Alleviation of Ammonium Toxicity in Salvia splendens ‘Vista Red’ with Silicon Supplementation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Treatments, and Experimental Conditions
2.2. Measurement of Plant Growth Parameters and Destructive Sampling
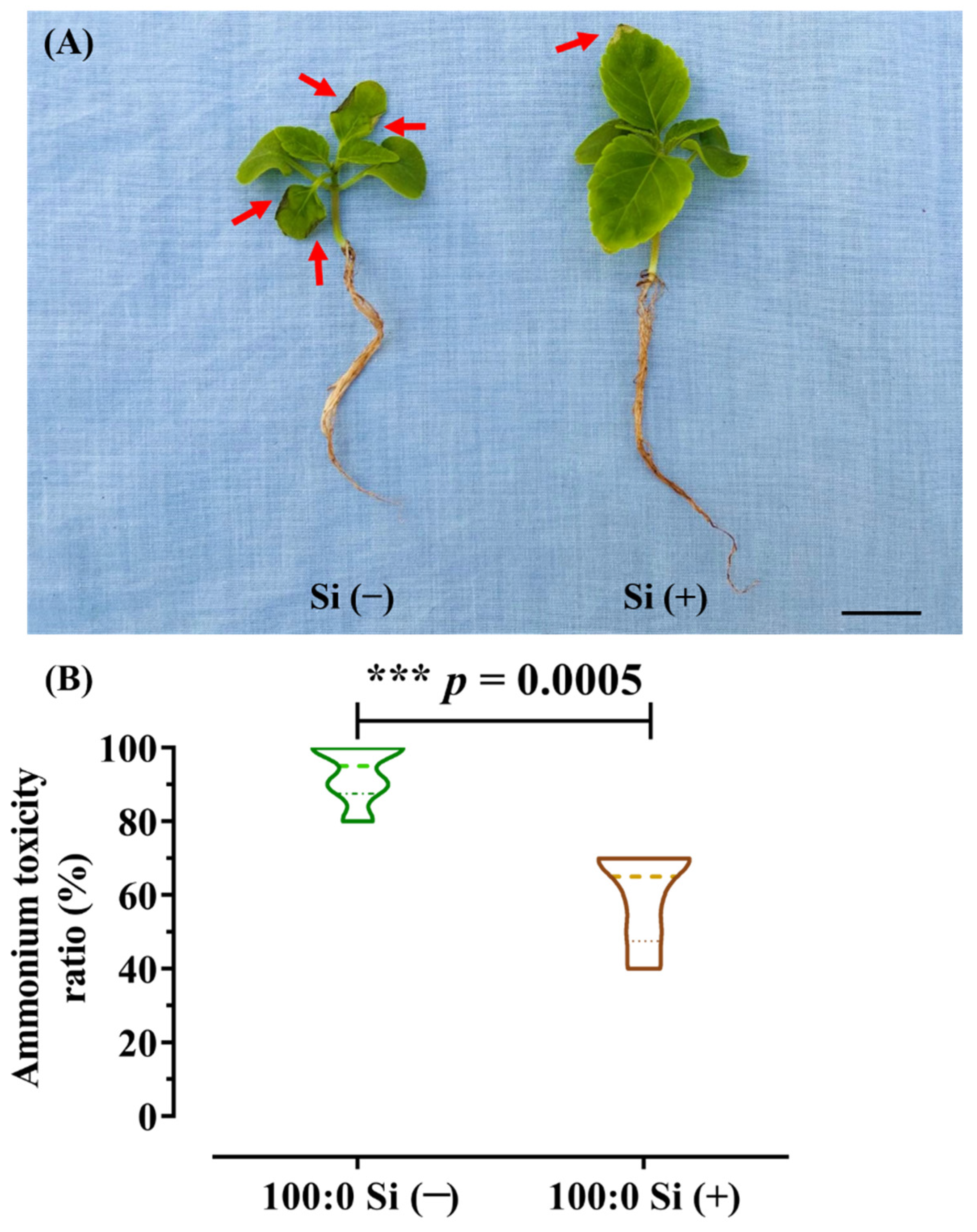
2.3. Calculation of the Ammonium Toxicity Ratio (%)
2.4. Estimation of the Photosynthetic Capacity
2.5. Determinations of Si, K, Ca, and Mg Concentrations
2.6. Analysis of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Leaf Samples
2.7. Quantifications of O2·−, H2O2, MDA, and Carotenoids in Leaf Samples
2.8. Statistical Analysis and Graphing
3. Results
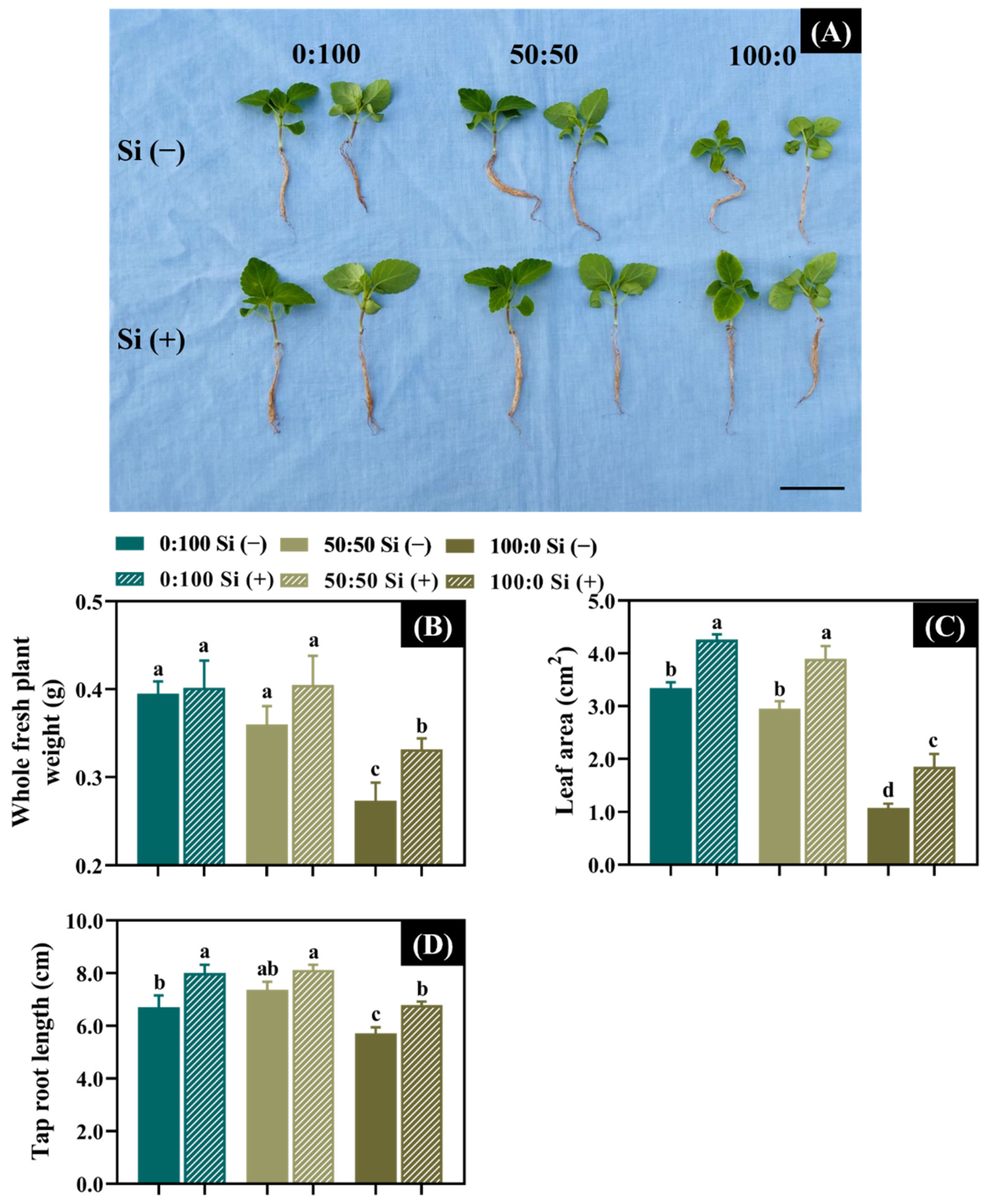
3.1. Effects of the Three NH4+:NO3− Ratios and Si Supplementation on the Plant Growth Attributes
3.2. NH4+ Toxicity Ratio as Influenced by Si Application
3.3. Photosynthetic Ability as Affected by the N Form and Si Supplementation
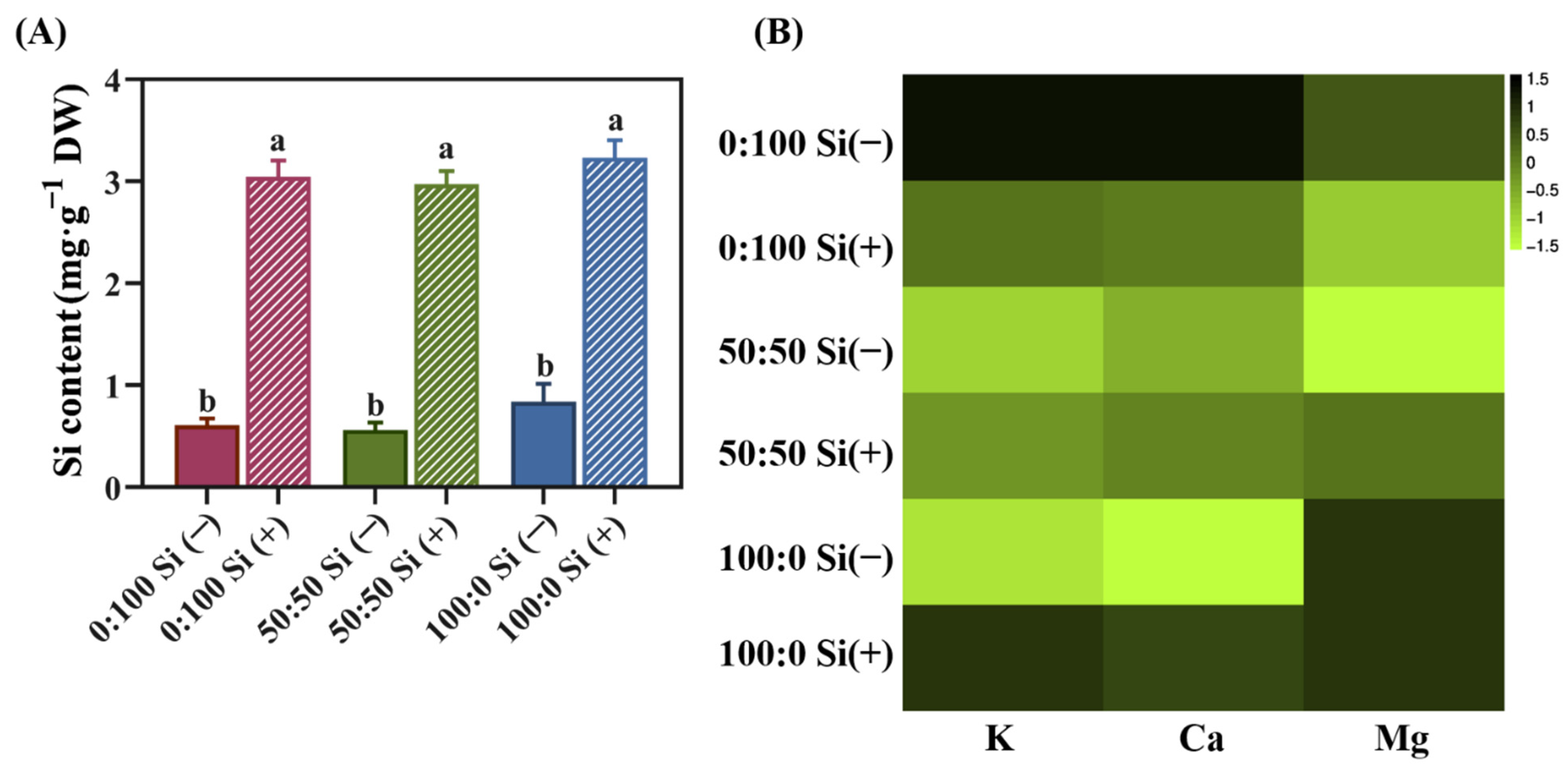
3.4. The Accumulation of Silicon (Si), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), and Magnesium (Mg)
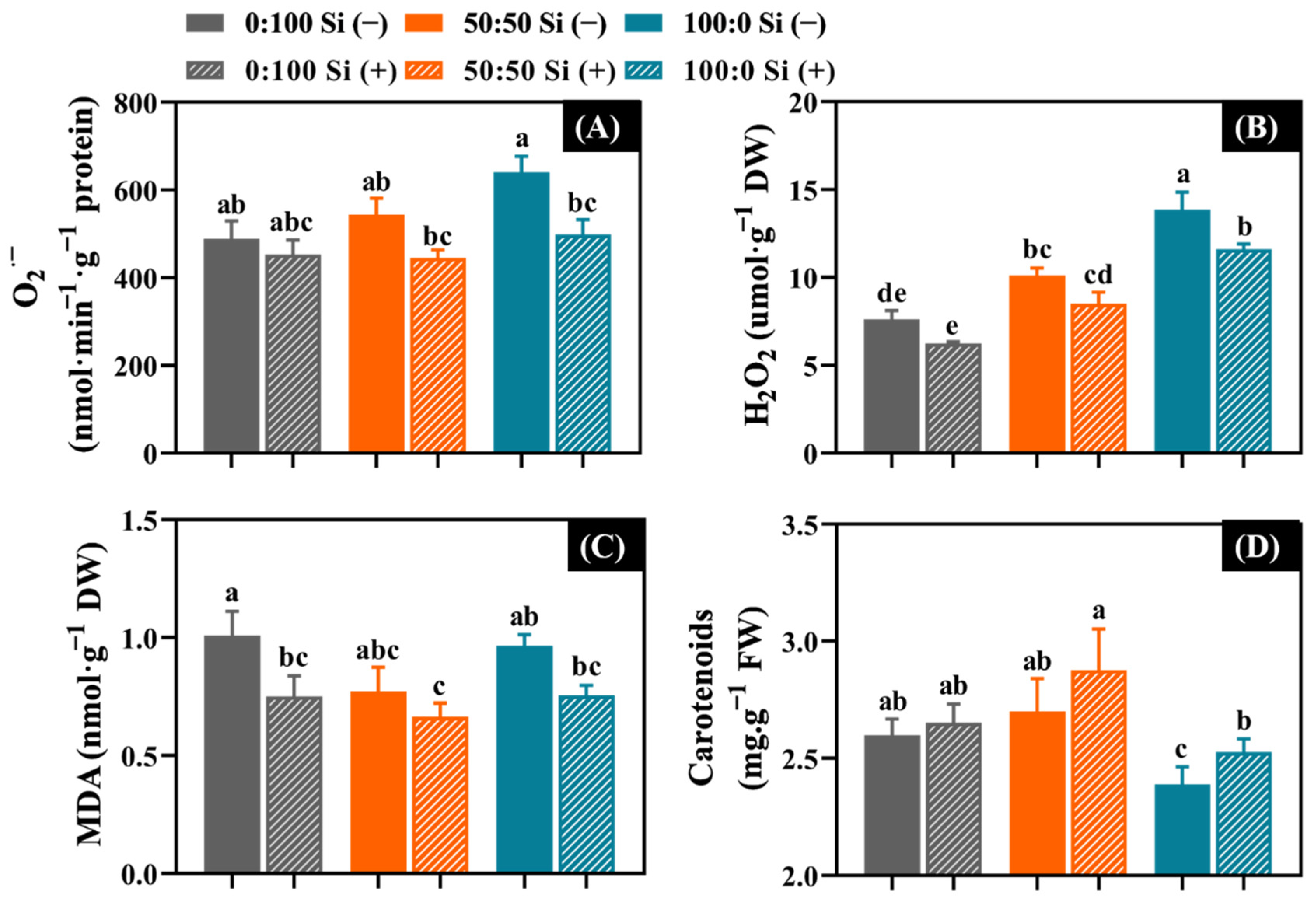
3.5. Responses of Antioxidant Capacity to N Forms and Si Application
3.6. Oxidative Damage as Affected by the Three NH4+:NO3− Ratios and Si Supplementations
3.7. Responses between Antioxidant Capacity and Si Supplementation Are Supported by PCA Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Si Promoted Plant Growth and Alleviated the NH4+ Toxicity Degree
4.2. Si Ameliorated Damaged Photosynthetic Capacity Caused by NH4+ Toxicity
4.3. Si Alleviated the Inhibition of Key Cation Uptakes under NH4+ Toxicity
4.4. Improved Antioxidative Enzyme Activities by Si Contributed to the Mitigation of NH4+ Toxicity
4.5. Si Decreased the ROS Accumulation, Lipid Peroxidation, and Pigment Degradation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xing, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bloszies, S.A.; Tu, C.; Hu, S. Effects of NH4+–N/NO3−–N ratios on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter yield and nitrate concentration of spinach. Exp. Agric. 2015, 51, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.; Bio, A.; Domínguez-Valdivia, M.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; Lamsfus, C.; Martins-Louçao, M.A. How does glutamine synthetase activity determine plant tolerance to ammonium? Planta 2006, 223, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhele, B.; Zhan, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X. Nitrogen assimilation in crop plants and its affecting factors. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.E.; Burger, M.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Roots, nitrogen transformations, and ecosystem services. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-X.; Wang, Z.-H.; Stewart, B. Responses of crop plants to ammonium and nitrate N. Adv. Agron. 2013, 118, 205–397. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Root GS and NADH-GDH play important roles in enhancing the ammonium tolerance in three bedding plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachiya, T.; Inaba, J.; Wakazaki, M.; Sato, M.; Toyooka, K.; Miyagi, A.; Kawai-Yamada, M.; Sugiura, D.; Nakagawa, T.; Kiba, T.; et al. Excessive ammonium assimilation by plastidic glutamine synthetase causes ammonium toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roosta, H.R.; Sajjadinia, A.; Rahimi, A.; Schjoerring, J.K. Responses of cucumber plant to NH4+ and NO3− nutrition: The relative addition rate technique vs. cultivation at constant nitrogen concentration. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 121, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Growth, quality, and nitrogen assimilation in response to high ammonium or nitrate supply in cabbage (Brassica campestris L.) and lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, R.; Ariz, I.; Cruz, C.; Moran, J.F. Mechanisms of ammonium toxicity and the quest for tolerance. Plant Sci. 2016, 248, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, D.T.; Kronzucker, H.J. NH4+ toxicity in higher plants: A critical review. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 159, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.-X.; Xin, H.-B.; Li, Z.-J.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Nie, S.; Zhao, Z.-N.; Cui, R.-F.; Zhang, R.-G.; Yun, Q.-Z.; et al. High-quality assembly of the reference genome for scarlet sage, Salvia splendens, an economically important ornamental plant. GigaScience 2018, 7, giy068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, B.T.; González-Gallegos, J.G.; Xiang, C.-L.; Kriebel, R.; Drummond, C.P.; Walked, J.B.; Sytsma, K.J. Salvia united: The greatest good for the greatest number. Taxon 2017, 66, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.R.; Lee, C.W. Influence of ammonium, nitrate, and chloride on solution pH and ion uptake by ageratum and salvia in hydroponic culture. J. Plant Nutr. 1996, 19, 1343–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Decreased solution pH and increased K+ uptake are related to ammonium tolerance in hydroponically cultured plants. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirooz, P.; Amooaghaie, R.; Ahadi, A.; Sharififar, F.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M. Silicon and nitric oxide synergistically modulate the production of essential oil and rosmarinic acid in Salvia officinalis under Cu stress. Protoplasma 2021, 259, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.N.S.; Silva Júnior, G.B.D.; Prado, R.D.M.; David, C.H.O.D.; Souza Junior, J.P.D.; Teodoro, P.E. Silicon mitigates ammonium toxicity in plants. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viciedo, D.O.; de Mello Prado, R.; Lizcano Toledo, R.; dos Santos, L.C.N.; Calero Hurtado, A.; Nedd, L.L.T.; Castellanos Gonzalez, L. Silicon supplementation alleviates ammonium toxicity in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-P.; Verma, K.K.; Tian, D.-D.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Liang, Y.-J.; Huang, X.; Li, C.-N.; Li, Y.-R. Exploration of silicon functions to integrate with biotic stress tolerance and crop improvement. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashry, R.M.; El-Saadony, M.T.; El-Sobki, A.E.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Al-Otaibi, S.; El-Shehawi, A.M.; Saad, A.M.; Elshaer, N. Biological silicon nanoparticles maximize the efficiency of nematicides against biotic stress induced by Meloidogyne incognita in eggplant. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Aziz, T.; Maqsood, M.; Farooq, M.; Abdullah, Y.; Ramzani, P.; Bilal, H. Silicon nutrition mitigates salinity stress in maize by modulating ion accumulation, photosynthesis, and antioxidants. Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Detterbeck, A.; Clemens, S.; Dietz, K.-J. Silicon-induced reversibility of cadmium toxicity in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3573–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.S.; de Mello Prado, R.; Hurtado, A.C.; De Andrade, R.A.; Da Silva, G.P. Ammonia toxicity affect cations uptake and growth in papaya plants inclusive with silicon addition. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2020, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, D. Cadmium accumulation, activities of antioxidant enzymes, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content in Pistia stratiotes L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Zhu, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C. Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought. Plant Sci. 2005, 169, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Ahanger, M.A.; Alam, P.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Ali, S.; Ashraf, M. Silicon (Si) supplementation alleviates NaCl toxicity in mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] through the modifications of physio-biochemical attributes and key antioxidant enzymes. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Jeong, B.R. Silicon alleviates temperature stresses in poinsettia by regulating stomata, photosynthesis, and oxidative damages. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, B.R. Pre-and/or postharvest silicon application prolongs the vase life and enhances the quality of cut peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) flowers. Plants 2021, 10, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, S.; Fuentes, S.; Gupta, D. Silicon modulates nitro-oxidative homeostasis along with the antioxidant metabolism to promote drought stress tolerance in lentil plants. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1382–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopolitis, C.N.; Ries, S.K. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1977, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 867–880. [Google Scholar]
- Cakmak, I.; Marschner, H. Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amako, K.; Chen, G.-X.; Asada, K. Separate assays specific for ascorbate peroxidase and guaiacol peroxidase and for the chloroplastic and cytosolic isozymes of ascorbate peroxidase in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 1994, 35, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Mavis, R.D.; Stellwagen, E. Purification and subunit structure of glutathione reductase from bakers’ yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-X.; von Tiedemann, A. Impact of fungicides on active oxygen species and antioxidant enzymes in spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) exposed to ozone. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 116, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Choudhuri, M. Implications of water stress-induced changes in the levels of endogenous ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide in Vigna seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 1983, 58, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.A.; Pieper, R.K.; McClellan, L. Specificity of the thiobarbituric acid reaction: Its use in studies of lipid peroxidation. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, K.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, B.; Chen, Z.; Xu, K. Silicon enhanced the resistance of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) to ofloxacin on the growth, photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant system. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Y.X.; Huang, L. ImageGP: An easy-to-use data visualization web server for scientific researchers. iMeta 2022, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; von Wirén, N. Ammonium as a signal for physiological and morphological responses in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, G.P.; de Mello Prado, R.; Ferreira, R.P.S. Absorption of nutrients, growth and nutritional disorders resulting from ammonium toxicity in rice and spinach plants. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2016, 28, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, R.F.; Júnior, A.A.S.; Maggio, M.A.; de Mello Prado, R. Silicon alleviates ammonium toxicity in cauliflower and in broccoli. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.N.S.; de Mello Prado, R.; Caione, G. Silicon and excess ammonium and nitrate in cucumber plants. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, R.; Prado, R.; Leal, A.; Troleis, M.; Junior, G.S.; Monteiro, C.; Santos, L.; Carvalho, R. Mitigation of ammonium toxicity by silicon in tomato depends on the ammonium concentration. Acta Agric. Scand. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2016, 66, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Nikolic, M.; Bélanger, R.; Gong, H.; Song, A. Effect of silicon on crop growth, yield and quality. In Silicon in Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Vasanthi, N.; Saleena, L.M.; Raj, S.A. Silicon in crop production and crop protection—A review. Agric. Rev. 2014, 35, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Silicon mitigates ammonium toxicity in cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis) ‘Ssamchu’. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 922666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Reddy, V.R. Combined effects of phosphorus nutrition and elevated carbon dioxide concentration on chlorophyll fluorescence, photosynthesis, and nutrient efficiency of cotton. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, O.; Uzen, N.; Temiz, M. Effect of N-fertigation frequency on the lint yield, chlorophyll, and photosynthesis rate of cotton. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 17, 909–920. [Google Scholar]
- Kura-Hotta, M.; Satoh, K.; Katoh, S. Relationship between photosynthesis and chlorophyll content during leaf senescence of rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol. 1987, 28, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Yu, X.; Kjær, K.H.; Rosenqvist, E.; Ottosen, C.-O.; Wu, Z. Screening and validation of tomato genotypes under heat stress using Fv/Fm to reveal the physiological mechanism of heat tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 118, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Badgujar, G.; Reddy, V.R.; Fleisher, D.H.; Bunce, J.A. Carbon dioxide diffusion across stomata and mesophyll and photo-biochemical processes as affected by growth CO2 and phosphorus nutrition in cotton. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, G.; Li, Z.; Ning, T.; Zheng, Y. Responses of photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence, and grain yield of maize to controlled-release urea and irrigation after anthesis. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Du, Q.; Li, J. Interactive effects of nitrate-ammonium ratios and temperatures on growth, photosynthesis, and nitrogen metabolism of tomato seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 214, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.E.A.; Rodrigues, F.Á.; Moreira, W.R.; DaMatta, F.M. Leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll a fluorescence in wheat plants supplied with silicon and infected with Pyricularia oryzae. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, K.; Emam, Y.; Pessarakli, M. Effect of silicon on photosynthetic gas exchange, photosynthetic pigments, cell membrane stability and relative water content of different wheat cultivars under drought stress conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.; Leishman, M.R. Consistent alleviation of abiotic stress with silicon addition: A meta-analysis. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 1340–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhat, H.F.; Bibi, N.; Zia, Z.; Abbas, S.; Hammad, H.M.; Fahad, S.; Ashraf, M.R.; Shah, G.M.; Rabbani, F.; Saeed, S. Silicon mitigates biotic stresses in crop plants: A review. Crop Prot. 2018, 104, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittsánszky, A.; Pilinszky, K.; Gyulai, G.; Komives, T. Overcoming ammonium toxicity. Plant Sci. 2015, 231, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ding, R. Effect of exogenous silicon (Si) on H+-ATPase activity, phospholipids and fluidity of plasma membrane in leaves of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, H.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; Di, D.; Lin, X.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Shi, W.; Li, G. Induction of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase protects root growth from ammonium toxicity by regulating potassium homeostasis in Arabidopsis and rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 4548–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkos, K.D.; Britto, D.T.; Kronzucker, H.J. Optimization of ammonium acquisition and metabolism by potassium in rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. IR-72). Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.A.; Silva, J.A.; Fujita, M. Plant response and tolerance to abiotic oxidative stress: Antioxidant defense is a key factor. In Crop Stress and Its Management: Perspectives and Strategies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 261–315. [Google Scholar]
- Rezayian, M.; Niknam, V.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Oxidative damage and antioxidative system in algae. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumanović, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Natić, M.; Kuča, K.; Jaćević, V. The significance of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense system in plants: A concise overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 552969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, S.; Ueda, M.; Kitajima, S.; Takeda, T.; Shigeoka, S.; Kurano, N.; Miyachi, S.; Miyake, C.; Yokota, A. Characterization of ascorbate peroxidases from unicellular red alga Galdieria partita. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, X.; Zeng, G.; Zheng, B.; Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, X. Effects of selenium and silicon on enhancing antioxidative capacity in ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) under cadmium stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9999–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souri, Z.; Khanna, K.; Karimi, N.; Ahmad, P. Silicon and plants: Current knowledge and future prospects. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 906–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.-M.; Hua, W.-P.; Cao, X.-Y.; Yan, J.-A.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.-Z. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Gene 2020, 742, 144603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.-H.; Wang, Y.-K.; Lu, X.-M.; Jia, S.-S. Effects of exogenous silicon on physiological characteristics of cucumber seedlings under ammonium stress. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2014, 25, 1395–1400. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Mokhberdoran, F.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y. Silicon dioxide nanoparticles improve plant growth by enhancing antioxidant enzyme capacity in bamboo (Pleioblastus pygmaeus) under lead toxicity. Trees 2020, 34, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.U.; Xuebin, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Du, Z.; Imtiaz, M.; Mehmood, F.; Hongfei, L.; Hussain, B.; Ashraf, M.N. Alleviatory effects of silicon on the morphology, physiology, and antioxidative mechanisms of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) roots under cadmium stress in acidic nutrient solutions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, W.U.; Shah, A.A.; Yasin, N.A.; Naz, S.; Ali, A.; Tahir, A.; Batool, A.I. Synergistic effects of nitric oxide and silicon on promoting plant growth, oxidative stress tolerance and reduction of arsenic uptake in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, H.; Bor, M.; Özdemir, F.; Türkan, İ. The effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation, antioxidative enzymes and proline content of sesame cultivars. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, P.F.; Li, W.; Lu, J. Effects of ammonium on the antioxidative response in Hydrilla verticillata (Lf) Royle plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2010, 73, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hao, D.; Jin, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, T.; Su, Y. Internal ammonium excess induces ROS-mediated reactions and causes carbon scarcity in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, T. Silicon attenuates cadmium toxicity in Solanum nigrum L. by reducing cadmium uptake and oxidative stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Nutrient Source | Ammonium to Nitrate Ratio Combined with (+) or without (−) Si | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0:100 Si (−) | 0:100 Si (+) | 50:50 Si (−) | 50:50 Si (+) | 100:0 Si (−) | 100:0 Si (+) | |
| NH4H2PO4 | - | - | 2.0 | 2.0 | - | - |
| (NH4)2SO4 | - | - | 4.5 | 4.5 | 13.0 | 13.0 |
| K2SO4 | - | - | 4.5 | 3.5 | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| CaCl2·6H2O | - | - | - | - | 4.9 | 4.9 |
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | 6.9 | 6.9 | 5.9 | 5.9 | - | - |
| KNO3 | 4.8 | 3.8 | - | - | - | - |
| Mg(NO3)2·6H2O | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | - | - |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| KH2PO4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | - | - | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| K2SiO3 | - | 1.0 | - | 1.0 | - | 1.0 |
| NH4+:NO3− Ratio (A) | Si Supply (B) | Dry Weight (mg) | Shoot Length (cm) | Leaf Length (cm) | Leaf Width (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0:100 | − | 10.1 z | 2.4 | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| + | 11.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 1.0 | |
| 50:50 | − | 10.3 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 0.9 |
| + | 11.9 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 0.9 | |
| 100:0 | − | 5.6 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| + | 7.9 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 0.7 | |
| F-test | A | ** y | *** | * | ** |
| B | ** | ** | * | * | |
| A × B | * | *** | *** | *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Yang, J.; Jeong, B.R. Alleviation of Ammonium Toxicity in Salvia splendens ‘Vista Red’ with Silicon Supplementation. Toxics 2022, 10, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080446
Song J, Yang J, Jeong BR. Alleviation of Ammonium Toxicity in Salvia splendens ‘Vista Red’ with Silicon Supplementation. Toxics. 2022; 10(8):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080446
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jinnan, Jingli Yang, and Byoung Ryong Jeong. 2022. "Alleviation of Ammonium Toxicity in Salvia splendens ‘Vista Red’ with Silicon Supplementation" Toxics 10, no. 8: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080446
APA StyleSong, J., Yang, J., & Jeong, B. R. (2022). Alleviation of Ammonium Toxicity in Salvia splendens ‘Vista Red’ with Silicon Supplementation. Toxics, 10(8), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10080446








