Abstract
Plant-sourced Dietary Fibers (PDFs) have garnered significant attention due to their multifaceted health benefits, particularly in glycemic control, lipid metabolism regulation, and gut microbiota modulation. This review systematically investigates advanced modification strategies, including physical, chemical, bioengineering, and hybrid approaches, to improve the physicochemical properties and bioactivity of PDFs from legumes, cereals, and other sources. Key modifications such as steam explosion, enzymatic hydrolysis, and carboxymethylation significantly improve solubility, porosity, and functional group exposure, thereby optimizing the health-promoting effects of legume-sourced dietary fiber. The review further elucidates critical structure–function relationships, highlighting PDF’s prebiotic potential, synergistic interactions with polyphenols and proteins, and responsive designs for targeted nutrient delivery. In functional food applications, cereal-sourced dietary fibers serve as a versatile functional ingredient in engineered foods including 3D-printed gels and low-glycemic energy bars, addressing specific metabolic disorders and personalized dietary requirements. By integrating state-of-the-art modification techniques with innovative applications, this review provides comprehensive insights into PDF’s transformative role in advancing functional foods and personalized nutrition solutions.
1. Introduction
Dietary fiber, a carbohydrate resistant to digestion enzymes, offers several health benefits, including minimizing blood sugar fluctuations, lowering the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, maturing the immune system, and supporting regular bowel motions [1]. Plant-sourced Dietary Fibers (PDF) primarily exist as physical complexes of plant tissue particles and intracellular compounds, which are mostly made up of indigestible carbohydrates from plant cell walls [2,3,4]. The physical form of PDF determines the bioavailability of intracellular components, which depends on the porosity and structural complexity of the plant cell wall, as well as the morphology, size, and density of the plant component particles [5]. The health advantages of Plant-sourced Dietary Fibers (PDFs) might not be completely reflected in the experimental results from isolated and purified dietary fibers. According to the available research, intact cell walls can, through an encapsulation mechanism, alter fermentation rates and decrease the bioavailability and extraction efficiency of PDF. Studies on the bioavailability of common pulses through fermentation have shown that the process increases the bioavailability of legumes by disrupting the cell wall’s integrity [6]. Hemery, Y et al. and Hemery, Y.M et al. discovered that lowering the particle size of wheat bran increases the bioavailability of ferulic acid and sinapinic acid [7,8]. Similarly, Bai et al. found that increasing the pH can alter the chemical properties of okra cell walls, causing the cell walls to break, resulting in higher yields and solubility of okra polysaccharides when extracted with alkali [9]. The fact that the molecular weight of polysaccharides from blue honeysuckle with similar structural characteristics strongly influences their anti-gel, anti-glycation, and hypoglycemic in vitro effects also indicates the importance of physical properties on PDF functionality [8].
Based on the solubility of PDF in water, it can be divided into soluble dietary fiber (SDF) and insoluble dietary fiber (IDF). Both SDF and IDF have shown positive physiological effects. Moreover, for metabolic processes like decreasing blood sugar and blood lipids, preventing diabetes and coronary heart disease, and regulating human metabolism, soluble PDF is more advantageous than insoluble PDF [9,10]. In contrast to insoluble PDF, the beneficial health advantages of soluble PDF based on epidemiological studies have pushed the food sector to add soluble PDF into various foods [11,12,13]. Modification is therefore crucial for functional food application since it causes PDFs to undergo physical form changes that improve their bioactive properties. Soluble PDFs can be added to baked goods and other items, helping them act against a variety of illnesses because consumers are more conscious toward their diet and wish for natural remedies [14].
All these studies indicate that the physical structure of PDF and the content of soluble components are more important for its health functions. To investigate the potential contribution of modified PDF to improving the quality and health value of functional food applications, this study examines the impact of modification on the functional properties of plant-derived dietary fiber, as well as the complex relationship between the structure, physicochemical properties of plant-derived dietary fiber and its application in innovative functional foods.
2. Sources and Characteristics of PDF
2.1. Tissue-Specific Distribution of Dietary Fiber in Plants
Plant cell walls serve as the primary source of PDF [15], with its soluble and insoluble components detailed in Table 1. Figure 1 shows that dietary fibers in dicotyledons are primarily distributed within the cell walls of four anatomical structures: seed coats, stems, leaves, and fruits. The seed coats and vegetative tissues (stems and leaves) contain insoluble fibers such as cellulose and lignin that confer structural integrity, while fruit tissues are predominantly composed of soluble fibers including pectin and β-glucans. Notably, pectic polysaccharides and xyloglucans represent the major non-cellulosic polysaccharides in dicotyledonous cell walls. In monocotyledons, dietary fibers mainly localize to the cell walls of seed coats, endosperm, stems, leaves, and roots. Compared with dicotyledons, monocot cell walls exhibit higher arabinoxylan content but reduced abundance of heteroxylans and (1,3;1,4)-β-D-glucans, particularly in economically important poaceae species (cereals and grasses). Notably, mannans, galactomannans, and galactoglucomannans are frequently found in quite high concentrations in the walls of bean endosperm [16].

Table 1.
Dietary fiber content from different plant sources.
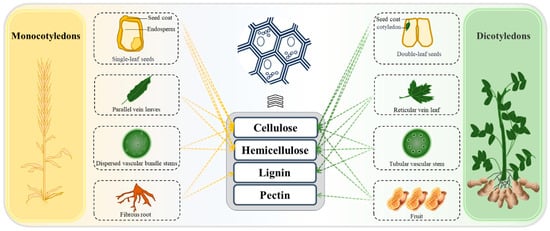
Figure 1.
Plant structural origins of Plant-sourced Dietary Fibers.
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of PDF
The microstructural modifications in the physical forms of PDF and their spatial arrangement critically influence the structural integrity of the cell wall and the viscoelastic properties of PDF, including solubility variations. For instance, steam explosion technology is widely employed in the modification of PDF sourced from fruits, vegetables, cereals, and nuts [26]. By increasing steam pressure and retention time, this technique reduces the transverse viscosity and mechanical strength of the fiber. During the instantaneous decompression phase, the rapid expansion of pore gases disrupts the crystalline structure of the fiber, thereby enhancing the content of soluble components [27]. Additionally, lignin depolymerization occurs via cleavage of β-O-4 ether linkages and other acid-labile bonds, while simultaneously degrading ester bonds between lignin and phenolic acids. This process liberates insoluble-bound phenolic compounds, ultimately improving their bioavailability [28]. The physical structure of PDF exhibits significant correlations with its physicochemical properties and physiological functionalities. Structural modification of PDF through fiber fragmentation and particle size reduction can effectively enhance its water absorption capacity and swelling properties [29]. Concurrently, increased porosity and increased degree of particle dispersion facilitate the exposure of hydrophobic groups, thereby augmenting oil retention capacity. Furthermore, the formation of a honeycomb-like microstructure significantly improves sodium cholate binding affinity [30], while elevated soluble component content and viscosity effectively retard glucose diffusion rates [31,32].
PDF serves as a crucial modulator of human digestive physiology, exhibiting significant associations with multiple health-promoting effects [33]. Contemporary research has increasingly emphasized the prebiotic potential of PDF in gut microbiota regulation [34,35]. Emerging evidence demonstrates that dysbiosis of gut microbiota is etiologically linked to various metabolic disorders, including inflammatory bowel diseases [36], colorectal inflammation, obesity, and metabolic syndrome [37,38,39]. This has stimulated substantial scientific interest in microbiota-targeted strategies that favor the proliferation of beneficial bacterial taxa [40]. In this context, dietary modulation through PDF supplementation has emerged as an effective nutritional intervention for gut microbial ecosystem remodeling [41,42]. The fermentability of PDF by gut microbiota is highly dependent on its crystallinity, porosity, and bacterial affinity. PDF utilization requires carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) to cleave specific chemical bonds [43,44]. Linear-structured cellulose exhibits low fermentability due to limited CAZyme accessibility, while branched, low-molecular-weight PDF demonstrates high fermentability [45,46]. For instance, highly fermentable fibers such as inulin [47], both branched and linear forms of Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) [48], and β-glucans [49] have been demonstrated to significantly promote the proliferation of beneficial gut microbiota, particularly Anaerostipes, Bilophila and Bifidobacterium. Concurrently, these fibers exhibit inhibitory effects against potentially pathogenic bacterial populations, including Bilophila and Proteobacteria. Moreover, PDF with looser, more porous physical structures exhibits greater accessibility to both enzymes and gut microbiota. A representative example is wheat bran arabinoxylan (AX), which preferentially enriches butyrate-producing Faecalibacterium [50].
3. Innovative Modification Techniques for PDF
For the high-value sustainable utilization of PDF, pretreatment is essential to disrupt their relatively dense physical structural barriers, thereby facilitating efficient extraction, conversion, and utilization of PDF.
3.1. Physical Modification
The glycosidic bonds of PDF can be modified through physical methods such as high temperature, high pressure [51], instant pressure release, ultrasound [52], explosion, high-speed impact, and shear force [53], which melt or break these bonds. Cavitation jets [54], a highly efficient fragmentation method utilizing high temperature, high pressure, and high shear force to alter intermolecular hydrogen bonds and crystalline structures of PDF, effectively reduces particle size, increases amorphous structures, and enhances soluble components, thereby improving its physicochemical and functional properties. For instance, Wu et al. applied cavitation jets to okara dietary fiber, significantly increasing SDF content and yielding higher shear viscosity [55].
Steam burst pretreatment is another emerging, efficient, and green modification technology for food ingredients. It relies on the rapid expansion of steam within material voids, inducing mechanical fracture and hydrogen bond disruption. This process cleaves glycosidic bonds and hydrogen bonds between lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose, explosively rupturing cell walls into porous, low-molecular-weight substances [56]. This method offers advantages such as broad applicability, environmental safety, and scalability for industrial production. Steam pretreatment combined with hot water extraction effectively isolates hemicellulose from bamboo shavings, significantly enhancing phagocytic activity and nitric oxide (NO) production in murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells, thereby improving immunomodulatory potency [57].
High hydrostatic pressure (HHP) and superfine grinding (SFGT) are widely adopted as efficient modification techniques for developing functional fiber ingredients, owing to their advantages in performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. These methods have been extensively applied to modify dietary fibers derived from various fruits and vegetables. For instance, Ling et al. investigated the effects of HHP and SFGT on the physicochemical and functional properties of pear pomace [58]. SFGT’s intense mechanical shearing disrupts chemical bonds in pear pomace, increasing soluble component content, while HHP alters the internal structure of fiber cells and cell membranes, enhancing functional properties such as water-holding and oil-binding capacities.
Compared with conventional spray-drying for food encapsulation, nanofibrous membranes of soluble cellulose produced by electrospinning technology exhibit superior stabilization effects on bioactive compounds, demonstrating great potential as novel delivery carriers for food ingredients [59,60]. The electrospinning nanofibrous membranes fabricated from PDF exhibit remarkable enhancement in both encapsulation efficiency and bioavailability of target bioactive compounds [61]. These advanced fibrous matrices, characterized by their outstanding biocompatibility and tunable biodegradability, represent a novel class of delivery systems with significant potential for the nano/microencapsulation of functional food ingredients [62,63]. Guar gum, a neutral polysaccharide extracted from leguminous plants, consists of supramolecular aggregates of galactomannan with multi-chain structures. After electrospinning treatment, the molecular aggregates of guar gum were effectively eliminated, and the local interchain coupling was disrupted, resulting in reduced fiber diameter and enhanced fiber uniformity. The resultant nano-guar gum films exhibited superior toughness and improved biodegradability [64].
3.2. Sustainable Chemical Modification
Chemical modification effectively depolymerizes PDF macromolecules, disrupts dense networks, and cleaves glycosidic bonds to generate reducing terminals. The chemical modification of PDF is engineered via acid/alkali-mediated structural modulation, or covalent functionalization (e.g., esterification) to tailor physicochemical properties [65,66].
Common acids used for chemical modification of PDF include hydrochloric acid, citric acid, malic acid, and lactic acid, with NaOH being the most frequently used alkali. When wheat bran undergoes modification using NaOH, epichlorohydrin, and dichloromethane, the resulting fibers develop porous, irregular structures with modified crystalline patterns and newly introduced active groups that collectively enhance adsorption capacity, creating an effective and environmentally friendly agent for wastewater dye removal [67]. FTIR analysis of hydrochloric acid-modified wheat bran showed significantly reduced absorption peak intensity at C-O stretching vibrations, indicating degradation of cellulose and lignin components. The increased soluble fraction content led to a more porous structure, exposing additional active groups that improved antioxidant capacity [68]. However, while controlled acid/alkali treatments effectively modify dietary fiber through microstructure disruption and polymerization degree reduction, excessive processing conditions must be carefully avoided to prevent undesirable macromolecular degradation and preserve functional properties [69].
Compared to the FTIR spectrum of native cellulose, carboxymethylated cellulose (CMF) exhibits characteristic peaks corresponding to -CH3 symmetric vibration and C-O-C stretching vibration, confirming the successful incorporation of carboxylate groups [70]. Similarly, carboxymethyl groups were detected in carboxymethylated goji berry pomace, consistent with the C=O stretching vibration in FTIR spectra [71]. Carboxymethylation of banana fibers resulted in reduced crystallinity, a more porous and looser fibrous structure, and an increased specific surface area, which significantly enhanced their heavy metal adsorption capacity [72]. The modified PDF developed a porous surface structure, exhibiting a high proportion of SDF and remarkable water-swelling ability. These modifications not only increased the viscosity of aqueous solutions but also endowed the PDF with superior cholesterol adsorption and bile salt binding capacities [73].
Acetylation primarily occurs on the side chains of polysaccharides and serves as an effective method to enhance the hydrophobicity of PDFs. By substituting hydrophilic hydroxyl groups with acetyl groups, acetylation alters the molecular chain orientation and polysaccharide conformation of PDFs while exposing additional polar groups to improve water solubility [74]. Recent studies have demonstrated that acetylated millet bran exhibits a significant increase in SDF content, forming a porous microstructure that enhances its sodium cholate and nitrite ion adsorption capacities [31]. Post-acetylation, the fiber’s surface morphology undergoes noticeable changes, accompanied by reduced crystallinity [75]. Furthermore, FTIR spectroscopy reveals C-H asymmetric stretching and carbonyl bending vibrations, confirming the successful introduction of acetyl groups into millet bran [31]. However, excessive acetylation of fibers may enable functional fiber-fortified foods to bind minerals such as calcium, iron, and zinc through carboxyl groups, thereby reducing their bioavailability and impairing fermentation by gut microbiota including Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. Prolonged consumption may consequently affect nutritional balance. Therefore, stringent process control is required for functional foods containing acetylated fibers, particularly for safety-sensitive products like infant foods.
The targeted introduction of functional groups to achieve specific physiological benefits has gained significant attention in medical therapeutic applications. Sulfate esterification alters sugar ring conformation, where mutual repulsion between similarly charged groups induces an extended chain configuration from originally coiled structures. This structural transformation is clearly observed in SEM images of both sulfate esterification seedless pear pomace dietary fiber and corn bran polysaccharides, which exhibit more ordered architectures with uniformly smooth surfaces [76]. FTIR spectroscopy confirms successful sulfation through S=O stretching vibration and C-O-S stretching vibration, demonstrating covalent incorporation of sulfate groups into PDF [77]. Importantly, gene expression analysis of tumor-suppression-related markers revealed that sulfated rice bran polysaccharides exhibit significant antitumor activity against HEP-G2 and B16 cell lines, demonstrating the considerable potential of sulfated polysaccharides in cancer intervention strategies [78]. Notably, sulfated fibers readily decompose at high temperatures (120 °C), releasing irritant SO2, while excessive intake may alter intestinal pH and consequently induce gut microbiota dysbiosis. Therefore, precise dosage control and stringent processing standards must be implemented prior to incorporating sulfated fibers into functional foods.
3.3. Bioengineering Modification
The bioengineering of PDF refers to the process of directed modification, synthesis, or optimization of dietary fibers using genetic engineering, enzymatic processing, fermentation [79], and related biotechnological approaches. This process aims to enhance their functional properties, bioavailability, and health-promoting effects.
Enzymatic modification primarily involves the use of cellulase and xylanase to degrade cellulose and hemicellulose, thereby increasing the SDF content and enhancing the functional properties of PDF. Liu et al. [80] investigated the cellulase-mediated modification of rice bran dietary fiber and found that the treated fiber exhibited increased porosity and reduced crystallinity due to hydrogen bond disruption [81]. Cellulase treatment resulted in a honeycomb-like network structure with abundant cavities, which not only provided additional space for water molecule storage via hydrogen bonding and dipole interactions but also facilitated more efficient cholesterol binding [82]. FTIR spectroscopy revealed broad and flattened absorption peaks, indicating that hydroxyl groups generated by cellulase hydrolysis promoted the cleavage of glycosidic bonds in the dietary fiber structure, thereby accelerating the degradation of small-molecular-weight sugars [81]. In contrast, xylanase can hydrolyze the insoluble arabinoxylan backbone in wheat bran, thereby increasing its SDF content. Furthermore, enzymatic modification reduced particle size, releasing bound phenolic compounds and other bioactive substances, ultimately improving the nutritional and functional quality of wheat bran [83].
Fermentation serves as a cost-effective and eco-friendly strategy for modifying PDF, effectively converting it into SDF while enhancing its functional properties [84,85]. Microbial selection critically influences PDF’s structural and bioactivity modifications [86,87]. For example, Bacillus subtilis fermentation of okara exhibits high cellulase activity, disrupting crystalline structures and releasing oligosaccharides via lignocellulose degradation [88]. Co-fermentation with lactic acid bacteria and Kluyveromyces marxianus significantly improves the hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic potential of okara IDF [89]. Meanwhile, Trichoderma viride enzymatically hydrolyzes defatted rice bran IDF, yielding SDF with enhanced solubility, surface-active groups, and improved water/oil-holding capacities [90]. FTIR spectroscopy indicates depolymerization of polysaccharide chains (peak shifts to lower wavenumbers, increased intensity) [91], while exposed hydroxyl groups and porous structures enhance free radical scavenging [92]. Additionally, strengthened hydrophobic and van der Waals interactions elevate cholesterol adsorption and pancreatic lipase inhibition [89].
While cellulase-producing strains such as Bacillus subtilis exhibit potential for dietary fiber modification, their native cellulase systems are inherently incomplete. Notably, the absence of exoglucanase-encoding genes significantly impairs their capacity to efficiently disrupt the crystalline structure of PDF. To overcome this limitation, genetic engineering approaches have been developed to enable heterologous overexpression of cellulase genes in B. subtilis, thereby substantially enhancing its cellulose degradation efficiency [93]. Moreover, the introduction of cellobiose dehydrogenase (CDH) genes into Aspergillus niger has demonstrated remarkable effects. CDH catalyzes the hydrolysis of cellobiose, lactose, and cello-oligosaccharides into carboxylic acids, resulting in a 28.57% increase in lignocellulolytic activity and significantly improved bioconversion rates [94]. These engineered microbial strategies represent promising avenues for targeted modification of PDF to meet the growing demands of functional food.
3.4. Hybrid Modification
Hybrid modification strategically integrates multiple techniques to address the inherent constraints of single-method approaches, thereby co-optimizing PDF production yield and functional quality. Recent studies demonstrate that high-temperature cooking effectively cleaves glycosidic bonds, facilitating the conversion of IDF to SDF. Subsequent ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic treatment further enhances SDF yield, surpassing the efficiency of individual modification approaches [95]. Similarly, while high-temperature cooking and cellulase treatment alone produce spherical microstructures in mung bean hull dietary fiber, their combined application generates porous lamellar structures. These structural modifications expose additional hydrophilic groups, significantly improving water solubility, water-holding capacity, and oil-holding capacity. The enhanced thermostability and physicochemical properties correlate with beneficial physiological effects, including reduced serum cholesterol levels, improved glucose adsorption capacity, and enhanced intestinal fermentability [96].
Enzyme–microbial synergistic fermentation has garnered considerable research attention due to its environmental friendliness and minimal byproduct formation. Guo et al. demonstrated that combined enzymatic (cellulase and xylanase) and microbial (Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium) modification of sea buckthorn increased amorphous structures and promoted the release of active groups [97]. This process significantly enhanced the binding capacity of negatively charged phenolic acid groups with NO2-, thereby improving nitrite-scavenging activity. Comparable structural modifications were observed in Aspergillus niger-cellulase co-treated Mesona chinensis Benth residue dietary fibers, where cross-linked molecular rearrangement generated more pronounced amorphous structures than enzymatic treatment alone [98]. The resulting honeycomb-like microstructure enhanced adsorption properties, substantially increasing the economic value of this agricultural byproduct.
3.5. Comparative Analysis of Modification Methods
Physical modification offers advantages such as simplicity and low cost, but excessive mechanical shear force can disrupt the crystalline structure of fibers, leading to the breakage of dietary fiber molecular chains and reduced hydration capacity [22]. Compared to physical modification, chemical modification can effectively control the solubility of dietary fibers; however, residual chemical reagents may pose food safety risks, and the required purification steps increase production costs [99]. In contrast to physical and chemical modifications, biological modification operates under mild conditions, offering eco-friendliness and specific catalytic advantages. Nevertheless, the substrate sensitivity of enzymes limits the modification efficiency of dietary fibers, while the high cost of enzymes, stringent reaction conditions, and technical complexity present additional challenges.
Combined modification strategies can compensate for the limitations of individual modification methods and meet diverse modification requirements [100]. While combined modification demonstrates significant advantages in functional optimization of dietary fibers, existing combined modification processes remain technically complex [101]. Moreover, potential interference between different modification methods may compromise the overall modification efficacy. Therefore, developing novel systematic modification approaches by evaluating the interplay between modification effects, safety considerations, cost factors, and application demands is crucial for advancing combined modification technologies.
4. Mechanisms of Functional Improvement in Modified PDF
The above discussion confirms that the physical structure of dietary fibers critically determines their functional activity. Moreover, different modification methods lead to distinct structural alterations in PDF [83]. Consequently, targeted structural modulation of PDF can enhance specific functionalities to meet diverse nutritional requirements, thereby driving revolutionary advancements in functional foods (Table 2). Figure 2 summarizes the functional enhancement mechanisms of modified plant-based dietary fibers in food applications, primarily including precise structure–function regulation, synergistic nutrient interactions, and smart responsive designs for precision nutrition.

Table 2.
The functional enhancement methods of Plant-sourced Dietary Fibers.
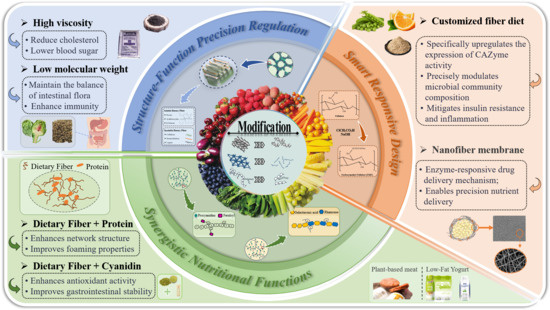
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of functional enhancement in Plant-sourced Dietary Fibers for functional food applications.
4.1. Structure–Function Precision Regulation
4.1.1. Modified Plant-Sourced Dietary Fiber Viscosity
The viscosity of dietary fiber is a critical mechanism influencing human health. High-viscosity fibers like psyllium and guar gum primarily offer cholesterol-lowering and glycemic control benefits, while low-viscosity soluble fibers (e.g., inulin and fructooligosaccharides) are more readily fermented by gut microbiota to produce SCFAs, thereby enhancing systemic immunity and intestinal barrier integrity. For instance, enzymatic hydrolysis by cellulase reduced the molecular weight of sunflower seed pectin from 800 kDa to 12.5 kDa, and artichoke pectin from 500 kDa to 80 kDa. The enzymatically modified pectins demonstrated preferential enrichment of gut Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillusv [111]. Fiber viscosity also determines its food applications. Lower-molecular-weight PDF from mung bean hull (45 kDa) demonstrates stronger hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity [112]. In orange juice, PDF disrupts the expanded network structure, increasing water solubility. In addition, the breakdown of PDF internal architecture reduces viscosity, improving fluidity and significantly diminishing gel-like properties. The decreased shear modulus yields a clearer juice texture, better meeting the sensory preferences of children and elderly consumers [113].
4.1.2. Modified Plant-Sourced Dietary Fibers with Hierarchical Porosity
The highly porous network microstructure endows PDF with superior adsorption capacity and enhanced probiotic colonization rates. When rice bran dietary fiber undergoes high-pressure homogenization modification, the disruption of hemicellulose and increased amorphous regions result in reduced crystallinity, forming a microporous structure with exposed hydrophilic groups. These functional groups exhibit ion-exchange capacity for Ca2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+, maintaining stable pH and ionic balance to improve both the palatability and nutrient bioavailability of PDF-fortified foods [81]. Juodeikiene, G. et al. demonstrated that ultrasonic treatment of soya press cake (okara) significantly increased porosity, elevating the SDF content from 2.896 to 2.963 g/100 g, while simultaneously providing an optimal nutrient matrix for lactic acid bacteria to enhance L-lactic acid production [114].
4.2. Synergistic Nutritional Functions
4.2.1. Polyphenol-Bound Plant-Sourced Dietary Fiber Complexes
Plant polyphenols are secondary metabolites characterized by a phenolic skeleton and abundant hydroxyl groups, exhibiting diverse biological activities such as cardiovascular disease prevention, anti-inflammatory effects, and anticancer properties [115,116]. The presence of numerous weakly acidic hydroxyl groups in polyphenols enhances the stability of fiber–polyphenol complexes in acidic environments. Compared to fiber alone, these complexes more readily bind hydrogen atoms from unsaturated bonds, thereby improving oil adsorption capacity, antioxidant activity, and the ability to scavenge reactive carbonyl species [117,118,119]. Moreover, multiple studies have demonstrated that PDFs can protect polyphenols during delivery to colonic target sites, where they are metabolized by gut microbiota to exert health benefits, thereby enhancing the bioaccessibility and bioavailability of polyphenols [120]. For instance, Lu et al. investigated the impact of dietary fiber–phenolic compound complexes on gut microbiota using an in vitro colonic fermentation model [121]. The results revealed that the unabsorbed complexes in the upper digestive tract were primarily fermented into dominant bacterial phyla, including Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, and exhibited superior modulation of gut microbial diversity compared to polyphenols alone. In contrast to natural cellulose, nanocellulose provides more binding sites, forming complexes with stronger antioxidant activity and sustained release properties. Li et al. compared nanocellulose–quercetin complexes with quercetin, demonstrating that nanocellulose effectively preserved the stability of quercetin throughout the gastrointestinal tract [121].
4.2.2. Protein-Bound Modified Plant-Sourced Dietary Fiber Complexes
Gelation represents an effective strategy for modulating textural characteristics in food systems, particularly in dairy and processed meat products, to address contemporary nutritional and health demands [122]. The formation of biopolymer complexes between PDF and proteins typically yields superior mechanical properties and enhanced structural stability compared to individual components [123]. Notably, covalently conjugated polysaccharide–protein complexes exhibit a distinctive lamellar and microporous architecture, wherein polysaccharide incorporation not only increases protein matrix flexibility but also significantly improves both foaming characteristics and gel network strength [124]. A representative example involves the Maillard reaction products (MRPs) generated between soy protein isolate (SPI) amino groups and α-lactose monohydrate carbonyl moieties. The emulsion stability, emulsifying activity, foaming capacity, foaming stability, and gel strength of these conjugates increased by 259%, 55.71%, 82.32%, 58.53%, and 3266%, respectively. This enhancement was attributed to the introduction of additional hydrophilic groups, as the covalent attachment of saccharide residues to SPI enhances protein solubility by exposing more free amino groups, thereby optimizing surface-active properties [125]. Parallel observations were made in oat β-glucan–SPI conjugates, where Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy revealed decreased N-H bending vibrations (amide II band), confirming successful cross-linking. Importantly, the degree of cross-linking exhibited positive correlation with β-glucan content, suggesting progressive SPI amino group engagement with polysaccharide carbonyls. This molecular interaction elongates the SPI polypeptide chain, ultimately enhancing both aqueous solubility and gel-forming capacity [126]. These findings underscore the potential of strategically modified Plant-sourced Dietary Fiber–protein complexes as functional ingredients in precision nutrition applications, particularly for designing foods with tailored textural and nutritional profiles.
4.3. Smart Responsive Design
Smart responsive design of dietary fibers refers to the targeted modification of fibers based on their utilization patterns and sites of bioactivity manifestation. This approach aims to achieve targeted functionality in the gastrointestinal tract or food matrices, optimizing both technological performance and health benefits.
4.3.1. Smart pH-Sensitive Modification of Plant-Sourced Dietary Fibers
Smart responsive design of PDF refers to the molecular engineering and functional modification of dietary fibers to enable controlled responsive behaviors to environmental stimuli (e.g., pH, enzymes, temperature, ionic strength, or gut microbiota) [127,128]. This allows for precise functional regulation in food processing, nutrient delivery, or health interventions [129,130,131]. The carboxyl groups in carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) exhibit distinct states under varying pH conditions. Under alkaline conditions (pH = 9), the carboxyl groups deprotonate, adopting a negatively charged state, with swelling ratios ranging from 308.03% ± 2.36 to 596.24% ± 1.22. Conversely, under acidic conditions (pH = 1.2), protonation occurs, resulting in reduced swelling capacity, with swelling ratios ranging from 152.25% ± 1.49 to 210.22% ± 1.42 [132,133,134]. Furthermore, the enzymatic degradation of cellulose by cellulase enables the development of diverse enzyme-responsive drug delivery systems [135]. For instance, CMC can be selectively hydrolyzed by cellulase, thereby triggering the controlled release of encapsulated therapeutics [136].
4.3.2. Combinatorial Customization of Modified Dietary Fiber for Personalized Gut-Targeted Delivery
Prolonged excessive intake of a single type of dietary fiber may induce intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, which can be mitigated through strategic fiber blending approaches. A closed-loop regulatory strategy for personalized nutritional intervention was developed by tailoring fiber blends based on individual microbiota signatures [137]. Fecal microbiota from obese donors was transplanted into germ-free mice, followed by alternating supplementation with 10% pea fiber, orange fiber, or barley bran under a diet high in saturated fats and low in fruits and vegetables (HiSF-LoFV). Key findings revealed that pea and orange fibers significantly enriched Bacteroide and activated metabolic pathways for arabinose and galacturonic acid, while barley bran preferentially upregulated β-glucanase gene expression and enriched xylan-degrading bacteria. The multi-fiber blend synergistically enhanced carbohydrate-active enzyme (CAZyme) activity and exhibited lower interindividual variability in microbial responses compared to single fibers. Highly consistent functional microbiota responses were further validated in human trials. This microbiota-directed approach enabled the design of targeted fiber combinations to modulate microbial functions, with the optimized blend demonstrating efficacy in alleviating insulin resistance and low-grade inflammation-associated dysbiosis [138].
Moreover, omics-driven strategies can be employed to achieve precision fermentation for fiber customization, representing a future direction for modifying PDF. Initially, genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) of plants with high-functionality fiber content can identify key biosynthetic genes. Studies have demonstrated that integrating quantitative genetics with transcriptomic data enables selection of optimal candidate genes for breeding plants with superior dietary fiber profiles [139]. Subsequently, by analyzing cellulosease genes correlated with short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production and predicting the metabolic networks of gut microbiota toward modified fibers through metagenomics, detailed glycomic characterization of PDF can be integrated with gut microbial and metabolomic data. Maldonado-Gomez Maria, X. et al. demonstrated through their research on the regulatory effects of structurally distinct fibers on human gut microbiota that oat, barley, and rye fibers composed of specific glycans can selectively drive butyrate production, with higher fiber content leading to elevated butyrate levels. This structure-dependent modulation of gut microbiota by dietary fibers enables the artificial customization of optimally fermentable PDF structures [140], providing a cutting-edge approach for developing functional food products with targeted health benefits.
5. Main Approaches for Functional Food Applications of PDF
5.1. Engineered Fiber Formulation Design
5.1.1. Low-Calorie Functional Foods
Rapid urbanization and economic development have led to reduced physical activity and lifestyle changes, with unhealthy diets being a major contributor to the rising prevalence of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. To mitigate NCD risks, reducing sugar and caloric intake is strongly recommended. The incorporation of low-viscosity pectin into yogurt beverages enhances textural viscosity while reducing subjective hunger perception, thereby exerting an appetite-suppressing effect. Studies have demonstrated that consumption of a low-calorie beverage supplemented with 8 g of low-viscosity pectin fiber significantly reduces energy intake during the subsequent meal. Moreover, compared to beverages consumed 90 min before the test meal, those ingested 15 min prior elicited greater satiety and lower subsequent energy intake [141,142].
β-Glucan exhibits exceptional thickening, emulsifying, and gelling properties, endowing it with potential as a key ingredient in the food industry. The incorporation of β-glucan enhances beverage viscosity and color stability while modifying the structure, texture, and sensory acceptability of baked goods [143]. Relevant studies demonstrate that yogurt supplemented with 0.4% (w/w) barley-derived β-glucan and yogurt containing 0.2% (w/w) citrus peel pectin exhibit superior proteolytic activity, which significantly improves bioaccessibility during in vitro-simulated gastric digestion. This is evidenced by increased soluble protein content from 25% to 34% and 35%, respectively. Furthermore, compared to control yogurt without dietary fiber supplementation, the β-glucan-fortified yogurt showed enhanced release of free amino acids (FAAs) during simulated gastric digestion, increasing from 3 to 8 mg/protein, consequently improving gastrointestinal absorption and nutrient bioavailability [144]. Additionally, incorporating polydextrose as a fat replacer and resistant starch to optimize the texture and sensory properties of low-fat biscuits enables the production of high-fiber, low-calorie multigrain biscuits with a soft yet crisp texture [145]. This approach aligns with growing consumer demand for nutrient-dense functional foods [146].
5.1.2. Microbiota-Targeting Functional Foods
Furthermore, dietary intake of PDF can exert hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, and hypotensive effects through stimulated colonic fermentation [147,148,149]. Supplementation with anthocyanin-prebiotic (rice bran soluble fiber and inulin) formulations in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients effectively delays glucose absorption and modulates serum lipid profiles [150]. Relevant studies indicate that propionate and butyrate, produced by gut microbial fermentation of SDF, primarily activate intestinal gluconeogenesis (IGN) gene expression via the gut–brain neural circuit, thereby maintaining glucose and energy homeostasis [151].
5.2. Innovative Product Applications
5.2.1. 3D-Printed Personalized Nutrition Foods
The utilization of 3D printing to process PDF-based foods enables the production of customized engineered foods tailored to individual characteristics and nutritional requirements [152]. Since the addition of IDF at levels >5% may impart undesirable textural roughness to food products, while soluble fibers exceeding 3% could lead to excessive viscosity and sliminess, it is essential to optimize their incorporation levels in food formulations. Only through such precise dosage control can the optimal physiological functionality of dietary fibers be effectively realized. For instance, cod protein composite gels (CPCGs) formulated with inulin, soybean SDF, flaxseed oil, and homogenized steamed cod demonstrated that, when maintaining identical flaxseed oil content with a 5:5 ratio of inulin to SDF, the hardness, chewiness, and viscosity of CPCG were significantly reduced while its swallowability was improved. Furthermore, SDF physically embedded within the gel matrix, resulting in a more compact CPCG network structure that enhanced the printing precision and stability of the 3D-printed composite hydrogel [153].
Compared to conventional market-available biscuits, 3D-printed biscuits exhibit superior acceptability due to their esthetic versatility, enhanced crispness, and optimized flavor profiles. Okara fiber modified through the synergistic combination of 500 W ultrasonic treatment and high-speed homogenization at 15,000 rpm demonstrated optimal swelling capacity, water-holding capacity (WHC), and oil-holding capacity (OHC). When incorporated into dough at 6% addition level, the modified okara fiber produced cookie dough with reduced hardness, enhanced elasticity, and maximum adhesion force, ultimately yielding cookies with optimal 3D-printing performance. Furthermore, the abundant hydrophilic groups in the dietary fiber contributed to improved crispness of the final product. The PDF-modified 3D-printed cookies also exhibited diversified flavors and shapes, which not only cater to modern consumers’ sensory preferences but also show potential for obesity mitigation through controlled nutrient delivery [154].
5.2.2. Low-Glycemic-Index (GI) Energy Bar
Energy bars represent a convenient and nutritionally complete food category with demonstrated physiological regulatory effects. Substituting refined carbohydrates and fats in traditional energy bars with PDF and protein modulates meal-associated energy intake while improving short-term glucose and insulin homeostasis [155,156].
The incorporation of kale at 30% (w/w) into multigrain bars significantly improved their physicochemical properties: hardness decreased from 298.2 N to 94.6 N, chewiness was reduced by approximately six-fold, antioxidant activity increased from 23.6 mM trolox equivalents/g dry matter (d.m.) to 29.3 mM trolox equivalents/g d.m., and total polyphenol content rose from 334 mg gallic acid equivalents/100 g d.m. to 422 mg gallic acid equivalents/100 g d.m. The resulting product not only provides rapid satiety but also delivers naturally beneficial bioactive compounds [157]. For athletic populations, consumption of low-glycemic-index (GI) nutritional energy bars promotes fat oxidation while reducing carbohydrate oxidation, leading to measurable improvements in running and jumping agility. Controlled studies simulating soccer match conditions demonstrate that athletes consuming lentil-based, low-GI nutrition bars during halftime exhibit reduced carbohydrate oxidation rates, thereby preserving glycogen stores. This metabolic adaptation correlates with enhanced second-half performance metrics, including sprint speed, heading accuracy, and total distance covered [158].
5.3. Sensory Properties and Consumer Acceptance
The poor solubility and weak water-holding capacity of PDF often result in inferior quality characteristics in processed foods, including inadequate mechanical properties, loose structure, and coarse texture, thereby limiting its broader application in food processing [159]. To address these challenges, texture modification of PDF is essential to alter its physicochemical properties and ultimately enhance the palatability of high-fiber food products [160]. Notably, corncob fermented with Ganoderma lucidum exhibits a significant increase in SDF content compared to unfermented corncob. This modification leads to dough with higher free phenolic content and total antioxidant capacity, improving its extensibility, rheological properties, and leavening ability. Consequently, the resulting gluten-free breadsticks demonstrate increased breaking force and enhanced baking flavor profiles [161,162].
Cakes and cream fillings are significant contributors to food flavor and caloric content, primarily due to their high fat composition. While fats impart unique textural and functional properties to food products, low-calorie cream fillings formulated with fat replacers such as microcrystalline cellulose and maltodextrin can achieve comparable rheological and mechanical characteristics [163,164,165]. As an alternative fat substitute, PDF not only replicates these desirable properties but also offers additional health benefits, including improved digestibility and reduced risks of chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders. This positions PDF as a sustainable and cost-effective supplement that aligns with the food industry’s growing demand for low-fat and low-sugar products [166]. Notably, lemon fiber—enriched with bioactive compounds like flavonoids, vitamin C, and phenolic acids—exhibits exceptional water- and oil-holding capacities, along with significant colon fermentation potential [167]. Incorporating lemon fiber into cream fillings increases viscosity, enhances creaminess, and mimics the rheological and textural properties of traditional shortening. Remarkably, this substitution reduces fat content from 30% to 10%, meeting consumer preferences for low-fat, functional, and clean-label products [168].
Furthermore, the content and pre-/post-modification safety of PDF represent critical metrics for functional food applications. PDF modifications must comply with the GRAS certification requirements (FDA 21 CFR 170.30) for novel processing methods [169,170]. When using processing aids such as sodium hydroxide, enzymatic preparations (e.g., papain, lipase), or ethanol during modification, their types, quality specifications, and final residual levels must adhere to GB 2760 ‘Standards for Use of Food Additives’ [171].
6. Conclusions
This review focuses on innovative modification strategies for PDF and how these approaches uniquely enhance both nutritional and sensory properties in functional foods (Figure 3), representing a dual improvement that addresses key limitations of conventional fiber fortification. The transition from simple PDF addition to intelligent, structure-driven PDF design demonstrates potential for precise nutritional regulation, laying the foundation for precision nutrition applications.
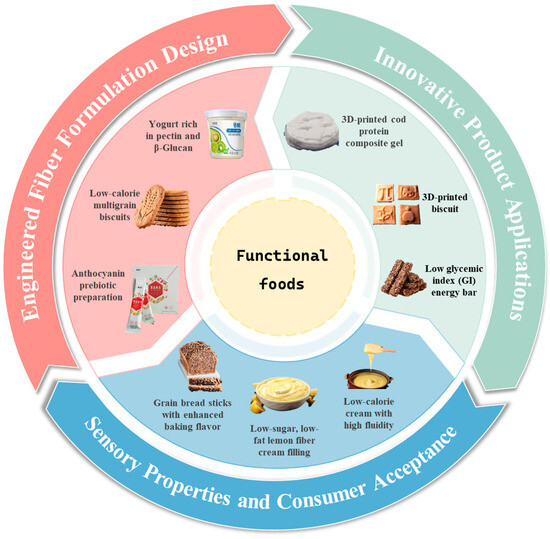
Figure 3.
Applications of Plant-sourced Dietary Fibers in functional foods.
Compared with existing methods, these innovative modification strategies enable texture customization and superior bioactive compound encapsulation without flavor compromise, representing a crucial solution to major industry challenges. Furthermore, PDF incorporation into functional foods through structure–function relationships can provide targeted health benefits. These findings offer researchers and food manufacturers novel pathways to develop next-generation functional foods, which are particularly valuable for addressing nutrition-related non-communicable diseases in developing regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. (Yansheng Zhao), Y.S., and S.F.; writing—original draft, Y.S., Y.Z. (Yansheng Zhao) and Y.Z. (Ying Zhu); writing—review and editing, J.B., L.Z. and S.F.; supervision, X.X. and Y.Z. (Ying Zhu); project administration, L.Z. and J.B.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. (Yansheng Zhao) and X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2024M751903), Zhenjiang Innovation Capacity Construction Plan—Construction of Discipline Key Laboratories (SS2024005), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Plant-sourced Dietary Fiber |
References
- Fuller, S.; Beck, E.; Salman, H.; Tapsell, L. New Horizons for the Study of Dietary Fiber and Health: A Review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mense, A.L.; Brewer, L.R.; Shi, Y.-C. Wheat bran layers: Composition, structure, fractionation, and potential uses in foods. Crit. Food Sci. 2024, 64, 6636–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mense, A.L.; Brewer, L.R.; Shi, Y.-C. Wheat bran arabinoxylans: Chemical structure, extraction, properties, health benefits, and uses in foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 23, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyran, M.R.; Saulnier, L. Cell wall fractions isolated from outer layers of rye grain by sequential treatment with α-amylase and proteinase: Structural investigation of polymers in two ryes with contrasting breadmaking quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9213–9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, C.; Ryden, P.; Edwards, C.H.; Grundy, M.M.L. Plant Cell Walls: Impact on Nutrient Bioaccessibility and Digestibility. Foods 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, E.; Tsopmo, A.; Oliviero, T.; Fogliano, V.; Udenigwe, C.C. Bioprocessing of common pulses changed seed microstructures, and improved dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemery, Y.M.; Anson, N.M.; Havenaar, R.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Noort, M.W.J.; Rouau, X. Dry-fractionation of wheat bran increases the bioaccessibility of phenolic acids in breads made from processed bran fractions. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Bai, J.; Shao, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L. Degradation of blue honeysuckle polysaccharides, structural characteristics and antiglycation and hypoglycemic activities of degraded products. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayici, M.E.; Mert-Ozupek, N.; Yalcin, F.; Basbinar, Y.; Ellidokuz, H. Soluble and Insoluble Dietary Fiber Consumption and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 2412–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntini, E.B.; Sardá, F.A.H.; de Menezes, E.W. The Effects of Soluble Dietary Fibers on Glycemic Response: An Overview and Futures Perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moturi, J.; Hosseindoust, A.; Tajudeen, H.; Mun, J.Y.; Ha, S.H.; Kim, J.S. Influence of dietary fiber intake and soluble to insoluble fiber ratio on reproductive performance of sows during late gestation under hot climatic conditions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Zhang, W.X.; Cheng, J.; Lu, Z.B. Antioxidant and physicochemical properties of soluble dietary fiber from garlic straw as treated by energy-gathered ultrasound. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.S.K.; Chia, P.F.W.; Ponnalagu, S.; Karnik, K.; Henry, C.J. The Role of Soluble Corn Fiber on Glycemic and Insulin Response. Nutrients 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Ain, H.B.; Saeed, F.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, M.A.; Niaz, B.; Tufail, T. Improving the physicochemical properties of partially enhanced soluble dietary fiber through innovative techniques: A coherent review. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, T.; Saeed, F.; Tufail, T.; Ul Ain, H.B.; Hussain, M.; Noreen, S.; Shah, M.A. Exploring the cholesterol-lowering effects of cereal bran cell wall-enriched diets. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, R.A.; Gidley, M.J.; Fincher, G.B. Heterogeneity in the chemistry, structure and function of plant cell walls. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Saeed, F.; Javed, M.; Afzaal, M.; Niaz, B.; Imran, A.; Naz, A.; Umar, M. Extraction and characterization of cereal bran cell wall in relation to its end use perspectives. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4615–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Costa, G.E.; da Silva Queiroz-Monici, K.; Pissini Machado Reis, S.M.; de Oliveira, A.C. Chemical composition, dietary fibre and resistant starch contents of raw and cooked pea, common bean, chickpea and lentil legumes. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajić, A.; Cvetković, B.; Mastilović, J.; Hadnađev, M.; Djordjević, M.; Djordjević, M.; Filipčev, B. Implementation of Plum Skin as a Structuring Agent in Plum Spread. Foods 2025, 14, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, M.; Cheikhrouhou, S.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Bureau, S.; Cuvelier, G.; Attia, H.; Ayadi, M.A. Characterization of pectins extracted from pomegranate peel and their gelling properties. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ni, Y. Effects of extraction methods on the structural characteristics and functional properties of dietary fiber extracted from kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa). Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, N.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Lei, H. Physical modifications of dietary fibers from kiwifruit pomace: Physicochemical, structural and functional properties. Food Chem. 2025, 484, 144422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Long, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.; Qin, W.; Tu, Z. Effects of microbial fermentation and microwave treatment on the composition, structural characteristics, and functional properties of modified okara dietary fiber. LWT 2020, 123, 109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesa, K.N.; Ahmad, N.; Mayangsari, Y.; Khandaker, M.U.; Iqbal, F.M.R.; Fibri, D.L.N.; Hassan, M.M.; Omara, T. Health Benefits of Okara for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, 5540118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Ren, D.; Lu, J. Physicochemical, functional, and microstructural properties of modified insoluble dietary fiber extracted from rose pomace. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Xia, Q.; Zha, B.P.; Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z.X. Triboelectric separation of wheat bran tissues: Influence of tribo-material, water content, and particle size. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbaghi, L.; Khamforoush, M.; Hatami, T. Carboxymethyl cellulose production from sugarcane bagasse with steam explosion pulping: Experimental, modeling, and optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ni, L.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, B. Principle and Application of Steam Explosion Technology in Modification of Food Fiber. Foods 2022, 11, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.K.; Wu, L.X.; Cai, W.D.; Xiao, G.S.; Duan, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.H. Subcritical water extraction-based methods affect the physicochemical and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers from wheat bran. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, J.; Yao, R.; Yan, S.; Wang, Q. Mechanism of lipid metabolism regulation by soluble dietary fibre from micronized and non-micronized powders of lotus root nodes as revealed by their adsorption and activity inhibition of pancreatic lipase. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, B.; Shi, P.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Liang, P. The influences of acetylation, hydroxypropylation, enzymatic hydrolysis and crosslinking on improved adsorption capacities and in vitro hypoglycemic properties of millet bran dietary fibre. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRorie, J.W., Jr.; McKeown, N.M. Understanding the Physics of Functional Fibers in the Gastrointestinal Tract: An Evidence-Based Approach to Resolving Enduring Misconceptions about Insoluble and Soluble Fiber. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Xu, J.; Wu, W.; Wen, Y.; Lu, S.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zhao, C. Structure-immunomodulatory activity relationships of dietary polysaccharides. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Gu, J.; Ni, Y. Insoluble and Soluble Dietary Fibers from Kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) Modify Gut Microbiota to Alleviate High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced TYPE 2 Diabetes in Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y.; Xu, T.; Wu, F. Dietary supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum dy-1 fermented barley suppresses body weight gain in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4907–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.S.; Law, J.W.F.; Letchumanan, V.; Hong, K.W.; Wong, S.H.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; Tan, L.T.H. A Keystone Gut Bacterium Christensenella minuta—A Potential Biotherapeutic Agent for Obesity and Associated Metabolic Diseases. Foods 2023, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaud, F.S.R.; Rodrigues, T.C. Fibra alimentar: Ingestão adequada e efeitos sobre a saúde do metabolismo. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 57, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Xiao, J.; Abdallah, H.M. Nutritional value of barley cereal and better opportunities for its processing as a value-added food: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Q.; Song, Y.T.; Zhou, J.; Duan, Y.Q.; Kong, T.Y.; Ma, H.L.; Zhang, H.H. Recent progress of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on intestinal microbiota, microbial metabolites and health: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 2917–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Sun, Q.C.; Meng, J.M.; Shang, A.; Mao, Q.Q.; Li, H.B. Targeting Gut Microbiota for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes Mellitus by Dietary Natural Products. Foods 2019, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.T.; Ding, Y.W.; Hu, Z.K.; Zhang, Z.H.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Xiao, X. Inter-individual variation in human microbiota drives differential impacts on the fermentability of insoluble bran by soluble (3-glucans from whole barley. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 111034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y. Effects of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) on the gut microbiota in high fat diet and low dose streptozocin-induced rats. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaker, B.R.; Tuncil, Y.E. A perspective on the complexity of dietary fiber structures and their potential effect on the gut microbiota. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 3838–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, A.L.; Li, N.A.; Zayas-Garriga, A.; Xie, R.R.; Zhu, D.C.; Sun, J.Z. Direct Conversion of Minimally Pretreated Corncob by Enzyme-Intensified Microbial Consortia. Agriculture 2024, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, P.; Zeng, S.; Ying, R.; Huang, M. Mechanistic Insights Into the Inhibitory Effects of Arabinoxylan and (1,3)(1,4)-β-Glucan on Starch Digestive Enzymes. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Arai, A. Preparation and Hydrolysis of Water-Stable Amorphous Cellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeputte, D.; Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Wang, J.; Sailer, M.; Theis, S.; Verbeke, K.; Raes, J. Prebiotic inulin-type fructans induce specific changes in the human gut microbiota. Gut 2017, 66, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Yu, X.; Luo, Y.; Chen, B.; Ma, D.; Zhu, J. Effect of Fructooligosaccharides Supplementation on the Gut Microbiota in Human: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Al-Ansi, W.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, M.; Qian, H.; Li, Y. Oat β-glucan alleviates DSS-induced colitis via regulating gut microbiota metabolism in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8976–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demuth, T.; Edwards, V.; Bircher, L.; Lacroix, C.; Nyström, L.; Geirnaert, A. In vitro Colon Fermentation of Soluble Arabinoxylan Is Modified Through Milling and Extrusion. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 707763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Song, J.; Zhang, K.; Dai, Z.; Li, D. Effect of dynamic high-pressure microfluidization on the physicochemical and structural properties of insoluble dietary fiber from fresh corn bract. J. Food Process. Pres. 2021, 45, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, N.; Song, J.; Luo, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, G.; Liu, C.; Wu, C. Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction of soluble dietary fiber from fresh corn bract and its physio-chemical and structural properties. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2022, 14, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhan, E.Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Y.S.; Xiao, X. Impacts of superfine grinding on structural characteristics and lipid-lowering effect of bitter melon polysaccharides. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 3813–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, P.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Effect of Cavitation Jets on Structure and Function of Okara Insoluble Dietary Fiber. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.L.; Teng, F.; McClements, D.J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.J. Effect of cavitation jet processing on the physicochemical properties and structural characteristics of okara dietary fiber. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, W.; Nie, Y.; Kang, F.; Goff, H.D.; Cui, S.W. Effect of steam explosion on dietary fiber, polysaccharide, protein and physicochemical properties of okara. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Q.; Qi, R.-T.; Pang, M.-R.; Liu, C.; Li, G.-Y.; Zhang, Y. Isolation, chemical characterization, and immunomodulatory activity of naturally acetylated hemicelluloses from bamboo shavings. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2017, 18, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure and superfine grinding treatment on physicochemical/functional properties of pear pomace and chemical composition of its soluble dietary fibre. LWT 2019, 107, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, A.B.; Nambiar, R.B.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Nanocellulose: Recent trends and applications in the food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Din, Z.-U.; Ullah, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Rani, S.; Jan, I.; Alam, M.; Rahman, Z.; Kamal, T.; Ali, S.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of Bio-based Nanocomposites Packaging Films Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofibers from Unripe Banana Peels. Starch-Starke 2022, 74, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, M.; Mousavi, M.; Yousefi, H.; Labbafi, M. All-cellulose nanocomposite film made from bagasse cellulose nanofibers for food packaging application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 104, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stijnman, A.C.; Bodnar, I.; Hans Tromp, R. Electrospinning of food-grade polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishir, M.R.I.; Saifullah, M.; Hashim, S.B.H.; Aalim, H.; Bilal, M.; Khan, S.; Marappan, G.; Tahir, H.E.; Zhihua, L.; Zhai, X.; et al. Micro and nano-encapsulated natural products in yogurt: An emerging trend to achieve multifunctional benefits in product quality and human health. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubambo, A.F.; de Freitas, R.A.; Sierakowski, M.-R.; Lucyszyn, N.; Sassaki, G.L.; Serafim, B.M.; Saul, C.K. Electrospinning of commercial guar-gum: Effects of purification and filtration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, W.; Oh, K.; Rajabi Abhari, A.; Youn, H.J.; Lee, H.L. Recycling of isopropanol for cost-effective, environmentally friendly production of carboxymethylated cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xia, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, K.; Fatehi, P.; Chen, J. Physicochemical impact of cellulose nanocrystal on oxidation of starch and starch based composite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, D. Structure Characterization and Dye Adsorption Properties of Modified Fiber from Wheat Bran. Molecules 2024, 29, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.J.; Wang, L.; Dong, L.; Yin, M.Y.; Wei, S.F.; Luo, P. Agrocybe cylindracea Dietary Fiber Modification: Sodium Hydroxide Treatment Outperforms High-Temperature, Cellulase, and Lactobacillus Fermentation. Molecules 2024, 29, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, J.; Qi, J. Functional and structural properties of dietary fiber from citrus peel affected by the alkali combined with high-speed homogenization treatment. LWT 2020, 128, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Alam, N.; Fatehi, P. Semitransparent films from low-substituted carboxymethylated cellulose fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 10407–10424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-G.; Yang, G.; Zhang, W.-W.; Thakur, K.; Hu, F.; Khan, M.R.; Ni, Z.-J.; Wei, Z.-J. Physicochemical and functional properties of carboxymethylated insoluble dietary fiber of Lycium barbarum seed dreg. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, K.; Gomathi, T.; Vijayalakshmi, K.; Saranya, M.; Sudha, P.N. Banana fiber Cellulose Nano Crystals grafted with butyl acrylate for heavy metal lead (II) removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, P.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Q. Effect of four modification methods on adsorption capacities and in vitro hypoglycemic properties of millet bran dietary fibre. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Kotera, M.; Suetsugu, M.; Murakami, H.; Urushihara, Y. Acetylation of plant cellulose fiber in supercritical carbon dioxide. Polymer 2011, 52, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserki, V.; Zafeiropoulos, N.E.; Simon, F.; Panayiotou, C. A study of the effect of acetylation and propionylation surface treatments on natural fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2005, 36, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, C.; Fan, F. Sulfation Modification and Properties Analysis of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Rosa sterilis Pomace. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Q.; Dai, L.H.; Ma, J.J.; Zhao, X.J.; Zhu, L. Preparation and Physiological activities of sulphated derivative extracted from corn bran. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 64, 012120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Song, S.; Wei, Y.X.; Wang, F.X.; Zhao, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J. Sulfated modification of the polysaccharide from Sphallerocarpus gracilis and its antioxidant activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, J.A.; Ma, H. Bioconversion of food industrial waste okara by microbial fermentation: Scope of omics study and possibility. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yi, C.; Quan, K.; Lin, B. Chemical composition, structure, physicochemical and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber modified by cellulase treatment. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhao, T.; Wan, H.; Li, M.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics of Rice Bran Dietary Fiber by Cellulase and High-Pressure Homogenization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Chen, J.-N.; Zhou, X.-J.; Lin, H.; Gao, Q.; Peng, X.; Tanokura, M.; Xue, Y. Effect of chemical and enzymatic modifications on the structural and physicochemical properties of dietary fiber from purple turnip (Brassica rapa L.). LWT 2021, 145, 111313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tan, B.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, D. Comparison of six modification methods on the chemical composition, functional properties and antioxidant capacity of wheat bran. LWT 2021, 149, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Bai, J.; Fan, S.; Daglia, M.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Changes in the structural, physicochemical and functional properties and in vitro fecal fermentation characteristics of barley dietary fiber fermented by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum dy-1. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 4276–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Bai, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Dong, Y. Inhibitory effect of fermented selected barley extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum dy-1 on the proliferation of human HT-29 Cells. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, Q.; Ackah, M.; Nie, S. Rethinking the classification of non-digestible carbohydrates: Perspectives from the gut microbiome. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Ba, K.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, X. Comparative analysis of barley dietary fiber fermented with and without Lactiplantibacillus plantarum dy-1 in promoting gut health and regulating hepatic energy metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Hu, M.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, S. Efficient conversion of insoluble dietary fiber to soluble dietary fiber by Bacillus subtilis BSNK-5 fermentation of okara and improvement of their structural and functional properties. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.T.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, Y.I.; Chung, Y.K. Effect of Rice Bran and Wheat Fibers on Microbiological and Physicochemical Properties of Fermented Sausages during Ripening and Storage. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, M.; Nie, S.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Yu, Q. Structural characteristics and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from defatted rice bran obtained through Trichoderma viride fermentation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, N.; Xia, Q.; Hou, Y.; Xu, G. Comparisons of three modifications on structural, rheological and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers from tomato peels. LWT 2018, 88, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C. Improved physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from millet bran fermented by Bacillus natto. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Gong, H.; Tang, H.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cui, W.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Enhanced lignocellulose degradation in Bacillus subtilis RLI2019 through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated chromosomal integration of ternary cellulase genes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 306, 141727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.D.; Liu, S.Z.; Duan, Y.Z.; Bao, C.L.; Wang, J.; Dong, B.; Cao, Y.H. Complete genome sequencing and investigation on the fiber-degrading potential of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain TL106 from the tibetan pig. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, L.; Duan, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, X. Preparation of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Mung Bean Hull by High-Temperature Cooking and Compound Enzyme Method and Its in vitro Hypoglycemic Effect. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2022, 37, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, J. Modification of bamboo shoot dietary fiber by high temperature cooking combined with cellulase. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; He, Z.; Wang, F.; Yuen, M.; Yuen, H.; Peng, Q. Effects of enzymes combined with Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium on the properties and in vitro hypoglycemic activity of sea buckthorn insoluble dietary fiber. Food Biosc. 2025, 68, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Tian, S.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Structural properties and adsorption capacities of Mesona chinensis Benth residues dietary fiber prepared by cellulase treatment assisted by Aspergillus niger or Trichoderma reesei. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornfine, C.; Hasenkopf, K.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert, U. Influence of chemical and physical modification on the bile acid binding capacity of dietary fibre from lupins (Lupinus angustifolius L.). Food Chem. 2010, 122, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Lin, X.; Walayat, N.; Liu, J.; Zhao, P. Dietary fiber modification: Structure, physicochemical properties, bioactivities, and application—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 7895–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Wu, L.; Zheng, J. Application of ultrasonic technology in extraction and modification of dietary fiber. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, X.-H. Mechanism by which β-glucanase improves the quality of fermented barley flour-based food products. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 126026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Duan, R.L.; Yu, H.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Bao, Y.L. Research Progress in the Extraction, Structural Characteristics, Bioactivity, and Commercial Applications of Oat β-Glucan: A Review. Foods 2024, 13, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Tan, B.; Wang, L. Individual and combined effects of cold plasma and enzymatic hydrolysis modification on soluble dietary fiber in wheat bran: Structural, physicochemical and functional properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2025, 123, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, G.; Li, L.; Liu, H. Comparison the Structural, Physicochemical, and Prebiotic Properties of Litchi Pomace Dietary Fibers before and after Modification. Foods 2022, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liu, H.N.; Ma, A.M.; Zhou, J.Z.; Xia, X.D. Synergetic effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Rhizopus oryzae on physicochemical, nutritional and antioxidant properties of whole-grain oats (Avena sativa L.) during solid-state fermentation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhan, Q.; Zhao, L. Effect of modifications on structure, physicochemical properties and lead ions adsorption behavior of dietary fiber of Flammulina velutipes. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Piao, C. Insoluble dietary fibre from okara (soybean residue) modified by yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. LWT 2020, 134, 110252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-L.; Ma, Y.-S. The effect of extrusion processing on the physiochemical properties of extruded orange pomace. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Jiang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, H. Effect of γ-irradiation combined with enzymatic modification on the physicochemical properties of defatted rice bran dietary fiber. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Lazarte, A.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Villamiel, M.; Rastall, R.A.; Moreno, F.J. In vitro fermentation properties of pectins and enzymatic-modified pectins obtained from different renewable bioresources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Wen, Q.; Li, L.; Wu, H.; Li, X. Antioxidant activities of water-soluble polysaccharide extracted from mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) hull with ultrasonic assisted treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Luo, G.; Lei, A.; Chen, H.; Zhang, F. Effects of high-pressure homogenization on rheological properties of orange juice. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juodeikiene, G.; Trakselyte-Rupsiene, K.; Navickaite, B.; Zadeike, D.; Bendoraitiene, J.; Bartkiene, E.; Lele, V.; Rueller, L.; Robert, J.; Arnoldi, A. Functionalization of soya press cake (okara) by ultrasonication for enhancement of submerged fermentation with Lactobacillus paracasei LUHS244 for wheat bread production. LWT 2021, 152, 112337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, M.X.; Xiao, Z.G.; Daglia, M.; Dragan, S.; Delmas, D.; Vong, C.T.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhao, Y.S.; Shen, J.; et al. Dietary polyphenols for managing cancers: What have we ignored? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Godos, J.; Currenti, W.; Micek, A.; Falzone, L.; Libra, M.; Giampieri, F.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Quiles, J.L.; Battino, M.; et al. The Effect of Dietary Polyphenols on Vascular Health and Hypertension: Current Evidence and Mechanisms of Action. Nutrients 2022, 14, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; He, J. Stability and Fat Adsorption Activity of the Complex of Soluble Dietary Fiber and Polyphenols from Lotus Root. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 22, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, Q.; Huang, H.; Hou, K.; Dong, R.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. The effect of bound polyphenols on the fermentation and antioxidant properties of carrot dietary fiber in vivo and in vitro. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Troise, A.D.; Qi, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, H.; Fogliano, V. Insoluble dietary fibre scavenges reactive carbonyl species under simulated physiological conditions: The key role of fibre-bound polyphenols. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Aguilar, G.A.; Blancas-Benítez, F.J.; Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G. Polyphenols associated with dietary fibers in plant foods: Molecular interactions and bioaccessibility. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H. Nanoformulations of quercetin and cellulose nanofibers as healthcare supplements with sustained antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, G.; Shi, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, F. Comparative Study of Heat- and Enzyme-Induced Emulsion Gels Formed by Gelatin and Whey Protein Isolate: Physical Properties and Formation Mechanism. Gels 2022, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Gao, S.; Liu, Z.; Rao, S.; Meng, X. Insight into the mechanism of enhancing myofibrillar protein gel hardness by ultrasonic treatment combined with insoluble dietary fiber from oat. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 178, 114539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Gan, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Dong, G. Conjugation of flaxseed protein and plant polysaccharides: Process optimization, structural characterization and technical-function evaluation. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.-M.; Xu, Z.-W.; Luo, C.; Xu, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-R.; Guo, S.-L.; Wu, X.-D.; Wan, Y. Modification of soy protein isolate by Maillard reaction and its application in microencapsulation of Limosilactobacillus reuteri. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 132, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Xue, B.; Sun, T.; Xie, J. Effect of Oat β-Glucan on the Structure and Properties of Soybean Protein Isolate During Maillard Reaction. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2023, 78, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wu, J.J.; Li, C.Z.; Chen, X.C.; Cui, H.Y. Fabrication of a dual-response intelligent antibacterial nanofiber and its application in beef preservation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Huang, X.W.; Zhang, J.N.; Liu, L.; Shi, J.Y.; Muhammad, A.; Zhai, X.D.; Zou, X.B.; Xiao, J.B.; Li, Z.H.; et al. Development of nanofiber indicator with high sensitivity for pork preservation and freshness monitoring. Food Chem. 2022, 381, 132224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.M.; Hu, W.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, C.Z.; Cui, H.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Lin, L. Controlled release and antibacterial properties of PEO/casein nanofibers loaded with Thymol/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in beef preservation. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Z.; Bai, M.; Chen, X.C.; Hu, W.; Cui, H.Y.; Lin, L. Controlled release and antibacterial activity of nanofibers loaded with basil essential oil-encapsulated cationic liposomes against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Luo, C.C.; Li, C.Z.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.; Cui, H.Y. Eugenol/silk fibroin nanoparticles embedded Lycium barbarum polysaccharide nanofibers for active food packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 32, 100841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, T.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Keshvari, H.; Farokhi, M. Carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/agarose hydrogel dressings containing silk fibroin/polydopamine nanoparticles for antibiotic delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, A.; Saxena, R.; Khan, S.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F. pH-responsive IPN beads of carboxymethyl konjac glucomannan and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as a controlled release carrier for ibuprofen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Yan, C.; Cui, L.; Zhu, J. A pH-responsive carboxymethyl cellulose/chitosan hydrogel for adsorption and desorption of anionic and cationic dyes. Cellulose 2021, 28, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.J.; Hong, X.; Ni, Y.S.; Li, Y.Z.; Pang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, J.B.; Zheng, Y.F. Recent trends and applications of cellulose nanocrystals in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B. Cellulose degradation and cellulase formation by Phialophora malorum. Arch. Microbiol. 1978, 118, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.T.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.S.; Daglia, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, X. Recent advances in targeted manipulation of the gut microbiome by prebiotics: From taxonomic composition to metabolic function. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 49, 100959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannoy-Bruno, O.; Desai, C.; Raman, A.S.; Chen, R.Y.; Hibberd, M.C.; Cheng, J.; Han, N.; Castillo, J.J.; Couture, G.; Lebrilla, C.B.; et al. Evaluating microbiome-directed fibre snacks in gnotobiotic mice and humans. Nature 2021, 595, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, U.M.; Murat, F.; Abrouk, M.; Pont, C.; Confolent, C.; Oury, F.X.; Ward, J.; Boros, D.; Gebruers, K.; Delcour, J.A.; et al. Combined meta-genomics analyses unravel candidate genes for the grain dietary fiber content in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2011, 11, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Gomez, M.X.; Ng, K.M.; Drexler, R.A.; Conner, A.M.S.; Vierra, C.G.; Krishnakumar, N.; Gerber, H.M.; Taylor, Z.R.; Treon, J.L.; Ellis, M.; et al. A diverse set of solubilized natural fibers drives structure-dependent metabolism and modulation of the human gut microbiota. mBio 2025, 16, e00425–e00470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, L.; Rizzo, G.; Zavoli, M.; Battino, M. A Plant-Based Food Guide Adapted for Low-Fat Diets: The VegPlate Low-Fat (VP_LF). Foods 2024, 13, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrigue, M.; Carter, B.; Roberts, S.A.; Drewnowski, A. A Low-Calorie Beverage Supplemented with Low-Viscosity Pectin Reduces Energy Intake at a Subsequent Meal. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, A.; Gupta, O.P.; Sagwal, V.; Kumar, A.; Patwa, N.; Mohan, N.; Ankush; Kumar, D.; Vir, O.; Singh, J.; et al. Beta-Glucan as a Soluble Dietary Fiber Source: Origins, Biosynthesis, Extraction, Purification, Structural Characteristics, Bioavailability, Biofunctional Attributes, Industrial Utilization, and Global Trade. Nutrients 2024, 16, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, L.; Rioux, L.-E.; Britten, M.; Turgeon, S.L. In vitro bioaccessibility of peptides and amino acids from yogurt made with starch, pectin, or β-glucan. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 46, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ahmed, S.; Mehmood, A.; Bilal, M.; Patil, P.J.; Akram, K.; Farooq, U. Effect of apple pomace on nutrition, rheology of dough and cookies quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3244–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Sabikhi, L.; Kumar, M.H.S.; Panjagari, N.R. Investigating the effect of resistant starch, polydextrose and biscuit improver on the textural and sensory characteristics of dairy-multigrain composite biscuits using response surface methodology. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedrahmati, S.; Shahidi, F.; Roshanak, S.; Mahallati, M.N. Application of jaban watermelon exocarp powder in low-calorie ice cream formulation and evaluation of its physicochemical, rheological, and sensory properties. J. Food Process. Pres. 2021, 45, 15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-T.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Hu, J.-L.; Yan, H.; Zhao, J.; Zou, L.; Hu, Y.-C. Physicochemical properties and biological functions of soluble dietary fibers isolated from common and Tartary buckwheat sprouts. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 183, 114944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Liu, T. The structural characteristics of dietary fibers from Tremella fuciformis and their hypolipidemic effects in mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teparak, C.; Uriyapongson, J.; Phoemsapthawee, J.; Tunkamnerdthai, O.; Aneknan, P.; Tong-un, T.; Panthongviriyakul, C.; Leelayuwat, N.; Alkhatib, A. Diabetes Therapeutics of Prebiotic Soluble Dietary Fibre and Antioxidant Anthocyanin Supplement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Randomised Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Goncalves, D.; Vinera, J.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 2014, 156, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, C.; Du, M.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Effects of gel spatial structure and water state on 3D printability: A case study of honey bee pupa protein and soybean dietary fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Prakash, S.; Zhu, B.; Dong, X. Role of dietary fiber and flaxseed oil in altering the physicochemical properties and 3D printability of cod protein composite gel. J. Food Eng. 2022, 327, 111053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yi, S.; Ye, T.; Leng, Y.; Hossen, M.A.; Sameen, D.E.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W. Effects of ultrasonic treatment and homogenization on physicochemical properties of okara dietary fibers for 3D printing cookies. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 77, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Noakes, M.; Keogh, J.; Foster, P.; Clifton, P. High protein high fibre snack bars reduce food intake and improve short term glucose and insulin profiles compared with high fat snack bars. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 15, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urita, Y.; Noda, T.; Watanabe, D.; Iwashita, S.; Hamada, K.; Sugimoto, M. Effects of a soybean nutrition bar on the postprandial blood glucose and lipid levels in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, H.; Kowalska, J.; Ignaczak, A.; Masiarz, E.; Domian, E.; Galus, S.; Ciurzyńska, A.; Salamon, A.; Zając, A.; Marzec, A. Development of a High-Fibre Multigrain Bar Technology with the Addition of Curly Kale. Molecules 2021, 26, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviani, M.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Gall, S.; Jochim, J.; Zello, G.A. The Effects of Low- and High-Glycemic Index Sport Nutrition Bars on Metabolism and Performance in Recreational Soccer Players. Nutrients 2020, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Bai, M.; Rashed, M.M.A.; Lin, L. The antibacterial activity of clove oil/chitosan nanoparticles embedded gelatin nanofibers against Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilms on cucumber. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Kausar, T.; Aslam, J.; Quddoos, M.Y.; Ali, A.; Kauser, S.; Zerlasht, M.; Rafique, A.; Noreen, S.; Iftikhar, K.; et al. Physical and Rheological Studies of Biscuits Developed with Different Replacement Levels of Pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima) Peel, Flesh, and Seed Powders. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, 4362094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, C.; Castorina, G.; Fiorillo, G.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Rollini, M.; Consonni, G.; Erba, D.; Negrini, N.; Marti, A. Gluten-free breadsticks with Ganoderma-fermented corncobs: Technological and nutritional features. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 4916–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.; Rakha, A.; Khan, M.R.; Zou, X.B. Complementing the dietary fiber and antioxidant potential of gluten free bread with guava pulp powder. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Majid, I.; Kaur, S.; Dar, B.N.; Nanda, V. An Updated Review on Exploring Hydrocolloids Application in Food Matrix: Current Insights Into Fruit, Bakery, Meat, and Dairy Based Products. J. Texture Stud. 2025, 56, 70020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomer, B.B.; Ghannadiasl, F. Enrichment of Oil Cake with Cinnamon Extract Positively Effects Antioxidant Activity and Textural Profile. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurko, E.; Nakilcioglu, E. Optimization of Spirulina-Enriched Vegan Cake Formulation Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, 70116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, N.A.; Di Monaco, R.; Masi, P.; Cavella, S. Reduced-Calorie Filling Cream: Formula Optimization and Mechanical Characterization. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 43, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, W.Q.; Li, C.Z.; Ye, Y.; Cui, H.Y.; Lin, L. Preparation and physicochemical effects of zein nanofiber membrane encapsulated with citral/HP-β-CD inclusion complex and its application on cheese. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmen, D.; Toker, O.S.; Ozturk, S.A. Lemon Fiber as a New Source of Fat Replacement in Filling Creams. J. Food Process. Eng. 2025, 48, 70056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Shehzad, A.; Omar, M.; Rakha, A.; Raza, H.; Sharif, H.R.; Shakeel, A.; Ansari, A.; Niazi, S. GRAS, plant- and animal-derived compounds as alternatives to conventional fungicides for the control of postharvest diseases of fresh horticultural produce. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palou, L.; Ali, A.; Fallik, E.; Romanazzi, G. GRAS, plant- and animal-derived compounds as alternatives to conventional fungicides for the control of postharvest diseases of fresh horticultural produce. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 122, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, H.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Study on the comparison of key issues of Codex Commission on Food Additives (CCFA) and corresponding food additive management in China. Chin. J. Food Hyg. 2021, 33, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).