CORAL Models for Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Optimal SMILES-Based Descriptors
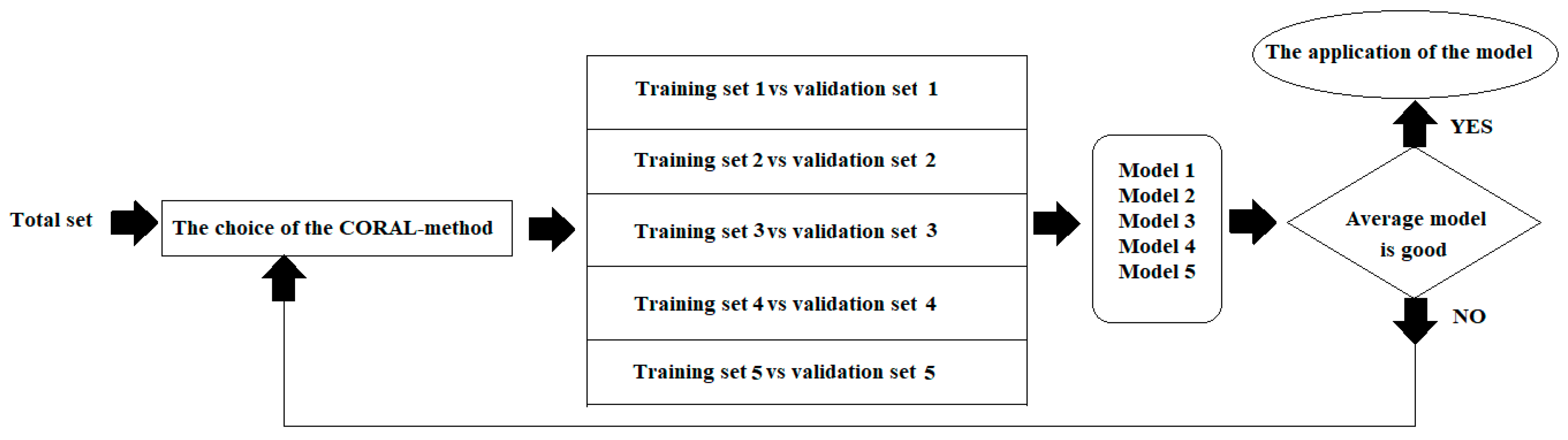
2.2. Monte Carlo Optimisation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Comments |
| QSAR | Quantitative stricture–activity relationship |
| DIN | Drug-induced nephrotoxicity |
| AIN | Acute interstitial nephritis |
| ATN | Acute tubular necrosis |
| SMILES | Simplified molecular input-line entry system |
| CIN | Chronic interstitial nephritis |
| PTCT | Proximal tubular cell toxicity |
| PTI | Proximal tubular injury |
| RAS | Renal artery stenosis |
| IIC | Index of ideality of correlation |
| DCW | Descriptor of correlation weights |
| TP | True positive |
| TN | True negative |
| FP | False positive |
| FN | False negative |
| MCC | Matthews correlation coefficient |
| A | Active training set |
| P | Passive training set |
| C | Calibration set |
| V | Validation set |
References
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intens. Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Pascual, M.T.; Soroko, S.; Savage, B.R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Ikizler, T.A.; Paganini, E.P.; Chertow, G.M. Spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: The PICARD experience. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, B.S.; Goldstein, S.L. Acute kidney injury and increasing nephrotoxic-medication exposure in noncritically-ill children. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Naimi, M.S.; Rasheed, H.A.; Hussien, N.R.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I. Nephrotoxicity: Role and significance of renal biomarkers in the early detection of acute renal injury. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2019, 10, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowska, E.; Domanski, L.; Dziedziejko, V.; Kajdy, A.; Stefanska, K.; Kwiatkowski, S. The Mechanism of Drug Nephrotoxicity and the Methods for Preventing Kidney Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, P.; Chowdhury, S.K.; Yucha, R.; Kelly, E.J.; Xiao, G. Emerging Kidney Models to Investigate Metabolism, Transport, and Toxicity of Drugs and Xenobiotics. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.Y.; Weber, E.J.; Sidorenko, V.S.; Chapron, A.; Yeung, C.K.; Gao, C.; Mao, Q.; Shen, D.; Wang, J.; Rosenquist, T.A.; et al. Human liver-kidney model elucidates the mechanisms of aristolochic acid nephrotoxicity. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e95978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.L.; Winter, L.M.F. Animal models in biological and biomedical research-experimental and ethical concerns. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019, 91 (Suppl. 1), e20170238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Norman, G.A. Limitations of Animal Studies for Predicting Toxicity in Clinical Trials: Is it Time to Rethink Our Current Approach? JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.; Pou Casellas, C.; Groenink, L.; Wever, K.E.; Masereeuw, R. Humans are animals, but are animals human enough? A systematic review and meta-analysis on interspecies differences in renal drug clearance. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.; Ahmed, S.; Gerritsen, K.G.F.; Mihaila, S.M.; Masereeuw, R. Kidney-based in vitro models for drug-induced toxicity testing. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3397–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengstler, J.G.; Sjogren, A.K.; Zink, D.; Hornberg, J.J. In vitro prediction of organ toxicity: The challenges of scaling and secondary mechanisms of toxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvine, A.R.; van Berlo, D.; Shekhani, R.; Masereeuw, R. A systematic review of in vitro models of drug-induced kidney injury. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2021, 27, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, C.; Erdogan Yucel, E.; Arslan, F.D.; Ekmekci, S.; Kisa, E.; Ulker, V.; Ucar, M.; Ilbey, Y.O.; Celik, O.; Isbilen Basok, B.; et al. All-trans retinoic acid prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Lu, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, W.; Wu, N.; Yu, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhang, X. Synthesis, extracorporeal nephrotoxicity, and 3D-QSAR of andrographolide derivatives. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 97, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, T.; Kanan, D.; Erol, I.; Yazdi, S.; Stein, M.; Durdagi, S. Targeting the NF-κB/IκBα complex via fragment-based E-Pharmacophore virtual screening and binary QSAR models. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2019, 86, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, F.; Gadaleta, D.; Lombardo, A.; Nicolotti, O.; Benfenati, E. Identification of structural alerts for liver and kidney toxicity using repeated dose toxicity data. Chem. Cent. J. 2015, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hua, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, R.; Li, X. In Silico Prediction and Insights Into the Structural Basis of Drug Induced Nephrotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 793332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.C.; Johnson, S.R.; Mandelbrot, D.A.; Pavlakis, M.; Horwedel, T.; Karp, S.J.; Egbuna, O.; Rodrigue, J.R.; Chudzinski, R.E.; Goldfarb-Rumyantzev, A.S.; et al. Timing of sirolimus conversion influences recovery of renal function in liver transplant recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2009, 23, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakovska, I.; Diukendjieva, A.; Worth, A.P. In Silico Models for Predicting Acute Systemic Toxicity. In In Silico Methods for Predicting Drug Toxicity; Methods in Molecular Biology; Benfenati, E., Ed.; Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 259–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a chemical language and information system. 1. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P.; Lombardo, A.; Roncaglioni, A.; Lavado, G.J.; Benfenati, E. The Monte Carlo method to build up models of the hydrolysis half-lives of organic compounds. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2021, 32, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Benfenati, E. Semi-correlations as a tool to build up categorical (active/inactive) model of GABA A receptor modulator activity. Struct. Chem. 2019, 30, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropov, A.A.; Toropova, A.P.; Benfenati, E. The index of ideality of correlation: QSAR model of acute toxicity for zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Sun, H.; Kang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Liu, H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Hou, T. ADMET Evaluation in Drug Discovery. 18. Reliable Prediction of Chemical-Induced Urinary Tract Toxicity by Boosting Machine Learning Approaches. Mol. Farm. 2017, 14, 3935–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Development of quantitative structure-activity relationship models to predict potential nephrotoxic ingredients in traditional Chinese medicines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassan, A.; Alves, V.M.; Amberg, A.; Anger, L.T.; Auerbach, S.; Beilke, L.; Bender, A.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Cross, K.P.; Hsieh, J.-H.; et al. In silico approaches in organ toxicity hazard assessment: Current status and future needs in predicting liver toxicity. Comput. Toxicol. 2021, 20, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chou, C.-L.; Zheng, C.-M.; Chiu, H.-W. Investigation of potential descriptors of chemical compounds on prevention of nephrotoxicity via QSAR approach. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1876–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Renal Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIN * | ATN | Altered Haemodynamics | CIN | Crystal Nephropathy | Glomerulo-Nephritis | Inflammation | PTCT | PTI | Thrombotic Micropathy | Tubular Obstruction | |
| Acyclovir | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Amphotericin B | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Ampicillin | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Ceftriaxone | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Cidofovir | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Ciprofloxacin | X | X | |||||||||
| Cisplatin | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Cyclosporine | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Foscarnet | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Ganciclovir | X | X | |||||||||
| Gentamicin | X | X | |||||||||
| Ibuprofen | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Indinavir | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Mannitol | X | ||||||||||
| Methotrexate | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Naproxen | X | X | |||||||||
| Penicillin | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Rifampicin | X | X | |||||||||
| Streptozocin | X | X | |||||||||
| Sulphadiazine | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Sulphamethoxazole | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Tacrolimus | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Tenofovir | X | X | |||||||||
| Triamterene | X | X | |||||||||
| Vancomycin | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Set | Set | Observed Classification Quality | The SAR Statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | TN | FP | FN | N | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | MCC | ||
| Training | A | 55 | 62 | 10 | 10 | 137 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.71 |
| P | 73 | 51 | 6 | 11 | 141 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.75 | |
| C | 48 | 45 | 27 | 25 | 145 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.28 | |
| Validation | 46 | 51 | 26 | 19 | 142 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.37 | |
| Total set | 222 | 209 | 69 | 65 | 565 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.53 | |
| Set | Set | Observed Classification Quality | The SAR Statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | TN | FP | FN | N | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | MCC | ||
| Training | A | 63 | 70 | 2 | 2 | 137 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.94 |
| P | 82 | 54 | 3 | 2 | 141 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.93 | |
| C | 48 | 44 | 28 | 25 | 145 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.27 | |
| Validation | 44 | 60 | 17 | 21 | 142 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.46 | |
| Total set | 237 | 228 | 50 | 50 | 565 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.65 | |
| Mission | Set | Observed Classification Quality | The SAR Statistics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | TN | FP | FN | N | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | MCC | ||
| Training | A | 47 | 63 | 9 | 18 | 137 | 0.72 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.61 |
| P | 61 | 52 | 5 | 23 | 141 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.63 | |
| C | 69 | 68 | 4 | 4 | 145 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.89 | |
| Validation | V | 60 | 70 | 7 | 5 | 142 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.83 |
| Total set | 237 | 253 | 25 | 50 | 565 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.74 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toropov, A.A.; Barnes, D.A.; Toropova, A.P.; Roncaglioni, A.; Irvine, A.R.; Masereeuw, R.; Benfenati, E. CORAL Models for Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Toxics 2023, 11, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040293
Toropov AA, Barnes DA, Toropova AP, Roncaglioni A, Irvine AR, Masereeuw R, Benfenati E. CORAL Models for Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Toxics. 2023; 11(4):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040293
Chicago/Turabian StyleToropov, Andrey A., Devon A. Barnes, Alla P. Toropova, Alessandra Roncaglioni, Alasdair R. Irvine, Rosalinde Masereeuw, and Emilio Benfenati. 2023. "CORAL Models for Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity" Toxics 11, no. 4: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040293
APA StyleToropov, A. A., Barnes, D. A., Toropova, A. P., Roncaglioni, A., Irvine, A. R., Masereeuw, R., & Benfenati, E. (2023). CORAL Models for Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Toxics, 11(4), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040293









