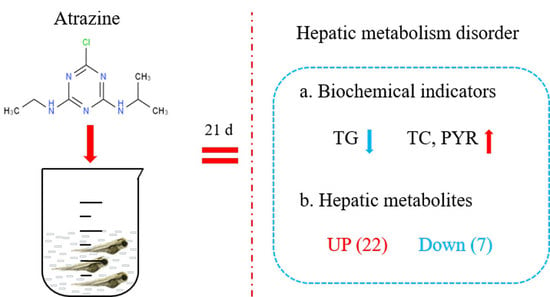
Atrazine Exposure Induces Hepatic Metabolism Disorder in Male Adult Zebrafish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Fish Exposure and Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Liver Parameters
2.4. GC/MS-Based Metabolomic Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of ATZ on Physiological Indicators in the Liver
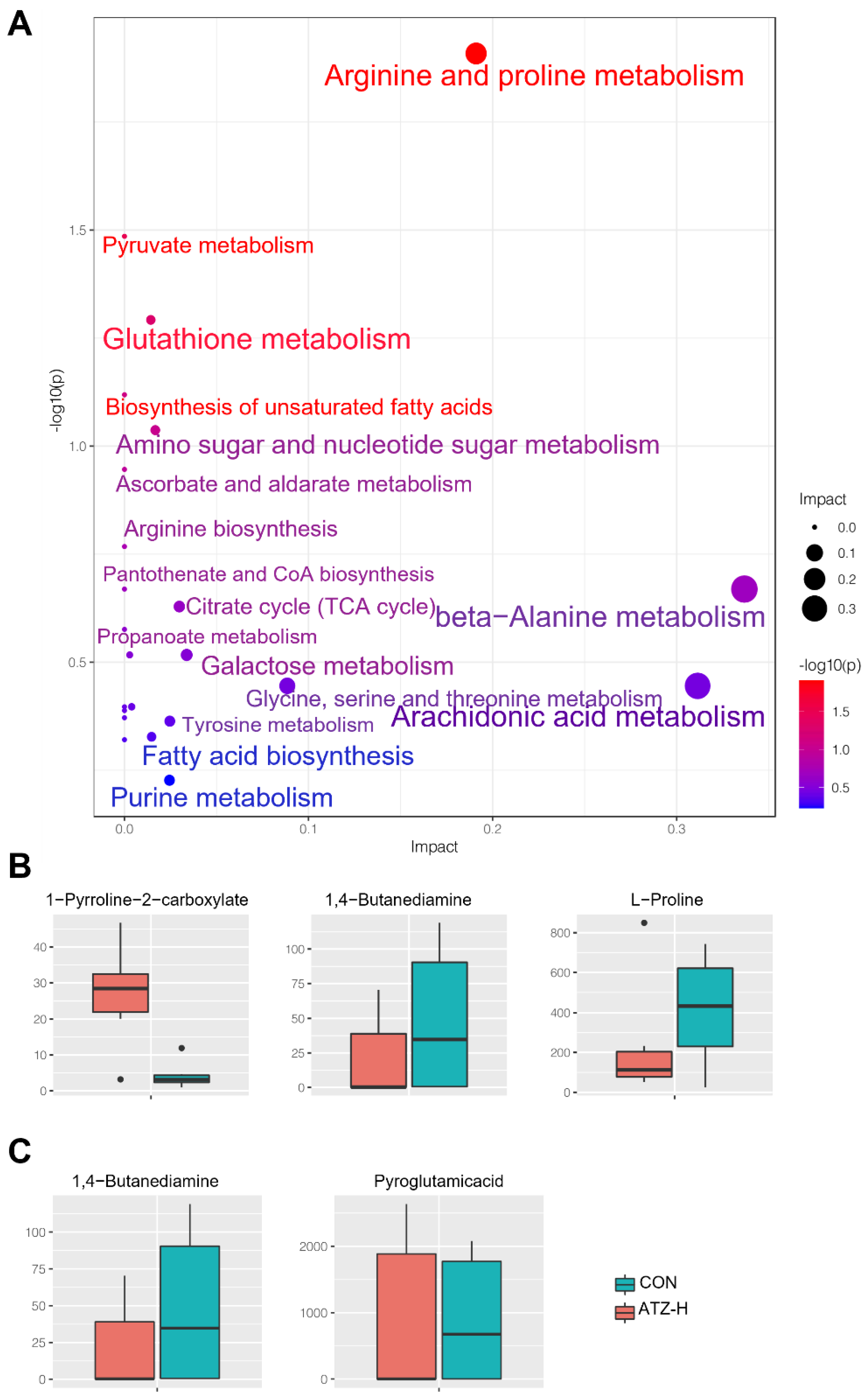
3.2. Metabolomic Alterations Induced by ATZ in the Liver
3.3. The Main Metabolic Pathways That Were Significantly Altered in ATZ−Exposed Zebrafish
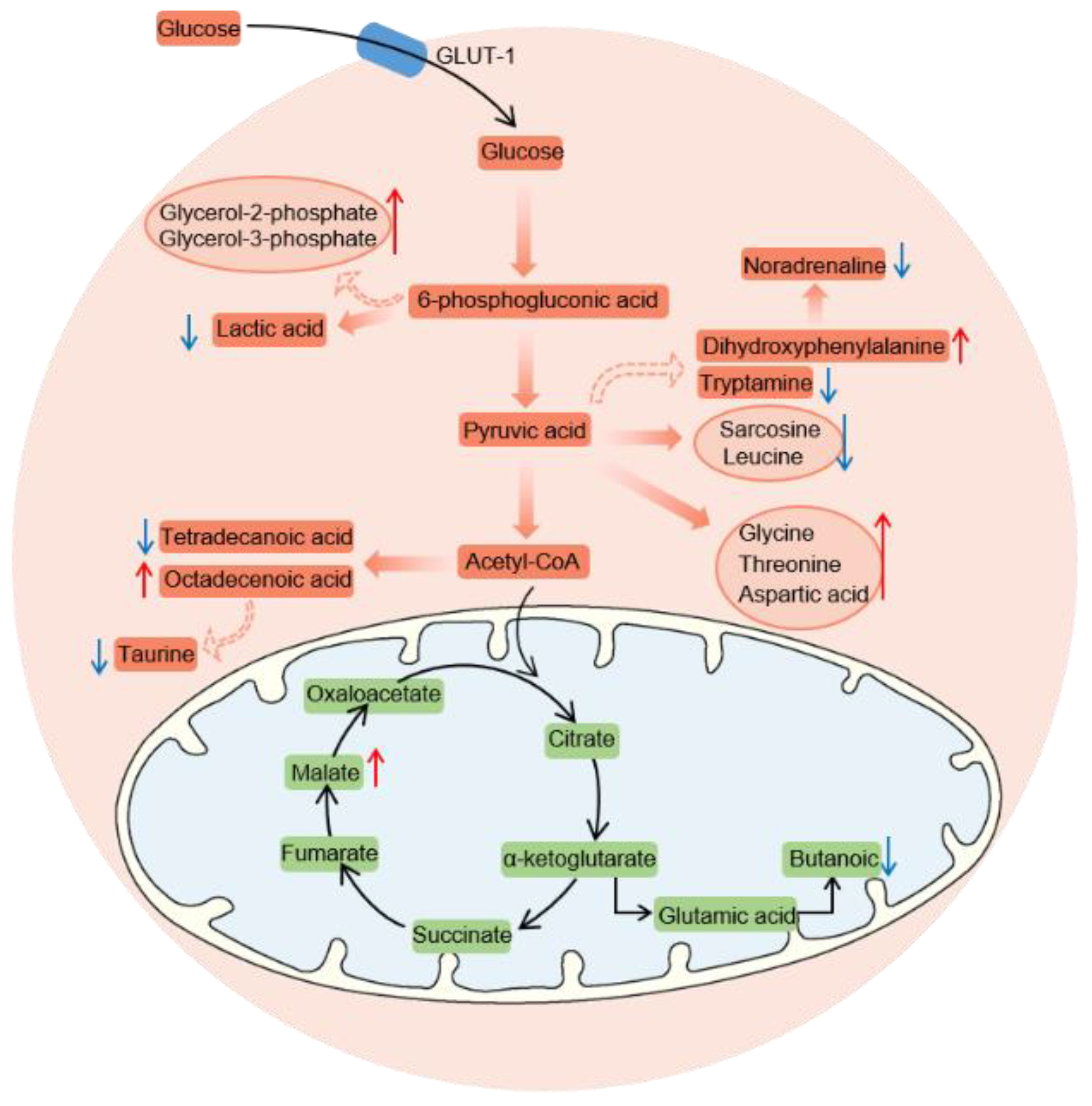
3.4. ATZ Induced the Changed Metabolites Involved in Different Pathways
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yen, J.; Donerly, S.; Levin, E.D.; Linney, E.A. Differential acetylcholinesterase inhibition of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and parathion in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Pan, Z.; Jin, C.; Ni, Y.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Gut microbiota: An underestimated and unintended recipient for pesticide-induced toxicity. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Bao, Z.; Jin, C.; Miao, W.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Toxic effects and mechanisms of three commonly used fungicides on the human colon adenocarcinoma cell line Caco-2. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, J.; Wang, W.; Lu, T.; Dong, Q.; Yang, H. Monitoring and risk assessment of pesticide residue in plant-soil-groundwater system about medlar planting in Golmud. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26413–26426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchowicz, P.R. QSPR studies on water solubility, octanol-water partition coefficient and vapour pressure of pesticides. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2020, 31, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamhewage, M.; Sheedy, C.; Munira, S.; Farenhorst, A. Pesticide Mixtures in the Water-Column Versus Bottom-Sediments of Prairie Rivers. Bull Environ Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, D.B.; Panuwet, P.; Nguyen, J.V.; Udunka, S.; Needham, L.L. Assessing exposure to atrazine and its metabolites using biomonitoring. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiely, T.; Donaldson, D.; Grube, A. Pesticide Industry Sales and Usage: 2000 and 2001 Market Estimates; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Gaynor, J.D.; Tan, C.S.; Drury, C.F.; Welacky, T.W.; Ng, H.Y.; Reynolds, W.D. Runoff and drainage losses of atrazine, metribuzin, and metolachlor in three water management systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Furnas, M.J.; Fabricius, K.; Haynes, D.; Carter, S.; Eaglesham, G.; Mueller, J.F. Monitoring pesticides in the Great Barrier Reef. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringolf, R.B.; Belden, J.B.; Summerfelt, R.C. Effects of atrazine on fathead minnow in a short-term reproduction assay. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, L.S.; Xie, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, W.; Dong, X.L. Effects of atrazine on DNA damage and antioxidative enzymes in Vicia faba. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Song, W.; Jiang, C.; Li, B.; Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, K. Combined effects of mulch film-derived microplastics and atrazine on oxidative stress and gene expression in earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shu, L.; Chen, L.; Sun, L.; Qian, H.; Liu, W.; Fu, Z. Oxidative stress response and gene expression with atrazine exposure in adult female zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2010, 78, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, X. Histopathological changes and antioxidant response in brain and kidney of common carp exposed to atrazine and chlorpyrifos. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, E.; Feng, X.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Atrazine and its main metabolites alter the locomotor activity of larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2016, 148, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, W.L.; Patino, R.; Maule, A.G. Interaction of xenobiotics with estrogen receptors alpha and beta and a putative plasma sex hormone-binding globulin from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2004, 136, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Immunotoxic effects of atrazine and its main metabolites environmental relevant concentrations on larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2017, 166, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanioka, N.; Jinno, H.; Tanaka-Kagawa, T.; Nishimura, T.; Ando, M. In vitro metabolism of simazine, atrazine and propazine by hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes of rat, mouse and guinea pig, and oestrogenic activity of chlorotriazines and their main metabolites. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.K.; Jones, T.L.; Filipov, N.M. Disposition of the herbicide 2-Chloro-4-(ethylamino)-6-(isopropylamino)-s-triazine (atrazine) and its major metabolites in mice: A liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis of urine, plasma, and tissue levels. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, C.; Luo, T.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Imazalil exposure induces gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic metabolism disorder in zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 202, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, D.; Qi, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Dong, K.; Zheng, M.; Wang, C. Metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal the toxicity of difenoconazole to the early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, M.; Zhou, J.; Jin, Y. Chlorpyrifos disturbs hepatic metabolism associated with oxidative stress and gut microbiota dysbiosis in adult zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 216, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Meng, Z.; Tian, S.; Teng, M.; Yan, J.; Jia, M.; Li, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. Neonicotinoid insecticides exposure cause amino acid metabolism disorders, lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in ICR mice. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Pinu, F.R.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Poojary, M.M.; Narayana, V.K.; Boughton, B.A.; Kanojia, K.; Dayalan, S.; Jones, O.A.H.; Dias, D.A. Review of recent developments in GC–MS approaches to metabolomics-based research. Metabolomics 2018, 4, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Arita, M.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E. GC/MS based metabolomics: Development of a data mining system for metabolite identification by using soft independent modeling of class analogy (simca). BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villas-Bôas, S.G.; Højer-Pedersen, J.; Åkesson, M.; Smedsgaard, J.; Nielsen, J. Global metabolite analysis of yeast: Evaluation of sample preparation methods. Yeast 2005, 22, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Tan, H.; Peng, T.; Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Qian, H.; Jin, Y.; Fu, Z. Developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphate flame retardants in early life stages of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Wu, Y.; Xu, C.; Jin, Y.; He, X.; Wan, J.; Yu, X.; Rao, H.; Tu, W. Multiple approaches to assess the effects of F-53B, a Chinese PFOS alternative, on thyroid endocrine disruption at environmentally relevant concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish Danio (Brachydanio) Rerio; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Wang, Q. Influence of Cd on atrazine degradation and the formation of three primary metabolites in water under the combined pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 16081–16091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, E.; Feng, X.; Fu, Z. The fungicide imazalil induces developmental abnormalities and alters locomotor activity during early developmental stages in zebrafish. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Lu, L.; Jin, C.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Ni, Y.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Effects of short term lead exposure on gut microbiota and hepatic metabolism in adult zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 209, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Fu, Z. Effects of environmental pollutants on gut microbiota. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fang, Y.Z.; Yang, S.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D. Glutathione Metabolism and Its Implications for Health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, C.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, T.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Ni, Y.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Insights into a Possible Mechanism Underlying the Connection of Carbendazim-Induced Lipid Metabolism Disorder and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 166, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aziz, R.L.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Abo El-Ela, F.I.; Hassan, N.E.Y.; El-Nahass, E.S.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Khalil, A.A.Y. Dose-dependent ameliorative effects of quercetin and l-Carnitine against atrazine- induced reproductive toxicity in adult male Albino rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prykhozhij, S.V.; Berman, J.N. The progress and promise of zebrafish as a model to study mast cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 74e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, G.; Lin, X.; Miao, W.; Fu, Z. Exposure of mice to atrazine and its metabolite diaminochlorotriazine elicits oxidative stress and endocrine disruption. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.N.; Xiang, L.R.; Qin, L.; Lin, J.; Li, J.L. Atrazine triggers hepatic oxidative stress and apoptosis in quails (Coturnix C. coturnix) via blocking Nrf2-mediated defense response. Ecotoxcol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hankemeier, T.; Ramautar, R. Next-generation capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry approaches in metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Chang, M.; Ren, J.; Xie, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Shen, G.; Li, H. Metabonomics reveals that triclocarban affects liver metabolism by affecting glucose metabolism, β-oxidation of fatty acids, and the TCA cycle in male mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 299, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandan, P.; Nagini, S. Cytochrome P450 Structure, Function and Clinical Significance: A Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The liver. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Bezerra, M.; Cohenm, D.E. Triglyceride Metabolism in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Hu, S.; Li, X.; He, W.; Wu, G. Amino acid metabolism in the liver: Nutritional and physiological significance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1265, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Lin, X.; Miao, W.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Fu, Z. Oral exposure of pubertal male mice to endocrine-disrupting chemicals alters fat metabolism in adult livers. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wang, D.; Teng, M.; Yan, J.; Miao, J.; Zhou, Z. 1H NMR-based metabolomics analysis of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) after exposure to diniconazole as well as its bioaccumulation behavior. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadli, F.K.; Treguier, M.; Briand, F.; Sulpice, T.; Ouguerram, K. Ezetimibe Enhances Macrophage-to-Feces Reverse Cholesterol Transport in Golden Syrian Hamsters Fed a High-Cholesterol Diet. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 375, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreth, J.; Lengeler, J.W.; Jahreis, K. Characterization of Pyruvate Uptake in Escherichia coli K-12. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8, e67125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Koning, T.J. Amino acid synthesis deficiencies. J. Inherit. Metab Dis. 2017, 40, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Bai, S.; Yao, Z.; Umar, A.A.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, H. Gut microbiota promotes host resistance to low-temperature stress by stimulating its arginine and proline metabolism pathway in adult Bactrocera dorsalis. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Duan, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, W.; He, S.; Li, J.; Yin, Y. Taurine is involved in energy metabolism in muscle, adipose tissue, and liver. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, M.P.; James, P.M. Supplemental dietary leucine and the skeletal muscle anabolic response to essential amino acids. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 550–557. [Google Scholar]
- Ritz-Timme, S.; Collins, M.J. Racemization of aspartic acid in human proteins. Ageing Res. Rev. 2002, 1, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Qian, M.; Jin, Y. Atrazine Exposure Induces Hepatic Metabolism Disorder in Male Adult Zebrafish. Toxics 2022, 10, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070400
Zhang H, Wang X, Qian M, Jin Y. Atrazine Exposure Induces Hepatic Metabolism Disorder in Male Adult Zebrafish. Toxics. 2022; 10(7):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070400
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hu, Xiaofang Wang, Mingrong Qian, and Yuanxiang Jin. 2022. "Atrazine Exposure Induces Hepatic Metabolism Disorder in Male Adult Zebrafish" Toxics 10, no. 7: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070400
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, X., Qian, M., & Jin, Y. (2022). Atrazine Exposure Induces Hepatic Metabolism Disorder in Male Adult Zebrafish. Toxics, 10(7), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070400