Bacterial Diversity, Chemical Composition, and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa-Based Total Mixed Ration Silage Inoculated with Lactobacillus reuteri and Lentilactobacillus buchneri
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TMR Silage Preparation
2.2. Fermentation and Chemical Analysis of TMR
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fermentation Profile of TMR Silage Inoculated with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains
3.2. Chemical Characteristics of TMR Silage Inoculated with Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains
3.3. Diversity Parameters of the Bacterial Community of TMR Silage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| TMR | Total mixed ration |
| Lr A4-2 | Lactobacillus reuteri A4-2 |
| Lb 9-2 | Lentilactobacillus buchneri 9-2 |
| CON | Control |
| FM | Fresh material |
| LA | Lactic acid |
| AA | Acetic acid |
| PA | Propionic acid |
| DM | Dry matter |
| WSC | Water-soluble carbohydrate |
| NH3-N | Ammonia nitrogen |
| CP | Crude protein |
| aNDF | Neutral detergent fiber |
| ADF | Acid detergent fiber |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| SCA | Spearman correlation analysis |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
| SEM | Standard error of means |
References
- Gao, R.; Luo, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, M.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z. Effects of Replacing Ensiled-Alfalfa with Fresh-Alfalfa on Dynamic Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Compositions, and Protein Fractions in Fermented Total Mixed Ration with Different Additives. Animals 2021, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, A.V.I.; Lazzari, G.; Jobim, C.C.; Daniel, J.L.P. Ensiling Total Mixed Ration for Ruminants: A Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Bai, C.; Xu, H.; Na, N.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, G.; Liu, S.; Xue, Y. Succession of Bacterial Community During the Initial Aerobic, Intense Fermentation, and Stable Phases of Whole-Plant Corn Silages Treated With Lactic Acid Bacteria Suspensions Prepared From Other Silages. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Xu, S.; Bao, J.; Deng, J.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Z. Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility, and Aerobic Stability of Total Mixed Ration Silage in Response to Varying Proportion Alfalfa Silage. Animals 2022, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum Inoculants Delay Spoilage of High Moisture Alfalfa Silages by Regulating Bacterial Community Composition. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, T.; Gresner, N.; Südekum, K.H. Effect of Wilting Intensity, Dry Matter Content and Sugar Addition on Nitrogen Fractions in Lucerne Silages. Agriculture 2019, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besharati, M.; Palangi, V.; Ghozalpour, V.; Nemati, Z.; Ayaşan, T. Essential Oil and Apple Pomace Affect Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Alfalfa Silage. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 51, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netthisinghe, A.; Woosley, P.; Rowland, N.; Willian, T.; Gilfillen, B.; Sistani, K. Alfalfa Forage Production and Nutritive Value, Fermentation Characteristics and Hygienic Quality of Ensilage, and Soil Properties after Broiler Litter Amendment. Agronomy 2021, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovic, J.; Sokolovic, D.; Markovic, J. Alfalfa-most important perennial forage legume in animal husbandry. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2009, 25, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ling, Q.; Na, N.; Xu, H.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T.; Xue, Y. Effects of Adding Pre-Fermented Fluid Prepared from Red Clover or Lucerne on Fermentation Quality and In Vitro Digestibility of Red Clover and Lucerne Silages. Agriculture 2021, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, B.; Jia, T.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Z. Effects of Different Carbohydrate Sources on Alfalfa Silage Quality at Different Ensiling Days. Agriculture 2021, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Lv, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Pang, H.; Tan, Z. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on the Fermentation Profile and Microbiological Composition of Wheat Fermented Silage Under the Freezing and Thawing Low Temperatures. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 671287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, R.J.; Morrison, S.Y.; Chase, L.E. Varying Proportions of Alfalfa and Corn Silage for Lactating Dairy Cows. 2022. Available online: https://ecommons.cornell.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/4026050f-cab5-456d-83c7-e05e6554ad5e (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle, 8th Revised ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Du, Z.; Cai, Y. Fermentation Regulation and Ethanol Production of Total Mixed Ration Containing Apple Pomace. Fermentation 2023, 9, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nawaz, A.; Hano, C.; Walayat, N.; Lorenzo, J.M. Strategies to Increase the Value of Pomaces with Fermentation. Fermentation 2021, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, R.; Gupta, D.K. Utilization of Pomace from Apple Processing Industries: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perussello, C.A.; Zhang, Z.; Marzocchella, A.; Tiwari, B.K. Valorization of Apple Pomace by Extraction of Valuable Compounds. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 776–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Na, N.; Yin, G.; Liu, S.; Xue, Y. Dynamics of Bacterial and Fungal Communities and Metabolites During Aerobic Exposure in Whole-Plant Corn Silages With Two Different Moisture Levels. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, H.; Sun, L.; Na, N.; Xu, H.; Chang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, Y. Bacterial succession pattern during the fermentation process in whole-plant corn silage processed in different geographical areas of northern China. Processes 2021, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Ke, W.C.; Ding, W.R.; Ding, L.M.; Xu, D.M.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, P.; Yang, F.Y. Profiling of metabolome and bacterial community dynamics in ensiled Medicago sativa inoculated without or with Lactobacillus plantarum or Lactobacillus buchneri. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Niu, H.; Tong, Q.; Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Ma, D. The Microbiota Dynamics of Alfalfa Silage During Ensiling and After Air Exposure, and the Metabolomics After Air Exposure Are Affected by Lactobacillus casei and Cellulase Addition. Front. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 519121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, Y. Dynamics of Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Community in High-Moisture Alfalfa Silage with or without Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.J.; Hu, W.; Mills, J.A.; Kung, L. The Development of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Lactobacillus buchneri and Their Effects on the Fermentation of Alfalfa Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 5005–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.P.; Pereira, O.G.; Leandro, E.S.; Da Silva, T.C.; Ribeiro, K.G.; Mantovani, H.C.; Santos, S.A. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria with Bacteriocinogenic Potential on the Fermentation Profile and Chemical Composition of Alfalfa Silage in Tropical Conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Bai, J.; Mudassar, S.; Muhammad, I.; Guo, X. Ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase pretreatments of corn stalk silage at two different temperatures: Ensiling characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.A. An automated procedure for the determination of soluble carbohydrates in herbage. JSFA 1977, 28, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunniff, P. Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. J. AOAC Int. 1997, 80, 127A. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.H.; Ding, Z.T.; Chen, X.Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ke, W.C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Usman, S.; Guo, X. The effects of Lactobacillus plantarum with feruloyl esterase-producing ability or high antioxidant activity on the fermentation, chemical composition, and antioxidant status of alfalfa silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 273, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Xu, D.; Xie, D.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Effects of antibacterial peptide-producing Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus buchneri on fermentation, aerobic stability, and microbial community of alfalfa silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, X.; Ren, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, C.; Zhong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H. Influence of Peanut, Sorghum, and Soil Salinity on Microbial Community Composition in Interspecific Interaction Zone. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 678250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jia, S.; Yang, F.; et al. Impacts of Low Temperature and Ensiling Period on the Bacterial Community of Oat Silage by SMRT. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriola, K.G.; Kim, S.C.; Staples, C.R.; Adesogan, A.T. Effect of applying bacterial inoculants containing different types of bacteria to corn silage on the performance of dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3973–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Sun, R.; Zi, X.; Li, M. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on Silage Fermentation and Bacterial Community of Three Tropical Forages. Front. Anim. Sci. 2022, 3, 878909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ji, C.; Mu, J.; Wang, Y.; Harrison, M.T.; Liu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Microbial fermentation in co-ensiling forage-grain ratoon rice and maize to improve feed quality and enhance the sustainability of rice-based production systems. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2025, 20, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, P.; Tremblay, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F. Dynamic Succession of Microbiota during Ensiling of Whole Plant Corn Following Inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri and Lactobacillus hilgardii Alone or in Combination. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Sun, L.; Xin, X.; Xu, L.; Du, S. Physicochemical characteristics and microbial community succession during oat silage prepared without or with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02228-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xin, X.; Xu, L.; Du, S. Fermentation Characteristics, Microbial Compositions, and Predicted Functional Profiles of Forage Oat Ensiled with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum or Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Fermentation 2022, 8, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Xia, G.; Cao, Y. Effects of replacing commercial material with apple pomace on the fermentation quality of total mixed ration silage and its digestibility, nitrogen balance and rumen fermentation in wethers. Grassl. Sci. 2020, 66, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigh, Y.A.; Ganai, A.M.; Ahmad, H.A. Utilisation of Apple pomace as livestock feed: A review. Indian J. Small Rumin. 2015, 21, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Yu, M.; Du, J.; Zhao, T.; Yi, Q.; Tang, H.; Yuan, B. The Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri on the Fermentation Quality, In Vitro Digestibility, and Aerobic Stability of Silphium perfoliatum L. Silage. Animals 2024, 14, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
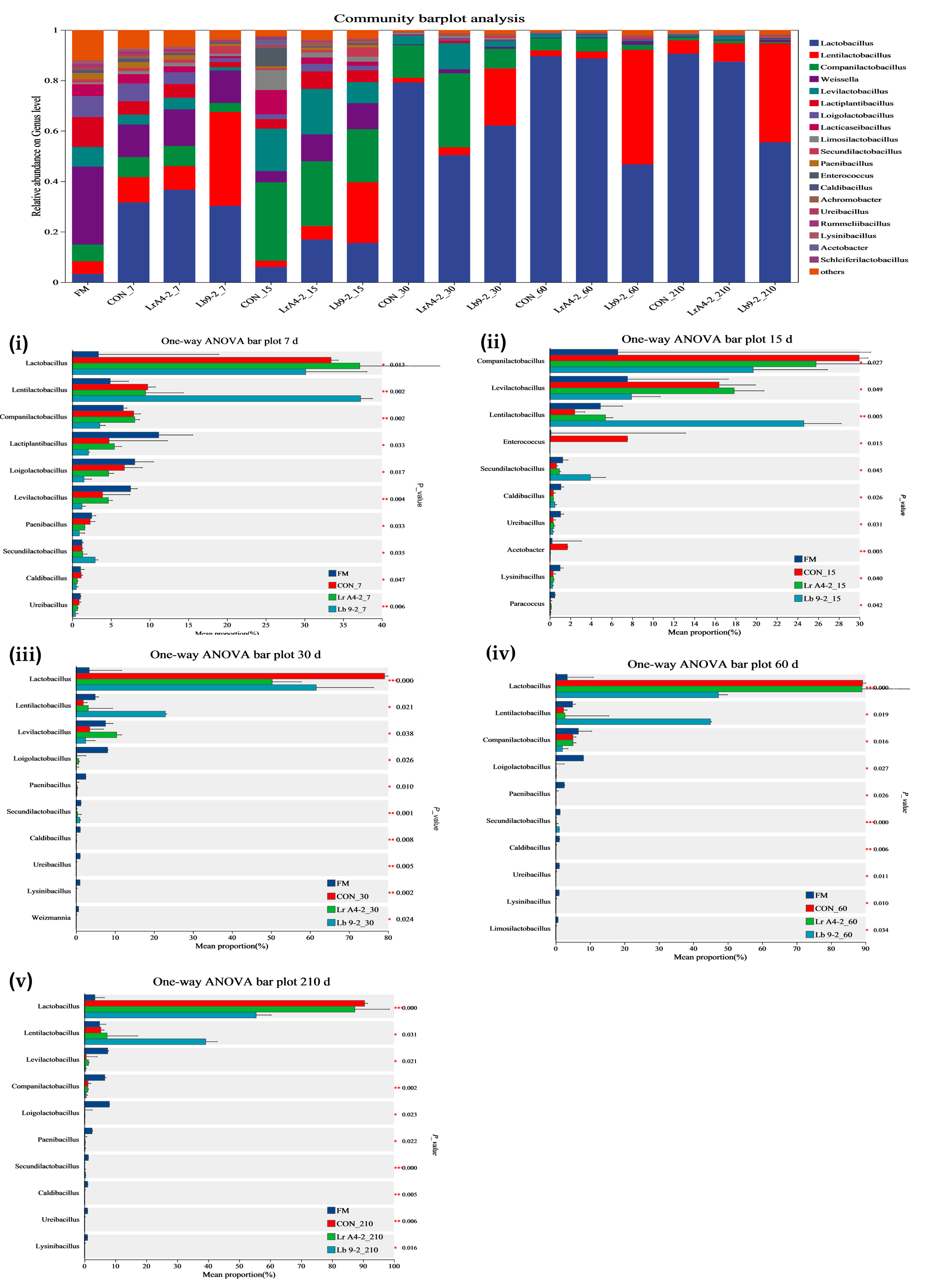
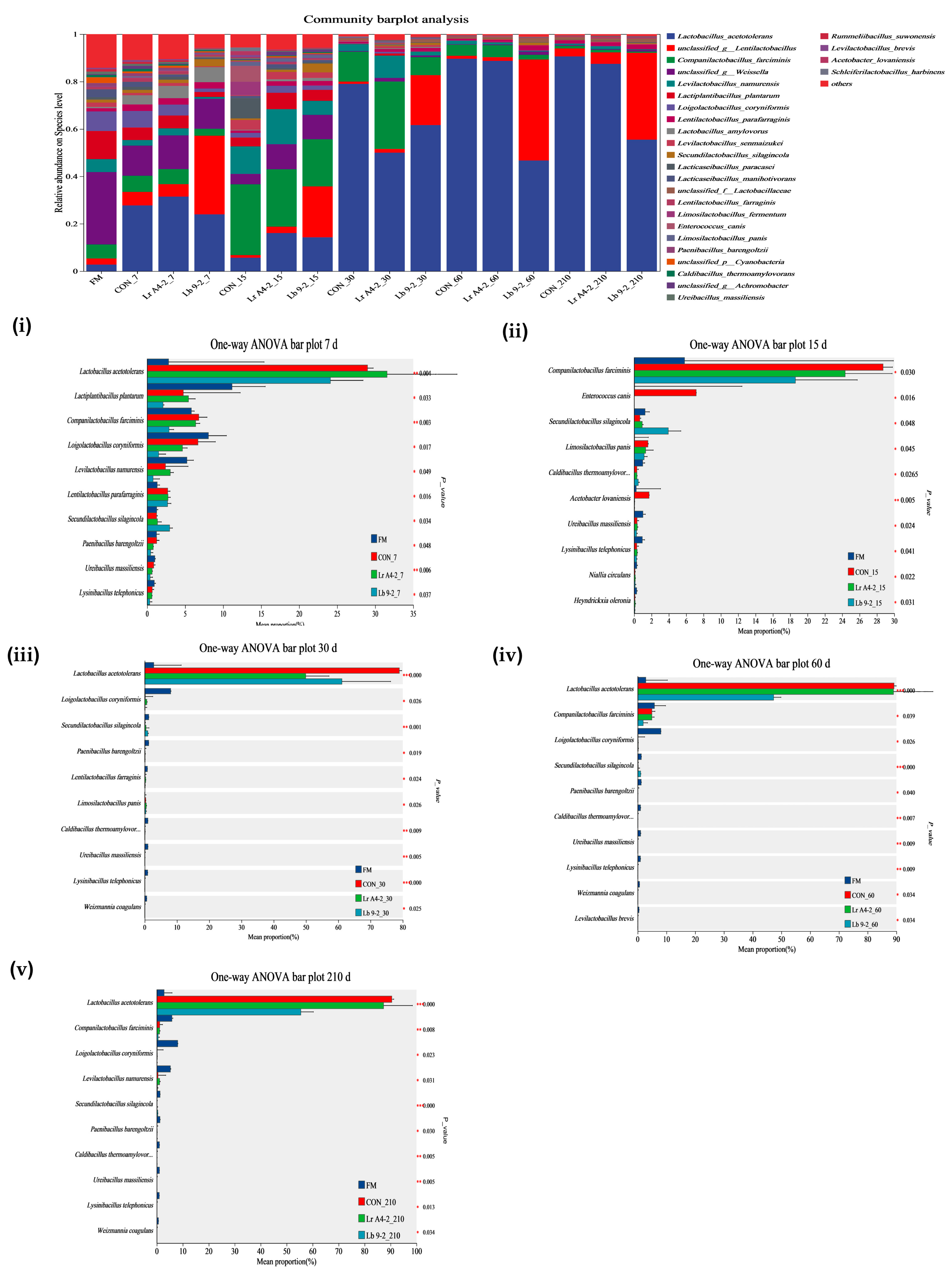


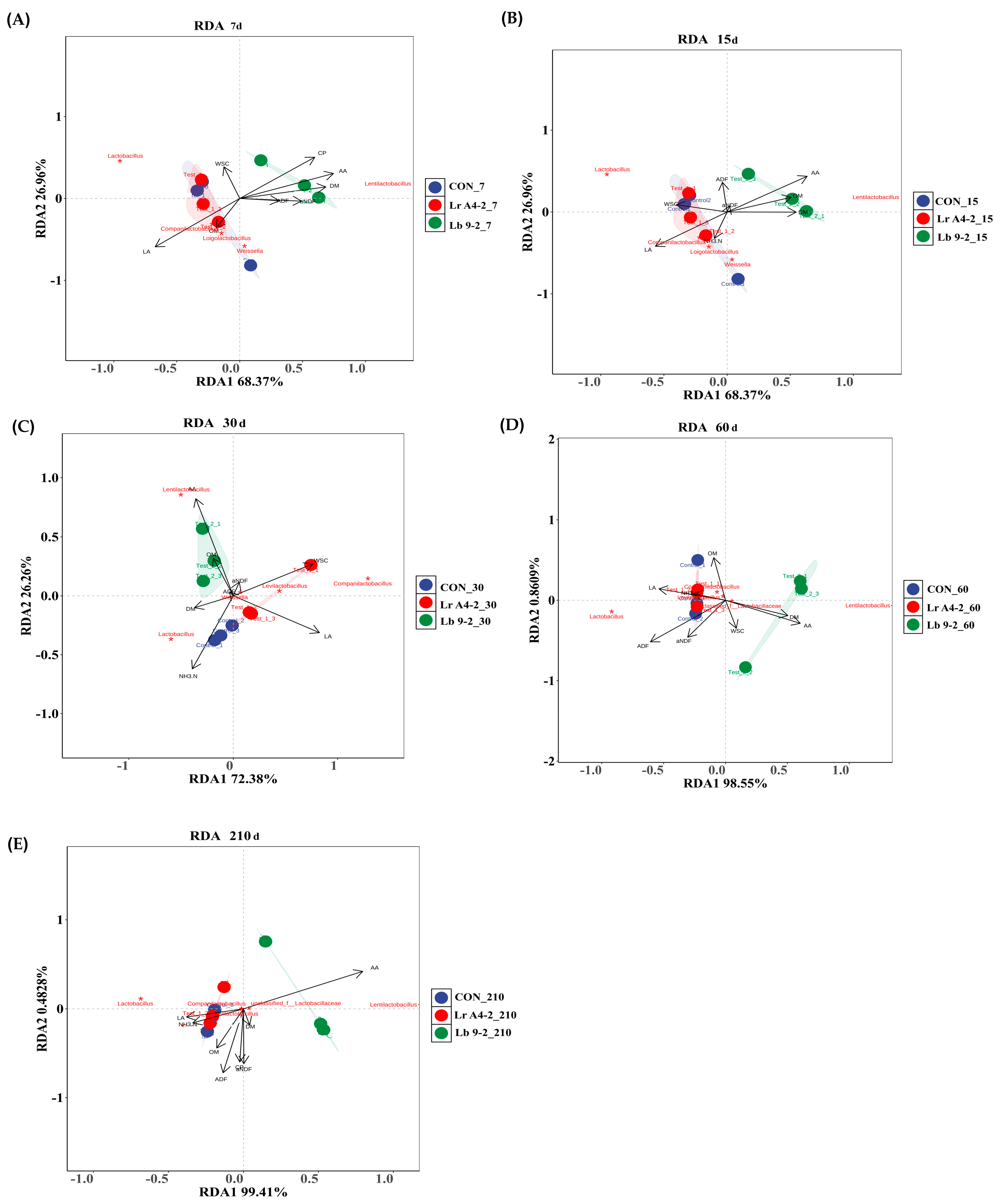
| Items | Dietary Treatment 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lr A4-2 TMR | Lb 9-2 TMR | Control TMR | |
| Ingredients (% DM) | |||
| Whole-crop corn silage | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| Apple pomace | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| Fresh alfalfa | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| Concentrate Corn grain (50%)
| 47 | 47 | 47 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 3 Chemical composition (% DM) | |||
| DM | 45.8 | 45.8 | 45.8 |
| aNDF | 26.7 | 26.7 | 26.7 |
| ADF | 18.5 | 18.5 | 18.5 |
| CP | 16.7 | 16.7 | 16.7 |
| Ca | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 |
| P | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| Item | pH | LA | AA | PA | WSC | NH3-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/kg DM | ||||||
| Ensiling duration | ||||||
| 7 d | 4.360 ABC | 32.44 C | 16.99 C | 4.336 A | 34.66 A | 14.48 B |
| 15 d | 4.313 C | 37.09 BC | 20.62 C | 6.193 AB | 27.96 A | 18.14 B |
| 30 d | 4.320 ABC | 43.88 ABC | 26.43 BC | 8.590 ABC | 25.43 A | 21.92 B |
| 60 d | 4.380 B | 51.1 AB | 35.73 AB | 14.29 BC | 21.06 A | 25.86 A |
| 210 d | 4.513 A | 53.73 A | 44.70 A | 15.17 C | 16.98 A | 26.95 A |
| Inoculation | ||||||
| Control | 4.370 a | 42.03 a | 25.21 a | 4.860 a | 30.46 a | 18.11 a |
| Lr A4-2 | 4.382 a | 49.08 a | 28.15 a | 3.080 a | 25.38 b | 14.60 b |
| Lb 9-2 | 4.380 a | 39.64 a | 33.32 a | 5.070 a | 38.76 a | 12.57 c |
| SEM 1 | 0.034 | 1.425 | 1.196 | 0.260 | 2.420 | 0.425 |
| p-value | ||||||
| T | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| D | 0.856 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| T × D | 0.870 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Item | DM, g/kg FW | aNDF | ADF | CP | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/kg DM | |||||
| Ensiling duration | |||||
| 7 d | 444.3 AB | 275.6 A | 192.1 A | 173.8 A | 102.7 A |
| 15 d | 450.8 A | 290.6 A | 197.7 A | 177.4 A | 101.1 A |
| 30 d | 439.2 B | 290.0 A | 198.9 A | 181.3 A | 110.5 A |
| 60 d | 429.8 AB | 279.6 A | 196.5 A | 187.5 A | 104.5 A |
| 210 d | 433.6 AB | 191.8 A | 190.7 A | 714.1 A | 106.1 A |
| Inoculation | |||||
| Control | 496.8 a | 291.1 b | 194.1 a | 202.2 a | 84.86 a |
| Lr A4-2 | 497.3 a | 300.1 a | 200.1 a | 203.9 a | 81.06 a |
| Lb 9-2 | 491.5 a | 300.5 a | 203.8 a | 200.4 a | 77.03 a |
| SEM 1 | 0.622 | 0.802 | 0.607 | 0.467 | 0.667 |
| p-value | |||||
| T | <0.001 | 0.057 | 0.432 | 0.017 | 0.373 |
| D | 0.099 | 0.096 | 0.202 | 0.086 | 0.339 |
| T × D | 0.394 | 0.351 | 0.387 | 0.345 | 0.092 |
| Item | Shannon | ACE | Chao1 | Simpson | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensiling duration | |||||
| 7 d | 2.66 A | 357 A | 455 A | 0.14 B | 0.994 C |
| 15 d | 2.45 A | 350 A | 308 B | 0.15 B | 0.996 B |
| 30 d | 1.23 B | 216 A | 184 C | 0.46 AB | 0.997 A |
| 60 d | 0.76 B | 244 A | 162 C | 0.66 A | 0.998 A |
| 210 d | 0.75 B | 211 A | 145 C | 0.67 A | 0.998 A |
| Inoculation | |||||
| Control | 1.41 a | 315 a | 251 ab | 0.513 c | 0.996 a |
| Lr A4-2 | 1.67 b | 300 a | 239 a | 0.322 a | 0.997 a |
| Lb 9-2 | 1.63 a | 302 a | 262 b | 0.430 b | 0.997 a |
| SEM 1 | 0.135 | 47.24 | 30.71 | 0.039 | 0.001 |
| p-value | |||||
| T | 0.009 | 0.753 | 0.866 | <0.001 | 0.916 |
| D | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| T × D | 0.001 | 0.236 | 0.208 | <0.001 | 0.296 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanif, A.; Li, F.; Usman, S.; Sheoran, N.; Guo, X. Bacterial Diversity, Chemical Composition, and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa-Based Total Mixed Ration Silage Inoculated with Lactobacillus reuteri and Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Fermentation 2025, 11, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040164
Hanif A, Li F, Usman S, Sheoran N, Guo X. Bacterial Diversity, Chemical Composition, and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa-Based Total Mixed Ration Silage Inoculated with Lactobacillus reuteri and Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Fermentation. 2025; 11(4):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040164
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanif, Anum, Fuhou Li, Samaila Usman, Neha Sheoran, and Xusheng Guo. 2025. "Bacterial Diversity, Chemical Composition, and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa-Based Total Mixed Ration Silage Inoculated with Lactobacillus reuteri and Lentilactobacillus buchneri" Fermentation 11, no. 4: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040164
APA StyleHanif, A., Li, F., Usman, S., Sheoran, N., & Guo, X. (2025). Bacterial Diversity, Chemical Composition, and Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa-Based Total Mixed Ration Silage Inoculated with Lactobacillus reuteri and Lentilactobacillus buchneri. Fermentation, 11(4), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040164







