Abstract
This study demonstrates that the consortium, which consists of the microbial flora of methane production (MFMP) and Clostridium cellulovorans grown with cellulose, can perform the direct conversion of cellulosic biomass to methane. The MFMP was taken from a commercial methane fermentation tank and was extremely complicated. Therefore, C. cellulovorans grown with cellobiose could not perform high degradation ability on cellulosic biomass due to competition by various microorganisms in MFMP. Focusing on the fact that C. cellulovorans was cultivated with cellulose, which is armed with cellulosome, so that it is now armed C. cellulovorans; the direct conversion was carried out by the consortium which consisted of MFMP and the armed C. cellulovorans. As a result, the consortium of C. cellulovorans grown with cellobiose and MFMP (CCeM) could not degrade the purified cellulose and mandarin orange peel. However, MFMP and the armed C. cellulovorans reduced 78.4% of the total sugar of the purified cellulose such as MN301, and produced 6.89 mL of methane simultaneously. Furthermore, the consortium consisted of MFMP and the armed C. cellulovorans degraded mandarin orange peel without any pretreatments and produced methane that was accounting for 66.2% of the total produced gas.
1. Introduction
Although the first-generation biofuels, which are made from corn and sugarcane, have become widespread, there is concern about competition with food supply. Without competing for food, second-generation biofuels are produced from non-edible biomass such as agricultural wastes and cellulosic substrates [1,2].
A plant cell wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, pectin, etc. Cellulose is a fiber of d-glucose monomers and has strong crystalline [3]. Moreover, cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin compose the rigid and complex structures [4]. Hemicellulose is a heteropolymer such as xylan, glucuronoxylan, arabinoxylan, glucomannan, and xyloglucan. In addition, lignin, phenol compounds, reinforces the structure of cellulose and hemicellulose, making it more difficult to degrade. Thus, since rigid and complex structures are constructed in cellulosic biomass, it is very difficult to degrade them enzymatically.
Orange juice is one of the major fruit juices and almost the same amount of orange waste as orange juice comes out as a byproduct in orange juice factories. Therefore, it has been considered that such orange wastes are available for non-edible biomass all over the world. However, d-limonene, which is included in citrus, has an extremely toxic effect on fermenting microorganisms [5,6]. Depending on the type of citrus, the orange peel contains approximately 3% limonene. Therefore, it was necessary to separate d-limonene before the cultivation or to protect microorganisms from d-limonene by encapsulation or immobilization [7,8]. Recently, it was reported that Clostridium cellulovorans can degrade orange wastes in the culture including d-limonene and Clostridium beijerinckii can carry out isopropanol–butanol–ethanol (IBE) fermentation, which is a bacterial fermentation process producing isopropanol instead of acetone on acetone–ethanol–butanol (ABE) fermentation [9,10,11]. Thus, the breakthrough was obtained utilizing orange wastes for second-generation biofuels without any pre-treatment.
Some Clostridia, such as C. cellulovorans and Clostridium thermocellum, are known to have the ability to degrade cellulosic biomass efficiently using cellulosomes and secreted non-cellulosomal enzymes [12]. Among those species, we have been studying C. cellulovorans, which is a mesophilic and anaerobic cellulolytic bacterium [13]. C. cellulovorans degrades not only cellulose but also hemicelluloses consisting of xylose, fructose, galactose, and mannose [14,15,16]. Whole-genome sequencing of C. cellulovorans and the exoproteome profiles revealed 57 cellulosomal protein-encoding genes and 168 secreted-carbohydrase-encoding genes [17,18]. Furthermore, the high degradation ability on plant cell walls has so far been reported [19]. C. cellulovorans grown in the culture with cellulose has large protuberances on its surface [20] and the protuberances contain cellulosomes [21]; on the other hand, C. cellulovorans grown in the culture with cellobiose does not have the protuberances (Figure 1a,b). C. cellulovorans acquires a high ability to degrade the plant cell wall with cellulosome, in other words, C. cellulovorans is armed with cellulosome to attack the plant cell wall. Therefore, it can be said that it is the armed C. cellulovorans that grow with cellulose. Although C. cellulovorans has high degradation ability on plant cell walls in the C. cellulovorans monoculture, there are challenges in that C. cellulovorans cannot perform high degradation ability in the co-culture or consortia of other microorganisms. Most of the reports used C. cellulovorans grown with cellobiose, and these challenges were most likely derived using C. cellulovorans grown with cellobiose. Therefore, this study focuses on utilizing the armed C. cellulovorans especially for the consortium of other microorganisms.

Figure 1.
(a) Cell surface of C. cellulovorans grown with cellobiose and (b) cell surface of C. cellulovorans grown with cellulose. White bar indicates 2 μm. Modified from [21].
Many studies on methane (CH4) fermentation have been reported in a wide range of study fields [22]. Methane fermentation using cellulosic biomass is also second-generation biomethane. Since methane production is carried out by the complex microbial flora including methanogens, the second-generation biomethane process needs the consortium to be constructed with microbial flora of methane production (MFMP) and microorganisms which can degrade cellulosic biomass, such as C. cellulovorans. The consortium of C. cellulovorans with MFMP (CCeM) can degrade sugar beet pulp, which is the residue in a sugar refinery factory, and ferments biogas included methane simultaneously [23]. However, the relict sugars in sugar beet pulp were possible to help C. cellulovorans to survive and coexist with MFMP, and the same CCeM could not carry out degrading the purified cellulose and producing methane.
In the present study, we investigated the degradation ability on cellulosic biomass of CCeM that was consistent with the armed C. cellulovorans (ACCeM).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Mandolin oranges were purchased at a grocery store in Japan in 2017. Flavedo and albedo, hereafter called removed peel, were cut into strips with scissors just after removing from a mandolin orange. The strip size was approximately 10 mm in length and 2 mm in width (Figure 2). The peel was used as fresh, not dried, and ground. Furthermore, the peel was not treated by any chemicals. The dried weight of the removed peel was measured, it contained 71.6% water. The substrate concentration of removed peel, the purified celluloses, such as Avicel (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and MN301 (MACHEREY-NAGEL, Düren, Deutschland), and cellobiose (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was 0.5% (w/v) of the dry weight. Avicel is crystalline cellulose powder that is industrially refined from natural cellulose, and the particle size of Avicel is less than 50 μm. MN301 is also industrially refined cellulose powder, and 80% of the particle size is less than 160 μm.
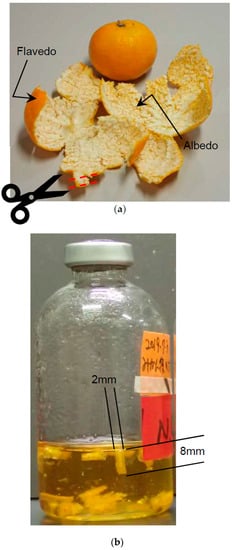
Figure 2.
(a) Removed peel before cutting. (b) Strips of removed peel in the medium.
2.2. Microorganism and Culture Condition
The medium was partially modified by Clostridium cellulovorans medium [11]. One litter medium contained 4 g of yeast extract, 1 mg of Resazurin salt, 1 g of L-cysteine-HCl, 5 g of NaHCO3, 0.45 g of K2HPO4, 0.45 g of KH2PO4, 0.3675 g of NH4Cl, 0.9 g of NaCl, 0.1575 g of MgCl2.6H2O, 0.12 g of CaCl2.2H2O, 0.85 mg of MnCl2.4H2O, 0.942 mg of CoCl2.6H2O, 5.2 mg of Na2EDTA, 1.5 mg of FeCl2.4H2O, 0.07 mg of ZnCl2, 0.1 mg H3BO3, 0.017 mg of CuCl2.2H2O, 0.024 mg of NiCl2.6H2O, 0.036 mg of Na2MoO4.2H2O, 6.6 mg of FeSO4.7H2O, and 0.1 g of p-aminobenzoic acid and was adjusted to pH 7. C. cellulovorans 743B (ATCC 35296) was used and anaerobically cultivated in 0.5% (w/v) cellobiose, Avicel and MN301 at 37 °C stationary for 19 h, for 4 days and 2 days respectively. The MFMP was obtained from methane fermentation digested liquid in January 2017 at Gifu in Japan. The MFMP was anaerobically cultivated in Clostridium cellulovorans medium with 0.5% (w/v) glucose (Wako) and 0.25% (w/v) cellobiose, or 0.5% (w/v) ryegrass leaves at 37 °C for 19 h stationary. The ryegrass leaves were obtained in May 2017 at Aichi in Japan, and were dried and grained to a powder.
2.3. Data Deposition
The sequences of MFMP that are reported in this paper have been deposited in the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ) (accession 104 no. DRR160954).
2.4. Measurement of Total Sugar Concentration
The total sugar concentration was measured from the precipitation after centrifugation which was 20,000 rpm at 4 °C for 5 min. The precipitation was washed by phosphate buffered salts and 5N NaOH. The total sugar concentration of the washed precipitation was measured by the phenol-sulfuric acid method as d-glucose equivalents.
2.5. Gas Concentration
The produced gas volume of the head space in the culture vial was collected and measured by a syringe (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan). The concentrations of CH4, H2, and CO2 were measured by a gas chromatograph GC-8A (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with a Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD) and a column SINCARBON ST (full length 6 m, inner diameter 3 mm; Shinwa, Kyoto, Japan). The column temperature was 200 °C. Argon was a carrier gas and set at a flow rate of 50 mL/min. The injection volume of each sample was 5 mL. The concentration of CH4 was also measured by a gas chromatograph GC-2010plus (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with a capillary column Rt-Q-BOND (30 m, inner diameter. 0.32 mm; RESTEK, Centre, PA, USA). The oven temperature was 250 °C and the column temperature was 150 °C. Nitrogen was the carrier gas and set at a flow rate of 1.21 mL/min. The injection volume of each sample was 0.5 mL.
2.6. Organic Acid Concentration
The concentration of organic acids was measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), CBM-20A, LC-20AD, CTO-20AC, SPD-20A, and DGU-20A3 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with a UV detector and a column KC-811 (300 mm × 2 mm, inner diameter. 8 mm; Showa Denko, Tokyo, Japan). The column temperature was 60 °C. The Bromothymol blue (BTB) post-column method was used. The eluent was 2 mM perchloric acid, and the flow rate was 1.0 mL/min. The reagent was 0.2 mM BTB and 15 mM disodium hydrogen phosphate, and the flow rate was 1.2 mL/min at the wavelength of 445 nm. The injection volume of each sample was 20 μL.
2.7. Cell Growth
Cell growth was measured by Lumitester PD-20, LuciPac Pen and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) eliminating enzyme (Kikkoman Biochemifa, Tokyo, Japan). It is known that integrated intracellular ATP concentration correlates with cell growth [24]. Cell growth was estimated by measuring ATP concentration of 0.1 mL of cell culture according to the manufacturer’s instruction and was expressed by the relative light unit (RLU) value.
2.8. Statistics
The data were analyzed for statistical significance using Welch’s t-test. The difference was assessed with a two-sided test with an α level of 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Degrading Cellulose and Removed Peel under Cocultivation with Methanogens and Non-Armed C. cellulovorans
C. cellulovorans was pre-cultivated in media containing 0.5% (w/v) of cellobiose, which meant C. cellulovorans was not armed with cellulosome. Anaerobic batch cultivations of C. cellulovorans, CCeM, and MFMP were carried out in a 50-mL medium containing 0.5% (w/v) of Avicel and removed peel at 37 °C without shaking.
According to measured cell growth of precultures, inoculation amounts for monocultures of C. cellulovorans and MFMP were decided so that initial RLU values of each monoculture came close to 2000. RLU values of the preculture of C. cellulovorans and MFMP were 45,310 and 50,494, respectively. The inoculation volume was decided as 2 mL for 50 mL monoculture; it was 26 times the dilution so that the initial RLU value of monoculture of C. cellulovorans and MFMP were 1743 and 1942, respectively. CCeM was inoculated 2 mL each from both precultures so that concentrations of cell growth against substrate became the same as the monoculture.
RLU values increased for 1 day of cultivation and then cell growth was observed in all cultures (Figure 3a,b). Interestingly, RLU profiles of CCeM and MFMP were quite similar, even CCeM included C. cellulovorans and MFMP both. The total sugar concentrations were significantly reduced in C. cellulovorans monocultures with Avicel and removed peel after 11 days of cultivation, it was demonstrated that C. cellulovorans could degrade Avicel and removed peel. However, the total sugar concentrations in CCeM with Avicel and removed peel were almost the same as that of MFMP; C. cellulovorans could not degrade Avicel and removed peel in cultures included MFMP (Figure 3c,d). It was thought that C. cellulovorans did not grow in CCeM because cell growths of CCeM and MFMP were almost the same. Methane in the head space was not detected in CCeM with removed peel and that was slightly detected in CCeM and MFMP with Avicel (Figure 3e,f).
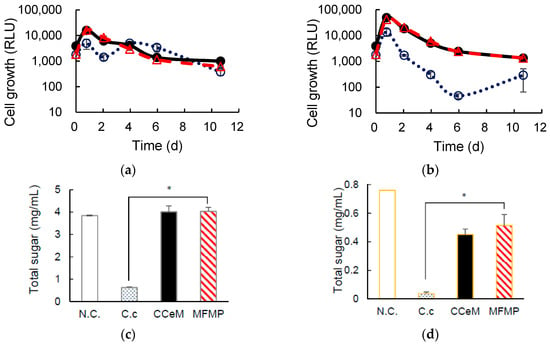
Figure 3.
Cultivation of C. cellulovorans, cellobiose and MFMP (CCeM) and microbial flora of methane production (MFMP) with Avicel. (a) Cell growth, where C. cellulovorans (○_open circle), CCeM (●_closed circle) and MFMP (Δ_open triangle) are included; (c) total sugar concentration; (e) gas production of H2 (hatched bar), CH4 (closed bar), and CO2 (open bar) are included. Cultivation of C. cellulovorans, CCeM, and MFMP with removed peel. (b) Cell growth, where C. cellulovorans (○_open circle), CCeM (●_closed circle), and MFMP (Δ_open triangle) are included; (d) total sugar concentration; (f) gas production of H2 (hatched bar), CH4 (closed bar), and CO2 (open bar) are included. Values with error bars are mean ± SE of three independent samples. SE means a standard error. An asterisk indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
3.2. Cellulose Degradation and Methane Production under Cocultivation with Methanogens and the Armed C. cellulovorans
C. cellulovorans was pre-cultivated in media containing 0.5% (w/v) of MN301 for 2 days, which meant C. cellulovorans was armed with cellulosome. Anaerobic batch cultivations of the armed C. cellulovorans, ACCeM, and MFMP were carried out in a 40-mL medium containing 0.5% (w/v) of MN301 at 37 °C without shaking. RLU values of the preculture of the armed C. cellulovorans and MFMP were 6786 and 38,538, respectively. RLU value of the armed C. cellulovorans culture did not increase over 10,000 like the non-armed C. cellulovorans. Therefore, inoculation amounts for monocultures of the armed C. cellulovorans and MFMP were decided so that initial RLU values of each monoculture became close to 1000. Inoculation volumes of the armed C. cellulovorans and MFMP were decided as 7 mL and 1.2 mL, respectively. The armed C. cellulovorans was 6.69 times dilution and MFMP was 40.17 times dilution so that initial RLU values of monoculture of the armed C. cellulovorans and MFMP were 1014 and 959, respectively. ACCeM was inoculated in 7 mL of the armed C. cellulovorans preculture and 1.2 mL of MFMP preculture so that concentrations of cell growth against substrate became the same as the monoculture. Cell growths in the armed C. cellulovorans monoculture, ACCeM culture, and MFMP monoculture were measured for 7 days of cultivation. RLU values in ACCeM culture and MFMP monoculture rapidly increased more than 100,000 for 10 h of cultivation. The RLU value in the armed C. cellulovorans monoculture increased for 2 days of cultivation and then decreased slowly. Interestingly, the RLU value in ACCeM culture was higher than that in MFMP monoculture after 2 days of cultivation. It suggested that the armed C. cellulovorans grew for a couple of days of cultivation and coexisted with MFMP (Figure 4a). The total sugar concentration in the armed C. cellulovorans monoculture decreased to 0.38 mg/mL from 5 mg/mL for 7 days of cultivations; it indicated that 92.4% of MN301 was degraded by the armed C. cellulovorans for 1 week (Figure 4b). The total sugar concentration in ACCeM culture did not decrease for 3 days of cultivation, however it rapidly decreased from 4 days of cultivation. It also suggested that the armed C. cellulovorans survived for 3 days using brought in cellulosome while adapting to coexisting MFMP. Total sugar concentration in ACCeM culture decreased to 1.08 mg/mL for 7 days of cultivation, therefore it was demonstrated that ACCeM could degrade 78.4% of MN301 for 1 week. The total sugar concentration in MFMP monoculture did not decrease for 27 days of cultivation, it indicated that MFMP did not have a capability to degrade MN301. The total sugar concentrations in the armed C. cellulovorans monoculture and ACCeM culture was significantly low than that in MFMP for 7 days of cultivation (Figure 4c). Total gas volume in the ACCeM culture rapidly increased for 10 h of cultivation, and the total gas volume kept for 1–7 days of cultivation. Interestingly, the methane proportion in the total gas increased for 1–7 days of cultivation, even though total gas volume did not increase. Furthermore, methane volume continuously increased for 21 days of cultivation. Finally, methane volume increased 6.89 mL for 1–21 days of cultivation, therefore it revealed that methane production rate from MN301 was 0.014 mL/h (Figure 4d). Organic acid concentrations in the culture supernatant of ACCeM were measured. Lactic acid concentration was slightly detected for 1 day of cultivation and was not detected after 2 days of cultivation (Figure 4e). Formic acid concentration was temporally increased at 1 day of cultivation, and then it was not detected after 2 days of cultivation. Acetic acid concentration increased for 6 days of cultivation that was the same term when the total sugar concentration reached 78.4%. Acetic acid concentration turned to decrease from 8 days of cultivation. On the other hand, propionic acid concentration increased but did not turn to decrease. It was suggested that MN301 was degraded by C. cellulovorans and acetic acid and methane were produced, and methane was continuously produced utilizing acetic acid after cellulose was degraded. Moreover, it suggested that acetic acid was converted to methane in preference to propionic acid.
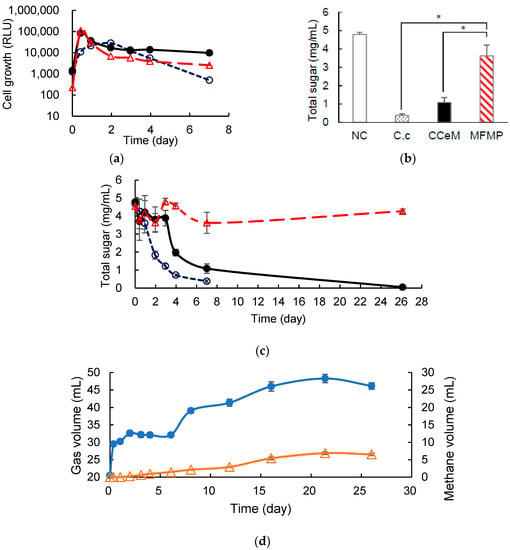
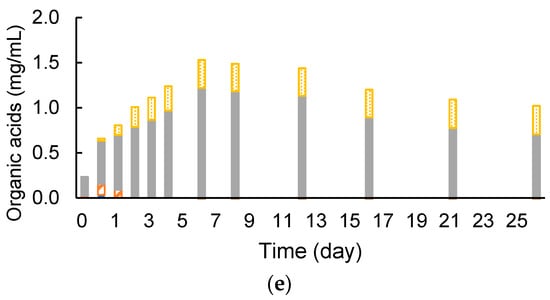
Figure 4.
Cultivation of C. cellulovorans, CCeM, and MFMP with Avicel. (a) Cell growth, where C. cellulovorans (○_open circle), CCeM (●_closed circle), and MFMP (Δ_open triangle) are included; (b) total sugar concentration; (c) time course of total sugar, where C. cellulovorans (○_open circle), CCeM (●_closed circle), and MFMP (Δ_open triangle) are included; (d) time course of gas production, where total gas volume (●_closed circle) and methane volume (Δ_open triangle) are included; (e) time course of organic acids concentration of CCeM, where lactic acid (closed bars), formic acid (open bars), acetic acid (closed bars), and propionic acid (dotted bars) are included. Values with error bars are mean ± SE of three independent samples. SE means a standard error. An asterisk indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
3.3. Removed Peel Degradation and Methane Production under Cocultivation with Methanogens and the Armed C. cellulovorans
It was confirmed that the armed C. cellulovorans could degrade cellulose and MFMP also worked to produce methane simultaneously. Anaerobic batch cultivations of ACCeM was carried out in a 20-mL medium containing 0.5% (w/v) of removed peel, which was an actual agricultural waste, at 37 °C without shaking. The armed C. cellulovorans was pre-cultivated in media containing 0.5% (w/v) of MN301 for 2 days. According to measured cell growth of precultures, inoculation amounts for monocultures of the armed C. cellulovorans and MFMP were decided so that initial RLU values of each monoculture closely became 1000. RLU values of the preculture of the armed C. cellulovorans and MFMP were 3448 and 38,538, respectively. Inoculation volumes of the armed C. cellulovorans and MFMP were decided at 8.5 mL and 0.8 mL, respectively. The armed C. cellulovorans was 3.44 times dilution and MFMP was 36.6 times dilution so that the initial RLU values of ACCeM were 1002 for the armed C. cellulovorans and 1052 for MFMP. The degradation of removed peel was observed for 5 days of cultivation (Figure 5a). Gas production started immediately after inoculation and continued for 4 days of cultivation. However, methane was not detected for these early 4 days of cultivation (Figure 5b). Methane began to be detected after 12 days of cultivation. Interestingly, the increment of methane was 4.7 mL for 12–26 days of cultivation against that the total gas was 7.1 mL for the same term, therefore methane occupied 66.2% of the increased gas. This methane concentration is good performance as the fuel for a biogas power generation. Furthermore, methane productivity was 0.014 mL/h for 12–26 days of cultivation, which was equal to that of MN301 substrate. Acetic acid concentration in the culture supernatant increased the same amount as the MN301 substrate. However, the acetic acid concentration was 2.5 times higher than that in the culture supernatant with MN301 (Figure 5c). It suggested that there was room to convert much acetic acid to methane to improve methane production.
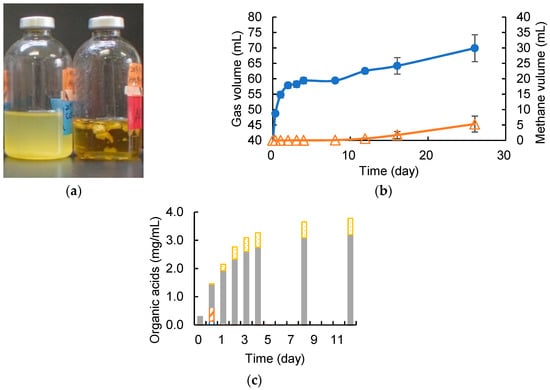
Figure 5.
(a) CCeM culture (left), negative control (right); (b) time course of gas production, where total gas volume (●_closed circle) and methane volume (Δ_open triangle) are included; (c) time course of organic acids concentration of CCeM, where lactic acid (closed bars), formic acid (open bars), acetic acid (closed bars), and propionic acid (dotted bars) are included. Values with error bars are mean ± SE of three independent samples. SE means a standard error. An asterisk indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Since reducing carbon dioxide to conserve the global environment is one of the purposes to replace fossil fuels with biofuels, it is desirable to adopt the biofuel process that has a low environmental load. A sulfuric acid degradation of cellulosic biomass brings about corrosion of a reactor and needs a waste liquid treatment, and the steam explosion process requires a lot of energy to create high pressure and temperature [25,26], therefore these are not low environmental load methods. The enzymatic saccharification is environmental-friendly, because it is a mesophilic process and does not use acids. However, the degradation cost is high because the purified enzymes are expensive and used in large quantities. Instead of using expensive enzymes, the cost will be reduced to utilize microorganisms that can produce enzymes. Furthermore, since C. cellulovorans has many genomes related to cellulosome and non-cellulosomal [27], there is potential to improve the efficiency of the enzymatic saccharification. In addition, when the sulfuric acid process or the steam explosion process is used to saccharide cellulosic biomass, various microorganisms attached to the biomass and brought into the saccharification process are not a problem, because they are treated by high temperature and heat or acid. However, there is the key issue that the microorganisms which produce enzymes must survive and perform its saccharification ability coexisting other various microorganisms, because a lot of microorganisms are brought into the culture apparatus together with cellulosic biomass. In this respect, the present study provided a method that enables the co-culture of various microbiota and C. cellulovorans, which has been difficult until now. Although there are few reports only co-culture C. cellulovorans and one other microbe [28], many experiences can be performed from cellulose to methane using a consortium and the armed C. cellulovorans. Notably, this armed C. cellulovorans is non-GMO (non- Genetically Modified Organisms) and is not modified with genome editing, such as CRISPR/Cas9 [29], therefore anyone can easily cultivate the armed C. cellulovorans from a cellulosic substrate medium and use it anywhere. It is useful and powerful that the armed C. cellulovorans, which anyone can use, degrades orange wastes including d-limonene and the production of methane, which accounts for 66% of the total gas volume, was produced from the consortia.
However, for stable biogas production, it is essential that the carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio) in the culture medium have the desired values. In order for sustainable biogas production from cellulosic biomass, it is necessary to investigate in detail how these components are indispensable for microbial growth change. On the other hand, since the sulfur content contained in the cellulosic biomass is small, simplification of a desulphurization equipment in the biogas plant can be expected.
Moreover, an orange contains beta-cryptoxanthin (β-cry), especially in the orange peel [30]. β-cry is a natural carotenoid pigment, and carotenoids are known to contribute to the defense system of the human body against reactive oxygen species. Inverse associations of serum β-cry with the risk for cancer, diabetes, and liver dysfunction have been reported [31,32,33,34]. The enzymatic degradation of orange peel can extract carotenoids contained in the culture. This means orange peel, which was disposed of so far, can be converted to useful raw material to have functional foods. In addition, the enzymatic saccharification does not decompose the compound by high temperature and pressure and by acid, therefore the enzymatic saccharification is the most advanced process to extract the useful compounds.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed that C. cellulovorans by growing with cellulose instead of cellobiose can coexist with complex microbiota such as methanogenic microbiota. Therefore, it provided a useful method for researching the co-culture of C. cellulovorans with various other microorganisms. Furthermore, C. cellulovorans and methanogenic microflora coexisted with each other while keeping the cellulose degradation ability and the methane production ability. As a result, the biogas was produced containing 66.2% of methane using mandarin orange peel as a carbon source, and when the biogas contains 60% or more of methane, the biogas can be used directly as fuel for a gas engine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T. and H.T.; methodology, Y.T. and H.T.; validation, Y.T. and H.T.; resources, Y.T.; data curation, H.T.; writing—original draft preparation, H.T.; writing—review and editing, Y.T.; supervision, Y.T.; project administration, H.T.; funding acquisition, Y.T.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Daimasa Engineering Co. LTD for sample preparation and assignment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Naik, S.N.; Goud, V.V.; Rout, P.K.; Dalai, A.K. Production of first and second generation biofuels: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, P.M.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Stephens, E.; Marx, U.C.; Mussgnug, J.H.; Posten, C.; Kruse, O.; Hankamer, B. Second generation biofuels: High-efficiency microalgae for biodiesel production. Bioenergy Res. 2008, 1, 20–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brethauer, S.; Studer, M.H. Biochemical conversion processes of lignocellulosic biomass to fuels and chemicals—A review. Chimia 2015, 69, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, K.A.; Zhao, L.; Emptage, M. Bioethanol. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohmann, K.; Baldwin, E.A.; Buslig, B.S. Production of ethanol from enzymatically hydrolyzed orange peel by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 45, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Winniczuk, P.P.; Parish, M.E. Minimum inhibitory concentrations of antimicrobials against microorganisms related to citrus juice. Food Microbiol. 1997, 14, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.G. Removal of peel oil from citrus peel press liquors before anaerobic digestion. Environ. Technol. Lett. 1983, 4, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbafrani, M.; Talebnia, F.; Niklasson, C.; Taherzade, M.J. Protective effect ofencapsulation in fermentation of limonene-contained media and orange peel hydrolyzate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Tamaru, Y. Direct IBE fermentation from mandarin orange wastes by combination of Clostridium cellulovorans and Clostridium beijerinckii. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.; Woods, D.R. Acetone-Butanol Fermentation Revisited. Microbiol. Rev. 1986, 50, 484–524. [Google Scholar]
- Vieiraa, C.F.S.; Filhob, F.M.; Filhoa, R.M.; Marianoa, A.P. Acetone-free biobutanol production: Past and recent advances in the Isopropanol-Butanol-Ethanol (IBE) fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 287, 121425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, R.H.; Kosugi, A. Cellulosomes: Plant-cell-wall-degrading enzyme complexes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleat, R.; Mah, R.A.; Robinson, R. Isolation and characterization of an anaerobic, cellulolytic bacterium, Clostridium cellulovorans sp. nov. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koukiekolo, R.; Cho, H.Y.; Kosugi, A.; Inui, M.; Yukawa, H.; Doi, R.H. Degradation of corn fiber by Clostridium cellulovorans cellulases and hemicellulases and contribution of scaffolding protein CbpA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beukes, N.; Chan, H.; Doi, R.H.; Pletschke, B.I. Synergistic associations between Clostridium cellulovorans enzymes XynA, ManA and EngE against sugarcane bagasse. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2008, 42, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dredge, R.; Radloff, S.E.; van Dyk, J.S.; Pletschke, B.I. Lime pretreatment of sugar beet pulp and evaluation of synergy between ArfA, ManA and XynA from Clostridium cellulovorans on the pretreated substrate. 3 Biotech 2011, 1, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tamaru, Y.; Miyake, H.; Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M.; Doi, R.H. Comparative genomics of the mesophilic cellulosome-producing Clostridium cellulovorans and its application to biofuel production via consolidated bioprocessing. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Bae, J.; Esaka, K.; Morisaka, H.; Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M. Exoproteome profiles of Clostridium cellulovorans on various carbon sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6576–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaru, Y.; Ui, S.; Murashima, K.; Kosugi, A.; Chan, H.; Doi, R.H.; Liu, B. Formation of protoplasts from cultured tobacco cells and Arabidopsis thaliana by the action of cellulosomes and pectate lyase from Clostridium cellulovorans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2614–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, B.G.; Anderson, K.L. Comparison of staining techniques for scanning electron microscopic detection of ultrastructural protuberances on cellulolytic bacteria. Biotech. Histochem. 1998, 73, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, B.G.; Anderson, K.L. Regulation of cellulose inducible structures of Clostridium cellulovorans. Can. J. Microbiol. 1999, 45, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Ni, B.J.; Han, X.; Fan, L.; Yuan, Z. Dissecting microbial community structure and methane-producing pathways of a full-scale anaerobic reactor digesting activated sludge from wastewater treatment by metagenomic sequencing. Microb. Cell Factories 2015, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, H.; Tamaru, Y. Biomethane production from sugar beet pulp under cocultivation with Clostridium cellulovorans and methanogens. AMB Express 2019, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, H.; Maeda, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Tanaka, A. Calorimetric studies of the growth of anaerobic microbes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 122, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.M.; Waghmare, J.S.; Sonawane, K.D.; Waghmare, S.R. Bio-ethanol and bio-butanol production from orange peel waste. Biofuels 2015, 6, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, H.S.; Vadlani, P.V.; Madl, R.L.; Saida, L.; Abeykoon, J.P. Ethanol Production from Orange Peels: Two-Stage Hydrolysis and Fermentation Studies Using Optimized Parameters through Experimental Design. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3422–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaru, Y.; Miyake, H.; Kuroda, K.; Nakanishi, A.; Matsushima, C.; Doi, R.H.; Ueda, M. Comparison of the mesophilic cellulosome-producing Clostridium cellulovorans genome with other cellulosome-related clostridial genomes. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ng, S.K.; Jia, Y.; Cai, M.; Lee, P.K.H. Physiological and molecular characterizations of the interactions in two cellulose-to-methane cocultures. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A Programmable Dual-RNA–Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.M.; Eldridge, A.L.; Beecher, G.R.; Buzzard, I.M.; Bhagwat, S.; Davis, C.S.; Douglas, L.W.; Gebhardt, S.; Haytowitz, D.; Schakel, S. Carotenoid content of U.S. foods: An update of the database. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1999, 12, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluijs, I.; Beulens, J.W.; Grobbee, D.E.; van der Schouw, Y.T. Dietary carotenoid intake is associated with lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly men. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, Y.; Azqueta, A.; Luna, L.; Bonilla, F.; Domínguez, G.; Collins, A.R. The carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin stimulates the repair of DNA oxidation damage in addition to acting as an antioxidant in human cells. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burri, B.J. Beta-cryptoxanthin as a source of vitamin A. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 95, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, F.; Hu, K.Q.; Russell, R.M.; Wang, X.D. β-Cryptoxanthin suppresses the growth of immortalized human bronchial epithelial cells and non-small-cell lung cancer cells and up-regulates retinoic acid receptor β expression. Cancer Cell Biol. 2006, 119, 2084–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).