Comparative Effects of Maturity and Processing on Chemical Composition and Bioactivities in Toona sinensis Leaves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sample Preparation and UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS/MS Analysis
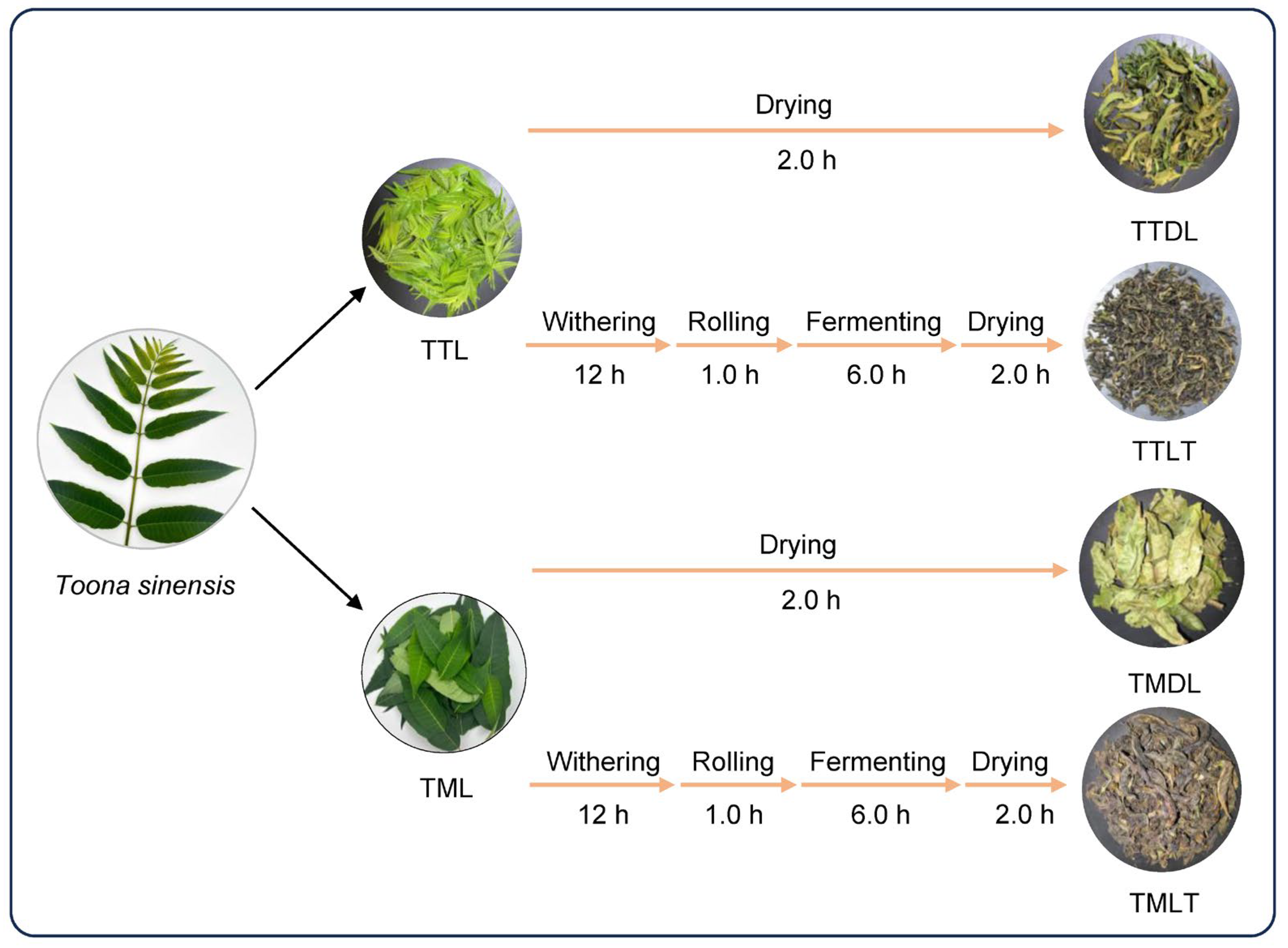
2.3. Manufacturing of Various Toon Leaf Teas
2.4. Determination of Chemical Components
2.5. Quantification of Rutin, Quercetin, and Kaempferol Using UPLC
2.6. Measurement of α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity
2.7. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Metabolite Profiles of Tender and Mature Toon Leaves
3.1.1. Flavonoids and Flavonoid Glycosides
3.1.2. Phenolic Acids
3.1.3. Limonoids
3.1.4. Amino Acids and Organic Acids
3.1.5. Other Compounds
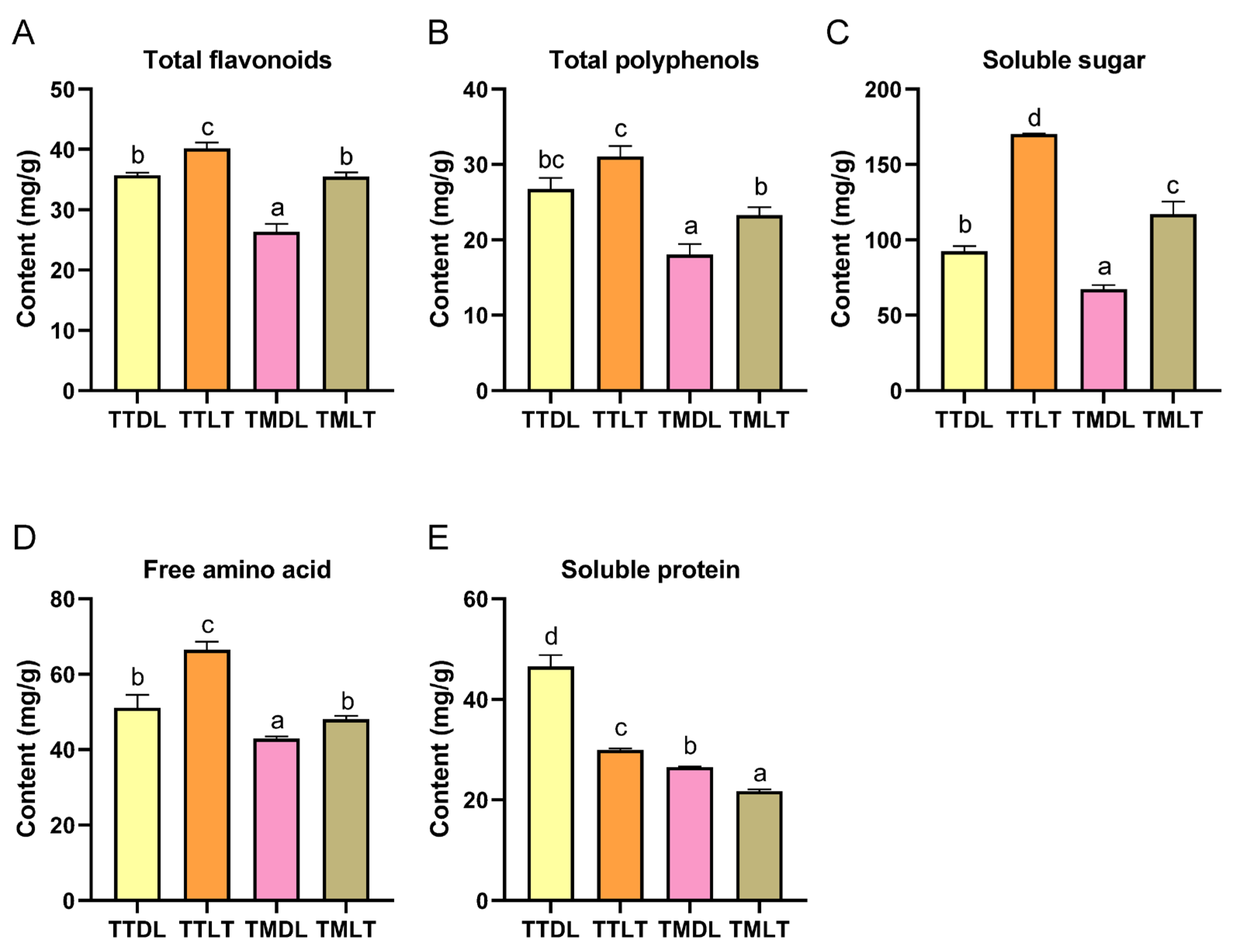
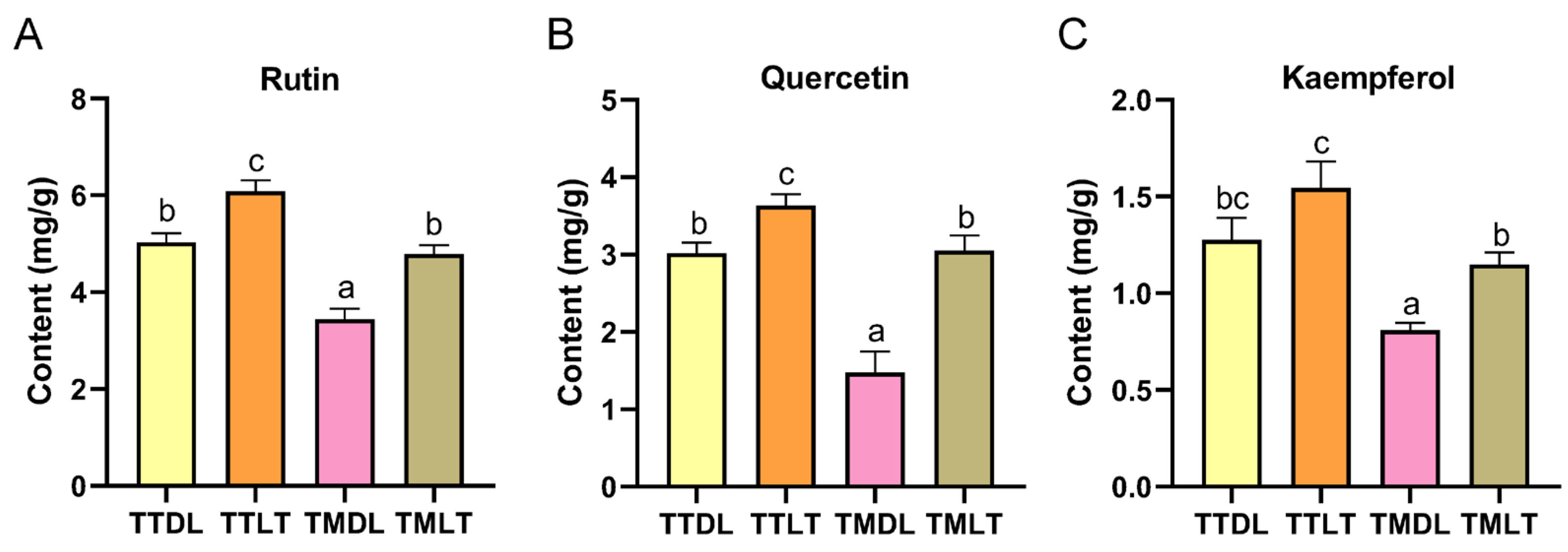
3.2. Quantification of Active Components in Various Toon Leaf Teas
3.3. Antioxidant Capacity Determination of Various Toon Leaf Teas
3.4. Comparison of α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity in Various Toon Leaf Teas
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Active Components and Bioactivities in Various Toon Leaf Teas
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Lan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, H.; Li, W. Traditional uses, chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of the Toona sinensis plant. Molecules 2024, 29, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, B.; Lei, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Analysis of nutrient composition and antioxidant characteristics in the tender shoots of Chinese toon picked under different conditions. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 109, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Liang, F.; Huang, Q.; Wu, C. Toona sinensis: A comprehensive review on its traditional usages, phytochemisty, pharmacology and toxicology. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Wang, L.; Ni, J. Diversity of red, green and black cultivars of Chinese Toon [Toona sinensis(A. Juss.) Roem]: Anthocyanins, flavonols and antioxidant activity. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 3206–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Tsai, M.J.; Hsu, C.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsu, H.K.; Weng, C.F. Toona sinensis Roem (Meliaceae) leaf extract alleviates hyperglycemia via altering adipose glucose transporter 4. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2554–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.X.; Rana, M.M.; Liu, G.F.; Gao, M.J.; Li, D.X.; Wu, F.G.; Li, X.B.; Wan, X.C.; Wei, S. Green tea flavour determinants and their changes over manufacturing processes. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yin, X.; Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Ning, J. Improving the flavor of summer green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) using the yellowing process. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyatip, P.; Padumanonda, T.; Yongram, C.; Kasikorn, T.; Sungthong, B.; Puthongking, P. Impact of tea processing on tryptophan, melatonin, phenolic and flavonoid contents in mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves: Quantitative analysis by LC-MS/MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, D.; Han, T.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Xie, Z. Comparative investigation of metabolite signatures and hypoadiposity effect between Dali tea and Yunkang tea. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, H. Re-rolling treatment in the fermentation process improves the aroma quality of black tea. Foods 2023, 12, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opra-Janiijevi, A.; Ulum, D.; Vidic, D.; Tahirovi, A.; Bai, N. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the endemic Crataegus microphylla Koch subsp. malyana K. I. Chr. & Janji from Bosnia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 113, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, M.; Dominguez-López, I.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. The chemistry behind the Folin-Ciocalteu method for the estimation of (Poly)phenol content in food: Total phenolic intake in a mediterranean dietary pattern. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17543–17553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Di, H.; Yang, S.; Tian, Y.; Tong, Y.; Huang, H.; Escalona, V.H.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Variation in nutritional components and antioxidant capacity of different cultivars and qrgans of basella alba. Plants 2024, 13, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Mao, H.; Lu, F.; Ma, C.; Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, C.; Xiao, R. Widely targeted metabolomics and HPLC analysis elaborated the quality formation of Yunnan pickled tea during the whole process at an industrial scale. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 135716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, X.; Ho, C.T.; Li, D.; Guo, H.; Xie, Z. A new strategy for grading of Lu’an guapian green tea by combination of differentiated metabolites and hypoglycaemia effect. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Long, P.; Meng, Q.; Ho, C.T.; Zhang, L. An emerging strategy for evaluating the grades of Keemun black tea by combinatory liquid chromatography-Orbitrap mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics and inhibition effects on α-glucosidase and α-amylase. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Wu, G.; Han, D.; Stipkovits, L.; Wu, X.; Tang, S.; Brennan, M.A.; Brennan, C.S. The effects of bioactive compounds from blueberry and blackcurrant powders on the inhibitory activities of oat bran pastes against α-amylase and α-glucosidase linked to type 2 diabetes. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandohee, J.; Kyereh, E.; Kulshrestha, S.; Xu, B.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Review of the recent developments in metabolomics-based phytochemical research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 3734–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.; Saurina, J.; Puignou, L.; Núñez, O. Classification and authentication of paprika by UHPLC-HRMS fingerprinting and multivariate calibration methods (PCA and PLS-DA). Foods 2020, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.; Ren, Y.F.; Ye, Z.H.; Zhu, H.Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, X.T.; Hou, R.Y.; Granato, D.; Cai, H.M. A comparative UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS-based metabolomics approach coupled with machine learning algorithms to differentiate Keemun black teas from narrow-geographic origins. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Teng, H. Absorption, metabolism and bioavailability of flavonoids: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7730–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, D.; Li, D. Effects of maturity and processing on the volatile components, phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activity of Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) leaf. Foods 2023, 12, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Han, Z.; Cui, Y.; Ho, C.T.; Wan, X.; Zhang, L. Identification of 4-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid as astringent compound of Keemun black tea by efficient integrated approaches of mass spectrometry, turbidity analysis and sensory evaluation. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Peng, S.; Ye, H.; Li, D.; Granato, D.; Guo, H.; Xie, Z. Metabolite differentiation and antiobesity effects between different grades of Yuexi Cuilan green tea. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.H.; Xie, Y.T.; Guo, J.M.; Wang, X.P.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, W.; Qiang, L.; Kong, L.Y.; Liu, Y.P. Limonoids from the fresh young leaves and buds of Toona sinensis and their potential neuroprotective effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12326–12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Song, Y.; Mao, X.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhao, Q.J. Limonoids isolated from Toona sinensis and their radical scavenging, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, V.; Singh, N.; Shrivastva, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Dharmani, P.; Mishra, V.; Palit, G. Gedunin and photogedunin of Xylocarpus granatum show significant anti-secretory effects and protect the gastric mucosa of peptic ulcer in rats. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Verma, M.; Mishra, S.K.; Srivastava, S.; Lakshmi, V.; Misra-Bhattacharya, S. Gedunin and photogedunin of Xylocarpus granatum possess antifilarial activity against human lymphatic filarial parasite Brugia malayi in experimental rodent host. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, L. Menghai Huangye, a novel albino tea germplasm with high theanine content and a high catechin index. Plant Sci. 2021, 311, 110997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, F.; Kang, J.; Li, Q.; Warusawitharana, H.K.; Li, B. Quality chemistry, physiological functions, and health benefits of organic acids from tea (Camellia sinensis). Molecules 2023, 28, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.; Fu, Z.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X. Revealing novel insights into the enhancement of quality in black tea processing through microbial intervention. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Qian, J.; Cai, C.; Xie, Y.; Lin, Y. Dynamic change of oligopeptides and free amino acids composition in five types of tea with different fermentation degree processed from the same batch of fresh tea (Camelilia sinensis. L.) leaves. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, G.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, X. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity of tea polysaccharides with different degrees of fermentation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proença, C.; Ribeiro, D.; Freitas, M.; Fernandes, E. Flavonoids as potential agents in the management of type 2 diabetes through the modulation of α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3137–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.S.; Xie, H.X.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.M.; Jiang, C.S. An updated overview of synthetic α-glucosidase inhibitors: Chemistry and bioactivities. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 2488–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic composition, antioxidant potential and health benefits of citrus peel. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound Name | RT (min) | Adduct m/z | Formula | Ion Mode | Fragments | VIP | p-Value | FC(TTL/TML) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids and flavonoid glycosides | ||||||||
| Melilotoside | 9.44 | 325.0926 | C15H18O8 | [M − H]− | 163, 119, 93 | 1.36 | 7.00 × 10−11 | 3.13 |
| Rutin | 11.51 | 609.146 | C27H30O16 | [M − H]− | 609, 301, 300, 271, 151 | 3.39 | 1.00 × 10−12 | 3.88 |
| Morin | 11.86 | 303.0497 | C15H10O7 | [M + H]+ | 303, 257, 229, 153, 137 | 5.25 | 1.00 × 10−9 | 3.27 |
| Quercetin 3-Glucoside | 11.86 | 465.1028 | C21H20O12 | [M + H]+ | 303, 229, 153, 85 | 9.13 | 3.00 × 10−9 | 3.13 |
| Kaempferol-3-O-Rutinoside | 12.13 | 593.1503 | C27H30O15 | [M − H]− | 593, 285, 255, 227 | 1.39 | 4.00 × 10−9 | 2.12 |
| Kaempferol 3-O-Sophoroside | 12.24 | 611.1611 | C27H30O16 | [M + H]+ | 465, 303, 145, 85 | 1.11 | 8.00 × 10−8 | 3.12 |
| Quercetin-3-O-A-L-Arabinopyranoside | 12.30 | 433.0773 | C20H18O11 | [M − H]− | 433, 300, 271, 255 | 3.32 | 3.00 × 10−11 | 3.72 |
| Quercetin | 14.65 | 301.0352 | C15H10O7 | [M − H]− | 301, 178, 151, 107 | 1.65 | 3.00 × 10−13 | 11.64 |
| Kaempferol | 15.74 | 285.0404 | C15H10O6 | [M − H]− | 285, 151, 137, 93 | 1.23 | 7.00 × 10−10 | 4.60 |
| Phenolic acids | ||||||||
| Quinic Acid | 1.38 | 193.0708 | C7H12O6 | [M + H]+ | 178, 133, 122 | 1.52 | 8.00 × 10−9 | 0.38 |
| 5-O-Galloylquinic Acid | 4.43 | 345.0819 | C14H16O10 | [M + H]+ | 153, 125 | 1.11 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 0.18 |
| Methyl Gallate | 9.38 | 183.03 | C8H8O5 | [M − H]− | 183, 124, 78 | 1.45 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 0.41 |
| Limonoids | ||||||||
| 1A-Methoxy-12A-Acetoxydihydrocedrelone | 17.20 | 307.1914 | C18H28O4 | [M − H]− | 189, 235, 185, 121 | 1.05 | 1.00 × 10−8 | 0.28 |
| Photogedunin | 17.53 | 513.2123 | C28H34O9 | [M − H]− | 513, 495 | 2.64 | 8.00 × 10−9 | 3.99 |
| 7-Deacetoxy-7A-Hydroxygedunin | 20.04 | 441.2274 | C26H32O6 | [M + H]+ | 441 423, 423, 161 | 1.47 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 0.54 |
| Gedunin | 20.57 | 483.2376 | C28H34O7 | [M + H]+ | 423, 379, 161, 137 | 2.09 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 3.07 |
| Amino acids | ||||||||
| D-Proline | 1.60 | 116.0706 | C5H9NO2 | [M + H]+ | 70 | 1.03 | 3.00 × 10−6 | 2.21 |
| L-Glutamic Acid | 1.28 | 148.0604 | C5H9NO4 | [M + H]+ | 129, 84 | 3.64 | 1.00 × 10−10 | 0.29 |
| Gamma-Glutamylglutamine | 1.36 | 276.1191 | C10H17N3O6 | [M + H]+ | 147, 130 | 4.10 | 8.00 × 10−8 | 2.34 |
| L-Proline | 1.37 | 116.0706 | C5H9NO2 | [M + H]+ | 116, 70, 43 | 2.93 | 1.00 × 10−8 | 2.86 |
| Fructose-Proline | 1.41 | 278.1234 | C11H19NO7 | [M + H]+ | 260, 242, 214, 128 | 6.52 | 1.00 × 10−9 | 7.31 |
| Fructosyl Valine | 1.47 | 280.1391 | C11H21NO7 | [M + H]+ | 244, 216, 198, 118 | 3.34 | 5.00 × 10−9 | 2.81 |
| Fructosyl Isoleucine | 2.45 | 292.1401 | C12H23NO7 | [M − H]− | 130, 101 | 1.36 | 7.00 × 10−11 | 3.57 |
| Organic acids | ||||||||
| 4-O-Beta-D-Glucosyl-4-Hydroxycinnamate | 9.44 | 344.134 | C15H17O8 | [M + NH4]+ | 165, 147, 119 | 2.74 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 2.93 |
| Fulgidic Acid | 15.31 | 327.2175 | C18H32O5 | [M − H]− | 327, 229, 171 | 2.75 | 2.00 × 10−9 | 0.33 |
| Pinellic Acid | 15.88 | 329.2334 | C18H34O5 | [M − H]− | 329, 229, 211, 171 | 1.85 | 3.00 × 10−9 | 0.36 |
| 11E-Octadecadienoic Acid | 20.20 | 293.2121 | C18H30O3 | [M − H]− | 275, 223, 195 | 3.39 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 0.43 |
| Dimorphecolic Acid | 20.92 | 295.2277 | C18H32O3 | [M − H]− | 277, 195, 171 | 2.48 | 9.00 × 10−8 | 0.44 |
| Other compounds | ||||||||
| Trehalosamine | 1.21 | 342.1395 | C12H23NO10 | [M + H]+ | 324, 306, 288, 174 | 4.99 | 4.00 × 10−11 | 4.60 |
| 5-Cytidylic Acid | 1.41 | 324.1294 | C9H14N3O8P | [M + H]+ | 324, 112 | 1.53 | 3.00 × 10−11 | 3.37 |
| Guanosine | 3.70 | 282.0843 | C10H13N5O5 | [M + H]+ | 150, 133, 108 | 1.62 | 2.00 × 10−11 | 5.61 |
| Atramycin B | 8.44 | 451.1391 | C25H24O8 | [M − H]− | 361, 289, 171, 128 | 1.15 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 6.98 |
| Shogaol | 20.05 | 277.2159 | C17H24O3 | [M + H]+ | 135, 93, 91, 79 | 7.99 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 0.33 |
| Abietinol | 22.08 | 289.2527 | C20H32O | [M + H]+ | 271, 201, 149, 121, 107, 93 | 2.83 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 3.11 |
| Trigonosin C | 24.14 | 609.2702 | C34H40O10 | [M + H]+ | 609, 591 | 4.05 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 0.46 |
| Sample | α-Glucosidase IC50 (μg/mL) | α-Amylase IC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| TTDL | 743.40 ± 27.94 b | 1911.00 ± 42.61 b |
| TTLT | 471.60 ± 28.08 a | 1034.00 ± 82.48 a |
| TMDL | 1110.00 ± 23.66 d | 3943.00 ± 75.10 d |
| TMLT | 875.30 ± 27.61 c | 2312.00 ± 41.20 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xu, S.; Fan, W.; Wu, L.; Ji, Y.; Qu, C. Comparative Effects of Maturity and Processing on Chemical Composition and Bioactivities in Toona sinensis Leaves. Foods 2025, 14, 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152717
Wu G, Chen Z, Tang Y, Xu S, Fan W, Wu L, Ji Y, Qu C. Comparative Effects of Maturity and Processing on Chemical Composition and Bioactivities in Toona sinensis Leaves. Foods. 2025; 14(15):2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152717
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guohuo, Zhaoyun Chen, Yan Tang, Shuolei Xu, Wenli Fan, Li Wu, Yuntao Ji, and Changqing Qu. 2025. "Comparative Effects of Maturity and Processing on Chemical Composition and Bioactivities in Toona sinensis Leaves" Foods 14, no. 15: 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152717
APA StyleWu, G., Chen, Z., Tang, Y., Xu, S., Fan, W., Wu, L., Ji, Y., & Qu, C. (2025). Comparative Effects of Maturity and Processing on Chemical Composition and Bioactivities in Toona sinensis Leaves. Foods, 14(15), 2717. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14152717






