to the sensory evaluation standards (Table S1). The experimental scheme was approved by the ethics committee of Yangzhou University (No. YZU-LPXY-012, Hanjiang District, Yangzhou, China) and conformed with the ethical principles specified in the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
All samples were repeated three times. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 22 (Statistical Package for the Social Science, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The results were presented as the means ± SEs and the differences among the different samples were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA, Tukey). Values of p < 0.05 or p < 0.01 were considered to be statistically significant. The heatmap data were processed using the min–max normalization method. The graphics were created using GraphPad Prism 9 (San Diego, CA, USA) software.
3. Results
3.1. Growth of Strains in SHLE
The growth of the 12 strains in this study in SHLE is shown in Figure 1. Overall, Lactobacillus plantarum (S7, 67 and P11) grew better. There were also differences in strains within the same species. For example, the hsryfm1301 and grx10 strains of Lactobacillus rhamnosus grew better whereas the LV108 strain grew poorly. The strain grx08 in Lactobacillus fermentum grew better whereas M91 grew worse. Finally, five strains—S7, 67, grx10, 1301 and grx08—were selected for further study.
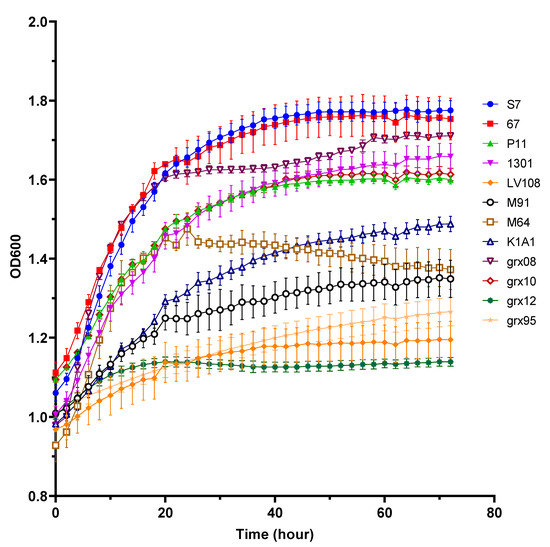
Figure 1.
Growth curves of different lactic acid bacteria in SHLE.
3.2. Changes in pH, Titratable Acidity and Viable Count during SHLE Fermentation
The degree of pH reduction relative to the unfermented SHLE represented the growth performance of the strain. After 18 h of fermentation, the selected 5 strains of LAB could reduce the pH of SHLE to 4.0 or below (Figure 2A). Among them, the pH value of L. plantarum S7 and L. rhamnosus grx10 decreased to below 3.5 after 40 h of fermentation. Total acidity (measured as the titrated acidity) directly affects the mouthfeel and flavor of a beverage. After fermentation, the titrated acidity significantly increased and each strain basically reached a relatively stable acidity at 72 h of fermentation (Figure 2B). Among them, L. plantarum (S7 and 67) had a faster acid production rate. L. plantarum S7 and L. rhamnosus grx10 had titrated acidity above 100°T at the end of fermentation. In contrast, the acid production curves of L. fermentum grx08 and L. rhamnosus hsryfm1301 were relatively flat. The number of viable bacteria is an important indicator of viable bacteria in beverages. The number of viable bacteria of the five strains fermented in SHLE for 18 h to the end of fermentation was maintained above 108 CFU/mL (Figure 2C). Among them, the viable count of L. fermentum grx08 slowly increased, but remained the highest at the end of fermentation.
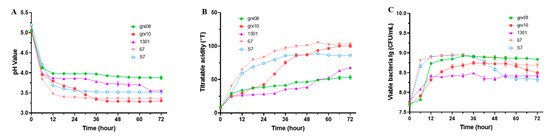
Figure 2.
Changes in pH value (A), titratable acidity (B) and viable bacteria count (C) of SHLE fermented by different LAB. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of replicate experiments (n = 3).
3.3. Effects of LAB Fermentation on the Components of SHLE
The active substances showed a gradual decreasing trend during the fermentation of lactic acid bacteria (Figure 3). Polysaccharides were the most utilized or influenced by the lactic acid bacteria (Figure 3A) and polyphenols were the least utilized (Figure 3C). In the comparison of different species/strains, it could be seen that L. plantarum (S7 and 67) consumed more polysaccharides and flavonoids (Figure 3A,B). L. rhamnosus hsryfm1301 had the least utilization of polysaccharides (Figure 3A), but had a great influence on the utilization of polyphenols (Figure 3C). L. fermentum grx08 had the least effect on the utilization of flavonoids (Figure 3B).
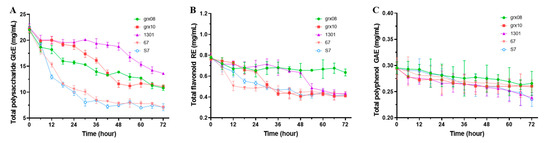
Figure 3.
Changes in the contents of functional components in SHLE fermented by LAB. (A) Total polysaccharide, (B) total flavonoid and (C) total polyphenol. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of replicate experiments (n = 3).
3.4. Effects of LAB Fermentation on the Inhibition of the Energy Digestive Enzyme Activity of SHLE
LAB fermentation significantly increased the inhibition rate of the pancreatic lipase activity of SHLE (p < 0.05) and finally stabilized at approximately 93% (Figure 4a). Conversely, fermentation resulted in a slightly lower inhibition of the α-glucosidase activity of SHLE (Figure 4b). Figure 4c shows that the five types of LAB fermentation for 72 h increased the lipase activity inhibition rate of SHLE to the inhibition level of 0.5 mg/mL orlistat (positive control). However, the α-glucosidase activity inhibition rate slightly decreased after fermentation (Figure 4d). The reduction in L. fermentum grx08 and L. plantarum S7 fermentation was, however, not significant (p > 0.05).
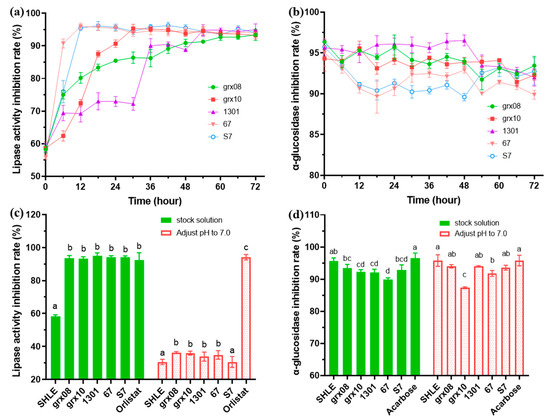
Figure 4.
Effects of different LAB fermentations on the inhibition of SHLE energy-digesting enzyme activity. (a) The change in lipase activity inhibition rate during fermentation, (b) the change in α-glucosidase activity inhibition rate during fermentation, (c) inhibition rate of lipase activity in 72 h fermentation samples and (d) inhibition rate of α-glucosidase activity in 72 h fermentation samples. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of replicate experiments (n = 3). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
The pH generally has an effect on the enzyme activity. After adjusting the pH of the samples before and after SHLE fermentation to 7, the inhibition rate of the lipase activity significantly decreased; except for L. plantarum S7, the rest were significantly higher than those of SHLE (p < 0.05). The effect of pH on the inhibition rate of the α-glucosidase activity was less than that of lipase. After a pH adjustment, only L. rhamnosus grx10 and L. plantarum 67 exhibited significantly lower α-glucosidase activity inhibition rates than SHLE (p < 0.05).
3.5. Effects of Different LAB Fermentations on the Flavor of SHLE
The fermentation of LAB significantly improved the sensory score of SHLE (p < 0.05, Figure 5). Fermentation removed the bad flavors of grass, bitterness and cassia of SHLE. At the same time, fermentation significantly increased the sour taste and fruity flavor of SHLE and gave SHLE a cool taste (p < 0.05). In terms of the sour taste, the fermentation of L. rhamnosus grx10 and L. plantarum (S7 and 67) was too high and the sour taste was stronger whereas the sour taste of L. rhamnosus hsryfm1301 and L. fermentum grx08 was softer. In the presence of a fruit aroma, L. fermentum grx08 and L. rhamnosus grx10 were better than L. plantarum S7 and 67 (p < 0.05).
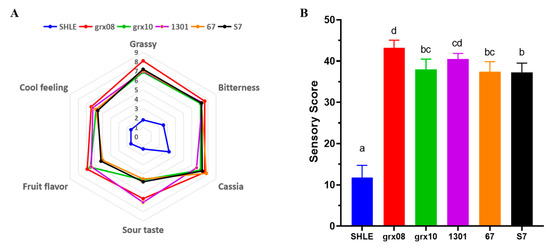
Figure 5.
Effects of fermentation with different lactic acid bacteria on SHLE flavor. (A) Sensory scoring radar chart and (B) total score of sensory evaluation. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of replicate experiments (n = 10). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
The differences in the substance content, inhibition of energy-related enzyme activity and sensory score of SHLE fermented by different strains were compared by a heatmap (Figure 6). Judging from the inhibition rate of the enzyme activity and the sensory evaluation, L. fermentum grx08 and L. rhamnosus hsryfm1301 could be used as alternative strains for SHLE fermentation; the two strains also retained relatively more active substances in the fermentation.
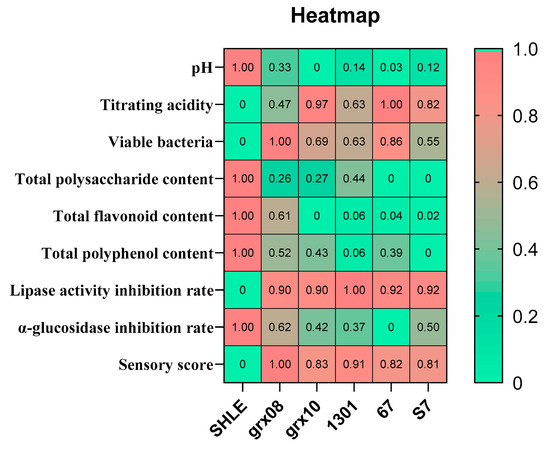
Figure 6.
Heatmap analysis of the substance content, the activity of inhibiting energy-related enzymes and the sensory flavor of SHLE by the fermentation of different strains. The data were processed by min–max normalization with the formula (x − min)/(max − min). The changes in color and shade from green to red represent the magnitude of the value from 0 to 1.
4. Discussion
An enhancement of the anti-obesity effects of herbal or botanical materials by microbial fermentation has been reported in several studies. Bifidobacterium breve-fermented Pueraria (Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi) was better than an unfermented one in improving high-fat-diet-induced dyslipidemia in mice [34]. Dealcoholized apple juice sequentially fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and L. plantarum improved obesity and fatty livers in mice on a high-fat diet better than unfermented apple juice [35]. However, only Hong et al. [36] studied the potential of yogurt fermented with safflower extract to inhibit pancreatic lipase in vitro; Noureen et al. [37] studied the inhibitory effect of fermented rice bran on lipase activity. Our previous study also found that SHLE fermented with L. fermentum grx08 significantly enhanced the anti-obesity efficacy [28]. In this paper, we established an in vitro method for screening the strains suitable for growth in SHLE, which could enhance the anti-obesity activity and improve the flavor but could not be over-grown or consume too many active substances.
The nutritional composition of SHLE is relatively comprehensive and 50% of the selected LAB could grow normally in it. In terms of species, L. plantarum (S7, 67 and P11) grew well in SHLE, which may be related to the fact that this species generally comes from plant fermentation materials. L. plantarum generally carries genes for enzymes that decompose plant-derived nutrients such as polysaccharides. Therefore, L. plantarum S7 and 67 consumed the most total substances. There are also differences in strains within the same species. For example, L. rhamnosus grx10 grew best, hsryfm1301 grew moderately and LV108 grew very poorly.
Flavonoids are important substances for the inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity [38]. During the fermentation process, LAB consumed a portion of the flavonoids, but the inhibition rate of the lipase activity increased. One of the reasons may be that fermentation reduces acidity and has an effect on the activity of enzymes [18]. As a result, except for L. plantarum S7, the fermentation of the other four LAB still significantly improved the lipase activity inhibition rate of SHLE. Flavonoids containing different groups have different inhibitory effects on pancreatic lipase activity and a few new methoxy flavonoids may be produced by fermentation that have a stronger inhibitory ability [38]. For example, Xu et al. [39] found that β-glucuronidase produced by Lactobacillus brevis RO1 enhanced baicalin to baicalein and wogonoside to wogonin in Scutellaria baicalensis during fermentation, which improved the biological activity. The fermentation of 3-hydroxyflavone with Beauveria bassiana (ATCC 13144) yielded 3,4′-dihdroxyflavone, flavone 3-O-β-D-4-O-methylglucopyranoside and two minor metabolites [40]. These results all indicate the possibility of fermentation to produce new flavonoids. Obesity requires a long-term adherence to a treatment. A good flavor of weight-loss functional drinks is an important basis for consumers to insist on when drinking for a long time. However, there are few research reports on improving the flavor of functional diet drinks through LAB fermentation. In this study, fermentation removed the grassy taste of SHLE, which was consistent with the report by Shi et al. [24] who observed that the grassy taste of peas was removed by fermentation with LAB. The removal of the cassia odor in this fermentation may have been related to the conversion of cinnamaldehyde with the cassia flavor into cinnamyl alcohol with a fruit flavor by microbial fermentation [41]. The bitterness was removed in this fermentation; one of the reasons may have been that the fermentation metabolized the bitter substances [42]. Another reason may be that the sour taste produced by the fermentation masked the bitter taste. Ye et al. [43] also believed that the microbial fermentation of tea to convert substances such as alkaloids and polyphenols reduced bitterness and astringency. Studies have shown that bitter compounds such as ginsenosides in ginseng [44] and momordicoside in balsam pears [45] exist in the form of glycosides; however, microorganisms can de-bitter them by the hydrolysis of glycosides [45]. Finally, the number of viable bacteria after fermentation reached more than 108 CFU/mL, which met the requirements of viable bacteria-type LAB beverages (the number of viable bacteria ≥ 106 CFU/mL).
Overall, these results indicated that the LAB fermentation of SHLE could improve the inhibition of the pancreatic lipase activity and maintain the original level of SHLE inhibition of the α-glucosidase activity, showing an inhibition of fat and carbohydrate digestion as well as the absorption potential and may have beneficial effects on obesity. In addition, fermentation improved the original grassy, cassia and bitter taste of SHLE, boosting its overall sensory score. However, the mechanisms by which these beneficial effects were achieved along with wider population acceptance and in vivo weight-loss effects require further study.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study showed that different strains of LAB had the ability to ferment SHLE and partially inhibit the activities of pancreatic lipase and α-glucosidase in vitro. It also removed the undesired grassy, cassia and bitter tastes. Judging from the inhibition rate of the enzyme activity and the sensory evaluation, SHLE fermented with L. fermentum grx08 and L. rhamnosus hsryfm1301 is a good candidate as a functional drink for weight loss with a good flavor. However, further studies are needed to evaluate the anti-obesity potential of these fermented products in appropriate in vivo models.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation8100482/s1. Table S1. Sensory evaluation standard.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.G.; investigation, X.Y. (Xiantao Yan), Z.Z., J.W., X.Y. (Xun Yin), X.L., W.W. and Y.W.; data curation, X.Y. (Xiantao Yan), T.L. and D.C.; funding acquisi-tion, D.C., X.Y. (Xiantao Yan), Y.W. and R.G.; methodology, X.Y. (Xiantao Yan) and T.L.; project administration, R.G.; supervision, D.C.; writing—original draft, X.Y. (Xiantao Yan); writing—review and editing, X.Y. (Xiantao Yan), D.C. and W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20211325), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. 19KJA140004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31972094), Jiangsu Science and Technology Projects (No. XZ-SZ202042), Key Laboratory of Probiotics and Dairy Deep Processing of Yangzhou (No. YZ2020265), the Research Project of the Zhejiang Federation of Social Sciences (2021N40) and the Key Research Project of Guangdong Provincial Department of Education (2018 WQNCX113).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Neeland, I.J.; Poirier, P.; Despres, J.P. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Heterogeneity of Obesity: Clinical Challenges and Implications for Management. Circulation 2018, 137, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chi, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caci, G.; Albini, A.; Malerba, M.; Noonan, D.M.; Pochetti, P.; Polosa, R. COVID-19 and Obesity: Dangerous Liaisons. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrelli, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Nicoletti, M.; Menichini, F.; Conforti, F. In vitro investigation of the potential health benefits of wild Mediterranean dietary plants as anti-obesity agents with alpha-amylase and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, A.J.; Fujioka, K.; Hompesch, M. Evolution of pharmacological obesity treatments: Focus on adverse side-effect profiles. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Garza, A.L.; Milagro, F.I.; Boque, N.; Campion, J.; Martinez, J.A. Natural inhibitors of pancreatic lipase as new players in obesity treatment. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotti, L.; Monteiro, A.F.M.; de Oliveira Viana, J.; Mendonca Junior, F.J.B.; Ishiki, H.M.; Tchouboun, E.N.; Santos, R.; Scotti, M.T. Multi-Target Drugs Against Metabolic Disorders. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, R.J.; Tschop, M.H.; Wilding, J.P. Anti-obesity drugs: Past, present and future. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.B.; Daily, J.W. Anti-Obesity Effects of Chang-Chul-Eui-Ee-In-Tang (sic) in Female Rats with Diet-Induced Obesity. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2011, 17, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, S.; Tian, J.; Piao, C.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of the Chinese Herbal Formula, JTTZ, for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes with Obesity and Hyperlipidemia: A Multicenter Randomized, Positive-Controlled, Open-Label Clinical Trial. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 9519231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chang, B.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, S.P.; Zhen, Z.; Zhang, L.L.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, W.Q.; Liu, H.F.; et al. Chinese herbal medicine for obesity: A randomized, double-blinded, multicenter, prospective trial. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azushima, K.; Tamura, K.; Haku, S.; Wakui, H.; Kanaoka, T.; Ohsawa, M.; Uneda, K.; Kobayashi, R.; Ohki, K.; Dejima, T.; et al. Effects of the oriental herbal medicine Bofu-tsusho-san in obesity hypertension: A multicenter, randomized, parallel-group controlled trial (ATH-D-14-01021.R2). Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hioki, C.; Yoshimoto, K.; Yoshida, T. Efficacy of bofu-tsusho-san, an oriental herbal medicine, in obese Japanese women with impaired glucose tolerance. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2004, 31, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, C.; Song, Y.-K.; Ko, S.-G. Efficacy and safety of Euiiyin-tang in Korean women with obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 51, 102423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenon, G.B.; Li, K.X.; Chang, Y.-H.; Yang, A.W.; Da Costa, C.; Li, C.G.; Cohen, M.; Mann, N.; Xue, C.C.L. Efficacy and Safety of a Chinese Herbal Medicine Formula (RCM-104) in the Management of Simple Obesity: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 435702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignjatovic, V.; Ogru, E.; Heffernan, M.; Libinaki, R.; Lim, Y.; Ng, F. Studies on the use of "Slimax", a Chinese herbal mixture, in the treatment of human obesity. Pharm. Biol. 2000, 38, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2022 Consumer Trends: People Will Still Turn to Dietary Supplements, Nutrition for Preventative Health in 2022. Available online: https://www.nutritionaloutlook.com/view/2022-consumer-trends-people-will-still-turn-to-dietary-supplements-nutrition-for-preventative-health-in-2022 (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Gil-Rodriguez, A.M.; Beresford, T.P. Lipase inhibitory activity of skim milk fermented with different strains of lactic acid bacteria. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Won, G.; Choi, S.-I.; Kim, G.-H.; Kang, C.-H. The Antioxidant, Anti-Diabetic, and Anti-Adipogenesis Potential and Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Human and Fermented Foods. Fermentation 2021, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.A.; Lee, J.; Park, S.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.W.; Lee, M.G.; Nam, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Oh, H.; Kim, S.; et al. Fermented ginseng extract, BST204, disturbs adipogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells through inhibition of S6 kinase 1 signaling. J. Ginseng. Res. 2020, 44, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tan, J.; Long, X.; Yi, R.; Zhao, X.; Park, K.-Y. Anti-obesity effect of fermented lemon peel on high-fat diet-induced obese mice by modulating the inflammatory response. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 46, e14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevijvere, S.; Jaacks, L.M.; Monteiro, C.A.; Moubarac, J.C.; Girling-Butcher, M.; Lee, A.C.; Pan, A.; Bentham, J.; Swinburn, B. Global trends in ultraprocessed food and drink product sales and their association with adult body mass index trajectories. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20 (Suppl. 2), 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, N.D.; Khan, T.A.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Chiavaroli, L.; Au-Yeung, F.; Lee, J.J.; Noronha, J.C.; Comelli, E.M.; Blanco Mejia, S.; et al. Association of Low- and No-Calorie Sweetened Beverages as a Replacement for Sugar-Sweetened Beverages With Body Weight and Cardiometabolic Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e222092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Singh, A.; Kitts, D.D.; Pratap-Singh, A. Lactic acid fermentation: A novel approach to eliminate unpleasant aroma in pea protein isolates. LWT 2021, 150, 111927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Lee, G.-H.; Hoang, T.-H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Jang, G.-H.; Seok, C.-H.; Gwak, Y.-G.-S.; Lim, J.; Kim, J.; Chae, H.-J. GABA and Fermented Curcuma longa L. Extract Enriched with GABA Ameliorate Obesity through Nox4-IRE1 alpha Sulfonation-RIDD-SIRT1 Decay Axis in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, O.-K.; Yoon, H.-G.; Park, J.; You, Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.-H.; Choi, K.-C.; Lee, J.; Jun, W. Anti-obesity effect of extract from fermented Curcuma longa L. through regulation of adipogenesis and lipolysis pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 30428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiwati, K.T.; Lay, B.W. Curcuminoid cider fermented from Curcuma xanthorrhiza curcuminoids attenuates gene expression related to obesity-induced inflammation in hypercholesterolaemic rats. Int. Food Res. J. 2019, 26, 859–867. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.-T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, W.; Ma, W.; Qu, H.; Qian, J.-Y.; Gu, R. In Vitro Anti-Obesity Effect of Shenheling Extract (SHLE) Fermented with Lactobacillus fermentum grx08. Foods 2022, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeam, J.A.; Gad, H.A.; Esmat, A.; El-Hefnawy, H.M.; Singab, A.B. Aloe arborescens Polysaccharides: In Vitro Immunomodulation and Potential Cytotoxic Activity. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; An, Q.; Ye, X.M.; Zhao, Z.T.; Zhao, M.; Han, Y.; Ouyang, K.H.; et al. Investigation of Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Activity, and the Effects of Alfalfa Flavonoids on Growth Performance. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 8569237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, Z.; Ferrante, M.; Tadi, M.; Ansari, F.; Heydari, A.; Hosseini, M.S.; Conti, G.O.; Sadrabad, E.K. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of ethanolic extract of pomegranate peels, juice and seeds. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Jang, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S. Anti-obesity effect of Morus bombycis root extract: Anti-lipase activity and lipolytic effect. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.P.; Sampaio, G.R.; Freitas, R.; Torres, E. Polyphenols from guarana after in vitro digestion: Evaluation of bioacessibility and inhibition of activity of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Bose, S.; Shin, N.R.; Song, E.-J.; Nam, Y.-D.; Kim, H. Lactate-Fortified Puerariae Radix Fermented by Bifidobacterium breve Improved Diet-Induced Metabolic Dysregulation via Alteration of Gut Microbial Communities. Nutrients 2020, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Kong, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ling, T.; Xie, Z.; Khalilova, I.; Huang, J. Effects of Keemun and Dianhong Black Tea in Alleviating Excess Lipid Accumulation in the Liver of Obese Mice: A Comparative Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 849582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Lim, J.M.; Kothari, D.; Kwon, S.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Han, S.-G.; Kim, S.-K. Antioxidant Properties and Diet-Related alpha-Glucosidase and Lipase Inhibitory Activities of Yogurt Supplemented with Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) Petal Extract. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureen, H.; Alam, S.; Al Ayoubi, S.; Qayyum, A.; Sadiqi, S.; Atiq, S.; Naz, A.; Bibi, Y.; Ahmed, W.; Khan, M.M.; et al. Mechanism of rice bran lipase inhibition through fermentation activity of probiotic bacteria. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 5841–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, T.; Melzig, M.F. Polyphenolic Compounds as Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ji, G.E. Bioconversion of flavones during fermentation in milk containing Scutellaria baicalensis extract by Lactobacillus brevis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, W.; Mikell, J.R.; Hale, A.L.; Ferreira, D.; Khan, I.A. Microbial Metabolism. Part 6. Metabolites of 3- and 7-Hydroxyflavones. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennacchio, A.; Rossi, M.; Raia, C.A. Synthesis of cinnamyl alcohol from cinnamaldehyde with Bacillus stearothermophilus alcohol dehydrogenase as the isolated enzyme and in recombinant E. coli cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, H.V.H. Effects of Fermentation Conditions Using Lactobacillus plantarum on the Charantin, Stigmasterol Glucoside and beta-sitosterol Glucoside Contents of Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia L.) Juice. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.-H.; Ye, Y.; Yin, J.-F.; Jin, J.; Liang, Y.-R.; Liu, R.-Y.; Tang, P.; Xu, Y.-Q. Bitterness and astringency of tea leaves and products: Formation mechanism and reducing strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-G.; Choi, S.-Y.; Suh, H.J.; Park, H.J. Bitterness Reduction and Enzymatic Transformation of Ginsenosides from Korean Red Ginseng (Panax Ginseng) Extract. J. Food Biochem. 2011, 35, 1267–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, F.A.; Annuar, M.S.; Sharifuddin, Y. Biotransformation of Momordica charantia fresh juice by Lactobacillus plantarum BET003 and its putative anti-diabetic potential. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).