Static and Dynamic Changes in Local Brain Connectivity in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
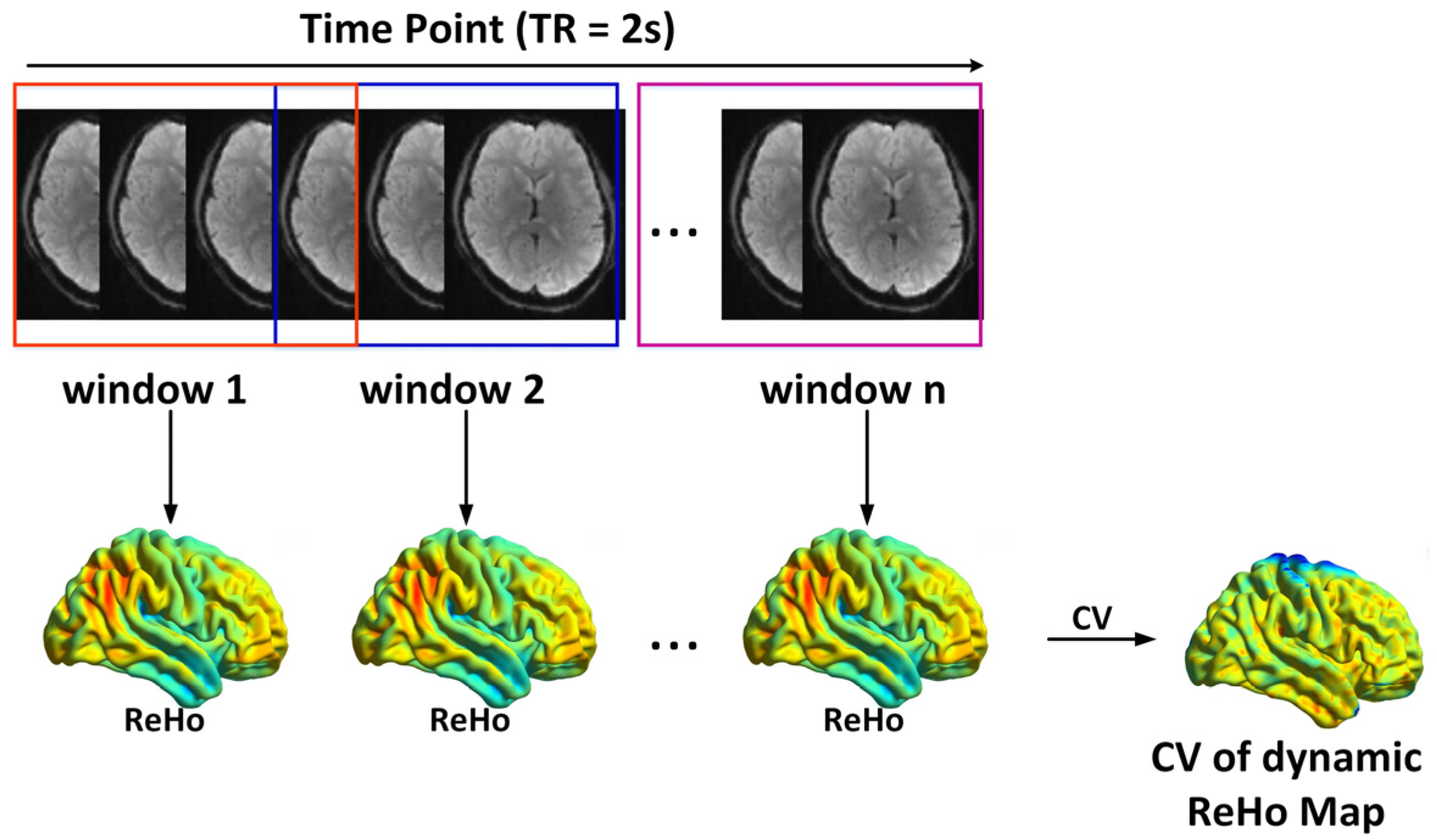
2.4. Static and Dynamic ReHo Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
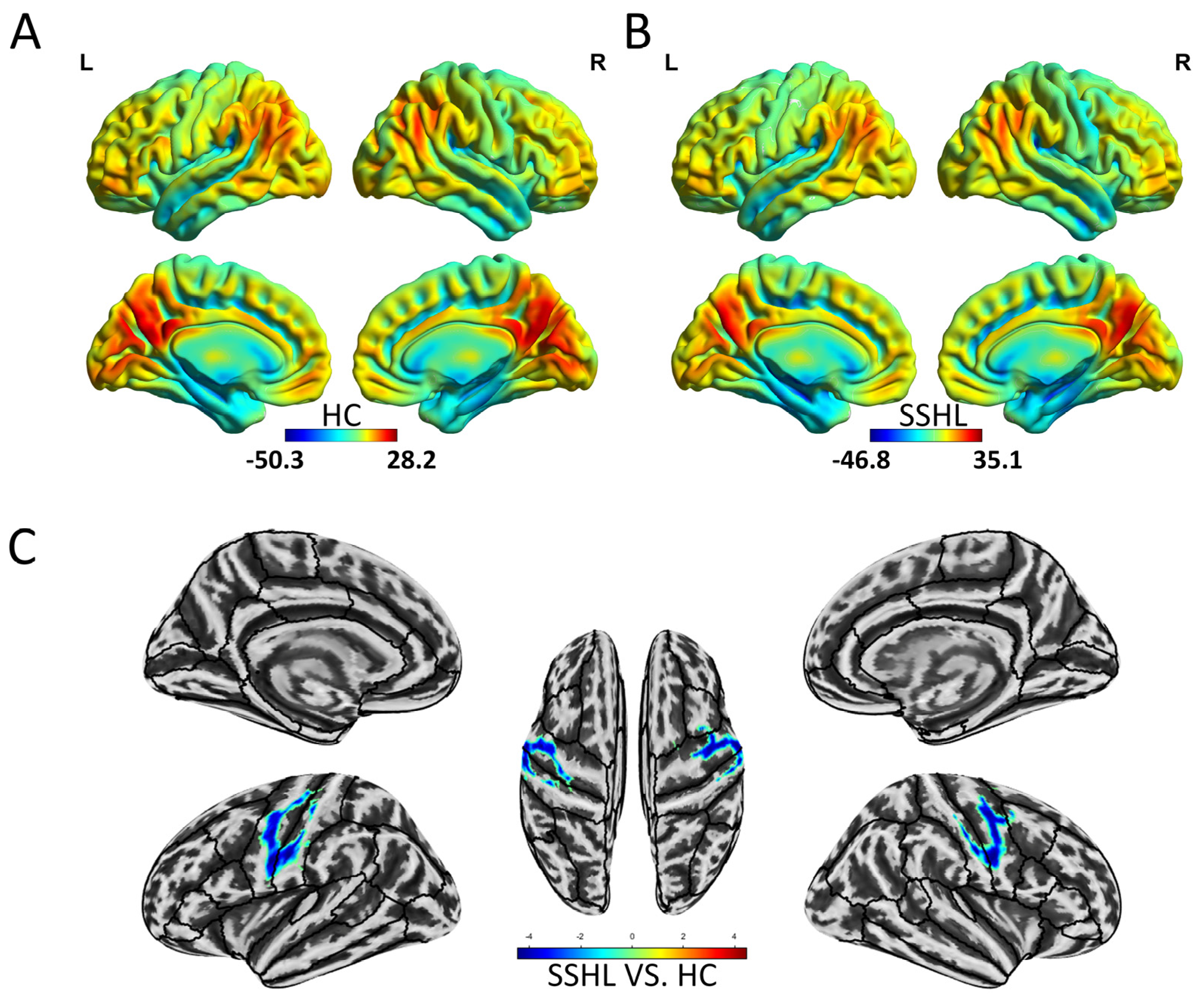
3.1. Spatial Distribution and Group Differences of Static ReHo
3.2. Spatial Distribution and Group Differences of Dynamic ReHo
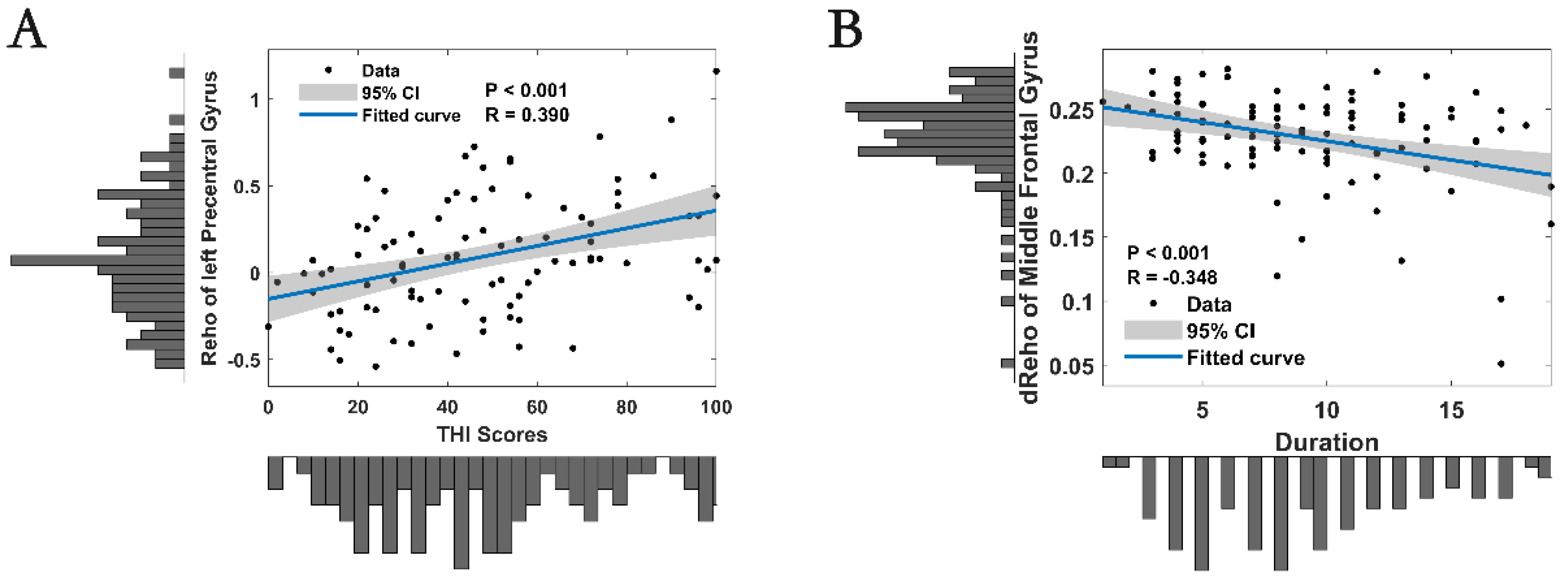
3.3. Correlation Analysis
3.4. Classification of SSHL Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, D.H.; Fagan, P.A.; Ryugo, D.K. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A critique on corticosteroid therapy. Hear. Res. 2022, 422, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.; Heman-Ackah, S.E.; Shaikh, J.A.; Roehm, P.C. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Chung, C.H.; Wang, C.H.; Chien, W.C.; Chen, H.C. Increased incidence in hospitalised patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A 14-year nationwide population-based study. Int. J. Audiol. 2019, 58, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.Y.; Nam, H.J.; Kim, M.H. A Nationwide Population-Based Study for the Recurrence and Comorbidities in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.Y.; Lee, J.; Kong, T.H.; Seo, Y.J. Importance of small vessel disease as a possible cause of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.E.; Durstenfeld, A.; Roehm, P.C. Viral causes of hearing loss: A review for hearing health professionals. Trends Hear. 2014, 18, 2331216514541361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Cheon, H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.G.; Koo, J.W.; Hong, S.K. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss associated with inner ear lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.Y.F.; Camara-Lemarroy, C.R. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss as an initial presentation in multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 105, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Lim, H.; Lee, K.; Hong, C.E.; Choi, H.S. High Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Several Autoimmune Diseases according to a Population-Based National Sample Cohort Study. Audiol. Neurootol. 2019, 24, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161 (Suppl. S1), S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, Z.; Kolb, B.E.; Mohajerani, M.H. A systematic review of altered resting-state networks in early deafness and implications for cochlear implantation outcomes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2024, 59, 2596–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, T.E.; Domingo, D.; Hassan, J.; Vuong, A.; Hordacre, B.; Clark, C.; Katrakazas, P.; Shekhawat, G.S. Resting-state Networks in Tinnitus: A Scoping Review. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2022, 32, 903–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zou, Y.; Kong, X.; Leng, Y.; Yang FZhou GLiu, B.; Fan, W. Exploring functional connectivity alterations in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A multilevel analysis. Brain Res. 2024, 1824, 148677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, X.; Zou, Y.; Leng, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, B.; Fan, W. Altered static and dynamic intrinsic brain activity in unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1257729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fan, J.; Zhan, H.; Huang, J.; Cao, R.; Xiang, X.; Tian, S.; Ren, H.; Tong, M.; Li, Q. Abnormal regional signal in the left cerebellum as a potential neuroimaging biomarker of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 967391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Fan, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Lei, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.; Shi, H. Disrupted functional brain connectome in unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2016, 335, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponticorvo, S.; Manara, R.; Pfeuffer, J.; Cappiello, A.; Cuoco, S.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Troisi, D.; Scarpa, A.; Cassandro, E.; Di Salle, F.; et al. Long-Range Auditory Functional Connectivity in Hearing Loss and Rehabilitation. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.T.; Chen, J.W.; Yan, L.F.; Hu, B.; Chen, T.Q.; Chen, Z.H.; Sun, J.T.; Shang, Y.X.; Lu, L.J.; Cui, G.B.; et al. Dynamic alterations of functional connectivity and amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in patients with unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 772, 136470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, N.C.; Banerjee, A. Dynamicity of brain network organization & their community architecture as characterizing features for classification of common mental disorders from whole-brain connectome. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 268. [Google Scholar]
- Liégeois, R.; Li, J.; Kong, R.; Orban, C.; Van De Ville, D. Resting brain dynamics at different timescales capture distinct aspects of human behavior. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabet, L.B.; Pascual-Leone, A. Neural reorganization following sensory loss: The opportunity of change. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.G.; Yang, Z.; Colcombe, S.J.; Zuo, X.N.; Milham, M.P. Concordance among indices of intrinsic brain function: Insights from inter-individual variation and temporal dynamics. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Tan, Y.; Yang, S.; Miao, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, H.; Yao, D.; Luo, C. Temporal Dynamic Synchronous Functional Brain Network for Schizophrenia Classification and Lateralization Analysis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2024, 43, 4307–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ren, J.; Lei, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Fu, L.; Li, Q.; Guo, C.; Teng, X.; Wu, Z.; et al. Aberrant patterns of spontaneous brain activity in schizophrenia: A resting-state fMRI study and classification analysis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Dai, L.; Chen, W.; Lu, J.; Hu, C.; Zhao, H.; Ke, J. Dynamics and concordance alterations of regional brain function indices in vestibular migraine: A resting-state fMRI study. J. Headache Pain 2024, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Zhang, F.; Sun, S.; Shaocheng, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J. Abnormal Local Brain Activity and Cognitive Impairments in Young Non-Disabled Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Resting-State Functional MRI Study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 60, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, X.-M.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Miao, X.-Q.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Salvi, R.; Xu, J.-J.; Qi, J.-W. The relationship between changes in functional connectivity gradients and cognitive-emotional disorders in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.W.; Jacobson, G.P.; Spitzer, J.B. Development of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1996, 122, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.G.; Wang, X.D.; Zuo, X.N.; Zang, Y.F. DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (Resting-State) Brain Imaging. Neuroinformatics 2016, 14, 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Duan, X.; Cui, Q.; Chen, H.; Liao, W. More than just statics: Temporal dynamics of intrinsic brain activity predicts the suicidal ideation in depressed patients. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xiao, S.; Chen, G.; Zhong, S.; Zhong, H.; Sun, S.; Chen, P.; Tang, X.; Yang HJia, Y.; Yin, Z.; et al. Disruption of the gut microbiota-inflammation-brain axis in unmedicated bipolar disorder II depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cheng, Q.; Leng, Y.; Ma, H.; Yang, F.; Liu, B.; Fan, W. Neuroimaging Insights: Structural Changes and Classification in Ménière’s Disease. Ear Hear. 2024, 45, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortier-Lebel, N.; Nakajima, T. Exploring the Consistent Roles of Motor Areas Across Voluntary Movement and Locomotion. Neuroscientist 2024, 31, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurabi, A.; Keithley, E.M.; Housley, G.D.; Ryan, A.F.; Wong, A.C. Cellular mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, D.D.; Bruno, R.M. Stability of cross-sensory input to primary somatosensory cortex across experience. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:2024.08.07.607026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, A.; Yusuf, P.A.; Land, R. Higher-order auditory areas in congenital deafness: Top-down interactions and corticocortical decoupling. Hear. Res. 2017, 343, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf PAHubka, P.; Tillein, J.; Kral, A. Induced cortical responses require developmental sensory experience. Brain 2017, 140, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.P.; Robbins, T.W. The role of prefrontal cortex in cognitive control and executive function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.D.; Hase, Y.; Clarkson, A.N.; Kalaria, R.N. The role of the medial prefrontal cortex in cognition, ageing and dementia. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.S.; Oh, E.S.; Reed, N.S.; Lin, F.R.; Deal, J.A. Hearing Loss and Cognition: What We Know and Where We Need to Go. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 13, 769405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, A.; Scarpa, A.; Di Girolamo, S.; De Luca, P.; Cassandro, C.; Viola, P.; Ricciardiello, F.; Greco, A.; Vincentiis, M.; Ralli, M.; et al. Hearing Loss and Cognitive Impairment: Epidemiology, Common Pathophysiological Findings, and Treatment Considerations. Life 2021, 11, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, C.; Qian, J.; Zhu, G.; Xu, X.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Che, Z. Aberrant Intra- and Inter-Network Connectivity in Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss with Tinnitus. Curr. Med. Imaging 2024, 20, e15734056308400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, B.; Qin, P.; Gao, W.; Liu, C.; Zi, D.; Ding, X.; Yu, Y.; Cui, G.; Lu, L. Altered Brain Activity and Functional Connectivity in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 9460364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Gao, W.; Yang, A.; Lv, K.; Xia, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Cerebral Blood Flow Pattern Changes in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 856710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Duan, L.; Ou, Y.; Ling, Q.; Cao, L.; Qian, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X. The cerebellum and cognitive neural networks. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1197459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prati, J.M.; Pontes-Silva, A.; Gianlorenço, A.C.L. The cerebellum and its connections to other brain structures involved in motor and non-motor functions: A comprehensive review. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 465, 114933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.C.; Xu, X.M.; Xu, Z.G.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J.J.; Hu, J.H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.C. Abnormal cerebellar network and effective connectivity in sudden and long-term sensorineural hearing loss. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 964349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.T.; Bai, K.; Li, G.Z.; Hu, B.; Chen, J.W.; Shang, Y.X. Functional to structural plasticity in unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Neuroimaging evidence. Neuroimage 2023, 283, 120437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Frank, E.; Kreuzer, P.; Kleinjung, T.; Vielsmeier, V.; Landgrebe, M.; Hajak, G.; Langguth, B. Transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of tinnitus: 4-year follow-up in treatment responders--a retrospective analysis. Brain Stimul. 2011, 4, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, Y. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation improves both hearing function and tinnitus perception in sudden sensorineural hearing loss patients. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, P.M.; Poeppl, T.B.; Rupprecht, R.; Vielsmeier, V.; Lehner, A.; Langguth, B.; Schecklmann, M. Individualized Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Treatment in Chronic Tinnitus? Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Rao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Burton, P.C.; Rishiq, D.; Abrams, H. Neuromodulatory Effects of Auditory Training and Hearing Aid Use on Audiovisual Speech Perception in Elderly Individuals. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Harper, M.; Pedersen, E.; Goman, A.; Suen, J.J.; Price, C.; Applebaum, J.; Hoyer, M.; Lin, F.R.; Reed, N.S. Hearing Loss, Loneliness, and Social Isolation: A Systematic Review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 162, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Abuduxukuer, K.; Hou, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G.; Zhou, Y. Is there a correlation between sensory impairments and social isolation in middle-aged and older Chinese population? Cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence from a nationally representative survey. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1098109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Subjects | SSHL | HC | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 102 | 73 | N/A |
| Age (years) | 38.89 ± 12.11 | 38.01 ± 16.52 | 0.685 |
| Gender (male/female) | 52/50 | 37/36 | 0.969 |
| Education level (years) | 12.67 ± 3.20 | 12.74 ± 2.93 | 0.878 |
| Duration (days) | 9.03 ± 4.27 | N/A | N/A |
| Effected side (left/right) | 56/46 | N/A | N/A |
| PTA (dBHL) | 73.66 ± 10.38 | 13.25 ± 5.08 | <0.001 |
| THI score | 47.54 ± 26.37 | N/A | N/A |
| Brain Regions | Voxels | MNI Coordinates | T Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | |||
| Static ReHo (SSHL vs. HC) | |||||
| Left cerebellum posterior lobe | 91 | −15 | −69 | −30 | 4.1 |
| Left precentral gyrus/Left postcentral gyrus | 143 | −57 | −6 | 45 | −4.6 |
| Right precentral gyrus/Right postcentral gyrus/Right middle frontal gyrus | 148 | 60 | 0 | 24 | −4.5 |
| Dynamic ReHo (SSHL vs. HC) | |||||
| Bilateral middle frontal gyrus, bilateral superior frontal gyrus | 100 | −27 | 9 | 66 | 5.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, Q.; Lei, Z.; Yang, F.; Ding, M.; Fan, W. Static and Dynamic Changes in Local Brain Connectivity in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060619
Zeng J, Li J, Liu B, Yu Q, Lei Z, Yang F, Ding M, Fan W. Static and Dynamic Changes in Local Brain Connectivity in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060619
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Junchao, Jing Li, Bo Liu, Qun Yu, Ziqiao Lei, Fan Yang, Mingyue Ding, and Wenliang Fan. 2025. "Static and Dynamic Changes in Local Brain Connectivity in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060619
APA StyleZeng, J., Li, J., Liu, B., Yu, Q., Lei, Z., Yang, F., Ding, M., & Fan, W. (2025). Static and Dynamic Changes in Local Brain Connectivity in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Bioengineering, 12(6), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060619







