The Influence of pH-Driven Interaction Between Soy Protein Isolate and Soy Isoflavones on the Structural and Functional Properties of Their Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SPI
2.3. Preparation of SI
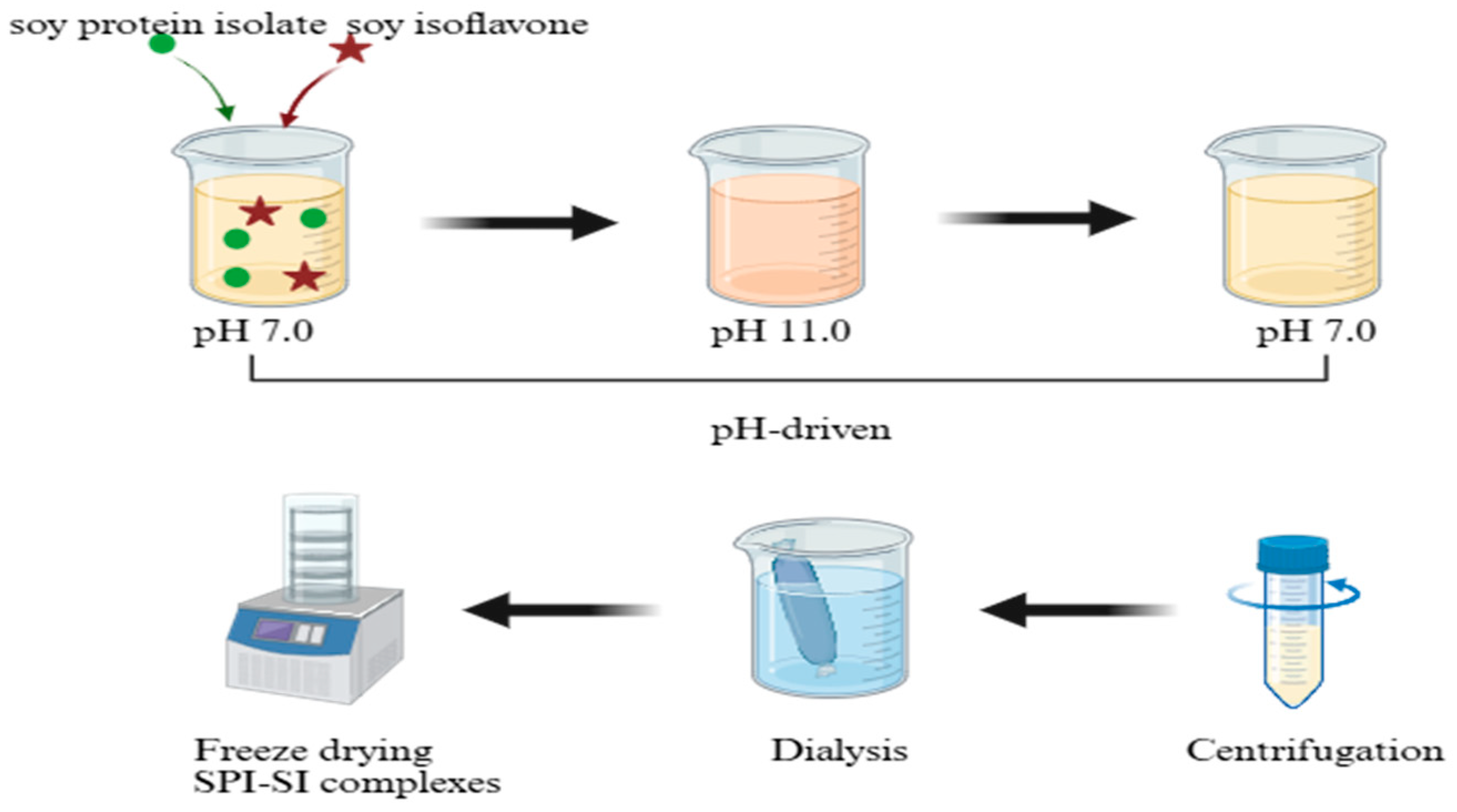
2.4. Preparation of SPI-SI Complexes
2.5. Characterization of the SPI-SI Complexes
2.5.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
2.5.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
2.5.4. Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Analysis
2.5.5. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.5.6. Atomic Force Microscopy Observation Analysis
2.5.7. Thermal Stability Analysis
2.5.8. Solubility Analysis
2.5.9. Surface Hydrophobicity Analysis
2.5.10. Surface Free Sulfhydryl Content Analysis
2.5.11. Emulsifying Activity Index and Emulsifying Stability Index Analysis
2.5.12. Water Holding Capacity and Oil Binding Capacity Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index
3.2. Zeta Potential
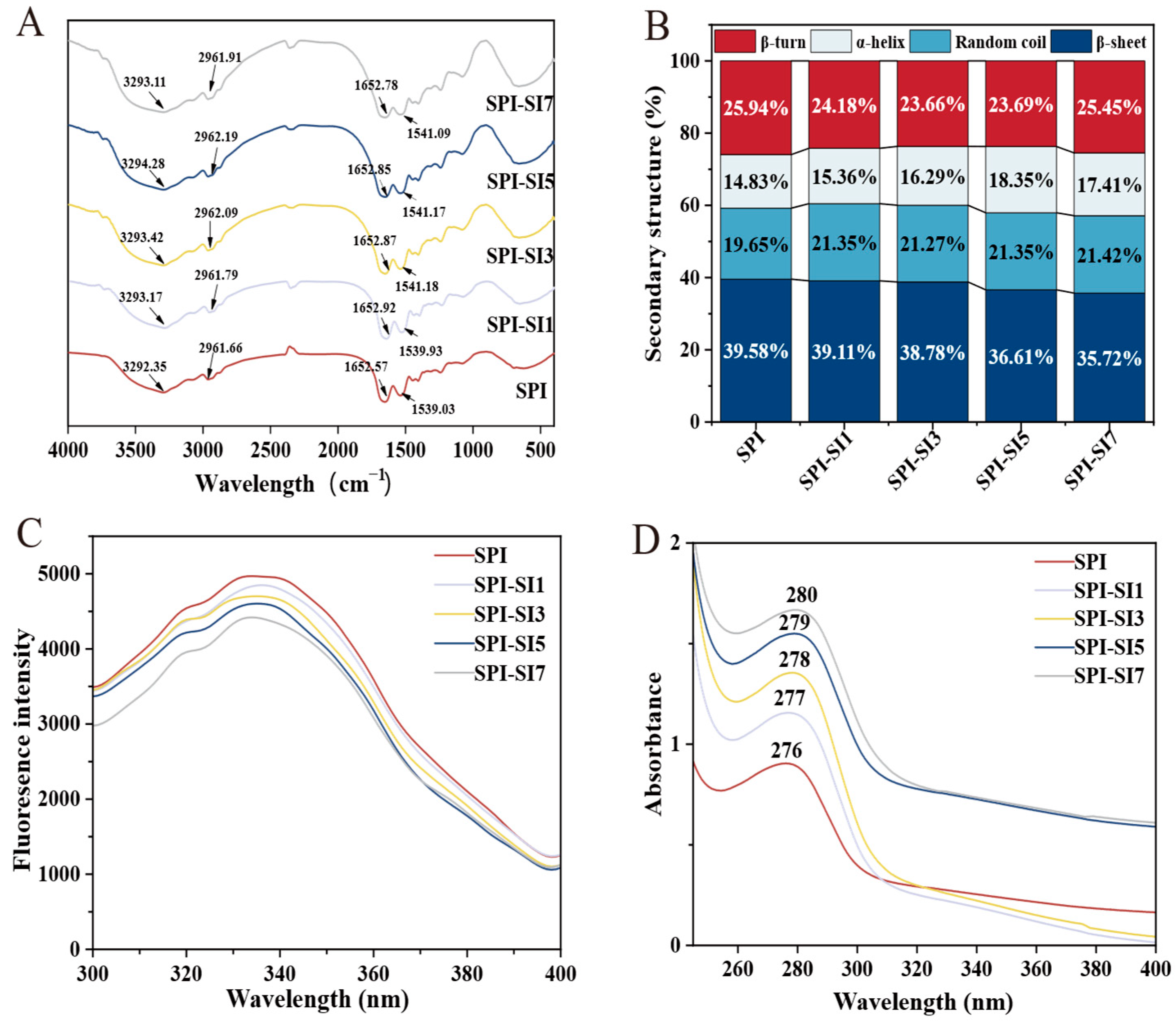
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.4. Fluorescence Spectra
3.5. Ultraviolet Spectra
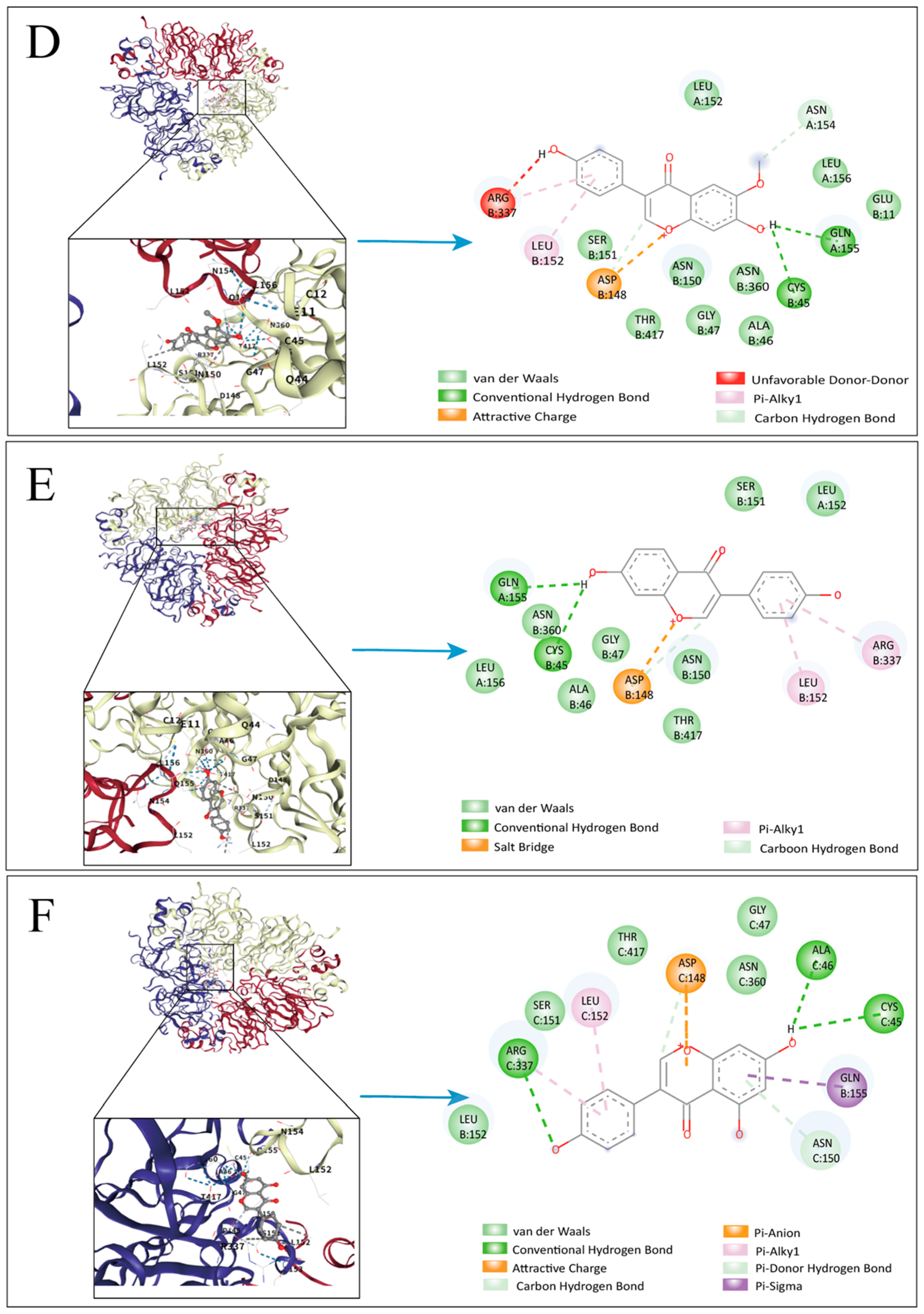
3.6. Molecular Docking
3.7. Atomic Force Microscopy Observation
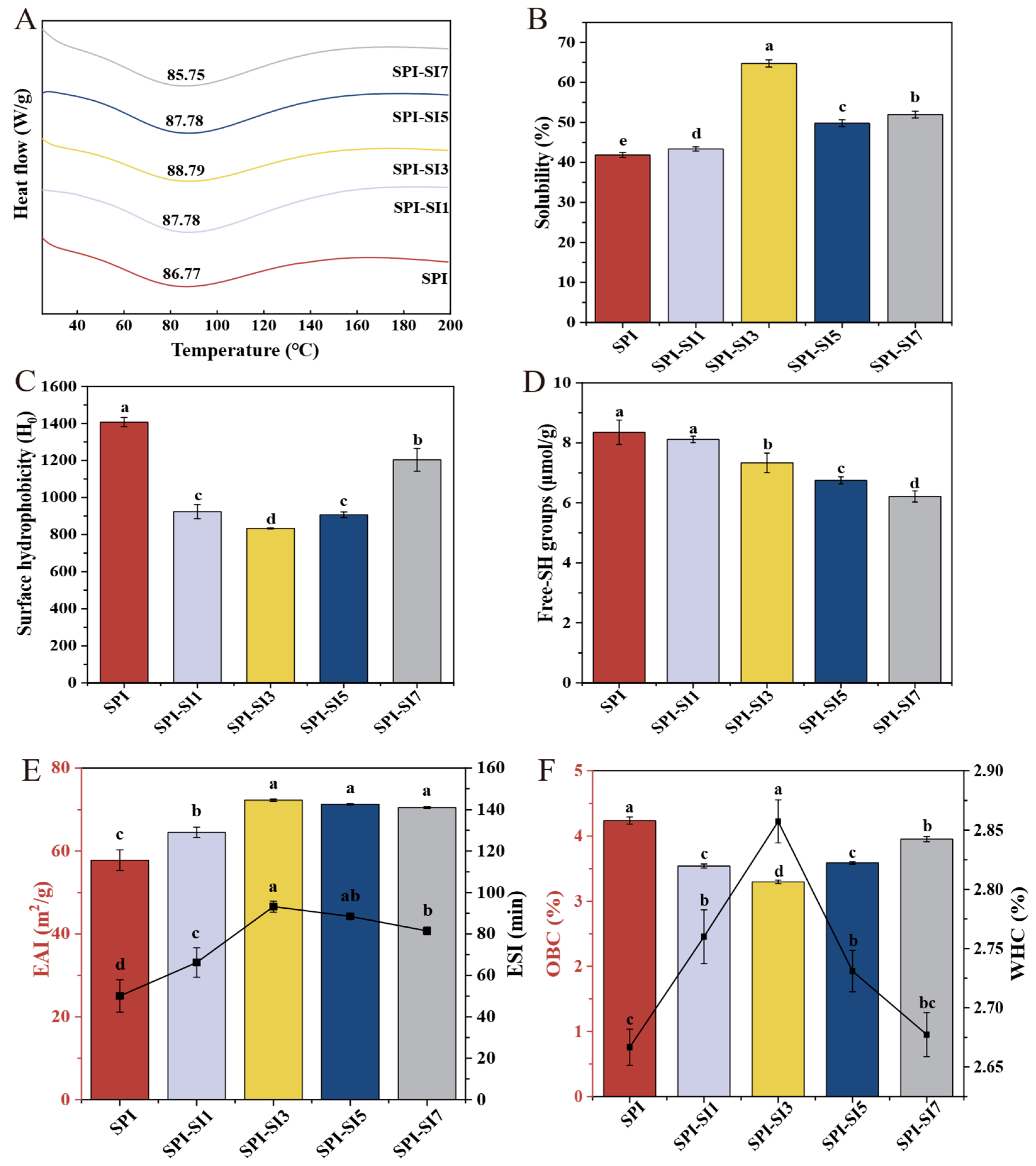
3.8. Thermal Stability
3.9. Solubility
3.10. Surface Hydrophobicity
3.11. Surface Free Sulfhydryl
3.12. Emulsifying Activity Index and Emulsifying Stability Index
3.13. Water Holding Capacity and Oil Binding Capacity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wójciak, M.; Drozdowski, P.; Skalska-Kamińska, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Ziemlewska, A.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Latalska, M. Protective, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Aging Effects of Soy Isoflavones on Skin Cells: An Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, R.H.; Sabreen, S.; Mohi-ud-din, R.; Wani, T.U.; Jaleel, A.; Jan, R.; Banday, N.; Maqbool, M.; Mohi-ud-din, I.; Mir, B.I.; et al. Isoflavones of Soy: Chemistry and Health Benefits. In Edible Plants in Health and Diseases: Volume 1: Cultural, Practical and Economic Value; Masoodi, M.H., Rehman, M.U., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.; Appukuttan, J.; Chandrapala, J.; Majzoobi, M. Impact of Conventional and Advanced Techniques on Stability of Natural Food Colourants. Foods 2025, 14, 3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, C.; Li, K.; Qin, W.; Wu, D.; Hu, B.; Yang, W.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Q. Influence of soybean protein isolate-dextran conjugates on the characteristics of glucono-δ-lactone-induced tofu. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 139, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; He, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Effect of ultrasonication on the stability and storage of a soy protein isolate-phosphatidylcholine nanoemulsions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuardi, A.U.P.; Yuliana, N.D.; Ogawa, M.; Akazawa, T.; Suhartono, M.T. Emulsifying properties and antioxidant activity of soy protein isolate conjugated with tea polyphenol extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3591–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Li, C. Conformational changes and functional properties of whey protein isolate-polyphenol complexes formed by non-covalent interaction. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 129622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.M.; Jun, S.; Li, Q.X.; Wall, M.M.; Ho, K.K.H.Y. Formation and physical characterization of soy protein-isoflavone dispersions and emulsions. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 176, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lin, W.; Yang, X.; Bao, Z. Complexation of soy protein microgels and isoflavones: Implication in modulating bioavailability. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 18, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Barnes, S.; Setchell, K.D.R. Perspective: Isoflavones—Intriguing Molecules but Much Remains to Be Learned about These Soybean Constituents. Adv. Nutr. 2025, 16, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Kuang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Huang, T.; Li, J. Construction of faba bean protein isolate delivery vector based on pH-driven technology: Formation mechanism, structural characterization, and delivery potential. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhou, C.; Yang, S.; Hong, J.; Xie, A.; Cui, Q. Green development of whey protein-based complex system for the intestinal delivery of curcumin: Focus on formation mechanism, stability, and in vitro digestive characteristics. Food Chem. X 2025, 28, 102563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Qin, Q.; Jiao, X.; Meng, G.; Liu, W.; Li, G. pH-driven preparation of pea protein isolate-curcumin nanoparticles effectively enhances antitumor activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astawan, M.; Prayudani, A.P. The overview of food technology to process soy protein isolate and its application toward food industry. World Nutr. J. 2020, 4, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, B.; Hung, Y.; Su, N. Isolation of individual isoflavone species from soybean by solvent extraction followed by the combination of macroporous resin and aluminium oxide separation. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migues, V.H.; David, J.M.; Gomes, A.F.; David, J.P. Determination of soybean isoflavone by HPLC/DAD and simple UV spectroscopic analysis: A comparative study. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xia, N.; Liu, Y.; Hua, S.; Tan, G. Enhancing encapsulation of curcumin by pH-driven and sodium alginate blending with ovalbumin as a carrier. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Yang, T.; Gao, B.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Fan, F. Effect of cold plasma treatment time on walnut protein isolate: Revealing structural changes and improving functional properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311, 143693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisaidoobe, A.B.; Chung, S.J. Intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence in the detection and analysis of proteins: A focus on Förster resonance energy transfer techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22518–22538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Yu, Y.; Yu, D.; Xu, S.; Wang, L. Study of soybean protein isolate-tannic acid non-covalent complexes by multi-spectroscopic analysis, molecular docking, and interfacial adsorption kinetics. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durowoju, I.B.; Bhandal, K.S.; Hu, J.; Carpick, B.; Kirkitadze, M. Differential scanning calorimetry—A method for assessing the thermal stability and conformation of protein antigen. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 55262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregi, P.; Guo, Y.; Adeloye, J.B. Whey proteins-polyphenols interactions can be exploited to reduce astringency or increase solubility and stability of bioactives in foods. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz Torres, L.F.; Rodríguez Celestino, V.; Centeno Leija, S.; Serrano Posada, H.; Ceballos Magaña, S.G.; Aguilar Padilla, J.; Mancilla Margalli, N.A.; Osuna Castro, J.A. Development of a rapid, high-sensitivity, low-cost fluorescence method for protein surface hydrophobicity determination using a Nanodrop fluorospectrometer. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, C.; Guo, M. Effects of high intensity ultrasound on acid-induced gelation properties of whey protein gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liang, G.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Gao, D.; Qin, F.; Goff, H.D.; Chen, J. Impact of soy proteins, hydrolysates and monoglycerides at the oil/water interface in emulsions on interfacial properties and emulsion stability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbut, S. Measuring water holding capacity in poultry meat. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Liao, P.; Wang, Y.; Tian, T.; Tong, X.; Lyu, B.; Cheng, L.; Miao, L.; Qi, W.; Jiang, L. Soy protein isolate-catechin non-covalent and covalent complexes: Focus on structure, aggregation, stability and in vitro digestion characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Guo, M. Interactions between β-lactoglobulin and 3, 3′-diindolylmethane in model system. Molecules 2019, 24, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Fu, Y.; Man, H.; Yan, X.; Huang, Y.; Sun, S.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Comparative study of binding interactions between different dietary flavonoids and soybean β-conglycinin and glycinin: Impact on structure and function of the proteins. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Zeng, X.-A.; Waseem, M.; Siddique, R.; Javed, M.R.; Verma, D.K.; Ali, M. Soy protein-polyphenols conjugates interaction mechanism, characterization, techno-functional and biological properties: An updated review. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Dou, B.; Zhang, X. Effect of MTGase conditions on surface hydrophobicity, functional properties and solution properties of soybean 7 S globulin and correlation analysis of its indexes. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sui, X.; Jiang, L. Relationship between surface hydrophobicity and zeta potential as well as particle size distribution of soybean protein isolates from different varieties. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Fan, F.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y. Interactions of black and green tea polyphenols with whole milk. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, F. Preparation and Properties of Walnut Protein Isolate–Whey Protein Isolate Nanoparticles Stabilizing High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions. Foods 2024, 13, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonaro, M.; Maselli, P.; Nucara, A. Relationship between digestibility and secondary structure of raw and thermally treated legume proteins: A Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic study. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, G.; Cao, W.; Li, J.; Taha, A.; Hu, H.; Pan, S. Interaction between pH-shifted β-conglycinin and flavonoids hesperetin/hesperidin: Characterization of nanocomplexes and binding mechanism. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 140, 110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dai, T.; Hu, P.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Li, T. Characterization the non-covalent interactions between beta lactoglobulin and selected phenolic acids. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Wohlers, A.; Kuhnert, N. Promiscuity in Polyphenol–Protein Interactions—Monitoring Protein Conformational Change upon Polyphenol–Protein Binding by Nano-Differential Fluorimetry (Nano-DSF). Molecules 2025, 30, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Bai, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, B. Interaction mechanism of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) seed protein and flavonoids: Fluorescent and 3D-QSAR studies. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 101023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, T.; Feng, W.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Yi, D. Novel protein hydrocolloids constructed by hydrophobic rice proteins and walnut proteins as loading platforms for nutraceutical models. Food Biophys. 2021, 16, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Rodrigues, F.H.; Delgado, G.G.; da Costa, T.S.; Tasic, L. Applications of fluorescence spectroscopy in protein conformational changes and intermolecular contacts. BBA Adv. 2023, 3, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, A.; Song, Y.; Zhao, J. Virtual Screening of Soybean Protein Isolate-Binding Phytochemicals and Interaction Characterization. Foods 2023, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, B. Ultrasound-assisted preparation of protein–polyphenol conjugates and their structural and functional characteristics. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 100, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, G.V.; Balakrishnan, G.; Chennamsetty, N.; Hoffman, L.; Bongers, J.; Tao, L.; Huang, Y.; Slaney, T.; Das, T.K.; Leone, A. Probing the tryptophan environment in therapeutic proteins: Implications for higher order structure on tryptophan oxidation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1944–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Spectroscopic and computational evaluation on the binding of safranal with human serum albumin: Role of inner filter effect in fluorescence spectral correction. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 203, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Xiong, L.; Yang, F. Effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the functional and structural properties of soybean protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, M.; Ejaz, S.A.; Tamam, N.; Siddique, F.; Riaz, N.; Qais, F.A.; Chtita, S.; Iqbal, J. Identification of potent inhibitors of NEK7 protein using a comprehensive computational approach. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahi, M.; Gharagozlou, M.; Niakousari, M.; Hedayati, S. Protein–Chlorogenic Acid Interactions: Mechanisms, Characteristics, and Potential Food Applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X. Study of the binding mechanism between hydroxytyrosol and bovine serum albumin using multispectral and molecular docking. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, Y.; Takehira, M.; Joti, Y.; Ogasahara, K.; Tanaka, T.; Ono, N.; Kunishima, N.; Yutani, K. Thermodynamics of protein denaturation at temperatures over 100 C: CutA1 mutant proteins substituted with hydrophobic and charged residues. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Han, M.; Huang, M.; Xu, X. Enhanced heat stability and antioxidant activity of myofibrillar protein-dextran conjugate by the covalent adduction of polyphenols. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Pu, M.; He, S.; Ninan, N.; Cheng, M. pH-regulated preparation and structural characterization of non-covalent complexes of soybean isolate proteins with different charged polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 298, 140004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Awana, M.; Rani, K.; Kumari, S.; Sasi, M.; Dahuja, A. Soybean (Glycine max) isoflavone conjugate hydrolysing β-glucosidase (Gm ICHG): A promising candidate for soy isoflavone bioavailability enhancement. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xie, F.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, L.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Effects of soybean protein isolate-polyphenol conjugate formation on the protein structure and emulsifying properties: Protein-polyphenol emulsification performance in the presence of chitosan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 609, 125641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Lou, M.; Meng, F.; Jin, H.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L. Development and characteristics of emulsion gels with microwave-assisted ferulic acid covalently modified soy protein: Structure, function and digestive properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, X.-Q. Foaming properties and air–water interfacial behavior of corn protein hydrolyzate–tannic acid complexes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Xing, K.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Elfalleh, W.; Cheng, J.; Yu, D. Combining multi–spectroscopy analysis and interfacial properties to research the effect of ultrasonic treatment on soybean protein isolate–tannic acid complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Zhu, G.; Huang, G.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. A novel pickering emulsion produced using soy protein-anthocyanin complex nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, L. Noncovalent interaction between proanthocyanidins and soy protein isolate fibers: Structure, functionality and interaction mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 160, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Sun, J.; Pei, M.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; He, S.; Liu, L. Impact of non-covalent bound polyphenols on conformational, functional properties and in vitro digestibility of pea protein. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Yang, S.; Dai, S.; Tong, X.; Liao, P.; Cheng, L.; Qi, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Relationship between flexibility and interfacial functional properties of soy protein isolate: Succinylation modification. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6454–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Z.; Su, R.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Dual modification of soy protein isolate by phlorotannins and enzymatic hydrolysis: Stability and digestive properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.S.; Nickerson, M.T. Food proteins: A review on their emulsifying properties using a structure–function approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ban, Q.; Wang, X. Enhancing the stability of oil-in-water emulsions by non-covalent interaction between whey protein isolate and hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalesi, M.; Dowling, S.; Comerford, J.; Sweeney, C.; Esteghlal, S.; FitzGerald, R.J. Emulsification Properties of Plant and Milk Protein Concentrate Blends. Foods 2025, 14, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, W.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Ahmad, R.; Kim, K.; Kim, H. Enhancement of Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Chicken Breast Protein Through Polyphenol Conjugation: A Novel Ingredient for Protein Supplements. Molecules 2025, 30, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ritzoulis, C.; Du, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. Recent progress on protein-polyphenol complexes: Effect on stability and nutrients delivery of oil-in-water emulsion system. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 765589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Bi, X.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, D.; Peng, X.; Jia, N.; Liu, D. Catechins affect the oil-holding capacity of meat batters by changing the structure and emulsifying properties of surface proteins at the fat globules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Fan, F. The Influence of pH-Driven Interaction Between Soy Protein Isolate and Soy Isoflavones on the Structural and Functional Properties of Their Complexes. Foods 2025, 14, 3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223951
Yang J, Lu Y, Deng Y, Yang J, Guo L, Fan F. The Influence of pH-Driven Interaction Between Soy Protein Isolate and Soy Isoflavones on the Structural and Functional Properties of Their Complexes. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223951
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jing, Yanling Lu, Yanmei Deng, Jiaojiao Yang, Lei Guo, and Fangyu Fan. 2025. "The Influence of pH-Driven Interaction Between Soy Protein Isolate and Soy Isoflavones on the Structural and Functional Properties of Their Complexes" Foods 14, no. 22: 3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223951
APA StyleYang, J., Lu, Y., Deng, Y., Yang, J., Guo, L., & Fan, F. (2025). The Influence of pH-Driven Interaction Between Soy Protein Isolate and Soy Isoflavones on the Structural and Functional Properties of Their Complexes. Foods, 14(22), 3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223951





