Modeling the Viscosity of Concentrated Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Dilute Dispersions
2.2. Non-Dilute Dispersions
3. New Viscosity Model for Concentrated Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions
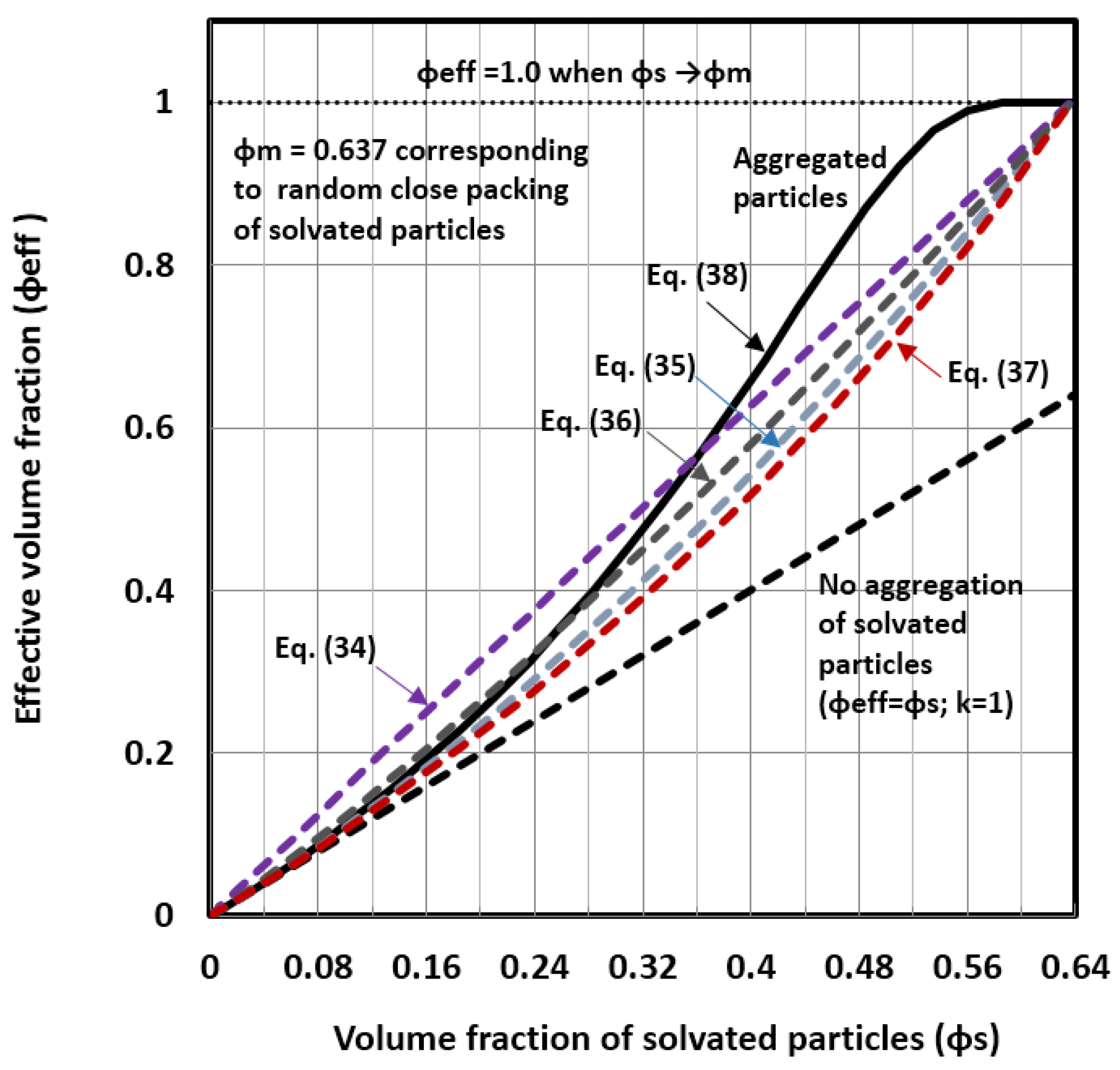
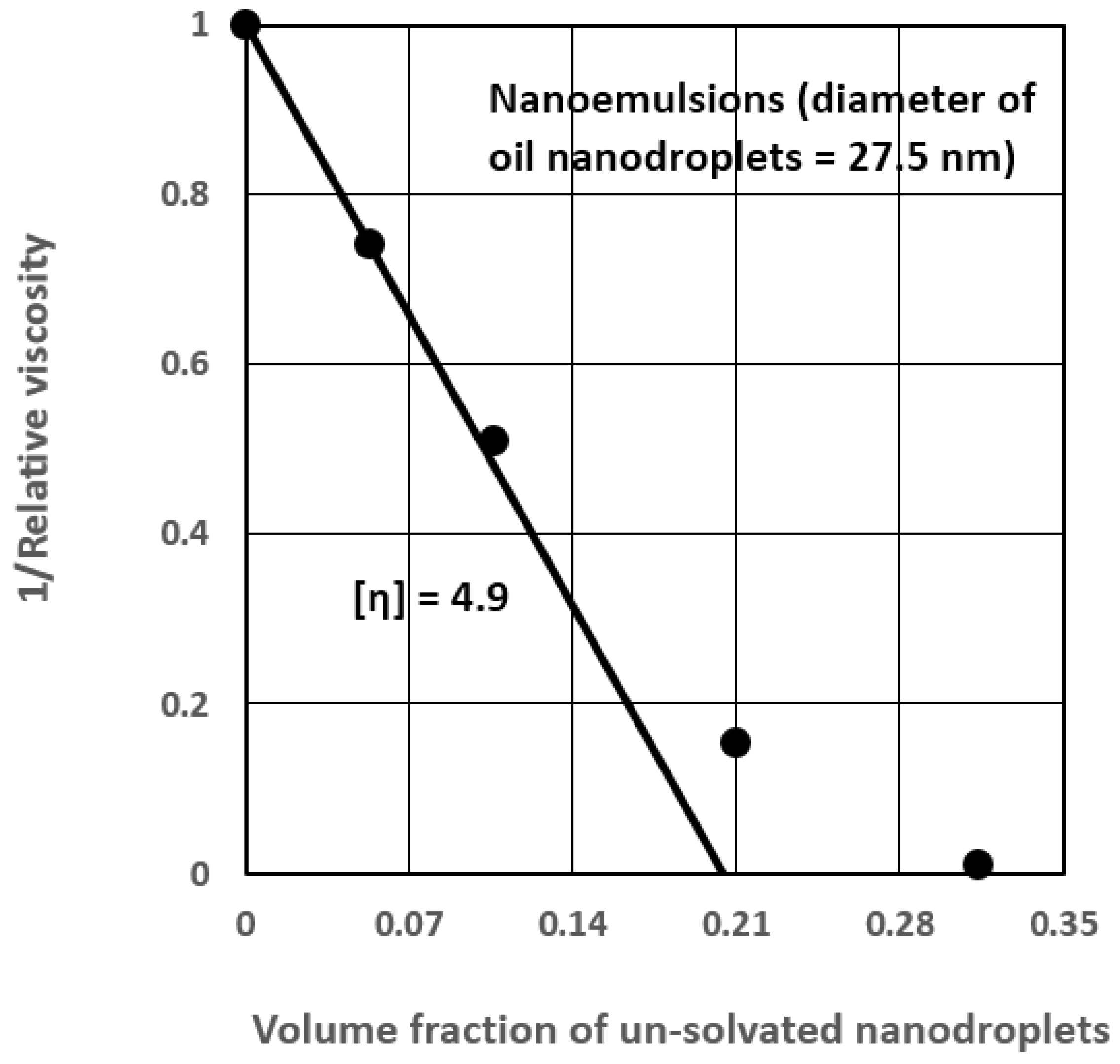
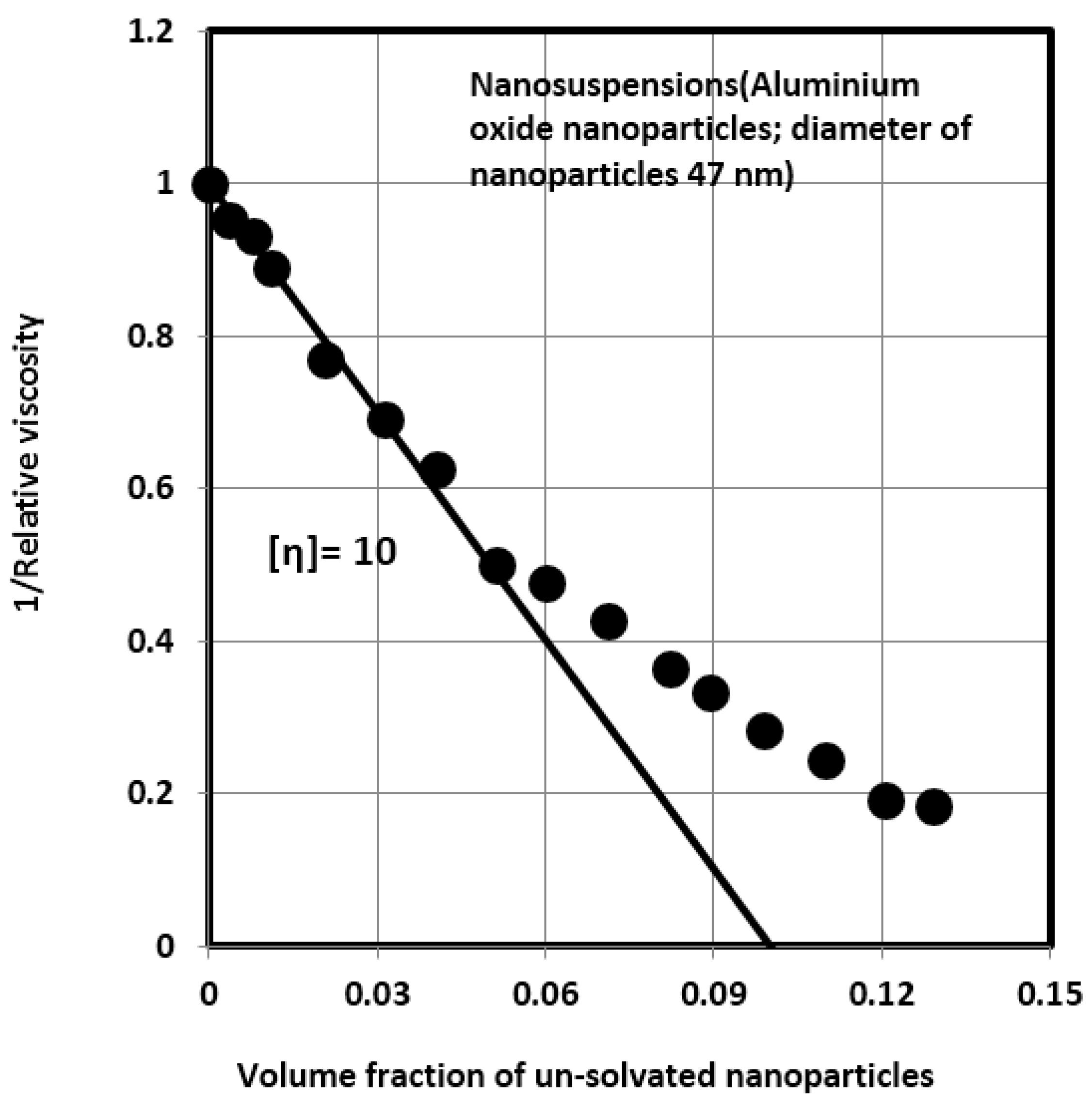
Estimation of the Solvation and Aggregation Coefficients
4. Comparison of Model Predictions with Experimental Data and Discussion
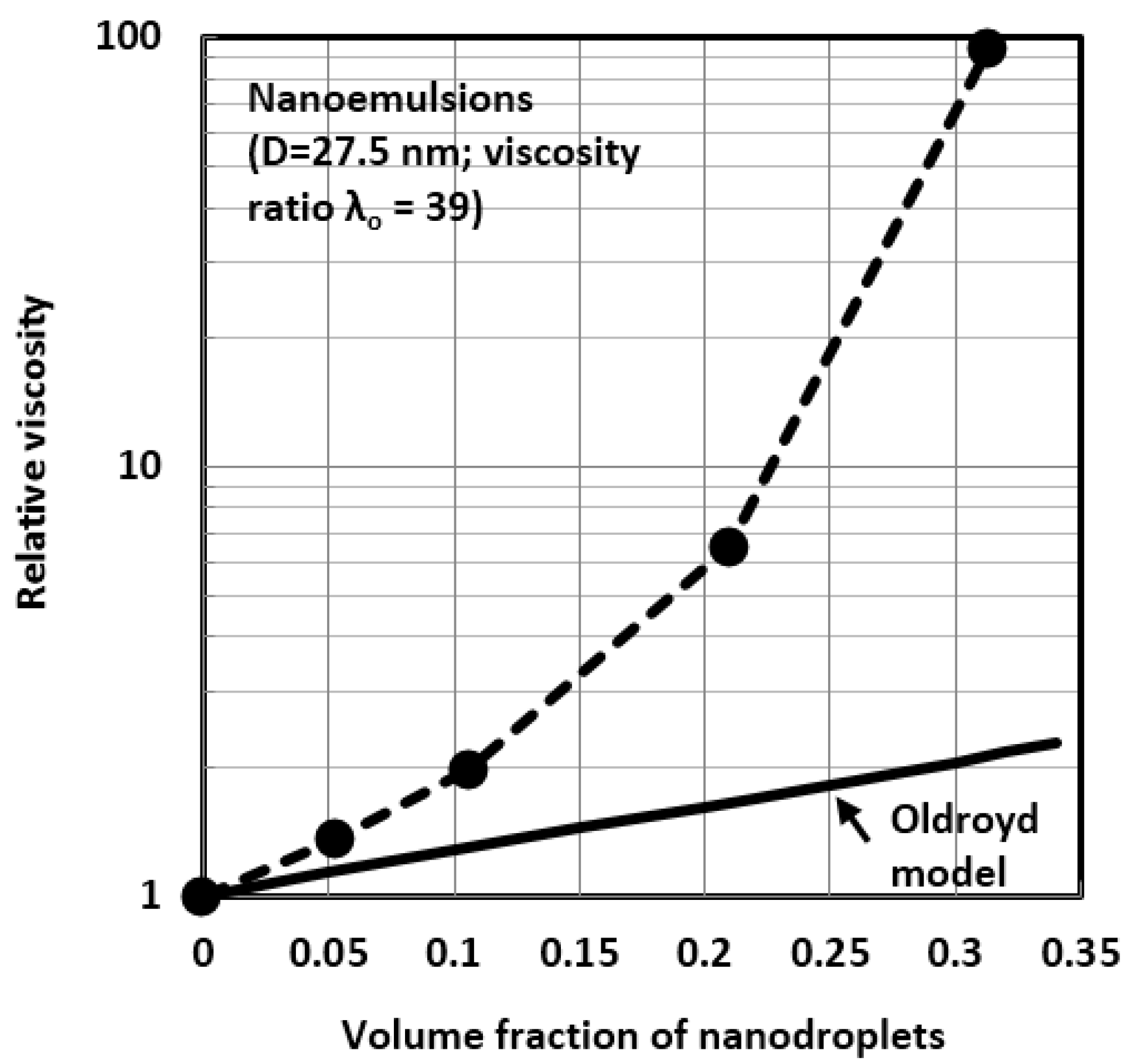
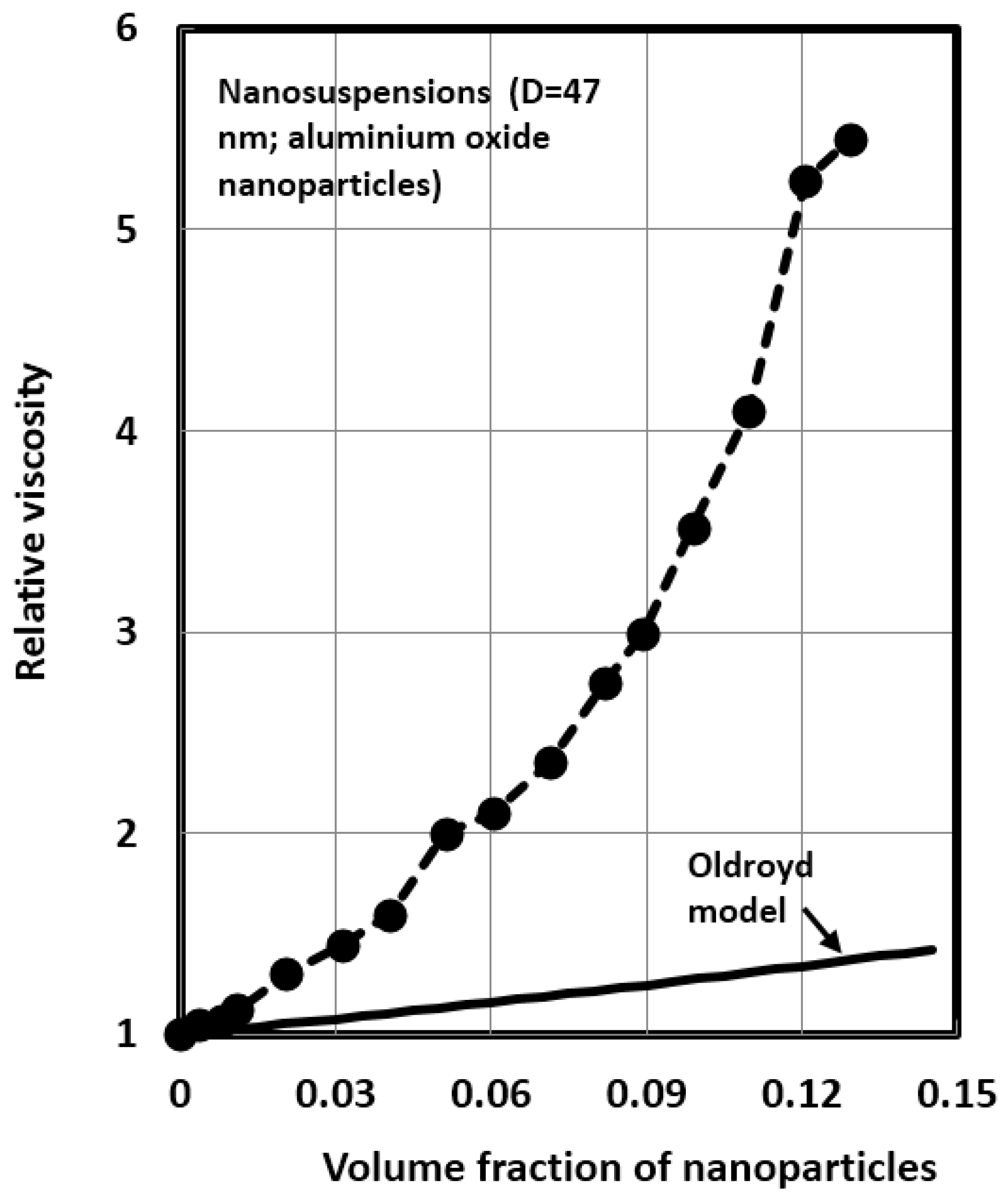
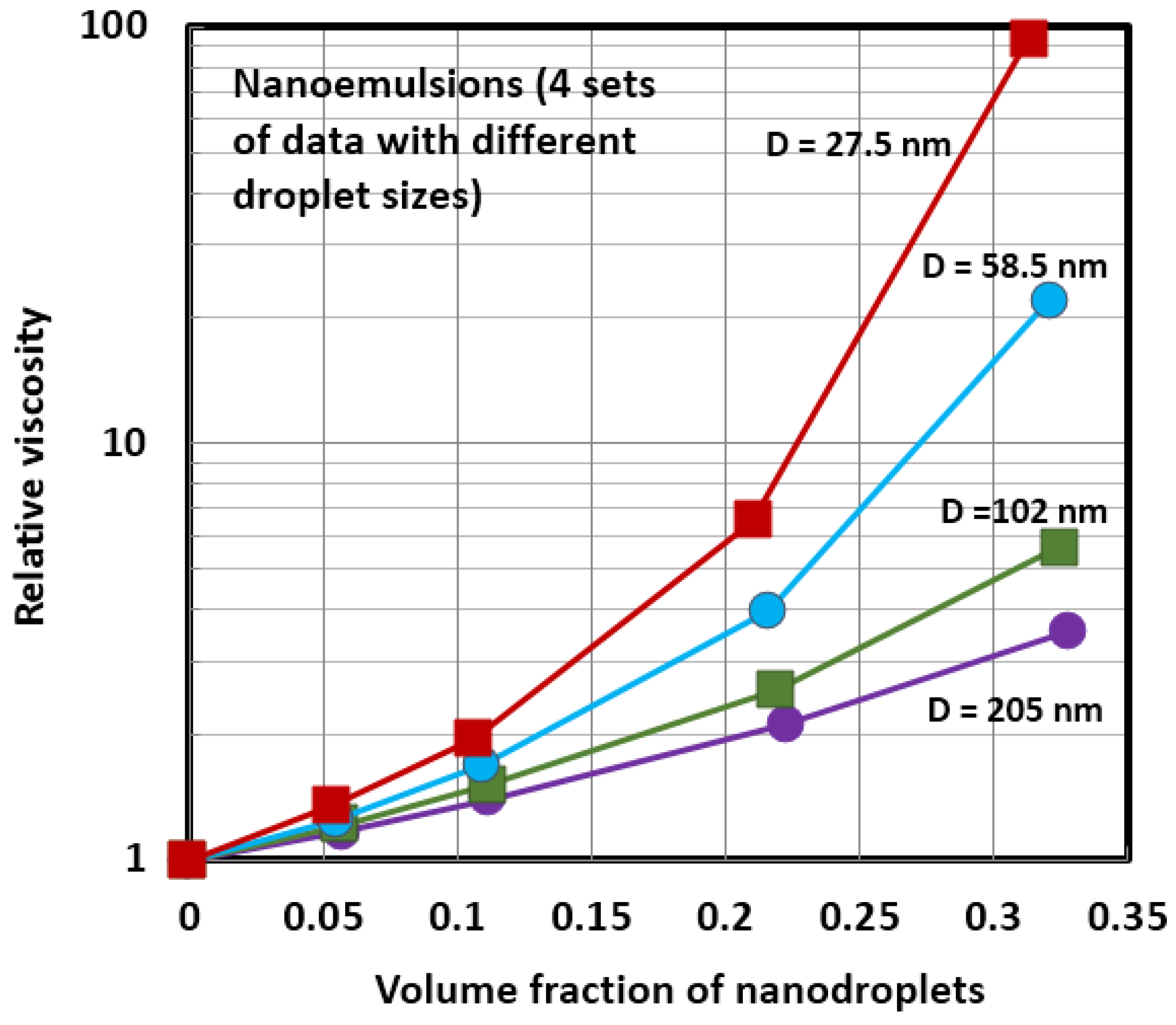
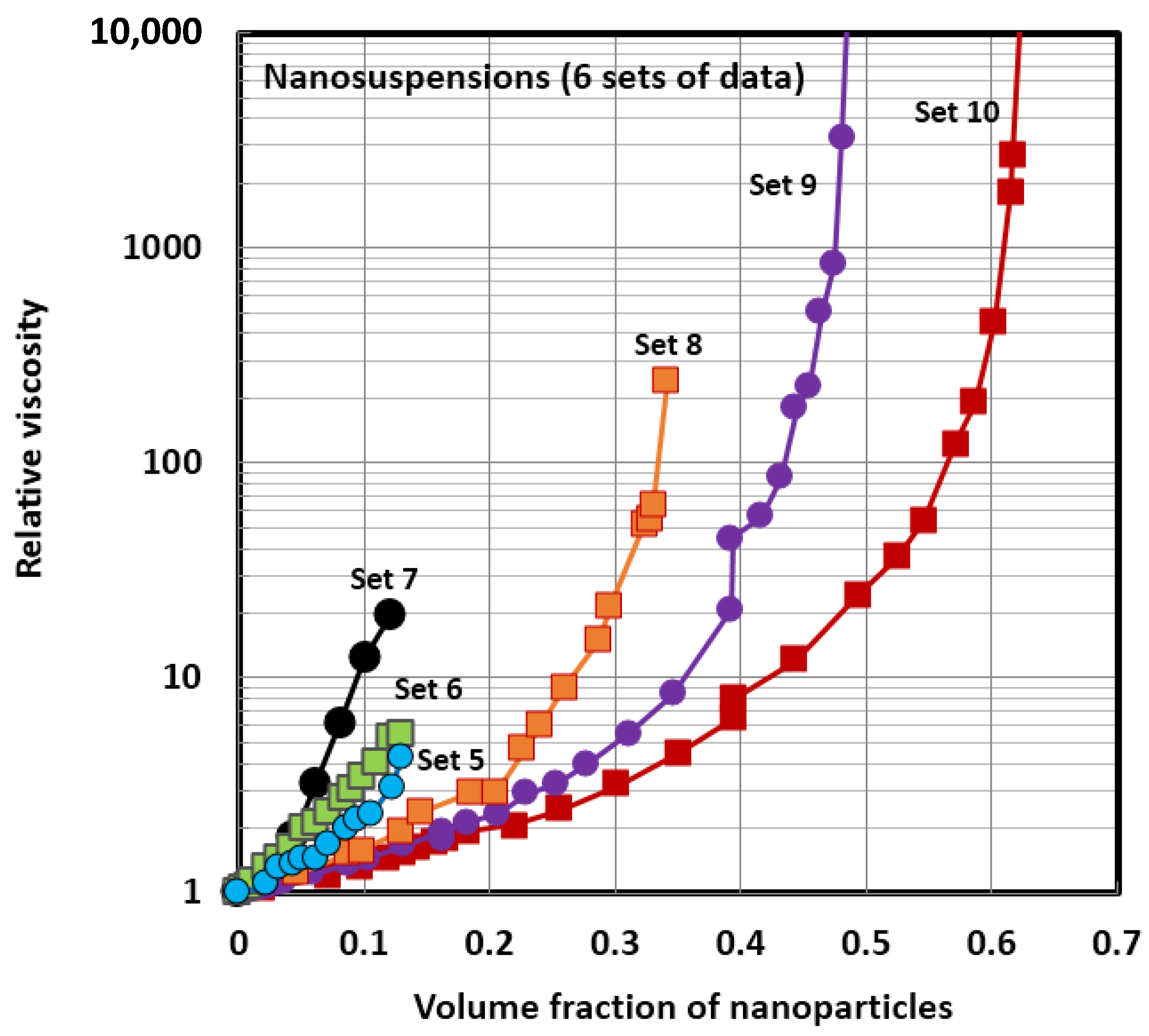
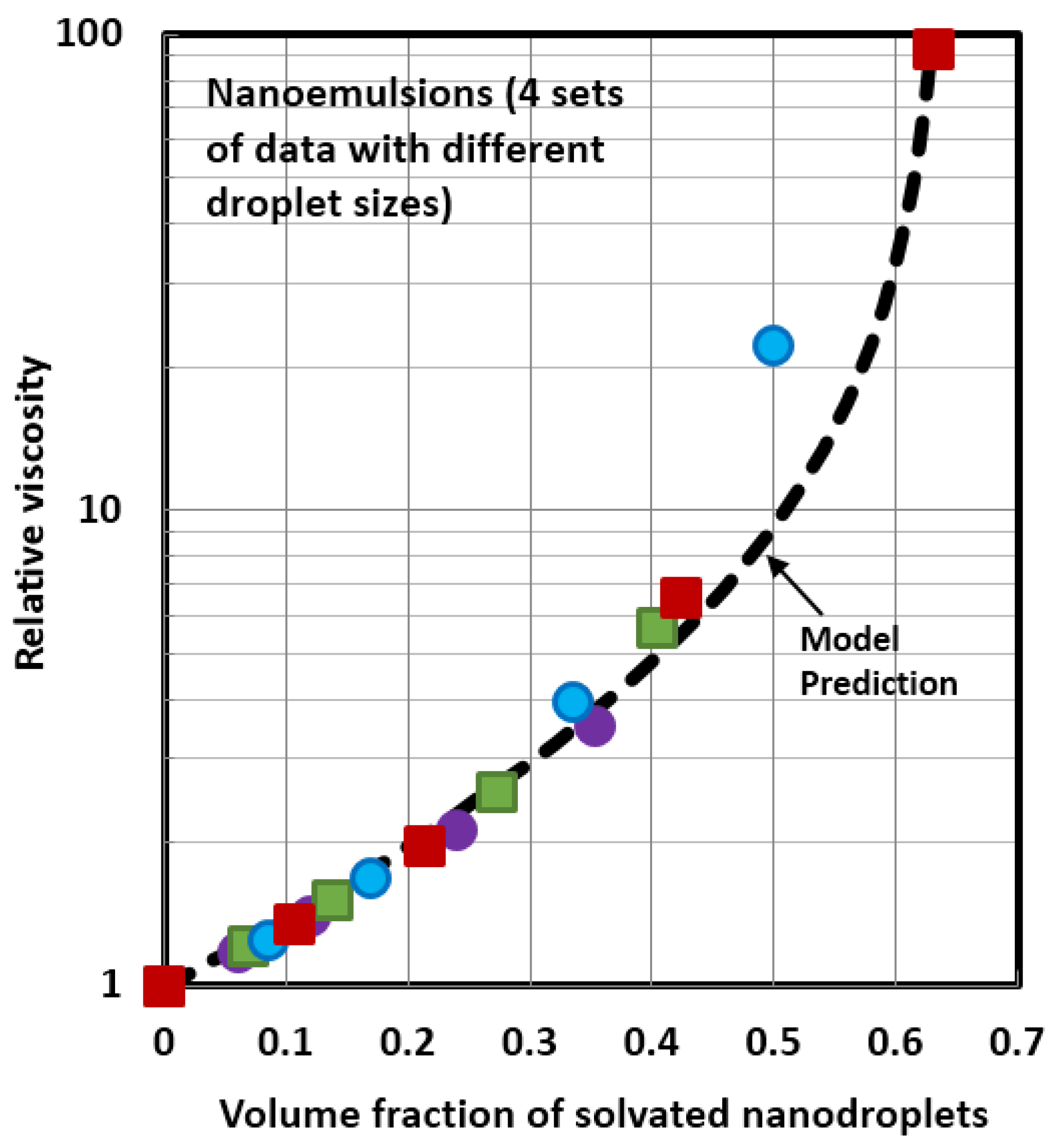
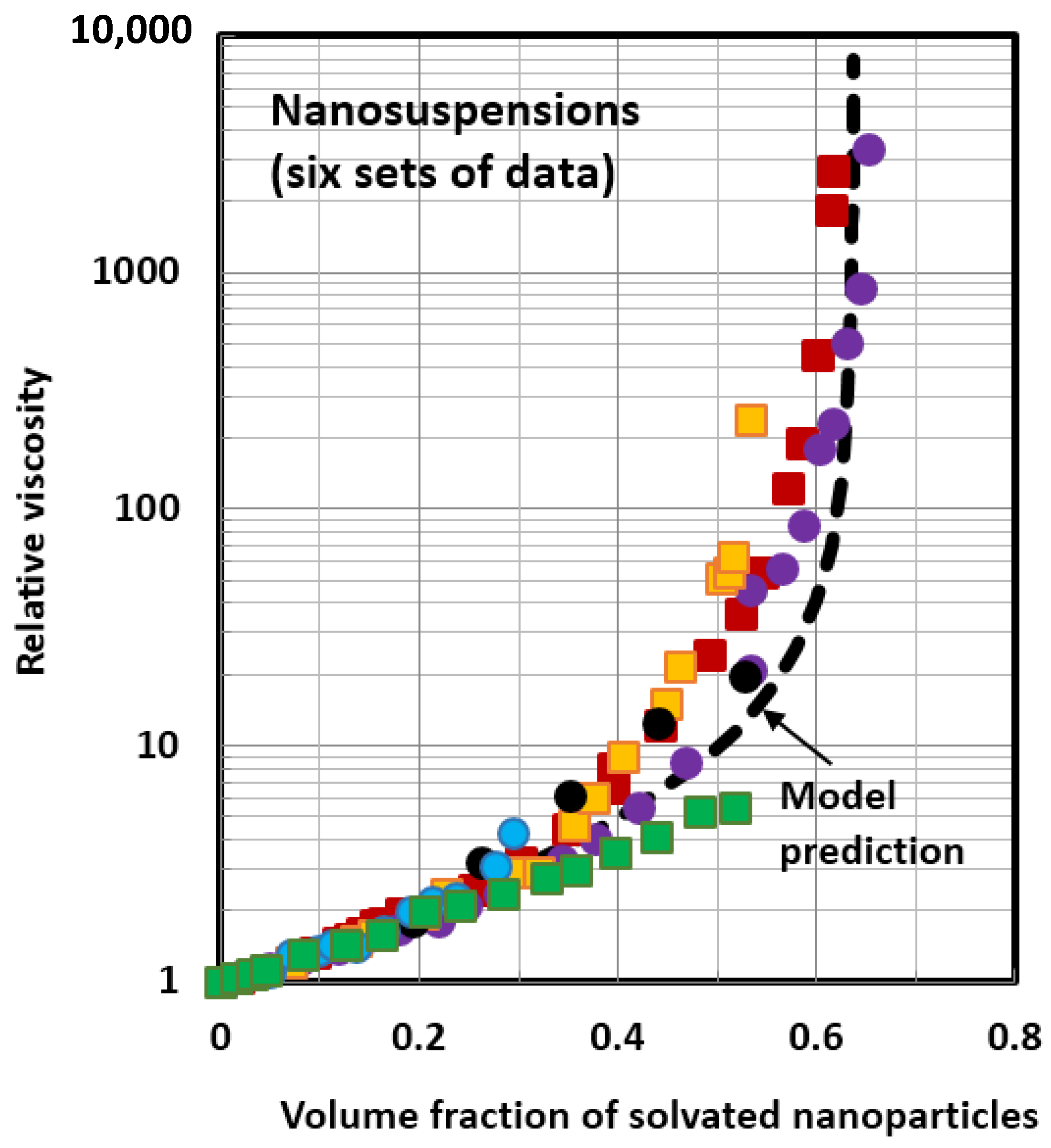
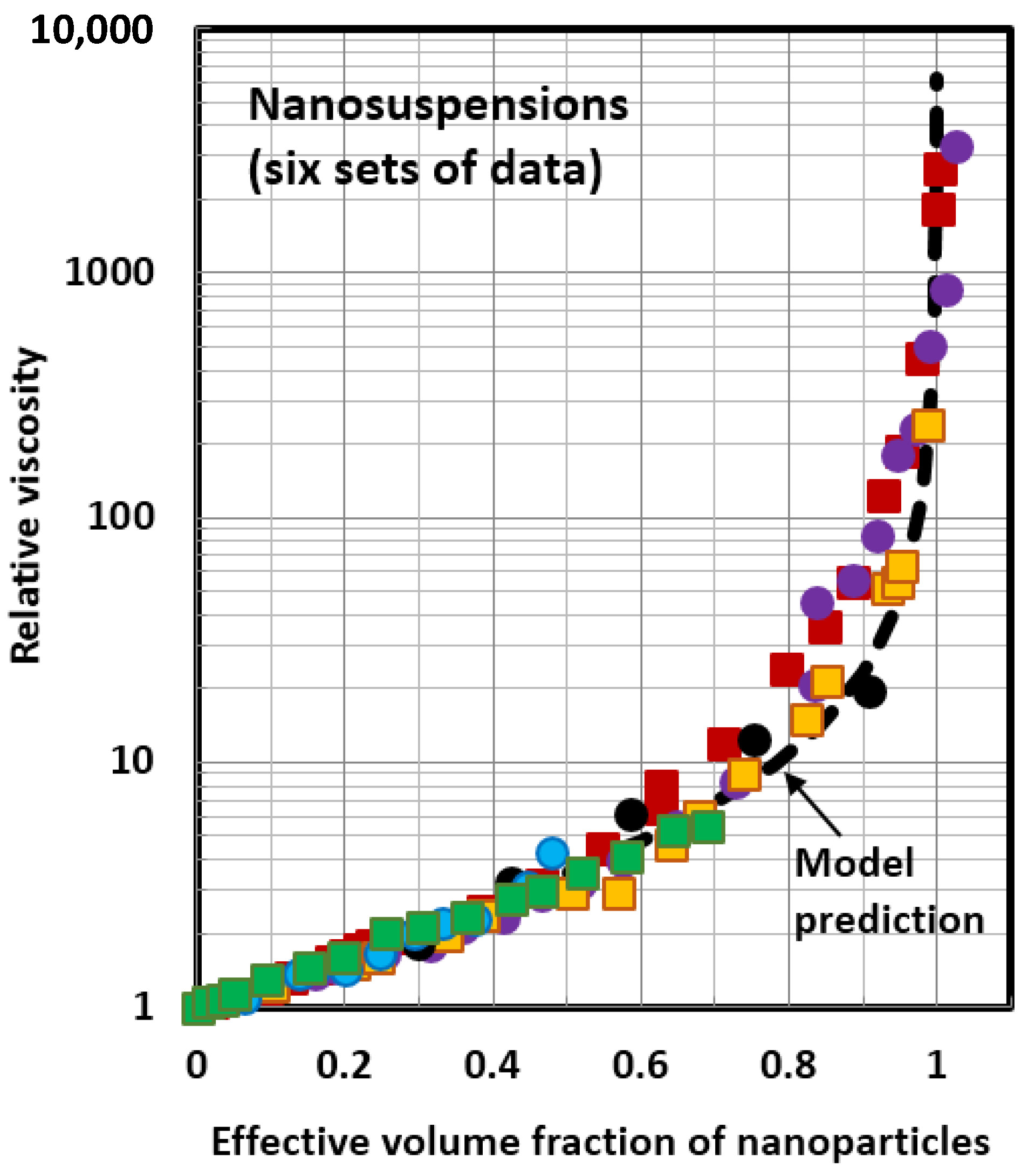
4.1. Scaling of Relative Viscosity of Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions
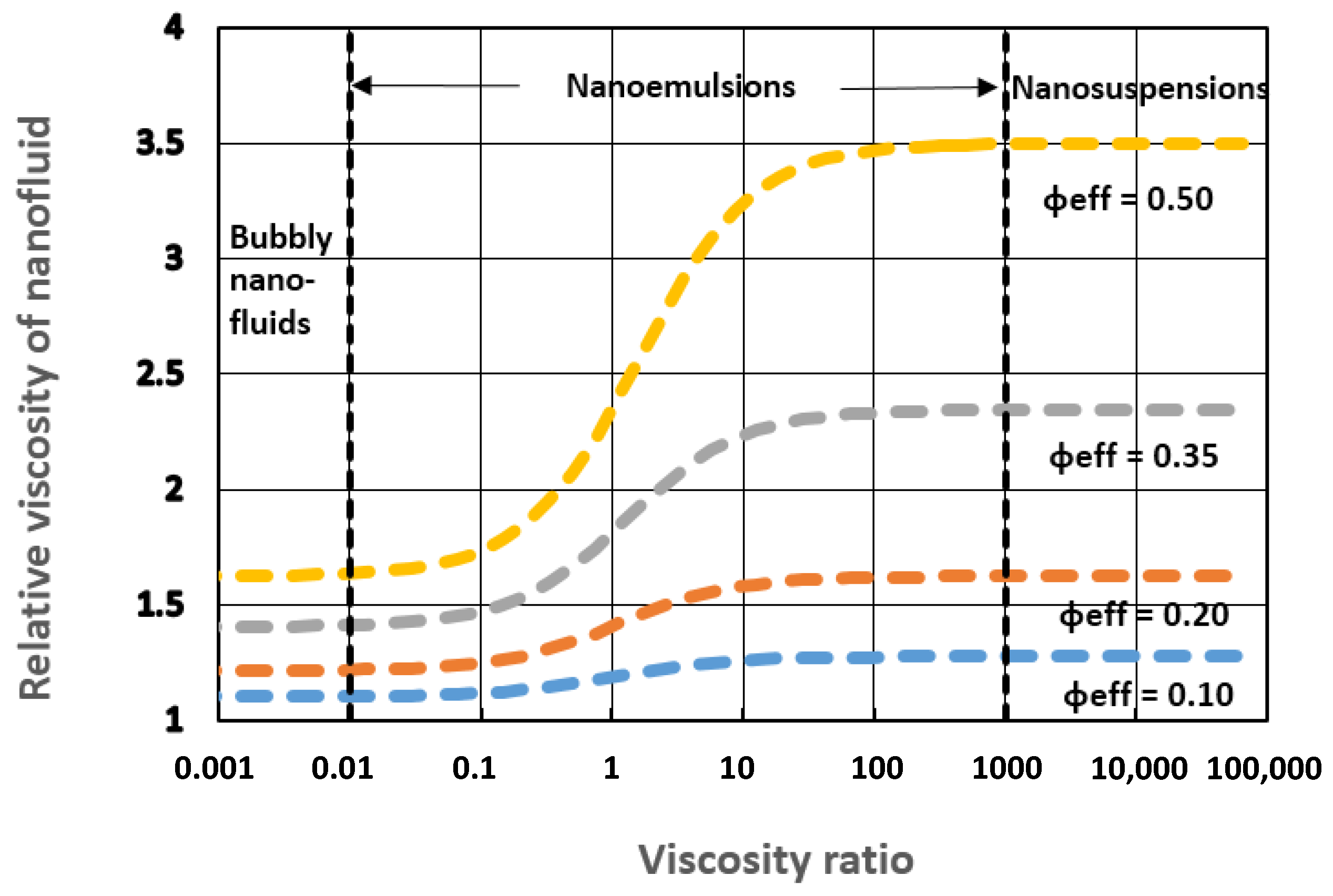
4.2. Influence of Viscosity Ratio on the Relative Viscosity of Nanoemulsions
5. Conclusions
- •
- The relative viscosity of a nanofluid is strongly affected by factors such as solvation and aggregation of nanoparticles/nanodroplets. In the case of nanoemulsions, the additional factor affecting the viscosity is the viscosity ratio (ratio of nanodroplet viscosity to base fluid viscosity).
- •
- The relative viscosity data for different nanofluids can be collapsed together on to a single unique curve if the data are plotted as relative viscosity versus volume fraction of solvated nanoparticles/nanodroplets. This scaling approach is valid for both nanosuspensions and nanoemulsions.
- •
- A new modified version of the Oldroyd model describes the relative viscosity versus particulate concentration behavior of nanoemulsions and nanosuspensions reasonably well. The model takes into consideration the influences of the viscosity ratio, solvation and aggregation of nanoparticles/nanodroplets.
- •
- The influence of the viscosity ratio on the relative viscosity of nanoemulsions is important. The relative viscosity of a nanoemulsion increases substantially with the increase in the viscosity ratio.
- •
- Systematic experimental studies on the effect of viscosity ratio on viscous behavior of nanoemulsions are lacking. More work needs to be done in this area.
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, S.K.; Choi, S.U.S.; Yu, W.; Pradeep, T. Nanofluids; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.R.; Agrawal, Y.K. Nanosuspension: An approach to enhance solubility of drugs. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. Stability of nanosuspensions in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, P.; Kumar, G.A. Nanosuspension technology: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Pharmaceutical. Sci. 2010, 2, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, N.; Farhadi, M.; Ganji, D.D.; Sedighi, K. Experimental investigation on the viscosity of nanofluids. Int. J. Eng. 2012, 25, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubul, I.M.; Saidur, R.; Amalina, M.A. Latest developments on the viscosity of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Ghosh, P.; Sarkar, J. Investigation of thermal conductivity and viscosity of nanofluids. J. Environ. Res. Dev. 2012, 7, 768–777. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.C.M.; Kumar, J.; Suresh, S. Review of nanofluid theoretical viscosity models. Int. J. Eng. Innov. Res. 2012, 1, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, F.; Kwek, D.; Crivoi, A. Viscosity affected by nanoparticle aggregation in Al2O3-water nanofluids. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, B.; Hammouda, B. Thermal conductivity and viscosity of self-assembled alcohol/polyalphaolefin nanoemulsion fluids. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Shahrjerdi, A.; Vazifeshenas, Y. A review of relations for physical properties of nanofluids. Australian J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 417–435. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Park, S.D.; Kang, S.; Bang, I.C.; Kim, J.H. Investigation of viscosity and thermal conductivity of SiC nanofluids for heat transfer applications. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namburu, P.K.; Kulkarni, D.P.; Misra, D.; Das, D.K. Viscosity of copper oxide nanoparticles dispersed in ethylene glycol and water mixture. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2007, 32, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Desgranges, F.; Galanis, N.; Roy, G.; Mare, T.; Boucher, S.; Angue Mintsa, H. Viscosity data for Al2O3—Water nanofluid—Hysteresis: Is heat transfer enhancement using nanofluids reliable? Int. J. Thermal Sci. 2008, 47, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Mujumdar, A.S. Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: A review. Int. J. Ther. Sci. 2007, 46, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Mujumdar, A.S. A review of nanofluids. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 25, 613–630. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Ding, Y.; He, T.; Tan, C. Rheological behavior of ethylene glycol based titania nanofluids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 444, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Desgranges, F.; Roy, G.; Galanis, N.; Mare, T.; Boucher, S.; Angue Mintsa, H. Temperature and particle-size dependent viscosity data for water-based nanofluids—Hysteresis phenomenon. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2007, 28, 1492–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. New models for the viscosity of nanofluids. J. Nanofluids 2014, 3, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, M.; Garg, J.; Kang, Y.T.; Chen, G. Thermal conductivity and viscosity of water-in-oil nanoemulsions. Coll. Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 326, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, S.; Puupponen, S.; Merilainen, A.; Joneidi, A.; Seppala, A.; Saari, K.; Ala-Nissila, T. Turbulent heat transfer characteristics in a circular tube and thermal properties of N-decane-in-water nanoemulsion fluids and micelles-in-water fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 81, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chao, L.; Jian, X.; Hao, J.; Sun, D. Highly stable concentrated nanoemulsions by the phase inversion composition method at elevated temperature. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14547–14552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Han, Z. A new type of nanoengineered heat transfer fluids: Nanoemulsion fluids. In Proceedings of the ASME 2006 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 November 2006; pp. 333–336.
- Yang, B.; Han, Z.H. Thermal conductivity enhancement in water-in-FC72 nanoemulsion fluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 261914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.H.; Yang, B. Therophysical characteristics of water-in-FC72 nanoemulsion fluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 92, 013118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hammouda, B.; Cao, F.; Yang, B. Experimental study of thermophysical properties and nanostructure of self-assembled water/polyalphaolefin nanoemulsion fluids. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Han, Z.; Cao, F.; Xu, J.; Ahuja, H. Thermophysical properties of nanostructured heat transfer fluids. In Proceedings of the Second International Energy 2030 Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 4–5 November 2008.
- Pal, R. Rheology of Particulate Dispersions and Composites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R. Evaluation of theoretical viscosity models for concentrated emulsions at low capillary numbers. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 81, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. Eine neue Bestimmung der Molekuldimension. Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 1906, 19, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. Berichtigung zu meiner Arbeit: Eine neue Bestimmung der Molekuldimension. Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 1911, 34, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Rheology of emulsions containing polymeric liquids. In Encyclopedia of Emulsion Technology; Chapter 3; Becher, P., Ed.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.I. The viscosity of a fluid containing small drops of another liquid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1932, 138, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Rheology of simple and multiple emulsions. Curr. Opin. Coll. Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N. Concentration dependence of the viscosity of high polymer solutions. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1950, 5, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K.; Green, J.T. The determination of the bulk stress in a suspension of spherical particles to the order c2. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 56, 401–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Effect of Brownian motion on bulk stress in a suspension of spherical particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 83, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, R. The viscosity of suspensions of rigid spheres. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1952, 3, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, H.C. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, M. The viscosity of a concentrated suspensions of spherical particles. J. Coll. Sci. 1951, 6, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, I.M.; Dougherty, T.J. Mechanism for non-Newtonian flow in suspensions of rigid particles. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1959, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldroyd, J.G. The elastic and viscous properties of emulsions and suspensions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1953, 218, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Novel viscosity equations for emulsions of two immiscible liquids. J. Rheol. 2001, 45, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waarden, M. Viscosity and electroviscous effect of emulsions. J. Coll. Sci. 1954, 9, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yin, Y. Determination of solvation layer thickness by a magnetophotonic approach. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4196–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Edible nanoemulsions: Fabrication, properties, and functional performance. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2297–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.W.; Zheng, R.T.; Ohtani, H.; Zhu, D.S.; Chen, G. Experimental investigation of heat conduction mechanisms in nanofluids. Clue on clustering. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4128–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, N.R.; Philip, J.; Raj, B. Effect of clustering on the thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 109, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. A new model for the viscosity of asphaltene solutions. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgers, R. Relative viscosity and concentration. Rheol. Acta 1962, 2, 305–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. A new linear viscoelastic model for emulsions and suspensions. Poly. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.; Nielsen, L. Dynamic mechanical properties of particulate-filled composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1970, 14, 1449–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Dingenouts, N.; Ballaquff, M.; Senf, H.; Richtering, W. Comparison of the effective radius of sterically stabilized latex particles determined by small angle X-ray scattering and by zero shear viscosity. Langmuir 1998, 14, 5083–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.A.R.; Leary, B.; Boger, D.V. The rheology of a sterically stabilized suspension at high concentration. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 1992, 150, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.A.R.; Leary, B.; Boger, D.V. The rheology of a concentrated colloidal suspension of hard spheres. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 1991, 147, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Set No | Type of Nanofluid | Type and Diameter of un-Solvated Nanoparticles (nm) | Temperature (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nanoemulsion | oil nanodroplets; 205 nm | 20 | Van der Waarden [44] |
| 2 | nanoemulsion | oil nanodroplets; 102 nm | 20 | Van der Waarden [44] |
| 3 | nanoemulsion | oil nanodroplets; 58.5 nm | 20 | Van der Waarden [44] |
| 4 | nanoemulsion | oil nanodroplets; 27.5 nm | 20 | Van der Waarden [44] |
| 5 | nanosuspension | Al2O3 ; 36 nm | 22–25 | Nguyen et al. [14] |
| 6 | nanosuspension | Al2O3 ; 47 nm | 22–25 | Nguyen et al. [14] |
| 7 | nanosuspension | CuO ; 29 nm | 22–25 | Nguyen et al. [18] |
| 8 | nanosuspension | Poly(styrene) latex; 146 nm | 20 | Weiss et al. [53] |
| 9 | nanosuspension | Polymer; 56 nm | 20 | Jones et al. [54] |
| 10 | nanosuspension | Silica; 50 nm | 20 | Jones et al. [55] |
| Set No | Type of Nanofluid and Diameter (nm) | Intrinsic Viscosity, [η] | Solvation Coefficient, ks | Thickness of Solvation Nanolayer, (nm) | Volume Fraction of Solvated Layer in the Solvated Droplet, |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nanoemulsion (205) | 2.65 | 1.077 | 2.58 | 0.072 |
| 2 | Nanoemulsion (102) | 3.05 | 1.243 | 3.83 | 0.195 |
| 3 | Nanoemulsion (58.5) | 3.8 | 1.555 | 4.64 | 0.357 |
| 4 | Nanoemulsion (27.5) | 4.9 | 2.018 | 3.63 | 0.504 |
| 5 | Nanosuspension (36) | 5.65 | 2.26 | 5.62 | 0.557 |
| 6 | Nanosuspension (47) | 10 | 4.0 | 13.80 | 0.75 |
| 7 | Nanosuspension (29) | 11 | 4.4 | 9.26 | 0.773 |
| 8 | Nanosuspension (146) | 3.9 | 1.56 | 11.66 | 0.359 |
| 9 | Nanosuspension (56) | 3.39 | 1.36 | 3.02 | 0.265 |
| 10 | Nanosuspension (50) | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pal, R. Modeling the Viscosity of Concentrated Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions. Fluids 2016, 1, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids1020011
Pal R. Modeling the Viscosity of Concentrated Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions. Fluids. 2016; 1(2):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids1020011
Chicago/Turabian StylePal, Rajinder. 2016. "Modeling the Viscosity of Concentrated Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions" Fluids 1, no. 2: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids1020011
APA StylePal, R. (2016). Modeling the Viscosity of Concentrated Nanoemulsions and Nanosuspensions. Fluids, 1(2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids1020011





