A Comprehensive Study of Meat Quality and Flavor Characteristics of Different Sexes of Yanbian Yellow Cattle Using GC-IMS and LC-MS/MS Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Moisture, Protein, Fat, Meat Color, and Shear Force
2.3. Fatty Acids
2.4. Determination of Amino Acids
2.5. Volatile Flavor Compounds (VOCs)
2.5.1. E-Nose
2.5.2. GC-IMS
2.5.3. Relative Odor Activity Value
2.6. Metabolite Extraction and LC-MS/MS Detection
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Moisture, Protein, Fat, Meat Color, and Shear Force Analysis
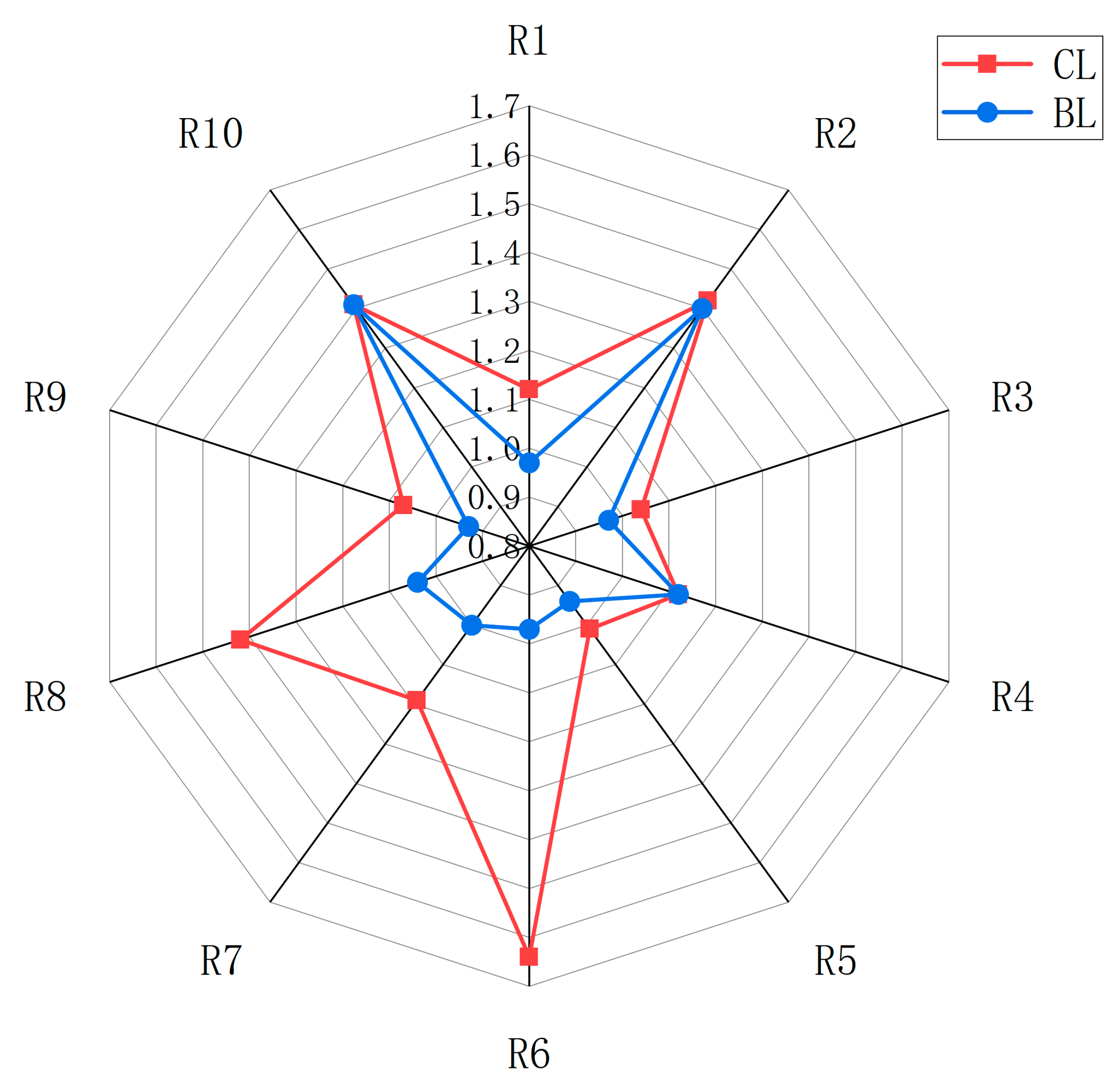
3.2. Fatty Acids and Amino Acids
3.3. E-Nose
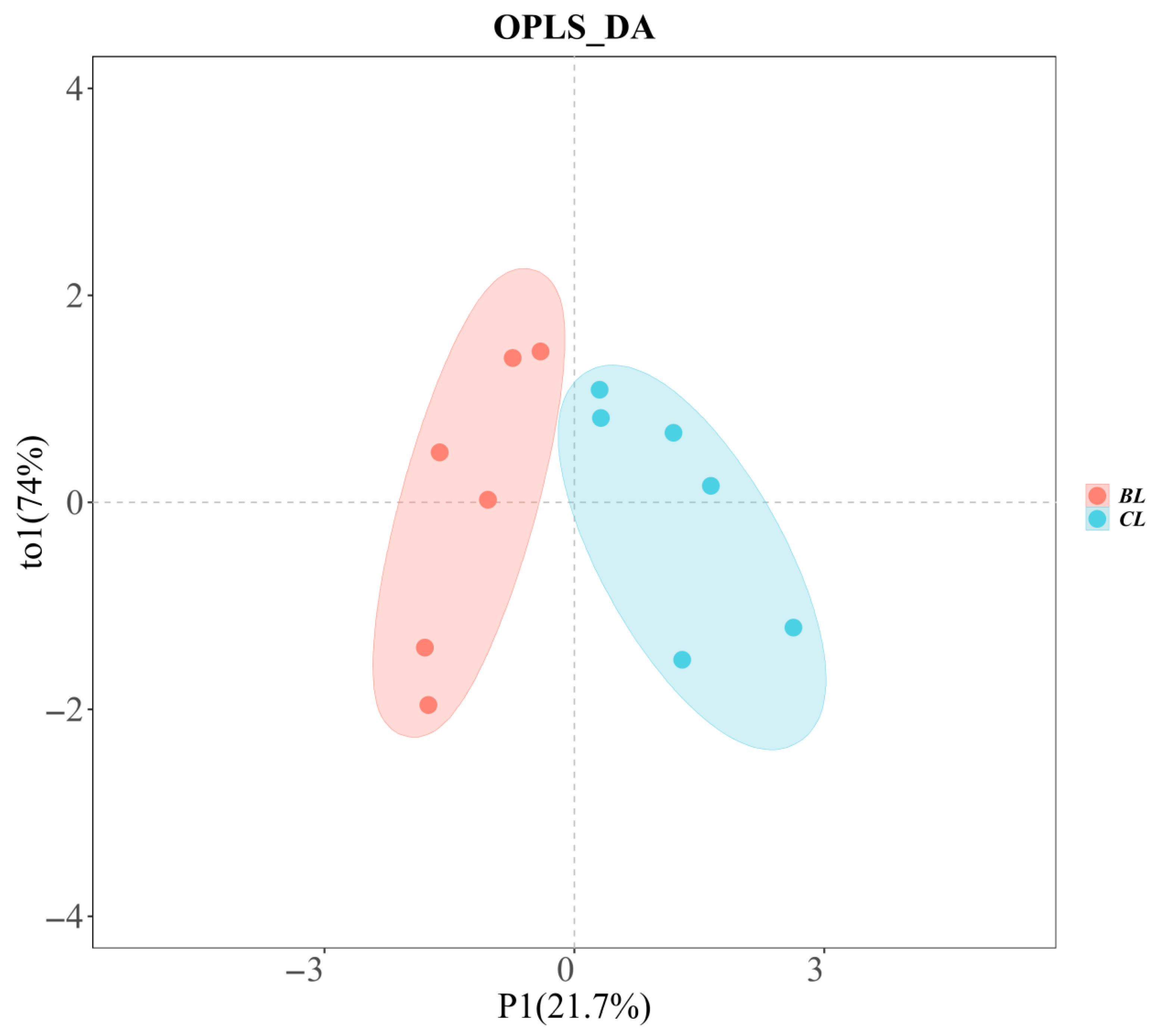
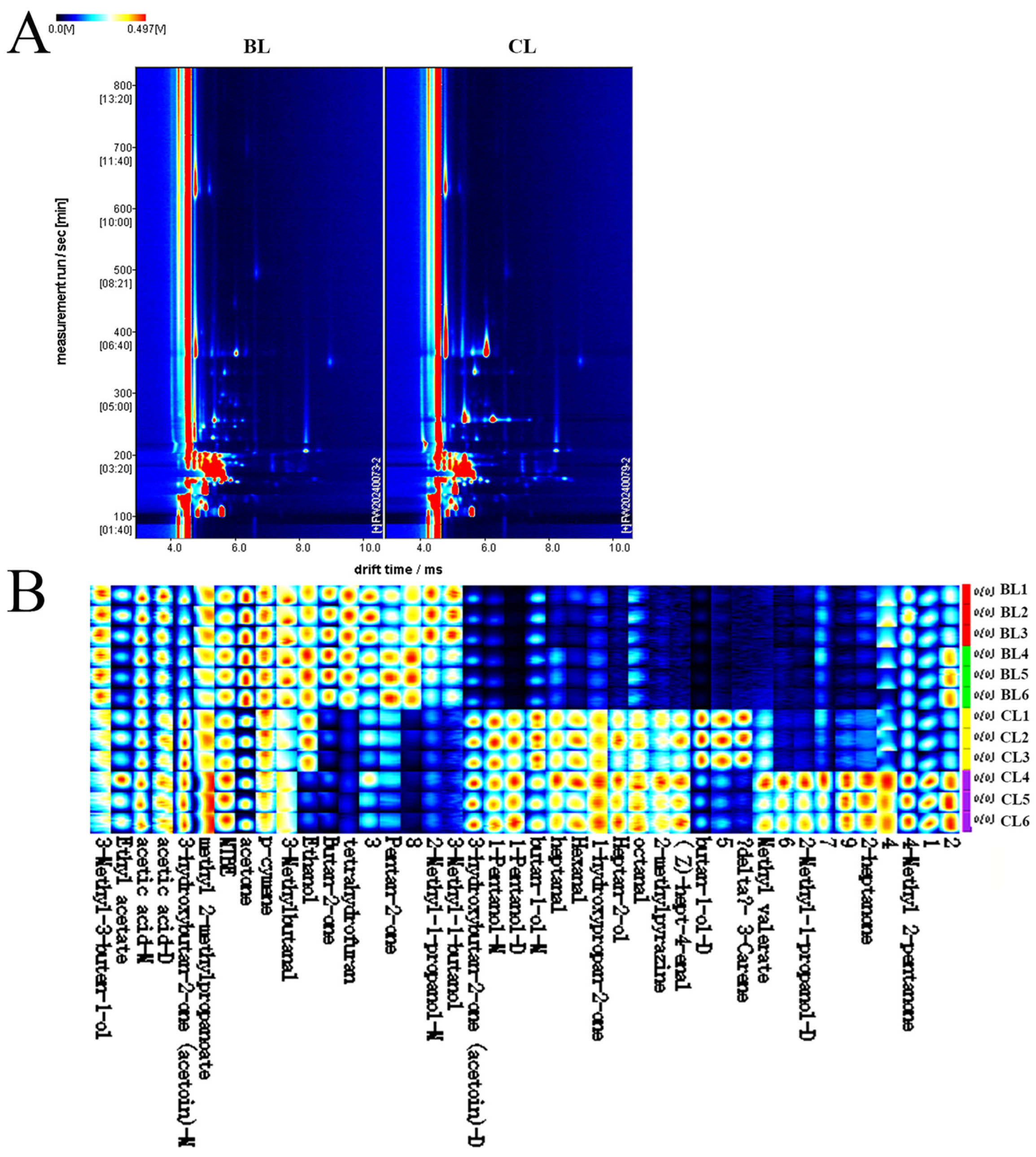
3.4. GC-IMS
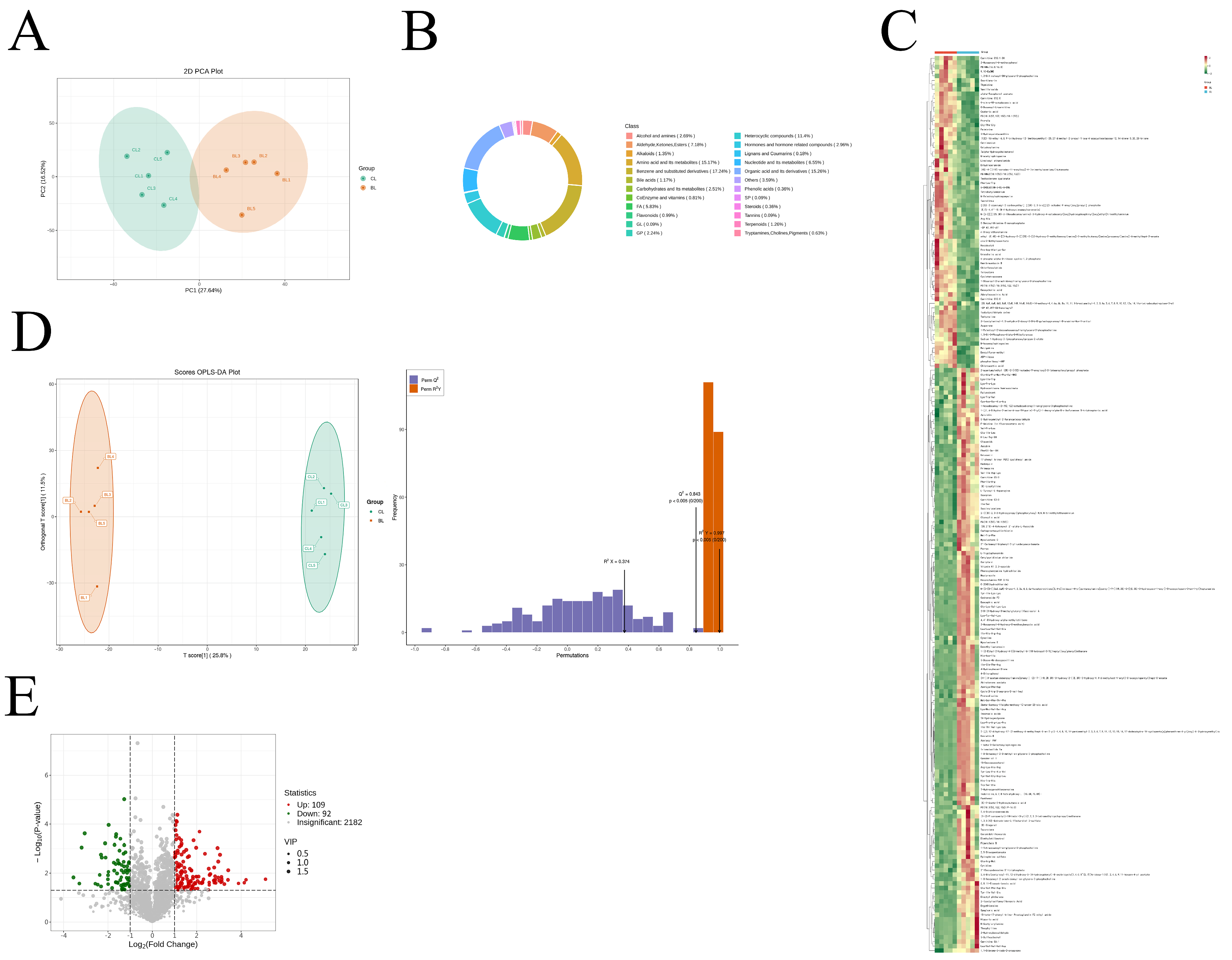
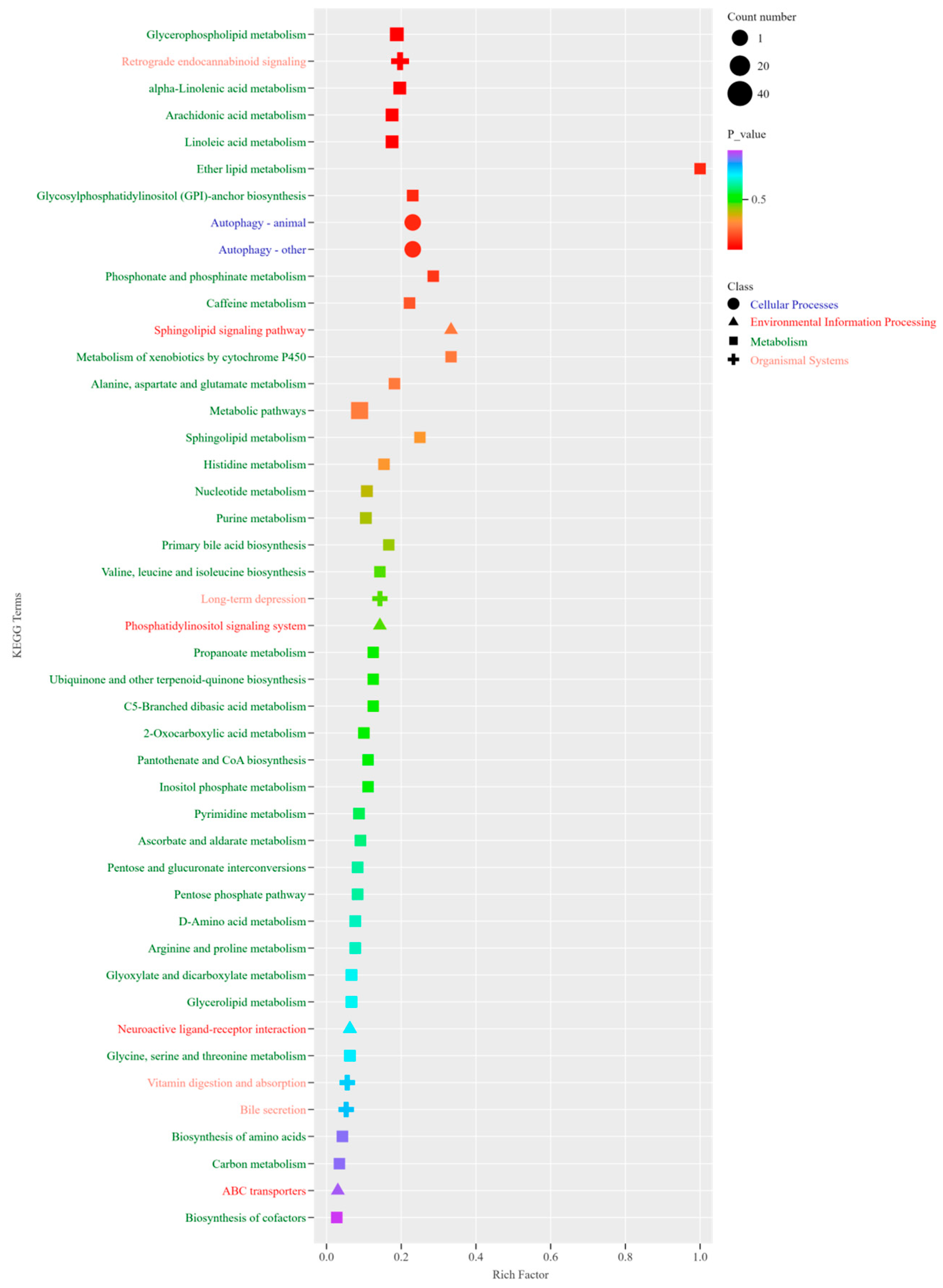
3.5. Metabolite Composition of Yanbian Yellow Cattle of Different Sexes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BL | Bull |
| CL | Cow |
References
- Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Han, Y.; Xu, L.; Jin, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, H. Analysis of volatile compounds between raw and cooked beef by HS-SPME–GC–MS. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wang, Y.; Piao, S.; Piao, X.; Piao, H.; Li, W. Study on the Quality Characteristics of Beef of Yanbian Yellow Cattle. China Cattle Sci. 2004, 30, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Bai, J.; Song, J.; Hao, B.; Zhang, L.; Xia, G. Effects of Vitamin A on Yanbian Yellow Cattle and Their Preadipocytes by Activating AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Intestinal Microflora. Animals 2022, 12, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Qu, K.; Lyv, S.; Wang, X.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, E.; Xie, J.; et al. The Association of the Copy Number Variation of the MLLT10 Gene with Growth Traits of Chinese Cattle. Animals 2020, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z. Metabolomic comparison of meat quality and metabolites of geese breast muscle at different ages. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y. Effects of Age and Sex on Fattening and Meat Quality of House-Feeding Yaks. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Minzu University, Sichuan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cafferky, J.; Hamill, R.M.; Allen, P.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Cromie, A.; Sweeney, T. Effect of Breed and Gender on Meat Quality of M. longissimus thoracis et lumborum Muscle from Crossbred Beef Bulls and Steers. Foods 2019, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Deng, S.; Wang, X. Research progress on influence factors of mutton flavor. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2016, 43, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Zhan, J.; Tang, X.; Li, T.; Duan, S. Characterization and identificationof pork flavor compounds and their precursors in Chinese indigenous pig breeds byvolatile profiling and multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaslyng, M.D.; Meinert, L. Meat flavour in pork and beef—From animal tomeal. Meat Sci. 2017, 132, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleicher, J.; Ebner, E.E.; Bak, K.H. Formation and analysis of volatile and odorcompounds in meat-a review. Molecules 2022, 27, 6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.T.N.; Legako, J.F.; Miller, M.F.; Brooks, J.C. Effects of USDA quality grade and cooking on water-soluble precursors of beef flavor. Meat Sci. 2018, 146, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zou, Y.; Liao, G.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G. Identification of characteristic flavor compounds and small molecule metabolites during the ripening process of Nuodeng ham by GC-IMS, GC–MS combined with metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moufid, M.; Hofmann, M.; El Bari, N.; Tiebe, C.; Bartholmai, M.; Bouchikhi, B. Wastewater monitoring by means of e-nose, VE-tongue, TD-GC-MS, and SPME-GC-MS. Talanta 2021, 221, 121450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Liu, Z.; Su, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F. Comparison of muscle fiber characteristics and meat quality between newborn and adult Haimen goats. Meat Sci. 2024, 207, 109361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ning, F.; Zhao, L.; Ming, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, W.; Yi, S.; Luo, L. Quality assessment of royal jelly based on physicochemical properties and flavor profiles using HS-SPME-GC/MS combined with electronic nose and electronic tongue analyses. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Tong, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, M.; Lin, Z.; Cai, S.; Chen, Y.; Mo, D. Characterization of different meat flavor compounds in Guangdong small-ear spotted and Yorkshire pork using two-dimensional gas chromatography–time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multi-omics. LWT 2022, 169, 114010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.3-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Moisture in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.5-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Protein in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.6-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Fat in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Dai, Z.; Feng, M.; Feng, C.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.; Guo, B.; Yan, L. Effects of sex on meat quality traits, amino acid and fatty acid compositions, and plasma metabolome profiles in White King squabs. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilertsen, K.-E.; Mhre, H.K.; Jensen, I.J.; Devold, H.; Olsen, J.O.; Lie, R.K.; Brox, J.; Berg, V.; Elvevoll, E.O.; Sterud, B.; et al. A Wax Ester and Astaxanthin-Rich Extract from the Marine Copepod Calanus finmarchicus Attenuates Atherogenesis in Female Apolipoprotein EDeficient Mice3. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.124-2016; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Amino Acid in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Harlina, P.W.; Zhou, G.; Peng, Z. Sensory characteristics of low sodium dry-cured beef and their relation to odor intensity and electronic nose signals. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerth, C.R.; Legako, J.F.; Woerner, D.R.; Brooks, J.C.; Lancaster, J.M.; O’Quinn, T.G.; Nair, M.; Miller, R.K. A current review of U.S. beef flavor I: Measuring beef flavor. Meat Sci. 2024, 210, 109437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, L.; Antequera, T.; Ventanas, J.; Benítez-Donoso, R.; Córdoba, J.J. Free amino acids and other non-volatile compounds formed during processing of Iberian ham. Meat Sci. 2001, 59, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, H.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, G.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Yin, Y.; Xu, K. Comprehensive characterization of the differences in metabolites, lipids, and volatile flavor compounds between Ningxiang and Berkshire pigs using multi-omics techniques. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 139807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Ross, A.B.; Yoo, M.J.Y.; Farouk, M.M. Metabolic fingerprinting of in-bag dry- and wet-aged lamb with rapid evaporative ionisation mass spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 128999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, D.; Piao, C.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Mu, B.; et al. Evaluation of the flavor profiles of Yanbian-style sauced beef from differently treated raw beef samples. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, L.F.; Balieiro, J.C.C.; Ferrinho, A.M.; Martins Td, S.; da Silva Corte, R.R.P.; de Amorim, T.R.; Furlan, J.d.J.M.; Baldi, F.; Pereira, A.S.C. Gender status effect on carcass and meat quality traits of feedlot Angus× Nellore cattle. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza, A.; Rey, A.; Carrasco, C.L.; López-Bote, C.J. Effect of gender on growth performance, carcass traits and meat quality of calves of Avileña-Negra Ibérica breed. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 10, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tan, J.; Mu, B.; Li, H.; Gao, T.; Li, C.; Meng, X.; Zhao, C.; Piao, C.; Li; et al. A Comparative Study on Beef Quality of Chinese Simmental Bull and Cow. Meat Res. 2015, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Barragán-Hernández, W.; Dugan, M.E.R.; Aalhus, J.L.; Penner, G.; Vahmani, P.; López-Campos, Ó.; Juárez, M.; Segura, J.; Mahecha-Ledesma, L.; Prieto, N. Effect of Feeding Barley, Corn, and a Barley/Corn Blend on Beef Composition and End-Product Palatability. Foods 2021, 10, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.J.; Scramlin, S.M.; Dilger, A.C.; Souza, C.M.; McKeith, F.K.; Killefer, J. Contribution of lean, fat, muscle color and degree of doneness to pork and beef species flavor. Meat Sci. 2009, 82, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureš, D.; Bartoň, L. Growth performance, carcass traits and meat quality of bulls and heifers slaughtered at different ages. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 57, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumova, E.; Chodova, D.; Volek, Z.; Ketta, M. The effect of feed restriction, sex and age on the carcass composition and meat quality of nutrias (Myocastor coypus). Meat Sci. 2021, 182, 108625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Realini, C.E.; Middlewood, P.; Pavan, E.; Ross, A.B. Metabolic fingerprinting using Rapid evaporative ionisation mass spectrometry can discriminate meat quality and composition of lambs from different sexes, breeds and forage systems. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Ma, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M. Flavor profile analysis of grilled lamb seasoned with classic salt, chili pepper, and cumin (Cuminum cyminum) through HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-GC-IMS, E-nose techniques, and sensory evaluation on Sonit sheep. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalali, S.; Li, C.; Xu, B. Insight into the effect of frozen storage on the changes in volatile aldehydes and alcohols of marinated roasted beef meat: Potential mechanisms of their formation. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Liu, Q.; Ma, C.; Muhoza, B.; Huang, Y.; Sun, M.; Song, S.; Ho, C.-T. Characteristic flavor fingerprint disclosure of dzo beef in Tibet by applying SAFE-GC-O-MS and HS-GC-IMS technology. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaville, R.; Hammadi, M.; Portetelle, D. Role of the somatotropic axis in the mammalian metabolism. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2002, 23, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.A.; Enright, W.J.; Tucker, H.A.; Merkel, R.A. Estrogen and androgen elicit growth hormone release via dissimilar patterns of hypothalamic neuropeptide secretion. Steroids 2001, 66, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiyanti, A.; Oki, Y.; Suda, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Chikuni, K.; Obara, Y.; Katoh, K. Effects of GH gene polymorphism and sex on carcass traits and fatty acid compositions in Japanese Black cattle. Anim. Sci. J. 2009, 80, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.S.; Cho, S.B.; Baek, K.H.; Choi, C.B. Effects of Testosterone, 17β-estradiol, and Progesterone on the Differentiation of Bovine Intramuscular Adipocytes. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larick, D.; Turner, B.E. Headspace volatiles and sensory characteristics of ground beef from forage-and grain-fed heifers. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.S.; Cooper, S.L.; Enser, M.; Mottram, D.S.; Sinclair, L.A.; Wilkinson, R.G.; Wood, J.D. Dietary manipulation of fatty acid composition in lamb meat and its effect on the volatile aroma compounds of grilled lamb. Meat Sci. 2005, 69, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkata Reddy, B.; Sivakumar, A.S.; Jeong, D.W.; Woo, Y.-B.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Byun, J.-Y.; Kim, C.-H.; Cho, S.-H.; Hwang, I. Beef quality traits of heifer in comparison with steer, bull and cow at various feeding environments. Anim. Sci. J. 2015, 86, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.E. Fetal Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Responses to Estradiol Sulfate. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4966–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidely, P. Quantitative bibliographic review on the use of anabolic hormones with steroidogenic action in ruminants for meat production. II. Principal mode of action. Reproduction, nutrition, development. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 1993, 33, 297–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.A.; McTernan, P.G.; Harte, A.L.; Barnett, A.H.; Kumar, S. The regulation of HSL and LPL expression by DHT and flutamide in human subcutaneous adipose tissue. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2002, 4, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Attribute | Cow | Bull | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triceps brachii | Longissimus dorsi | Gluteus medius | Triceps brachii | Longissimus dorsi | Gluteus medius | |
| Moisture (%) | 74.93 ± 1.23 a | 70.80 ± 1.78 c | 73.48 ± 1.26 b | 75.06 ± 1.24 a | 70.34 ± 1.96 c | 71.98 ± 0.93 b* |
| Protein (%) | 20.31 ± 1.52 a | 21.43 ± 1.74 a | 22.46 ± 1.38 a | 21.55 ± 0.81 a | 22.65 ± 1.14 a | 22.48 ± 1.24 a |
| Fat (%) | 5.25 ± 1.66 b | 9.69 ± 2.29 a | 3.53 ± 1.05 c | 4.02 ± 0.89 a | 4.74 ± 0.80 a* | 4.31 ± 0.91 a |
| L* | 33.53 ± 0.93 a | 31.02 ± 0.98 b | 32.06 ± 1.18 ab* | 30.44 ± 1.16 b* | 29.86 ± 1.93 b | 35.87 ± 1.59 a |
| a* | 12.87 ± 1.71 a | 12.36 ± 1.58 a | 13.16 ± 1.32 a | 11.48 ± 1.93 a | 11.19 ± 1.87 a | 13.73 ± 1.99 a |
| b* | 9.30 ± 1.10 b | 10.39 ± 1.73 a | 9.51 ± 1.73 b | 9.50 ± 1.80 a | 8.85 ± 1.77 a | 9.37 ± 1.62 a |
| Shear force(N) | 182.03 ± 14.34 a* | 115.54 ± 8.92 c* | 146.16 ± 9.16 b* | 235.71 ± 15.48 a | 146.51 ± 14.16 c | 188.62 ± 8.61 b |
| Number | Fatty Acid Type | Triceps Brachii | Longissimus Dorsi | Gluteus Medius | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cow | Bull | Cow | Bull | Cow | Bull | ||
| 1 | C6:0 | 3.44 ± 0.43 b | 3.15 ± 0.45 a | 4.06 ± 0.31 a | 3.58 ± 0.93 a | 3.88 ± 0.3 ab | 3.326 ± 0.70 a |
| 2 | C10:0 | ND | ND | 1.06 ± 0.16 | ND | ND | ND |
| 3 | C11:0 | 1.201 ± 0.23 b* | 1.52 ± 0.12 a | 1.65 ± 0.31 a | 1.56 ± 0.19 a | 1.30 ± 0.23 b | 1.43 ± 0.24 a |
| 4 | C12:0 | 0.58 ± 0.55 | ND | 1.31 ± 0.15 | ND | ND | ND |
| 5 | C14:0 | 29.69 ± 6.54 b | 11.41 ± 2.99 a* | 43.65 ± 5.62 a | 11.46 ± 4.01 a* | 11.81 ± 3.96 c | 1.59 ± 0.87 b* |
| 6 | C14:1 | 3.69 ± 1.15 b | 2.19 ± 0.77 a | 7.63 ± 2.12 a | 2.09 ± 0.76 a* | 1.32 ± 0.28 c | 0.81 ± 0.55 b |
| 7 | C15:0 | 2.45 ± 0.75 b | 2.16 ± 0.74 a | 5.26 ± 0.99 a | 1.94 ± 0.95 a* | 1.15 ± 0.26 b | 0.97 ± 0.63 a |
| 8 | C16:0 | 232.25 ± 43.94 ab | 126.87 ± 19.51 a* | 269.72 ± 26.31 a | 111.01 ± 47.77 a* | 18.31.13 ± 11.74 b* | 70.81 ± 47.08 a |
| 9 | C16:1 | 17.53 ± 8.43 c | 12.3 ± 6.50 a | 56.85 ± 6.16 a | 14.38 ± 6.51 a* | 28.80 ± 3.67 b | 10.18 ± 5.57 a* |
| 10 | C17:0 | 5.32 ± 2.91 b | 4.26 ± 1.64 a | 13.52 ± 1.40 a | 4.74 ± 1.80 a* | 1.55 ± 0.23 c* | 3.54 ± 1.14 a |
| 11 | C17:1 | 4.28 ± 2.39 b | 3.00 ± 1.21 a | 7.46 ± 0.70 a | 3.06 ± 1.13 a* | ND | 2.59 ± 1.46 a |
| 12 | C18:0 | 130.23 ± 19.9 b | 86.15 ± 10.0 a* | 241.87 ± 22.49 a | 70.87 ± 34.65 b* | 3.60 ± 0.80 c* | 6.77 ± 0.67 c |
| 13 | C18:1n9t | 3.51 ± 0.38 b | 3.72 ± 1.03 a | 19.28 ± 1.43 a | 5.29 ± 3.14 a* | 4.01 ± 1.08 b | 3.20 ± 1.86 a |
| 14 | C18:1n9c | 133.67 ± 24.27 b | 139.20 ± 36.11 a | 561.91 ± 85.5 a | 170.56 ± 72.9 a* | 77.28 ± 22.8 c* | 112.19 ± 36.61 a |
| 15 | C18:2n6c | 29.24 ± 7.42 b | 18.77 ± 3.94 a* | 36.03 ± 3.66 a | 19.23 ± 4.10 a* | ND | 12.21 ± 8.35 b |
| 16 | C20:0 | ND | ND | 1.75 ± 0.12 | ND | ND | ND |
| 17 | C20:1 | 1.04 ± 0.16 b | ND | 1.61 ± 0.28 a | ND | ND | ND |
| 18 | C18:3n | 1.21 ± 0.23 b | ND | 1.68 ± 0.19 a | ND | ND | ND |
| 19 | C20:3n6 | 2.97 ± 0.61 b | ND | 3.30 ± 0.31 ab | ND | 3.57 ± 0.99 a | ND |
| 20 | C20:4n6 | 12.32 ± 2.62 a | 5.88 ± 2.22 a* | 7.40 ± 0.83 b | 5.32 ± 0.58 a* | 14.28 ± 3.17 a | 4.53 ± 2.09 a* |
| SFA | 405.22 ± 72.70 b | 225.10 ± 40.11 ab* | 593.64 ± 52.80 a | 225.15 ± 89.72 a* | 203.19 ± 55.40 c | 134.21. ± 45.13 b | |
| MUFA | 229.77 ± 35.56 b | 154.33 ± 30.31 b* | 656.33 ± 94.44 a | 217.24 ± 84.40 a* | 97.65 ± 17.60 c | 115.14 ± 51.79 b | |
| PUFA | 41.74 ± 5.76 a | 25.58 ± 6.17 a* | 49.65 ± 4.64 a | 26.08 ± 6.49 a* | 20.63 ± 3.04 b | 18.76 ± 7.61 a | |
| Substance Name | CAS | Retention Index (RI) | Retention Time (Rt)/s | Drift Time (Dt)/min | Relative Peak Area (%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | CL | ||||||
| 1-Pentanol-D | C71410 | 1254.5 | 336.073 | 1.51165 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 1.67 ± 0.13 | <0.05 |
| 1-Pentanol-M | C71410 | 1255.6 | 336.979 | 1.25331 | 1.03 ± 0.08 | 4.42 ± 0.10 | <0.05 |
| 2-Heptanol | C543497 | 1335.7 | 415.728 | 1.37889 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.44 ± 0.06 | <0.05 |
| 2-Methyl-1-propanol-D | C78831 | 1096.2 | 228.482 | 1.17253 | 0.34 ± 0.07 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | <0.05 |
| 2-Methyl-1-propanol-M | C78831 | 1092.7 | 226.943 | 1.35747 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.24 | <0.05 |
| n-Butanol-D | C71363 | 1144.7 | 257.188 | 1.37751 | 0.34 ± 0.08 | 3.87 ± 1.74 | <0.05 |
| n-Butanol-M | C71363 | 1147.7 | 259.117 | 1.18109 | 1.67 ± 0.22 | 3.93 ± 0.73 | <0.05 |
| ethanol | C64175 | 981.2 | 184.157 | 1.04303 | 1.10 ± 0.04 | 0.81 ± 0.37 | >0.05 |
| 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol | C763326 | 1251.1 | 333.358 | 1.16878 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | >0.05 |
| CIS-4-heptenol | C6728310 | 1253.4 | 335.197 | 1.61856 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | <0.05 |
| isopentanol | C123513 | 1206.3 | 298.938 | 1.23976 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | <0.05 |
| sterols | 5.35 ± 0.46 | 16.4 ± 2.59 | <0.05 | ||||
| 2-Heptanone | C78933 | 898.2 | 162.5 | 1.24903 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.45 ± 0.23 | <0.05 |
| 2-Butanone | C110430 | 1144.7 | 257.169 | 1.25255 | 10.54 ± 0.50 | 2.73 ± 0.38 | <0.05 |
| 2-Pentanone | C107879 | 981.1 | 184.128 | 1.37244 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | <0.05 |
| 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone-D | C513860 | 1289.7 | 366.128 | 1.3332 | 3.54 ± 0.22 | 11.2 ± 0.92 | <0.05 |
| 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone-M | C513860 | 1293.5 | 369.482 | 1.05432 | 11.84 ± 0.22 | 18.15 ± 0.51 | <0.05 |
| acetone | C67641 | 812.7 | 142.855 | 1.12104 | 43.70 ± 0.75 | 25.04 ± 0.37 | <0.05 |
| hydroxyacetone | C116096 | 1290.6 | 366.912 | 1.23909 | 0.14 ± 0.00 | 0.36 ± 0.00 | <0.05 |
| 4-Methyl-2-pentanone | C108101 | 1014.1 | 194.996 | 1.18292 | 4.68 ± 0.46 | 4.97 ± 0.55 | >0.05 |
| ketone | 74.82 ± 0.36 | 63.07 ± 2.08 | <0.05 | ||||
| 3-Methylbutyraldehyde | C590863 | 921.5 | 168.299 | 1.18256 | 6.00 ± 0.11 | 5.24 ± 0.33 | <0.05 |
| heptanal | C111717 | 1184.1 | 283.23 | 1.32767 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 0.58 ± 0.04 | <0.05 |
| N-hexanal | C66251 | 1091.1 | 226.239 | 1.26743 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 1.08 ± 0.09 | <0.05 |
| n-octanal | C124130 | 1292.3 | 368.474 | 1.40462 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.80 ± 0.07 | <0.05 |
| aldehyde | 6.82 ± 0.14 | 7.69 ± 035 | <0.05 | ||||
| Methyl valerate | C624248 | 1093.5 | 227.298 | 1.56413 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.07 | <0.05 |
| Propyl 2-methylpropionate | C547637 | 929.6 | 170.383 | 1.14595 | 4.24 ± 0.45 | 4.45 ± 1.26 | >0.05 |
| ethyl acetate | C141786 | 879.3 | 157.943 | 1.34077 | 0.48 ± 0.10 | 0.72 ± 0.15 | <0.05 |
| esters | 4.79 ± 0.57 | 5.44 ± 1.42 | >0.05 | ||||
| Acetic acid-D | C64197 | 1485.6 | 633.257 | 1.14937 | 0.43 ± 0.03 | 0.47 ± 0.04 | >0.05 |
| Acetic acid-M | C64197 | 1486.3 | 634.511 | 1.05296 | 8.34 ± 0.18 | 8.76 ± 0.60 | >0.05 |
| acidic | 8.78 ± 0.21 | 9.23 ± 0.55 | >0.05 | ||||
| p-umbelliferyl hydrocarbons | C99876 | 1290.9 | 367.146 | 1.16878 | 0.81 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.04 | <0.05 |
| Methyl tert-butyl ether | C1634044 | 673.3 | 115.787 | 1.12559 | 2.52 ± 0.24 | 2.81 ± 0.55 | >0.05 |
| 3-Carene | C13466789 | 1145 | 257.36 | 1.62654 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.25 ± 0.16 | <0.05 |
| tetrahydrofuran (THF) | C109999 | 871.6 | 156.111 | 1.22905 | 0.70 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | <0.05 |
| 2-Methylpyrazine | C109080 | 1253.7 | 335.435 | 1.39246 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | <0.05 |
| other | 4.20 ± 0.23 | 4.23 ± 0.37 | >0.05 | ||||
| Odorant | Threshold Value (μg/kg) | ROAV | Odor Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | CL | |||
| 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone-M | 140 | 100 | 100 | Buttery, Green |
| 3-Hydroxy-2-butanone-D | 140 | 29.8986 | 61.7080 | Buttery, Green |
| 1-Pentanol-D | 150.2 | 0.0630 | 0.8576 | Green |
| 1-Pentanol-M | 150.2 | 0.8109 | 2.2699 | Green |
| n-Butanol-D | 480 | 0.0838 | 0.7103 | Alcohol |
| n-Butanol-M | 480 | 0.4114 | 0.6315 | Alcohol |
| 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol | 363,000 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | Sweet, fruity |
| isopentanol | 4 | 7.0946 | 1.9284 | Apple, Brandy |
| 2-Heptanone | 83,000 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | |
| 2-Pentanone | 1380 | 0.0150 | 0.0150 | Fruity |
| acetone | 832 | 6.2106 | 2.3271 | Nutty, Bitter |
| Hydroxyacetone | 10,000 | 0.0017 | 0.0028 | Nutty, Bitter |
| 4-Methyl-2-pentanone | 138,000 | 0.0040 | 0.0028 | Sweet, fruity |
| Ethyl acetate | 5 | 11.3514 | 11.1074 | Fruity, Sweet |
| Acetic acid-D | 99,000 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 | Sour |
| Acetic acid-M | 99,000 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 | Sour |
| Ethanol | 950,000 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | Alcohol |
| Methyl valerate | 110 | 0.0537 | 0.1753 | Fruity |
| Propyl 2-methylpropionate | 183,000 | 0.0027 | 0.0019 | Fruity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, J.; Mu, B.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Gao, T.; Meng, X.; Zhao, C.; Piao, C.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; et al. A Comprehensive Study of Meat Quality and Flavor Characteristics of Different Sexes of Yanbian Yellow Cattle Using GC-IMS and LC-MS/MS Technologies. Foods 2025, 14, 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183175
Tan J, Mu B, Li H, Li C, Gao T, Meng X, Zhao C, Piao C, Li T, Wang J, et al. A Comprehensive Study of Meat Quality and Flavor Characteristics of Different Sexes of Yanbian Yellow Cattle Using GC-IMS and LC-MS/MS Technologies. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183175
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Jinlong, Baide Mu, Hongshu Li, Chenguang Li, Tingting Gao, Xiangji Meng, Changcheng Zhao, Chunxiang Piao, Tingyu Li, Juan Wang, and et al. 2025. "A Comprehensive Study of Meat Quality and Flavor Characteristics of Different Sexes of Yanbian Yellow Cattle Using GC-IMS and LC-MS/MS Technologies" Foods 14, no. 18: 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183175
APA StyleTan, J., Mu, B., Li, H., Li, C., Gao, T., Meng, X., Zhao, C., Piao, C., Li, T., Wang, J., Li, H., & Li, G. (2025). A Comprehensive Study of Meat Quality and Flavor Characteristics of Different Sexes of Yanbian Yellow Cattle Using GC-IMS and LC-MS/MS Technologies. Foods, 14(18), 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183175





