Effect of Ultrasound Time on Structural and Gelling Properties of Pea, Lupin, and Rice Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Freeze-Dried Plant Protein
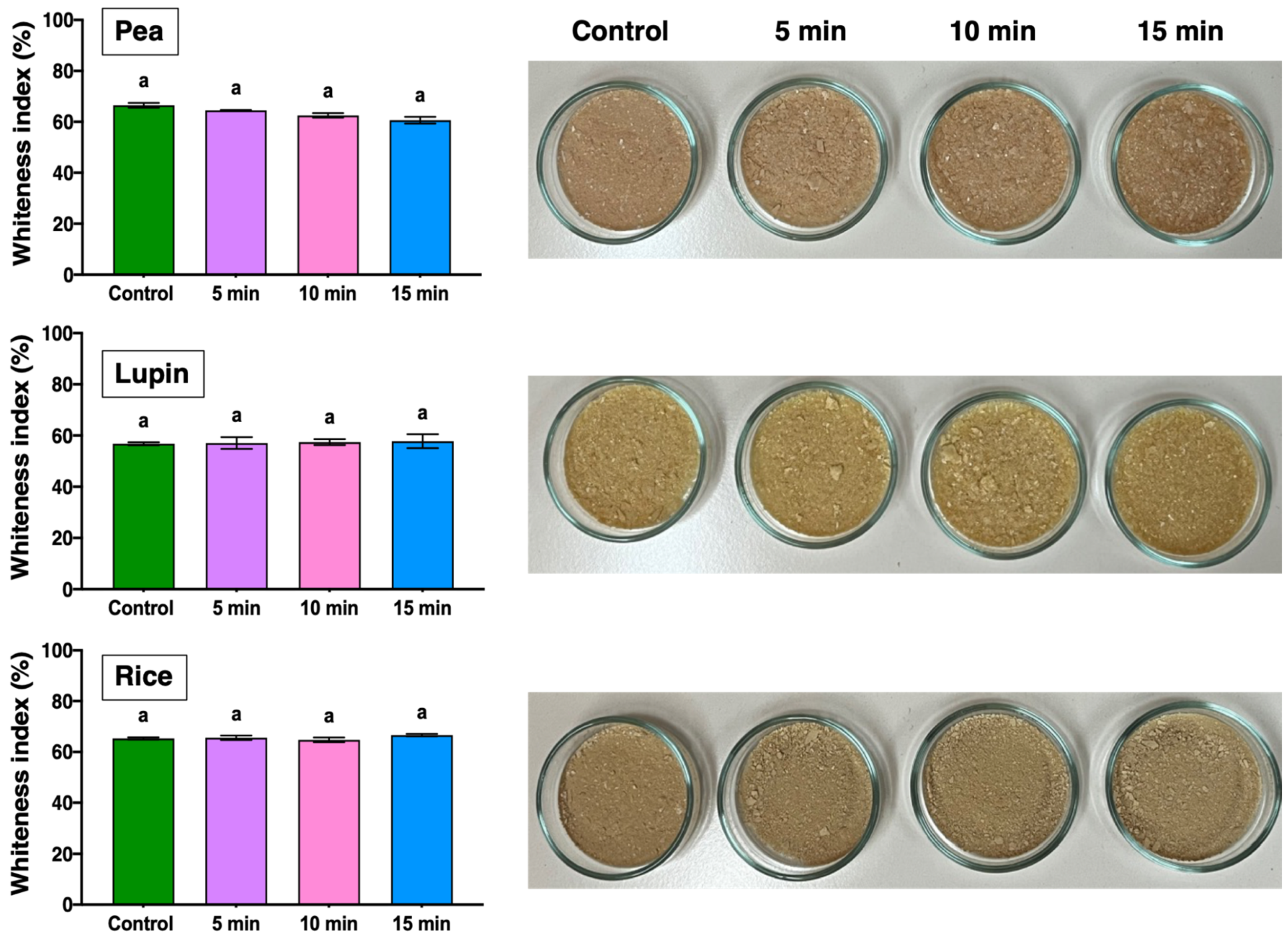
2.1.1. Optical Properties
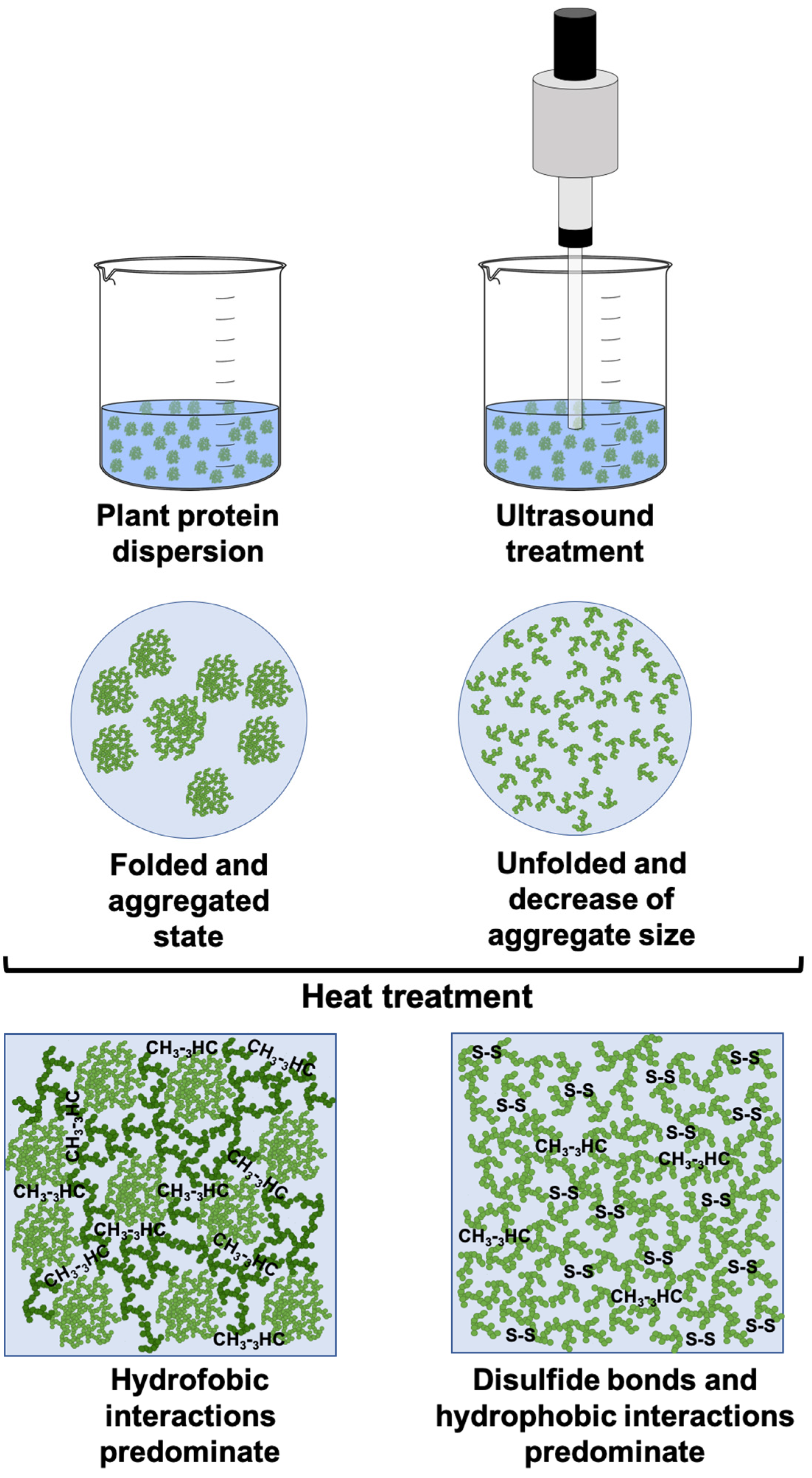
2.1.2. FT-IR Spectra and Changes in the Secondary Structure of Proteins
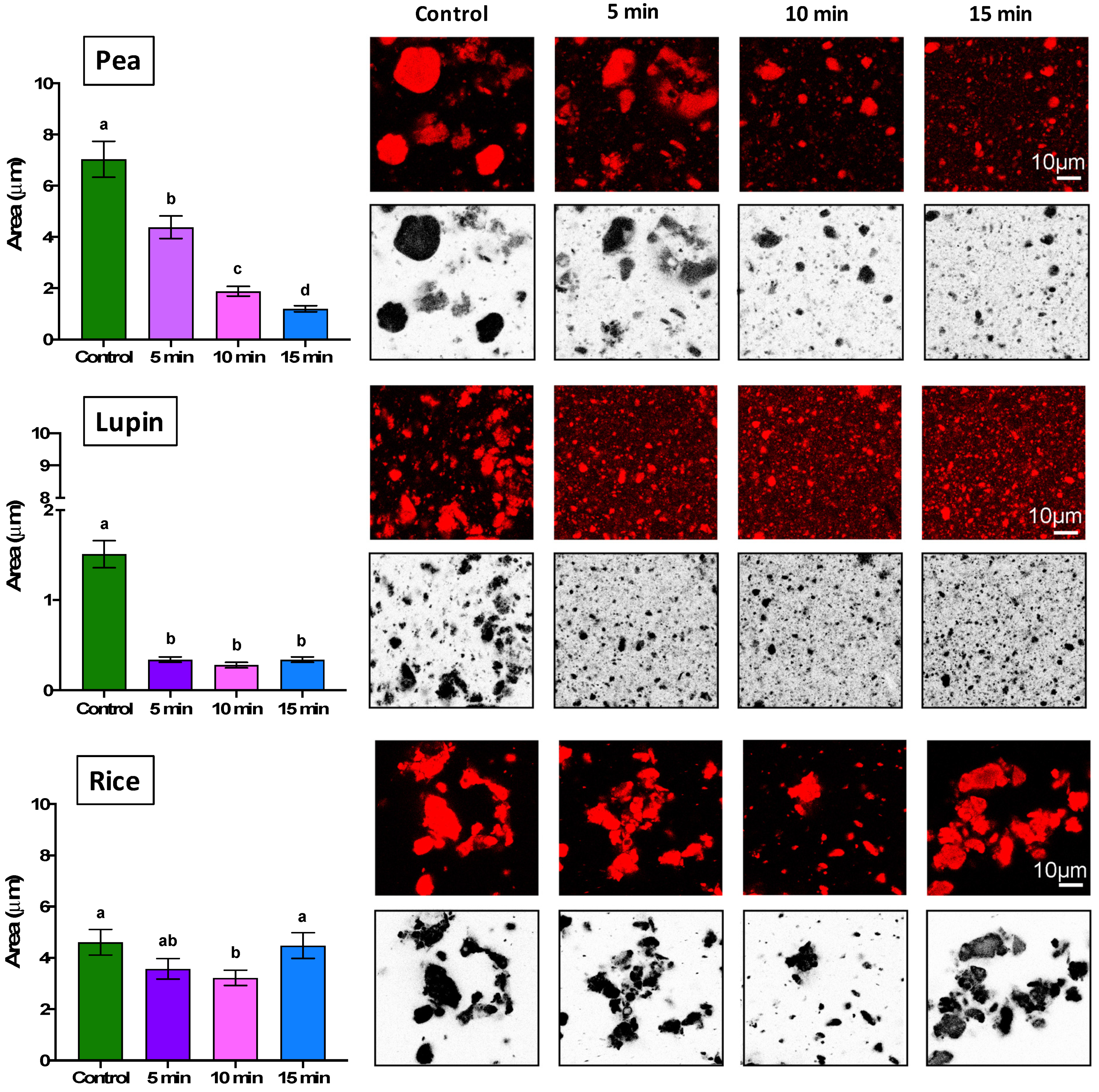
2.1.3. Particle Size and Microstructure of Protein Aggregates
2.2. Characterization of Plant Protein Gels
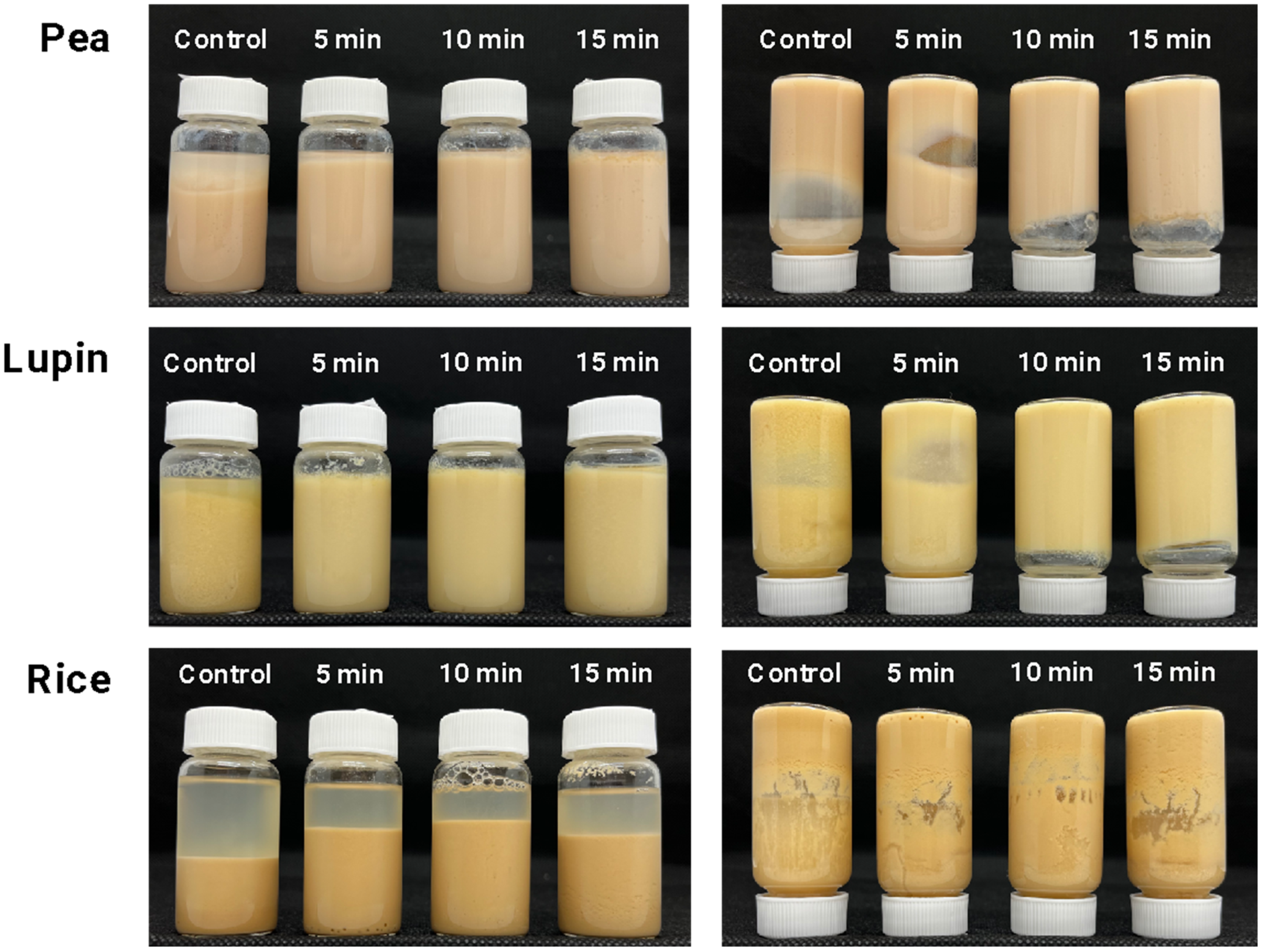
2.2.1. Gel Strength
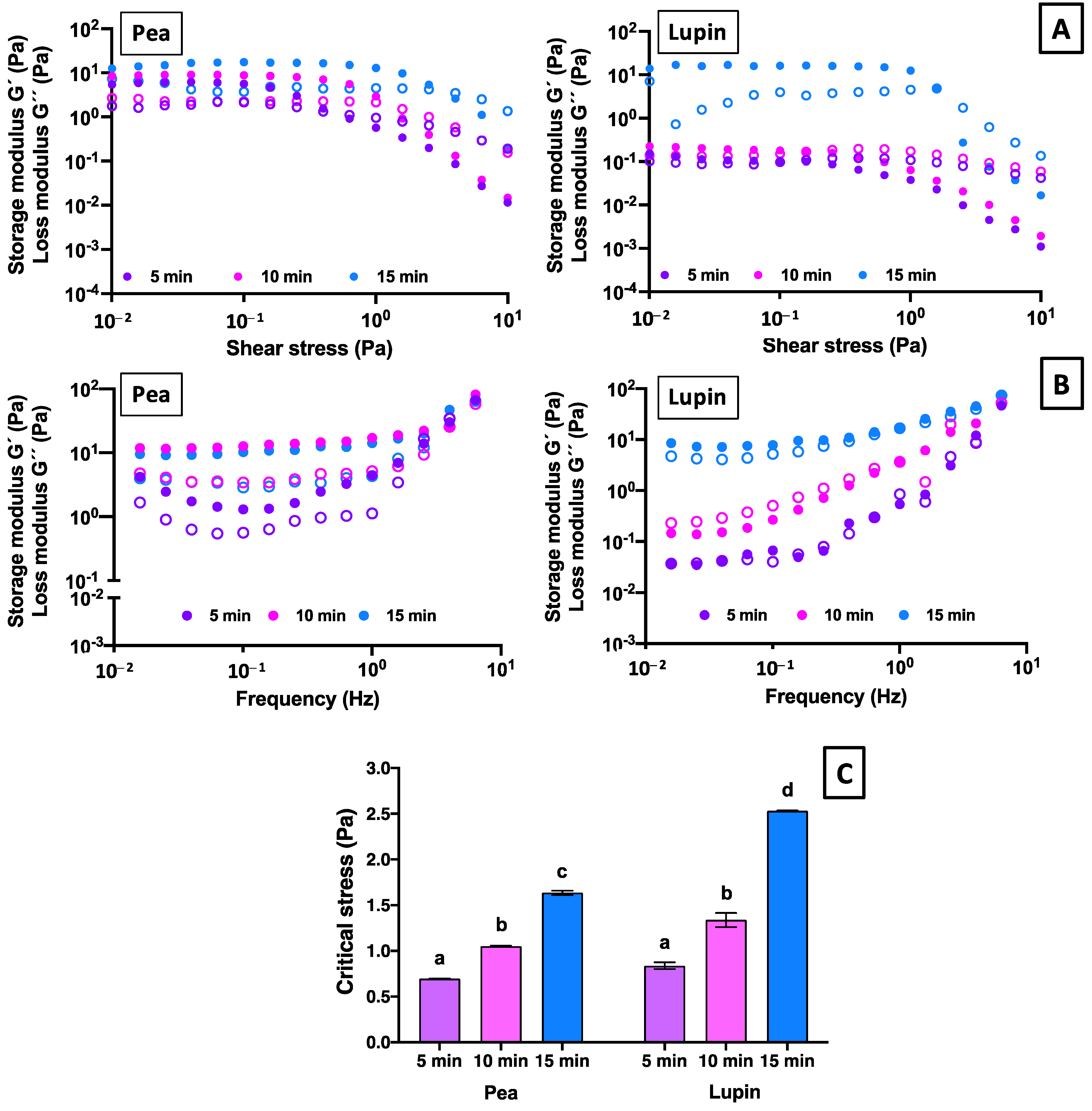
2.2.2. Viscoelastic Properties
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Ultrasound Treatment
4.3. Characterization of Freeze-Dried Plant Protein
4.3.1. Optical Properties
4.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
4.3.3. Microstructure
4.4. Preparation and Characterization of Plant Protein Gels
4.4.1. Preparation of Plant Protein Gels
4.4.2. Gel Strength
4.4.3. Viscoelastic Properties
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faber, I.; Castellanos, N.; Van de Sompel, L.; Davydova, A.; Perez, F. Attitudes and knowledge towards plant-based diets of young across four European countries: Exploratory survey. Appetite 2020, 145, 104498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mullins, A.P.; Arjmandi, B.H. Health benefits of plant-based nutrition: Focus on beans in cardiometabolic diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tso, R.; Forde, C.G. Unintended consequences: Nutritional impact and potential pitfalls of switching from animal-to plant-based foods. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circus, V.E.; Robinson, R. Exploring perceptions of sustainable proteins and meat attachment. Br. Food J. 2019, 121, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L.; Cakebread, J.A.; Loveday, S.M. Food proteins from animals and plants: Differences in the nutritional and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.K.; Greis, M.; Lu, J.; Nolden, A.A.; McClements, D.J.; Kinchla, A.J. Functional performance of plant proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Xiong, Y.L. Plant protein-based alternatives of reconstructed meat: Science, technology, and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Drusch, S.; Klost, M.; Kieserling, H. Current knowledge on the interfacial behaviour limits our understanding of plant protein functionality in emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mezzenga, R. Food protein amyloid fibrils: Origin, structure, formation, characterization, applications and health implications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 334–356. [Google Scholar]
- Jansens, K.J.A.; Rombouts, I.; Grootaert, C.; Brijs, K.; Van Camp, J.; Van der Meeren, P.; Rousseau, F.; Schymkowitz, J.; Delcour, J.A. Rational design of amyloid-like fibrillary structures for tailoring food protein techno-functionality and their potential health implications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 84–105. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. A brief review of the science behind the design of healthy and sustainable plant-based foods. NPJ Sci. Food 2021, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, A.G.A.; Laurindo, J.B.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Influence of emerging technologies on the utilization of plant proteins. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 809058. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, S.Y.J.; Srv, A.; Chiang, J.H.; Henry, C.J. Plant proteins for future foods: A roadmap. Foods 2021, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahagún, M.; Benavent-Gil, Y.; Rosell, C.M.; Gómez, M. Modulation of in vitro digestibility and physical characteristics of protein enriched gluten free breads by defining hydration. LWT 2020, 117, 108642. [Google Scholar]
- Trikusuma, M.; Paravisini, L.; Peterson, D.G. Identification of aroma compounds in pea protein UHT beverages. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Koosis, A.O.; Wang, Q.; True, A.D.; Xiong, Y.L. Interfacial dilatational and emulsifying properties of ultrasound-treated pea protein. Food Chem. 2021, 250, 129271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.X.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Bing, D.J. Composition, physicochemical properties of pea protein and its application in functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2593–2605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Unraveling the mechanism by which high intensity ultrasound improves the solubility of commercial pea protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z. Functional properties and structural changes of rice proteins with anthocyanins complexation. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Yu, D.; Xie, F. Effect of ultrasound on the properties of rice bran protein and its chlorogenic acid complex. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 79, 105758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.; Wen, L.; Cui, B.; Yu, B.; Zhao, H.; et al. Preparation of high-solubility rice protein using an ultrasound-assisted glycation reaction. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111737. [Google Scholar]
- Igartúa, D.E.; Dichano, M.C.; Ferrari, S.B.; Palazolo, G.G.; Cabezas, D.M. Combination of pH-shifting, ultrasound, and heat treatments to enhance solubility and emulsifying stability of rice protein isolate. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Ali, H.A.; Shah, U.; Hackett, M.J.; Gulzar, M.; Karakyriakos, E.; Johnson, S.K. Technological strategies to improve gelation properties of legume proteins with the focus on lupin. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 68, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadimu, G.J.; Gill, H.; Farahnaky, A.; Truong, T. Investigating the impact of ultrasound pretreatment on the physicochemical, structural, and antioxidant properties of lupin protein hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 2004–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, B.; Kasapis, S.; Farahnaky, A. Effect of low frequency ultrasound on the functional characteristics of isolated lupin protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107345. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsang-O’Dwyer, M.; Bez, J.; Petersen, I.L.; Joehnke, M.S.; Detzel, A.; Busch, M.; Krueger, M.; Ispiryan, L.; O’Mahony, J.A.; Arendt, E.K.; et al. Techno-functional, nutritional and environmental performance of protein isolates from blue lupin and white lupin. Foods 2020, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piornos, J.A.; Burgos-Díaz, C.; Ogura, T.; Morales, E.; Rubilar, M.; Maureira-Butler, I.; Salvo-Garrido, H. Functional and physicochemical properties of a protein isolate from AluProt-CGNA: A novel protein-rich lupin variety (Lupinus luteus). Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, E.; Burgos-Díaz, C.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Jorkowski, J.; Quilaqueo, M.; Rubilar, M. Influence of O/W emulsion interfacial ionic membranes on the encapsulation efficiency and storage stability of powder microencapsulated astaxanthin. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 126, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akharume, F.U.; Aluko, R.E.; Adedeji, A.A. Modification of plant proteins for improved functionality: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 198–224. [Google Scholar]
- Avelar, Z.; Vicente, A.A.; Saraiva, J.A.; Rodrigues, R.M. The role of emergent processing technologies in tailoring plant protein functionality: New insights. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswara Rao, M.; Sunil, C.K.; Rawson, A.; Chidanand, D.V.; Venkatachalapathy, N. Modifying the plant proteins techno-functionalities by novel physical processing technologies: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 4070–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Effect of ultrasound on protein functionality. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, B.K.; Yong, H.I.; Choi, Y.S. Improvement of structural, physicochemical, and rheological properties of porcine myofibrillar proteins by high-intensity ultrasound treatment for application as Pickering stabilizers. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Teng, F.; Zhang, S.; Qi, B.; Wu, C.; Li, Y. Application of ultrasound treatment for modulating the structural, functional and rheological properties of black bean protein isolates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Lamsal, B.P. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and modification of plant-based proteins: Impact on physicochemical, functional, and nutritional properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1457–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, A.; Thakur, K.; Parmar, V.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, R.; Kaur, G.; Singh, B.; Suhag, R. New insights into tailoring physicochemical and techno-functional properties of plant proteins using conventional and emerging technologies. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 3845–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Bakry, A.M.; Khalifa, I.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Effect of different oils and ultrasound emulsification conditions on the physicochemical properties of emulsions stabilized by soy protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, F.; Chen, L.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Effect of ultrasound-assisted alkaline treatment on functional property modifications of faba bean protein. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the structural, rheological, emulsifying and gelling properties of insoluble potato protein isolates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 85, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Lei, Y.; Yang, M. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on the structure, functional properties of chickpea protein isolate and its digestibility in vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Sun, G.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Liang, Y.; Hua, D.L.; Mo, H.Z. The improvement and mechanism of gelation properties of mung bean protein treated by ultrasound. LWT 2023, 182, 114811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekvani, K.; Singh, N.; Chen, Y.; Kaur, A.; Yu, L. Pulse proteins: Secondary structure, functionality and applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Cheung, I.W.; Pan, S.; Li-Chan, E.C. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on physicochemical and functional properties of aggregated soybean β-conglycinin and glycinin. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Byanju, B.; Rahman, M.M.; Hojilla-Evangelista, M.P.; Lamsal, B.P. Effect of high-power sonication pretreatment on extraction and some physicochemical properties of proteins from chickpea, kidney bean, and soybean. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wang, R.; Feng, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T. Design of novel edible hydrocolloids by structural interplays between wheat gluten proteins and soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Wanasundara, J.P. Functionality of plant proteins and importance of aggregation state. In Functionality of Plant Proteins; Wanasundara, J.P.D., Schmitt, C., Lamsal, B.P., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, C.; Bovetto, L.; Buczkowski, J.; Reis, G.D.O.; Pibarot, P.; Amagliani, L.; Dombrowski, J. Plant proteins and their colloidal state. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101510. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Kornet, R.; Ntone, E.; Meijers, M.G.; van den Hoek, I.A.; Sagis, L.M.; Hinderink, E.B. Plant protein aggregates induced by extraction and fractionation processes: Impact on techno-functional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Singh, A.; Sari, T.P.; Homroy, S. Rice protein: Emerging insights of extraction, structural characteristics, functionality, and application in the food industry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Du, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, Y. Modulating molecular interactions in pea protein to improve its functional properties. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; van’t Hag, L.; Haritos, V.S.; Dhital, S. Lupin proteins: Structure, isolation and application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Shen, W.; Peng, D.; Jin, W.; Huang, Q. Self-assembly of rice proteins: A perspective on elevating rice protein techno-functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 104624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, N.; Singh, S.K.; Singha, P. A comprehensive review on the recent trends in extractions, pretreatments and modifications of plant-based proteins. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O´Sullivan, J.; Murray, B.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I. The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, M.H.; de Oliveira, A.P.H.; de Souza Soares, L.; dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; de Barros, F.A.R.; Vidigal, M.C.T.R.; de Oliveira, E.B. Effects of protein concentration during ultrasonic processing on physicochemical properties and techno-functionality of plant food proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Plant-based food hydrogels: Constitutive characteristics, formation, and modulation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, S.; Formica, F.A.; Denkel, C. Mixing plant-based proteins: Gel properties of hemp, pea, lentil proteins and their binary mixtures. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, L.; Kyriakopoulou, K.; Fernandez, D.; Bergia, R.; Dhital, S. Techno-functional and rheological characterisation of protein isolates from two Australian lupin species as affected by processing conditions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.G.L.; Queiroz, L.S.; Petersen, H.O.; Marie, R.; Silva, N.F.N.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Casanova, F. High-intensity ultrasound treatment on casein: Pea mixed systems: Effect on gelling properties. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayarri, S.; González-Tomás, L.; Costell, E. Viscoelastic properties of aqueous and milk systems with carboxymethyl cellulose. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, M.; Joyner, H.S. Effect of formulation on structure-function relationships of concentrated emulsions: Rheological, tribological, and microstructural characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, H.M.; Dominguez-Timon, F.; Díaz, M.T.; Pedrosa, M.M.; Borderías, A.J.; Tovar, C.A. Evaluation of gels made with different commercial pea protein isolate: Rheological, structural and functional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ultrasound Time | Gel Strength (g-Force) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pea | Lupin | Rice | |
| Control | n.d | n.d | n.d |
| 5 min | 7.00 ± 0.07 a | n.d | n.d |
| 10 min | 7.05 ± 0.52 a | 6.77 ± 0.55 a | n.d |
| 15 min | 7.77 ± 0.29 a | 6.97 ± 0.42 a | n.d |
| Protein Type | Ultrasound Time | Storage Modulus (Pa) | Loss Modulus (Pa) | tan δ (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pea | 5 min | 5.18 ± 1.04 b | 1.59 ± 0.65 bc | 0.30 ± 0.07 c |
| 10 min | 16.12 ± 0.98 a | 6.47 ± 1.86 a | 0.30 ± 0.01 c | |
| 15 min | 13.48 ± 1.00 a | 4.15 ± 0.22 ab | 0.32 ± 0.03 c | |
| Lupin | 5 min | 0.79 ± 0.22 c | 1.01 ± 0.23 c | 1.35 ± 0.32 a |
| 10 min | 2.96 ± 1.05 bc | 0.73 ± 0.10 c | 0.67 ± 0.02 b | |
| 15 min | 14.34 ± 3.60 a | 5.14 ± 2.20 a | 0.35 ± 0.06 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riquelme, N.; Díaz-Calderón, P.; Luarte, A.; Arancibia, C. Effect of Ultrasound Time on Structural and Gelling Properties of Pea, Lupin, and Rice Proteins. Gels 2025, 11, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040270
Riquelme N, Díaz-Calderón P, Luarte A, Arancibia C. Effect of Ultrasound Time on Structural and Gelling Properties of Pea, Lupin, and Rice Proteins. Gels. 2025; 11(4):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040270
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiquelme, Natalia, Paulo Díaz-Calderón, Alejandro Luarte, and Carla Arancibia. 2025. "Effect of Ultrasound Time on Structural and Gelling Properties of Pea, Lupin, and Rice Proteins" Gels 11, no. 4: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040270
APA StyleRiquelme, N., Díaz-Calderón, P., Luarte, A., & Arancibia, C. (2025). Effect of Ultrasound Time on Structural and Gelling Properties of Pea, Lupin, and Rice Proteins. Gels, 11(4), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040270









