Organic Acid-Induced Structural Modifications Improve Melt-Stretch Properties and Mouthfeel of Plant-Based Cheese Alternatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Zein-Based Cheese Formulation
2.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) Imaging
2.4. Small Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS) Determination
2.5. Fourier Transforms Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Determination
2.6. Moisture, Color, Water-Holding Capacity (WHC), and Free Oil Release
2.7. Analysis of Stretchability
2.8. Rheological Determination
2.9. Measurement of Friction Behavior
2.10. Texture Profile Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Zein-Based Cheese
3.1.1. Effect of Organic Acids on the Morphology of Zein-Based Cheese
3.1.2. Effect of Organic Acids on Lamellar Features
3.1.3. Effect of Organic Acids on FTIR Spectra
3.2. Functional Properties of Zein-Based Cheese
3.2.1. Effect of Organic Acids on Moisture, Color, WHC, and Free Oil Release
3.2.2. Effect of Organic Acids on Stretchability
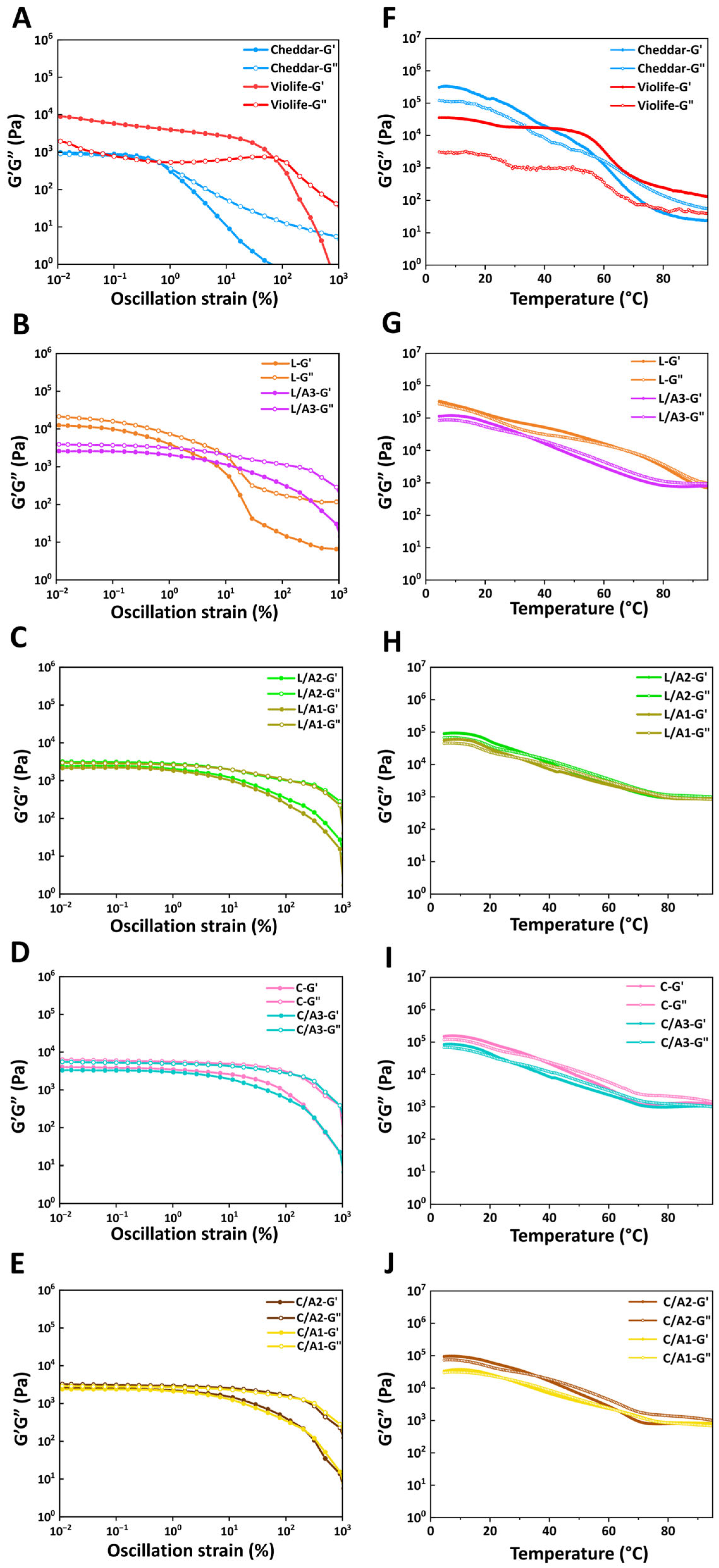
3.2.3. Effect of Organic Acids on Oscillatory Strain Sweeps
3.2.4. Effect of Organic Acids on Oscillatory Temperature Sweeps
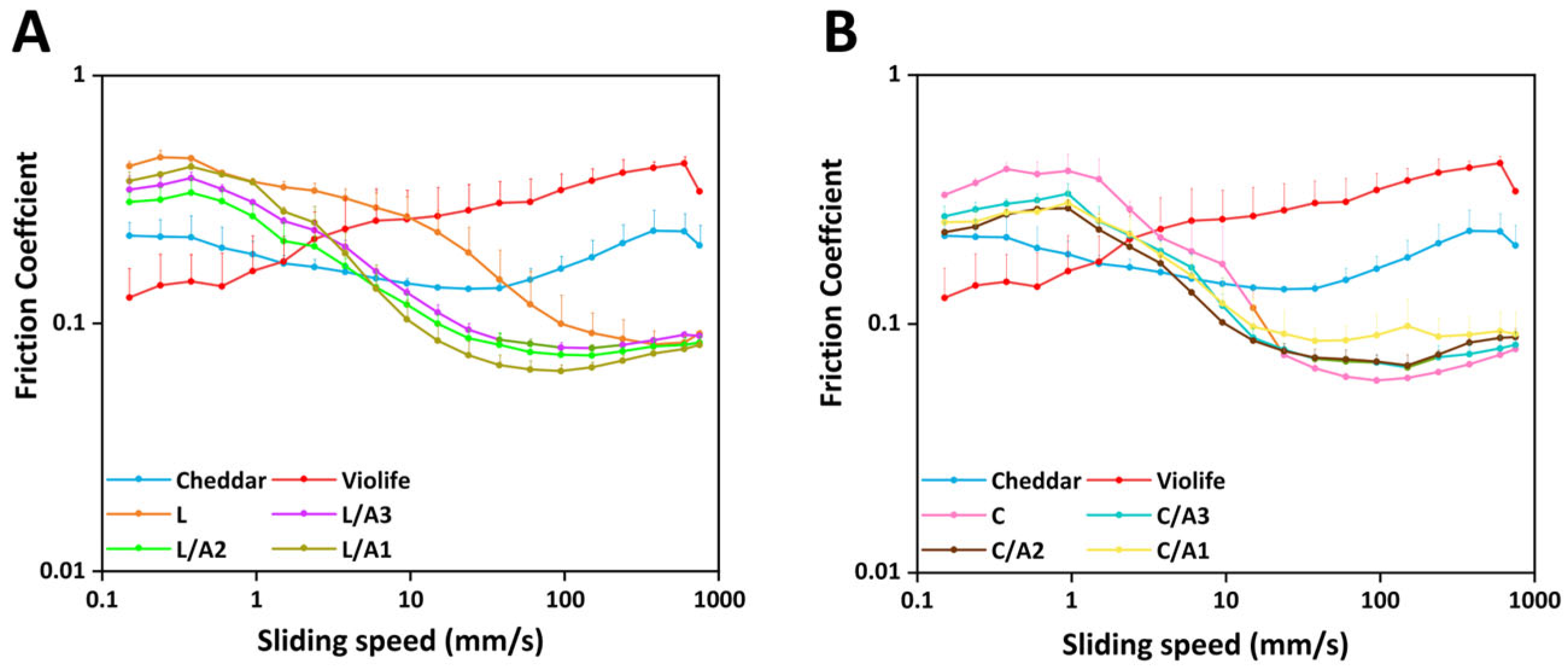
3.2.5. Effect of Organic Acids on Tribological Measurement
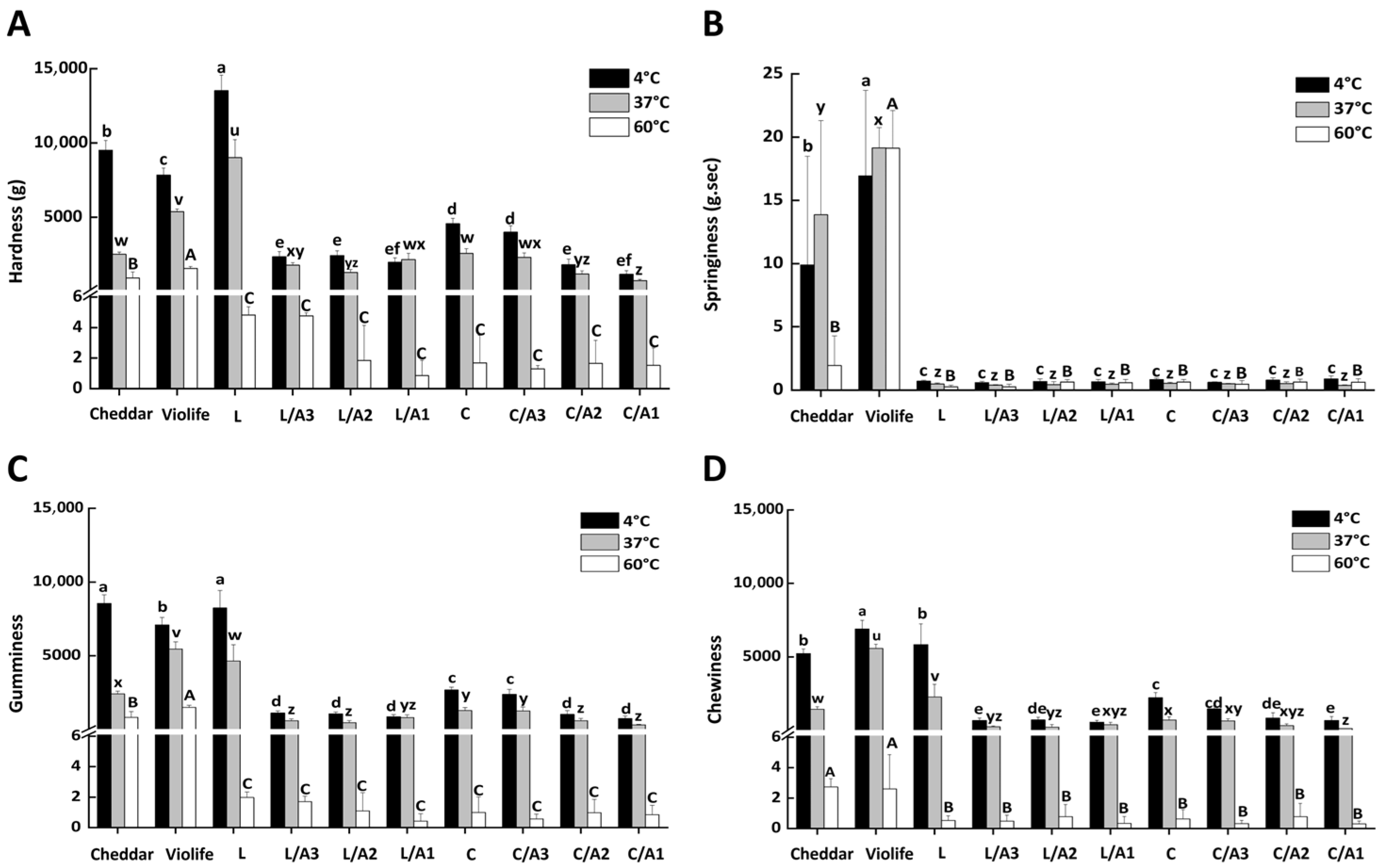
3.2.6. Effect of Organic Acids on Texture Qualities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HBG | Highland barley β-glucan |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| Dm | Mass fractal dimension |
| Ds | Surface fractal dimension |
References
- Grossmann, L.; McClements, D.J. The science of plant-based foods: Approaches to create nutritious and sustainable plant-based cheese analogs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, P.; Kelly, A.L.; Sheehan, J.J. Structure-function relationships in cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2692–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Luan, G. Application of zein in gluten-free foods: A comprehensive review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattice, K.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Evaluating the use of zein in structuring plant-based products. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, T.J.; Bean, S.R.; Boyle, D.L.; Park, S.-H. Improved viscoelastic zein-starch doughs for leavened gluten-free breads: Their rheology and microstructure. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattice, K.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Physical properties of plant-based cheese products produced with zein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, G.; Li, S.; Meng, Q.; Ye, F.; Chen, J.; Ming, J.; Zhao, G.; Lei, L. Replacement of fat with highland barley β-glucan in zein-based cheese: Structural, rheological, and textual properties. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sly, A.C.; Taylor, J.; Taylor, J.R.N. Improvement of zein dough characteristics using dilute organic acids. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattice, K.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Functionalizing zein through antisolvent precipitation from ethanol or acetic acid. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Q. Understanding the Dissolution of α-Zein in Aqueous Ethanol and Acetic Acid Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 12057–12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, B.L.; Taylor, J.; Taylor, J.R.N. Formation of a viscoelastic dough from isolated total zein (α-, β- and γ-zein) using a glacial acetic acid treatment. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 71, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Xu, M.; Hu, Y.; Luan, G. Effect of plasticizer and zein subunit on rheology and texture of zein network. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Government Publishing Office. 21 CFR 184.1061—Lactic Acid. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-B/part-184/subpart-B/section-184.1061/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- U.S. Government Publishing Office. 21 CFR 184.1033—Citric Acid. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-B/part-184/subpart-B/section-184.1033/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Wei, L.; Dou, M.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z. Characterization of zein-based films plasticized with deep eutectic solvents and their use in the preservation of harvested mango fruit. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Chiba, A.; Yarno, T. Interpretation of small angle X-ray scattering from starch on the basis of fractals. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 34, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5009.3-2016; Determination of Moisture Content in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Chailangka, A.; Leksawasdi, N.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Sommano, S.R.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Rachtanapun, P.; Castagnini, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Phimolsiripol, Y. Improving vitamin D stability and antioxidant activity in imitation mozzarella cheese by conjugated cricket protein with fructooligosaccharide. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 183, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, B.K.S.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S.; Bansal, N. Simulated oral processing, in vitro digestibility and sensory perception of low fat Cheddar cheese containing sodium alginate. J. Food Eng. 2020, 270, 109749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, N.; Roos, Y.H.; Crowley, S.V.; Arendt, E.K.; O’Mahony, J.A. Composition and physicochemical properties of commercial plant-based block-style products as alternatives to cheese. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Luan, G. Effect of zein subunit and plasticizer on rheology and adhesion properties of zein-based adhesives. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Cao, S.; Hu, Y.; Luan, G. Impacts of ethanol-plasticization and extrusion on development of zein network and structure of zein-starch dough. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhang, F.; Guo, W.; Yu, K.; Yang, C.; Qu, F. Multiple phase transitions and microstructural rearrangements shape milk fat crystal networks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamod, W.R.W.; Bakar, N.A.; Hashim, N.; Isnolamran, N.H.; Shamsudin, S.A.J.M.J. The effect of virgin coconut oil content on the rheological profile of virgin coconut oil-based lamellar liquid crystal of mixed Tween 80: BRIJ 30 System. Malays. J. Microsc. 2021, 17, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Junejo, S.A.; Zhang, B.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q. Multi-scale structures and physicochemical properties of waxy starches from different botanical origins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Pashalidis, I.; Theocharis, C.R. Discrimination of Cheese Products Regarding Milk Species’ Origin Using FTIR, 1H-NMR, and Chemometrics. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, F.J.; Gidley, M.J.; Flanagan, B.M. Infrared Spectroscopy as a Tool to Characterise Starch Ordered Structure—A Joint FTIR–ATR, NMR, XRD and DSC Study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 139, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Z.; Liang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q. Investigating on the Interaction Behavior of Soy Protein Hydrolysates/β-Glucan/Ferulic Acid Ternary Complexes under High-Technology in the Food Processing: High Pressure Homogenization versus Microwave Treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, W.; Wei, D.; Zhu, W.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y. High-elongation zein films for flexible packaging by synergistic plasticization: Preparation, structure and properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapis, S.; Bannikova, A. Chapter 2—Rheology and Food Microstructure. In Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications; Ahmed, J., Ptaszek, P., Basu, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 7–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, F.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Li, M. Lubricating properties of starch-soybean lecithin compound gels using tribology analysis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 207, 116409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cheddar | Violife | L | L/A3 | L/A2 | L/A1 | C | C/A3 | C/A2 | C/A1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | −1.57 ± −0.08 | −1.86 ± 0.00 | −1.58 ± 0.04 | −1.48 ± −0.13 | −1.24 ± −0.06 | −1.38 ± −0.26 | −1.16 ± 0.02 | −1.16 ± 0.00 | −1.22 ± 0.01 | −1.24 ± 0.04 |
| Dm (nm) | 1.57 ± 0.08 | 1.86 ± 0.00 | 1.58 ± 0.04 | 1.48 ± 0.13 | 1.24 ± 0.06 | 1.38 ± 0.26 | 1.16 ± 0.02 | 1.16 ± 0.00 | 1.22 ± 0.01 | 1.24 ± 0.04 |
| L* | 72.8 ± 0.5 b | 81.2 ± 0.1 a | 64.0 ± 3.2 c | 57.3 ± 1.2 de | 58.3 ± 0.6 d | 58.9 ± 0.8 d | 55.1 ± 1.2 e | 44.5 ± 1.2 g | 50.5 ± 0.8 f | 43.8 ± 1.9 g |
| a* | 2.2 ± 0.2 e | 4.9 ± 0.1 d | 8.7 ± 1.3 abc | 7.3 ± 2.2 c | 7.6 ± 0.4b c | 8.0 ± 0.5 abc | 9.4 ± 0.9 a | 9.2 ± 0.3 ab | 9.7 ± 0.5 a | 10.0 ± 0.4 a |
| b* | 24.4 ± 0.3 e | 25.9 ± 0.1 de | 38.0 ± 3.0 ab | 33.4 ± 8.3 bc | 40.2 ± 0.6 a | 31.6 ± 3.3 cd | 40.9 ± 1.4 a | 33.4 ± 2.6 bc | 37.4 ± 0.9 abc | 31.4 ± 2.1 cd |
| WHC (%) | 97.8 ± 3.7 a | 93.3 ± 2.8 b | 99.7 ± 0.1 a | 97.0 ± 4.6 ab | 99.7 ± 0.1 a | 99.7 ± 0.0 a | 99.4 ± 0.2 a | 99.6 ± 0.3 a | 99.5 ± 0.2 a | 99.6 ± 0.4 a |
| FOR (cm2) | 32.1 ± 1.0 a | 5.2 ± 0.8 d | 11.9 ± 32.3 b | 7.3 ± 0.5 c | 7.6 ± 0.6 c | 7.2 ± 0.2 c | 5.3 ± 0.2 d | 4.2 ± 0.4 d | 4.0 ± 0.6 d | 3.6 ± 0.2 d |
| Stretch (cm) | 26.2 ± 2.9 b | 2.5 ± 0.4 e | 9.0 ± 2.3 d | 16.5 ± 1.6 c | 19.5 ± 3.0 c | 10.2 ± 1.5 d | 35.2 ± 5.8 a | 22.8 ± 1.8 b | 9.4 ± 1.6 d | 7.5 ± 1.8 d |
| Secondary Structure (%) | Zein | L | L/A3 | L/A2 | L/A1 | C | C/A3 | C/A2 | C/A1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very low-frequency β-sheet | 10.9 ± 0.0 b | 35.3 ± 3.8 a | 12.9 ± 0.1 b | 6.6 ± 0.7 c | 10.1 ± 1.1 b | 11.4 ± 0.1 b | 13.0 ± 2.7 b | 11.1 ± 0.1 b | 10.6 ± 0.0 b |
| Low-frequency β-sheet | 22.4 ± 0.2 de | 39.1 ± 1.7 a | 14.3 ± 0.6 f | 20.6 ± 0.1 e | 24.2 ± 0.8 cd | 26.9 ± 0.9 b | 27.8 ± 2.3 b | 26.7 ± 0.0 b | 26.1 ± 0.3 bc |
| Random coil | 29.3 ± 0.1 d | 33.5 ± 1.2 c | 38.4 ± 0.8 a | 35.4 ± 0.7 bc | 33.7 ± 0.7 c | 36.5 ± 0.1 ab | 35.5 ± 2.9 bc | 35.8 ± 0.0 bc | 35.1 ± 0.4 bc |
| α-helix structure | 26.5 ± 0.3 d | 20.1 ± 1.2 e | 34.3 ± 1.9 a | 31.0 ± 0.3 b | 29.7 ± 0.8 bc | — | — | 29.0 ± 0.1 c | 28.9 ± 0.3 c |
| β-Turn | 15.0 ± 0.1 b | 7.3 ± 1.7 d | 13.1 ± 0.5 c | 13.0 ± 0.3 c | 12.4 ± 0.8 c | 27.4 ± 1.2 a | 26.6 ± 1.0 a | — | — |
| High-frequency β-sheet | 6.7 ± 0.1 c | — | — | — | — | 9.1 ± 0.2 b | 10.1 ± 0.6 a | 8.9 ± 0.0 b | 9.9 ± 0.4 a |
| Ordered conformation | 55.6 ± 0.1 c | 59.2 ± 0.5 b | 48.5 ± 1.4 e | 51.6 ± 0.4 d | 53.9 ± 0.3 c | 36.0 ± 1.0 f | 37.9 ± 2.2 f | 64.6 ± 0.0 a | 64.8 ± 0.4 a |
| Disordered conformation | 44.4 ± 0.1 d | 40.8 ± 0.5 e | 51.4 ± 1.4 b | 48.4 ± 0.4 c | 46.1 ± 0.3 d | 64.0 ± 1.0 a | 62.1 ± 2.2 a | 35.4 ± 0.0 f | 35.1 ± 0.4 f |
| Various Samples | v1 (mm/s) | f1 |
|---|---|---|
| Cheddar | 0.38 | 0.22 ± 0.05 |
| Violife | 597.16 | 0.44 ± 0.03 |
| L | 0.38 | 0.46 ± 0.00 |
| L/A3 | 0.38 | 0.38 ± 0.02 |
| L/A2 | 0.38 | 0.34 ± 0.05 |
| L/A1 | 0.38 | 0.43 ± 0.02 |
| C | 0.95 | 0.41 ± 0.07 |
| C/A3 | 0.95 | 0.33 ± 0.03 |
| C/A2 | 0.95 | 0.29 ± 0.02 |
| C/A1 | 0.95 | 0.31 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Ye, F.; Fang, C.; Lei, L. Organic Acid-Induced Structural Modifications Improve Melt-Stretch Properties and Mouthfeel of Plant-Based Cheese Alternatives. Foods 2025, 14, 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213724
Xu C, Liu L, Liu J, Ye F, Fang C, Lei L. Organic Acid-Induced Structural Modifications Improve Melt-Stretch Properties and Mouthfeel of Plant-Based Cheese Alternatives. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213724
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Can, Lijun Liu, Jia Liu, Fayin Ye, Cuilan Fang, and Lin Lei. 2025. "Organic Acid-Induced Structural Modifications Improve Melt-Stretch Properties and Mouthfeel of Plant-Based Cheese Alternatives" Foods 14, no. 21: 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213724
APA StyleXu, C., Liu, L., Liu, J., Ye, F., Fang, C., & Lei, L. (2025). Organic Acid-Induced Structural Modifications Improve Melt-Stretch Properties and Mouthfeel of Plant-Based Cheese Alternatives. Foods, 14(21), 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213724







