Flavonoid-Based Nanogels: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract
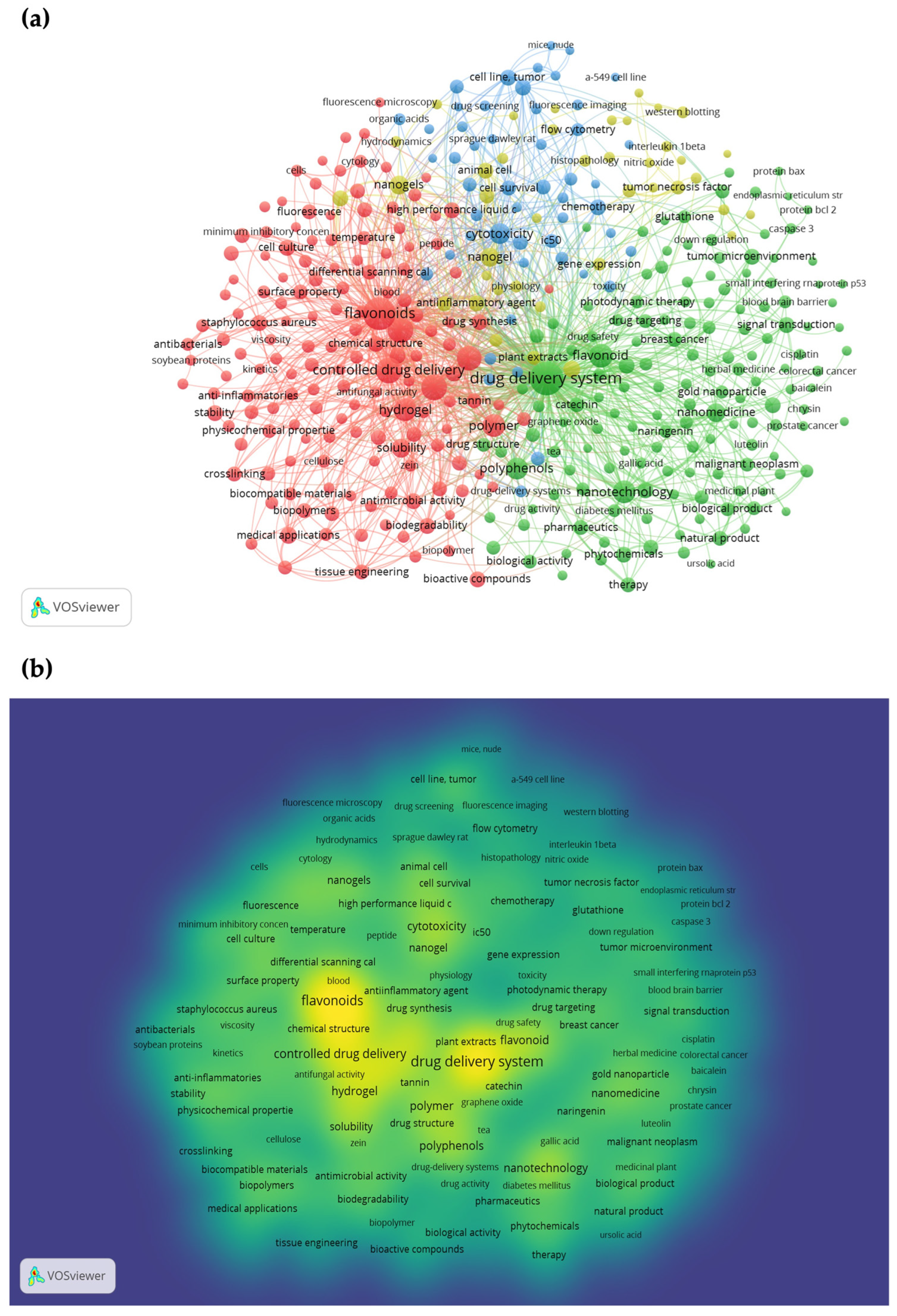
1. Introduction
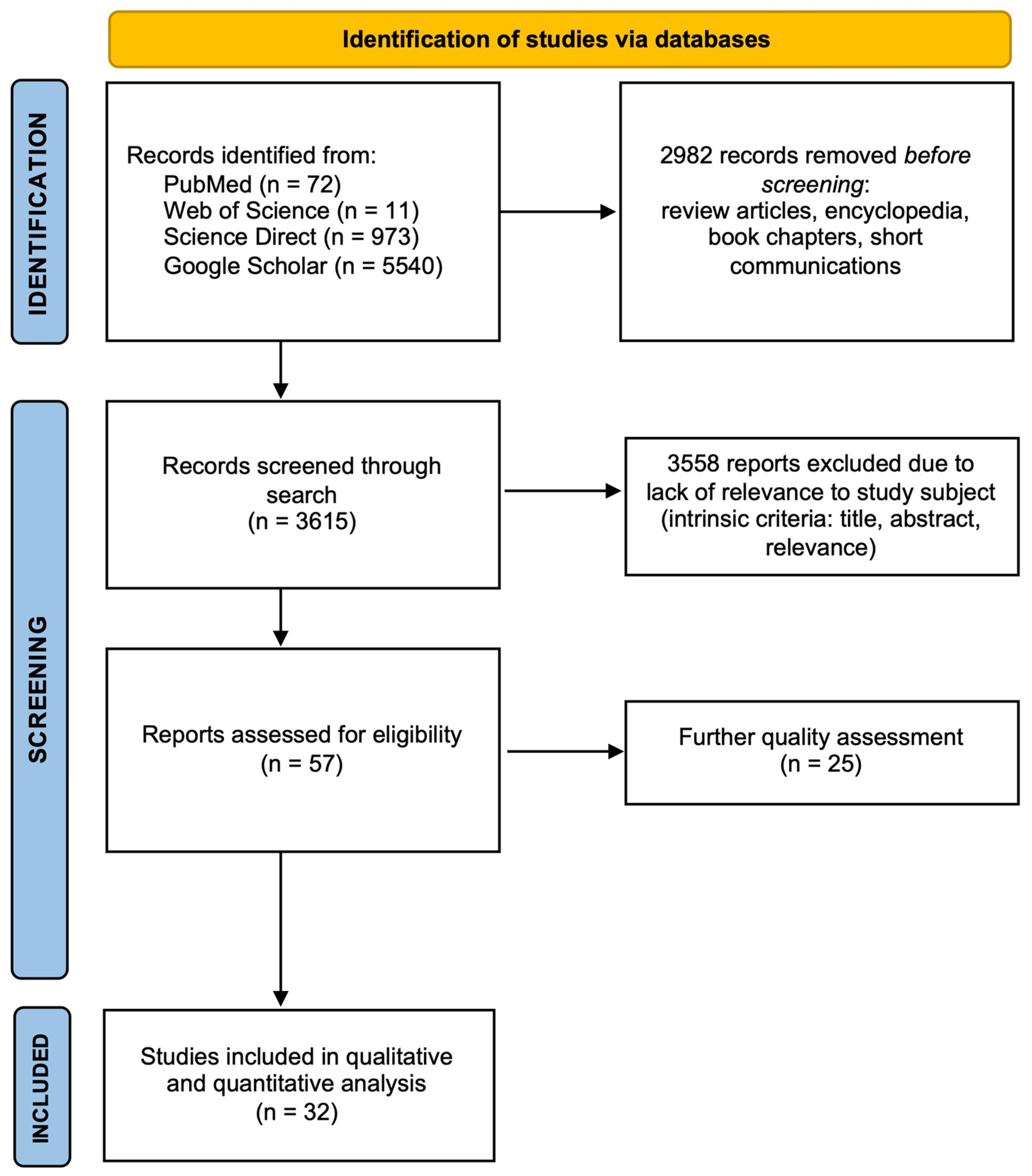
2. Methods
3. General Classification and Formulation Techniques for Nanogels
3.1. Classification of Nanogels
3.1.1. Based on Matrix Composition
3.1.2. Based on Formulation Technique
Physically Crosslinked Nanogels
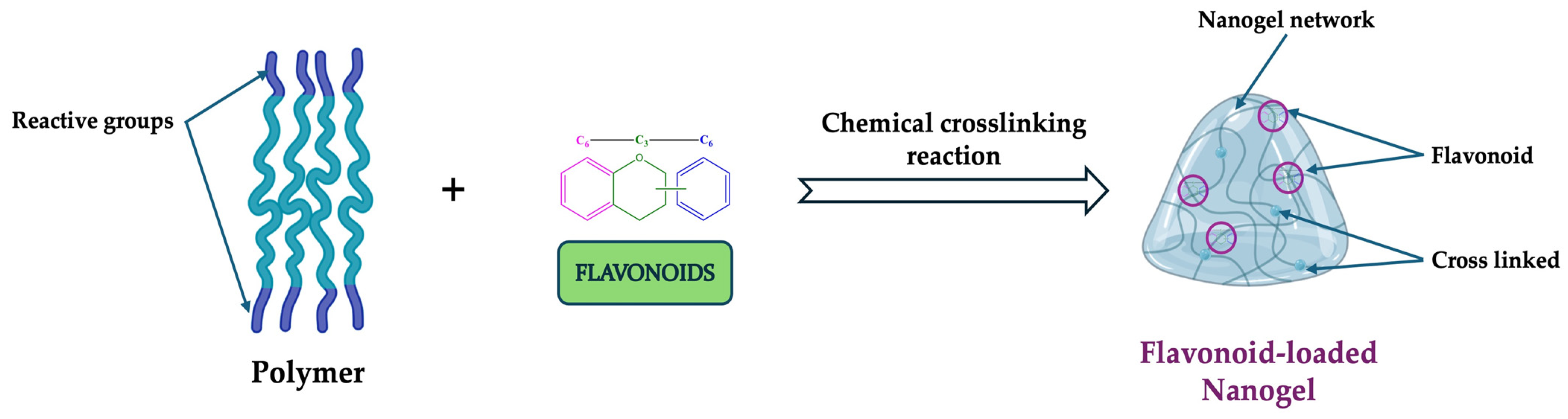
Chemically Crosslinked Nanogels
Stimuli-Responsive Nanogels
3.2. Formulation Techniques for Nanogels
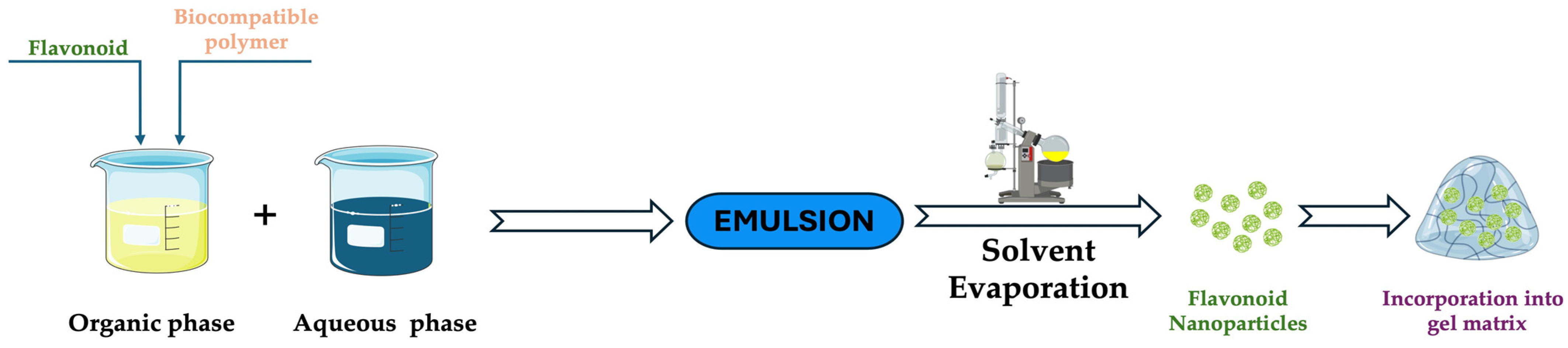
3.2.1. Emulsion Polymerization Technique
3.2.2. Solvent Evaporation Technique
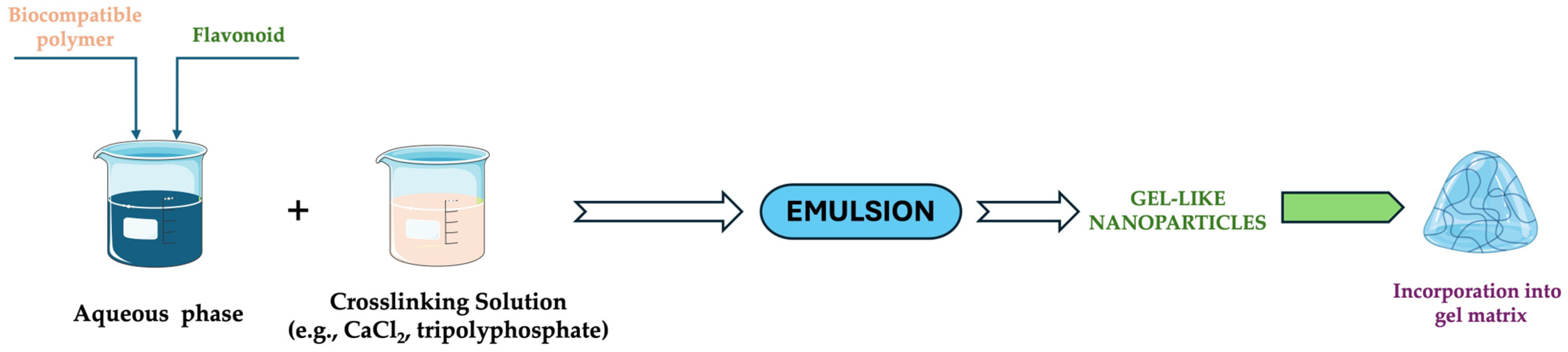
3.2.3. Ionic Gelation Technique
3.2.4. Photopolymerization Technique
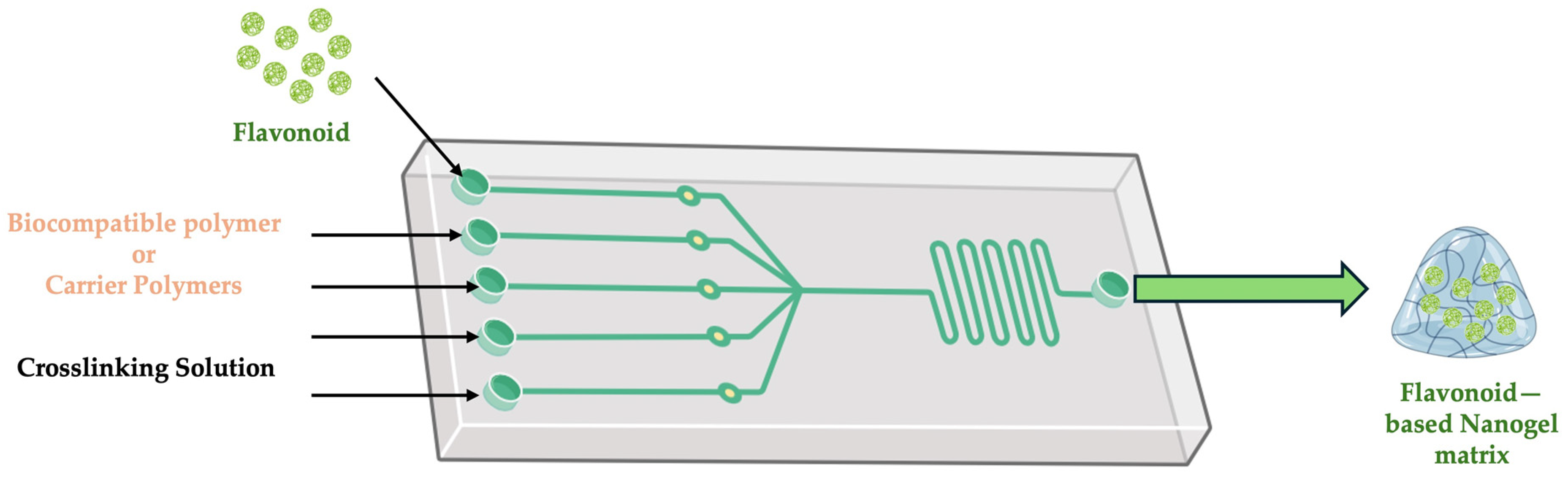
3.2.5. Microfluidic Technique
4. Structural Characterization of Flavonoid-Loaded Nanogels
5. Applications of Flavonoid-Loaded Nanogels in Therapy
5.1. Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy
5.2. Therapeutic Systems
6. Challenges and Future Directions
- ▪
- ▪
- ▪
- ▪
- Isoflavones have low bioavailability, making it difficult for them to pass through the intestinal epithelium and be absorbed, leading to weak biological activity [153].
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology in Healthcare and Medicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Javaid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Rab, S.; Suman, R. Applications of Nanotechnology in Medical Field: A Brief Review. Glob. Health J. 2023, 7, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tian, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Allahou, L.W.; Chang, J.; Williams, G.; Knowles, J.C.; Poma, A. Nanotechnology in Healthcare, and Its Safety and Environmental Risks. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Feng, L.; Xie, N.; Shen, G. Nanotechnology’s Frontier in Combatting Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases: Prevention and Treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, S.; Palaniappan, T.; Wang, J.-W.; Wacker, M.G. Revisiting Nanomedicine Design Strategies for Follow-on Products: A Model-Informed Approach to Optimize Performance. J. Control. Release 2024, 376, 1251–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isles, M.P. Nanomedicines and Nanosimilars—Why a Robust Centralised Regulatory Framework Is Essential to Enhance Patient Safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 787239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetzos, C. Nanosimilars: A Scientific or A Regulatory Debate? AAPS J. 2024, 26, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metselaar, J.M.; Lammers, T. Challenges in Nanomedicine Clinical Translation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H. Progress and Challenges in the Translation of Cancer Nanomedicines. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 85, 103045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacharodi, A.; Singh, P.; Meenatchi, R.; Tawfeeq Ahmed, Z.H.; Kumar, R.R.S.; Neha, V.; Kavish, S.; Maqbool, M.; Hassan, S. Revolutionizing Healthcare and Medicine: The Impact of Modern Technologies for a Healthier Future—A Comprehensive Review. Health Care Sci. 2024, 3, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigham, A.; Zarepour, A.; Khosravi, A.; Iravani, S.; Zarrabi, A. Sustainable Nanomaterials for Precision Medicine in Cancer Therapy. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 27, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Thareja, P. Hydrogels Differentiated by Length Scales: A Review of Biopolymer-Based Hydrogel Preparation Methods, Characterization Techniques, and Targeted Applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 163, 110935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, K.S.; Desale, S.S.; Bronich, T.K. Nanogels: An Overview of Properties, Biomedical Applications and Obstacles to Clinical Translation. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajudheen, F.; Umashankar, M.S.; Narayanasamy, D. A Comprehensive Review of Nanogel-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Cureus 2024, 16, e68633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anooj, E.S.; Charumathy, M.; Sharma, V.; Vibala, B.V.; Gopukumar, S.T.; Jainab, S.I.B.; Vallinayagam, S. Nanogels: An Overview of Properties, Biomedical Applications, Future Research Trends and Developments. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1239, 130446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Sudhakar, K.; Mishra, V. Fabrication and Biomedical Potential of Nanogels: An Overview. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 68, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espuche, B.; Moya, S.E.; Calderón, M. Nanogels: Smart Tools to Enlarge the Therapeutic Window of Gene Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 653, 123864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, D.; Mishra, S.; Das Paul, S.; Paliwal, R.; Satapathy, T. The Functional Nanogel: An Exalted Carrier System. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.Y.; Zhu, Y.X.; Jia, H.R.; Wang, S.H.; Wu, F.G. Nanogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Recent Biomedical Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 139, 101167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Saha, S.; Jakhmola, V. Nanogel: Types, Methods of Preparation, Limitation, Evaluation and Application—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2023, 13, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, E.; Giannitelli, S.M.; Trombetta, M.; Rainer, A. Synthesis of Nanogels: Current Trends and Future Outlook. Gels 2021, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Deng, C.; Suuronen, E.J.; Zhong, Z. Click Hydrogels, Microgels and Nanogels: Emerging Platforms for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4969–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Singh, S.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, B.; Kumar, A. Single-, Dual-, and Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Nanogels for Biomedical Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.C.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S. Plant Flavonoids: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liga, S.; Paul, C.; Péter, F. Flavonoids: Overview of Biosynthesis, Biological Activity, and Current Extraction Techniques. Plants 2023, 12, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant Flavonoids: Classification, Distribution, Biosynthesis, and Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, H.; Chen, X. A Review of Classification, Biosynthesis, Biological Activities and Potential Applications of Flavonoids. Molecules 2023, 28, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Channakesavula, C.N.; Stone, S.R.; Kaur, P. Synthetic Biology towards Improved Flavonoid Pharmacokinetics. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Md, S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Rizwanullah, M.; Fatima, S.; Ahmed, N.; Alyazedi, F.M.; Karim, S.; Ahmad, J. Nanogels as Potential Delivery Vehicles in Improving the Therapeutic Efficacy of Phytopharmaceuticals. Polymers 2022, 14, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z.; Zhang, Y.S. Chapter 2—Self-Assembled Nanogels: From Particles to Scaffolds and Membranes. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Cancer Theranostics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Hu, B.; Yuan, X.; Cai, L.; Gao, H.; Yang, Q. Nanogel: A Versatile Nano-Delivery System for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siafaka, P.I.; Özcan Bülbül, E.; Okur, M.E.; Karantas, I.D.; Üstündağ Okur, N. The Application of Nanogels as Efficient Drug Delivery Platforms for Dermal/Transdermal Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, K.; Haddadi, N.S.; Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Farzaei, M.H.; Rohani, M.M.; Akramian, F.; Naseri, R.; Sureda, A.; Ghanaatian, N.; Abdolghaffari, A.H. Natural Flavonoids for the Prevention of Colon Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21519–21546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; Manchope, M.F.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Ferraz, C.R.; Saraiva-Santos, T.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Fattori, V.; Artero, N.A.; Badaro-Garcia, S.; de Freitas, A.; et al. Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone Interacts with NFκB Ser276 and Inhibits Zymosan-Induced Joint Pain and Inflammation, and RAW 264.7 Macrophage Activation. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renault–Mahieux, M.; Mignet, N.; Seguin, J.; Alhareth, K.; Paul, M.; Andrieux, K. Co–Encapsulation of Flavonoids with Anti–Cancer Drugs: A Challenge Ahead. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 623, 121942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awlqadr, F.H.; Majeed, K.R.; Altemimi, A.B.; Hassan, A.M.; Qadir, S.A.; Saeed, M.N.; Faraj, A.M.; Salih, T.H.; Abd Al-Manhel, A.J.; Najm, M.A.A.; et al. Nanotechnology-Based Herbal Medicine: Preparation, Synthesis, and Applications in Food and Medicine. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Available online: https://scholar.google.com (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Rational Design of Smart Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 615665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.Z.; Park, N. Nanohydrogels: Advanced Polymeric Nanomaterials in the Era of Nanotechnology for Robust Functionalization and Cumulative Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.; Pich, A.; Hellweg, T.; Hoare, T.; Lyon, L.A.; Crassous, J.J.; Suzuki, D.; Gumerov, R.A.; Schneider, S.; Potemkin, I.I.; et al. Nanogels and Microgels: From Model Colloids to Applications, Recent Developments, and Future Trends. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6231–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, A.; Malrautu, P.; Laha, A.; Luo, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Collagen Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery Systems and Tissue Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balladka Kunhanna, S.; Bailore, N.N.; Pushparekha. Emerging Trends in the Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Nanogels Derived from Pullulan, Collagen and Gelatin. In Nano Hydrogels: Physico-Chemical Properties and Recent Advances in Structural Designing; Jose, J., Thomas, S., Thakur, V.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, S.; Kulkarni, G.T.; Dhiman, N.; Kharkwal, H. Protein-Based Nanohydrogels for Bioactive Delivery. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 573748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnadi, K.; Herdiana, Y.; Rochima, E.; Putra, O.N.; Gazzali, A.M.; Muchtaridi, M. Collagen-Based Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery System in Wound Healing Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 11321–11341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satchanska, G.; Davidova, S.; Petrov, P.D. Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, B.; Santagapita, P.; Perullini, M. Exploring the Conditions to Generate Alginate Nanogels. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 102, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Fang, C.W.; Chiu, I.H.; Khan, A.; Wu, Y.C.; Lin, I.L.; Tsai, M.J.; Wu, P.C. Synthesis and Evaluation of Alginate-Based Nanogels as Sustained Drug Carriers for Caffeine. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 23991–24002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Z.X. Alginate-Based Platforms for Cancer-Targeted Drug Delivery. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1487259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Hyaluronic Acid Nanogels with Enzyme-Sensitive Cross-Linking Group for Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 205, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.S.; Laomeephol, C.; Thamnium, S.; Chamni, S.; Luckanagul, J.A. Hyaluronic Acid Nanogels: A Promising Platform for Therapeutic and Theranostic Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, E.; Scialla, S. Nanogels Based on Hyaluronic Acid as Potential Active Carriers for Dermatological and Cosmetic Applications. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qian, J.; Ding, F. Recent Advances in Engineered Chitosan-Based Nanogels for Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6986–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamfil, D.; Vasile, C. Nanogels of Natural Polymers. In Polymer Gels Perspectives and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 71–110. [Google Scholar]
- Manivong, S.; Garcia Ac, A.; Patten, S.A.; Fernandes, J.C.; Benderdour, M.; Banquy, X.; Moldovan, F.; Roullin, V.G. Chitosan-Based Nanogels: Synthesis and Toxicity Profile for Drug Delivery to Articular Joints. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslzad, S.; Heydari, P.; Abdolahinia, E.D.; Amiryaghoubi, N.; Safary, A.; Fathi, M.; Erfan-Niya, H. Chitosan/Gelatin Hybrid Nanogel Containing Doxorubicin as Enzyme-Responsive Drug Delivery System for Breast Cancer Treatment. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2023, 301, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zi, Y.; Peng, J.; Shi, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, J. Gelatin as a Bioactive Nanodelivery System for Functional Food Applications. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, F.; Raza, Z.A.; Batool, S.R.; Zahid, M.; Onder, O.C.; Rafique, A.; Nazeer, M.A. Preparation, Properties, and Applications of Gelatin-Based Hydrogels (GHs) in the Environmental, Technological, and Biomedical Sectors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 601–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Copeland, C.E.; Kwon, Y.C. Harnessing Nanoreactors: Gelatin Nanogels for Human Therapeutic Protein Delivery. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 5527–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, C.; Wei, K.; Yao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, K.; Han, F.; Mak, A.F.T.; Li, B.; Bian, L. Supramolecular Hydrogels Cross-Linked by Preassembled Host–Guest PEG Cross-Linkers Resist Excessive, Ultrafast, and Non-Resting Cyclic Compression. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, E.; Cappella, F.; Masi, M.; Rossi, F. PEGylation Influences Drug Delivery from Nanogels. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padín-González, E.; Lancaster, P.; Bottini, M.; Gasco, P.; Tran, L.; Fadeel, B.; Wilkins, T.; Monopoli, M.P. Understanding the Role and Impact of Poly (Ethylene Glycol) (PEG) on Nanoparticle Formulation: Implications for COVID-19 Vaccines. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 882363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitayama, Y.; Takigawa, S.; Harada, A. Effect of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Concentration and Chain Length on Polymer Nanogel Formation in Aqueous Dispersion Polymerization. Molecules 2023, 28, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesan, M.; Lotfi, M.; Gholipour-Kanani, A.; Shafiee, M. Surface Activity Characterization of Synthesized Polyvinyl Alcohol-Based Nanogel at Air-Water Interface under Highly Dynamic Conditions. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 42, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.B.; Rajput, R.L.; Narkhede, J.S.; Mujumdar, A.; Patil, P.B. Synthesis and Evaluation of UV Cross-Linked Poly (Acrylamide) Loaded Thymol Nanogel for Antifungal Application in Oral Candidiasis. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.; Andrade, S.; Ramalho, M.J.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C. Polymeric Nanoparticles-Loaded Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Systematic Review on In Vivo Findings. Polymers 2022, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Niu, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, A. Properties of Poly (Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) and Progress of Poly (Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid)-Based Biodegradable Materials in Biomedical Research. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neamtu, I.; Rusu, A.G.; Diaconu, A.; Nita, L.E.; Chiriac, A.P. Basic Concepts and Recent Advances in Nanogels as Carriers for Medical Applications. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhi, R. Cross-Linked Hydrogel for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastella, P.; Todaro, B.; Luin, S. Nanogels: Recent Advances in Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimaran, V.; Nivetha, R.P.; Tamilanban, T.; Narayanan, J.; Vetriselvan, S.; Fuloria, N.K.; Chinni, S.V.; Sekar, M.; Fuloria, S.; Wong, L.S.; et al. Nanogels as Novel Drug Nanocarriers for CNS Drug Delivery. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1232109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinelli, F.; Saadati, M.; Zare, E.N.; Makvandi, P.; Masi, M.; Sacchetti, A.; Rossi, F. A Perspective on the Applications of Functionalized Nanogels: Promises and Challenges. Int. Mater. Rev. 2023, 68, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, R.; Kong, Z.; Zhao, D.; Liu, M.; Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Hua, Y.; et al. Smart Nanogels for Cancer Treatment from the Perspective of Functional Groups. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1329311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante-Torres, M.; Romero-Fierro, D.; Arcentales-Vera, B.; Palomino, K.; Magaña, H.; Bucio, E. Hydrogels Classification According to the Physical or Chemical Interactions and as Stimuli-Sensitive Materials. Gels 2021, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajebi, S.; Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Rabiee, M.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Tahriri, M.; Tayebi, L.; Hamblin, M.R. Stimulus-Responsive Polymeric Nanogels as Smart Drug Delivery Systems. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroborty, S.; Nath, N.; Mahal, A.; Barik, A.; Panda, A.R.; Fahaduddin; Bal, T.; Obaidullah, A.J.; Elawady, A. Stimuli-Responsive Nanogels: A Smart Material for Biomedical Applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 403, 124828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.G.; Sun, X.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X. Intelligent Responsive Nanogels: New Horizons in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 669, 125050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, E.J.; Lim, J.H.; Cho, H.K.; Hong, W.J.; Jeon, H.H.; Chung, B.G. Dual Stimuli-Triggered Nanogels in Response to Temperature and PH Changes for Controlled Drug Release. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinelli, F.; Sacchetti, A.; Perale, G.; Rossi, F. Is Nanoparticle Functionalization a Versatile Approach to Meet the Challenges of Drug and Gene Delivery? Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, X.; Wu, Z.; Wen, X.; Xie, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, P.; et al. Phase Transition Behaviors of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Nanogels with Different Compositions Induced by (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate and Ethyl Gallate. Molecules 2023, 28, 7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieh, A.; Khoee, S.; Mahdavian, A.R. Emulsion and Miniemulsion Techniques in Preparation of Polymer Nanoparticles with Versatile Characteristics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 152–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Dong, S.; Zhang, P.; Hao, J. Effect of Environmental Factors on the Emulsion Polymerization of Nanogels. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 790, 139353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, P.A.; Schork, F.J. Fundamentals of Emulsion Polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4396–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Obireddy, S.R.; Lai, W.F. Preparation and Use of Nanogels as Carriers of Drugs. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Yin, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q. An Environmentally Friendly Inverse Microemulsion Method to Synthesize Polyacrylamide. Materials 2022, 15, 5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyret, S.; Vincent, B. The Properties of Polyampholyte Microgel Particles Prepared by Microemulsion Polymerization. Polymer 1997, 38, 6129–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landfester, K.; Weiss, C.K. Encapsulation by Miniemulsion Polymerization. In Modern Techniques for Nano- and Microreactors-Reactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 229, pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Deng, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, W. Self-Assembled Nanogels Based on Ionic Gelation of Natural Polysaccharides for Drug Delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 703559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc-Musioł, B.; Siemiradzka, W.; Dolińska, B. Formulation and Evaluation of Hydrogels Based on Sodium Alginate and Cellulose Derivatives with Quercetin for Topical Application. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.; Huang, J.; Zhu, C.; Sobhy, M.; Farag, M.A.; Fang, Y.; Sobhy, R.; Walayat, N.; Khalifa, I.; Maqsood, S.; et al. Chitosan Dual Gel-like Functionalized with Flavonoid Extract and Cinnamaldehyde Oil Using Dual Cross-Linking Agents: Characterization, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Effects. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 9, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Qu, Y.; Jia, X.; Yin, L. Curcumin Loaded Zein-Alginate Nanogels with “Core-Shell” Structure: Formation, Characterization and Simulated Digestion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, N.; Singh, M. Fabrication and Characterization of a Bilayered System Enabling Sustained Release of Bioflavonoids Derived from Mandarin Biomass. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2023, 3, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Han, J.-y.; Gao, Y.-j.; Jiang, S.-l.; Sun, F. Surface Morphology and Property of UV-Cured Film Containing Photopolymerizable Polysiloxane-Based Nanogels with Initiating Capability. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2019, 10, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.M.; Schlögl, S.; Wiesner, T.; Haas, M.; Griesser, T. Recent Advances in Type I Photoinitiators for Visible Light Induced Photopolymerization. ChemPhotoChem 2022, 6, e202200091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, D.; Kavalli, T.; Xiao, P.; Schmitt, M.; Lalevée, J. Photopolymerization Using Bio-Sourced Photoinitiators. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 3543–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumur, F. Recent Advances in Visible Light Photoinitiating Systems Based on Flavonoids. Photochem 2023, 3, 495–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Xing, J. Investigation of Chrysin Inhibition on Free Radical Photopolymerization during the Preparation of Nanogels under Green LED Irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 438, 114518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitelli, S.M.; Limiti, E.; Mozetic, P.; Pinelli, F.; Han, X.; Abbruzzese, F.; Basoli, F.; Del Rio, D.; Scialla, S.; Rossi, F.; et al. Droplet-Based Microfluidic Synthesis of Nanogels for Controlled Drug Delivery: Tailoring Nanomaterial Properties via Pneumatically Actuated Flow-Focusing Junction. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 11415–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimondi, S.; Ferreira, H.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Microfluidic Devices: A Tool for Nanoparticle Synthesis and Performance Evaluation. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 14205–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Sun, R.; Han, S.; Yang, Z.; Teng, L. Microfluidics for Nano-Drug Delivery Systems: From Fundamentals to Industrialization. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 3277–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forigua, A.; Kirsch, R.L.; Willerth, S.M.; Elvira, K.S. Recent Advances in the Design of Microfluidic Technologies for the Manufacture of Drug Releasing Particles. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amreen, K.; Goel, S. Review—Miniaturized and Microfluidic Devices for Automated Nanoparticle Synthesis. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 017002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Town, A.; Niezabitowska, E.; Kavanagh, J.; Barrow, M.; Kearns, V.R.; García-Tuñón, E.; McDonald, T.O. Understanding the Phase and Morphological Behavior of Dispersions of Synergistic Dual-Stimuli-Responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Nanogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 6303–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabanov, A.V.; Vinogradov, S.V. Nanogels as Pharmaceutical Carriers: Finite Networks of Infinite Capabilities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5418–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, K.P.; Menard, N. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; 280p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Senesi, A.J.; Lee, B. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering for Nanoparticle Research. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11128–11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, L.; Yang, D.; Kanaev, A. Dynamic Light Scattering: A Powerful Tool for In Situ Nanoparticle Sizing. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, S.K.; Khusnutdinov, R.; Murmiliuk, A.; Inam, W.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Dynamic Light Scattering and Transmission Electron Microscopy in Drug Delivery: A Roadmap for Correct Characterization of Nanoparticles and Interpretation of Results. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 5354–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seger, C.; Sturm, S.; Stuppner, H. Mass Spectrometry and NMR Spectroscopy: Modern High-End Detectors for High Resolution Separation Techniques–State of the Art in Natural Product HPLC-MS, HPLC-NMR, and CE-MS Hyphenations. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 970–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, D.; Sun, D.; Gu, J. Current Status of in Vivo Bioanalysis of Nano Drug Delivery Systems. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comby-Zerbino, C.; Dagany, X.; Chirot, F.; Dugourd, P.; Antoine, R.; Antoine, R. The Emergence of Mass Spectrometry for Characterizing Nanomaterials. Atomically Precise Nanoclusters and Beyond. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4896–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Pearce, C.M.; Anastasiadi, R.-M.; Resmini, M.; Castilla, A.M. Covalently Crosslinked Nanogels: An NMR Study of the Effect of Monomer Reactivity on Composition and Structure. Polymers 2019, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, M.-P.; Modh, H.; Champanhac, C.; Wang, J.-W.; Storm, G.; Krämer, J.; Mailänder, V.; Pastorin, G.; Wacker, M.G. Nanomedicine at the Crossroads—A Quick Guide for IVIVC. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 113829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.P.; Patravale, V.B. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation for Pharmaceutical Nano- and Microsystems. In Characterization of Pharmaceutical Nano and Microsystems; Peltonen, L., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, K. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation: Perspectives on Model Development. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.; Costa, C.P.; Moreira, J.N.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Using the Quality by Design (QbD) Approach to Optimize Formulations of Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions: A Review. Nanomedicine 2020, 28, 102206. [Google Scholar]
- Mohseni-Motlagh, S.F.; Dolatabadi, R.; Baniassadi, M.; Baghani, M. Application of the Quality by Design Concept (QbD) in the Development of Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, M.; Singh, A.; Amiji, M.M. Quality-by-Design Concepts to Improve Nanotechnology-Based Drug Development. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attama, A.A.; Nnamani, P.O.; Onokala, O.B.; Ugwu, A.A.; Onugwu, A.L. Nanogels as Target Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy: A Review of the Last Decade. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 874510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuggino, J.C.; Blanco, E.R.O.; Gugliotta, L.M.; Alvarez Igarzabal, C.I.; Calderón, M. Crossing Biological Barriers with Nanogels to Improve Drug Delivery Performance. J. Control. Release 2019, 307, 221–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Sayah, M.H. Multifunctional Stimuli-Responsive Hybrid Nanogels for Cancer Therapy: Current Status and Challenges. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 476–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, S.-J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xue, P.; Kang, Y.; Sun, Z.-J.; Xu, Z. Bioengineered Nanogels for Cancer Immunotherapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5136–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Ma, R.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Cui, F.; Li, T.; et al. Research Progress on Preparation, Loading, and Application of Nanogels to Protect Food Bioactive Ingredients. Nano Today 2025, 62, 102690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalathillam, S.; Rejinold, N.S.; Nair, A.; Lakshmanan, V.K.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Curcumin Loaded Chitin Nanogels for Skin Cancer Treatment via the Transdermal Route. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.R.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, G.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Park, J.R.; Jun, D.R.; Ryu, T.K.; Park, J.W.; Shin, E.; Choi, S.W. Fabrication of Dihydroxyflavone-Conjugated Hyaluronic Acid Nanogels for Targeted Antitumoral Effect. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kholy, S.A.; Osman, S.S.; Abdel-Sattar, R.; El Sayed, I.E.T. Synthesis of Quercetin-Loaded Carboxymethyl Cellulose Nanogel: Morphological Structure and in Vitro Release. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 15, 7495–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Wu, J. pH-Sensitive nanogels for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Adl, K.; Ghobashy, M.M.; Ismail, A.F.M.; El-Morsy, A.; Shoman, N.A. Radiation-induced nanogel engineering based on pectin for pH-responsive rutin delivery for cancer treatment. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Dong, X.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y. Nanogels of Dual Inhibitor-Modified Hyaluronic Acid Function as a Potent Inhibitor of Amyloid β-Protein Aggregation and Cytotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadian, N.; Hashemi, M. Effects of Apigenin and Apigenin- Loaded Nanogel on Induction of Apoptosis in Human Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Galen Med. J. 2018, 7, e1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, Y.L.; Kaur, P.; Yang, B.G.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, L.; Cui, Y.L. A Novel Inhalable Quercetin-Alginate Nanogel as a Promising Therapy for Acute Lung Injury. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.R.; Ji, H.W.; Chen, J.P.; Liu, X.F.; Song, B.B.; Zhong, S.Y.; Rifai, A.; Nisbet, D.R.; Barrow, C.J.; Williams, R.J.; et al. Biomimetic Triumvirate Nanogel Complexes via Peptide-Polysaccharide-Polyphenol Self-Assembly. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deghiedy, N.M.; Abdel-Naby, D.H.; Aziz, M.M.; El-Sheikh, M.M. Fisetin-Loaded Pluronic-Based Nanogel: Radiation Synthesis for Alleviating Neurocognitive Impairments in a Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease via Modulation of the Apoptotic Cascade. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Yu, C.; Zhu, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Zang, Z.; Guan, Y. Gallic Acid-Loaded Sodium Alginate-Based (Polyvinyl Alcohol-Co-Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel Membranes for Cutaneous Wound Healing: Synthesis and Characterization. Molecules 2022, 27, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akrawi, S.H.; Gorain, B.; Nair, A.B.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Shah, J.N.; Venugopala, K.N. Development and Optimization of Naringenin-Loaded Chitosan-Coated Nanoemulsion for Topical Therapy in Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.P.; Abraham, A. PVP- Coated Naringenin Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications–In Vivo Toxicological Evaluations. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 257, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, G.; Vigani, B.; Valentino, C.; Ruggeri, M.; Marchesi, N.; Pascale, A.; Giovilli, G.; Malavasi, L.; Sandri, G.; Rossi, S. Chondroitin Sulphate-Chitosan Based Nanogels Loaded with Naringenin-β-Cyclodextrin Complex as Potential Tool for the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Formulation Study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 907–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, M.; Sagbas Suner, S. Poli(Rutin) Micro/Nanogels for Biomedical Applications. Hittite J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xia, M.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Shen, H.; Ji, G.; Meng, Q.; Xie, Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Nanogels/Gels for Oral Delivery of Myricetin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 91, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lu, Y.R.; Kou, N.; Hu, M.J.; Wang, Q.S.; Cui, Y.L. Intranasal Delivery of Icariin via a Nanogel-Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Compound System to Improve Its Antidepressant-like Activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, A.; Alotaibi, N.M. Formulation and Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Nanogel for Oral Delivery of Diosmin. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 36, 535–540. [Google Scholar]
- Dabeek, W.M.; Marra, M.V. Dietary Quercetin and Kaempferol: Bioavailability and Potential Cardiovascular-Related Bioactivity in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathna, S.H.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Flavonoid Bioavailability and Attempts for Bioavailability Enhancement. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3367–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila-Gálvez, M.Á.; Giménez-Bastida, J.A.; González-Sarrías, A.; Espín, J.C. New insights into the metabolism of the flavanones eriocitrin and hesperidin: A comparative human pharmacokinetic study. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, E.; Sun, S.; Shen, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, X.; Zheng, R.; Farag, M.A.; Xiao, J. Flavonoids for gastrointestinal tract local and associated systemic effects: A review of clinical trials and future perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaru, B.; Drețcanu, G.; Pop, T.D.; Stǎnilǎ, A.; Diaconeasa, Z. Anthocyanins: Factors Affecting Their Stability and Degradation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Xie, K.; Liao, X.; Tan, J. Factors affecting the stability of anthocyanins and strategies for improving their stability: A review. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, Y.-H.; Ho, C.-T.; Pan, M.-H. Bioavailability and health benefits of major isoflavone aglycones and their metabolites. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 74, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, K.; Mandal, A.K.; Afzal, O.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Sahoo, A.; Alossaimi, M.A.; Almalki, W.H.; Alzahrani, A.; Barkat, M.A.; Almeleebia, T.M.; et al. Emergence of Nano-Based Formulations for Effective Delivery of Flavonoids against Topical Infectious Disorders. Gels 2023, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Pujol, E.J.; Martínez, G.; Casado-Jurado, D.; Vázquez, J.; León-Barberena, J.; Rodríguez-Lucena, D.; Torres, Y.; Alcudia, A.; Begines, B. Hydrogels and Nanogels: Pioneering the Future of Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, A.; Ithape, H.; Singh, P.K. Deep-insights: Nanoengineered gel-based localized drug delivery for arthritis management. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 20, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecorini, G.; Ferraro, E.; Puppi, D. Polymeric Systems for the Controlled Release of Flavonoids. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Islam, T.; Nurunnabi, M. Mucoadhesive carriers for oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 504–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spleis, H.; Sandmeier, M.; Claus, V.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Surface design of nanocarriers: Key to more efficient oral drug delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 313, 102848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnikov, I.D.; Belogurova, N.G.; Poddubnaya, I.V.; Kudryashova, E.V. Mucosal Adhesive Chitosan Nanogel Formulations of Antibiotics and Adjuvants (Terpenoids, Flavonoids, etc.) and Their Potential for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Basic Constituent | Type of Polymer | Characteristics | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural polymers | Collagen |
| [45,46,47,48,49] |
| Alginate |
| [49,50,51,52,53] | |
| Hyaluronic acid |
| [54,55,56] | |
| Chitosan |
| [57,58,59,60] | |
| Gelatin |
| [61,62,63] | |
| Synthetic polymers | PEG, polyglycolic derivatives |
| [50,64,65,66] |
| polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) |
| [67,68] | |
| polyacrylamide |
| [69,70] | |
| poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) |
| [71,72] |
| Flavonoid-Based Nanogel Characterization | Key Characteristics | References |
|---|---|---|
| Swelling Measurement |
| [24,31,57,108,109] |
| Mechanical Measurements |
| [13,110] |
| Electron Microscopy Measurements | Nanogels can be studied for determining morphological characteristics using a variety of robust and well-established techniques:
| [14,75] |
| X-ray Scattering Techniques |
| [14,75,111] |
| Rheology | Any route of administration has significant effects on the therapeutic efficacy and biopharmaceutical performance of incorporated flavonoids due to the change in viscosity of nanogel | [75] |
| Thermal analysis |
| [13,44] |
| Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) |
| [112,113] |
| Hyphenated Techniques (LC–MS, HRMS, NMR) |
| [114,115,116,117] |
| Model-Informed Drug Development (MIDD) |
| [117,118,119,120,121,122,123] |
| Flavonoid | Results | References |
|---|---|---|
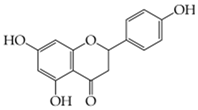 Naringenin (5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-chroman-4-one) |
| [140] |
| [141] | |
| [142] | |
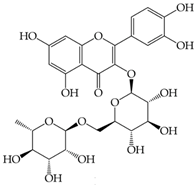 Rutin (3,3′,4′,5,7-pentahydroxyflavone-3-rhamnoside) |
| [143] |
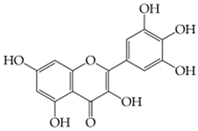 Myricetin (3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-chromen-4-one) |
| [144] |
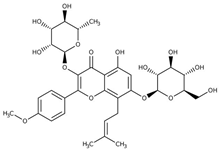 Icariin (5-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-{[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4H-chromen-4-one) |
| [145] |
 Diosmin (5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-yl 6-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside) |
| [146] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liga, S.; Paul, C. Flavonoid-Based Nanogels: A Comprehensive Overview. Gels 2025, 11, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040267
Liga S, Paul C. Flavonoid-Based Nanogels: A Comprehensive Overview. Gels. 2025; 11(4):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040267
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiga, Sergio, and Cristina Paul. 2025. "Flavonoid-Based Nanogels: A Comprehensive Overview" Gels 11, no. 4: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040267
APA StyleLiga, S., & Paul, C. (2025). Flavonoid-Based Nanogels: A Comprehensive Overview. Gels, 11(4), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040267








