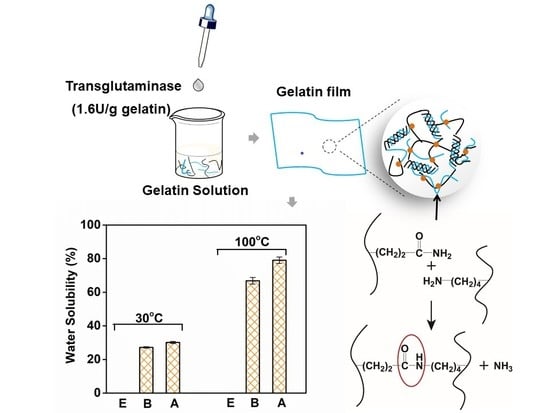
Innovative Water-Insoluble Edible Film Based on Biocatalytic Crosslink of Gelatin Rich in Glutamine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Gelatin
2.3. Glutamine Analysis
2.4. Preparation of Gelatin Films
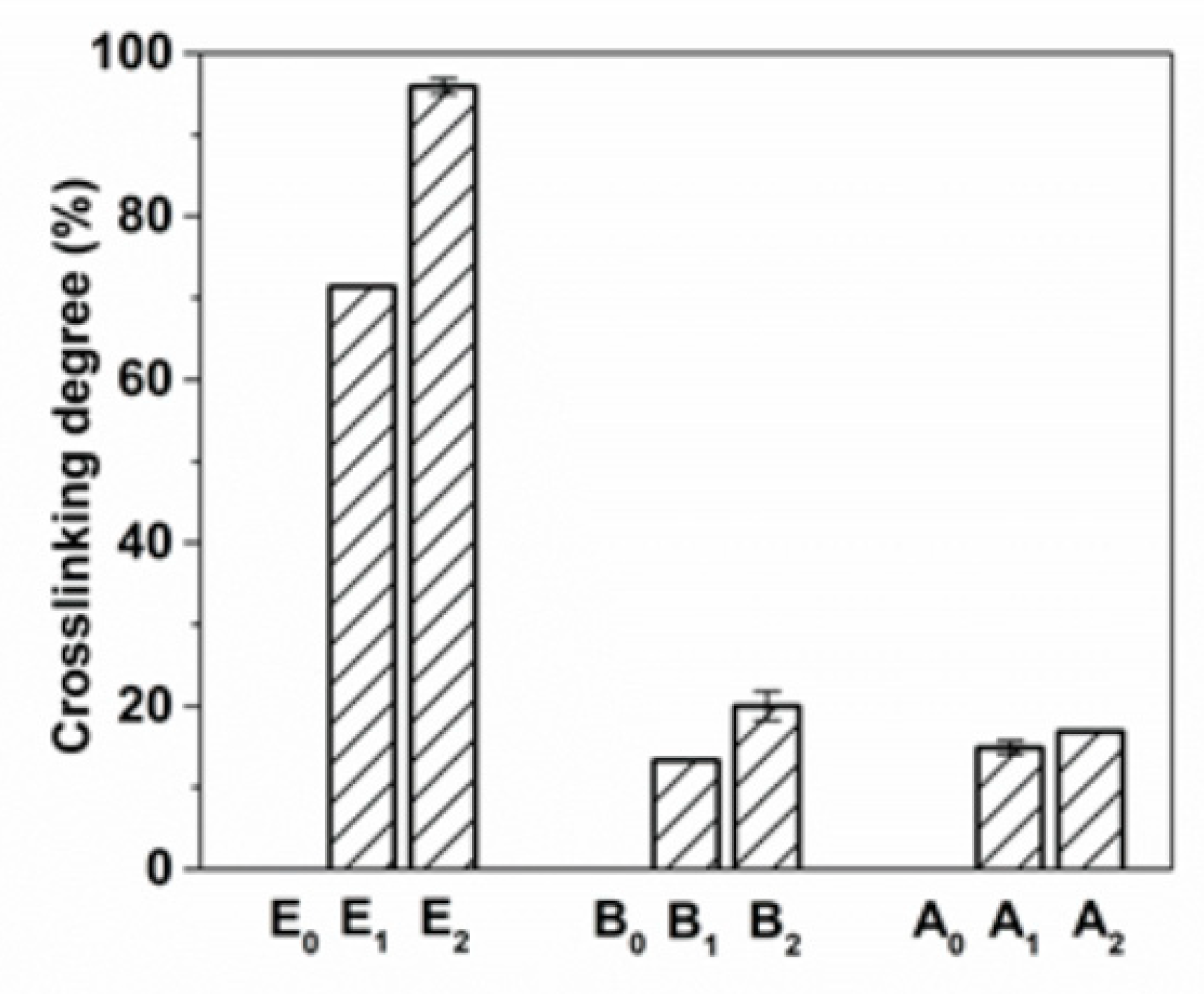
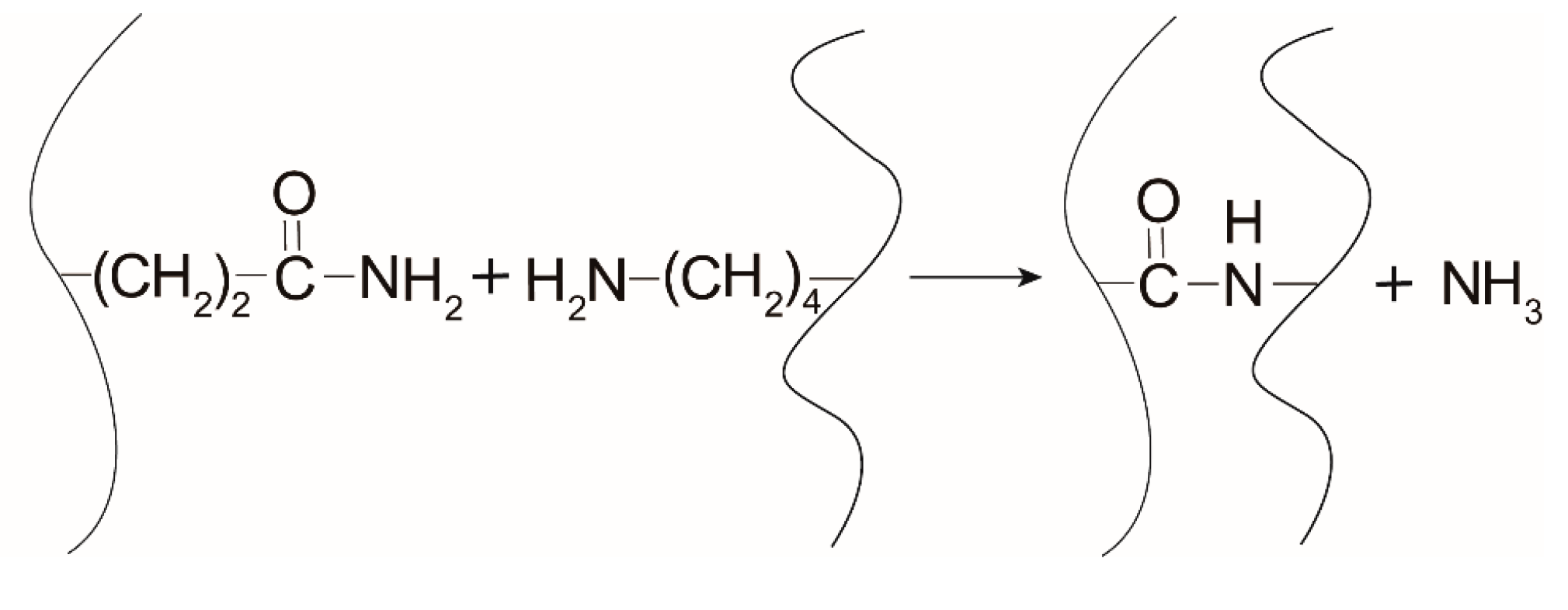
2.5. Cross-linking Degree
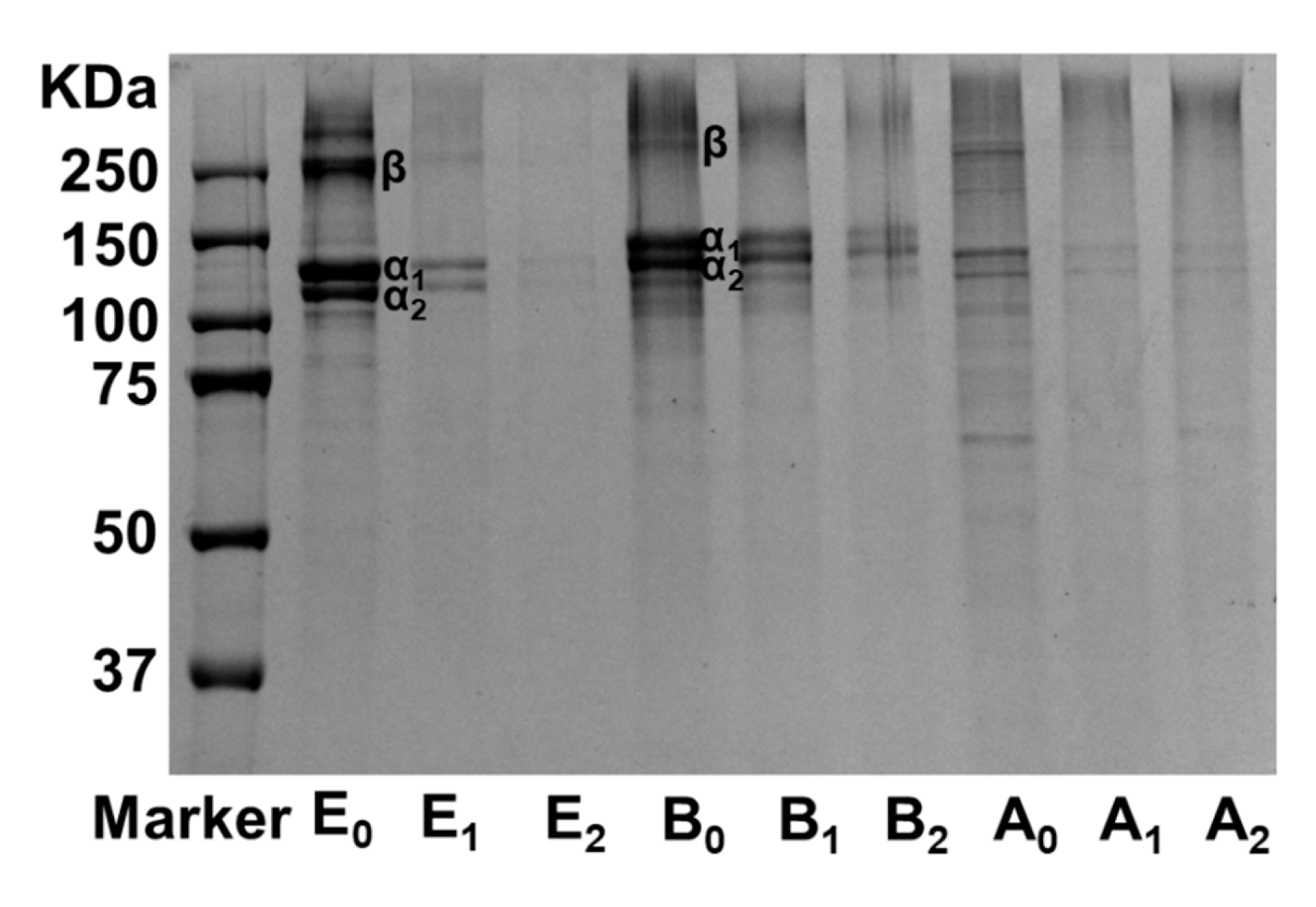
2.6. Molecular Weight Distribution
2.7. Water Solubility
2.8. Mechanical Properties
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Glutamine on Crosslinking Degree of Gelatin Films With Mtgase Modification
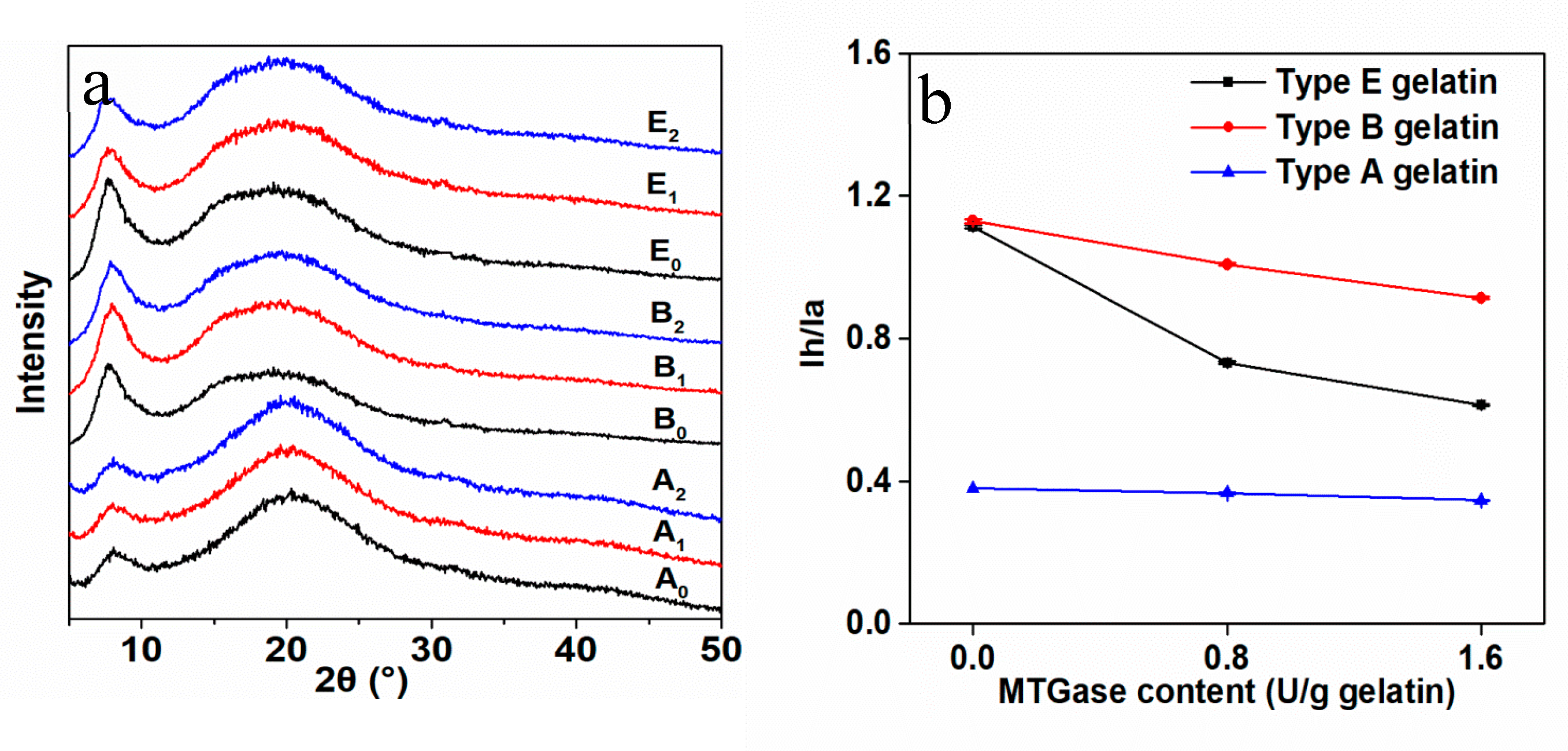
3.2. Structural Changes in Gelatin Films by Mtgase Modification
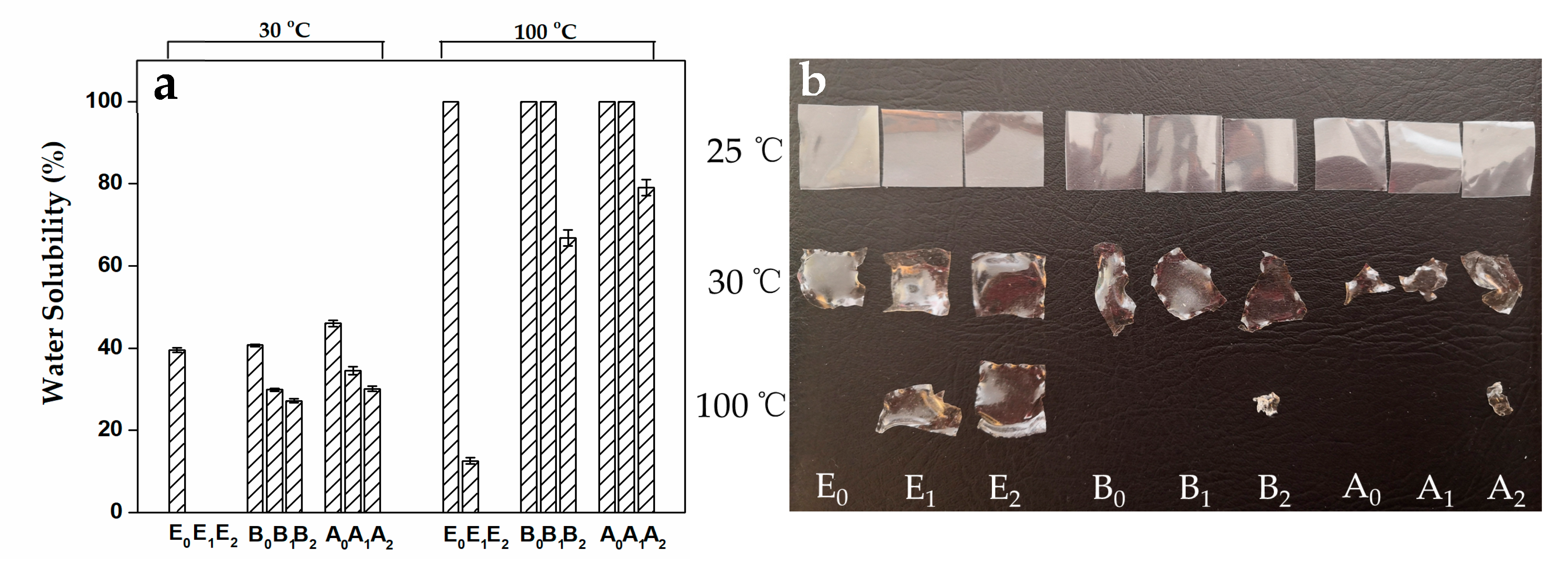
3.3. Water Solubility and Mechanical Properties of Gelatin Films with the Modification of Mtgase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- New Plastics Economy Global Commitment Spring 2019 Report Launched. 2019. Available online: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/news/spring-2019-report (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falguera, V.; Quintero, J.P.; Jiménez, A.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ibarz, A. Edible films and coatings: Structures, active functions and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallis, A. Edible Films and Coatings for Food Applications; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennadios, A.; Hanna, M.A.; Kurth, L.B. Application of edible coatings on meats, poultry and seafoods: A review. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, B.; Ramshaw, J.A.M. The collagen triple-helix structure. Matrix Biol. 1997, 15, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Pérez-Mateos, M.; Gómez-Estaca, J.; López-Caballero, E.; Giménez, B.; Montero, P. Fish gelatin: A renewable material for developing active biodegradable films. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, S.; Schaich, K.M.; Liu, L.; Piergiovanni, L.; Yam, K.L. Development of polyion-complex hydrogels as an alternative approach for the production of bio-based polymers for food packaging applications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejska, I.; Piotrowska, B. The water vapour permeability, mechanical properties and solubility of fish gelatin-chitosan films modified with transglutaminase or 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) and plasticized with glycerol. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, R.A.; Grosso, C.R.F. Characterization of gelatin based films modified with transglutaminase, glyoxal and formaldehyde. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chiou, B.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; McHugh, T.H.; Zhong, F. Study of combined effects of glycerol and transglutaminase on properties of gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N.; Rubini, K. Stabilization of gelatin films by crosslinking with genipin. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4827–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Jin, Z. Fabrication of circular microfluidic network in enzymatically-crosslinked gelatin hydrogel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, M.; Chen, T.; Williams, C.M.; Markley, K.M.; Payne, G.F. Mechanical properties of biomimetic tissue adhesive based on the microbial transglutaminase-catalyzed crosslinking of gelatin. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marniello, L.; Pierro, P.D.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Sorrentino, A. Transglutaminase in food biotechnology. Res. Signpost 2008, 37/661, 185–211. [Google Scholar]
- Motoki, M.; Seguro, K. Transglutaminase and its use for food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idson, B.; Sraswell, E. Gelatin. Adv. Food Res. 1957, 7, 235–338. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, A.G.; Courts, A. The Science and Technology of Gelatin; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ma, X.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W. A simple and eco-friendly method of gelatin production from bone: One-step biocatalysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kn, K.S.; Stehle, P.; Fürst, P. Quantitative analyses of glutamine in peptides and proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1808–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, P.; Gil, M.H.; Figueiredo, M. Tailoring the properties of gelatin films for drug delivery applications: Influence of the chemical cross-linking method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 70, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 680–685, 538–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, V.; Francescangeli, A.; Taglienti, A. New gelatin-based hydrogels via enzymatic networking. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duconseille, A.; Astruc, T.; Quintana, N.; Meersman, F.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.M. Reactions and potential industrial applications of transglutaminase. review of literature and patents. Food Biotechnol. 1995, 9, 119–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, J.E.; Finlayson, J.S. The ε-(γ-Glutamyl)Lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv. Protein Chem. 1977, 31, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Hrynets, Y.; Pietrasik, Z.; Betti, M. Incorporating tyramine with transglutaminase weakens gelatin gels—A rheological investigation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, S.; García, M.A.; Pinotti, A. Correlations between structural, barrier, thermal and mechanical properties of plasticized gelatin films. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badii, F.; MacNaughtan, W.; Mitchell, J.R.; Farhat, I.A. The Effect of Drying Temperature on Physical Properties of Thin Gelatin Films. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, F.; Silva, M.A.; Drake, A.F.; Ross-Murphy, S.B.; Dreiss, C.A. Enzymatically cross-linked tilapia gelatin hydrogels: Physical, chemical, and hybrid networks. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3741–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, H.; Dickinson, E. Influence of transglutaminase treatment on the thermoreversible gelation of gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofner, C.M., III; Zhang, Y.; Jobeck, V.C.; Bowman, B.J. Crosslinking studies in gelatin capsules treated with formaldehyde and in capsules exposed to elevated temperature and humidity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xue, Z.; Sui, K.; Dong, X.; Wang, D. Cooking-Inspired Versatile Design of an Ultrastrong and Tough Polysaccharide Hydrogel through Programmed Supramolecular Interactions. Adv. Mater. 2019, 1902381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Name | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type E gelatin | E0 | E1 | E2 |
| Type B gelatin | B0 | B1 | B2 |
| Type A gelatin | A0 | A1 | A2 |
| MTGase concentration (U/g gelatin) | 0 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| Amino Acid | Type E Gelatin | Type B Gelatin | Type A Gelatin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutamine | 22.33 ± 1.06 | 13.83 ± 0.35 | 27.52 ± 0.79 |
| Lysine | 21.37 ± 0.00 | 21.47 ± 0.33 | 21.41 ± 0.06 |
| Sample | RH 50% | RH 80% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Youngs Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (Mpa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Toughness (MJm−3) | Youngs Modulus (Mpa) | Tensile Strength (Mpa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Toughness (MJm−3) | |
| E0 | 1796.64 ± 20.13 d | 88.48 ± 1.52 c | 6.92 ± 0.14 c | 3.15 ± 0.10 e | 1.02 ± 0.04 e | 1.34 ± 0.04 ef | 141.99 ± 7.10 de | 0.76 ± 0.03 g |
| E1 | 2007.78 ± 25.11 b | 92.25 ± 1.02 b | 7.29 ± 0.21 b | 4.08 ± 0.11 b | 1.34 ± 0.05 b | 2.23 ± 0.07 b | 172.01 ± 5.60 b | 1.37 ± 0.02 c |
| E2 | 2090.86 ± 19.23 a | 96.83 ± 1.23 a | 7.65 ± 0.18 a | 5.40 ± 0.17 a | 1.64 ± 0.06 a | 3.64 ± 0.09 a | 186.97 ± 8.34 a | 2.19 ± 0.04 a |
| B0 | 1811.07 ± 15.18 d | 84.32 ± 2.01 d | 6.90 ± 0.14 c | 3.46 ± 0.12 d | 0.96 ± 0.03 ef | 1.27 ± 0.04 f | 136.29 ± 4.81 e | 0.87 ± 0.03 f |
| B1 | 1843.25 ± 20.01 c | 89.56 ± 1.54 c | 7.21 ± 0.09 b | 3.73 ± 0.09 c | 1.12 ± 0.04 d | 1.41 ± 0.03 eg | 154.45 ± 5.72 c | 1.11 ± 0.02 d |
| B2 | 1868.23 ± 15.26 c | 94.09 ± 1.16 b | 7.42 ± 0.11 ab | 3.84 ± 0.16 c | 1.22 ± 0.06 c | 1.94 ± 0.07 c | 177.65 ± 6.88 ab | 1.52 ± 0.02 b |
| A0 | 1609.35 ± 19.16 f | 71.06 ± 1.32 f | 4.21 ± 0.19 f | 1.62 ± 0.07 g | 0.85 ± 0.03 g | 1.22 ± 0.03 g | 88.13 ± 2.41 g | 0.58 ± 0.01 h |
| A1 | 1655.57 ± 15.42 e | 72.63 ± 0.99 f | 4.61 ± 0.08 e | 1.66 ± 0.05 g | 0.85 ± 0.02 g | 1.59 ± 0.05 d | 115.85 ± 3.79 f | 0.99 ± 0.02 e |
| A2 | 1668.75 ± 10.39 e | 78.04 ± 1.28 e | 5.73 ± 0.11 d | 2.03 ± 0.06 f | 0.93 ± 0.01 f | 1.61 ± 0.02 d | 118.09 ± 2.90 f | 0.95 ± 0.01 e |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W. Innovative Water-Insoluble Edible Film Based on Biocatalytic Crosslink of Gelatin Rich in Glutamine. Foods 2020, 9, 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040503
Ma Y, Yang R, Zhao W. Innovative Water-Insoluble Edible Film Based on Biocatalytic Crosslink of Gelatin Rich in Glutamine. Foods. 2020; 9(4):503. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040503
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yanli, Ruijin Yang, and Wei Zhao. 2020. "Innovative Water-Insoluble Edible Film Based on Biocatalytic Crosslink of Gelatin Rich in Glutamine" Foods 9, no. 4: 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040503
APA StyleMa, Y., Yang, R., & Zhao, W. (2020). Innovative Water-Insoluble Edible Film Based on Biocatalytic Crosslink of Gelatin Rich in Glutamine. Foods, 9(4), 503. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9040503