Development and Characterization of Spray-Dried Curcumin–Lecithin Complexes with Improved Solubility and In Vitro Digestive and Thermal Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spray Drying of Curcumin–Lecithin Complexes
2.2. The Yield, Moisture Content, Water Activity, and Color Analysis
2.3. Bulk and Tapped Density, Hausner Ratio (HR), Carr Index (CI), Wettability, and Water Dissolubility
2.4. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analyses
2.5. Determination of Curcumin Content Using HPLC and LC/MS/MS
2.6. Entrapment Efficiency (EE%) and Loading Ratio of Curcumin
2.7. Thermal Stability
2.8. Stability in Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.10. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Spray-Dried Lecithin–Curcumin Complexes
3.2. Morphology of Spray-Dried Lecithin–Curcumin Complexes
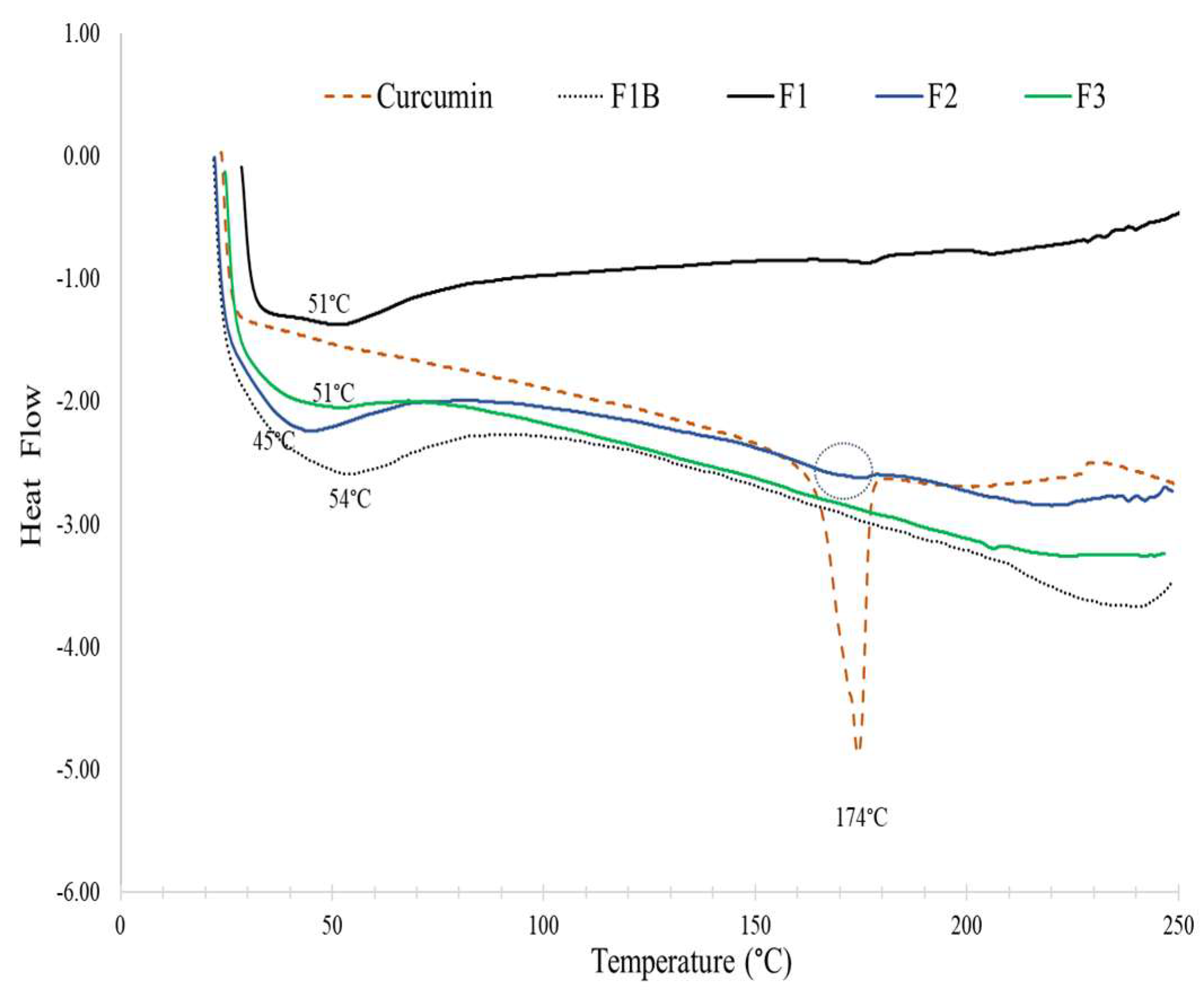
3.3. DSC, FTIR, and XRD Analysis
3.4. Thermal Stability
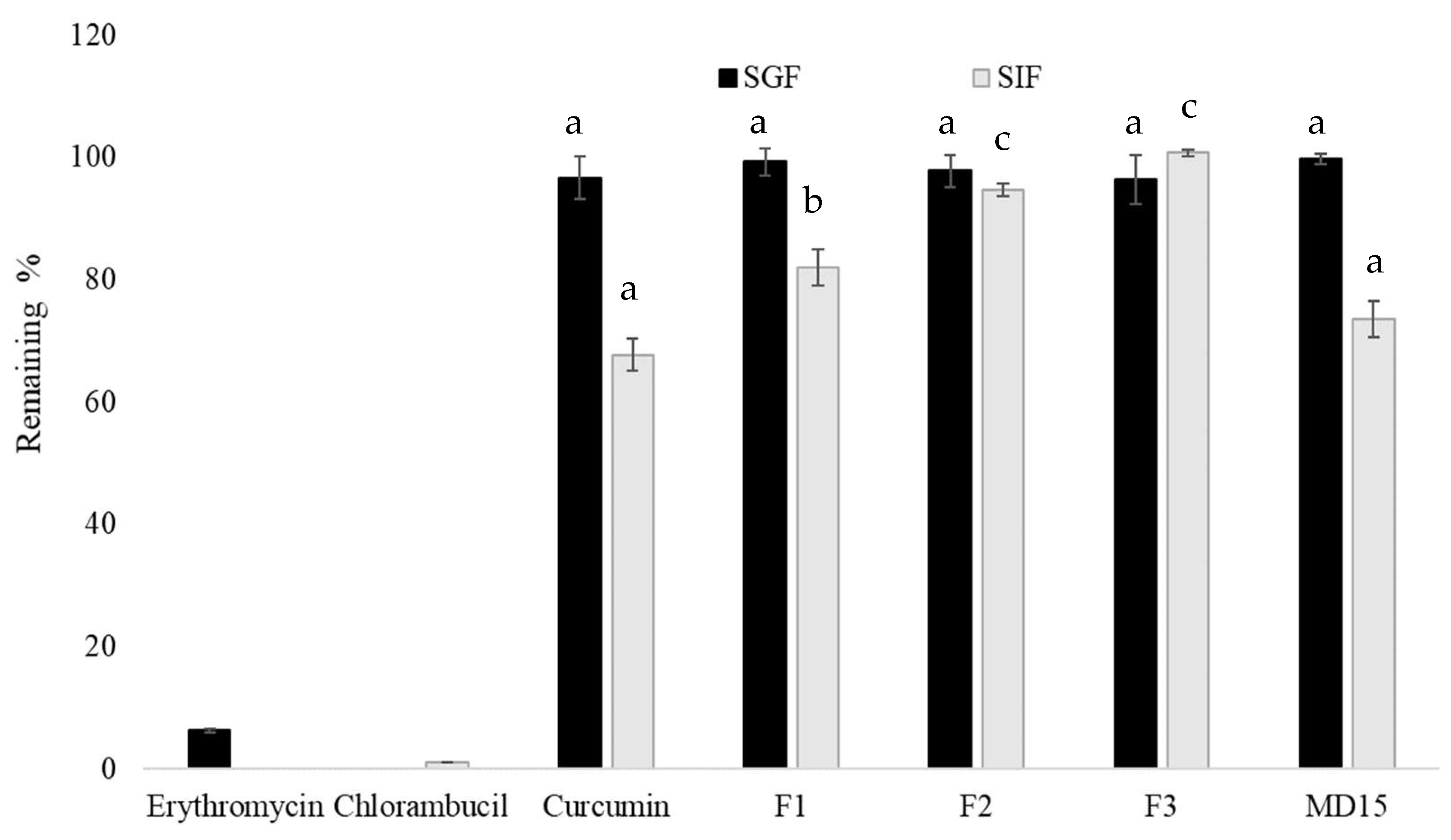
3.5. Stability Under Simulated Digestion Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obeid, M.A.; Alsaadi, M.; Aljabali, A.A. Recent Updates in Curcumin Delivery. J. Liposome Res. 2023, 33, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaqbeh, H.; Obaidat, R.; Al-Shar’i, N. Evaluation and Characterization of Curcumin-β-Cyclodextrin and Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponge Inclusion Complexation. Polymers 2021, 13, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebib, B.; Mouloungui, Z.; Noirot, V. Stabilization of Curcumin by Complexation with Divalent Cations in Glycerol/Water System. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2010, 2010, 292760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tai, K.; Ma, P.; Su, J.; Dong, W.; Gao, Y.; Mao, L.; Liu, J.; Yuan, F. Novel γ-Cyclodextrin-Metal–Organic Frameworks for Encapsulation of Curcumin with Improved Loading Capacity, Physicochemical Stability and Controlled Release Properties. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 128978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, J.B.; Fonseca, L.M.; Siebeneichler, T.J.; Crizel, R.L.; dos Santos, F.N.; dos Santos Hackbart, H.C.; Kringel, D.H.; Meinhart, A.D.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Curcumin Encapsulation in Capsules and Fibers of Potato Starch by Electrospraying and Electrospinning: Thermal Resistance and Antioxidant Activity. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xia, Y.; Liao, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Tong, Z.; Li, B. Thermal Degradation Kinetics Study of Curcumin with Nonlinear Methods. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masih, R.; Iqbal, M.S. Thermal degradation kinetics and pyrolysis GC–MS study of curcumin. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.U.; Dalvi, S.V. Understanding Stability Relationships among Three Curcumin Polymorphs. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, A.A.; Dalvi, S.V. Solid-state phase transformations and storage stability of curcumin polymorphs. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanphui, P.; Goud, R.N.; Khandavilli, U.B.R.; Bhanothb, S.; Nangia, A. New Polymorphs of Curcumin. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5013–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowiak, K.; Tajber, L.; Miklaszewski, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Sweeteners Show a Plasticizing Effect on PVP K30—A Solution for the Hot-Melt Extrusion of Fixed-Dose Amorphous Curcumin-Hesperetin Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tønnesen, H.H.; Másson, M.; Loftsson, T. Studies of Curcumin and Curcuminoids. XXVII. Cyclodextrin Complexation: Solubility, Chemical and Photochemical Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 244, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabet, S.; Rashidinejad, A.; Melton, L.D.; McGillivray, D.J. Recent Advances to Improve Curcumin Oral Bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlang, B.; Pawar, Y.B.; Bansal, A.K. Identification of Permeability-Related Hurdles in Oral Delivery of Curcumin Using the Caco-2 Cell Model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, M.; Pfeiffer, E.; Schulz, S.I.; Dempe, J.S. Curcumin Uptake and Metabolism. BioFactors 2013, 39, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can Karaca, A.; Rezaei, A.; Qamar, M.; Assadpour, E.; Esatbeyoglu, T.; Jafari, S.M. Lipid-Based Nanodelivery Systems of Curcumin: Recent Advances, Approaches, and Applications. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönenberger, K.A.; Ranzini, C.; Laval, J.; Bellenger, P.; Tenon, M.; Fança-Berthon, P. The Influence of Food Matrices on the Bioavailability of Curcuminoids from a Dried Colloidal Turmeric Suspension: A Randomized, Crossover, Clinical Trial. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; McClements, D.J. Formulation of More Efficacious Curcumin Delivery Systems Using Colloid Science: Enhanced Solubility, Stability, and Bioavailability. Molecules 2020, 25, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhai, Y.; Heng, X.; Che, F.Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, D.; Zhai, G. Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Advancements. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, S.; Amalraj, A.; Jacob, J.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S.; Guo, Q. Preparation, Characterization and in Vitro Study of Liposomal Curcumin Powder by Cost Effective Nanofiber Weaving Technology. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 5117–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.; Suriyarak, S.; Devahastin, S.; Chiewchan, N.; Borompichaichartkul, C. Enhancement of Encapsulation Efficiency and in Vitro Bioaccessibility of Spray-Dried Curcumin Microcapsules by Selected Bio-Coating Materials. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chang, C.; Gu, L.; Liu, C.; Li, J. Development of Egg Yolk Lipoprotein Hydrolysate for Nano-Delivery of Curcumin: Structure-Function Relationship. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 97, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xue, C. Effects of Colloidal Delivery Systems for Curcumin Encapsulation and Delivery. Food Chem. 2025, 488, 144859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Zheng, L.; Chang, Q.; Qin, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, P.; Xi, C. Curcumin-Loaded WPI-FUC Emulsion as a Microcapsule Core Material Enhances the Applicability and Stability of Curcumin—Preparation and Characterization of a New Type of Microcapsule. LWT 2025, 224, 117854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, W.S.; Almughem, F.A.; Almehmady, A.M.; Jarallah, S.J.; Alsharif, W.K.; Alzahrani, N.M.; Alshehri, A.A. Phytosomes as an Emerging Nanotechnology Platform for the Topical Delivery of Bioactive Phytochemicals. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Sangiovanni, E.; Angarano, M.; Rajizadeh, M.A.; Mehrabani, M.; Piazza, S.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Pardakhty, A.; Mehrbani, M.; Dell’Agli, M.; et al. Phytosomes as Innovative Delivery Systems for Phytochemicals: A Comprehensive Review of Literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 6983–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, L.; Hu, G.; Chen, X.; Jia, J. Development of Quercetin-Phospholipid Complex to Improve the Bioavailability and Protection Effects against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity in SD Rats. Fitoterapia 2016, 113, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, M.; Cao, J.; Wu, Z.; Weng, P.; Yan, M. Oolong Tea Polyphenols–Phospholipids Complex Reduces Obesity in High Fat Diet-Induced Mice Model. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryaki, S.; Macit, M.; Zemheri, I.E.; Süt, P.A.; Duman, G.; Telci, D. Anticancer Activity of Soy Lecithin-Based Curcumin in Prostate Cancer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, 142, e56816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Yang, T.; Korma, S.A.; Sitohy, M.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Selim, S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Salem, H.M.; Mahmmod, Y.; Soliman, S.M.; et al. Impacts of Turmeric and Its Principal Bioactive Curcumin on Human Health: Pharmaceutical, Medicinal, and Food Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1040259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, M.; Shahbazi, K.; Dakkali, M.S.; Akbari, M.; Almasi Ghale, R.; Hashemi, S.; Sashourpour, M.; Mojab, F.; Aminzadeh, S. Phytosomes: A Promising Nanocarrier System for Enhanced Bioavailability and Therapeutic Efficacy of Herbal Products. Phytomed. Plus 2025, 5, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, J.; Appendino, G.; Dern, A.S.; Schneider, E.; McKinnon, T.P.; Brown, M.J.; Togni, S.; Dixon, B.M. Comparative Absorption of a Standardized Curcuminoid Mixture and Its Lecithin Formulation. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczylo, T.H.; Verschoyle, R.D.; Cooke, D.N.; Morazzoni, P.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J. Comparison of Systemic Availability of Curcumin with That of Curcumin Formulated with Phosphatidylcholine. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 60, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, G.N.; Xie, Y.; Moaddel, R.; Sanghvi, M.; Dossou, K.S.S.; Kashuba, A.D.M.; Sandler, R.S.; Hawke, R.L. Randomized Pharmacokinetic Crossover Study Comparing 2 Curcumin Preparations in Plasma and Rectal Tissue of Healthy Human Volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 57, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tong, P.; Yang, R.; You, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T. Solidified Phospholipid-TPGS as an Effective Oral Delivery System for Improving the Bioavailability of Resveratrol. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Xiang, M.; Mao, Y.; Huang, L.; He, Q.; Dong, Y. Insights into Structure-Antioxidant Activity Relationships of Polyphenol-Phospholipid Complexes: The Effect of Hydrogen Bonds Formed by Phenolic Hydroxyl Groups. Food Chem. 2025, 485, 144471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chai, S.; Chen, Z.; An, X.; Shen, W. Effects of Curcumin Concentration and Temperature on the Spectroscopic Properties of Liposomal Curcumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.-Q.; Cai, W.-Q.; Wang, Z.-X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Su, B.-L.; Corke, H.; Zhang, B.-B. Structural Characteristics, Binding Behaviors, and Stability of Ternary Nanocomplexes of Lecithin, Polyvinylpyrrolidone, and Curcumin. LWT 2023, 175, 114489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, M.; Lu, F.; He, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, T. Dual Strategy for Improving the Oral Bioavailability of Resveratrol: Enhancing Water Solubility and Inhibiting Glucuronidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9249–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machmudah, S.; Trisanti, P.N.; Widiyastuti; Wahyudiono; Adschiri, T.; Goto, M. Liposomal Encapsulation of Curcumin Employing Soy Lecithin in Ultrasonic Environment under Dense Carbon Dioxide. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 109, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppula, S.; Shaik, B.; Maddi, S. Phytosomes as a New Frontier and Emerging Nanotechnology Platform for Phytopharmaceuticals: Therapeutic and Clinical Applications. Phytother. Res. 2025, 39, 2217–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, K.; Mukherjee, K.; Gantait, A.; Saha, B.P.; Mukherjee, P.K. Curcumin-Phospholipid Complex: Preparation, Therapeutic Evaluation and Pharmacokinetic Study in Rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 330, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, H.; Shakeri, A.; Rashidi, B.; Jalili, A.; Banikazemi, Z.; Sahebkar, A. Phytosomal Curcumin: A Review of Pharmacokinetic, Experimental and Clinical Studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Yang, X.; Du, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T. Dual Strategies to Improve Oral Bioavailability of Oleanolic Acid: Enhancing Water-Solubility, Permeability and Inhibiting Cytochrome P450 Isozymes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 99, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; Jia, X.; Zhou, J.; Lv, H. Solid Dispersion of Berberine-Phospholipid Complex/TPGS 1000/SiO2: Preparation, Characterization and in Vivo Studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, X.; Harold, C.; Su, B.L.; Zhang, B.B.; Yang, Q.Q. Synergistic Effect of Lecithin and Alginate, CMC, or PVP in Stabilizing Curcumin and Its Potential Mechanism. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, A.; Özçelik, B.; Sramek, M.; Gibis, M.; Kohlus, R.; Weiss, J. Presence of Electrostatically Adsorbed Polysaccharides Improves Spray Drying of Liposomes. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, E206–E221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroglu, O.; Atalı, B.; Yıldırım, R.M.; Karadag, A. Characterization of Nanoliposomes Loaded with Saffron Extract: In Vitro Digestion and Release of Crocin. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 4402–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Zárate, M.; Vázquez-Sánchez, A.Y.; Hernández-Medina, D.M.; Rojas, R.; Martínez-Ávila, G.C.G.; Gómez-García, R.; Michel-Michel, M.R.; Aguilar-Zárate, P. Optimization of Spray-Drying Microencapsulation of Curcumin as a Strategy for Enhancing Water Solubility and Evaluation of Antioxidant Activities. In Sustainable Engineering and Agro-Food Processing: Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources; Apple Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Huynh, T.M.; Nguyen, T.N.Q.; Le, T.H. Enhancing the Stability of Synthesized Curcumin by Spray-Drying Microencapsulation with Soy Lecithin and Gum Arabic. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, C.; Aghababaei, F.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Turitich, L.; Trujillo, A.J.; Ferragut, V. Characterization and Oxidation Stability of Spray-Dried Emulsions with Omega-3 Oil and Buttermilk Processed by Ultra-High-Pressure Homogenization (UHPH). LWT 2022, 162, 113493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Krishnaswamy, K. The Influence of Flavoring Components on the Physicochemical Properties of Spray-Dried High Oleic (HO) and Tofu Line (TL) Soymilk Powder. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 1070453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarian, B.; Sampaio, F.C.; de Faria, J.T.; Pitangui, C.G.; Lovaglio, F.; Casazza, A.A.; Converti, A.; Perego, P. Optimization of Spray Drying Microencapsulation of Olive Pomace Polyphenols Using Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Network. LWT 2018, 93, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.M.; Pereira, S.V.; Siqueira, S.; Salomão, W.F.; Freitas, L.A.P. Curcuminoid Content and Antioxidant Activity in Spray Dried Microparticles Containing Turmeric Extract. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peanparkdee, M.; Yooying, R. Enhancement of Solubility, Thermal Stability and Bioaccessibility of Vitexin Using Phosphatidylcholine-Based Phytosome. NFS J. 2023, 31, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Q.; Xu, X.; Li, N. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Phytosome-Loaded Chitosan Microsphere System for Curcumin Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 448, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressman, J.B.; Berardi, R.R.; Dermentzoglou, L.C.; Russell, T.L.; Schmaltz, S.P.; Barnett, J.L.; Jarvenpaa, K.M. Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) PH in Young, Healthy Men and Women. Pharm. Res. 1990, 7, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Guan, R.; Lyu, F.; Liu, M.; Gao, J.; Cao, G. Optimization of Preparation Conditions for Lysozyme Nanoliposomes Using Response Surface Methodology and Evaluation of Their Stability. Molecules 2016, 21, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadag, A.; Cakmakoglu, S.K.; Bekiroglu, H.; Karasu, S.; Ozer, H.; Sagdic, O.; Yildirim, R.M. Innovative Utilization of Olive Mill Wastewater Phenolics Extracted by Lecithin: Spray-Dried Powders in Cake Formulations. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 7979–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Tan, H.; Nguyen, V.T. Effect of Ultrasound Homogenisation on the Stability of Curcumin Microencapsulated by Spray-Drying. Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapala, K.P.; Auty, M.A.E.; Mulvihill, D.M.; O’Mahony, J.A. Influence of Emulsifier Type on the Spray-Drying Properties of Model Infant Formula Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontul, I.; Topuz, A. Spray-Drying of Fruit and Vegetable Juices: Effect of Drying Conditions on the Product Yield and Physical Properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millqvist-Fureby, A.; Smith, P. In-Situ Lecithination of Dairy Powders in Spray-Drying for Confectionery Applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, W.J. Dehydrated Dairy Products: Dairy Ingredients in Non-Dairy Foods. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences: Second Edition; Academic Press: Jackson, MS, USA, 2011; pp. 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.-J.; Chen, X.D.; Pearce, D. Surface Characterization of Four Industrial Spray-Dried Dairy Powders in Relation to Chemical Composition, Structure and Wetting Property. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2002, 26, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidon, G.E.; Meyer, P.J.; Mudie, D.M. Chapter 10—Particle, Powder, and Compact Characterization. In Developing Solid Oral Dosage Forms (Second Edition); Qiu, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, G.G.Z., Yu, L., Mantri, R.V., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 271–293. ISBN 978-0-12-802447-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani, M.; Pezeshki, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Tabibiazar, M.; Ahmadzadeh Nobari Azar, F.; Ghorbani, M. Phytosomal Nanocarriers for Encapsulation and Delivery of Resveratrol- Preparation, Characterization, and Application in Mayonnaise. LWT 2021, 151, 112093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudyka, J.; Ceja-Vega, J.; Ivanchenko, K.; Morocho, Z.; Panella, M.; Gamez Hernandez, A.; Clarke, C.; Perez, E.; Silverberg, S.; Lee, S. Concentration-Dependent Effects of Curcumin on Membrane Permeability and Structure. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 7, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabi-Khozani, Z.; Sarabandi, K.; Rezaei, A. Co-Delivery of Hydrophobic Curcumin and Hydrophilic Vitamin C by Nanoliposomes Decorated by Chitosan and Gelatin. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 11, 100937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q.; Song, Z. Lecithin-Based Mixed Polymeric Micelles for Activity Improvement of Curcumin against Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2025, 36, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T.; Singh, J.; Kaur, S.; Sandhu, S.; Singh, G.; Kaur, I.P. Enhancing Bioavailability and Stability of Curcumin Using Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (CLEN): A Covenant for Its Effectiveness. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Pan, M.H.; Cheng, A.L.; Lin, L.I.; Ho, Y.S.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, J.K. Stability of Curcumin in Buffer Solutions and Characterization of Its Degradation Products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1997, 15, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-Q.; Zhu, J.-F.; Wang, X.-B.; Ba, K. Improving the Stability of Liposomal Curcumin by Adjusting the Inner Aqueous Chamber PH of Liposomes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, S.; Sus, N.; Haas, K.; Jehle, S.; Kienhöfer, E.; Waehler, R.; Adler, G.; Venturelli, S.; Frank, J. Increasing Post-Digestive Solubility of Curcumin Is the Most Successful Strategy to Improve Its Oral Bioavailability: A Randomized Cross-Over Trial in Healthy Adults and In Vitro Bioaccessibility Experiments. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2100613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
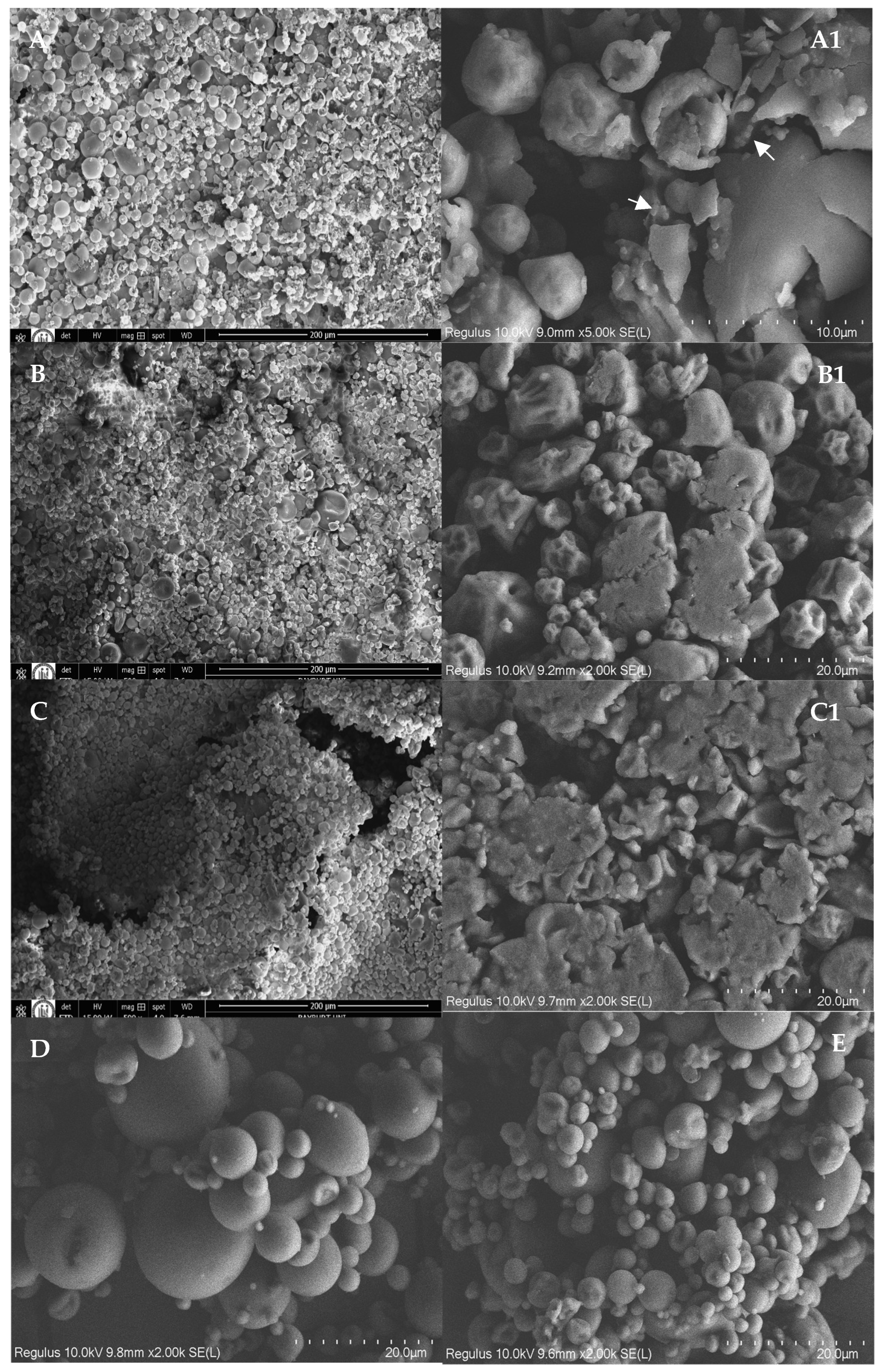
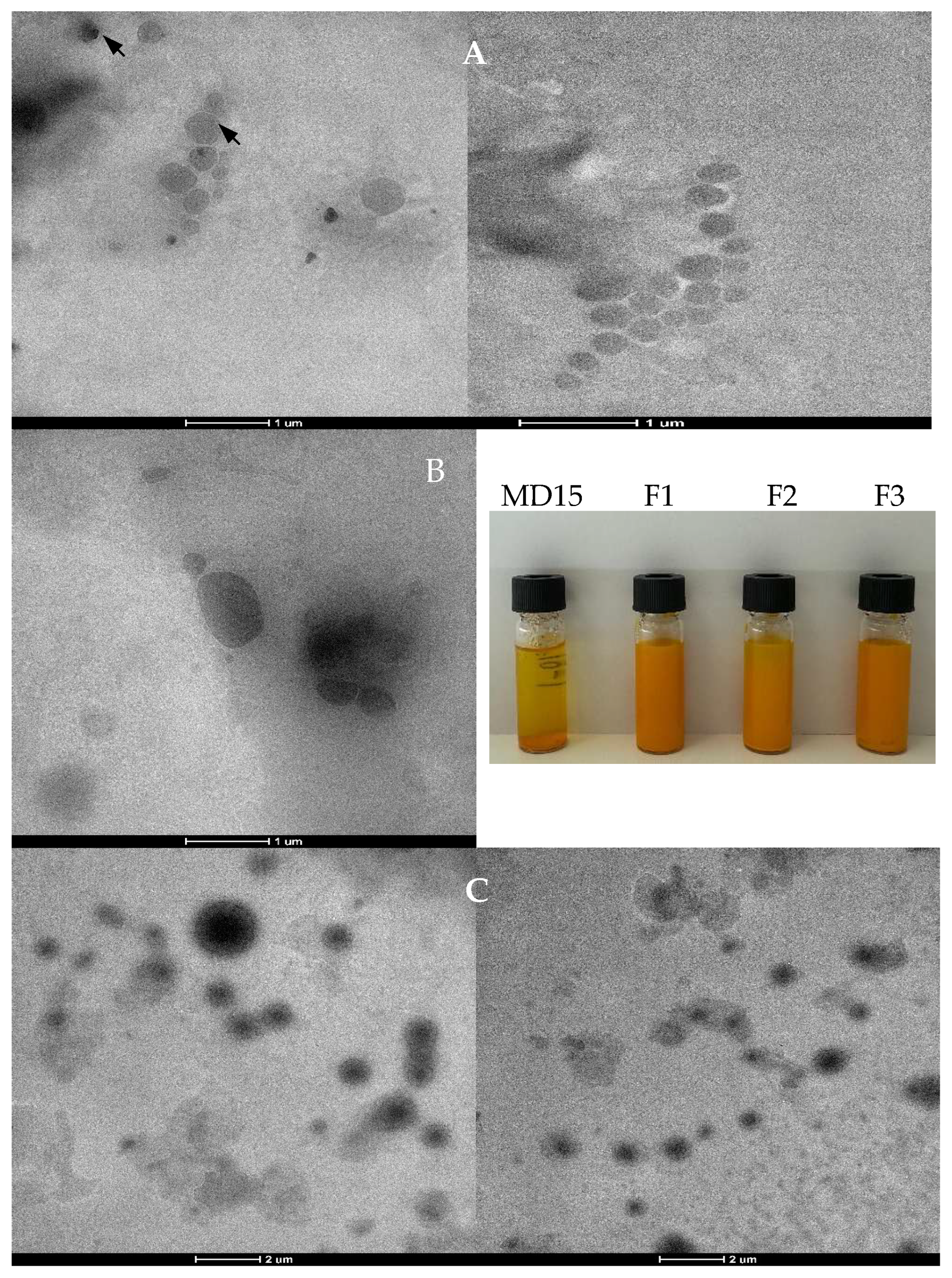


| Sample | Lec:Cur:MD | Yield (%) | aw | Moisture (%) | EE% | Loading Rate (%) | D4,3 (µm) | Dv,0.1 (µm) | Dv,0.5 (µm) | Dv,0.9 (µm) | Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 5:2:15 | 86.33 ± 3.51 c | 0.49 ± 0.09 b | 3.88 ± 0.28 a | 93.97 ± 0.27 b | 8.20 ± 0.12 a | 12.92 ± 1.05 a | 2.81 ± 0.19 a | 10.04 ± 1.94 a | 26.42 ± 4.06 a | 2.35 ± 0.13 b |
| F2 | 5:2:5 | 76.00 ± 3.00 b | 0.47 ± 0.00 a | 4.04 ± 0.86 a | 93.05 ± 1.52 b | 14.06 ± 0.43 c | 69.45 ± 2.32 c | 5.91 ± 0.74 b | 63.39 ± 3.51 c | 148.24 ± 17.1 c | 2.25 ± 0.14 ab |
| F3 | 5:1:5 | 70.01 ± 2.85 a | 0.48 ± 0.00 a | 4.40 ± 0.25 a | 86.50 ± 0.25 a | 8.99 ± 0.16 b | 36.81 ± 3.01 b | 5.24 ± 0.51 b | 34.06 ± 2.09 b | 72.31 ± 6.30 b | 1.97 ± 0.12 a |
| MD5 | 0:1:5 | 50.37 ± 2.06 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 1.01 ± 0.15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MD15 | 0:1:15 | 74.70 ± 1.37 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 0.47 ± 0.06 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sample | Bulk Density (g/mL) | Tapped Density (g/mL) | CI | HR | Wettability (s) | Dissolubility (%) | L | a | b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 15.73 ± 0.70 a | 1.19 ± 0.01 a | 69.00 ± 4.85 b | 84.69 ± 0.89 d | 81.33 ± 0.10 e | 10.18 ± 0.12 a | 42.04 ± 0.03 d |
| F2 | 0.25 ± 0.00 b | 0.37 ± 0.00 b | 30.34 ± 0.60 b | 1.44 ± 0.01 b | 106.80 ± 13.22 d | 80.63 ± 0.53 b | 76.89 ± 0.08 c | 19.22 ± 0.11 c | 40.33 ± 0.07 c |
| F3 | 0.28 ± 0.01 c | 0.40 ± 0.02 c | 31.35 ± 1.74 b | 1.46 ± 0.04 b | 88.00 ± 12.14 c | 85.07 ± 0.50 d | 79.87 ± 0.39 d | 13.08 ± 0.58 b | 42.18 ± 0.23 d |
| MD5 | 0.42 ± 0.01 e | 0.60 ± 0.01 d | 29.63 ± 2.04 b | 1.42 ± 0.04 b | 22.00 ± 1.58 a | 71.79 ± 0.80 a | 68.36 ± 0.04 a | 27.49 ± 0.05 e | 33.90 ± 0.02 a |
| MD15 | 0.36 ± 0.01 d | 0.63 ± 0.03 e | 42.57 ± 2.58 c | 1.74 ± 0.08 c | 30.80 ± 1.92 a | 82.06 ± 0.25 c | 73.66 ± 0.01 b | 22.41 ± 0.01 d | 37.63 ± 0.01 b |
| F1 | F2 | F3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic diameter, µm | 1.32 ± 0.16 | 1.83 ± 0.13 | 1.25 ± 0.13 |
| D10, µm | 0.70 ± 0.09 | 0.90 ± 0.08 | 0.54 ± 0.05 |
| D50, µm | 0.95 ± 0.19 | 1.15 ± 0.13 | 0.94 ± 0.11 |
| D90, µm | 1.38 ± 0.33 | 1.49 ± 0.24 | 1.47 ± 0.28 |
| Span | 0.63 ± 0.17 | 0.50 ± 0.10 | 0.99 ± 0.28 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −54.1 ± 1.04 | −53.8 ± 1.05 | −54.0 ± 1.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mankan, E.; Sagdic, O.; Karadag, A. Development and Characterization of Spray-Dried Curcumin–Lecithin Complexes with Improved Solubility and In Vitro Digestive and Thermal Stability. Foods 2025, 14, 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183157
Mankan E, Sagdic O, Karadag A. Development and Characterization of Spray-Dried Curcumin–Lecithin Complexes with Improved Solubility and In Vitro Digestive and Thermal Stability. Foods. 2025; 14(18):3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183157
Chicago/Turabian StyleMankan, Erkan, Osman Sagdic, and Ayse Karadag. 2025. "Development and Characterization of Spray-Dried Curcumin–Lecithin Complexes with Improved Solubility and In Vitro Digestive and Thermal Stability" Foods 14, no. 18: 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183157
APA StyleMankan, E., Sagdic, O., & Karadag, A. (2025). Development and Characterization of Spray-Dried Curcumin–Lecithin Complexes with Improved Solubility and In Vitro Digestive and Thermal Stability. Foods, 14(18), 3157. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14183157







