Assessing Hydrological Alterations and Environmental Flow Components in the Beht River Basin, Morocco, Using Integrated SWAT and IHA Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
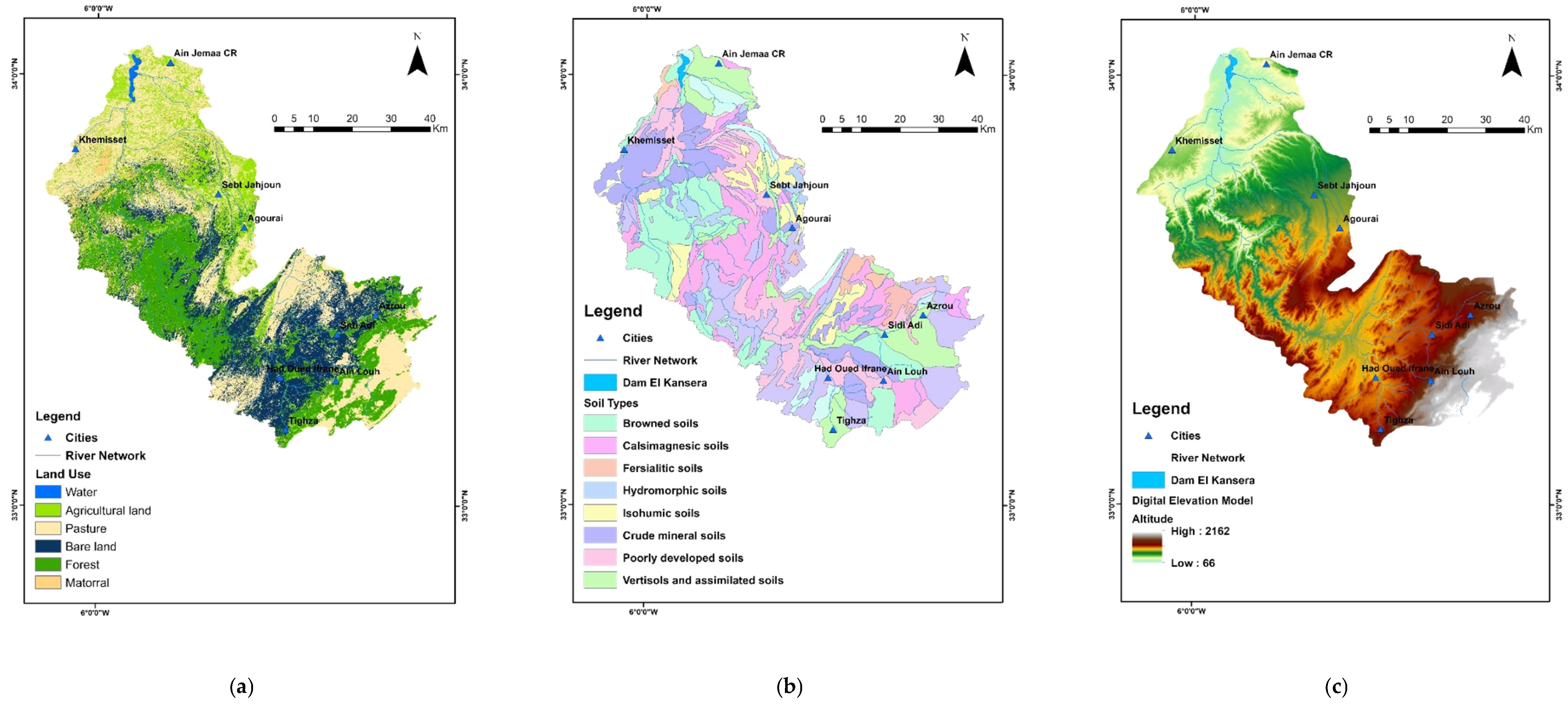
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Overall Methodology
2.3. Model Choices and Description
2.3.1. SWAT Model Setup
- Data requirements
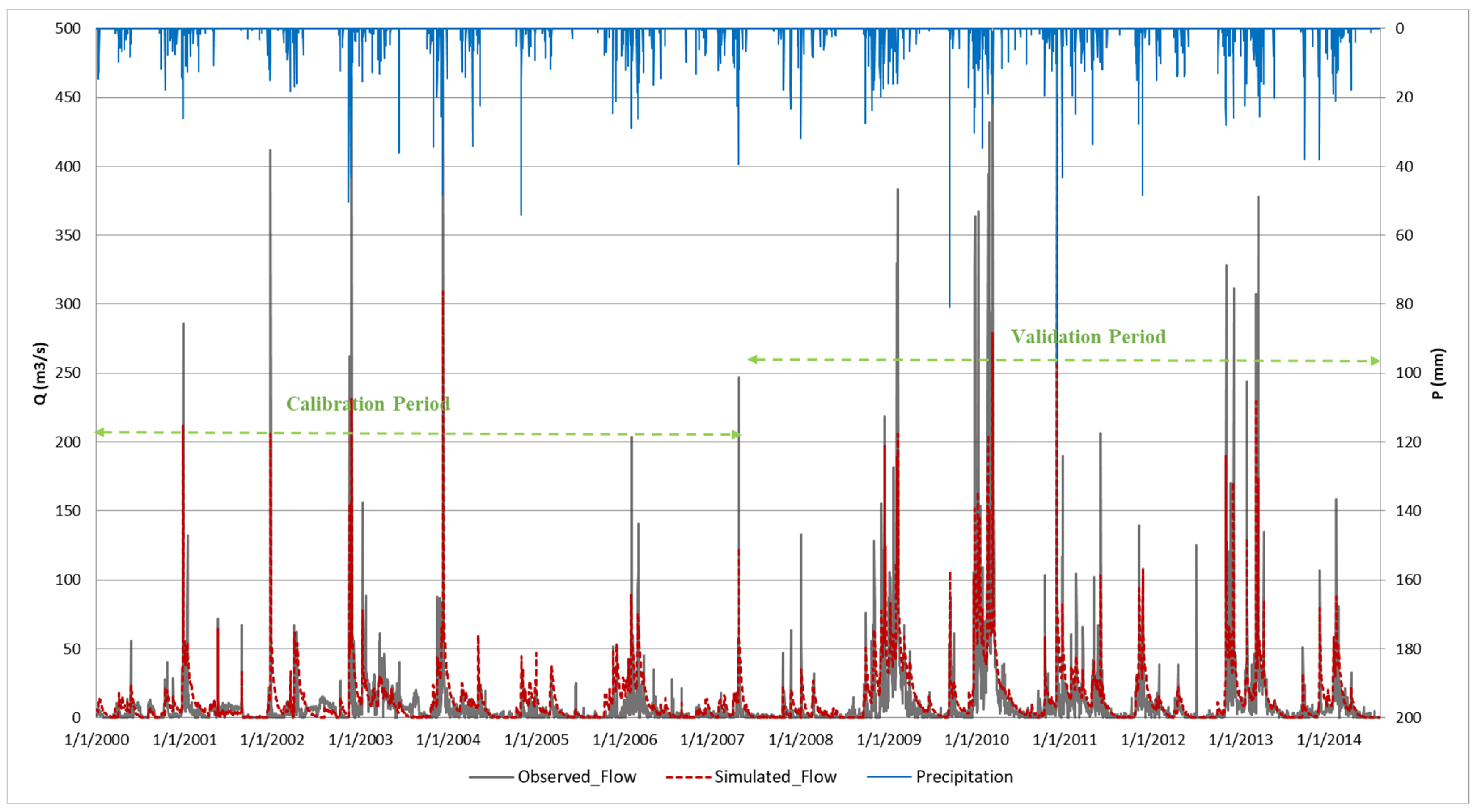
- Model Calibration and Validation
2.3.2. IHA Model Setup
- Data requirements
2.3.3. Drought Analysis Using the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
3. Results
3.1. SWAT Model
3.1.1. Sensitivity Analysis
3.1.2. Model Calibration/Validation
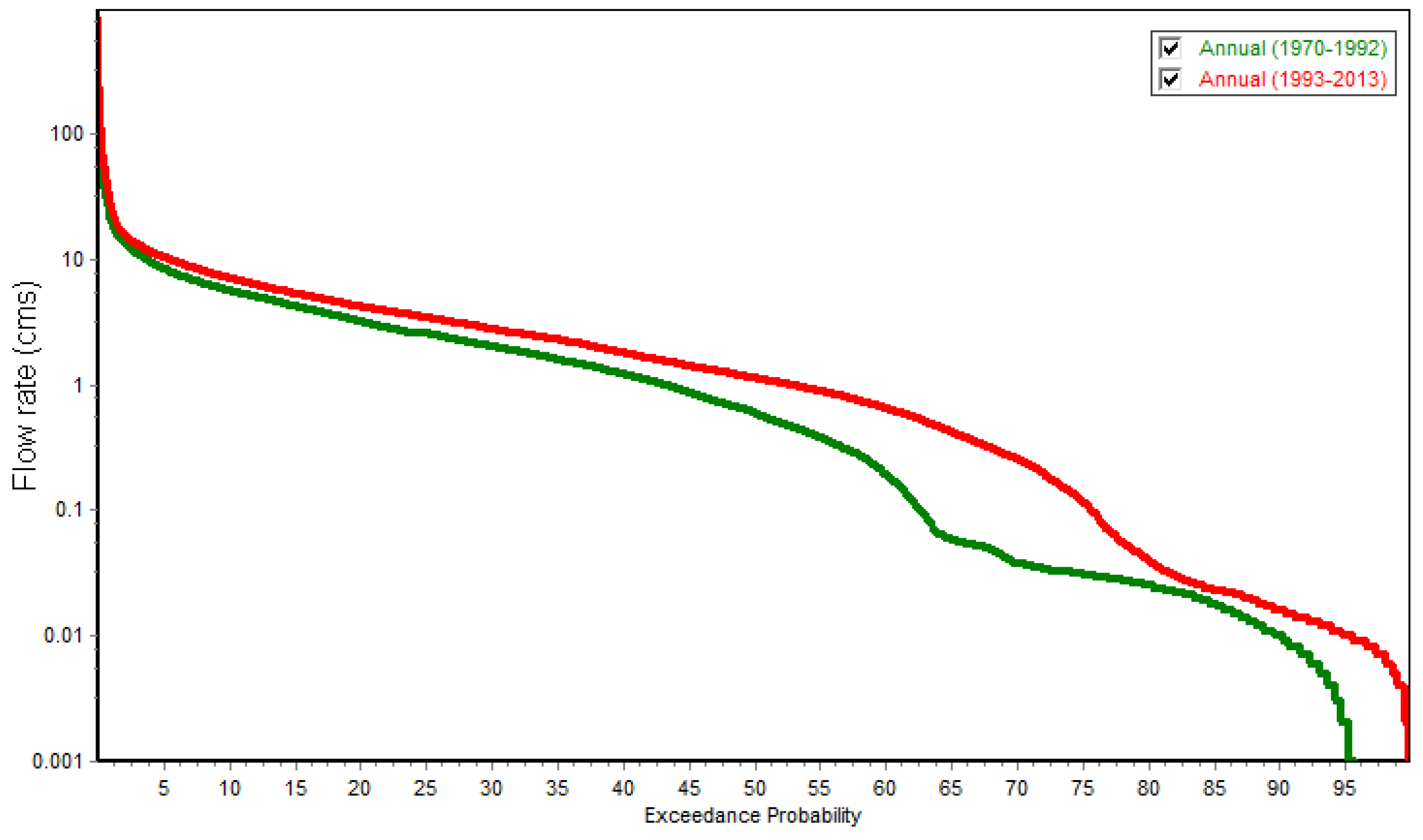
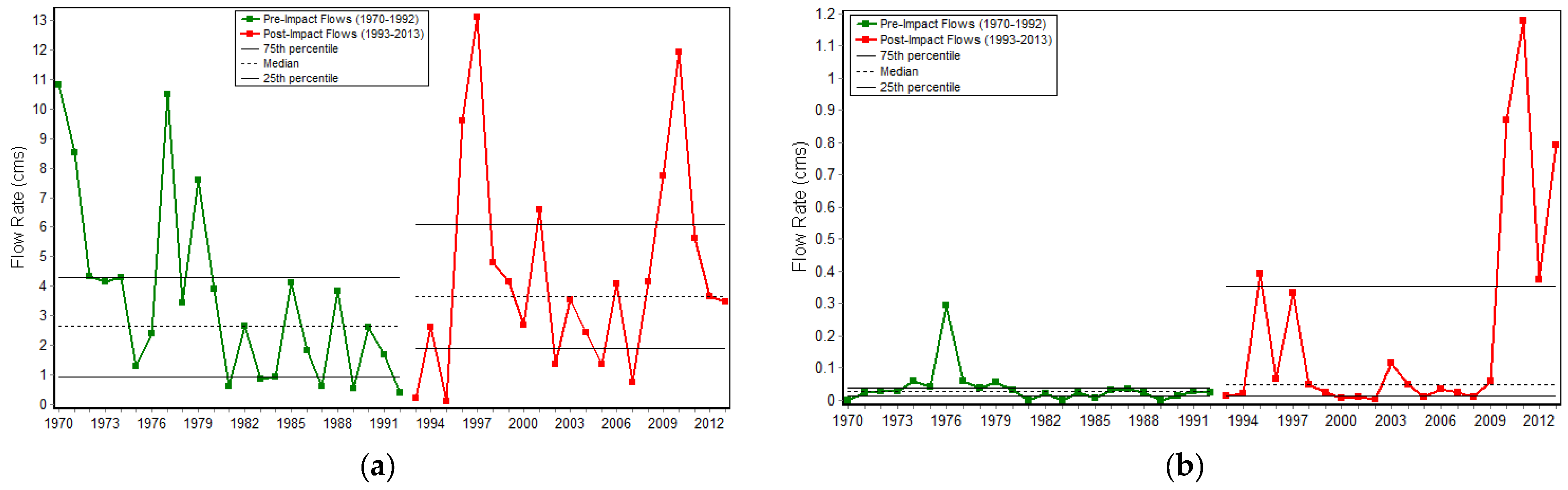
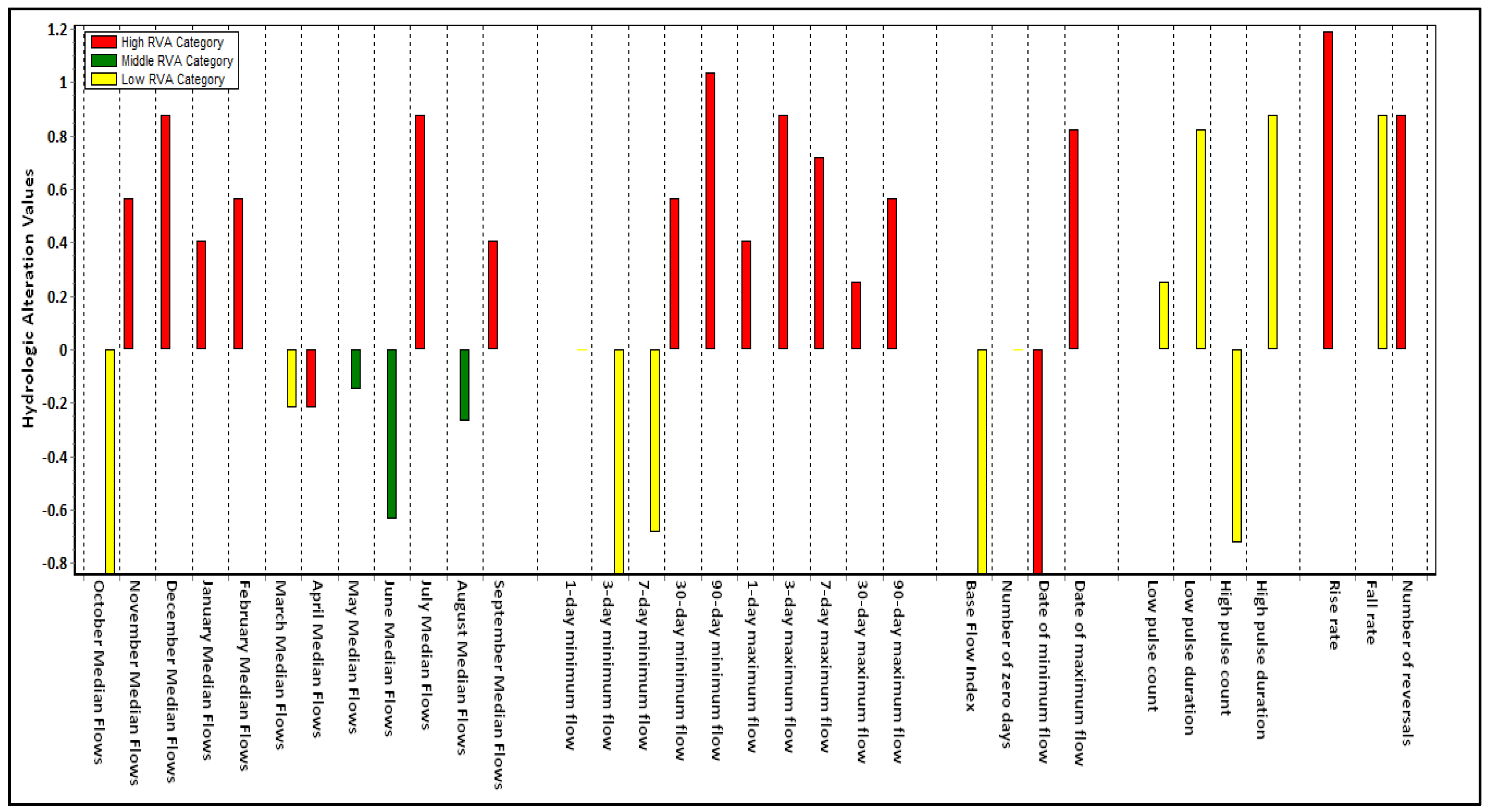
3.2. IHA Model
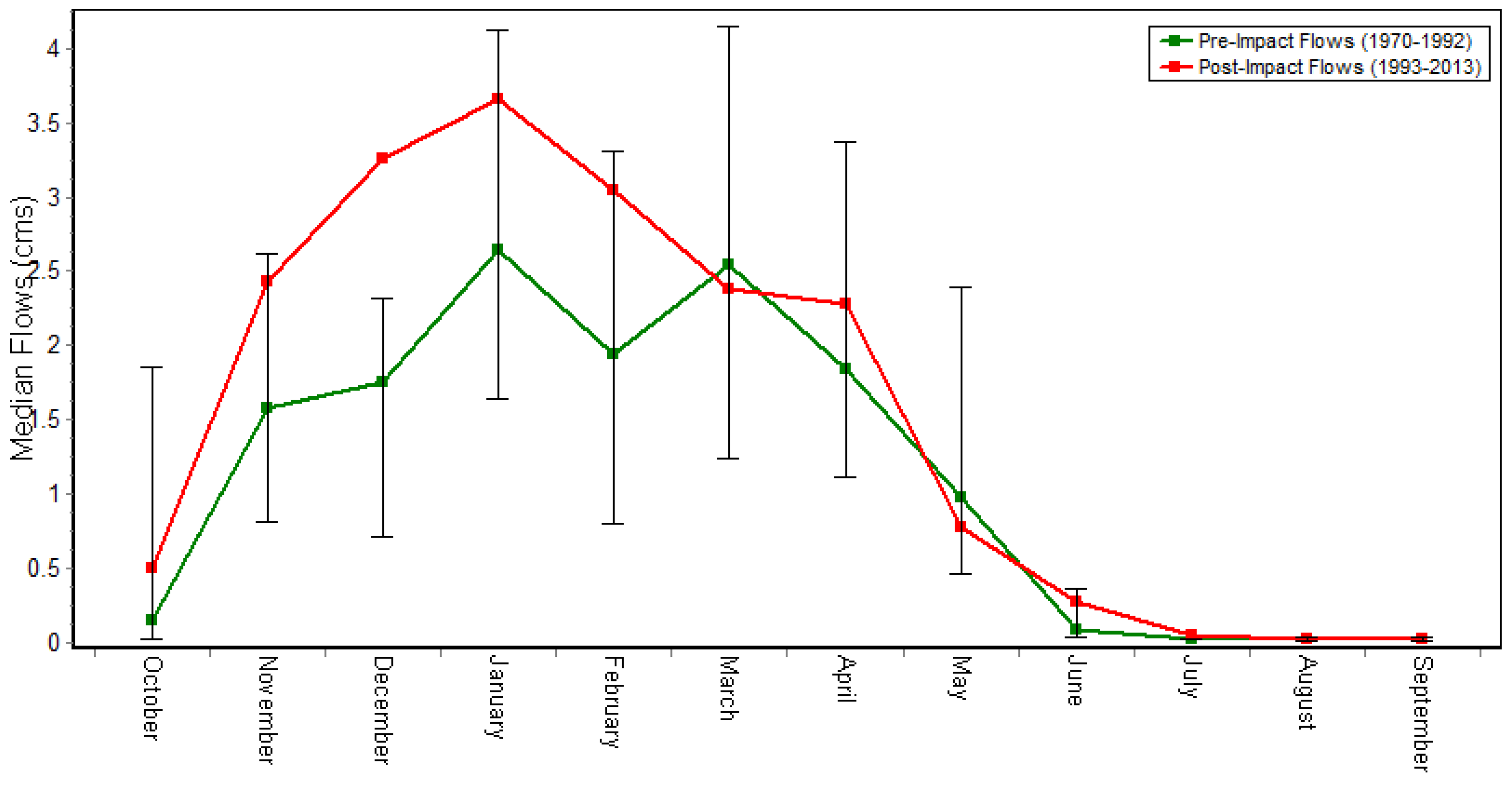
3.2.1. IHA Components
- 1.
- Group 1: Magnitude of monthly flows
- 2.
- Group 2: Magnitude and duration of extreme conditions
- 3.
- Group 3: Timing of extreme annual water conditions
- 4.
- Group 4: High and low-flow pulses
- 5.
- Group 5: Rate and frequency of flow changes
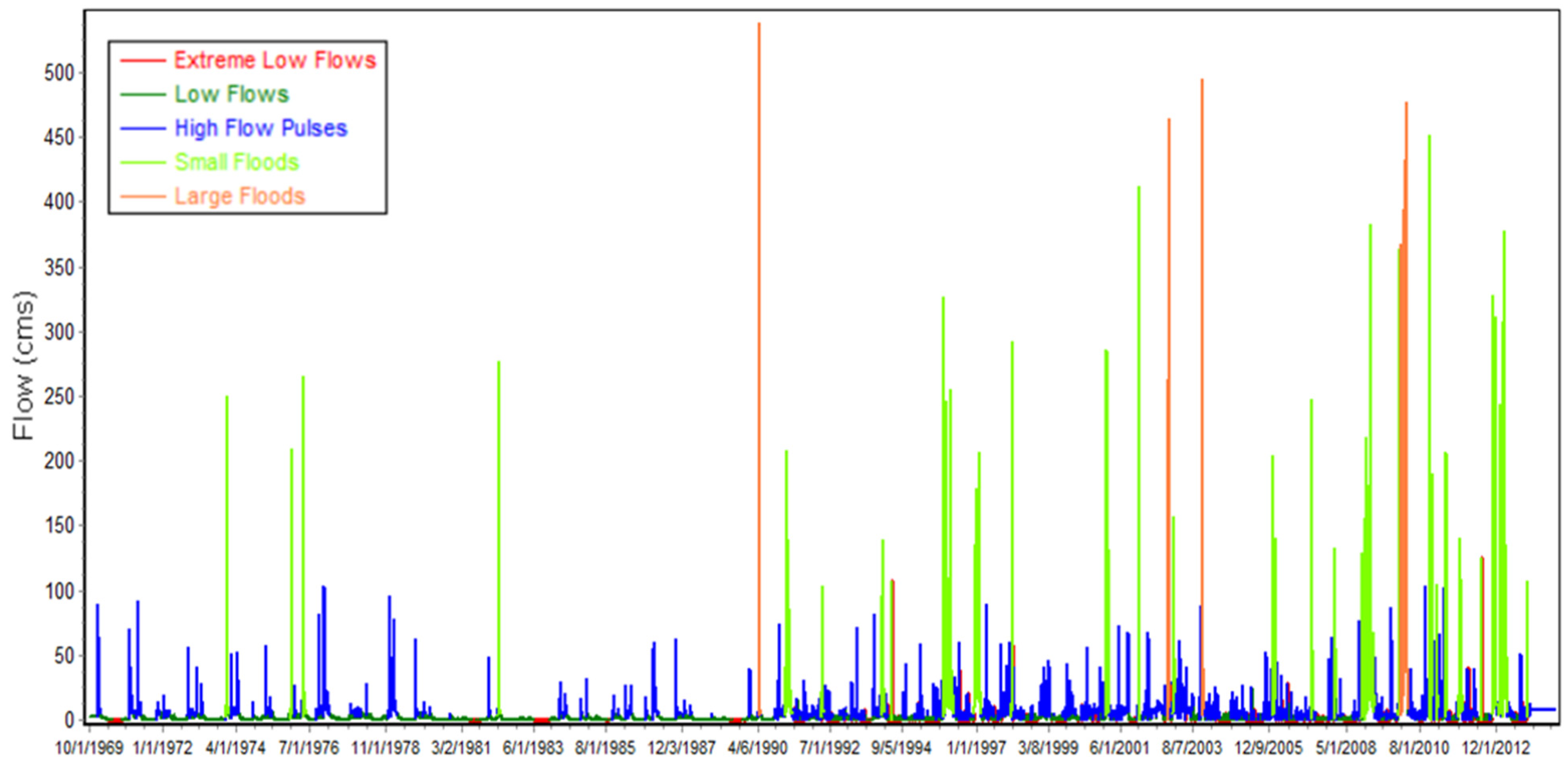
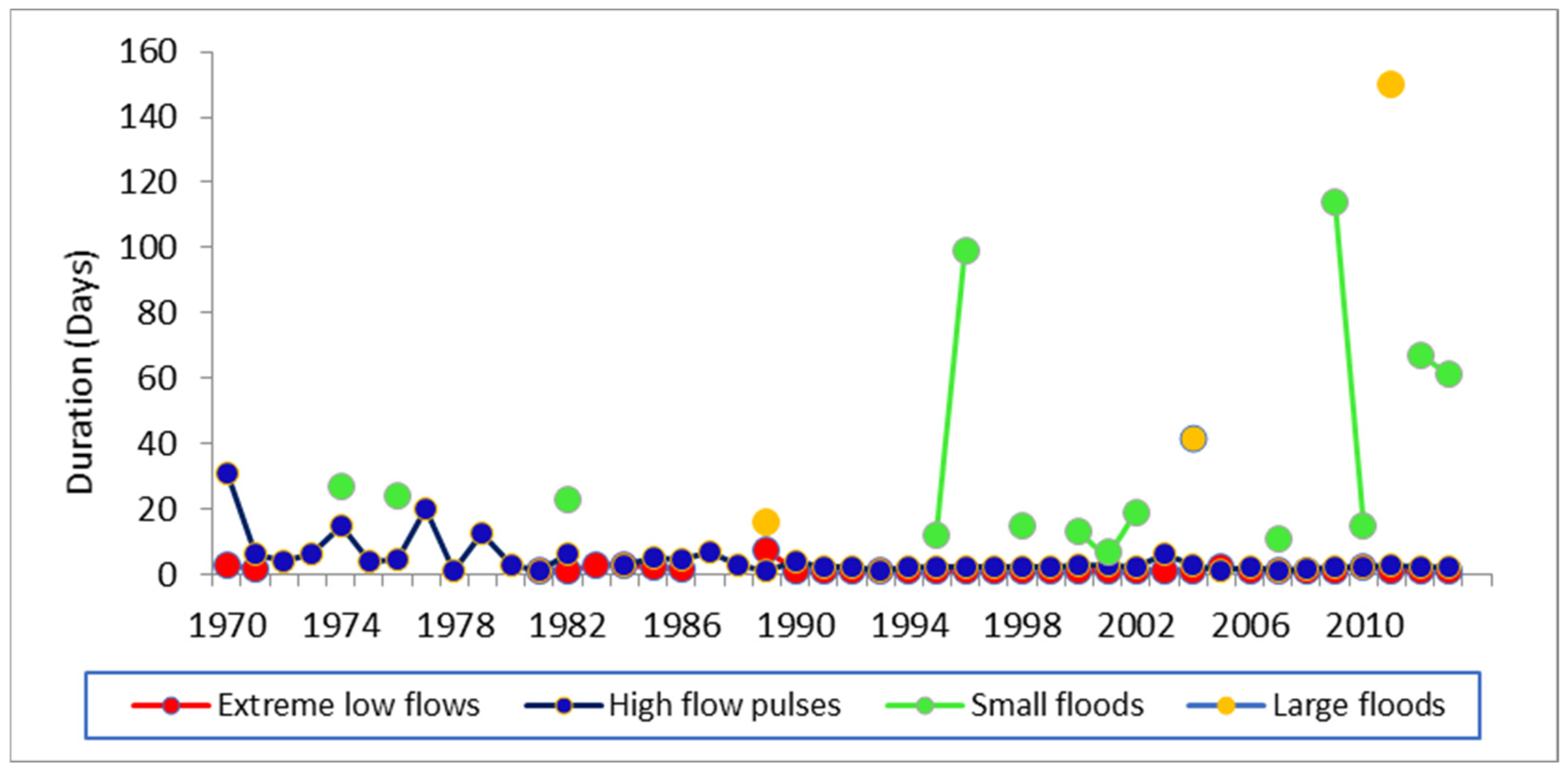
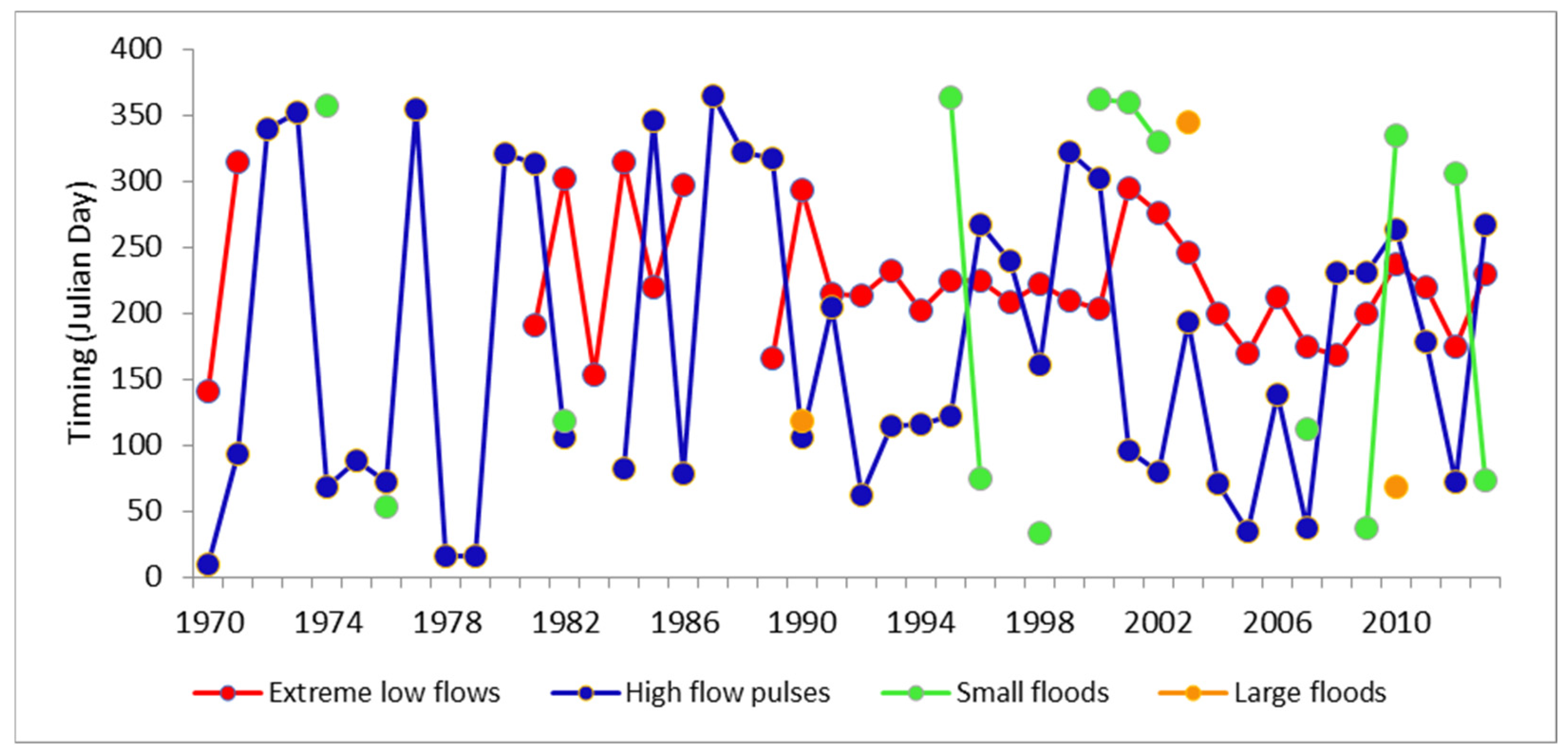
3.2.2. Environmental Flow Components, Duration and Timing
- 1.
- Environmental flow components
- 2.
- Flow duration and timing of environmental flow components
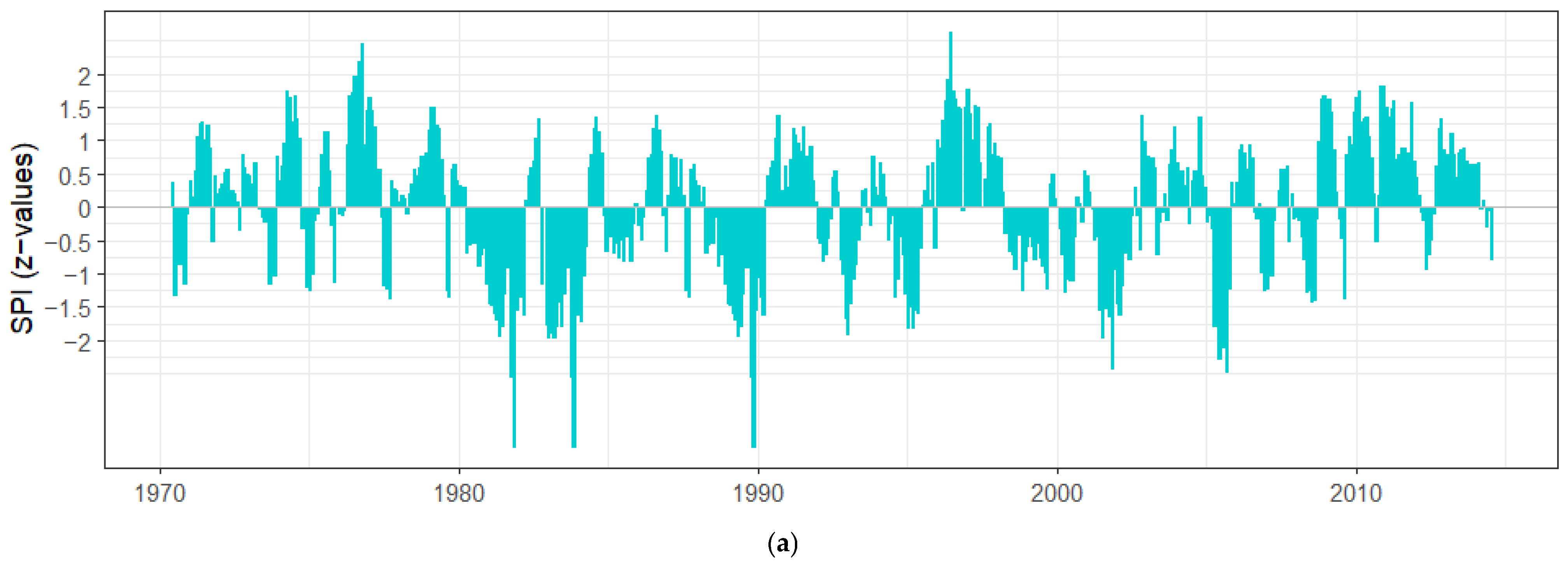
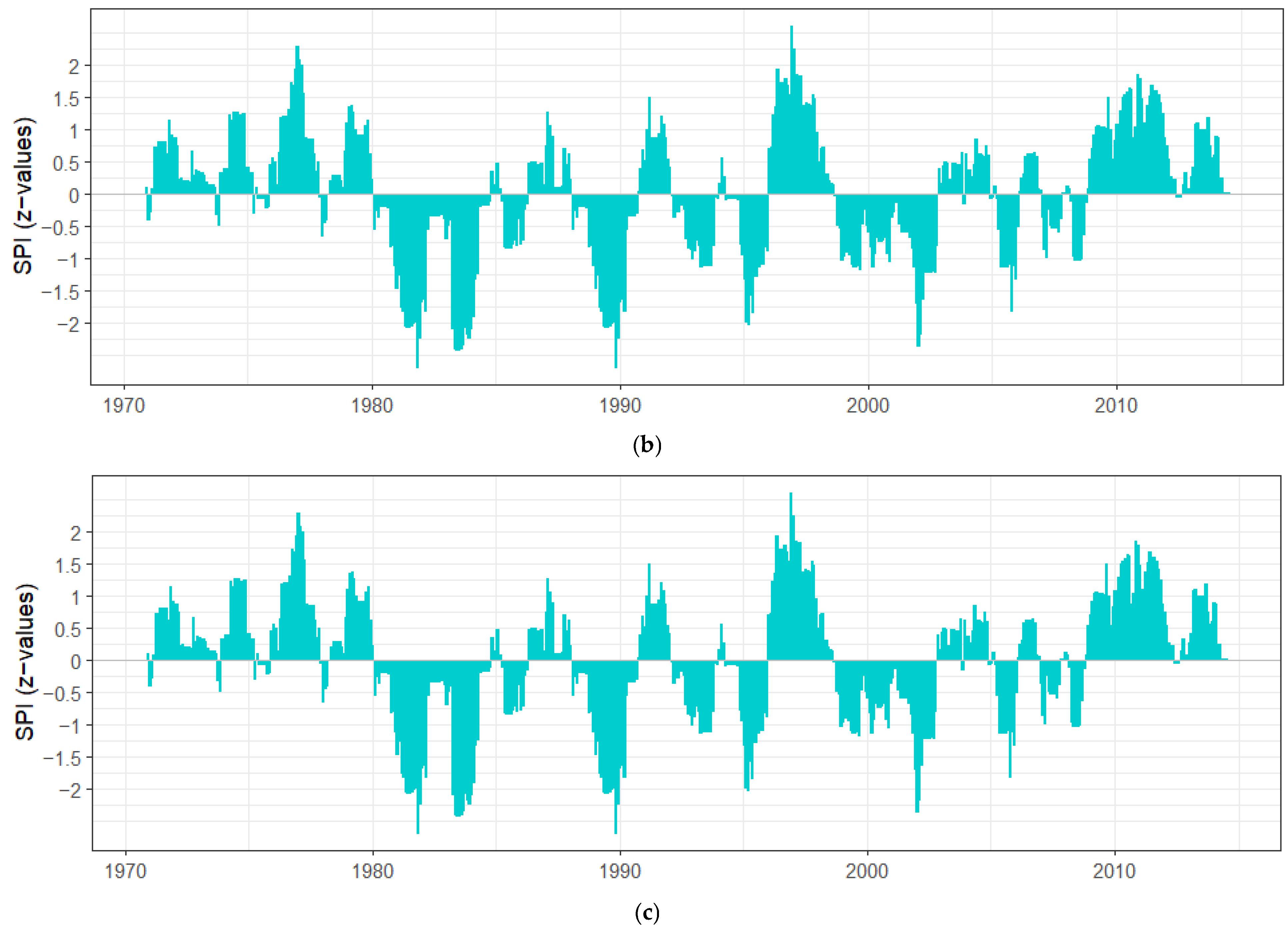
3.3. Drought Analysis Using Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantoush, S.A.; Saber, M.; Abdel-Fattah, M.; Sumi, T. Integrated Strategies for the Management of Wadi Flash Floods in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) Arid Zones: The ISFF Project. In Wadi Flash Floods: Challenges and Advanced Approaches for Disaster Risk Reduction; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudyi, D.; Hasnaoui, M.D.; Fekri, A. Flood risk management practices in Morocco: Facts and challenges. In Wadi Flash Floods. Natural Disaster Science and Mitigation; Sumi, T., Kantoush, S.A., Saber, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 35–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Climate Risk Profile: Morocco. 2021. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org (accessed on 21 September 2022).
- Taleb, H. Water management in Morocco. In Management of Intentional and Accidental Water Pollution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Kadi, M.; Ziyad, A. Integrated water resources management in Morocco. In Global Water Security; Water Resources Development and Management; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Supporting Morocco’s Journey to Disaster and Climate Resilience. Morocco Integrated Disaster Risk Management and Resilience. 2022. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/results/2022/08/11/supporting-morocco-s-journey-to-disaster-and-climate-resilience (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Han, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Chung, S.W.; Kim, S.J.; Park, M.; Lim, K.J.; Kim, J. Evaluation of the effect of channel geometry on streamflow and water quality modeling and modification of channel geometry module in SWAT: A case study of the Andong Dam Watershed. Water 2019, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D.E.; Craig, J.F.; Davidson, N.; Delany, S.; Seddon, M. Biodiversity Impacts of Large Dams; Background Paper No.1; IUCN/UNEP/WCD: Gland, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriqi, A.; Ardiçlioglu, M.; Muceku, Y. Investigation of seepage effect on river dike’s stability under steady state and transient conditions. Pollack Period. 2016, 11, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, E.M.; Sena, M.G.T.; da Silva, A.G.R.; Pereira, F.J.S.; Lopes, F.B. Uncertainties of the rainfall regime in a tropical semi-arid region: The case of the State of Ceará. Rev. Agro@Mbiente On-Line 2016, 10, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, H. Drought events and their effects on vegetation productivity in China. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouadila, A.; Benaabidate, L.; Bouizrou, I.; Aqnouy, M. Implementation of distributed hydrological modeling in a semi-arid Mediterranean Catchment Azzaba; Morocco. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulighe, G.; Bonati, G.; Colangeli, M.; Traverso, L.; Lupia, F.; Altobelli, F.; Dalla Marta, A.; Napoli, M. Predicting streamflow and nutrient loadings in a semi-arid Mediterranean watershed with ephemeral streams using the SWAT model. Agronomy 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näschen, K.; Diekkrüger, B.; Leemhuis, C.; Steinbach, S.; Seregina, L.S.; Thonfeld, F.; Van der Linden, R. Hydrological modeling in data-scarce catchments: The Kilombero floodplain in Tanzania. Water 2018, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; van Dijk, A.I.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. In Satellite Precipitation Measurement. Advances in Global Change Research; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D., Kummerow, C., Nakamura, K., Turk, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 69, pp. 625–653. [Google Scholar]
- Wanzala, M.A.; Stephens, E.M.; Cloke, H.L.; Ficchi, A. Hydrological model preselection with a filter sequence for the national flood forecasting system in Kenya. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2025, 18, e12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufala, M.; El Hmaidi, A.; Chadli, K.; Essahlaoui, A.; El Ouali, A.; Taia, S. Hydrological modeling of water and soil resources in the basin upstream of the Allal El Fassi dam (Upper Sebou watershed; Morocco). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouslihim, Y.; Kacimi, I.; Brirhet, H.; Khatati, M.; Rochdi, A.; Pazza, N.E.; Miftah, A.; Yaslo, Z. Hydrologic Modeling Using SWAT and GIS; Application to Subwatershed Bab-Merzouka (Sebou; Morocco). J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 8, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Briak, H.; Mrabet, R.; Moussadek, R.; Aboumaria, K. Use of a calibrated SWAT model to evaluate the effects of agricultural BMPs on sediments of the Kalaya river basin (North of Morocco). Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markhi, A.; Laftouhi, N.; Grusson, Y.; Soulaimani, A. Assessment of potential soil erosion and sediment yield in the semi-arid N′ fis basin (High Atlas; Morocco) using the SWAT model. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukri, F.; Raclot, D.; Naimi, M.; Chikhaoui, M.; Nunes, J.P.; Huard, F.; Hérivaux, C.; Sabir, M.; Pépin, Y. Distinct and combined impacts of climate and land use scenarios on water availability and sediment loads for a water supply reservoir in northern Morocco. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettam, A.; Taleb, A.; Sauvage, S.; Boithias, L.; Belaidi, N.; Sanchez-Perez, J.M. Applications of a SWAT model to evaluate the contribution of the Tafna catchment (north-west Africa) to the nitrate load entering the Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouziyne, Y.; Abouabdillah, A.; Bouabid, R.; Benaabidate, L.; Oueslati, O. SWAT manual calibration and parameters sensitivity analysis in a semi-arid watershed in North-western Morocco. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumen, Z.; Nabih, S.; Elhassnaoui, I.; Lahrach, A. Hydrologic Modeling Using SWAT: Test the Capacity of SWAT Model to Simulate the Hydrological Behavior of Watershed in Semi-Arid Climate. In Decision Support Methods for Assessing Flood Risk and Vulnerability; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 162–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.S.; Brändle, J.M.; Seliger, C.; Zeiringer, B.; Ferreira, T.; Schmutz, S. Advancing towards functional environmental flows for temperate floodplain rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declaration, B. The Brisbane Declaration: Environmental flows are essential for freshwater ecosystem health and human well-being. In Proceedings of the 10th International River Symposium, Brisbane, Australia, 3–6 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, B. Methodologies for the assessment of environmental flows. In Environmental Flows: An Introduction for Water Resources Managers; National Institute of Ecology: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 129–182. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, V.; Sharma, U.; Kumar, R. Assessment of river ecosystems and environmental flows: Role of flow regimes and physical habitat variables. Clim. Change Environ. Sustain. 2017, 5, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Boston, MA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; Volume 17, pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallaoui, A. Contribution à l’étude Du Phosphore et Des Métaux Lourds Contenus Dans Les Sédiments et de Leur Influence Sur Les Phénomènes d’eutrophisation et de La Pollution. Cas Du Bassin Versant de l’oued Beht et de La Retenue de Barrage El Kansera. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculté des Sciences, Université Moulay Ismail, Meknès, Morocco, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhili, F.; Mohammed, B.; Nouzha, B.; Hamid, L.; Abrerrahim, L. Etude de la qualité physicochimique et de la contamination métallique des eaux de surface du bassin versant de Beht (Maroc). Eur. Sci. J. 2015, 11, 132–147. [Google Scholar]
- El Gaatib, R. Cartographie Décisionnelle de l’aménagement Intégré Du Bassin Versant de l’Oued Beht: Analyse Spatiale de l’aléa Érosif Des Sols Pour La Gestion Des Risques Naturels d’envasement de La Retenue Du Barrage El Kansera (Maroc). Ph.D. thesis, Université Mohammed V—Rabat, Ecole Mohammadia d’Ingénieurs, Rabat, Morocco, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- El Gaatib, R.; Larabi, A.; Faouzi, M. Integrated elaboration of priority planning of vulnerable areas to soil erosion hazard using Remote Sensing and GIS techniques: A pilot case of the Oued Beht Watershed (Morocco). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 3110–3126. [Google Scholar]
- El Gaatib, R.; Larabi, A. Integrated evaluation of soil erosion hazard and risk management in the Oued Beht watershed using remote sensing and GIS techniques: Impacts on El Kansra Dam Siltation (Morocco). J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2014, 6, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yacine, E.A.; Essahlaoui, A.; Oudija, F.; Mimich, K.; Nassiri, L. Assessment of soil erosion by (RUSLE) using remote sensing and GIS case of watershed of Beht in upstream of Ouljat Sultan dam (Morocco). ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 14, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Daide, F.; Afgane, R.; Lahrach, A.; Chaouni, A.A. Beht watershed (Morocco) rainfall-runoff simulation with the HEC-HMS hydrological model. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2022, 23, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation, Version 2005; USDA-ARS Grassland Soil and Water Research Laboratory, and Texas A&M University: Temple, TX, USA; Blackland Research and Extension Center: Temple, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gassman, P.W.; Reyes, M.R.; Green, C.H.; Arnold, J.G. The Soil and Water Assessment Tool: Historical Development, Applications, and Future Research Directions. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool. Theoretical Documentation. Version 2009; Technical Report No.406; Texas Water Resources Institute: Forney, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brirhet, H. Intégration Des Modèles Globaux et Distribués Dans La Modélisation Hydrologique Du Bassin Versant d’Issan, Région de Souss. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah, Fez, Morocco, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Johnson, C.A.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Estimating uncertain flow and transport parameters using a sequential uncertainty fitting procedure. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, J.; Maximov, I.; Siber, R.; Bogner, K.; Mieleitner, J.; Zobrist, J.; Srinivasan, R. Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Bowden, W.B.; Davie, T.; Fenemor, A. Multi-variable and multi-site calibration and validation of SWAT in a large mountainous catchment with high spatial variability. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 1057–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Liew, M.W.; Veith, T.L. Guidelines for Using the Sensitivity Analysis and Auto-Calibration Tools for Multi-Gage or Multi-Step Calibration in SWAT. 2010, pp. 1–30. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268344153_Guidelines_for_Using_the_Sensitivity_Analysis_and_Auto-calibration_Tools_for_Multi-gage_or_Multi-step_Calibration_in_SWAT (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D.P. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Wigington, R.; Braun, D. How much water does a river need? Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Nature Conservancy. Indicators of Hydrologic Alteration Version 7.1 User’s Manual; The Nature Conservancy: Arlington, VA, USA, 2009; Available online: https://rdrr.io/rforge/IHA/ (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Mathews, R.; Richter, B.D. Application of the Indicators of hydrologic alteration software in environmental flow setting. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadil, A.; Rhinane, H.; Kaoukaya, A.; Kharchaf, Y.; Bachir, O.A. Hydrologic modeling of the Bouregreg watershed (Morocco) using GIS and SWAT model. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2011, 3, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Navarro, E.; Hallack-Alegría, M.; Martínez-Pérez, S.; Ramírez-Hernández, J.; Mungaray-Moctezuma, A.; Sastre-Merlín, A. Hydrological modeling and climate change impacts in an agricultural semiarid region. Case study: Guadalupe River basin, Mexico. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 175, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Bressiani, D.; Srinivasan, R.; Jones, C.A.; Mendiondo, E.M. Effects of different spatial and temporal weather data resolutions on the stream flow modeling of a semi-arid basin, Northeast Brazil. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Kang, G.; Chu, C.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Comparison of SWAT and GWLF model simulation performance in humid south and semi-arid north of China. Water 2017, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouadila, A.; Bouizrou, I.; Aqnouy, M.; En-Nagre, K.; El Yousfi, Y.; Khafouri, A.; Hilal, I.; Abdelrahman, K.; Benaabidate, L.; Abu-Alam, T.; et al. Streamflow Simulation in Semiarid Data-Scarce Regions: A Comparative Study of Distributed and Lumped Models at Aguenza Watershed (Morocco). Water 2023, 15, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqnouy, M.; El Messari, J.E.S.; Ismail, H.; Bouadila, A.; Moreno Navarro, J.G.; Loubna, B.; Mansour, M.R.A. Assessment of the SWAT model and the parameters affecting the flow simulation in the watershed of Oued Laou (Northern Morocco). J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’barek, S.A.; Rochdi, A.; Bouslihim, Y.; Miftah, A. Multi-site calibration and validation of swat model for hydrologic modeling and soil erosion estimation: A case study in el grou watershed; Morocco. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2021, 22, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; Van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W.; et al. SWAT: Model use; calibration; and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouabdillah, A.; White, M.; Arnold, J.G.; De Girolamo, A.M.; Oueslati, O.; Maataoui, A.; Lo Porto, A. Evaluation of soil and water conservation measures in a semi-arid river basin in Tunisia using SWAT. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J. Hydrologic alteration associated with dam construction in a medium-sized coastal watershed of southeast China. Water 2016, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarauskienė, D.; Adžgauskas, G.; Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Jakimavičius, D. Analysis of hydrologic regime changes caused by small hydropower plants in lowland rivers. Water 2021, 13, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Abubaker, S.; Kisi, O. Hydrologic alteration at the upper and middle part of the yangtze river, China: Towards sustainable water resource management under increasing water exploitation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouziyne, Y.; Belaqziz, S.; Benaabidate, L.; Aboubdillah, A.; El Bilali, A.; Elbeltagi, A.; Tzoraki, O.; Chehbouni, A. Modeling long term response of environmental flow attributes to future climate change in a North African watershed (Bouregreg watershed, Morocco). Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, 22, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uday Kumar, A.K.V.J. Assessment of flow regime alteration in the Krishna River basin. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2022, 28, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, J.J.; Pegg, M.A. Juvenile growth of a macrohabitat generalist tied to hydrological character of large-river system. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, W.B.; Tilahun, S.A.; Moges, M.M.; Wondie, A.; Derseh, M.G.; Nigatu, T.A.; Mhiret, D.A.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Camp, M.V.; Walraevens, K.; et al. Hydrological foundation as a basis for a holistic environmental flow assessment of tropical highland rivers in ethiopia. Water 2020, 12, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouslihim, Y.; Rochdi, A.; El Amrani Paaza, N.; Liuzzo, L. Understanding the effects of soil data quality on SWAT model performance and hydrological processes in Tamedroust watershed (Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 160, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briak, H.; Moussadek, R.; Aboumaria, K.; Mrabet, R. Assessing sediment yield in Kalaya gauged watershed (Northern Morocco) using GIS and SWAT model. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouziyne, Y.; Abouabdillah, A.; Chehbouni, A.; Hanich, L.; Bergaoui, K.; McDonnell, R.; Benaabidate, L. Assessing hydrological vulnerability to future droughts in a Mediterranean watershed: Combined indices-based and distributed modeling approaches. Water 2020, 12, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yactayo, G.A. Modification of the SWAT Model to Simulate Hydrologic Processes in a Karst-Influenced Watershed. Doctoral Dissertation, Faculty of Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Al Khoury, I.; Boithias, L.; Labat, D. A Review of the Application of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) in Karst Watersheds. Water 2023, 15, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Pan, L.; Deng, Y.; Wan, Z.; Xia, R. Modified SWAT Model for Agricultural Watershed in Karst Area of Southwest China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, C.E.; Alcantara, N.R. Sensitivity of hydrological connectivity in a semiarid basin with a high-density reservoir network. Rev. Ambient. Água. 2019, 14, e2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chbouki, N.; Stockton, C.W.; Myers, D.E. Spatio-temporal patterns of drought in Morocco. Int. J. Climatol. 1995, 15, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrour, Y.; Thomas, Z.; Fovet, O.; Sebari, K.; Rousseau-Gueutin, P. Changes in precipitation and discharge in a Mediterranean catchment as a response to climate change and human activities. J Water Clim Change 2022, 13, 3253–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, H.R.; Wilby, R.L.; Moore, H.M. The impact of river regulation and climate change on the barred estuary of the Oued Massa, southern Morocco. River Res. Appl. 2001, 17, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakam, O.; Baali, A.; El Kamel, T.; Ahouach, Y.; Azennoud, K. Comparative evaluation of various drought indices (DIs) to monitor drought status: A case study of Moroccan Lower Sebou basin. Kuwait J. Sci. 2022, 49, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalley, W.; Niemann, J.D.; Shrestha, S. Hydrologic alteration by hydropower dams and climate change in the Sesan Basin. J. Appl. Water Eng. Res. 2024, 12, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Liang, S. Effects of dams on river flow regime based on IHA/RVA. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 368, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Adnani, A.; Habib, A.; Zourarah, B. Spatio-temporal dynamics and evolution of land use land cover using remote sensing and GIS in Sebou Estuary, Morocco. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2019, 11, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhasni, N.; Lahcen, C.; Timallouka, M. Bio-évaluation de la qualité des eaux de surface d’oued Beht (Maroc) Indice Biologique Global des réseaux de contrôle et de surveillance (IBG-RCS). Eur. Sci. J. 2017, 13, 94–111. [Google Scholar]
- Guellaf, A.; Kassout, J.; Boselli, V.A.; Bennas, N.; El Alami, M.; Errochdi, S.; Kettani, K. Short-term responses of aquatic ecosystem and macroinvertebrate assemblages to rehabilitation actions in martil river (North-Western Morocco). Hydrobiology 2023, 2, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobera Galán, G.; Muñoz Gràcia, I.; López Tarazón, J.A.; Vericat Querol, D.; Batalla, R.J. Effects of flow regulation on river bed dynamics and invertebrate communities in a Mediterranean river. Hydrobiologia 2017, 784, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmar, O.; Velasco, J.; Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C.; Mellado-Díaz, A.; Millán, A.; Wood, P.J. The influence of natural flow regimes on macroinvertebrate assemblages in a semiarid Mediterranean basin. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Zimmerman, J.K.H. Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: A literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; López-Moreno, J.I. Hydrological response to different time scales of climatological drought: An evaluation of the Standardized Precipitation Index in a mountainous Mediterranean basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-nicolás, M.; García-lópez, S.; Ruiz-ortiz, V.; Zazo, S.; Molina, J.L. Precipitation Variability and Drought Assessment Using the SPI: Application to Long-Term Series in the Strait of Gibraltar Area. Water 2022, 14, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bustins, J.A.; Pascual, D.; Pla, E.; Retana, J. Future variability of droughts in three Mediterranean catchments. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sensitivity Level | Parameters | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CN2.mgt | 0.14 |
| 2 | GW_DELAY.gw (days) | 31.02 |
| 3 | ESCO.hru | 0.75 |
| 4 | GW_REVAP.gw | 0.2 |
| 5 | GWQMN.gw (mm H2O) | 2190 |
| 6 | ALPHA_BF.gw (days) | 0.8 |
| 7 | EPCO.hru | 0.86 |
| 8 | SOL_AWC.sol (mm H2O/mm Soil) | 0.24 |
| 9 | REVAPMN.gw (mm H2O) | 400.22 |
| 10 | CH_K2.rte (mm/hr) | 83.31 |
| 11 | CH_N2.rte | 0.22 |
| Indices | Calibration | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| NSE | 0.68 | 0.61 |
| R2 | 0.7 | 0.73 |
| RSR | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| IHA Factor | Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | Variation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | October | 0.15 | 0.5 | 227.45 |
| November | 1.58 | 2.43 | 54.38 | |
| December | 1.75 | 3.26 | 85.92 | |
| January | 2.65 | 3.66 | 38.04 | |
| February | 1.95 | 3.04 | 56.26 | |
| March | 2.54 | 2.38 | −6.3 | |
| April | 1.85 | 2.28 | 23.24 | |
| Mai | 0.98 | 0.78 | −20.3 | |
| June | 0.1 | 0.28 | 193.48 | |
| July | 0.03 | 0.05 | 78.79 | |
| August | 0.02 | 0.02 | −2.35 | |
| September | 0.03 | 0.03 | 7.63 | |
| Group 2 | 1-day minimum | 0.012 | 0.013 | 2.25 |
| 3-day minimum | 0.017 | 0.015 | −9.18 | |
| 7-day minimum | 0.0185 | 0.0183 | −1.02 | |
| 30-day minimum | 0.02166 | 0.02163 | −0.13 | |
| 90-day minimum | 0.027 | 0.071 | 155.71 | |
| 1-day maximum | 61.95 | 84.58 | 36.52 | |
| 3-day maximum | 33.58 | 51.87 | 54.46 | |
| 7-day maximum | 18.83 | 32.84 | 74.4 | |
| 30-day maximum | 8.08 | 13.86 | 71.36 | |
| 90-day maximum | 5.45 | 6.853 | 25.53 | |
| Number of zero days | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Base flow index | 0.0058 | 0.0082 | 40.73 | |
| Group 3 | Date of minimum flow | 231 | 236 | 2.16 |
| Date of maximum flow | 317 | 334 | 5.36 | |
| Group 4 | Low pulse count | 9 | 8 | −11.11 |
| Low pulse duration | 2 | 1 | −50 | |
| High pulse count | 4 | 5 | 25 | |
| High pulse duration | 13 | 8.5 | −34.61 | |
| Group 5 | Rise rate | 0.0256 | 0.06288 | 145.62 |
| Fall rate | −0.1318 | −0.1632 | 23.82 | |
| Number of reversals | 171 | 183 | 7.01 | |
| Event | Start | End | Duration | Magnitude | Intensity | Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI-6 | 1 | 12/01/1980 | 07/01/1981 | 8 | −12.3 | 0.65 | 14.00% |
| 2 | 10/01/1981 | 03/01/1982 | 6 | −11.7 | 0.51 | ||
| 3 | 10/01/1982 | 07/01/1983 | 9 | −15 | 0.6 | ||
| 4 | 10/01/1983 | 03/01/1984 | 6 | −12.1 | 0.5 | ||
| 5 | 12/01/1988 | 07/01/1989 | 8 | −12.3 | 0.65 | ||
| 6 | 10/01/1989 | 03/01/1990 | 6 | −11.7 | 0.51 | ||
| 7 | 11/01/1992 | 03/01/1993 | 5 | −7.12 | 0.7 | ||
| 8 | 12/01/1994 | 05/01/1995 | 6 | −9.52 | 0.63 | ||
| 9 | 04/01/2000 | 07/01/2000 | 4 | −4.55 | 0.88 | ||
| 10 | 06/01/2001 | 11/01/2001 | 6 | −10.6 | 0.57 | ||
| 11 | 04/01/2005 | 10/01/2005 | 7 | −13.1 | 0.53 | ||
| 12 | 05/01/2008 | 08/01/2008 | 4 | −5.33 | 0.75 | ||
| SPI-12 | 1 | 12/01/1980 | 03/01/1982 | 16 | −29.5 | 0.54 | 16.30% |
| 2 | 04/01/1983 | 04/01/1984 | 13 | −26.9 | 0.48 | ||
| 3 | 12/01/1988 | 03/01/1990 | 16 | −29.5 | 0.54 | ||
| 4 | 06/01/1993 | 09/01/1993 | 4 | −4.41 | 0.91 | ||
| 5 | 01/01/1995 | 10/01/1995 | 10 | −14.5 | 0.69 | ||
| 6 | 05/01/1999 | 09/01/1999 | 5 | −5.58 | 0.9 | ||
| 7 | 11/01/2001 | 09/01/2002 | 11 | −16.1 | 0.68 | ||
| 8 | 05/01/2005 | 12/01/2005 | 8 | −9.77 | 0.82 | ||
| 9 | 05/01/2008 | 08/01/2008 | 4 | −4.04 | 0.99 | ||
| SPI-36 | 1 | 12/01/1981 | 10/01/1984 | 35 | −59.1 | 0.59 | 16.10% |
| 2 | 04/01/1985 | 12/01/1985 | 9 | −12.8 | 0.7 | ||
| 3 | 11/01/1989 | 01/01/1991 | 15 | −19.2 | 0.78 | ||
| 4 | 03/01/1995 | 10/01/1995 | 8 | −9.56 | 0.84 | ||
| 5 | 04/01/2001 | 10/01/2002 | 19 | −24.5 | 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daide, F.; Hasiotis, T.; Nabih, S.; Taia, S.; Lahrach, A.; Koutsovili, E.-I.; Tzoraki, O. Assessing Hydrological Alterations and Environmental Flow Components in the Beht River Basin, Morocco, Using Integrated SWAT and IHA Models. Hydrology 2025, 12, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12050109
Daide F, Hasiotis T, Nabih S, Taia S, Lahrach A, Koutsovili E-I, Tzoraki O. Assessing Hydrological Alterations and Environmental Flow Components in the Beht River Basin, Morocco, Using Integrated SWAT and IHA Models. Hydrology. 2025; 12(5):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12050109
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaide, Fatima, Thomas Hasiotis, Soumaya Nabih, Soufiane Taia, Abderrahim Lahrach, Eleni-Ioanna Koutsovili, and Ourania Tzoraki. 2025. "Assessing Hydrological Alterations and Environmental Flow Components in the Beht River Basin, Morocco, Using Integrated SWAT and IHA Models" Hydrology 12, no. 5: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12050109
APA StyleDaide, F., Hasiotis, T., Nabih, S., Taia, S., Lahrach, A., Koutsovili, E.-I., & Tzoraki, O. (2025). Assessing Hydrological Alterations and Environmental Flow Components in the Beht River Basin, Morocco, Using Integrated SWAT and IHA Models. Hydrology, 12(5), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12050109








