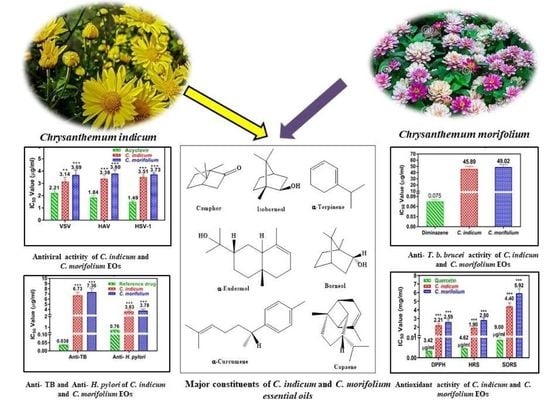
Chrysanthemum indicum and Chrysanthemum morifolium: Chemical Composition of Their Essential Oils and Their Potential Use as Natural Preservatives with Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Chemicals, Reagents and Strains
2.3. Essential Oils Preparation
2.4. GC/FID and GC/MS Analyses
2.5. Cytotoxic Assay
2.6. Antiviral Assay
2.7. Antimicrobial Assay
2.8. Anti-Mycobacterial Assay
2.9. Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Assay
2.10. Anti-Trypanosomal Assay
2.11. Antioxidant Determination
2.11.1. Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl Scavenging Capacity Assay
2.11.2. Superoxide Radical Scavenging (SORS) Activity
2.11.3. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging (HRS) Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Volatile Oil Constituents of Chrysanthemum indicum and C. morifolium Flower Heads
3.2. Antiviral Activity of Essential Oils of Chrysanthemum Indicum and C. morifolium Flower Heads
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity of C. indicum and C. morifolium Essential Oils
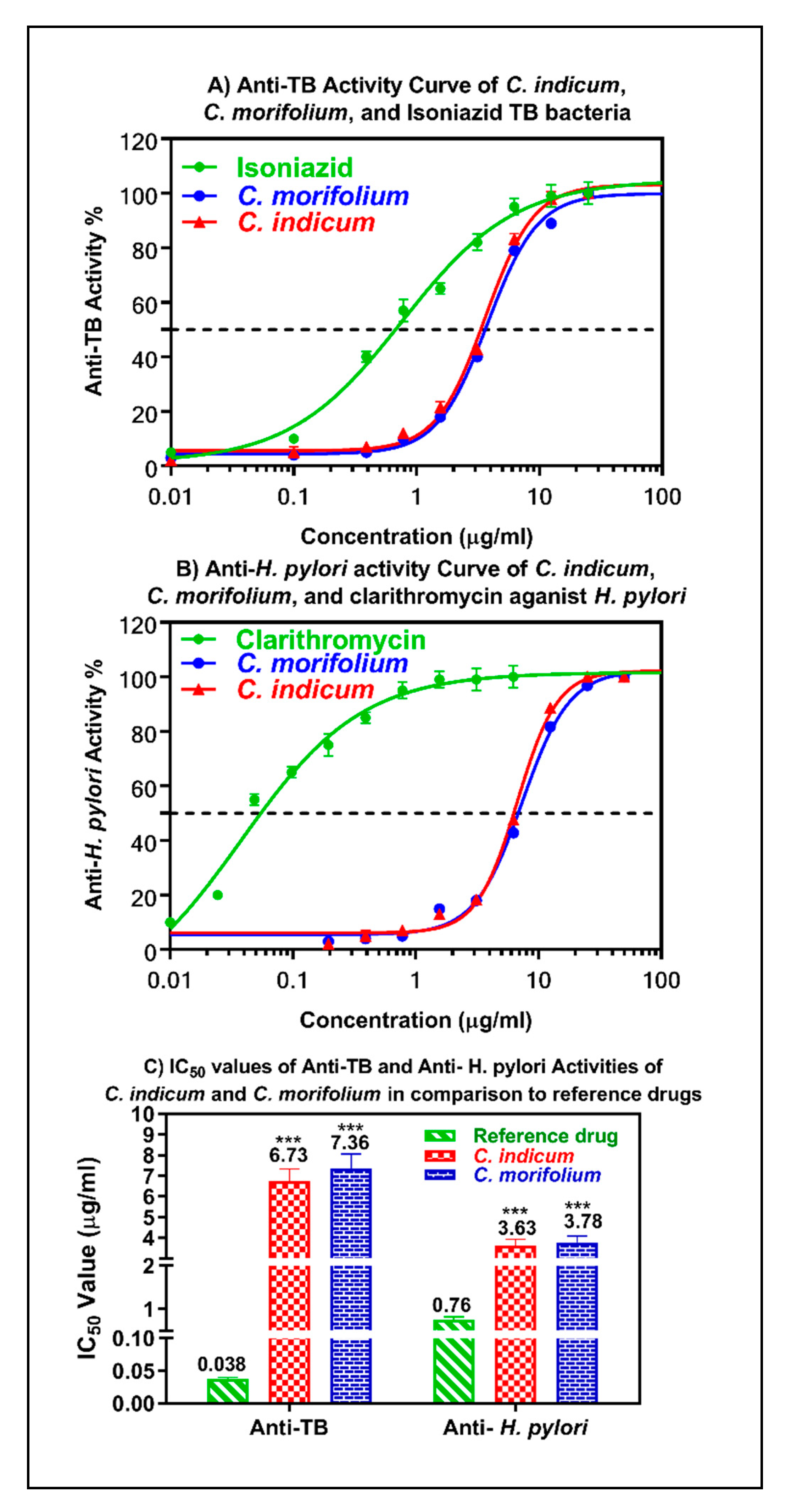
3.4. Anti-Mycobacterial and Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Activity of the Essential Oils
3.5. Anti-Trypanosomal Activity of Essential Oils
3.6. Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oils
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Mokni, R.; Youssef, F.S.; Jmii, H.; Khmiri, A.; Bouazzi, S.; Jlassi, I.; Jaidane, H.; Dhaouadi, H.; Ashour, M.L.; Hammami, S. The essential oil of Tunisian Dysphania ambrosioides and its antimicrobial and antiviral properties. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2019, 22, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Youssef, F.S.; Ashour, M.L.; Sasmakov, S.A.; Tiezzi, A.; Azimova, S.S. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the essential oils of three Uzbek Lamiaceae species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 33, 2394–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Youssef, F.S.; Ashour, M.L.; Akramov, D.K.; Sasmakov, S.A.; Ramazonov, N.S.; Azimova, S.S. A comparative study on chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from three Phlomis species from Uzbekistan. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrajabian, M.H. A review of Chrysanthemum, the eastern queen in traditional Chinese medicine with healing power in modern pharmaceutical sciences. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 13355–13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiart, C. Ethnopharmacology of Medicinal Plants: Asia and the Pacific; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 12, p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- Khare, C.P. Indian Medicinal Plants: An Illustrated Dictionary; Springer Reference; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 10, p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk, B.-E.; Wink, M. Medicinal Plants of the World: An Illustrated Scientific Guide to Important Medicinal Plants and Their Uses, 1st ed.; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 2004; p. 480. [Google Scholar]
- Mabberley, D.J. Mabberley’s Plant-Book: A Portable Dictionary of Plants, Their Classification and Uses, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 1021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.S.C. Chinese and Related North. American Herbs: Phytopharmacology and Therapeutic Values; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; p. 598. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Medicinal Plants in China: A Selection of 150 Commonly Used Species; WHO Regional Publications. Western Pacific Series; World Health Organization, Regional Office for the Western Pacific: Manila, Phillippines, 1997; Volume 7, p. 331. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, R.; Kubitzki, K.; Kadereit, J.W. The families and genera of vascular plants. TAXON 2005, 54, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Toguchida, I.; Harima, S.; Matsuda, H. Medicinal flowers. Inhibitors of nitric oxide production and absolute stereostructures of five new germacrane-type sesquiterpenes, kikkanols D, D monoacetate, E, F, and F monoacetate from the flowers of Chrysanthemum indicum L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukiya, M.; Akihisa, T.; Yasukawa, K.; Kasahara, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Koike, K.; Nikaido, T.; Takido, M. Constituents of compositae plants. 2. Triterpene diols, triols, and their 3-o-fatty acid esters from edible chrysanthemum flower extract and their anti-inflammatory effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3187–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, K.; Tsankova, E.; Van Hung, D. New Sesquiterpenoids from Chrysanthemum indicum var. tuneful. Planta Med. 1988, 54, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Morikawa, T.; Toguchida, I.; Harima, S.; Yoshikawa, M. Medicinal flowers. Absolute stereostructures of two new flavanone glycosides and a phenylbutanoid glycoside from the flowers of Chrysanthemum indicum L.: Their inhibitory activities for rat lens aldose reductase. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.J. A new anti-HIV flavonoid glucuronide from Chrysanthemum morifolium. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Sarkar, S.; Saha, S.K. Acacetin 7-O-[beta]-galactopyranoside from Chrysanthemum indicum. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 1760–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Murakami, T.; Toguchida, I.; Harima, S.; Matsuda, H. Medicinal flowers. I. Aldose reductase inhibitors and three new eudesmane-type sesquiterpenes, Kikkanols A, B, and C, from the flowers of Chrysanthemum indicum L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukiya, M.; Akihisa, T.; Tokuda, H.; Suzuki, H.; Mukainaka, T.; Ichiishi, E.; Yasukawa, K.; Kasahara, Y.; Nishino, H. Constituents of Compositae plants. Anti-tumor promoting effects and cytotoxic activity against human cancer cell lines of triterpene diols and triols from edible Chrysanthemum flowers. Cancer Lett. 2002, 177, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, M.; Hisama, M. Antimutagenic activity of flavonoids from Chrysanthemum morifolium. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Choi, G.; Yoon, T.; Cheon, M.S.; Kil Choo, B.; Kim, H.K. Anti-inflammatory activity of Chrysanthemum indicum extract in acute and chronic cutaneous inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.S. Identification of new dicaffeoylquinic acids from Chrysanthemum morifolium and their antioxidant activities. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xia, Q.; Xu, W.; Zheng, M. Chrysanthemum morifolium attenuated the reduction of contraction of isolated rat heart and cardiomyocytes induced by ischemia/reperfusion. Die Pharm. 2004, 59, 565–567. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.Q.; Chen, K.; Shi, Q.; Kilkuskie, R.E.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Lee, K.H. Anti-AIDS agents, 10. Acacetin-7-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside, an anti-HIV principle from Chrysanthemum morifolium and a structure-activity correlation with some related flavonoids. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, M.S.; Yoon, T.; Lee do, Y.; Choi, G.; Moon, B.C.; Lee, A.Y.; Choo, B.K.; Kim, H.K. Chrysanthemum indicum Linne extract inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Li, J.; You, T.; Hu, C. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of the extracts from the inflorescence of Chrysanthemum indicum Linné. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 101, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.-W. GC-MS analysis of essential oil of the flower of the Chrysanthemum morifolium by the different processing methods. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2006, 31, 456–459. [Google Scholar]
- Shunying, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huaidong, Y.; Yue, Y.; Guolin, Z. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of Chrysanthemum indicum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, F.S.; Hamoud, R.; Ashour, M.L.; Singab, A.N.B.; Wink, M. Volatile oils from the aerial parts of Eremophila maculata and their antimicrobial activity. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, I.M.; Youssef, F.S.; El-Shazly, M.; Ashour, M.L.; Singab, A.N.B.; Wink, M. Volatile constituents of Dietes bicolor (Iridaceae) and their antimicrobial activity. Z. Naturforsch. C 2015, 70, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Karam, M.; Shier, W.T. A simplified plaque reduction assay for antiviral agents from plants. Demonstration of frequent occurrence of antiviral activity in higher plants. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.L.; El-Readi, M.; Youns, M.; Mulyaningsih, S.; Sporer, F.; Efferth, T.; Wink, M. Chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil obtained from Bupleurum marginatum (Apiaceae). J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyaningsih, S.; Sporer, F.; Reichling, J.; Wink, M. Antibacterial activity of essential oils from Eucalyptus and of selected components against multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Din, M.I.G.; Youssef, F.S.; Ashour, M.L.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Singab, A.N.B. Comparative analysis of volatile constituents of Pachira aquatica Aubl. and Pachira glabra Pasq., their anti-mycobacterial and anti-helicobacter pylori activities and their metabolic discrimination using chemometrics. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2018, 21, 1550–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibret, E.; Ashour, M.L.; Rubanza, C.D.; Wink, M. Screening of some Tanzanian medicinal plants for their trypanocidal and cytotoxic activities. Phytother. Res. 2009, 24, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, W.; Koella, J.C. A comparison of three methods of estimating EC50 in studies of drug resistance of malaria parasites. Acta Trop. 1993, 55, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenadis, N.; Lazaridou, A.O.; Tsimidou, M.Z. Use of reference compounds in antioxidant activity assessment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5452–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, F.S.; Ashour, M.L.; Sobeh, M.; El-Beshbishy, H.A.; Singab, A.N.B.; Wink, M. Eremophila maculate-Isolation of a rare naturally-occurring lignan glycoside and the hepatoprotective activity of the leaf extract. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikimi, M.; Rao, N.A.; Yagi, K. The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1972, 46, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruoma, O.I. Deoxyribose Assay for Detecting Hydroxyl Radicals. Meth. Enzymol. 1994, 233, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, O.A.; Ogunwande, I.A.; Olorunloba, O.F.; Opoku, A.R. The essential oils of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. from Nigeria. Am. J. Essent. Oil Nat. Prod. 2014, 2, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.-S.; Kim, G.-H. Volatile flavor composition of gamguk (Chrysanthemum indicum) flower essential oils. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.; Romero, M.R.; Blazquez, A.G.; Kaufmann, D.; Ashour, M.L.; Kahl, S.; Marin, J.J.; Efferth, T.; Wink, M. Diversity of pharmacological properties in Chinese and European medicinal plants: Cytotoxicity, antiviral and antitrypanosomal screening of 82 herbal drugs. Diversity 2011, 3, 547–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, P.; Schön, K.; Reichling, J. Antiviral activity of Australian tea tree oil and eucalyptus oil against herpes simplex virus in cell culture. Die Pharm. 2001, 56, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Vermaak, I.; Viljoen, A.M. Camphor-A fumigant during the Black Death and a coveted fragrant wood in Ancient Egypt and Babylon-A review. Molecules 2013, 18, 5434–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaka, M.; Papanikolaou, E.; Sivropoulou, A.; Arsenakis, M.; Armaka, M. Antiviral properties of isoborneol, a potent inhibitor of herpes simplex virus type 1. Antivir. Res. 1999, 43, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Sassi, A.; Harzallah-Skhiri, F.; Chraief, I.; Bourgougnon, N.; Hammami, M.; Aouni, M. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activities of the essential oil of (Tunisian) Chrysanthemum trifurcatum (Desf.) Batt. and Trab. flowerheads. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2008, 11, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, M. Diversity of plant secondary metabolites with antiviral activities. Potential of DNA intercalating alkaloids against infections with the Corona virus SARS-CoV-2 causing COVID-19. Diversity 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Yu, H.-H.; Cha, J.-D.; You, Y.-O.; Kim, K.-J.; Jeong, S.-I.; Kil, B.-S. Antibacterial activity and chemical composition of essential oil of Chrysanthemum boreale. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippey, E.; Rowland, B. Coastal Plants: Perth and the South-West. Region; UWA Publishing: Perth, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Thabet, A.A.; Youssef, F.S.; El-Shazly, M.; Singab, A.N.B. GC-MS and GC-FID analyses of the volatile constituents of Brachychiton rupestris and Brachychiton discolor, their biological activities and their differentiation using multivariate data analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 34, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, J.E.; Drzewiecki, G. Naturally occurring flavonoids and human basophil histamine release. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1985, 77, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhar, F.; Nariman, F.; Yousefzadi, M.; Hadian, J.; Ebrahimi, S.N. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity and essential oil composition of Thymus caramanicus from Iran. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghini, L.; Leporini, L.; Tirillini, B.; Epifano, F.; Genovese, S. Chemical composition and inhibitory activity against Helicobacter pylori of the essential oil of Apium nodiflorum (Apiaceae). J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, B.-E.; Wink, M. Medicinal Plants of the World; CABI: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan, D.; El-Readi, M.Z.; Nibret, E.; Sporer, F.; Farrag, N.; El-Shazly, A.; Wink, M. Chemical composition of the essential oils of two Citrus species and their biological activities. Die Pharm. 2010, 65, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan, D.; Ashour, M.L.; Mulyaningsih, S.; El-Shazly, A.; Wink, M. Chemical composition of the essential oils of variegated pink-fleshed lemon (Citrus x limon L. Burm. f.) and their anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. Z. Naturforsch. C 2013, 68, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, H.; Baysal, A.H. Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of essential oil terpenes against pathogenic and spoilage-forming bacteria and cell structure-activity relationships evaluated by SEM microscopy. Molecules 2014, 19, 17773–17798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |







| Compound | RI | Content [%] | Identification Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cal. | Rep. | C. indicum | C. morifolium | |||
| 1. | Tricyclene | 904 | 905 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 2. | α- Pinene | 917 | 917 | 0.49 | 0.57 | MS, RI, AU |
| 3. | α-Fenchene | 930 | 934 | - | 0.20 | MS, RI |
| 4. | Camphene | 933 | 933 | 2.21 | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 5. | 1-Octen-3-ol | 961 | 964 | - | 0.63 | MS, RI |
| 6. | 2,3-Dehydro-1,8-cineole | 972 | 972 | 0.32 | - | MS, RI |
| 7. | 2-Pentylfuran | 975 | 972 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 8. | n-Decane | 1000 | 1000 | 0.67 | 0.61 | MS, RI |
| 9. | Psi-cumene | 1002 | 1004 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 10. | α-Terpinene | 1006 | 1006 | 5.73 | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 11. | o-Cymene | 1008 | 1006 | - | 0.60 | MS, RI |
| 12. | p-Cymene | 1009 | 1006 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 13. | m-Cymene | 1011 | 1010 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 14. | Cineole | 1015 | 1015 | 2.02 | tr | MS, RI, AU |
| 15. | D-Limonene | 1017 | 1017 | 0.02 | tr | MS, RI, AU |
| 16. | τ-Terpinene | 1046 | 1046 | tr | 0.18 | MS, RI, AU |
| 17. | α-p-Dimethylstyrene | 1070 | 1070 | - | 0.26 | MS, RI |
| 18. | Dehydro-p-cymene | 1070 | 1071 | 0.35 | - | MS, RI |
| 19. | Terpinolene | 1075 | 1075 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 20. | α-Thujone | 1082 | 1087 | 4.73 | 0.57 | MS, RI, AU |
| 21. | β-Thujone | 1093 | 1097 | 2.07 | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 22. | L-trans-Pinocarveol | 1119 | 1119 | - | 0.51 | MS, RI |
| 23. | Camphor | 1120 | 1124 | 36.69 | 14.56 | MS, RI, AU |
| 24. | cis-Verbenol | 1126 | 1131 | 0.97 | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 25. | Chrysanthenone | 1133 | 1131 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 26. | Borneol | 1136 | 1130 | tr | 7.95 | MS, RI, AU |
| 27. | Isoborneol | 1149 | 1154 | 7.64 | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 28. | Lavandulol | 1152 | 1152 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 29. | Myrtenal | 1155 | 1151 | tr | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 30. | Terpene-4-ol | 1159 | 1159 | 0.93 | - | MS, RI |
| 31. | Verbenol | 1166 | 1165 | tr | 0.87 | MS, RI, AU |
| 32. | α-Phellandren-8-ol | 1167 | 1167 | - | tr | MS, RI |
| 33. | α-Terpineol | 1169 | 1169 | tr | 0.65 | MS, RI, AU |
| 34. | Myrtenol | 1176 | 1178 | 0.59 | tr | MS, RI, AU |
| 35. | n-Dodecane | 1199 | 1200 | tr | 0.68 | MS, RI |
| 36. | Cuminal | 1206 | 1207 | 0.34 | - | MS, RI |
| 37. | Carveol | 1215 | 1217 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 38. | trans-Chrysanthenyl acetate | 1243 | 1243 | - | 0.42 | MS, RI |
| 39. | Isobornyl acetate | 1266 | 1268 | 0.69 | 1.23 | MS, RI |
| 40. | Carvacrol | 1274 | 1275 | tr | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 41. | Thymol | 1282 | 1285 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 42. | (-)-trans-Pinocarvyl acetate | 1303 | 1297 | 0.21 | - | MS, RI |
| 43. | α-terpinyl acetate | 1331 | 1325 | - | 0.89 | MS, RI |
| 44. | Copaene | 1367 | 1367 | tr | 5.61 | MS, RI |
| 45. | β-Elemene | 1382 | 1382 | - | 1.19 | MS, RI |
| 46. | β -Patchoulene | 1369 | 1370 | 0.34 | - | MS, RI |
| 47. | n-Decanoic acid | 1380 | 1380 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 48. | n-Tetradecane | 1399 | 1400 | tr | 1.27 | MS, RI |
| 49. | Caryophyllene | 1406 | 1406 | 0.32 | tr | MS, RI, AU |
| 50. | β-Farnesene | 1447 | 1446 | - | 1.06 | MS, RI |
| 51. | α-Curcumene | 1467 | 1464 | 1.23 | 10.50 | MS, RI |
| 52. | Zingiberene | 1486 | 1486 | - | 4.33 | MS, RI, AU |
| 53. | Varidiflorene | 1498 | 1499 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 54. | α-Bisabolene | 1500 | 1500 | - | 1.37 | MS, RI |
| 55. | Guaiene | 1506 | 1500 | - | tr | MS, RI |
| 56. | α-Muurolene | 1511 | 1508 | - | tr | MS, RI |
| 57. | Cadinene | 1509 | 1508 | 0.3 | - | MS, RI |
| 58. | α-Calacorene | 1523 | 1523 | - | tr | MS, RI |
| 59. | Spathulenol | 1535 | 1537 | 0.73 | - | MS, RI |
| 60. | trans-Nerolidol | 1548 | 1549 | - | tr | MS, RI |
| 61. | Caryophyllene oxide | 1562 | 1562 | 5.46 | 1.27 | MS, RI |
| 62. | Isoaromadendrene epoxide | 1583 | 1579 | tr | tr | MS, RI |
| 63. | Ent-Spathulenol | 1588 | 1578 | 1.38 | 1.27 | MS, RI |
| 64. | n-Hexadecane | 1599 | 1600 | - | tr | MS, RI |
| 65. | Widdrol | 1604 | 1606 | - | tr | MS, RI |
| 66. | Cubenol | 1608 | 1609 | - | 0.56 | MS, RI |
| 67. | α-Eudesmol | 1634 | 1630 | 4.4 | - | MS, RI |
| 68. | τ-Eudesmol | 1637 | 1638 | - | 8.92 | MS, RI |
| 69. | α-Cadinol | 1651 | 1651 | - | 1.05 | MS, RI |
| 70. | Cedren-13-ol, 8- | 1664 | 1668 | 4.94 | 0.56 | MS, RI |
| 71. | Bisabolol | 1665 | 1667 | - | 2.26 | MS, RI |
| 72. | Germacrone | 1691 | 1691 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 73. | n-Octadecane | 1799 | 1800 | 0.54 | 1.06 | MS, RI |
| 74. | Hexahydrofarnesyl acetone | 1827 | 1832 | 0.30 | tr | MS, RI |
| 75. | Nonacosane | 1903 | 1900 | 2.75 | 0.75 | MS, RI |
| 76. | Palmitic acid, methyl ester | 1910 | 1910 | 0.24 | - | MS, RI |
| 77. | Palmitic acid | 1951 | 1951 | 0.66 | 1.54 | MS, RI, AU |
| 78. | n-Eicosane | 1998 | 2000 | 0.38 | 1.32 | MS, RI |
| 79. | Methyl linoleate | 2072 | 2078 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 80. | Methyl oleate | 2082 | 2082 | tr | - | MS, RI |
| 81. | Heneicosane | 2103 | 2100 | tr | 4.88 | MS, RI |
| 82. | Methyl linolenate | 2113 | 2099 | 0.26 | - | MS, RI |
| 83. | Linoleic acid | 2118 | 2113 | tr | - | MS, RI, AU |
| 84. | Tricosane | 2304 | 2300 | 0.32 | 4.18 | MS, RI |
| 85. | Tetracosane | 2397 | 2400 | 0.29 | 1.34 | MS, RI |
| 86. | Pentacosane | 2503 | 2500 | 0.19 | 8.65 | MS, RI |
| 87. | Hexacosane | 2605 | 2600 | - | 0.29 | MS, RI |
| 88. | Heptacosane | 2705 | 2700 | - | 1.43 | MS, RI |
| 89. | Octacosane | 2799 | 2800 | - | 0.94 | MS, RI |
| Monoterpene hydrocarbons | 11.81 | 2.18 | ||||
| Oxygenated monoterpens | 54.86 | 27.65 | ||||
| Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons | 2.19 | 24.06 | ||||
| Oxygenated sesquiterpens | 16.91 | 15.89 | ||||
| Others | 5.93 | 29.20 | ||||
| Total identified components | 91.70 | 98.98 | ||||
| Microorganisms | C. indicum | C. morifolium | Positive Control * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIZ (mm) | MIC (µg/mL) | DIZ (mm) | MIC (µg/mL) | DIZ (mm) | MIC (µg/mL) | |
| Gram Positive Bacteria | ||||||
| Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051 | 20.0 ± 0.2 | 62.5 | 15.0 ± 0.7 | 125 | 31.6 ± 0.3 | 0.08 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 20.4 ± 0.5 | 250 | 19.5 ± 0.3 | 250 | 30.1 ± 0.6 | 0.16 |
| Staphylococcus capitis ATCC 35661 | 19.9 ± 0.4 | 125 | 16.1 ± 0.5 | 250 | 29.2 ± 0.1 | 0.08 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 14990 | 19.6 ± 0.7 | 250 | 17.4 ± 0.8 | 250 | 26.4 ± 0.2 | 0.16 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae ATCC 27956 | 19.2 ± 0.8 | 62.5 | 14.4 ± 0.6 | 125 | 30.1 ± 0.1 | 0.08 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 12344 | 21.9 ± 0.9 | 62.5 | 17.5 ± 0.3 | 125 | 29.7 ± 0.0 | 0.08 |
| Gram Negative Bacteria | ||||||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 13.8 ± 0.2 | >500 | 13.7 ± 0.8 | 500 | 32.1 ± 0.0 | 0.06 |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens ATCC 13525 | 12.3 ± 0.1 | >500 | 11.7 ± 0.1 | >500 | 27.3 ± 0.1 | 0.24 |
| Salmonella typhimurium ATCC 14028 | 12.1 ± 0.5 | >500 | 11.5 ± 0.1 | >500 | 24.6 ± 0.2 | 0.96 |
| Shigella flexneri ATCC 700930 | 11.2 ± 0.9 | >500 | 10.9 ± 0.5 | >500 | 21.2 ± 0.0 | 0.96 |
| Fungi | ||||||
| Aspergillus fumigatus ATCC 1022 | 15.8 ± 0.5 | >500 | 14.5 ± 0.5 | 500 | 26.3 ± 0.1 | 0.12 |
| Candida albicans ATCC 90028 | 13.6 ± 0.7 | >500 | 12.6 ± 0.2 | >500 | 24.8 ± 0.7 | 0.24 |
| Geotrichum candidum ATCC 12784 | 14.0 ± 0.5 | 500 | 13.3 ± 0.4 | >500 | 23.2 ± 0.3 | 0.48 |
| Syncephalastrum racemosum ATCC 14831 | 11.9 ± 0.6 | >500 | 11.2 ± 0.7 | >500 | 21.4 ± 0.5 | 0.48 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youssef, F.S.; Eid, S.Y.; Alshammari, E.; Ashour, M.L.; Wink, M.; El-Readi, M.Z. Chrysanthemum indicum and Chrysanthemum morifolium: Chemical Composition of Their Essential Oils and Their Potential Use as Natural Preservatives with Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. Foods 2020, 9, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101460
Youssef FS, Eid SY, Alshammari E, Ashour ML, Wink M, El-Readi MZ. Chrysanthemum indicum and Chrysanthemum morifolium: Chemical Composition of Their Essential Oils and Their Potential Use as Natural Preservatives with Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. Foods. 2020; 9(10):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101460
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoussef, Fadia S., Safaa Y. Eid, Elham Alshammari, Mohamed L. Ashour, Michael Wink, and Mahmoud Z. El-Readi. 2020. "Chrysanthemum indicum and Chrysanthemum morifolium: Chemical Composition of Their Essential Oils and Their Potential Use as Natural Preservatives with Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities" Foods 9, no. 10: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101460
APA StyleYoussef, F. S., Eid, S. Y., Alshammari, E., Ashour, M. L., Wink, M., & El-Readi, M. Z. (2020). Chrysanthemum indicum and Chrysanthemum morifolium: Chemical Composition of Their Essential Oils and Their Potential Use as Natural Preservatives with Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. Foods, 9(10), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9101460