Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Reveal Regulatory Pathways Underlying Quality Differences Between Wild and Cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Determination of Polysaccharide, Crude Protein, Mannitol, and Adenosine
2.3. Proteomics Profiling
2.4. Metabolic Profiling
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
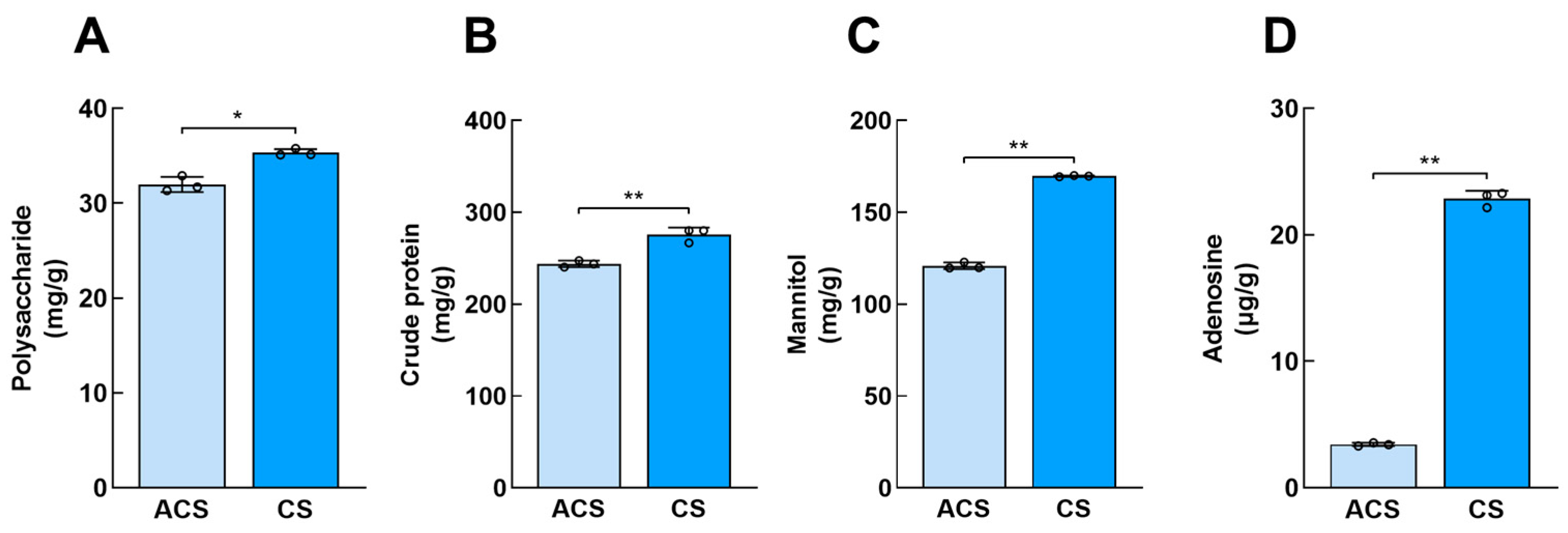
3.1. Analysis of Key Active Components of Wild and Cultivated O. sinensis
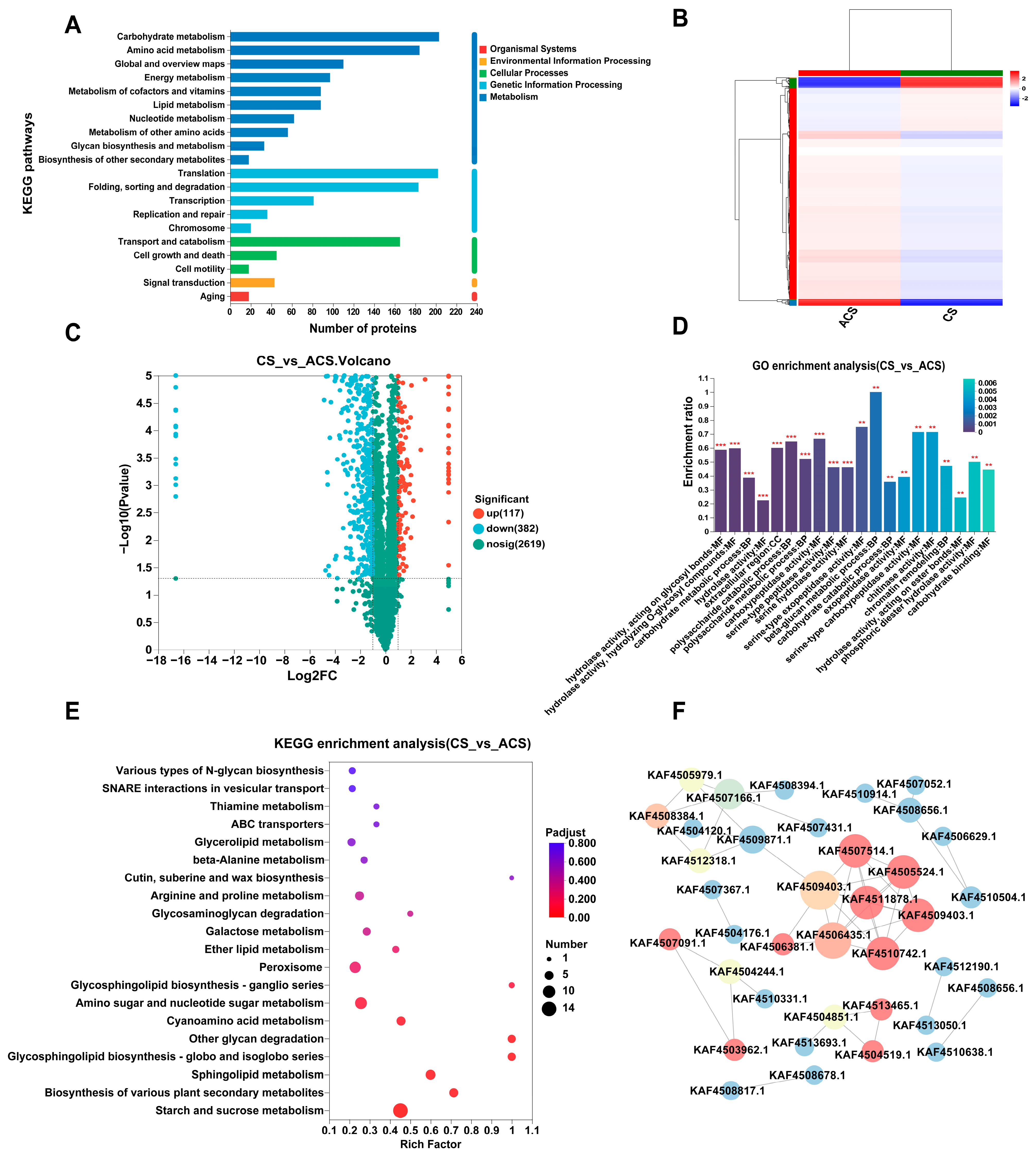
3.2. Proteomic Analyses of Wild and Cultivated O. sinensis
3.3. Comparative Analyses of the Metabolite Profiles of Wild and Cultivated O. sinensis
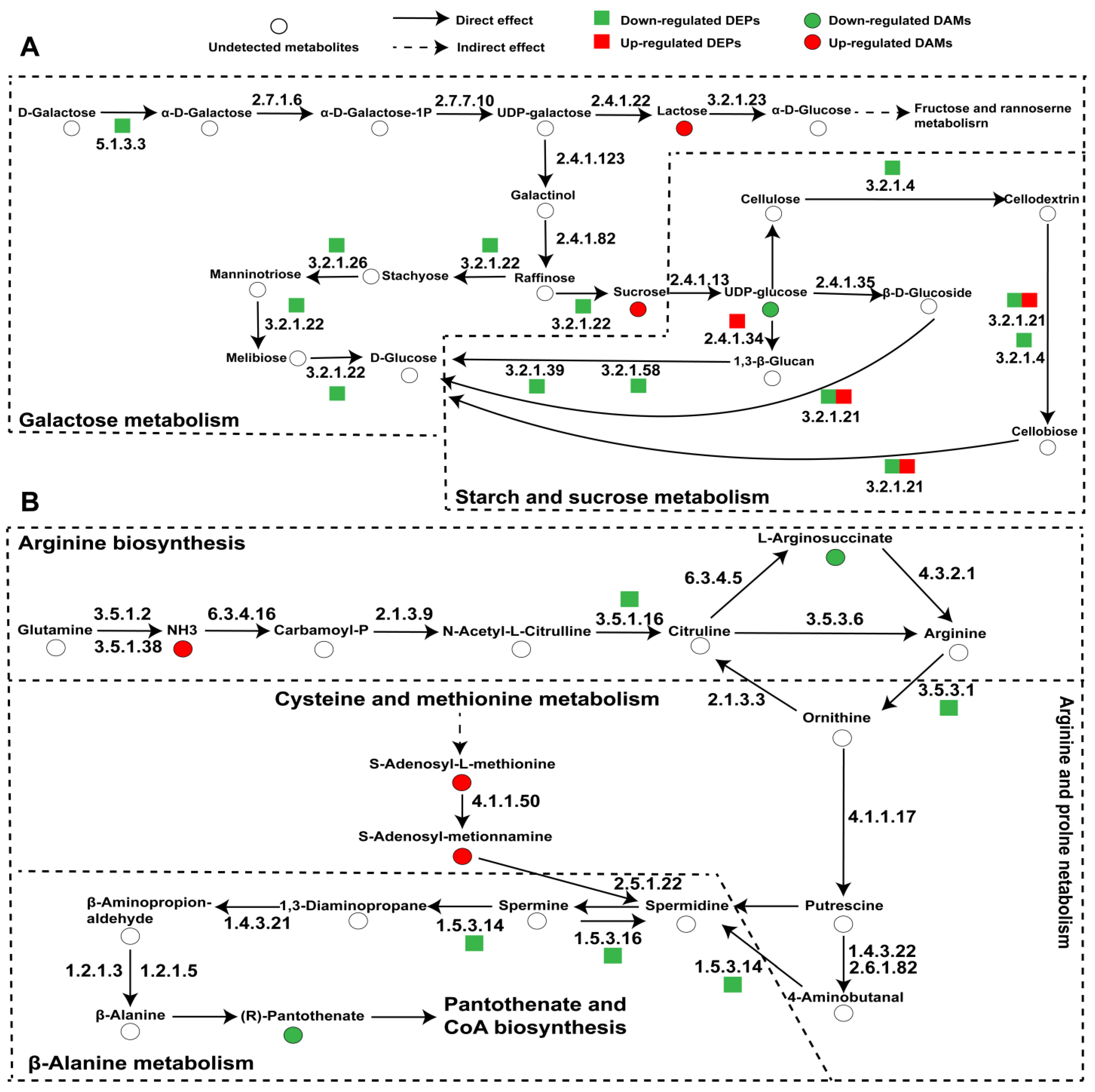
3.4. Combined Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses
3.5. Specifically Expressed Metabolic Process-Related Proteins and Metabolites in Wild and Cultivated O. sinensis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lo, H.C.; Hsieh, C.; Lin, F.Y.; Hsu, T.H. A systematic review of the mysterious Caterpillar Fungus Ophiocordyceps sinensis in Dong-ChongXiaCao (Dōng Chóng Xià Cǎo) and related bioactive ingredients. J. Tradit. Compl. Med. 2013, 3, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, N. Mechanism of Cordyceps sinensis and its Extracts in the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 881835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.K.; Wang, W.Q.; Wu, J.Y. Recent advances in Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharides: Mycelial fermentation, isolation, structure, and bioactivities: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Li, G.; Rong, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Pi, L.; Wei, L.; Bi, H. Exploratory studies of the antidepressant effect of Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide and its potential mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, D.; Tang, H.; Guo, J. Anti-inflammation effects of Cordyceps sinensis mycelium in focal cerebral ischemic injury rats. Inflammation 2011, 34, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Ke, Y.; Wang, X.; Long, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Guo, Y. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic activity of Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide (CSP-3). Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yao, H.Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, J.P.; Zhang, L.H.; Jia, Y.; Wang, R. Cardiovascular protection and antioxidant activity of the extracts from the mycelia of Cordyceps sinensis act partially via adenosine receptors. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide inhibits colon cancer cells growth by inducing apoptosis and autophagy flux blockage via mTOR signaling. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Pan, B.S.; Chang, M.M.; Huang, B.M. Functional study of Cordyceps sinensis and cordycepin in male reproduction: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Niyati, N.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Chinese caterpillar fungus (Ophiocordyceps sinensis) in China: Current distribution, trading, and futures under climate change and overexploitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Qian, Z.; Liu, X.; Dong, C. A breakthrough in the artificial cultivation of Chinese cordyceps on a large-scale and its impact on science, the economy, and industry. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhong, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X. Metabolic characterization of natural and cultured Ophicordyceps sinensis from different origins by 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 115, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yue, P.; Tong, X.; Gao, T.; Peng, T.; Guo, J. Comparative analysis of fatty acid metabolism based on transcriptome sequencing of wild and cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Peer J. 2021, 9, e11681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Han, R.; Cao, L. Artificial cultivation of the Chinese Cordyceps from injected ghost moth larvae. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 48, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Suh, J.H. Multi-omics approach in tea polyphenol research regarding tea plant growth, development and tea processing: Current technologies and perspectives. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Jahan, M.S.; Tang, K.; Jiang, S.; Guo, J.; Luo, S.; Luo, W.; Li, G. Comparative analysis of the medicinal and nutritional components of different varieties of Pueraria thomsonii and Pueraria lobata. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1115782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yin, D.; Zhou, Q.; Lv, L.; Dong, Z.; Shi, Y. Integration of proteomic and metabolomic characterization in atrial fibrillation-induced heart failure. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, C.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Qiu, M.; Fan, J. Integrating metabolomics and proteomics technologies provides insights into the flavor precursor changes at different maturity stages of arabica coffee cherries. Foods 2023, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lv, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. Proteomics and metabolomic analysis provide new insights into the drying changes of Agaricus sinodeliciosus. LWT 2024, 207, 116656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, B. Perspectives in Food & Medicine Homology. Food Med. Homol. 2024, 1, 9420018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, L.; Qu, Z.; Wang, H.; Dong, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, H. Integrated metabolomics and proteomics analysis to study the changes in Scutellaria baicalensis at different growth stages. Food Chem. 2023, 419, 136043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, F.; Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Ma, R.; Feng, K.; Jiang, R. Proteomic analysis of amino acid metabolism differences between wild and cultivated Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, P.; Jing, C.; Fu, B.; Teng, X.; Zhao, D.; Sun, L. Comparison of the metabolomic and proteomic profiles associated with triterpene and phytosterol accumulation between wild and cultivated ginseng. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 195, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, W.; Li, P.; Alolga, R.N.; Qi, L.W.; Yin, X. A comparative proteomic characterization and nutritional assessment of naturally- and artificially-cultivated Cordyceps sinensis. J. Proteom. 2018, 181, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Yi, Y. Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal metabolites difference between wild and cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Fu, B.; Chen, R.; Jiang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, R.; Xing, L.; Yuan, L.; Chen, X.; et al. DCABM-TCM: A Database of constituents absorbed into the blood and metabolites of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 4948–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Sun, X.; Yang, C.; Fan, Y. Integrated transcriptome and metabolome provide insight into flavonoid variation in goji berries (Lycium barbarum L.) from different areas in China. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 199, 107722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Xiao, M.; He, M.; Chang, X.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y. Characterization of Metabolite Landscape Distinguishes Medicinal Fungus Cordyceps sinensis and other Cordyceps by UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X Untargeted Metabolomics. Molecules 2023, 28, 7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Hernández, R.A.; Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Macías-Rubalcava, M.L.; Trujillo-Roldán, M.A. Overview of fungal terpene synthases and their regulation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB_T5009.5-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Protein in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Kamizake, N.K.K.; Gonçalves, M.M.; Zaia, C.T.B.V.; Zaia, D.A.M. Determination of total proteins in cow milk powder samples: A comparative study between the Kjeldahl method and spectrophotometric methods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2003, 16, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bai, S.; Bai, C.; Tu, Z.; Li, H.; Guo, P.; Liao, T.; Qiu, L. The viable but non-culturable (VBNC) status of Shewanella putrefaciens (S. putrefaciens) with thermosonication (TS) treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 109, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y. The key proteolytic enzyme analysis of industrial Aspergillus oryzae at solid-state koji fermentation with a local database extension. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Zuo, H.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.Q.; Hu, Y.J.; Qian, Z.M.; Li, W.J.; Xia, Z.N. Analysis of Soluble Proteins in Natural Cordyceps sinensis from Different Producing Areas by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Two-dimensional Electrophoresis. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Accumulation Characteristics of Natural Ophiocordyceps sinensis Metabolites Driven by Environmental Factors. Metabolites 2024, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Xiao, M.; He, M.; Chang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Metabolomic Profiling of Floccularia luteovirens from Different Geographical Regions Proposes a Novel Perspective on Their Antioxidative Activities. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, R.U.; Bhat, I.A.; Javid, H.; Wani, B.A.; Magray, J.A.; Nawchoo, I.A.; Gulzar, S. Exploring morphological variability, in vitro antioxidant potential, and HR-LCMS phytochemical profiling of Phlomis cashmeriana Royle ex Benth. across different habitats of Kashmir Himalaya. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yang, N.; Sui, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; Mu, L.; Tang, Z. Altitudinal variation on metabolites, elements, and antioxidant activities of medicinal plant Asarum. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarid-García, C.; Escamilla-Silva, E.M. Comparative study of the production of extracellular β-glucosidase by four different strains of Aspergillus using submerged fermentation. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 47, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C. Genome-Wide Identification of Callose Synthase Family Genes and Their Expression Analysis in Floral Bud Development and Hormonal Responses in Prunus mume. Plants 2023, 12, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggia, L.; Ametrano, C.G.; Sterflinger, K.; Tesei, D. An overview of genomics, phylogenomics and proteomics approaches in Ascomycota. Life 2020, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, R.; Lin, J.; Feng, R.; Ni, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, D.; Zhao, X. Application of omics technology in the research on edible fungi. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.W.; Li, L.J.; Tian, E.W. Advances in research of the artificial cultivation of Ophiocordyceps sinensis in China. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, L.; Nirina Ramamonjy, F.; Ursache, R. Imaging plant cell walls using fluorescent stains: The beauty is in the details. J. Microsc. 2024, 295, 102–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun-Waterhouse, D.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Liu, Z.-H.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Kang, W.-Y. Transformation from traditional medicine-food homology to modern food-medicine homology. Food Med. Homol. 2024, 1, 9420014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.L.; Yang, L.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, A.H.; Wang, X.J. Efficacy evaluation, active ingredients, and multitarget exploration of herbal medicine. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skácel, J.; Slusher, B.S.; Tsukamoto, T. Small molecule inhibitors targeting biosynthesis of Ceramide, the central hub of the sphingolipid network. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.H.; Tatum, S.M.; Symons, J.D.; Summers, S.A.; Holland, W.L. Ceramides and other sphingolipids as drivers of cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiechio, S.; Canonico, P.L.; Grilli, M. l-Acetylcarnitine: A Mechanistically Distinctive and Potentially Rapid-Acting Antidepressant Drug. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, Z.V.; Gordillo, R.; An, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, Q.; Yoshino, J.; Cautivo, K.M.; De Brabander, J.; Elmquist, J.K.; et al. An adipo-biliary-uridine axis that regulates energy homeostasis. Science 2017, 355, eaaf5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaralingam, M. Structure and conformation of nucleosides and nucleotides and their analogs as determined by x-ray diffraction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1975, 255, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morningstar, J.; Lee, J.; Mahon, S.; Brenner, M.; Nath, A.K. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Purine Intermediary Metabolism Indicates Cyanide Induces Purine Catabolism in Rabbits. Metabolites 2024, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, C.; Wang, T.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, M.; He, M.; Chang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Reveal Regulatory Pathways Underlying Quality Differences Between Wild and Cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070469
Tang C, Wang T, Fan Y, Wang J, Xiao M, He M, Chang X, Li Y, Li X. Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Reveal Regulatory Pathways Underlying Quality Differences Between Wild and Cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(7):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070469
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Chuyu, Tao Wang, Yuejun Fan, Jie Wang, Mengjun Xiao, Min He, Xiyun Chang, Yuling Li, and Xiuzhang Li. 2025. "Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Reveal Regulatory Pathways Underlying Quality Differences Between Wild and Cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 7: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070469
APA StyleTang, C., Wang, T., Fan, Y., Wang, J., Xiao, M., He, M., Chang, X., Li, Y., & Li, X. (2025). Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Reveal Regulatory Pathways Underlying Quality Differences Between Wild and Cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Journal of Fungi, 11(7), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070469






