A Cross-Cultural Evaluation of Liking and Perception of Salted Butter Produced from Different Feed Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Diets and Milk Production
2.2. Butter Manufacture
2.3. Consumer Study
2.3.1. Consumer Selection
2.3.2. Product Evaluation by Hedonic, Intensity and Just-About-Right Scales
2.4. Ranking Descriptive Analysis
2.5. Descriptive Analysis Evaluation
2.6. Volatile Analysis by HS-SPME-GC-MS
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Consumer Evaluation
3.1.1. Irish Consumers
3.1.2. German Consumers
3.1.3. USA Consumers
3.2. Cross-Cultural Perceptions of Butters
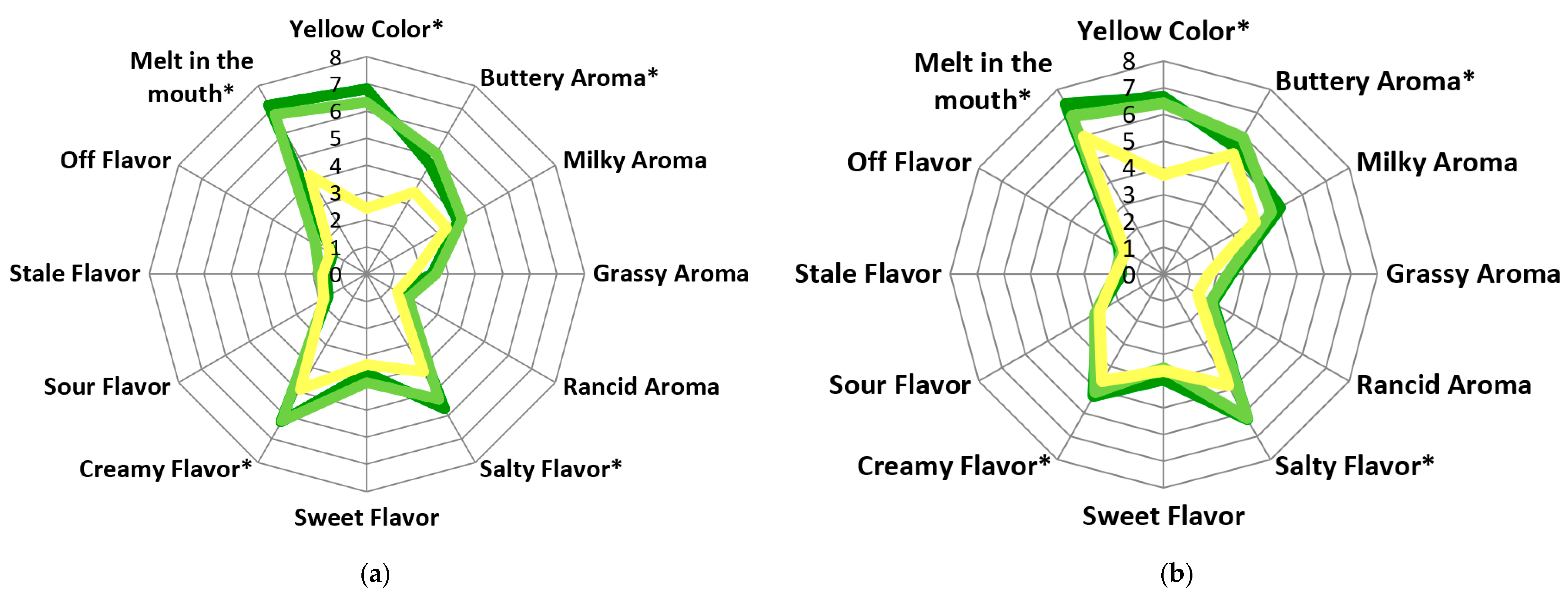
3.3. Ranking Descriptive Analysis
3.4. Descriptive Analysis Evaluation of FS-GRSS, FS-CLVR and FS-TMR Butters by Trained USA Panelists
3.5. Volatile Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Varela, P.; Peschel, A.O. Consumers’ categorization of food ingredients: Do consumers perceive them as ‘clean label’ producers expect? An exploration with projective mapping. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 71, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, C.L.; Widmar, N.J.O.; Thompson, N.M.; Townsend, J.; Wolf, C. US respondents’ willingness to pay for Cheddar cheese from dairy cattle with different pasture access, antibiotic use, and dehorning practices. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3234–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Torres, S.; López-Gajardo, A.; Mesias, F. Intensive vs. free-range organic beef. A preference study through consumer liking and conjoint analysis. Meat Sci. 2016, 114, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Font i Furnols, M.; Realini, C.; Montossi, F.; Sañudo, C.; Campo, M.M.; Oliver, M.A.; Nute, G.R.; Guerrero, L. Consumer’s purchasing intention for lamb meat affected by country of origin, feeding system and meat price: A conjoint study in Spain, France and United Kingdom. Food Qual. Prefer. 2011, 22, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, F.; Braghieri, A.; Piasentier, E.; Favotto, S.; Naspetti, S.; Zanoli, R. Effect of information about organic production on beef liking and consumer willingness to pay. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scozzafava, G.; Gerini, F.; Boncinelli, F.; Contini, C.; Marone, E.; Casini, L. Organic milk preference: Is it a matter of information? Appetite 2020, 144, 104477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampa, E.; Schipmann-Schwarze, C.; Hamm, U. Consumer perceptions, preferences, and behavior regarding pasture-raised livestock products: A review. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 82, 103872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.; Dillon, P.; Murphy, J.; Mehra, R.K.; Guinee, T.P.; Connolly, J.F.; Kelly, A.L.; Joyce, P. Effects of stocking density and concentrate supplementation of grazing dairy cows on milk production, composition and processing characteristics. J. Dairy Res. 1999, 66, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, S.; Carey, W.; Boland, T.; Lynch, M.; Kelly, A.; Rajauria, G.; Pierce, K. The effect of by-product inclusion level on milk production, nutrient digestibility and excretion, and rumen fermentation parameters in lactating dairy cows offered a pasture-based diet. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSO. Central Statistics Office, Milk Statistics December 2015. 2015. Available online: https://www.cso.ie/en/releasesandpublications/er/ms/milkstatisticsdecember2015/ (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- CSO. Central Statistics Office, Milk Statistics December 2015. 2017. Available online: https://www.cso.ie/en/releasesandpublications/er/ms/milkstatisticsdecember2017/ (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- McKay, Z.; Lynch, M.; Mulligan, F.; Rajauria, G.; Miller, C.; Pierce, K. The effect of concentrate supplementation type on milk production, dry matter intake, rumen fermentation, and nitrogen excretion in late-lactation, spring-calving grazing dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5042–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bord Bia. Export Performance and Prospects. Irish Food, Drink & Horticulture 2019–2020. 2019, p. 10. Available online: https://www.bordbia.ie/globalassets/bordbia.ie/industry/performance-and-prospects/2019-pdf/performance-and-prospects-2019-2020.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- Croissant, A.; Washburn, S.; Dean, L.; Drake, M. Chemical Properties and Consumer Perception of Fluid Milk from Conventional and Pasture-Based Production Systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4942–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, T.F.; Hennessy, D.; McAuliffe, S.; Kilcawley, K.N.; O’Donovan, M.; Dillon, P.; Ross, R.; Stanton, C. Effect of pasture versus indoor feeding systems on raw milk composition and quality over an entire lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9424–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.L.; Bertrand, J.A.; Wade, M.R.; Washburn, S.P.; Green, J.T., Jr.; Jenkins, T.C. Comparison of fatty acid content of milk from Jersey and Holstein cows consuming pasture or a total mixed ration. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.; Verdier-Metz, I.; Buchin, S.; Hurtaud, C.; Coulon, J.-B. How do the nature of forages and pasture diversity influence the sensory quality of dairy livestock products? Anim. Sci. 2005, 81, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, R.; Dhiman, T.R.; Ure, A.; Brennand, C.; Boman, R.; McMahon, D. Consumer Acceptability of Conjugated Linoleic Acid-Enriched Milk and Cheddar Cheese from Cows Grazing on Pasture. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Pustjens, A.M.; Erasmus, S.W.; Yang, Y.; Hettinga, K.A.; Van Ruth, S.M. Dairy farming system markers: The correlation of forage and milk fatty acid profiles from organic, pasture and conventional systems in the Netherlands. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Valenberg, H.J.F.; Hettinga, K.; Dijkstra, J.; Bovenhuis, H.; Feskens, E.F. Concentrations of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids in Dutch bovine milk fat and their contribution to human dietary intake. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agabriel, C.; Cornu, A.; Sibra, C.; Grolier, P.; Martin, B. Tanker Milk Variability According to Farm Feeding Practices: Vitamins A and E, Carotenoids, Color, and Terpenoids. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4884–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, T.F.; Faulkner, H.; McAuliffe, S.; Sullivan, M.G.O.; Hennessy, D.; Dillon, P.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Quality characteristics, chemical composition, and sensory properties of butter from cows on pasture versus indoor feeding systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9441–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Parohan, M.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary and circulating vitamin C, vitamin E, β-carotene and risk of total cardiovascular mortality: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 1872–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P. Physical chemistry of milk fat globules. Adv. Dairy Chem. 1995, 2, 131–178. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, A.; Lopetcharat, K.; Drake, M. Identification of the Characteristics That Drive Consumer Liking of Butter. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, L. Comparison of SDE and SPME for the analysis of volatile compounds in butters. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, P.R.; Miracle, E.R.; Krause, A.J.; Drake, M.; Cadwallader, K.R. Effect of Cold Storage and Packaging Material on the Major Aroma Components of Sweet Cream Butter. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7840–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallia, S.; Escher, F.; Dubois, S.; Schieberle, P.; Schlichtherle-Cerny, H. Characterization and Quantification of Odor-Active Compounds in Unsaturated Fatty Acid/Conjugated Linoleic Acid (UFA/CLA)-Enriched Butter and in Conventional Butter during Storage and Induced Oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7464–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtaud, C.; Faucon, F.; Couvreur, S.; Peyraud, J.-L. Linear relationship between increasing amounts of extruded linseed in dairy cow diet and milk fatty acid composition and butter properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. 2014 ISO 11136. 2014. Available online: https://www.iso.org/ics/67.240/x/ (accessed on 16 October 2020).
- Richter, V.B.; De Almeida, T.C.A.; Prudencio, S.H.; Benassi, M.D.T. Proposing a ranking descriptive sensory method. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Dool, H.; Kratz, P.D. A generalization of the retention index system including linear temperature programmed gas—liquid partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvreur, S.; Hurtaud, C.; Lopez, C.; Delaby, L.; Peyraud, J. The Linear Relationship between the Proportion of Fresh Grass in the Cow Diet, Milk Fatty Acid Composition, and Butter Properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1956–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Silva, S.P.; Prates, J.A.; Bessa, R.J.B.; Rosa, H.J.D.; Rego, O.A. Physicochemical traits and sensory quality of commercial butter produced in the Azores. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 88, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadalı, C.; Elmacı, Y. Characterization of volatile release and sensory properties of model margarines by changing fat and emulsifier content. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1900003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Jombart, L.; Valentin, D.; Kim, K.-O. Familiarity and liking playing a role on the perception of trained panelists: A cross-cultural study on teas. Food Res. Int. 2015, 71, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, J.; Bertrand, C.; Ali, R.; Husson, F.; Lê, S. SENSORY ANALYSIS COMPARISON OF EIGHT BISCUITS BY FRENCH AND PAKISTANI PANELS. J. Sens. Stud. 2007, 22, 665–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, W.; Drake, M. Identification and characterization of fluid milk consumer groups. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8860–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panthi, R.R.; Sundekilde, U.K.; Kelly, A.L.; Hennessy, D.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Mannion, D.; Fenelon, M.A.; Sheehan, J.J. Influence of herd diet on the metabolome of Maasdam cheeses. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtaud, C.; Peyraud, J.L. Effects of Feeding Camelina (Seeds or Meal) on Milk Fatty Acid Composition and Butter Spreadability. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 5134–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Sullivan, M.G.O.; Kerry, J.; Drake, M.; Miao, S.; Kaibo, D.; Kilcawley, K.N. A cross-cultural sensory analysis of skim powdered milk produced from pasture and non-pasture diets. Food Res. Int. 2020, 109749, 109749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, M.-P.; Lebeuf, Y.; Gervais, R.; Tremblay, G.; Vuillemard, J.; Fortin, J.; Chouinard, P. Milk volatile organic compounds and fatty acid profile in cows fed timothy as hay, pasture, or silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7181–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.; Yates, M.; Gerard, P.; Delahunty, C.; Sheehan, E.; Turnbull, R.; Dodds, T. Comparison of differences between lexicons for descriptive analysis of Cheddar cheese flavour in Ireland, New Zealand, and the United States of America. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, H.J.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Kerry, J.P.; Kilcawley, K.N. Correlating Volatile Lipid Oxidation Compounds with Consumer Sensory Data in Dairy Based Powders during Storage. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcawley, K.N.; Faulkner, H.; Clarke, H.J.; Sullivan, M.G.O.; Kerry, J.P. Factors Influencing the Flavour of Bovine Milk and Cheese from Grass Based versus Non-Grass Based Milk Production Systems. Foods 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisaki, M.; Endo, Y.; Fujimoto, K. Retardation of volatile aldehyde formation in the exhaust of frying oil by heating under low oxygen atmospheres. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panseri, S.; Soncin, S.; Chiesa, L.; Biondi, P.A. A headspace solid-phase microextraction gas-chromatographic mass-spectrometric method (HS-SPME-GC/MS) to quantify hexanal in butter during storage as marker of lipid oxidation. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, J.E.; Acree, T.E. Gas Chromatography Olfactometry (GC/O) of Dairy Products. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, H.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; McAuliffe, S.; Hennessy, D.; Stanton, C.; Sullivan, M.G.O.; Kerry, J.P.; Kilcawley, K.N. Effect of different forage types on the volatile and sensory properties of bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallia, S.; Escher, F.; Schlichtherle-Cerny, H. Aroma-active compounds of butter: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 226, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieberle, P.; Gassenmeier, K.; Guth, H.; Sen, A.; Grosch, W. Character Impact Odour Compounds of Different Kinds of Butter. LWT 1993, 26, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Dorau, R.; Lillevang, S.K.; Jensen, P.R.; Solem, C. From Waste to Taste—Efficient Production of the Butter Aroma Compound Acetoin from Low-Value Dairy Side Streams Using a Natural (Nonengineered) Lactococcus lactis Dairy Isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5891–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, E.; Villamiel, M.; Miralles, B.; Sanz, J.; Martínez-Castro, I. Changes in flavour and volatile components during storage of whole and skimmed UHT milk. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contarini, G.; Povolo, M.; Leardi, R.; Toppino, P.M. Influence of Heat Treatment on the Volatile Compounds of Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3171–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovolenta, S.; Romanzin, A.; Corazzin, M.; Spanghero, M.; Aprea, E.; Gasperi, F.; Piasentier, E. Volatile compounds and sensory properties of Montasio cheese made from the milk of Simmental cows grazing on alpine pastures. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7373–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, H.J.; Griffin, C.; Rai, D.K.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Kerry, J.P.; Kilcawley, K.N. Dietary Compounds Influencing the Sensorial, Volatile and Phytochemical Properties of Bovine Milk. Molecules 2019, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Irish Consumers | German Consumers | USA Consumers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS-CLVR | FS-GRSS | FS-TMR | FS-CLVR | FS-GRSS | FS-TMR | FS-CLVR | FS-GRSS | FS-TMR | ||
| Hedonics | ||||||||||
| Overall appearance | 6.51 ± 1.56 x | 6.46 ± 1.65 x | 5.99 ± 1.76 y | 5.62 ± 1.59 y | 5.69 ± 1.65 y | 5.44 ± 1.69 y | 6.46 ± 1.63 abx | 6.33 ± 1.57 bx | 6.98 ± 1.42 ax | |
| Color | 6.44 ± 1.61 x | 6.19 ± 1.80 | 5.80 ± 1.80 y | 5.66 ± 1.50 y | 5.88 ± 1.56 | 5.56 ± 1.38 y | 6.43 ± 1.64 abx | 6.18 ± 1.72 b | 6.91 ± 1.57 ax | |
| Flavor | 6.46 ± 1.74 | 6.44 ± 1.67 y | 6.28 ± 1.68 x | 6.19 ± 1.65 | 6.38 ± 1.66 y | 5.89 ± 1.69 y | 6.52 ± 1.75 b | 7.10 ± 1.55 ax | 6.76 ± 1.79 abx | |
| Salt | 6.00 ± 1.63 | 5.73 ± 1.79 | 5.78 ± 1.68 | 5.83 ± 0.75 | 5.87 ± 0.73 | 5.52 ± 0.72 | ||||
| Texture (firmness for USA) | 6.54 ± 1.58 | 6.35 ± 1.72 x | 6.05 ± 1.75 x | 6.40 ± 1.84 | 6.52 ± 1.51 x | 6.17 ± 1.84 x | 6.26 ± 1.67 a | 5.95 ± 1.69 aby | 5.50 ± 1.81 by | |
| Overall liking | 6.46 ± 1.67 x | 6.36 ± 1.76 y | 6.27 ± 1.66 y | 6.04 ± 1.74 y | 6.23 ± 1.61 y | 5.89 ± 1.90 z | 6.59 ± 1.65 x | 7.13 ± 1.47 xy | 6.85 ± 1.67 x | |
| Intensity Scale Evaluation | ||||||||||
| Color | 6.14 ± 1.89 a | 5.68 ± 2.41 ab | 5.22 ± 2.40 bx | 6.31 ± 0.80 a | 6.02 ± 0.76 a | 3.27 ± 0.81 ay | ||||
| Flavor | 6.34 ± 1.78 | 5.73 ± 2.01 | 6.21 ± 1.60 x | 6.38 ± 1.79 a | 6.14 ± 1.87 a | 5.29 ± 2.23 by | ||||
| Salt | 5.31 ± 2.00 y | 5.15 ± 2.15 y | 5.06 ± 1.96 | 6.17 ± 1.88 ax | 5.95 ± 1.81 ax | 5.28 ± 1.89 b | ||||
| Freshness | 6.34 ± 1.73 x | 6.10 ± 1.93 | 5.95 ± 1.82 | 5.56 ± 0.89 y | 5.78 ± 0.82 | 5.80 ± 0.97 | ||||
| Firmness | 5.46 ± 2.05 x | 5.34 ± 2.15 x | 5.61 ± 1.94 x | 3.62 ± 2.08 by | 3.42 ± 2.06 by | 4.53 ± 1.98 ay | ||||
| JAR Evaluation | ||||||||||
| Color | Not Yellow Enough | 23.96% | 31.25% | 41.67% | 7.41% b | 9.26% b | 51.85% a | 2.9% b | 4.9% b | 26.2% a |
| Just about Right | 62.50% | 53.125% | 42.71% | 37.96% | 38.89% | 42.59% | 57.3% ab | 49.5% b | 72.8% a | |
| Too Yellow | 13.54% | 15.625% | 15.63% | 54.63% | 51.85% | 5.56% | 39.8% | 45.6% | 1.0% | |
| Flavor | Not Enough Flavor | 18.75% | 26.04% | 17.71% | 18.52% | 24.07% | 42.59% | 26.2% | 21.4% | 33.0% |
| Just about Right | 62.50% | 60.42% | 56.25% | 51.85% | 53.70% | 41.67% | 58.3% | 70.9% | 63.1% | |
| Too Much Flavor | 18.75% | 13.54% | 26.04% | 29.63% | 22.22% | 15.74% | 15.5% a | 7.8% ab | 3.9% b | |
| Salt | Not Enough Salt | 18.75% | 27.08% | 16.67% | 17.59% | 21.30% | 30.56% | |||
| Just about Right | 62.50% | 51.04% | 59.38% | 38.89% | 41.67% | 37.04% | ||||
| Too Much Salt | 18.75% | 21.88% | 23.96% | 43.52% | 34.26% | 32.41% | ||||
| Texture | Not Firm Enough | 2.08% | 10.42% | 10.42% | 42.59% | 38.89% | 19.44% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 1.0% |
| Just about Right | 76.04 | 63.54 | 52.08 | 55.56% | 57.41% | 64.81% | 58.3% a | 48.5% ab | 35.9% b | |
| Much Too Firm | 21.88 | 26.04 | 37.50 | 1.85%b | 3.70% b | 15.74% a | 41.7% b | 51.5% ab | 63.1% a | |
| Irish Assessors | German Assessors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS-GRSS | FS-CLVR | FS-TMR | FS-GRSS | FS-CLVR | FS-TMR | |
| Color | ||||||
| Yellow color | 6.81 ± 0.9 a | 6.33 ± 1.37 a | 2.41 ± 0.85 by | 6.63 ± 1.12 a | 6.41 ± 1.46 a | 3.72 ± 1.37 bx |
| Aroma | ||||||
| Buttery | 4.66 ± 1.53 a | 5.13 ± 1.51 a | 3.48 ± 1.22 b | 5.48 ± 1.86 | 5.93 ± 1.99 | 5.20 ± 1.93 |
| Milky | 3.89 ± 1.45 y | 4.05 ± 1.29 | 3.40 ± 1.24 | 5.03 ± 2.56 x | 4.66 ± 2.25 | 3.93 ± 2.08 |
| Grassy | 2.41 ± 1.17 | 2.54 ± 1.34 | 1.71 ± 0.72 | 2.50 ± 1.92 | 2.42 ± 1.97 | 1.69 ± 1.11 |
| Rancid | 1.39 ± 0.69 | 1.76 ± 1.40 | 1.31 ± 0.73 | 2.11 ± 1.76 | 2.05 ± 1.64 | 1.49 ± 1.08 |
| Flavor | ||||||
| Salty | 5.71 ± 1.13 a | 5.33 ± 1.66 a | 4.16 ± 1.77 b | 6.24 ± 2.00 a | 6.23 ± 1.47 a | 4.81 ± 1.77 b |
| Sweet | 3.64 ± 1.50 | 3.99 ± 1.45 | 3.34 ± 1.41 | 3.92 ± 1.95 | 3.50 ± 1.76 | 3.61 ± 1.84 |
| Creamy | 6.29 ± 1.25 a | 6.24 ± 1.37 a | 4.91 ± 1.46 b | 5.27 ± 1.90 | 5.10 ± 1.90 | 4.60 ± 2.03 |
| Sour | 1.64 ± 0.57 y | 1.76 ± 1.15 | 1.83 ± 0.79 | 2.85 ± 1.67 x | 2.97 ± 2.20 | 2.79 ± 1.82 |
| Stale | 1.51 ± 0.81 | 1.76 ± 1.07 | 1.61 ± 0.74 | 1.59 ± 0.78 | 1.80 ± 1.49 | 1.83 ± 1.44 |
| Off flavor | 1.44 ± 0.63 | 2.16 ± 1.84 | 1.56 ± 1.01 | 1.90 ± 1.33 | 1.81 ± 1.25 | 1.66 ± 1.33 |
| Texture | ||||||
| Melt in the mouth | 7.19 ± 0.85 a | 6.79 ± 1.26 a | 4.19 ± 1.73 by | 7.36 ± 1.20 | 6.86 ± 1.46 | 5.96 ± 2.21 x |
| Feed System | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory Attribute | FS-CLVR | FS-GRSS | FS-TMR |
| Cooked/Nutty | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.06 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.1 |
| Milkfat | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 3.2 ± 0.1 |
| Grassy | 1.2 ± 0.1 b | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | ND c |
| Mothball | 1.3 ± 0.1 a | ND b | ND b |
| Stale | ND | ND | ND |
| Salty Taste | 11.1 ± 0.1 | 10.9 ± 0.7 | 11.2 ± 0.1 |
| Color Intensity | 4.2 ± 0.1 a | 3.4 ± 0.3 b | 1.8 ± 0.1 c |
| Feeding System | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile Compound | CAS NUMBER # | Odor Descriptors | RI | REF RI | FS-GRSS | FS-CLVR | FS-TMR |
| Aldehyde | |||||||
| Pentanal 2 | 110-62-3 | Pungent, almond like, chemical, malty, apple [22] | 731 | 733 | 0.054 ± 0.027 b | 0.489 ± 0.394 a | 0.049 ± 0.018 b |
| Hexanal 3 | 66-25-1 | Green, slightly fruity, lemon, herbal, grassy [22] | 836 | 839 | 0.032 ± 0.013 b | 0.060 ± 0.035 a | 0.049 ± 0.018 a |
| Heptanal 3 | 111-71-7 | Slightly fruity (balsam), fatty, oily [22] | 937 | 943 | 0.020 ± 0.008 a | 0.035± 0.027 a | 0.010 ± 0.004 b |
| Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | Bitter, almond, sweet cherry [22] | 1026 | 1028.9 | 0.020 ± 0.012 | 0.019 ± 0.011 | 0.028 ± 0.011 |
| Nonanal | 124-19-6 | Green, citrus, fatty, floral [22] | 1143 | 1150 | 0.039 ± 0.040 | 0.035 ± 0.028 | 0.024 ± 0.017 |
| Decanal 3 | 112-31-2 | Green [28] | 1246 | - | 0.001 ± 0.001 b | 0.003± 0.001 a | 0.002 ± 0.002 ab |
| Ketone | |||||||
| Acetone2 | 67-64-1 | Earthy, strong fruity, wood pulp, hay [22] | 529 | 533 | 0.224 ± 0.125 ab | 0.216 ± 0.052 a | 0.124 ± 0.027 b |
| Diacetyl (2,3-Butanedione) 2 | 431-03-8 | Buttery [50] | 628 | - | 0.044 ± 0.015 a | 0.079 ± 0.057 ab | 0.022 ± 0.009 b |
| 2-Butanone 2 | 78-93-3 | Buttery, sour milk, etheric [22] | 635 | 639 | 0.106 ± 0.019 b | 0.286 ± 0.156 a | 0.170 ± 0.082 ab |
| 2-Heptanone | 113-43-0 | Blue cheese, spicy, Roquefort [22] | 929 | 936 | 0.062 ± 0.011 | 0.077 ± 0.034 | 0.060 ± 0.007 |
| 2-Nonanone | 821-55-6 | Malty, fruity, hot milk, smoked cheese [22] | 1133 | 1140 | 0.017 ± 0.003 | 0.037 ± 0.033 | 0.013 ± 0.005 |
| 2-Pentanone | 107-87-9 | Orange peel, sweet, Fruity [22] | 725 | - | 0.029 ± 0.012 | 0.032 ± 0.010 | 0.031 ± 0.014 |
| Acid | |||||||
| Butanoic Acid 1 | 107-92-6 | Sweaty, butter, cheese, Strong, acid, fecal, rancid [22] | 860 | 864 | 0.015 ± 0.007 b | 0.024 ± 0.004 a | 0.017 ± 0.008 ab |
| Hexanoic Acid 1 | 142-62-1 | Acidic, sweaty, cheesy, sharp, goaty, bad breath [22] | 1045 | 1052 | 0.023 ± 0.009 | 0.041 ± 0.02 | 0.026 ± 0.010 |
| Nonanoic Acid 2 | 112-05-0 | Waxy, dirty and cheesy with a cultured dairy nuance ** | 22.7 | - | 0.014 ± 0.007 b | 0.026 ± 0.005 a | 0.014 ± 0.008 b |
| Hydrocarbons | |||||||
| Toluene2 | 108-88-3 | Nutty, bitter, almond, Plastic [22] | 789 | 794 | 0.794 ± 0.26 b | 1.793 ± 0.708 a | 0.139 ± 0.031 c |
| * o-Xylene | 108-38-3 | Geranium ** | 895 | - | 0.371 ± 0.304 | 0.303 ± 0.386 | 0.572 ± 0.449 |
| * p-Xylene | 106-42-3 | Not listed ** | 923 | - | 0.177 ± 0.187 | 0.087 ± 0.143 | 0.222 ± 0.136 |
| Lactone | |||||||
| δ-Hexalactone | 823-22-3 | Creamy, chocolate, sweet aromatic [50] | 1215 | - | 0.129 ± 0.033 | 0.114 ± 0.026 | 0.117± 0.022 |
| δ-Octalactone | 698-76-0 | Coconut like, peach [50] | 1413 | - | 0.026 ± 0.006 | 0.024 ± 0.007 | 0.022 ± 0.005 |
| δ-Decalactone | 705-86-2 | Coconut like, peach [50] | 1691 | 1620.9 | 0.020 ± 0.007 | 0.021 ± 0.010 | 0.019 ± 0.008 |
| Sulfide | |||||||
| Dimethyl Sulfide | 75-18-3 | Corn like, fresh pumpkin [50] | 534 | 538 | 0.011 ± 0.010 | 0.018 ± 0.016 | 0.009 ± 0.002 |
| Carbon Disulfide | 75-15-0 | Sulfury, onion, sweet corn, vegetable, cabbage, tomato, green, radish ** | 542 | 548 | 0.057 ± 0.018 | 0.132 ± 0.115 | 0.088 ± 0.088 |
| Ester | |||||||
| Ethyl Acetate 2 | 141-78-6 | Solvent, pineapple, Fruity, fruit gum [22] | 639 | - | 0.013 ± 0.010 ab | 0.033 ± 0.019 a | 0.010 ± 0.009 b |
| Ethyl Benzene | 100-41-4 | Not listed ** | 887 | - | 0.072 ± 0.046 | 0.103 ± 0.160 | 0.206 ± 0.213 |
| Diethyl Ether | 60-29-7 | Ethereal ** | 512 | - | 0.020 ± 0.022 | 0.024 ± 0.025 | 0.024 ± 0.026 |
| Other | |||||||
| Ethanol | 64-17-5 | Alcoholic, ethereal, medicinal ** | 503 | 506 | 0.038 ± 0.020 | 0.032 ± 0.018 | 0.028 ± 0.021 |
| 1-Pentene | 109-67-1 | Not listed ** | 565 | - | 0.061 ± 0.024 | 0.047 ± 0.024 | 0.076 ± 0.077 |
| α-Pinene | 80-56-8 | Mint, pine oil [27] | 950 | 951 | 0.038 ± 0.032 | 0.014 ± 0.010 | 0.036 ± 0.026 |
| Dodecane | 112-40-3 | Alkane ** | 1193 | - | 0.006 ± 0.004 | 0.007 ± 0.002 | 0.005 ± 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
C. Garvey, E.; Sander, T.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; Drake, M.; Fox, S.; G. O’Sullivan, M.; Kerry, J.P.; Kilcawley, K.N. A Cross-Cultural Evaluation of Liking and Perception of Salted Butter Produced from Different Feed Systems. Foods 2020, 9, 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121767
C. Garvey E, Sander T, O’Callaghan TF, Drake M, Fox S, G. O’Sullivan M, Kerry JP, Kilcawley KN. A Cross-Cultural Evaluation of Liking and Perception of Salted Butter Produced from Different Feed Systems. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121767
Chicago/Turabian StyleC. Garvey, Emer, Thorsten Sander, Tom F. O’Callaghan, MaryAnne Drake, Shelley Fox, Maurice G. O’Sullivan, Joseph P. Kerry, and Kieran N. Kilcawley. 2020. "A Cross-Cultural Evaluation of Liking and Perception of Salted Butter Produced from Different Feed Systems" Foods 9, no. 12: 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121767
APA StyleC. Garvey, E., Sander, T., O’Callaghan, T. F., Drake, M., Fox, S., G. O’Sullivan, M., Kerry, J. P., & Kilcawley, K. N. (2020). A Cross-Cultural Evaluation of Liking and Perception of Salted Butter Produced from Different Feed Systems. Foods, 9(12), 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121767








