Effect of Freeze-Dried Camel Rennet Extract on Coagulation of Camel–Goat Milk Mixture and Characterization of the Cheese Obtained
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Samples
2.2. Coagulant and Starter Cultures
2.2.1. Camel Abomasum
2.2.2. Freeze-Dried Microbial Coagulant
2.2.3. Mesophilic and Thermophilic Commercial Starter Cultures
2.3. Extraction and Freeze-Drying of Camel Rennet
2.4. Acidification Activity of Commercial Starter Cultures
2.5. Optimization of Enzymatic Coagulation
2.6. Cheese-Making Process of Camel and Goat Milk Mixture
2.7. Study of CC and MC Fresh Cheeses
2.7.1. Color Measurement
2.7.2. Crude Mineral Composition and Cheese Yield Measurement
2.7.3. Water Activity Measurement
2.7.4. Texture Profile Analysis
2.7.5. Fourier Transform InfraRed Spectroscopy Measurement
2.7.6. X-Ray Diffraction Measurement
2.7.7. Microstructure Under Environmental Scanning Electron Microscope
2.7.8. Sensory Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Starter Culture Performance in Camel–Goat Milk Mixture
3.2. Cheese Yields
3.3. Color Characteristics of Fresh Cheeses
3.4. Crude and Mineral Composition of Fresh Cheeses
3.5. Texture Parameters of Fresh Cheeses
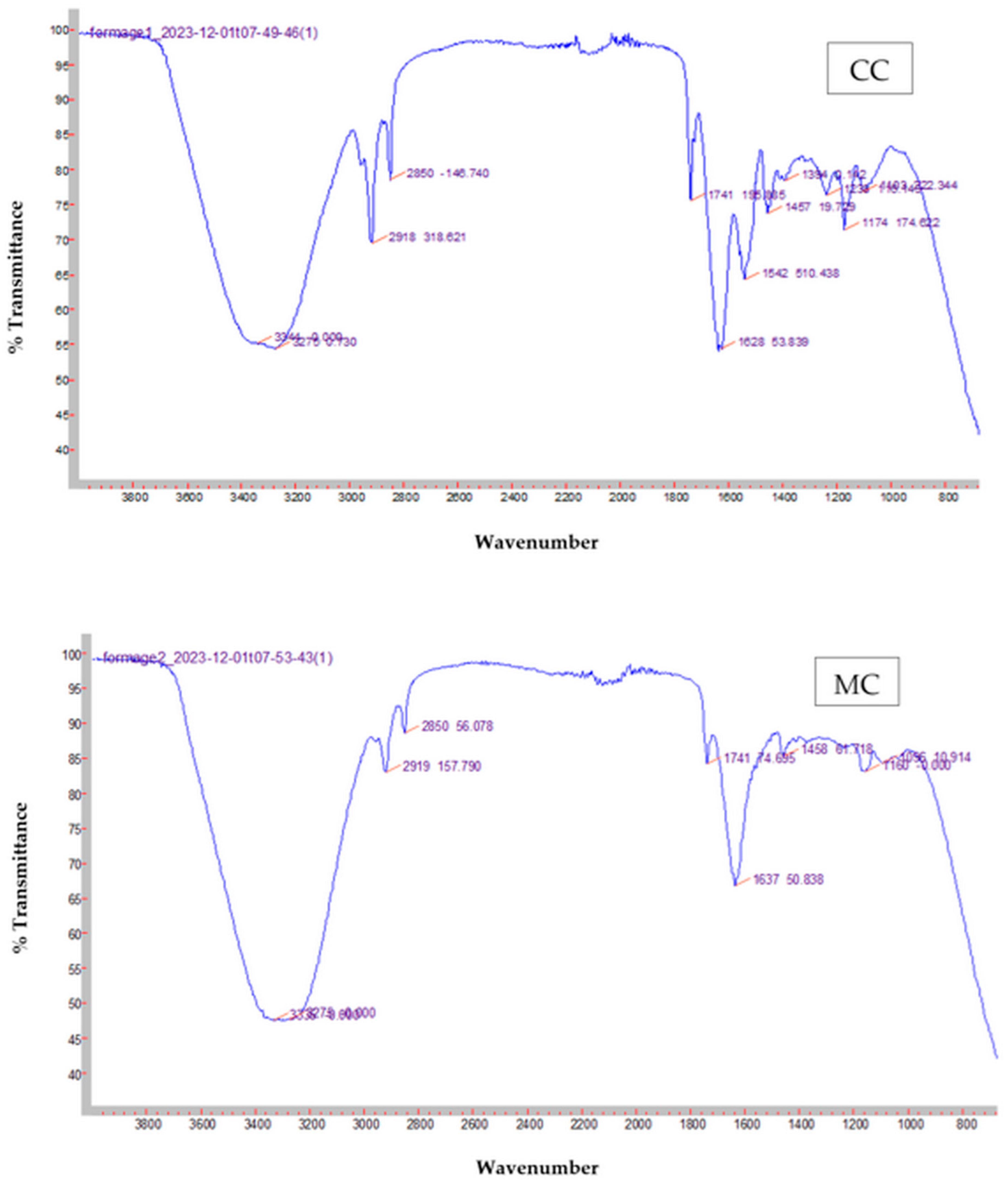
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements
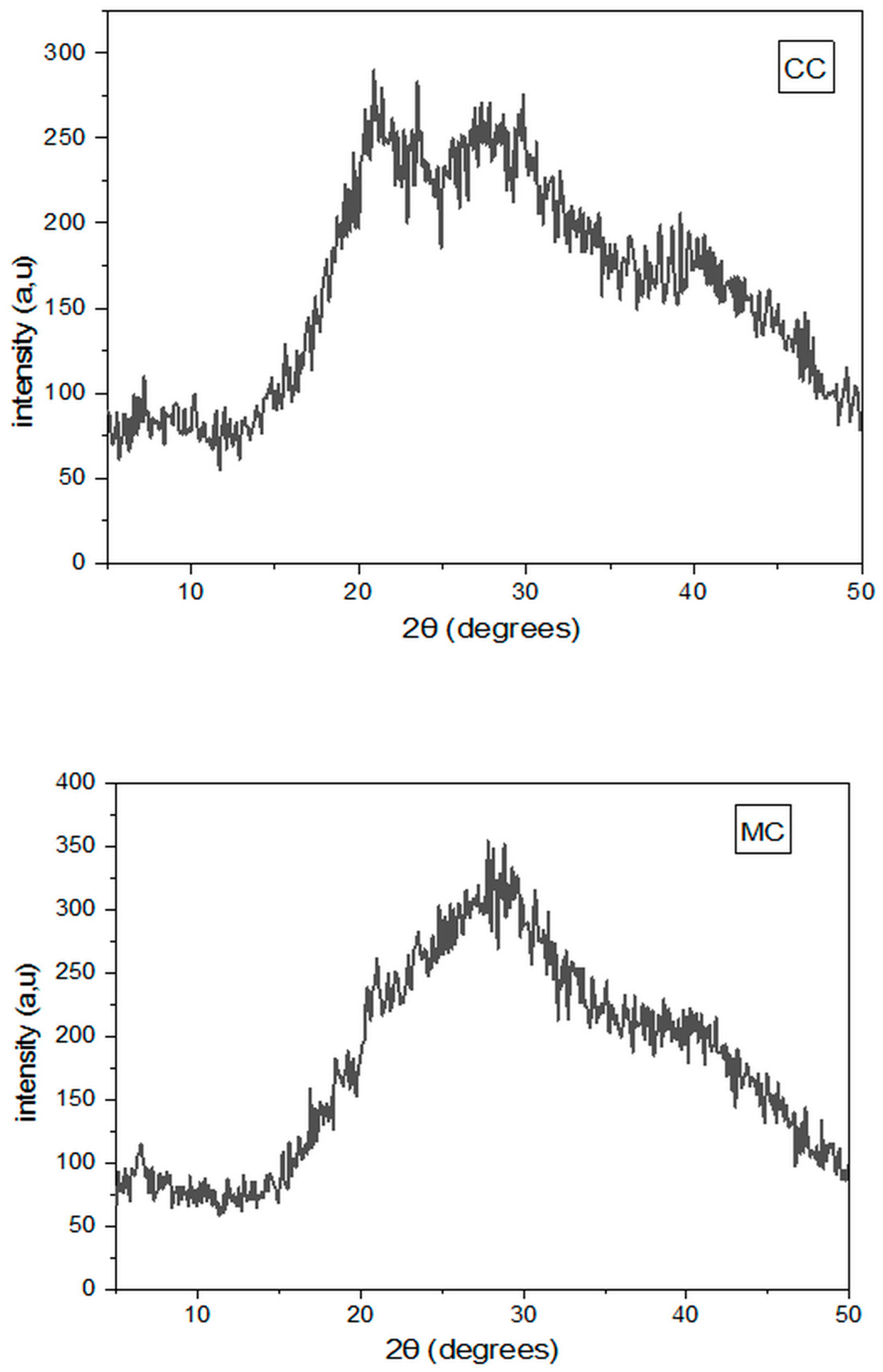
3.7. X-Ray Diffraction Measurements
3.8. Microstructure of Fresh Cheeses
3.9. Sensory Evaluation of Fresh Cheeses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seifu, E. Recent advances on camel milk: Nutritional and health benefits and processing implications—A review. AIMS Agric. Food 2022, 7, 777–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senoussi, A.; Abazi, A.; Bezziou, S.; Brahimi, Z. The camel in Algeria: Animal of the past, present and future: What is the scope of farming systems? Proceeding paper. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2023, 22, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Boudalia, S.; Gueroui, Y.; Zebsa, R.; Arbia, T.; Chiheb, A.E.; Benada, M.; Hadri, Z.; Youcefi, A.; Bousbia, A. Camel livestock in the Algerian Sahara under the context of climate change: Milk properties and livestock production practices. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 11, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssou, H.; Labiod, A.; Ramdani, A.; Khenenou, T. Dairy production in the indigenous Arbia goat breed and growth performance of their kids in Algeria. Vet. Stanica 2023, 54, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djouza, L.; Chehma, A. Production characteristics of Arbia goats in Biskra Wilayah, Algeria. Livest. Res. Rural. Dev. 2018, 30, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Seifu, E. Camel milk products: Innovations, limitations and opportunities. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2023, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.A.; Salman, H.M.; Ali, M.; Khaskheli, G.B.; Barham, G.S.; Barham, I.B.; Ahmed, S. A review on camel milk composition, techno-functional properties and processing constraints. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2024, 44, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhmatulina, A.; Abuova, A.; Issimov, A.; Faye, B. Camel milk processing opportunities: A review. J. Camel Pract. Res. 2024, 31, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wangoh, J.; Farah, Z.; Puhan, Z. Extraction of camel rennet and its comparison with calf rennet extract. Milchwissenchaft Milk Sci. 1993, 48, 322–325. [Google Scholar]
- Lambé, C.; Baviera, J.M.B.; Bolognesi, C.; Coccocelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; Lampi, E.; Mengelers, M.; Mortensen, A.; et al. Safety evaluation of the food enzyme rennet containing chymosin and pepsin A from the abomasum of suckling calves, goats and lambs. efsa J. 2023, 21, e08084. [Google Scholar]
- Derar, A.M.A.; El Zubeir, I.E.M. Effect of fortifying camel milk with sheep milk on the processing properties, chemical composition and acceptability of cheeses. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2016, 6, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Shahein, M.R.; Hassanein, A.M.; Rayan, A.F. Evaluation of soft cheese manufactured from camel and buffalo milk. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 2014, 9, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, A.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; AlMadhani, S.; Hamed, F.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Huppertz, T.; Ayyash, M. Low-fat akawi cheese made from bovine-camel milk blends: Rheological properties and microstructural characteristics. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 4843–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aissaoui-Zitoun, O.; Benyahia-Krid, F.A.; Boughellout, H.; Adoui, F.; Derouiche, M.; Bentazir, I.; Kharchi, B.; Zidoune, N.M. Manufacturing and characterization of unripened cheese with dromedary and goat’s milk mixture using chicken pepsin. In Proceedings of the 10th Cheese Symposium, Conférences Centre, Rennes, France, 4–6 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bouras, B.; Aissaoui-zitoun, O.; Benyahia, A.F.; Djeghim, F.; Djema, S.; Zidoune, M.N. New formulation and characterization of fresh camel and goat milk cheese coagulated with chicken pepsin. In Proceedings of the Global Meet on Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, Prime Meetings, Miami, FL, USA, 16–18 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bouras, B.; Aissaoui-zitoun, O.; Benyahia, A.F.; Djeghim, F.; Djema, S.; Zidoune, M.N. Manufacture and characterization of fresh cheese made from mixed milk of camel and goat. J. Camel Pract. Res. 2023, 30, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Athar, I.H.; Aslam, M.U. Evaluation of cheese prepared by processing camel milk. Pak. J. Zool. 2004, 36, 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Moula, N. Camel breeding in Algeria. In Proceedings of the 10th International Seminar of Veterinary Medicine: Camelids in Algeria and Maghreb, Constantine, Algeria, 20–21 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut, M.; Jeantet, R.; Brulé, G.; Schuck, P. Les Produits Industriels Laitiers, 1st ed.; Tech & Doc: Paris, France, 2000; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- CIE. Colorimetry-Technical Report, 2nd ed.; Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage: Bureau Central de la CIE, Vienna, Austria, 1986; pp. 5–36. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 21807; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Water Activity, 1st ed. International Standardization Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 1–5.
- Felfoul, I.; Bouazizi, A.; Tourki, I.; Guesmi, C.; Attia, H. Effect of storage conditions on physicochemical, sensory, and structural properties of dromedary and cow’s skim milk soft-brined cheese. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 45, e15970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felfoul, I.; Bouazizi, A.; Attia, H.; Karoui, R. Monitoring of acid-induced coagulation of dromedary and cow’s milk using different complementary analytical techniques. Food Control 2022, 136, 108867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, S.M.; Mohebbi, M.; Mirzababaee, S.M.; Hesarinejad, M.L.; Movahed, M.K. The effect of high hydrostatic pressure on the structure of whey proteins-guar mixture. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, H.; Bennasar, M.; Fuente, B.T. Study of the fouling of inorganic membranes by acidified milks using scanning electron microscopy and electrophoresis: I. Membrane with pore diameter 0.2 µm. J. Dairy Res. 1991, 5, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berodier, F.; Lavanchy, P.; Zannoni, M.; Casals, J.; Herrero, L.; Adamo, C. Guide d’évaluation olfacto-gustative des fromages à pâte dure et semi-dure. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, B.; Hansen, E.B.; Eshetu, M.; Ipsen, R.; Hailu, Y. Effect of starter cultures on properties of soft white cheese made from camel (Camelus dromedarius) milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-zoreky, N.S.; Almathen, F.S. Using recombinant camel chymosin to make white soft cheese from camel milk. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 127994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaschian, S.; Ramezan, Y.; Salami, M. Chemical, Textural and Ripening Characteristics of Semi-hard White Cheese Prepared from Camel Milk Using Camel Chymosin and Different Starter Cultures. Agric. Res. J. 2023, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, A.; Ul Haq, F.; Ali, K.; Khalid, M.U.; Zafar, U.; AL-Ansi, W. Development of camel milk soft cheese with different levels of salt, fat and solid not fat. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2024, 9, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadeer, Z.; Huma, N.; Rehman, M.A.; Ahmad, B.; Hafeez, H.; Ali, U.; Shah, F.U.H.; Tariq, M.R.; Nayik, G.A.; Ramniwas, S.; et al. Influence of thermophilic and mesophilic cultures blended with buffalo milk on camel milk cheese quality and proteolysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 5690–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemechu, A.; Gumi, B.; Girma, S.; Ayana, Z.; Goshu, G. Efficiency of cheese making from camel milk by blending with cow milk at different proportion. Asian J. Anim. Vet Sci. 2023, 6, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbye, M.; Mohamed, H.; Raziq, A.; Kamal-Eldin, A. The effects of camel chymosin and Withania coagulans extract on camel and bovine milk cheeses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczyński, K.Ł.; Sokolińska, D.C.; Bielska, P.; Teichert, J.; Biegalski, J.; Yiğit, A.; Chudy, S. The influence of the texture and color of goat’s salad cheese on the emotional reactions of consumers compared to cow’s milk cheese and Feta cheese. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CODEX STAN 283-1978; Norme Générale CODEX Pour le Fromage. Codex Alimentarius: Rome, Italy, 1999.
- Bouras, B.; Aissaoui-zitoun, O.; Benyahia, A.F.; Djeghim, F.; Djema, S.; Zidoune, M.N. Optimization of flocculation and clotting time of camel milk with camel and goat rennets, and chicken pepsin in comparison with cow milk using response surface method (RSM). Emir. J. Food Agric. 2022, 34, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbye, M.; Sobti, B.; Al Nuami, M.K.; Al Shamsi, Y.; Al Khateri, L.; Al Saedi, R.; Saeed, M.; Ramachandran, T.; Hamed, F.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Physicochemical properties, sensory quality, and coagulation behavior of camel versus bovine milk soft unripened cheeses. NFS J. 2019, 20, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekkaoui, S.; Felfoul, I.; Mosbah, S.; Djelfaoui, Z.; Adamou, A.; Boudjenah-Haroun, S. Impact of camel breeding system on the composition and cheese-making ability of the produced milk. Int. J. Biosci. 2022, 20, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Darnay, L.; Barko, A.; Hidas, K.; Patak, F.A.; Miklos, G.; Suranyi, J.; Laczay, P. Comparison of quality properties of pasteurized milk-based camel cheese depending on calf rennet concentration and microbial transglutaminase. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2024, 77, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnemr, A.M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Arafat, H.H.O.; Osman, S. Improving the quality of camel milk soft cheese using milky component (BMR) and sweet potato powder. Eur. J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 19, 566–577. [Google Scholar]
- Mbye, M.; Ayyash, M.; Mohamed, H.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Kamleh, R.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Effects of ultrafiltration followed by heat or high-pressure treatment on camel an bovine milk cheeses. NFS J. 2023, 31, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukria, O.; El Hadrami, E.M.; Sultanova, S.; Alqurashi, R.M.; Cahyana, Y.; Aït-Kaddour, A. Monitoring molecular structure changes of cow and camel milk mixtures during coagulation: A study based on TPA and 2DCOS-MIR spectroscopy. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.A.; Rasheed, S.; Jaweria, A.; Khaskheli, G.B.; Barham, G.S.; Ahmed, S. A review on processing opportunities for the development of camel dairy products. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2023, 43, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jrad, Z.; Oussaeif, O.; El-Hatmi, H. Recent Trends on Camel Milk Cheese Processing: Nutritional and Health Value; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Foda, M.I.; Bahgaat, W.K.; Kassem, J.M.; Aly, S.E. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra in relation to the composition of white soft cheese. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 26, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, A.; Alvarez, V.B.; Harper, W.J.; Rodriguez-Saona, L.E. Monitoring amino acids, organic acids, and ripening changes in Cheddar cheese using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørskov, K.E.; Christensen, L.B.; Wiking, L.; Hannibal, T.; Hammershøj, M. Detecting interactions between starch and casein in imitation cheese by FTIR and Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Boran, O.S.; Hayaloglu, A.A. Effect of various blends of camel chymosin and microbial rennet (Rhizomucor miehei) on microstructure and rheological properties of Iranian UF white cheese. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazizi, A.; Ben Touati, T.; Guesmi, C.; Attia, H.; Felfoul, I. Physicochemical, sensory and coagulation properties of dromedary and cows’ skim milk white brined cheeses. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, A.M.E.; Sidding, S.M.; Salih, Z.A. Quality assessment of white cheese produced by using camel milk and mixture of camel and cow milk. J. Food Process. Technol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
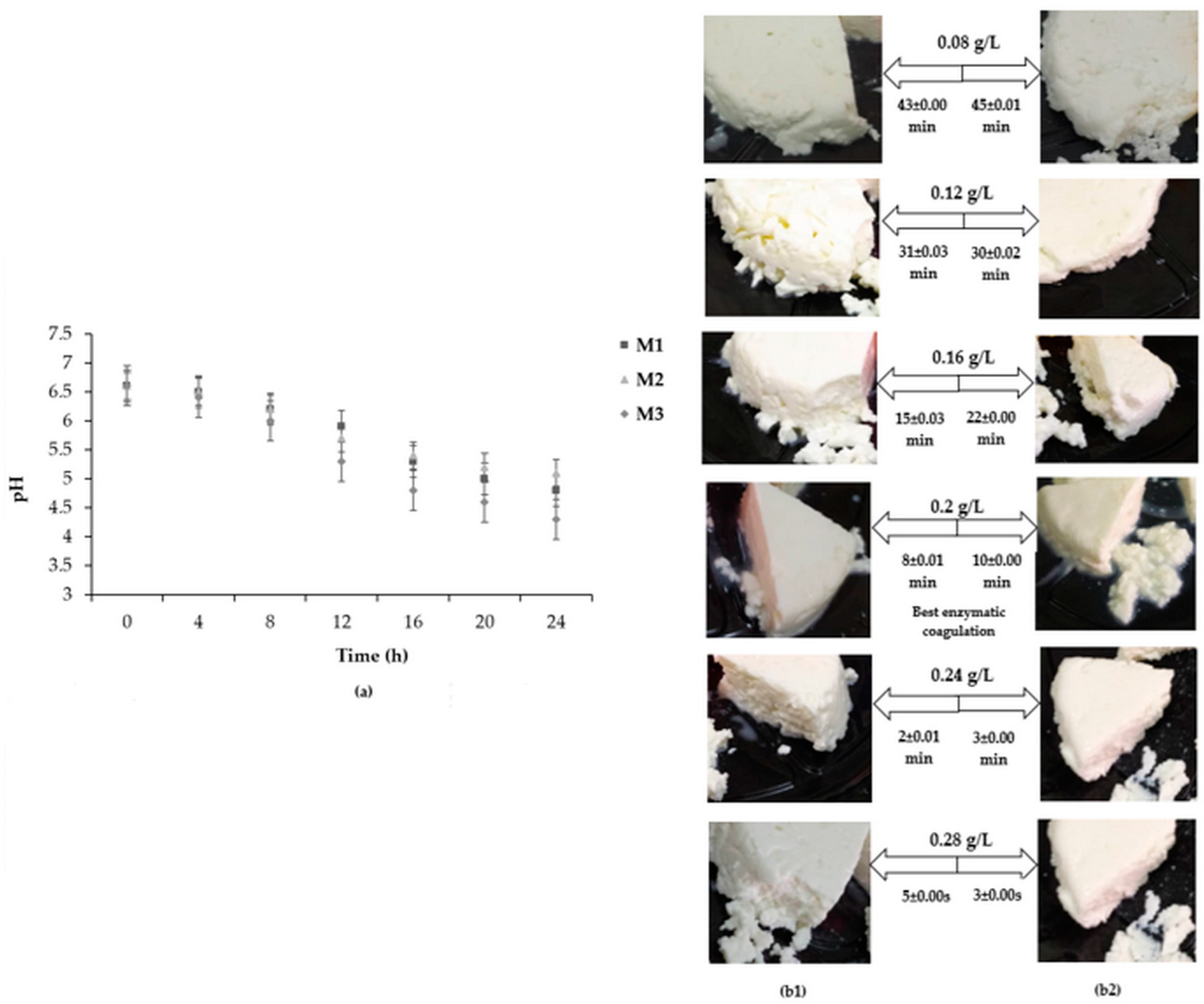

| FDCR/FDMC (g/L) | Cheese Yield (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CY1 | CY2 | p-Value | |
| 0.08 | 16.58 ± 0.20 | 9.79 ± 0.14 | * |
| 0.12 | 15.88 ± 0.12 | 14.04 ± 0.12 | * |
| 0.16 | 19.28 ± 0.15 | 14.44 ± 0.12 | * |
| 0.20 | 16.50 ± 0.09 | 14.92 ± 0.07 | * |
| 0.24 | 19.01 ± 0.13 | 12.95 ± 0.20 | * |
| 0.28 | 16.87 ± 0.11 | 10.00 ± 0.15 | * |
| Parameters | CC Cheese | MC Cheese | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical properties | |||
| pH | 4.50 ± 0.00 | 4.66 ± 0.00 | * |
| aw | 0.96 ± 0.00 | 0.97 ± 0.00 | * |
| Dry matter (DM) (%) | 34.99 ± 0.57 | 35.77 ± 0.18 | ns |
| Protein (%/DM) | 36.26 ± 1.75 | 27.20 ± 2.05 | * |
| Fat (%/DM) | 57.15 ± 1.05 | 67.09 ± 0.94 | * |
| MFFB (%) | 81.94 ± 1.31 | 84.51 ± 0.80 | ns |
| Yield (%) | 15.96 ± 0.10 | 13.55 ± 0.01 | * |
| Ashes (g/100 g) | 1.41 ± 0.02 | 3.55 ± 0.00 | * |
| Ca2+ (mg/100 g) | 4.33 ± 0.02 | 1.33 ± 0.01 | * |
| P (mg/100 g) | 2.86 ± 0.00 | 2.90 ± 0.02 | ns |
| Na+ (mg/100 g) | 123.66 ± 0.01 | 128.66 ± 0.00 | * |
| K+ (mg/100 g) | 73 ± 0.02 | 98.33 ± 0.00 | * |
| Mg2+ (mg/100 g) | 3 ± 0.00 | 1.33 ± 0.01 | * |
| Fe (mg/100 g) | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | ns |
| Mn (mg/100 g) | <0.06 | <0.06 | ns |
| Cu (mg/100 g) | <0.03 | <0.03 | ns |
| Color parameters | |||
| L* | 92.86 ± 0.23 | 93.97 ± 0.03 | * |
| a* | −1.03 ± 0.02 | −1.75 ± 0.01 | * |
| b* | 11.75 ± 0.00 | 10.26 ± 0.02 | * |
| C* | 11.78 ± 0.08 | 10.33 ± 0.11 | * |
| h° | 95.04 ± 0.11 | 99.70 ± 0.04 | * |
| Textural properties | |||
| Hardness (N) | 1.52 ± 0.32 | 1.20 ± 0.03 | ns |
| Cohesiveness (−) | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.00 | * |
| Springiness (mm) | 14.25 ± 0.63 | 18.16 ± 0.63 | * |
| Adhesiveness (N) | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.81 ± 0.02 | * |
| Chewiness (Nmm) | 7.12 ± 1.44 | 14.80 ± 1.04 | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouras, B.; Aissaoui-Zitoun, O.; Benyahia, F.A.; Djema, S.; Bouras, L.; Zidoune, M.N.; Felfoul, I. Effect of Freeze-Dried Camel Rennet Extract on Coagulation of Camel–Goat Milk Mixture and Characterization of the Cheese Obtained. Foods 2025, 14, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030334
Bouras B, Aissaoui-Zitoun O, Benyahia FA, Djema S, Bouras L, Zidoune MN, Felfoul I. Effect of Freeze-Dried Camel Rennet Extract on Coagulation of Camel–Goat Milk Mixture and Characterization of the Cheese Obtained. Foods. 2025; 14(3):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouras, Biya, Ouarda Aissaoui-Zitoun, Férial Aziza Benyahia, Souhila Djema, Leila Bouras, Mohammed Nassereddine Zidoune, and Imène Felfoul. 2025. "Effect of Freeze-Dried Camel Rennet Extract on Coagulation of Camel–Goat Milk Mixture and Characterization of the Cheese Obtained" Foods 14, no. 3: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030334
APA StyleBouras, B., Aissaoui-Zitoun, O., Benyahia, F. A., Djema, S., Bouras, L., Zidoune, M. N., & Felfoul, I. (2025). Effect of Freeze-Dried Camel Rennet Extract on Coagulation of Camel–Goat Milk Mixture and Characterization of the Cheese Obtained. Foods, 14(3), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030334









