Discovering Novel Bioactivities of Controversial Food Additives by Means of Simple Zebrafish Embryotoxicity (ZET) Assays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Toxicological Testing Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Target and Functional Prediction
3. Results and Discussion
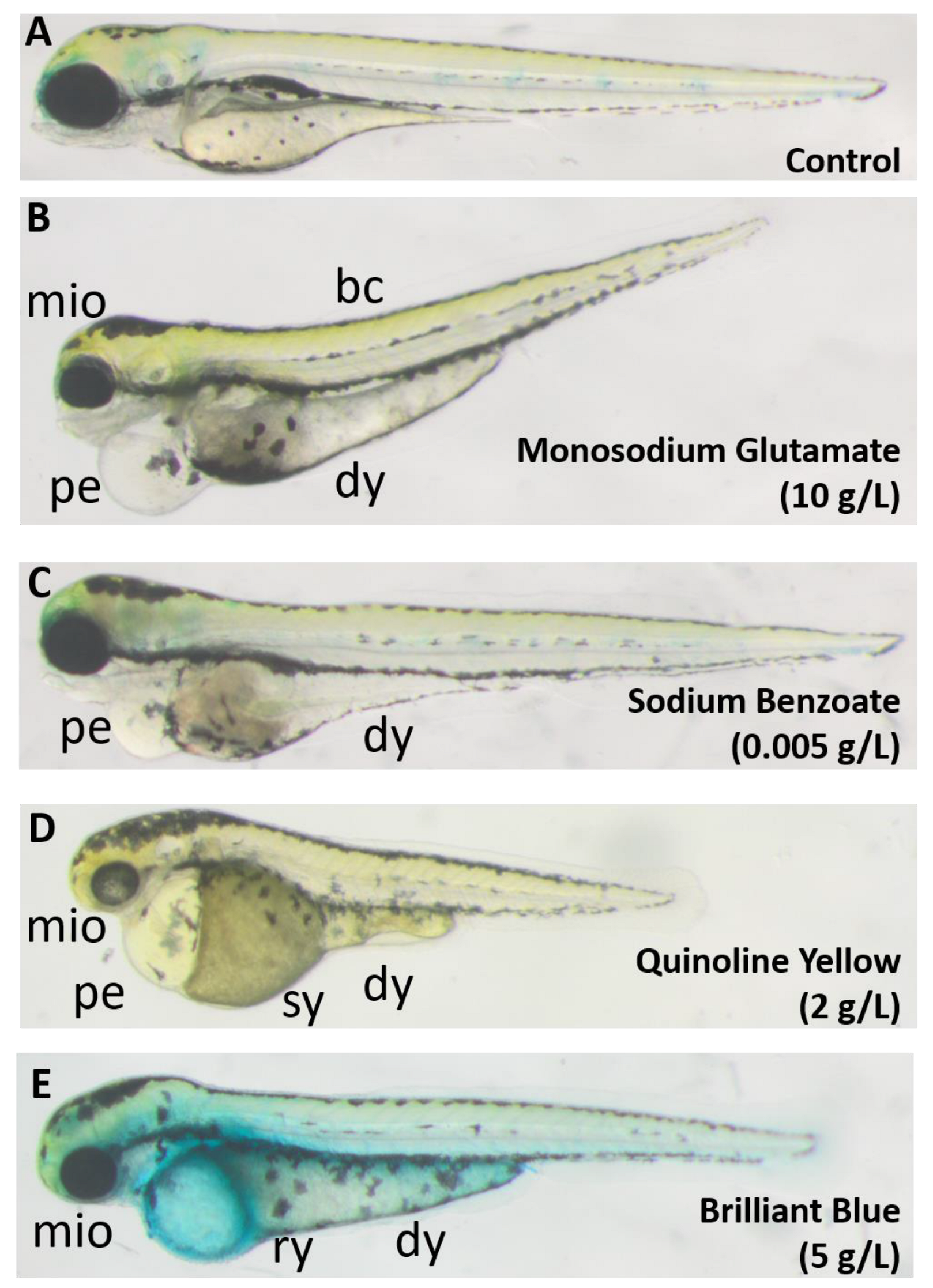
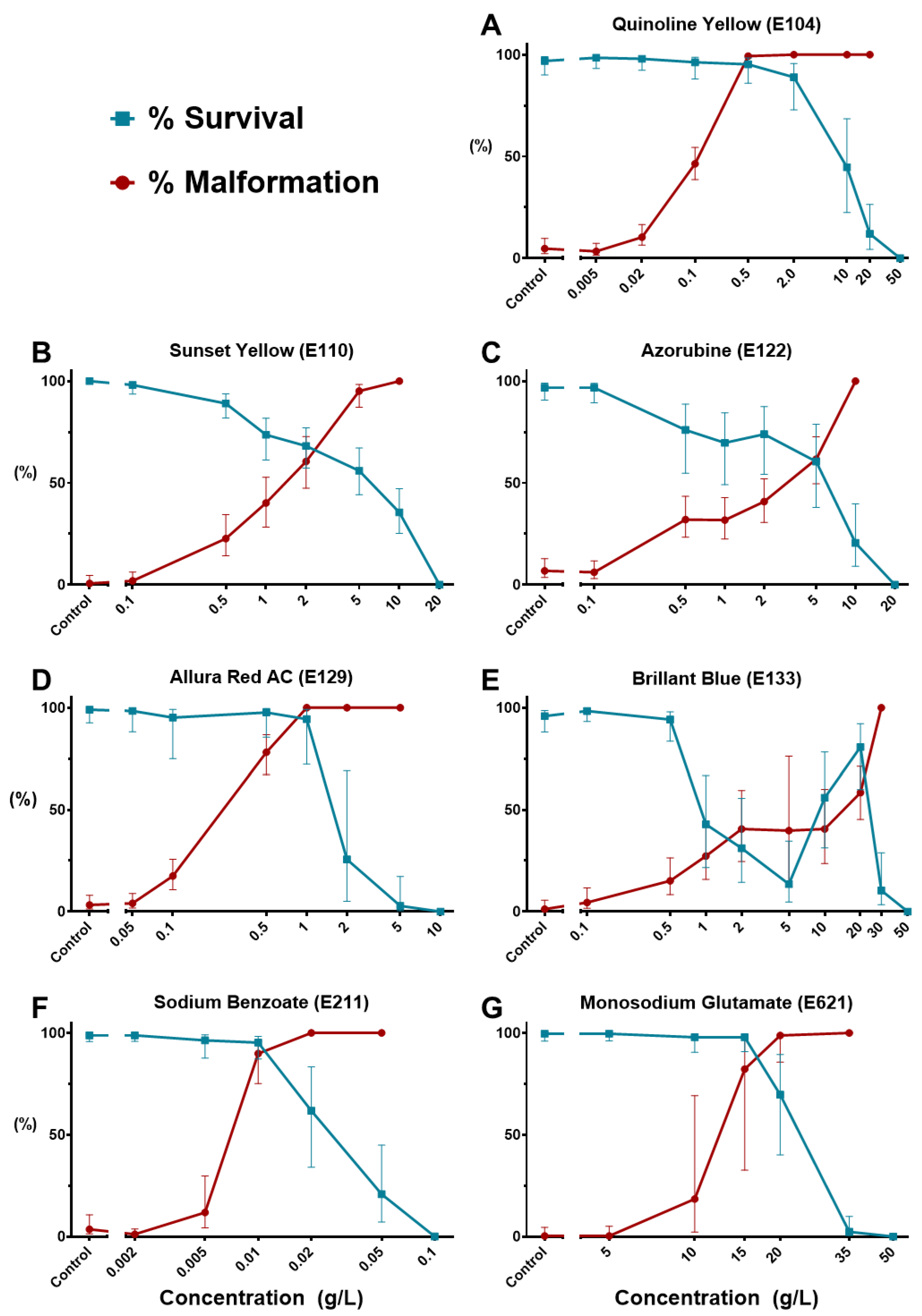
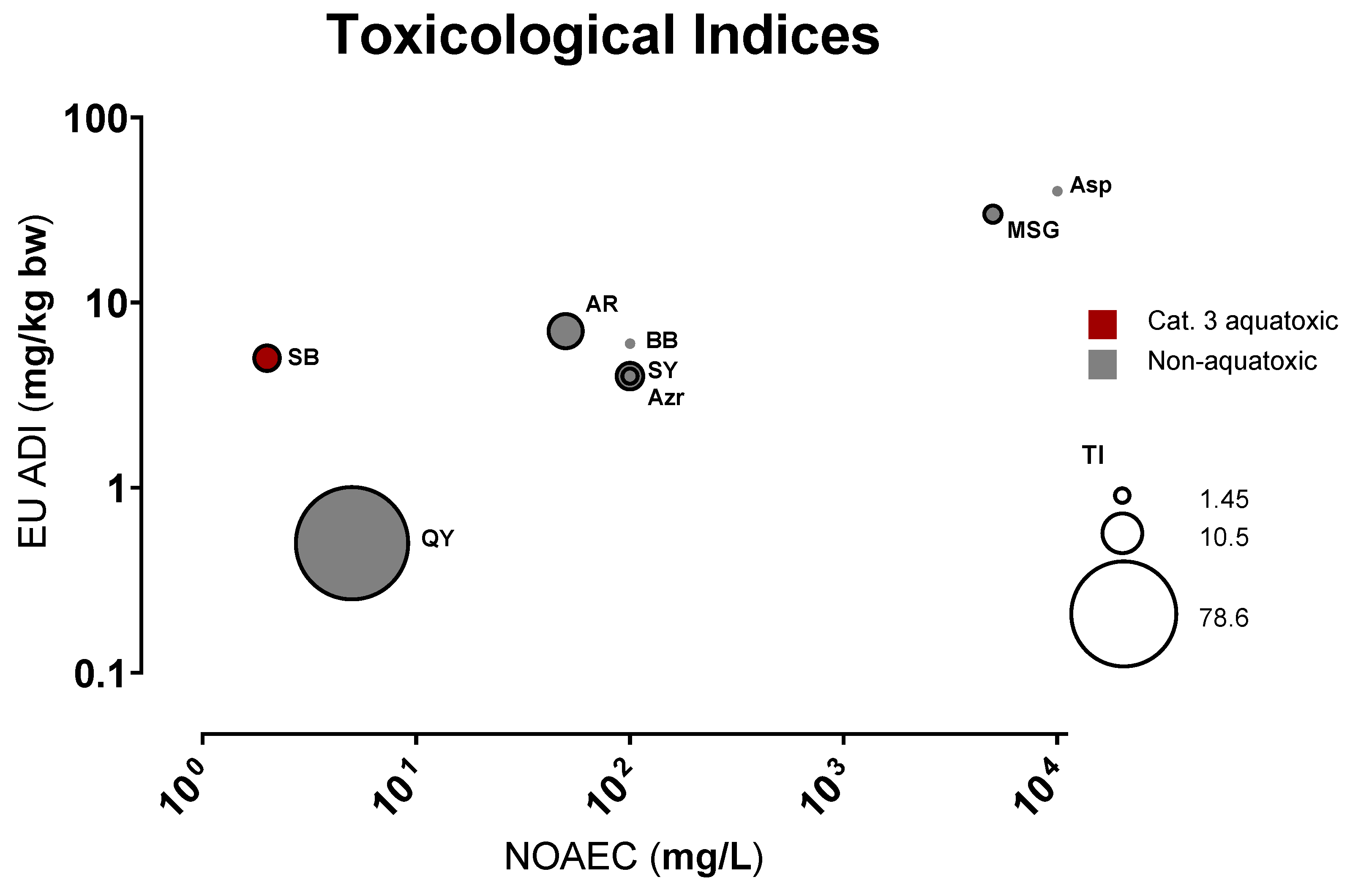
3.1. General Toxicological Results
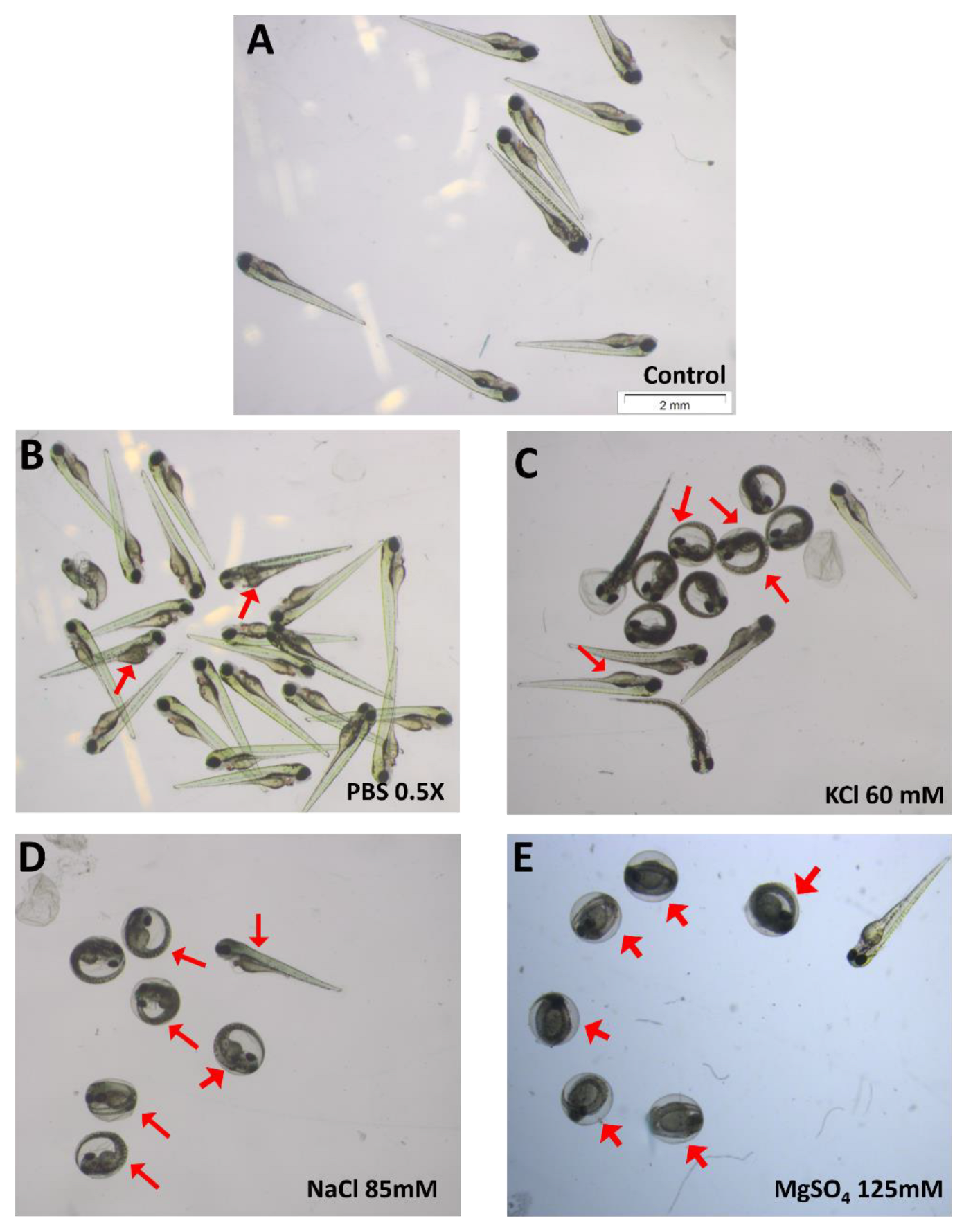
3.2. Effect of Non-Toxic Salts at High Concentration
3.3. Brilliant Blue (E133) Can Weaken the Zebrafish Larval Yolk Sac
3.4. Quinoline Yellow (E104): A Possible Metabolic Interferer
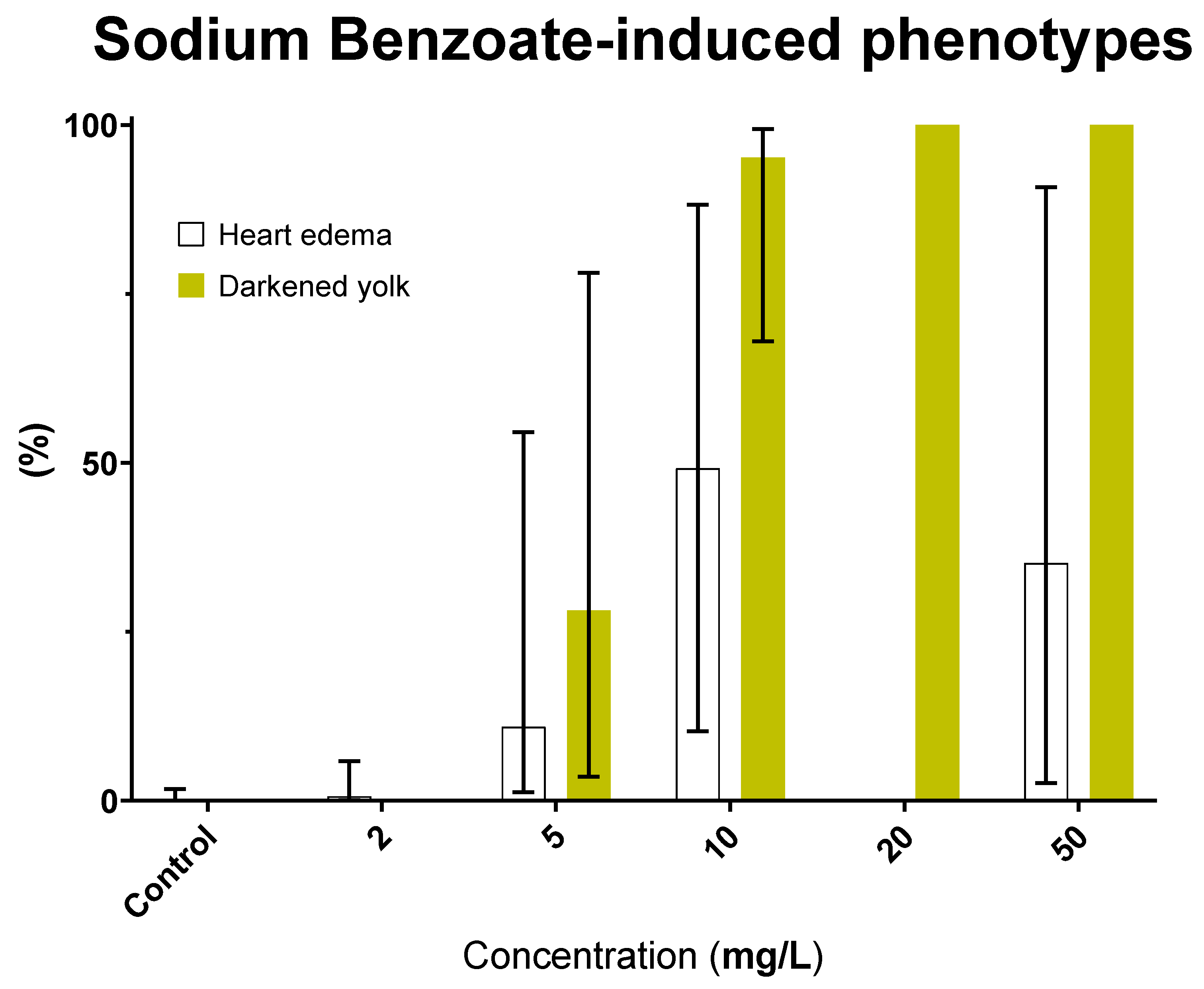
3.5. Sodium Benzoate (E211): Safety Concern
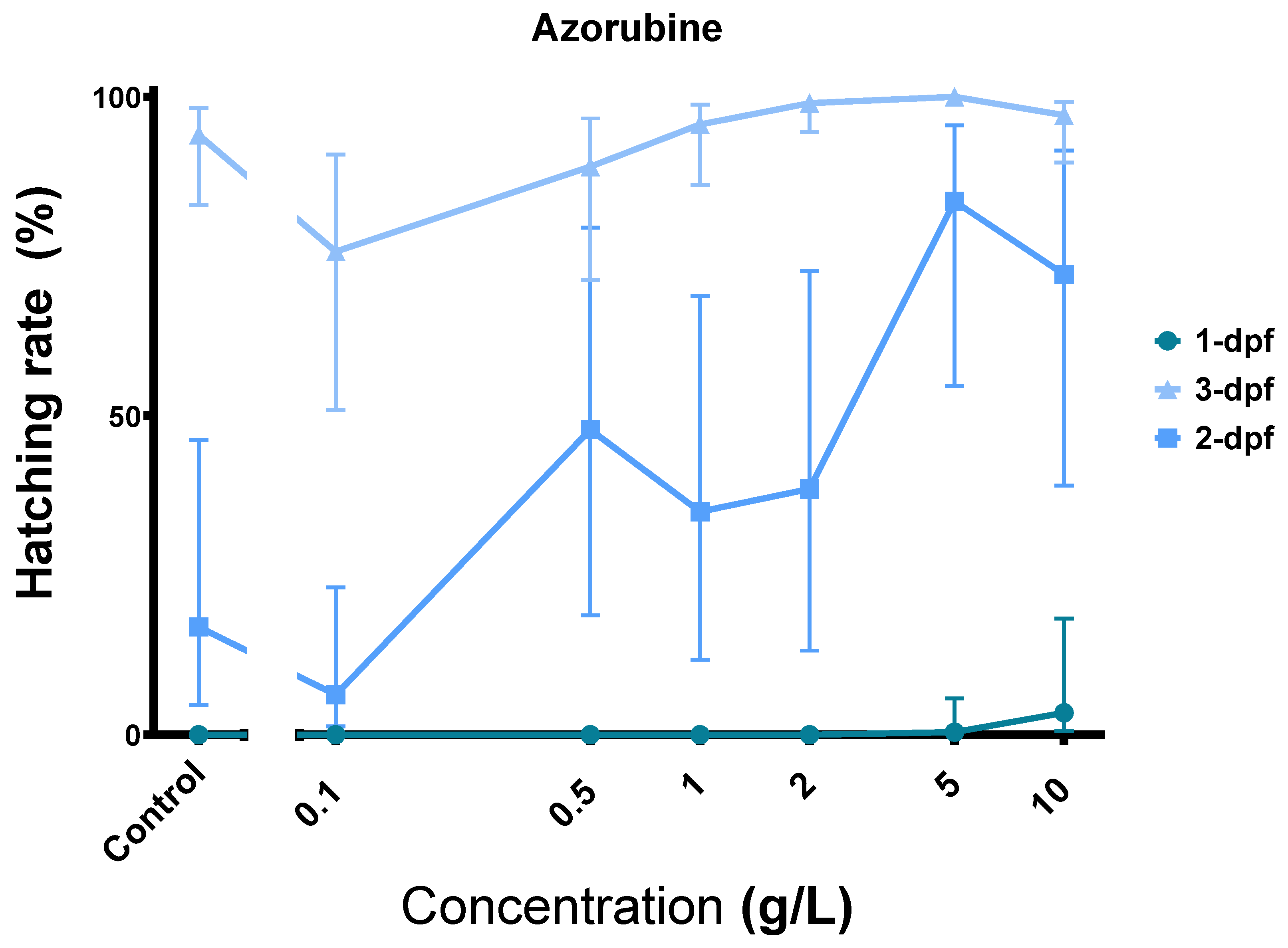
3.6. Azorubine (E122) Induces Precocious Zebrafish Hatching
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zengin, N.; Yuzbasioglu, D.; Unal, F.; Yilmaz, S.; Aksoy, H. The evaluation of the genotoxicity of two food preservatives: Sodium benzoate and potassium benzoate. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, B.F. Hyperkinesis and learning disabilities linked to artificial food flavors and colors. Am. J. Nurs. 1975, 75, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCann, D.; Barrett, A.; Cooper, A.; Crumpler, D.; Dalen, L.; Grimshaw, K.; Kitchin, E.; Lok, K.; Porteous, L.; Prince, E.; et al. Food additives and hyperactive behaviour in 3-year-old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; McLean, W.G.; Williams, D.P.; Howard, C.V. Synergistic interactions between commonly used food additives in a developmental neurotoxicity test. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 90, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oplatowska-Stachowiak, M.; Elliott, C.T. Food colors: Existing and emerging food safety concerns. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coultate, T.; Blackburn, R.S. Food colorants: Their past, present and future. Color. Technol. 2018, 134, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Nagababu, B.H. Applications of food color and bio-preservatives in the food and its effect on the human health. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 257/2010 of 25 March 2010 setting up a programme for the re-evaluation of approved food additives in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on food additives (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 80, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lara-Martin, P.A.; Chiaia-Hernandez, A.C.; Biel-Maeso, M.; Baena-Nogueras, R.M.; Hollender, J. Tracing Urban Wastewater Contaminants into the Atlantic Ocean by Nontarget Screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3996–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Ternes, T.A. Water Analysis: Emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 382–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troxell, K.; Ng, B.; Zamora-Ley, I.; Gardinali, P. Detecting Water Constituents Unique to Septic Tanks as a Wastewater Source in the Environment by Nontarget Analysis: South Florida’s Deering Estate Rehydration Project Case Study. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avallone, B.; Arena, C.; Simoniello, P.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Vitale, E.; Capriello, T.; Ferrandino, I.; Raggio, A.; Sasso, M.; Napolitano, G.; et al. Comparative Toxicity of Vegan Red, E124, and E120 Food Dyes on Three Rapidly Proliferating Model Systems. Environments 2022, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefsen, K.E.; Nizzetto, L.; Huggett, D.B. Presence, fate and effects of the intense sweetener sucralose in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Council. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 276, 33–79. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, P.; Li, C.Q. Zebrafish: A predictive model for assessing drug-induced toxicity. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, A. All eyes on zebrafish. Lab Anim. 2017, 46, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.B.; Truong, L.; Simonich, M.T.; Tanguay, R.L. Systematic Assessment of Exposure Variations on Observed Bioactivity in Zebrafish Chemical Screening. Toxics 2020, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, L.; Reif, D.M.; St Mary, L.; Geier, M.C.; Truong, H.D.; Tanguay, R.L. Multidimensional in vivo hazard assessment using zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 137, 212–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, J.C.; Leggiadro, C.; Sperker, S.A.; Woodland, C.; Ellis, L.D. Comparison of the Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity Assay and the General and Behavioral Embryo Toxicity Assay as New Approach Methods for Chemical Screening. Toxics 2020, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, E.J.; To, K.T.; St Mary, L.; Laber, C.H.; Bednar, A.J.; Truong, L.; Tanguay, R.L.; Garcia-Reyero, N. Developmental, Behavioral and Transcriptomic Changes in Zebrafish Embryos after Smoke Dye Exposure. Toxics 2022, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanray, N.; Maree, R.; Pruvot, B.; Stern, O.; Geurts, P.; Wehenkel, L.; Muller, M. Phenotype classification of zebrafish embryos by supervised learning. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixido, E.; Kiessling, T.R.; Krupp, E.; Quevedo, C.; Muriana, A.; Scholz, S. Automated Morphological Feature Assessment for Zebrafish Embryo Developmental Toxicity Screens. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 167, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otterstrom, J.J.; Lubin, A.; Payne, E.M.; Paran, Y. Technologies bringing young Zebrafish from a niche field to the limelight. SLAS Technol. 2022, 27, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rericha, Y.; Cao, D.; Truong, L.; Simonich, M.T.; Field, J.A.; Tanguay, R.L. Sulfonamide functional head on short-chain perfluorinated substance drives developmental toxicity. iScience 2022, 25, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.T.; St Mary, L.; Wooley, A.H.; Wilbanks, M.S.; Bednar, A.J.; Perkins, E.J.; Truong, L.; Tanguay, R.L.; Garcia-Reyero, N. Morphological and Behavioral Effects in Zebrafish Embryos after Exposure to Smoke Dyes. Toxics 2021, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hellfeld, R.; Brotzmann, K.; Baumann, L.; Strecker, R.; Braunbeck, T. Adverse effects in the fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test: A catalogue of unspecific morphological changes versus more specific effects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, J.; Frederick, C. merTools: Tools for Analyzing Mixed Effect Regression Models. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=merTools (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Fox, D.R.; Landis, W.G. Don’t be fooled-A no-observed-effect concentration is no substitute for a poor concentration-response experiment. Env. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JECFA. Summary of Evaluations Performed by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): 1956–1997 (First through Forty-Ninth Meetings); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of Allura Red AC (E 129) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of Azorubine/Carmoisine (E 122) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of Quinoline Yellow (E 104) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of Brilliant Blue FCF (E 133) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JECFA. Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Prepared by the Seventy Fourth Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of aspartame (E 951) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Reconsideration of the temporary ADI and refined exposure assessment for Sunset Yellow FCF (E 110). EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of benzoic acid (E 210), sodium benzoate (E 211), potassium benzoate (E 212) and calcium benzoate (E 213) as food additives. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Food Additives Nutrient Sources added to Food. Re-evaluation of glutamic acid (E 620), sodium glutamate (E 621), potassium glutamate (E 622), calcium glutamate (E 623), ammonium glutamate (E 624) and magnesium glutamate (E 625) as food additives. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JECFA. Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives: Prepared by the Eighty-Second Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- JECFA. Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Prepared by the Eighty-Fourth Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- JECFA. Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives: Prepared by the Ninety-Second Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose-Response Analysis Using R. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.J.; Dong, J.; Che, Y.J.; Zhu, M.F.; Wen, M.; Wang, N.N.; Wang, S.; Lu, A.P.; Cao, D.S. TargetNet: A web service for predicting potential drug-target interaction profiling via multi-target SAR models. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumanchi, S.; Wang, H.; Perttunen, S.; Tikkanen, I.; Lakkisto, P.; Paavola, J. Zebrafish Heart Failure Models. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 662583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rombough, P. Gills are needed for ionoregulation before they are needed for O2 uptake in developing zebrafish, Danio rerio. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhoff, J.H.; Giselbrecht, S.; Schmidts, M.; Schindler, S.; Beales, P.L.; Tonshoff, B.; Liebel, U.; Gehrig, J. Development of an automated imaging pipeline for the analysis of the zebrafish larval kidney. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, S.A.; Tucker, C.S.; del-Pozo, J.; Rose, K.N.; MacRae, C.A.; Bailey, M.A.; Mullins, J.J. Techniques for the in vivo assessment of cardio-renal function in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Giusti, A.; Ny, A.; de Witte, P.A. Nephrotoxic Effects in Zebrafish after Prolonged Exposure to Aristolochic Acid. Toxins 2020, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Zhong, D.; Jiang, H.; Han, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, R.; Qian, X.; Chen, D.; Jing, L. A new aminoglycoside etimicin shows low nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity in zebrafish embryos. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Jia, K.; Xiong, H.; Tian, G.; Xu, J.; Yuan, W.; Lu, C.; Xiao, X.; Lu, H. Oxyfluorfen exposure can cause acute kidney injury by promoting ROS-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatesta, F.; Emadi, C.; Price, E.R.; Wang, Y.; Greer, J.B.; Xu, E.G.; Schlenk, D.; Grosell, M.; Mager, E.M. The developing zebrafish kidney is impaired by Deepwater Horizon crude oil early-life stage exposure: A molecular to whole-organism perspective. Sci. Total Env. 2022, 808, 151988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraham-Davidi, I.; Ely, Y.; Pham, V.N.; Castranova, D.; Grunspan, M.; Malkinson, G.; Gibbs-Bar, L.; Mayseless, O.; Allmog, G.; Lo, B.; et al. ApoB-containing lipoproteins regulate angiogenesis by modulating expression of VEGF receptor 1. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.H.; Rajan, S.; Danoff, A.; White, R.J.; Hensley, M.R.; Quinlivan, V.H.; Recacha, R.; Thierer, J.H.; Tan, F.J.; Busch-Nentwich, E.M.; et al. A point mutation decouples the lipid transfer activities of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieusset, J.; Seydoux, J.; Anghel, S.I.; Escher, P.; Michalik, L.; Soon Tan, N.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Wahli, W.; Desvergne, B. Altered growth in male peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) heterozygous mice: Involvement of PPARgamma in a negative feedback regulation of growth hormone action. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colavecchia, M.V.; Hodson, P.V.; Parrott, J.L. CYP1A induction and blue sac disease in early life stages of white suckers (Catostomus commersoni) exposed to oil sands. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 967–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Walker, M.K.; Olson, J.R.; Peterson, R.E. Pathologic alterations in early life stages of lake trout, Salvelinus namaycush, exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo- p-dioxin as. Aquat. Toxicol. 1991, 19, 41–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elonen, G.E.; Spehar, R.L.; Holcombe, G.W.; Johnson, R.D.; Fernandez, J.D.; Erickson, R.J.; Tietge, J.E.; Cook, P.M. Comparative toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to seven freshwater fish species during early life-stage development. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, D.R.; Tang, S.; Miller, C.; Gagnon, D.; Shekh, K.; Alcaraz, A.J.G.; Janz, D.M.; Hecker, M. A Multi-Life Stage Comparison of Silver Nanoparticle Toxicity on the Early Development of Three Canadian Fish Species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3337–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jackson, D.G.; Dahl, G. The food dye FD&C Blue No. 1 is a selective inhibitor of the ATP release channel Panx1. J. Gen. Physiol. 2013, 141, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, L.A.; Riquelme, M.A.; Vargas, A.A.; Urrutia, C.; Saez, J.C. Pannexin 1 channels in skeletal muscles. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Bhattarai, B.R.; Lee, K.-H.; Cho, H.-J. Some of the Food Color Additives Are Potent Inhibitors of Human Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, 27, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maloney, J.P.; Halbower, A.C.; Fouty, B.F.; Fagan, K.A.; Balasubramaniam, V.; Pike, A.W.; Fennessey, P.V.; Moss, M. Systemic absorption of food dye in patients with sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1047–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucova, M.; Hojerova, J.; Pazourekova, S.; Klimova, Z. Absorption of triphenylmethane dyes Brilliant Blue and Patent Blue through intact skin, shaven skin and lingual mucosa from daily life products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raldua, D.; Andre, M.; Babin, P.J. Clofibrate and gemfibrozil induce an embryonic malabsorption syndrome in zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 228, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, B.; Frederickson, L.C.; Stenkamp, D.L. Mechanisms for persistent microphthalmia following ethanol exposure during retinal neurogenesis in zebrafish embryos. Vis. Neurosci. 2007, 24, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, P.; Cunha, D.L.; Moosajee, M. Animal and cellular models of microphthalmia. Ther. Adv. Rare Dis. 2021, 2, 2633004021997447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghib, K.; Boutlelis, D.A. Food Additive (Sodium benzoate)-induced Damage on Renal Function and Glomerular Cells in Rats; Modulating Effect of Aqueous Extract of Atriplex halimus L. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 20, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofinnade, A.T.; Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J.; Olowe, O.A. The potential toxicity of food-added sodium benzoate in mice is concentration-dependent. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, D.; Jack, M.M.; Coder, P.S.; Picut, C.A.; Rodricks, J.V. Extended One-Generation Reproductive Toxicity (EOGRT) study of benzoic acid in Sprague Dawley rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 122, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.; Inohaya, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Yoshizaki, N.; Iuchi, I.; Yasumasu, S. Purification and characterization of zebrafish hatching enzyme—An evolutionary aspect of the mechanism of egg envelope digestion. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 5934–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J. Ionic Stress Prompts Premature Hatching of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Fishes 2019, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.D.; El-Khoury, M.; Deslongchamps, G.; Benfey, T.J.; Crawford, B.D. Matrix Metalloproteinase 13 Activity is Required for Normal and Hypoxia-Induced Precocious Hatching in Zebrafish Embryos. J. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Souders, C.L., 2nd; Zhang, J.; Martyniuk, C.J. Tributyltin induces premature hatching and reduces locomotor activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos/larvae at environmentally relevant levels. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaee, S.M.; Rabbani, S.; Jovanovic, B.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.R.; Haghpanah, V. Efficacy of the hatching event in assessing the embryo toxicity of the nano-sized TiO2 particles in zebrafish: A comparison between two different classes of hatching-derived variables. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 116, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Huang, Q.; Fang, C.; Ye, T.; Qiu, L.; Dong, S. PFOS induced precocious hatching of Oryzias melastigma--from molecular level to individual level. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spulber, S.; Kilian, P.; Wan Ibrahim, W.N.; Onishchenko, N.; Ulhaq, M.; Norrgren, L.; Negri, S.; Di Tuccio, M.; Ceccatelli, S. PFOS induces behavioral alterations, including spontaneous hyperactivity that is corrected by dexamfetamine in zebrafish larvae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| FAs (Abbr.) | Chemical Structure | E Number | Usage | Supplier (Cat #) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinoline Yellow WS (QY) | 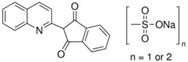 | E104 | Coloring agent | Sigma Aldrich (309052) |
| Sunset Yellow (SY) | 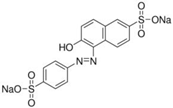 | E110 | Coloring agent | Sigma Aldrich (465224) |
| Azorubine (Azr) | 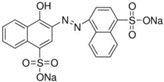 | E122 | Coloring agent | Sigma Aldrich (214515) |
| Allura Red AC (AR) | 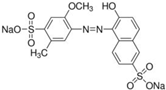 | E129 | Coloring agent | Sigma Aldrich (458848) |
| Brilliant Blue (BB) |  | E133 | Coloring agent | Sigma Aldrich (861146) |
| Sodium Benzoate (SB) | 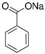 | E211 | Preservative | Sigma Aldrich (109169) |
| Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) |  | E621 | Flavor enhancer | Sigma Aldrich (49621) |
| Aspartame (Asp) | 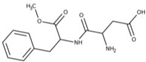 | E951 | Sweetener | Alfa Aesar (J61523) |
| FA | NOAEC (mg/L) | LC50 Estimate (mg/L) | LC50 95% CI (mg/L) | EC50 Estimate (mg/L) | EC50 95% CI (mg/L) | TI | TI Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QY | 5 | 6.89 × 103 | 5.39–8.38 × 103 | 87.7 | 73.1–102 | 78.6 | 52.7–115 |
| SY | 100 | 5.27 × 103 | 4.06–6.50 × 103 | 1.20 × 103 | 1.01–1.38 × 103 | 4.41 | 2.93–6.44 |
| Azr | 100 | 3.97 × 103 | 3.02–4.91 × 103 | 2.73 × 103 | 1.79–3.67 × 103 | 1.45 | 0.82–2.74 |
| AR | 50 | 1.84 × 103 | 1.57–2.11 × 103 | 253 | 206–301 | 7.26 | 5.21–10.3 |
| BB | 100 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| SB | 2 | 26.9 | 23.8–30.0 | 6.63 | 6.21–7.06 | 4.05 | 3.37–4.83 |
| MSG | 4500 | 20.1 × 103 | 19.2–21.1 × 103 | 10.9 × 103 | 10.4–11.5 × 103 | 1.85 | 1.68–2.03 |
| Asp | 10,000 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duy-Thanh, D.; Bich-Ngoc, N.; Van den Bossche, F.; Lai-Thanh, N.; Muller, M. Discovering Novel Bioactivities of Controversial Food Additives by Means of Simple Zebrafish Embryotoxicity (ZET) Assays. Toxics 2023, 11, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010008
Duy-Thanh D, Bich-Ngoc N, Van den Bossche F, Lai-Thanh N, Muller M. Discovering Novel Bioactivities of Controversial Food Additives by Means of Simple Zebrafish Embryotoxicity (ZET) Assays. Toxics. 2023; 11(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuy-Thanh, Dinh, Nguyen Bich-Ngoc, François Van den Bossche, Nguyen Lai-Thanh, and Marc Muller. 2023. "Discovering Novel Bioactivities of Controversial Food Additives by Means of Simple Zebrafish Embryotoxicity (ZET) Assays" Toxics 11, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010008
APA StyleDuy-Thanh, D., Bich-Ngoc, N., Van den Bossche, F., Lai-Thanh, N., & Muller, M. (2023). Discovering Novel Bioactivities of Controversial Food Additives by Means of Simple Zebrafish Embryotoxicity (ZET) Assays. Toxics, 11(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010008










